serology exam 2
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
What is the primary and secondary line of body defense against microbial pathogens?
Primary (natural innate)= non specific, no memory, skin, mucous membranes, NK, phagocytosis
secondary(acquired)= specific, memory, t cell, b cell
What infection is caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, why is it called that?
Atypical (not treated with penicillin) and walking (individuals don't stay home) pneumonia
What do mycoplasma colonies resemble?
Fried eggs, lack cell wall and wont stain w/ gram
How is primary atypical pneumonia usually diagnosed here in the USA?
Check for antibodies to M. pneumoniae IgM are for recent infections, IgG for possible reinfections, or by molecular panel
What are cold agglutinins?
autoantibodies against I antigens found in surface of RBC, they are present in some M. pneumoniae infections
What is the main reason testing for cold agglutinins is no longer recommended to diagnose infection with M.pneumoniae?
it is not specific enough for only infections with M. pneumoniae
What are rickettisae (be specific)?
Intracellular gram negative bacteria that are pleomorphic, are transmitted by ticks, mites, lice, or fleas
What is the most common rickettsial infection in the U.S. that causes serious illness or fatal if left untreated?
Rocky mountain spotted fever
What organism causes Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) and how is it transmitted?
Bite of american dog tick, caused by R. rickettsia
The pathogenesis of Rocky Mountain spotted fever involves:
tick to dog then human but can also be directly tick to human
How are rickettsial infections usually diagnosed?
Weil-felix test= antigens (ox-19,2,k) used to detect rickettsial antibody (not used) also can use indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) or enzyme immunoassay (EIA)
Where is rickettsia most commonly reported (geographical location in the USA)?
east (central USA to the east coast)
Vector for RMSF
american dog tick (Dermacentor variabilis)
epidemic typhus
Rickettsia prowazekii
Lice
Vector defecates while biting and rickettsia enters the body
Increased in natural disasters
Wash clothes in hot water or get rid of them
endemic typhus
Rickettsia typhi
Flea (carried by rats, opossums, cats, dogs)
Vector defecates while biting and rickettsia enters the body
What is the Weil-Felix reaction, is it commonly used in the USA?
Proteus OX-19, OX-2, OX-K used as antigens to detect rickettsial antibody, not commonly used
Which of the following are bacterial: spirochetes, mycoplasmas, rickettsiae?
all three are bacterial
Which of the following do not grow on ordinary lab media: spirochetes, mycoplasma, rickettsiae
rickettsia and spirochetes do not grow on ordinary lab media but mycoplasma can be grown on enriched media
A child complaining of fever and sore throat is examined in a physician’s office. A rapid group A serological streptococcal antigen test is performed in the office and the result negative. Control results were acceptable. What should be done and why?
A culture on sheep blood agar (beta hemolysis), the rapid assay might not be sensitive enough
What is the advantage of performing a serological test vs bacterial culture for the detection of Strep A infection, what about molecular testing?
The serological test will be significantly faster than a culture, molecular would be the most sensitive but also the more expensive option
What is the most common cause of bacterial pharyngitis?
strep A
Which organism causes scarlet fever, flesh eating bacteria, erysipelas, and impetigo?
strep A (pyogenes)
What is the sequelae to untreated Strep A infection? know mechanism.
Acute rheumatic fever, poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis- these are immunologically mediated and do not involve actively growing bacteria
Strep A is also called
strep pyogenes
Discuss antibodies such as anti-streptolysin O test (ASO), anti-DNAsae B, anti-streptokinase, anti-hyaluronidase, and why they may be useful to demonstrate prior streptococcal infection in patients.
