neurological and neuromuscular
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
1
New cards
what are hallmark signs of neurological issues in children?
headache and visual changes
2
New cards
what is torticollis?
contraction of the head due to lack of mobility
3
New cards
how do you treat torticollis?
physical therapy
4
New cards
when should torticollis resolve?
around 1 year
5
New cards
when is the brain fully developed?
adolescent
6
New cards
what should you tell parents to do if you suspect their child has a head injury?
immediately go to the emergency room
7
New cards
which posturing is considered worse?
decerebrate
8
New cards
what kind of lesions are associated with decorticate posturing?
lesions above the brain stem
9
New cards
what kind of lesions are associated with decerebrate posturing?
lesion to the midbrain or brainstem
10
New cards
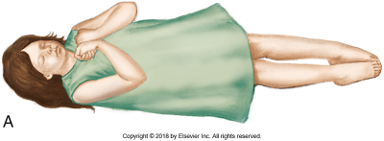
\
decorticate
11
New cards
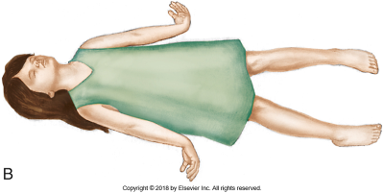
decerebrate
12
New cards
what kind of head injury occurs at the moment of impact?
primary head injury
13
New cards
what is the term for a head injury that occurs due to the body’s response to trauma?
secondary head injury
14
New cards
what is a common cause of primary head injury?
shearing of small veins and arteries
15
New cards
what are common causes of secondary head injury?
resultant swelling (edema) or bleeding
16
New cards
what two symptoms following a head injury indicate immediate hospitalization?
listlessness and vomiting
17
New cards
what is the diuretic of choice to treat increased CSF due to a head injury?
mannitol
18
New cards
what should you monitor for when giving mannitol?
tachycardia and hypotension
19
New cards
when do concussions usually resolve by?
1-3 weeks
20
New cards
a child presents to the ER with signs and symptoms of a concussion. their parent states that they had a concussion before, but it was many years ago, so it doesn’t matter. is this true?
no (consecutive concussions can cause increased damage even when separated by many years)
21
New cards
what are nursing actions that should be taken when a child is diagnosed with a concussion?
elevated HOB and do neurological check at least every 4 hours
22
New cards
what should CSF drainage look like?
clear
23
New cards
who is at the greatest risk for getting bacterial meningitis?
newborns and infants
24
New cards
what are individuals with bacterial meningitis at risk for?
secondary complications (sequalae) - SIADH, hearing loss, neurologic/intellectual disorders, limb loss
25
New cards
VP shunt, recent infections, immunosuppression, cochlear implants, and trauma are all risk factors for -
bacterial meningitis
26
New cards
photophobia, nuchal rigidity, and petechiae and purpura are all signs associated specifically with -
bacterial meningitis
27
New cards
what is the glass rash test?
a glass is placed on the skin to see if the rash will disappear with pressure
28
New cards
what is a worse result for the glass rash test?
if the rash does not disappear with pressure
29
New cards
how does an individual with viral meningitis present?
similar to bacterial meningitis but less severe
30
New cards
is bacterial or viral meningitis more severe?
bacterial
31
New cards
what common cause of viral meningitis?
enterovirus
32
New cards
a patient presents with symptoms that indicate they have some form of meningitis. what is an initial treatment given until it can be determined which type of meningitis they have?
antibiotics (in case they have bacterial)
33
New cards
a patent presents with meningitis and has a high fever, marked LOC change, and severe nuchal rigidity - what type of meningitis do you suspect?
bacterial
34
New cards
a parents presents with meningitis and have a low grade fever, no LOC change, and is only having some nuchal rigidity - what type of meningitis do you suspect?
viral
35
New cards
what kind of isolation is an individual with meningitis placed on?
droplet
36
New cards
what should you prepare for following a meningitis diagnosis?
lumbar puncture, labs and blood culture, assess vital signs and LOC
37
New cards
what is a priority intervention for a patient with meningitis?
administration of antibiotics
38
New cards
what kind of seizures are common in children under two?
febrile seizures
39
New cards
why are febrile seizures common in children under two?
the hypothalamus is not fully developed - can not regulate temperature
40
New cards
an abnormal electrical impulse in 1 area of the brain is known as a -
partial or focal seizure
41
New cards
seizures that occur throughout the brain, have bilateral an symmetrical symptoms, and have conscious impairment are known as -
generalized seizures
42
New cards
seizures associated with high fevers are known as -
febrile seizures
43
New cards
what is status epilepticus?
a prolonged seizure that lasts for at least 15 minutes
44
New cards
a partial seizures that does not cause a change in LOC are called -
simple partial seizure
45
New cards
a partial seizure that causes a change in LOC are called -
complex partial seizures
46
New cards
what is the most important thing to be able to report about a seizure?
the duration
47
New cards
what is the number one concern during and following seizures?
airway
48
New cards
a patient seizes and has dramatic muscle contraction and loss of consciousness. following the seizure, they are confused and exhausted. what type of seizure is this?
tonic-clonic
49
New cards
a patient seizes and has a brief period of LOC change, what kind of seizure do you suspect?
absence
50
New cards
a patient is having a seizure and is having short periods of muscle contractions - what kind of seizure is this?
myoclonic
51
New cards
when are infantile spasms common?
first 8 months of life
52
New cards
an 4 month old has sudden, brief, and symmetric muscle contractions. they flex their head, extended their arms, and drew up their legs. what do you suspect this is?
infantile spasms
53
New cards
what is infantile spasms associated with?
developmental delays/intellectual disabilities
54
New cards
what may some doctors request before an EEG?
