ANS Smooth muscle pt2 and Cardiac Muscle
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are the calcium sources for smooth muscel?
Extracellular fluid
and sarcoplasmic reticulum.
What is the calcium sensitive protein in smooth muscles?
Calmodulin
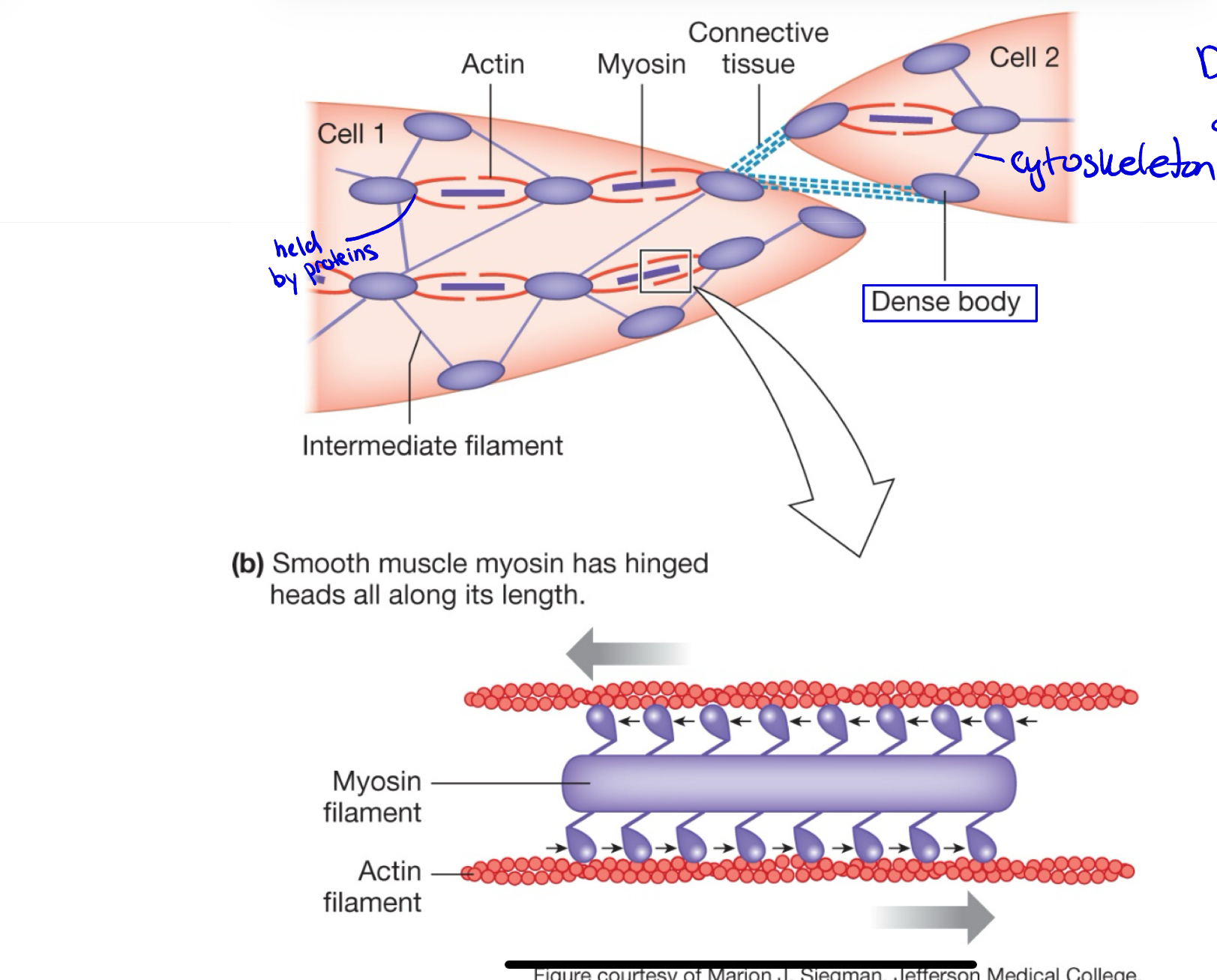
What are dense bodies in smooth muscle?
