Thyroid and Adrenal Glands
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Anatomy of thyroid gland
Follicle
Colloid
Parafollicular cells
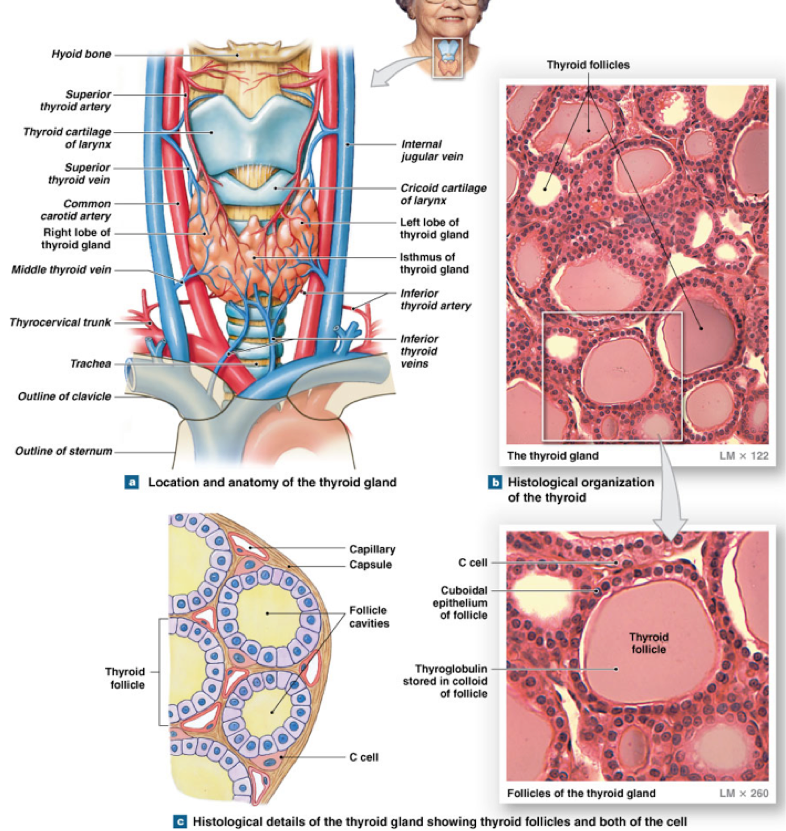
2 (connected) lobes just inferior to the thyroid cartilage (highly vascularized)
Follicle: the smallest functional unit
Fluid (colloid) filled sphere lined by simple cuboidal epithelial cells (follicle cells)
Synthesis/release of thyroid hormone
Parafollicular cells: C cells
Synthesis/release of calcitonin hormone
Calcitonin
Released when there is too much calcium in the blood
Inhibit osteoclasts
Increase excretion of calcium by the kidney
Prevent absorption of calcium by the digestive system
Thyroid hormones
Derived from the amino acid tyrosine
Iodine: is an essential dietary element: required for synthesis of thyroid hormones
Two forms of thyroid hormone:
T4 → thyroxine
