Why should firms profit maximise
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
20 marks
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Introduction
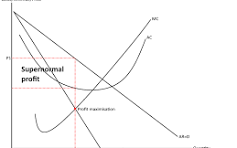
Profit maximisation occurs where marginal revenue equals marginal cost (MR = MC).
Traditional economic theory assumes firms should profit maximise to survive, grow, and operate efficiently.
However, this objective can be questioned due to alternative business goals and real-world constraints.
Paragraph 1: Profit maximisation ensures long run survival and competitiveness
Point:
Firms should profit maximise in order to ensure long run survival in competitive markets
Explanation:
Abnormal profit provides the financial buffer needed to cover costs, withstand demand shocks and compete against more efficient rivals
Example:
During covid, many experienced sharp falls in demand due to lockdowns, it was essentially a survival of the fittest
Analysis:
Firms that fail to profit maximise may be unable to reinvest or cut prices, making them vulnerable to competitors.
In competitive or contestable markets, inefficient firms are likely to exit, meaning profit maximisation becomes necessary for survival rather than choice.
Evaluation:
However, firms may accept lower profits in the short run to gain market share or survive economic downturns, suggesting profit maximisation may be a long-run objective rather than a short-run one.
Paragraph 2: Profit maximisation enables investment, growth and economies of scale.
Point:
Firms should profit maximise because profits fund investment and long term growth
Explanation:
Retained profits can be used for capital investment, research and development and expansion into new markets
Analysis:
Higher profits allow firms to expand output and benefit from economies of scale, reducing unit costs and increasing efficiency.
Lower costs improve competitiveness and reinforce profitability, creating a virtuous cycle of growth and profit maximisation.
Evaluation:
However, excessive growth may lead to diseconomies of scale, such as management inefficiencies, which can increase costs and reduce the benefits of profit maximisation.
Paragraph 3: Profit maximisation aligns with shareholder interests and economic efficiency
Point:
Firms should profit maximise to meet shareholder expectations and promote economic efficiency
Explanation:
Shareholders invest to receive dividends and capital gains, both of which depend on profits.
Profit maximisation encourages firms to minimise costs and allocate resources efficiently.
Analysis:
Firms that profit maximise are incentivised to be productively efficient, reducing waste and responding to consumer demand.
This can improve overall welfare through lower prices or better-quality goods.
Evaluation:
However, in firms with separation of ownership and control, managers may pursue alternative objectives (e.g. sales maximisation or satisficing), meaning profit maximisation may not always dominate decision-making.
Profit maximisation diagram
Shift in AD diagram