serological testing is needed because streptococcal bacteria are unlikely to be seen when signs and symptoms of sequelae appear, used to diagnose rheumatic fever
What is virulence and how may virulence by transferred among bacteria (like for antibiotic resistance)
is the extent of pathology caused by an organism when it infects a host. degree of damage is mediated by specific virulence factors
beta hemolysis
complete cell lysis
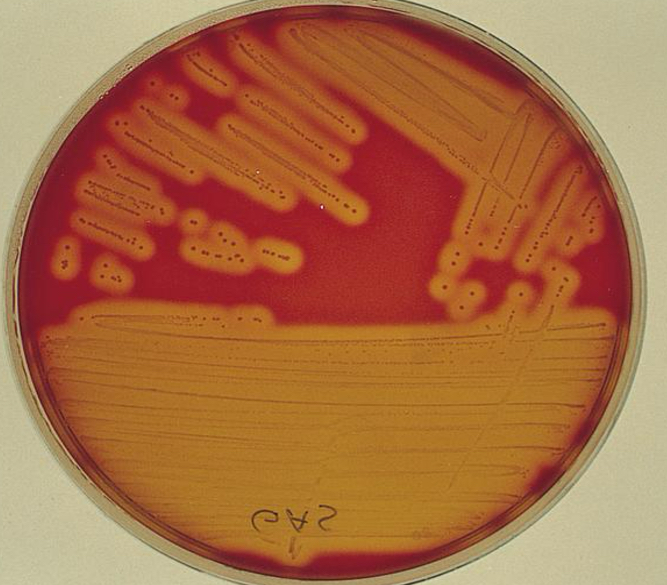
gamma hemolysis
no effect
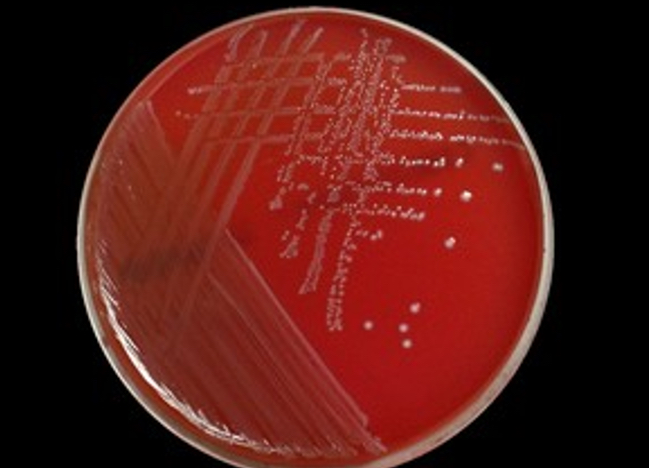
alpha hemolysis
partial cell lysis
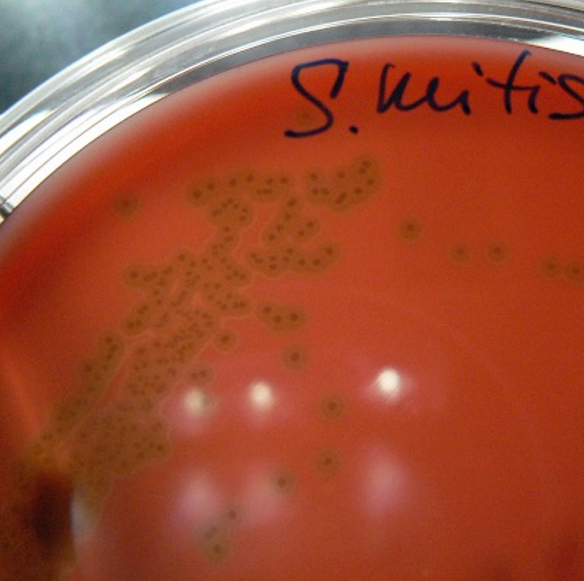
What is the hemolytic pattern seen in sheeps blood agar for Strep A
complete cell lysis (beta)
Which organism is thought to be the causative agent of some cases of gastric ulcers?
H. pylori
What is H. pylori? (be specific)
gram neg microaerophilic spiral bacteria
How is H.pylori believed to be transmitted
by fecal oral route
How is H. pylori diagnosed?
CLO test (rapid urease in stomach biopsy), urease breath test, best is ELISA
What is the most commonly reported tick-borne infection in the U.S?
lyme disease
How is Lyme disease transmitted?
Ixodes- black legged ticks, tick bites in the environment, tick has to be attached to feed for >24 hours
What are the symptoms of Lyme disease?