Contains 4 iodine atoms
T3 → triiodothyronine
Contains 3 iodine atoms
T4 is the most abundant form of thyroid hormone
T3 is the most biologically active form of thyroid hormone
T4 that is released into blood stream from thyroid gland is able to be de-iodinated into the most active form (T3) in some target cells including the kidney and the liver
Synthesis of thyroid hormones
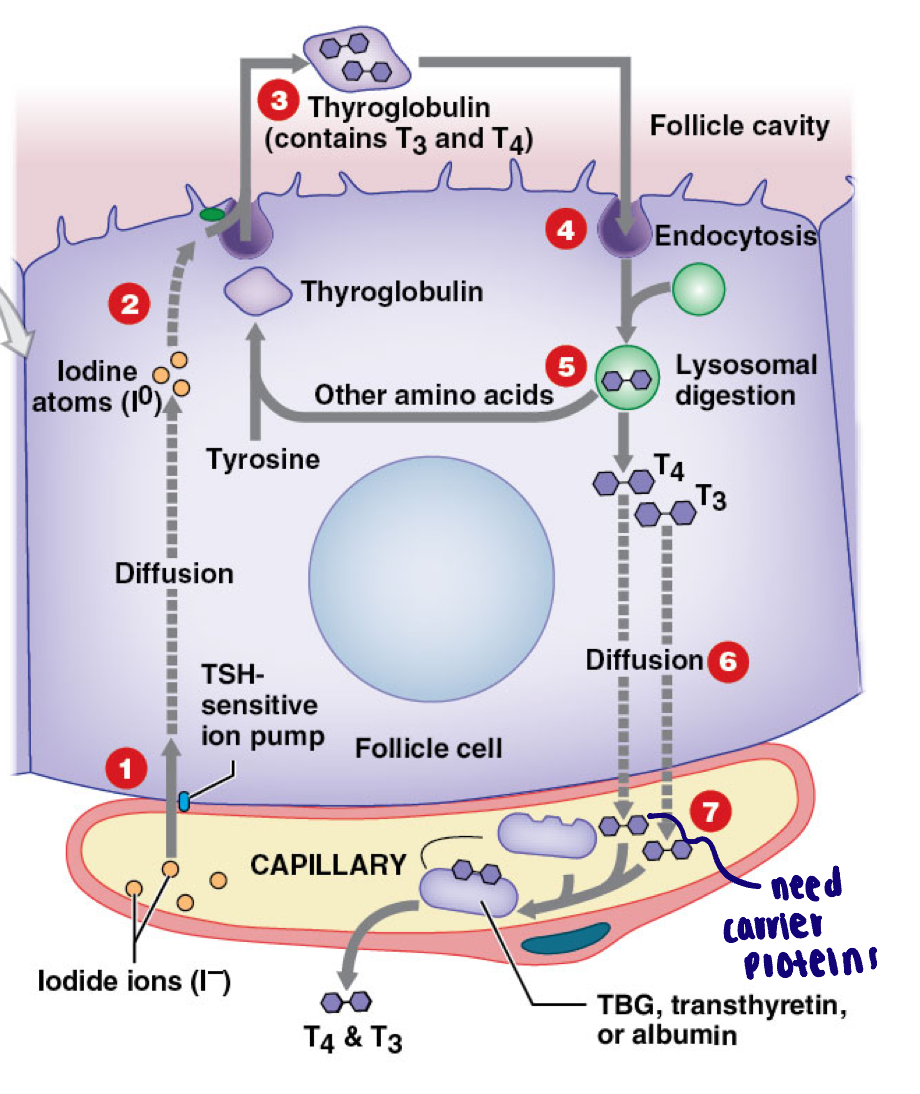
Iodide ions are transported FROM the blood into the follicular cell - TSH dependent (active transport)
Iodide ions converted into iodine atoms by thyroid peroxidase (then paired with thyroglobulin)
In colloid T3 and T4 are formed within thyroglobulin
Endocytosis of thyroglobulin
Lysosomal degradation of thyroglobulin to release T3 and T4
Diffusion of thyroid hormones into plasma
Transport in plasma
Regulation of thyroid hormone where?
