CNM - C4
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
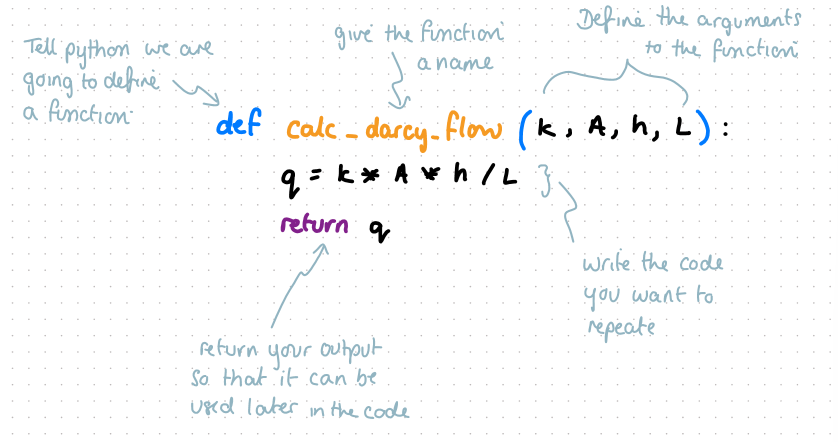
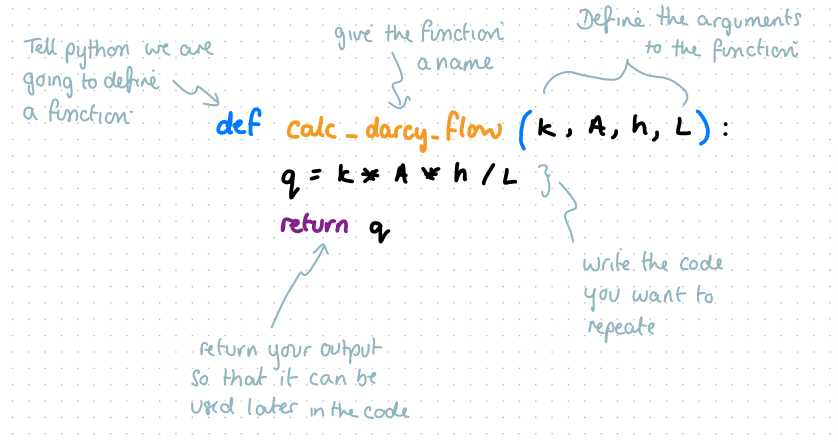
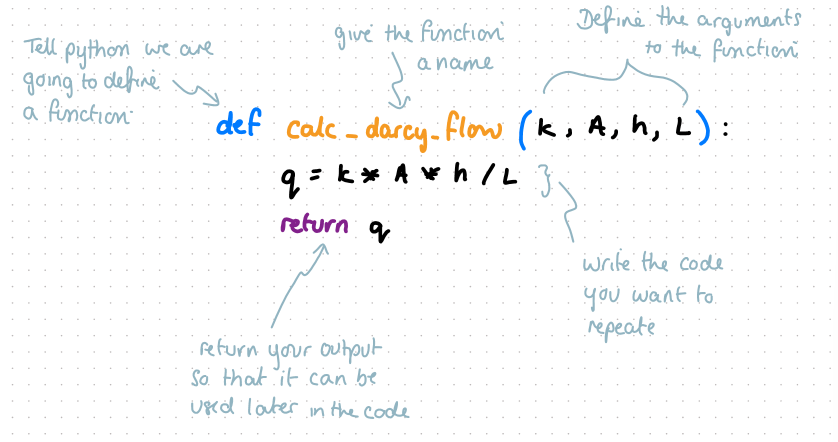
define darcy’s flow as a function
q = k*A*h/L
define, name, list args, new line with 4 spaces, function, new line, return output
give the code for calling this function if:
k = 0.3
A = 5.2
h = 1.7
L = 0.3

what do you have to use to get flow rate as an array from this function
a for loop and args as arrays

how do you use a keyword argument in a function - modify this code as an example

what is the difference between variables defined inside and outside a function
Scope
variables defined inside a function are in the local scope and can’t be accessed outside of it
variables defined outside of a function have global scope and can be accessed anywhere
so should have dif names
what is pandas
a module like numpy is
a module that allows us to work with tables of data