Localized rash in bullseye, early dissemination ( flu like, bell’s palsy, swollen knees, irregular heartbeat), late dissemination (rheumatological, neurological, cardiovascular)
How is Lyme disease most commonly diagnosed?
difficult to diagnose, lab test to detect AB
Is Lyme disease easily curable and diagnosed?
no its both hard to diagnose and treat
Name some bacterial infections transmitted by arthropods
lyme, RMSF
Which organism causes syphilis?
treponema pallidum
primary syphilis stage
ulcers on genitalia, goes away spontaneously, organisms multiply and disseminate via blood or lymph systems
secondary syphilis stage
lymphadenopathy, malaise, fever, pharyngitis, RASH, most contagious
latent syphilis stage
asymptomatic usually begins after 2 year after untreated infection
tertiary syphilis stage
gummas (granulomas) cardiovascular enlargement, neurosyphilis, deformities
How are Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum infections diagnosed?
through direct or serological tests
direct detection of syphilis
Treponemes in active lesions
Dark field microscopy
Fluorescent antibody staining
ONLY FOR ACTIVE LESIONS
non treponemal test VDRL
(detect IgG or IgM against cardiolipin (reagin)
VDRL = microscopic flocculation w/ microscope
Antigen – cardiolipin w lecithin + cholesterol
Antibody – reagin
Needs heat
Needs pos confirmation (NR, WR, or R)
CSF or serum
HAS FALSE POS TO MALARIA
non treponemal test RPR
RPR= macroscopic floccution
Antigen – cardiolipin + cholesterol
Antigen – reagin
Can be qualitative or semiquantitative
Serum
HAS FALSE POS TO MALARIA
treponemal
detect antibody to T pallidum
Fluorescent treponemal absorption (FTA-ABS) indirect
T pallidum particle agglutination (TP-PA) - pos will be clump in well in a smooth mat, neg will be button clump
ELISA
CLIA
MFI
What is flocculation?
small particles that clump together
In syphilis testing, what are biological false positives?
malaria, autoimmune diseases (lupus)
What antigen is used in the RPR and VDRL?
cardiolipin
How are RPR and VDRL same/different?
RPR is macro, VDRL is micro
When must the needle used in RPR be checked?
daily every shift
How is the delivery needle used in the RPR be checked, why do we check it?
you check that the amount is correctly dispensing 30 drops and that should be equal to 0.5 mL
How can the room temperature affect the RPR
it can falsely influence the sensitivity of the reaction
what is the speed of rotation for the RPR
100
How do the titers of nontreponemal tests for syphilis vary during the course of the infection
a decline is seen with patient treatment
Which serological test for syphilis is used to diagnose neurosyphilis
VDRL or ELISA
What is the absorbent in the FTA-ABS?
nonpathogenic treponemes
In the FTA, what is fixed to the slide?
T. pallidum
What is the most sensitive test for the diagnosis of syphilis?
FTA-ABS
Which test is best at monitoring the effectiveness of syphilis treatment?
RPR
Interpret the following results: RPR - Reactive| FTA-ABS – nonreactive
biological false positive
May assays such as Chemiluminescent and Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays be used for Syphilis testing?