Hypothalamus
Anterior pituitary
Thyroid gland
Hypothalamus - regulation of thyroid hormone
TRH: thyrotropin releasing hormone
Action → synthesis/release of TSH from anterior pituitary
Anterior pituitary - regulation of thyroid hormone
TSH: thyroid stimulating hormone
Action → synthesis and release of thyroid hormones
Thyroid gland- regulation of thyroid hormone
Thyroid hormones
Effects on target cells
Negative feedback on hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
Mediated by levels of thyroid hormone (going to release less TRH → less TSH → less thyroid hormones)
Actions of thyroid hormones
Stimulate growth and metabolism
Affects almost every cells of the body
Fast, strong, short increase in rate of cellular respiration
3 receptor locations within a cell
Cytoplasmic receptors: storage
Mitochondria receptors: increase rate of ATP production
Nucleus: increase gene transcription
Ex: sodium-potassium pump, glycolytic enzymes
Specific actions of thyroid hormones
Increased metabolic rate (heat production) leads to increased body temperature; true for children, little/no effect in adults
Increased heart rate and blood pressure
Simulate red blood cell formation - increase oxygen delivery
Accelerate turnover of minerals in bone (stimulate osteoclasts)
Hypothyroidism
Deficient thyroid hormone
Most common cause worldwide: iodine deficiency
Symptoms:
Tiredness, weakness
Dry skin
Feeling cold
Hair loss
Difficulty concentrating
Constipation
Weight gain with poor appetite
Goiter: abnormal enlargement of thyroid
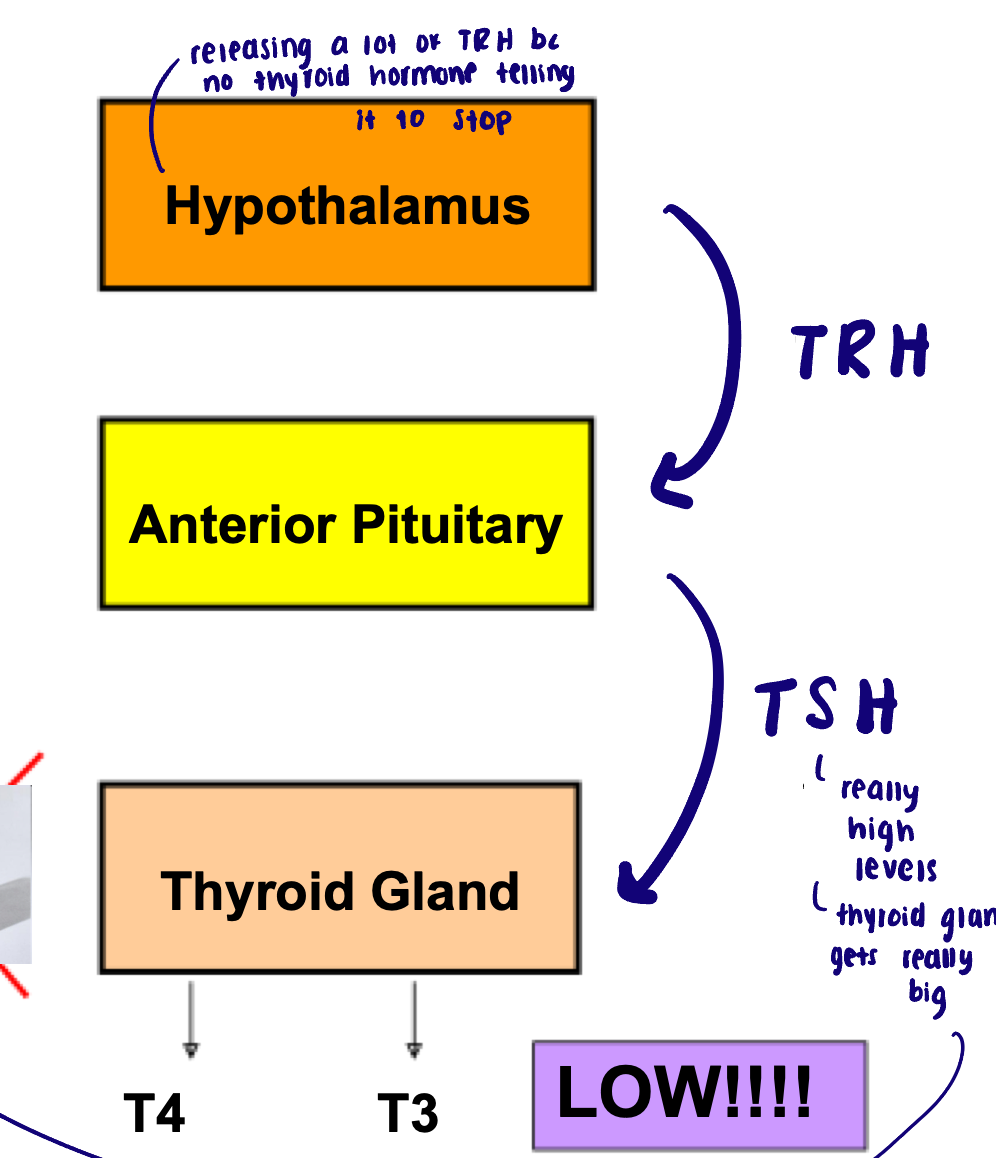
Hyperthyroidism
Excess thyroid hormone
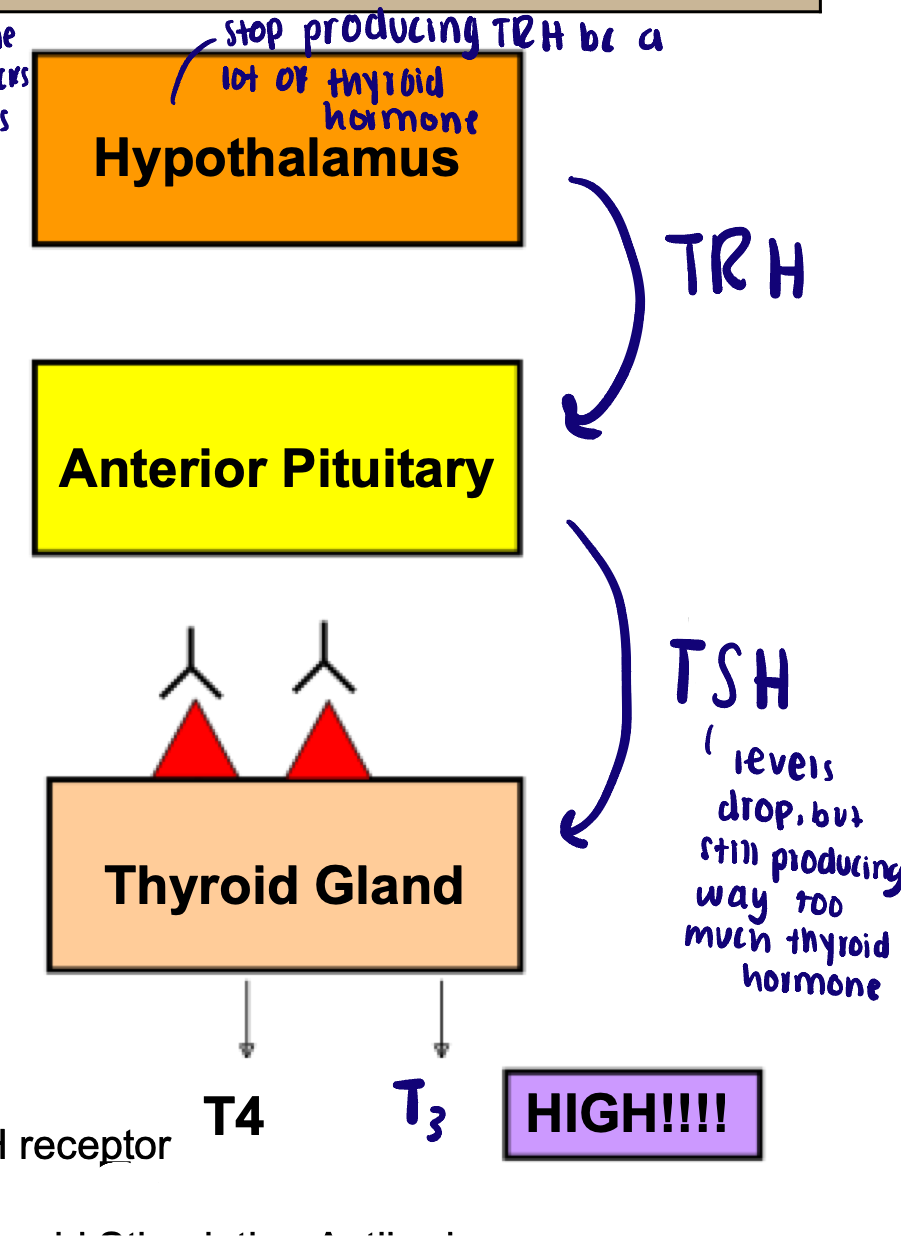
Most common cause: Grave’s disease (autoimmune disorder)