NPO
55
New cards
following a seizure, what are some interventions that can be made to maintain a patient airway?
jaw thrust, place on side, suction, O2
56
New cards
what medications can be given to a patient if their seizures to not resolve spontaneously?
benzodiazepines - diazepam and lorazepam
57
New cards
what is a common side effect of Dilantin?
bleeding gums
58
New cards
what is a side effect associated with phenobarbital?
vitamin D defiency
59
New cards
what is a newer, gentler drug used to treat seizures?
Keppra
60
New cards
impaired absorption of CSF resulting in excessive amounts of CSF within the cerebral ventricles -
hydrocephalus
61
New cards
an obstruction outside ventricular system causing decreased absorption of CSF is known as -
communicating hydrocephalus
62
New cards
impediment of CSF flow within ventricular system is known as -
non-communicating or obstructive hydrocephalus
63
New cards
what type of hydrocephalus is more common?
non-communicating or obstructive
64
New cards
what is a hallmark sign of hydrocephalus in infants?
bulging fontanels
65
New cards
a child with hydrocephalus’s head sounds hallow upon percussion, what is this called?
Macewen’s sign
66
New cards
headache and decreased visual acuity in an older child are signs of -
hydrocephalus
67
New cards
what is a common treatment for hydrocephalus?
surgical placement of a shunt
68
New cards
what is the priority NANDA associated with shunt placement to treat hydrocephalus?
risk for infection
69
New cards
when are infections associated with shunt placement most common?
within the first two months following shunt placement
70
New cards
a child has a shunt placed one week ago, what finding would be the most concerning for the nurse?
increased ICP (it shows that the shunt isn’t working properly)
71
New cards
what position should a child be placed in following the placement of a shunt?
on their non-operative side (prevents rapid CSF drainage and keeps pressure on valves)
72
New cards
what is the child at risk for if CSF drains to fast following shunt placement?
subdural hematoma
73
New cards
chronic non-progressive motor dysfunction caused by damage to the motor areas of the brain before, during, or after birth
cerebral palsy
74
New cards
what significantly increases a child’s risk for developing cerebral palsy?
low birth weight
75
New cards
when is the most common time to develop cerebral palsy?
during birth
76
New cards
abnormal posturing associated with cerebral palsy is called -
opisthotonos
77
New cards
an infant presents to their six month check up. the infant still has his startle reflex and has poor head control. what do you suspect?
cerebral palsy
78
New cards
a mother of a child with cerebral palsy asks if there is anything their child can take to help decrease the amount of twitchy they do. what could you suggest?
baclofen pump
79
New cards
a mother is worried because their child is uncontrollable movement in their legs and has not been successfully treated with alterative methods. what could you suggest?
rhizotomy (procedure to cut overactive nerves)
80
New cards
what are two surgeries associated with cerebral palsy?
Achilles tendon lengthening and hamstring release
81
New cards
what is important patient teaching that needs to be given following a rhizotomy?
the child needs to remain flat and should not bend or twist for at list 4 weeks
82
New cards
failure of the neural tube to close completely -
spinal bifida
83
New cards
when in gestation does spina bifida occur
week 4
84
New cards
the higher up the lesion occurs on a child with spina bifida -
the more deficits
85
New cards
what is an important consideration to make when taking care of a patient with spina bifida?
latex allergy
86
New cards
what is the diagnostic tool used to diagnosis spina bifida called?
transillumination
87
New cards
what dose transillumination do?
determines the structures within the sac
88
New cards
what type of spina bifida is normally asymptomatic?
occulta
89
New cards
what symptom can you see at birth that is associated with occulta spina bifida?
lack of movement in the legs
90
New cards
in what type of spina bifida do the meninges protrude and there is translucency seen?
meningocele
91
New cards
in which type of a spina bifida do you see both the meninges and spinal cord protrude, without translucency?
meningomyelocele
92
New cards
how should an infant with spina bifida be kept prior to surgery?
in prone position with moistened sterile gauze covering the area
93
New cards
what position should an infant with spina bifida be kept in postoperatively?
prone or on their side
94
New cards
what infection are infants with spina bifida prone to?
UTIs (frequent catheterization)
95
New cards
a genetic disorder that causes the progressive weakness and wasting of skeletal muscles -
spinal muscular atrophy
96
New cards
when is spinal muscular atrophy normally diagnosed?
within the 1st year
97
New cards
which type of spinal muscular atrophy is the most severe?
type 1
98
New cards
what is the most common cause of death in children with type 1 spinal muscular atrophy?
respiratory failure
99
New cards
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is only seen in -
males
100
New cards
what is the most common form of muscular dystrophy?
Duchenne muscular dystrophy