yes
What is seroresistance
failure of a patients serum to revert to nonreactive in non treponemal test following treatment for syphilis
Which organisms may be best visualized by darkfield microscopy
live organisms, best to visualize motile organisms from primary and secondary lesions
antibody response to Syphilis
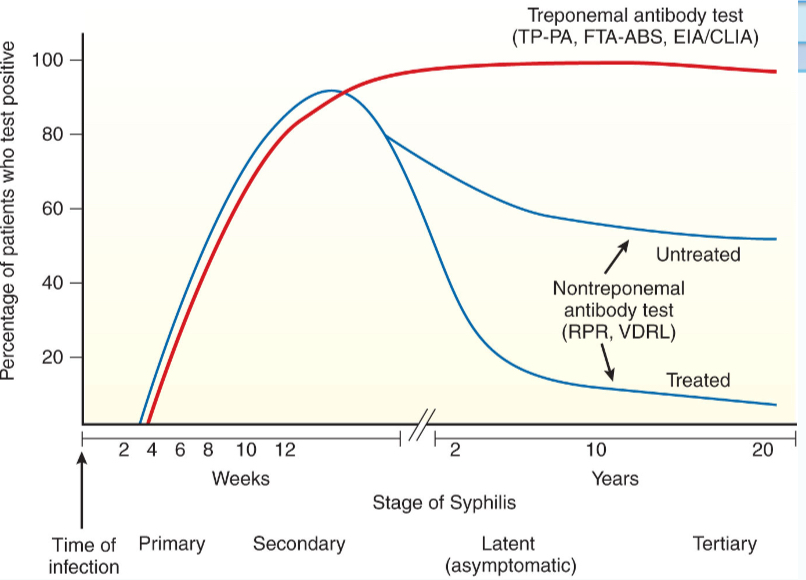
Which of the following tests is used to confirm a syphilis infection after another method is positive?
TP-PA
Why are some parasitic infections chronic in nature?
because parasites evade and suppress the hosts immune system while allow them to multiple over time
Examples of how parasites evade the immune system:
antigenic concealment - parasite antigens remain inside host cells
antigenic variation - parasites vary their surface antigens
antigenic shedding - parasites shed surface antigens which bind to the hosts antibodies and cells
antigenic mimicry - parasites express epitopes that are similar or identical to to the hosts molecules
Name a flagellate that looks like an old man with glasses
giardia
Name the most common intestinal protozoan infection in the U.S.
giardia
Name a flagellate that can be diagnosed from duodenal aspirates or the enterotest capsule
giardi
Which parasite can be found in the blood?
malaria - plasmodium
If I want to look for a parasite in a blood sample, what tube should I collect?
EDTA
Name a parasite that lives inside erythrocytes
malaria - plasmodium
How do we avoid blood transfusion transmitted malaria?
patient history and screening
Which sporozoan causes malaria
plasmodium
Which parasite has killed more people worldwide than any other?
plasmodium - malaria
Name a parasite that requires the Anopheles mosquito for its sexual cycle
plasmodium (malaria)
Which species of plasmodium has sausage-shaped or crescent-shaped gametocytes?
P. falciparum
Which species of plasmodium commonly has multiple ring forms within one RBC?
P. falciparum
Which species of plasmodium is most malignant?
P. falciparum
With which species of plasmodium does one see rings and gametocytes only?
P. falciparum
When is the best time to draw blood for malaria smears?
shortly after shaking chills and fever (paroxysm) . blood should be taken at 6-8 hr intervals so different stages of the parasite can be studied to identify species
How is a thick malaria smear prepared?
three drops of blood are placed on slide, allowed to dry, and placed in giemsa stain without fixation
Are blood donors typically screened for Malaria?
yes
Name a protozoan that can be found in municipal water supplies causes a profuse watery diarrhea, is a serious risk to immunocompromised patients, and appears as red spherical structures approximately 6 microns in diameter on a modified acid-fast stain.
cryptosporidium
Which protozoan can be spread by infective oocyst in cat feces?
Toxoplasma gondii
Which protozoan can cause neurologic problems if contacted by the fetus after the first trimester?
Toxoplasma gondii
Which protozoan is the major cause of encephalitis in AIDS patients?
toxoplasmosis
How is toxoplasmosis usually diagnosed?
TORCH panel, tissue sample to check for live organism, avidity
What are low avidity vs high avidity anti-Toxoplasma antibodies?
Low avidity= low avidity IgG mean infection within last 8 months (more recent)
high avidity= high IgG mean infection occurred 5 or more months before testing (past infection)
What is TORCH testing?
the serological test for toxoplasmosis, other infections, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes
Which antibody type may increase in parasitic infections?
IgE
Which WBC type may increase in parasitic infections and allergic reactions?
eosinophil
What is mycosis?
fungal infections
What is a yeast, how do they reproduce?
unicellular form that reproduces by budding