Antibody activates TSH receptor on thyroid gland → thinks TSH is present → produces a lot of thyroid hormone
Goiter and increased T4 and T3
Symptoms:
Increased: metabolism, food intake, weight loss, sweating, muscle weakness, nervousness, heart rate
Diarrhea and Polyuria
Graves opthalmopathy
Eye bulging
Anti-body binds to soft tissue around eye to fat → pushes eye forward
Parathyroid glands
4 small glands embedded on posterior surface of thyroid
Collection of parathyroid hormone (PTH) in response to decreases blood ca2+ levels
Effects of parathyroid hormone
Simulates osteoclasts
Enhances reabsorption of Ca2+ by kidney
Stimulates formation of calcitriol by kidney (promotes absorption of Ca2+ from digestive system)
Physiological roles of calcium
Normal plasma levels - 8.8-10.2 mg/dL
Nerve and muscle excitation
Muscle contraction
Blood coagulation
Bone mineral balance
Intracellular signaling
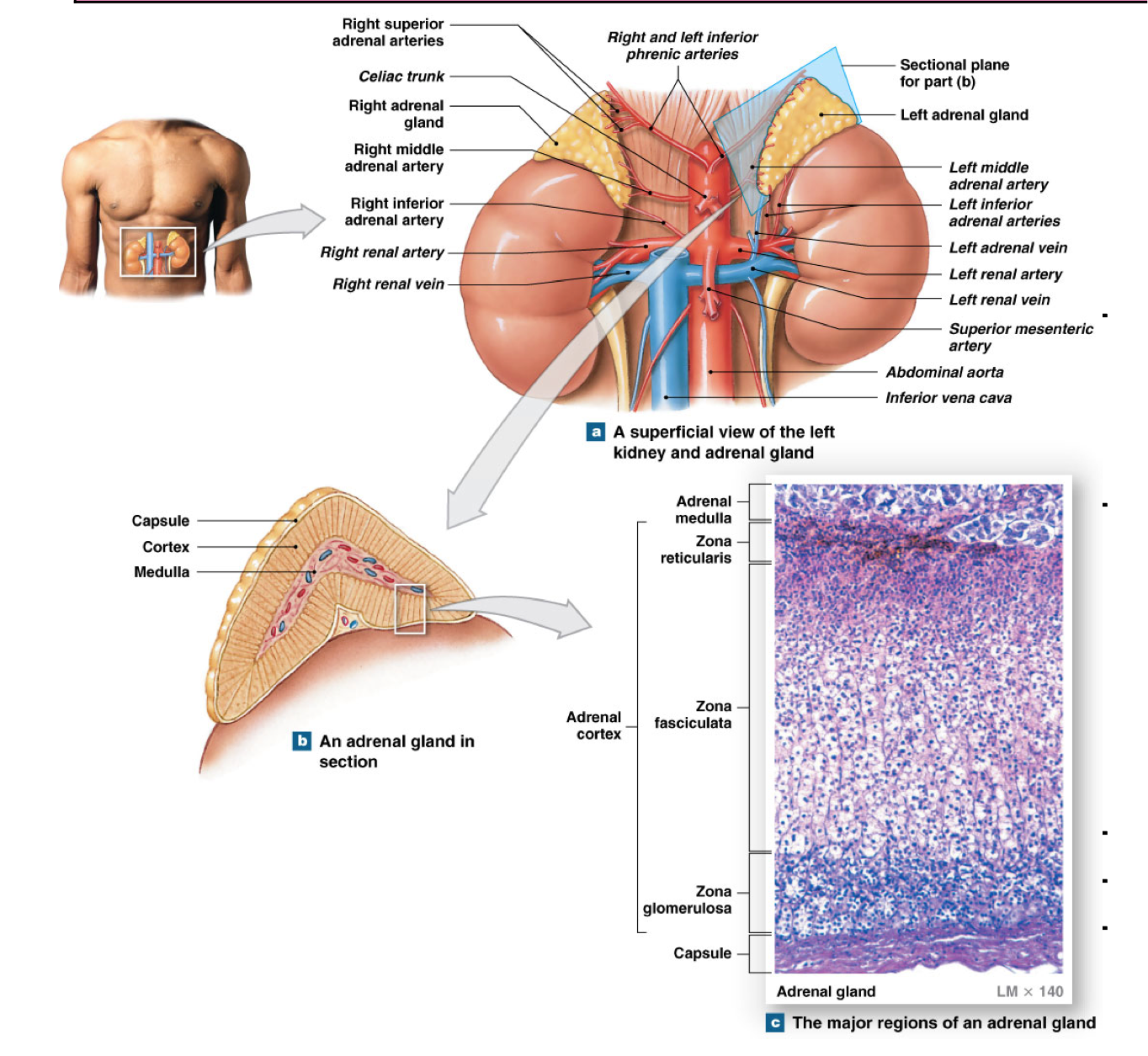
Anatomy of the adrenal glands
Retroperitoneal above each kidney
Composed of:
Outer cortex: corticosteroids (2 dozen steroid hormones)
Inner medulla: epinephrine and norepinephrine
Outer cortex further divided into
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasiculata
Zona reticularis
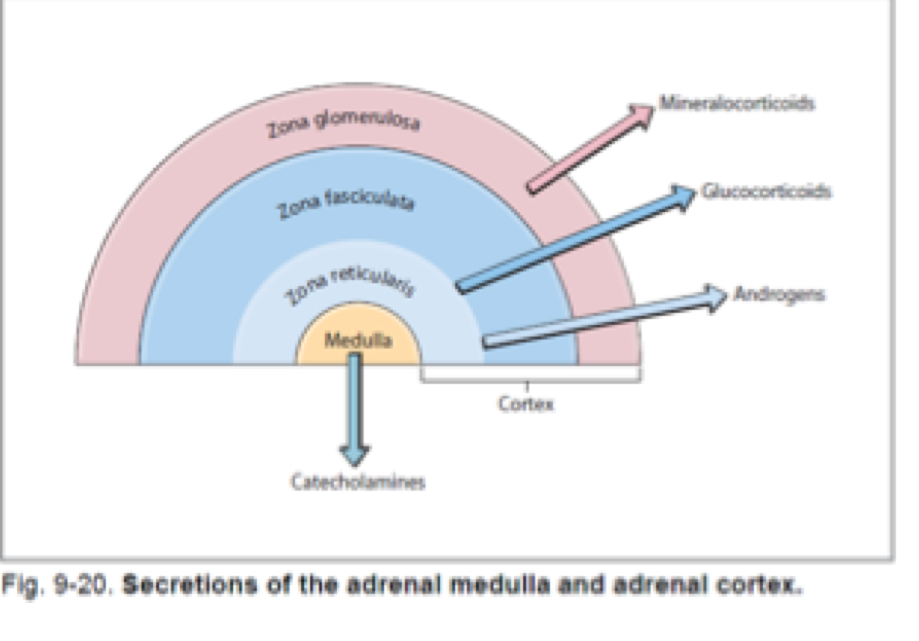
Hormones of the adrenal cortex
All adrenocortical hormones are steroids and are derived from cholesterol
Mineralcorticoids
Glucocorticoids
Adrenal androgens
Mineralcorticoids - give example
Zona glomerulosa
Regulation of sodium potassium levels in ECF
Ex: Aldosterone: released in response to low levels of Na”
Reabsorption of Na+ (and water) from forming urine in kidney, sweat glands, salivary glands at the expense of K+
Glucocorticoids - example
Zona fasiculata