used for stats, graphs, etc
import pandas as pd
what is a dataframe
a dataframe is to pandas what an array is to numpy
dataframes hold more types of data than arrays
can access data through labels rather than position
helpful with time series data
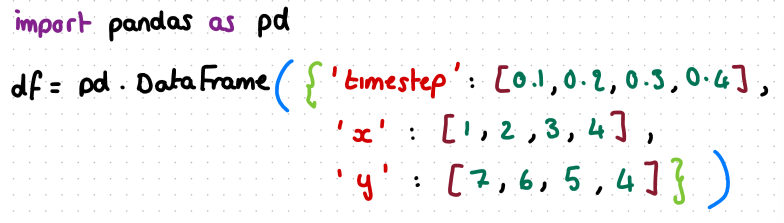
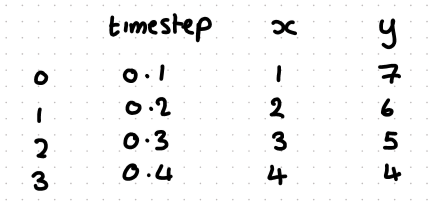
what dataframe would this code produce
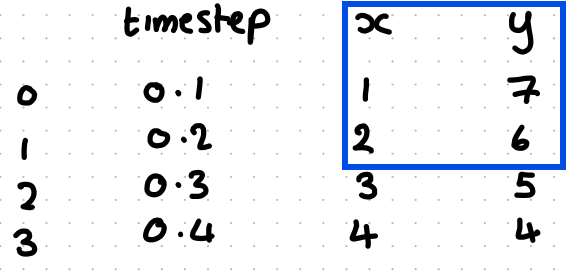
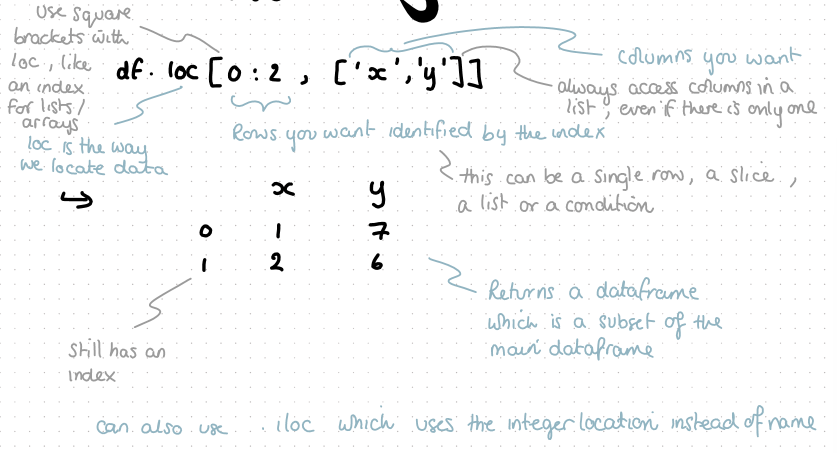
how to pull this section of the dataframe df
df.loc — meaning locate
line of code to import data from a file

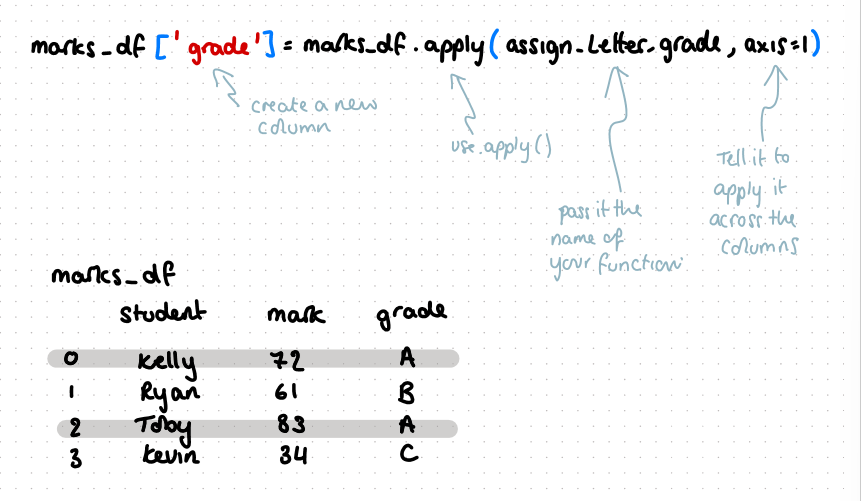
how do you add a new column to a dataframe
eg a new column which sums the x column value and y column value in each row and multiplies this by 2
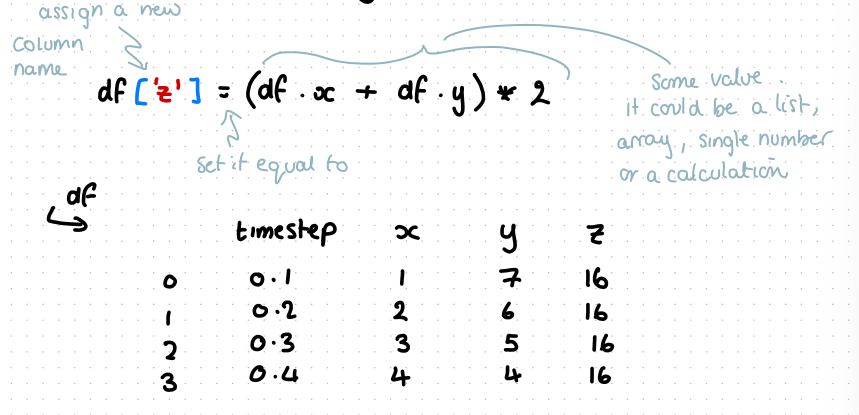
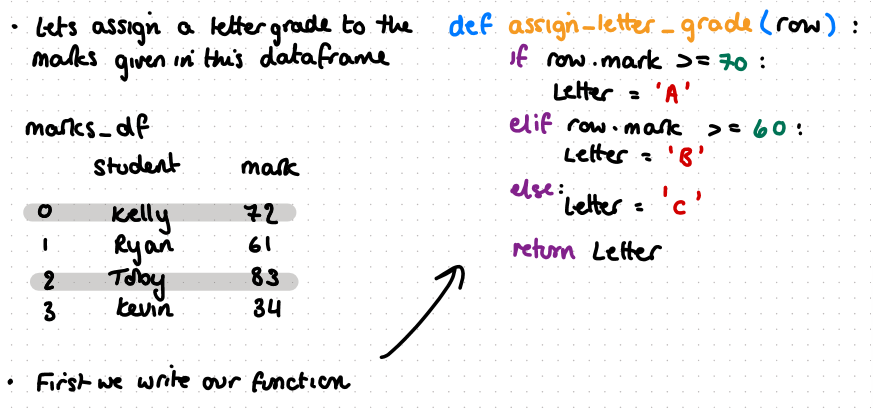
line of code to apply the function to the dataframe
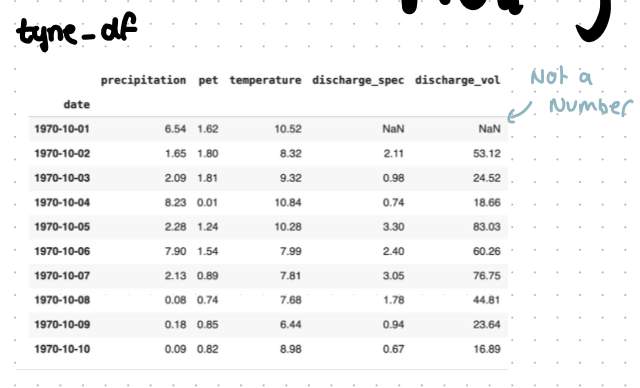
this is a dataframe of the rainfall and other values in tyne
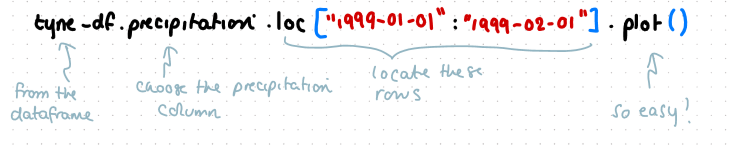
what is a line of code to plot the precipitaion in tyne from 01/01/1999 to 01/02/1999
What is a module in Python and how can you create your own?
A module is a separate file containing extra functionality, that you can create by saving a script with functions as a .py file and importing it
What is a file mode in Python, name 4 types and what they do
A file mode tells Python how a file should be opened and what operations are allowed.
"r" – Read only
"r+" – Read and write
"w" – Write only (deletes current content)
"a" – Append (keep current content and add to it)
open("file.txt", mode) - how to use - insert one of the above as ‘mode’
What does the following code do?
file = open("open_me.txt", "w")
file.write("Hello")
file.close()
Replaces the contents of open_me.txt with "Hello"
Why do we use a while loop in this code instead of a for loop?
Because for loops cannot calculate change