They serve as anchoring points for actin filaments
Single unit smooth muscle cells
connected by gap junctions and cells contract as a single unit.
A cluster of muscle cells that has ONE neurojunction
Ex: Small intestines
Multi-unit smooth muscle cells
are not electrically linked and each cell must be stimulated independently.
Every cell has its own neural junction
Ex: eye
Actin in smooth muscle:
more plentiful: 10-15 actin : 1 myosin
Associated with tropomyosin and calmodulin
Myosin in smooth muscle
Filements are longer
entire surface of filament covered with myosin heads
Sarcoplasmic reticulum in smooth muscle
Amount of SR varies and is less organized
No T-Tubules but caveolae
Extensive cytoskeleton in smooth muscle
intermediated filaments and dense bodies, Using it a lot more
What are the 4 ways in which excitation happens?
Autonomic neurotransmitters and hormones. Released by autonomic neurons.
Autonomic neurotransmitter: (can be acetylcholine) binds on smooth muscle cells and Na channel opens.
Hormone: Hormone, like oxytocin, binds to its hormone receptor on smooth muscle cells, causing turbulence opening Na channel.
Mechanical Stretch: After eating, the stretched stomach opens Na channel, (can be urination in the bladder.
Slow electrical activity: Ionic fluctuations in the ECF. Changes in the ECF. An acidic molecule made after a meal or other process, the acidic molecule made in the stomach is absorbed into the blood supply, and now all cells are bathing in it. The acidity is increasing.
Paracrine signals:
Histamine constricts the smooth muscle of the airways.
Nitric oxide relaxes the smooth muscle of blood vessels.
Smooth Muscle contraction
Calcium increases
Ca²⁺ comes from the SR and ECF.
Calcium binds to calmodulin
Forms a Ca²⁺–calmodulin complex.
Activates MLCK
The complex activates MLCK (myosin light chain kinase).
MLCK uses ATP to add a phosphate (PO₄) to light chains in myosin heads.
Myosin activates
Phosphorylated myosin can now break down ATP and bind to actin.
Contraction
ATP is used for myosin to pull on actin (the power stroke).
Relaxation of smooth muscle:
Repolarization
The cell membrane returns to its resting state (inside becomes more negative again).
This reduces calcium channel activity.
Calcium removal
Ca²⁺ is pumped out of the cytosol:
Back into the SR (sarcoplasmic reticulum)
Out to the ECF (extracellular fluid)
This movement goes against the concentration gradient, so it requires ATP.
Myosin dephosphorylation
The enzyme MLCP (myosin light chain phosphatase) removes the phosphate (PO₄) from the myosin head.
This inactivates myosin ATPase, stopping cross-bridge cycling.
Return to resting state
Dense bodies (which anchor actin filaments) return to their normal position as the muscle relaxes.
The cell returns to its resting length and tone.
cardiac Muscle is an intermediate Muscle
Like skeletal:
Striated
sarcomere structue
elastically linked to one another
has tweo sources of calcium
under autonomic as swll as hormonal control
Unlike skeleral muscel
Muscle fibers are shorter
may be branched
have single nucleus
Gap junctions in intercalated disks and desmosomes
Cardiac Muscle: excitations
Pacemaker cells (myocardial cells) automatically opens Na+ channels
Autonomic NT regulated the rate and rhythm of depolarization
Cardiac Muscle: contration
2 sources of Ca++: Sarcoplasmic reticulum and sarcolemma sodium Na+.
Ca+ binds to troponin… same as skeleton
H-zone disappears, fully contracted sarcomers
Cardiac Muscle: relaxastion
repolarizations
Return Ca++ back to SR and ECF, Ca++ declining
Tropomyosin back on myosin off