Regulation of carbohydrate levels in ECF
Anti-inflammatory properties
Cortisol, corticosterone: speed up rate of glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) and glycogen formation
Adrenal androgens
Zona reticularis
“Weak” androgens, useful as precursors for the production of estrogen and testosterone by other tissues
Influence muscle mass and sex drive in adult women
How is cortisol regulated
Hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis
Release of CRH is increased by stressors
Inhibition of release of CRH is initiated by cortisol (negative feedback loop)
Chronic high levels of cortisol desensitize receptor cells in the brain
Effect: continued release of CRH and continued production of cortisol
Chronic stress leads to chronically high levels of cortisol
Short term and long term stress response
Stress results from changes in the external environment
→ Neural signals from sensory receptors
Hypothalamus
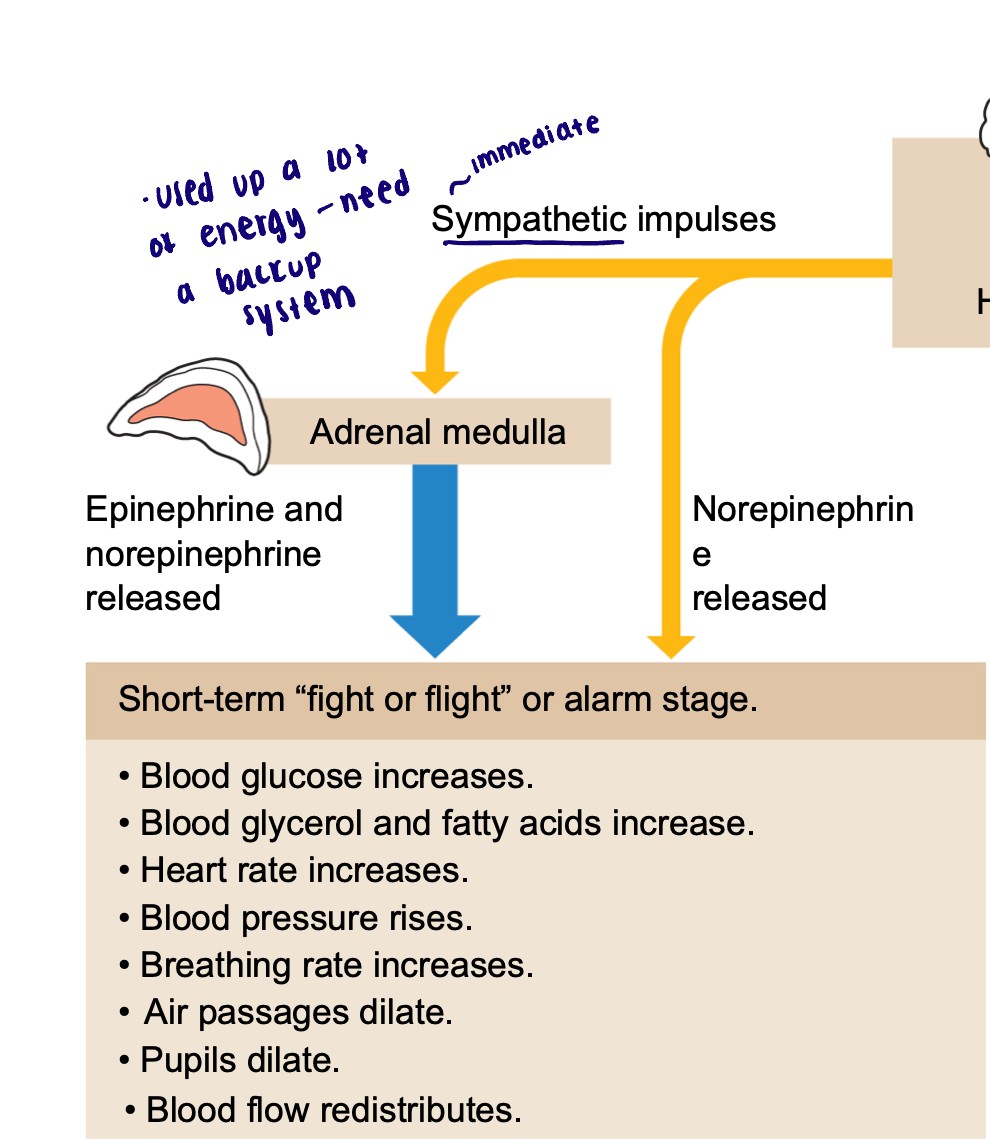
Short term stress response
→ Neural sympathetic impulses
→ Norepinephrine releases and
→ Adrenal medulla
→ Hormonal signals (epinephrine and norepinephrine released)
→ short term “fight or flight” or alarm stage
Blood glucose increases
Blood glycerol and fatty acids increase
Heart rate increases
Blood pressure rises
Breathing rate increases
Air passages dilate
Pupils dilate
Blood flow redistributes
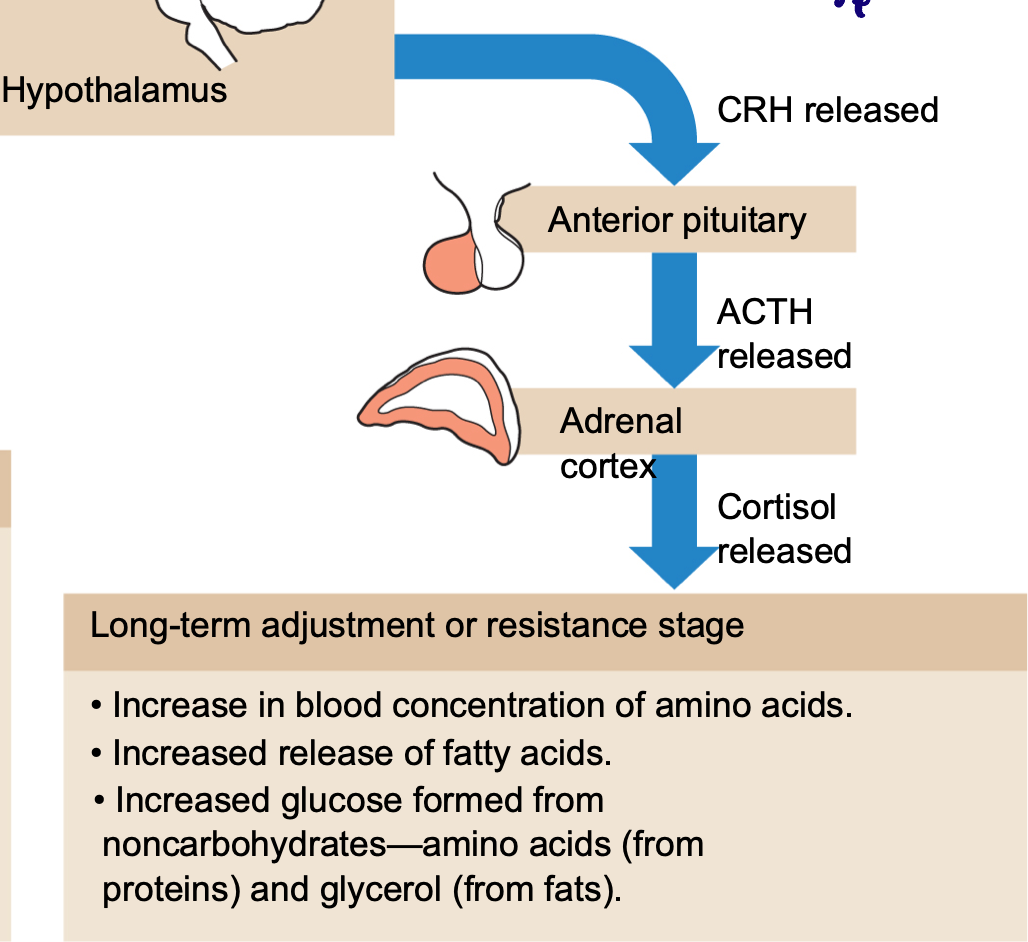
Long term stress response
→ Hormonal CRH released
→ Anterior pituitary
→ Hormonal ACTH released
→ Adrenal cortex
→ Hormonal cortisol released
→ Long term adjustment or resistance stage
Increase in blood concentration of amino acids
Increased release of fatty acids
Increased glucose formed from non-carbohydrates - amino acids