Bronsted-Lowry theory of acid and bases
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is a bronsted-lowry acid?
Acids are proton donors.
What is a bronsted-lowry base?
Bases are proton acceptors.
Acids dissociate according to what equilibrium?
HA(aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + A− (aq)
What is a strong acid?
Strong acids completely dissociate (ionise) into their ions.
What is a weak acid?
Weak acids partially dissociate (ionise) into their ions.
What is a conjugate acid?
A species which has gained a proton.
Conjugate acids act as acids in the backwards reaction i.e. they donate a proton to return to the original base.
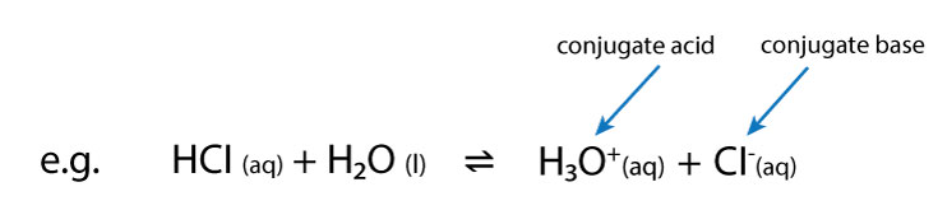
What is a conjugate base?
A species which has lost a proton.
Conjugate bases act as bases in the backwards reaction i.e. they accept a proton to return to the original acid.
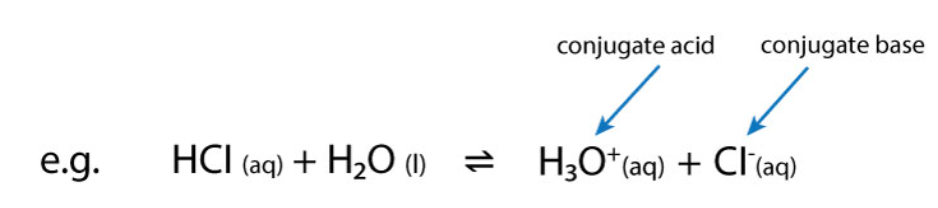
Identify the conjugate pairs in this reaction.
HCl and Cl- are a conjugate pair.
H2O and H3O+ are another conjugate pair.
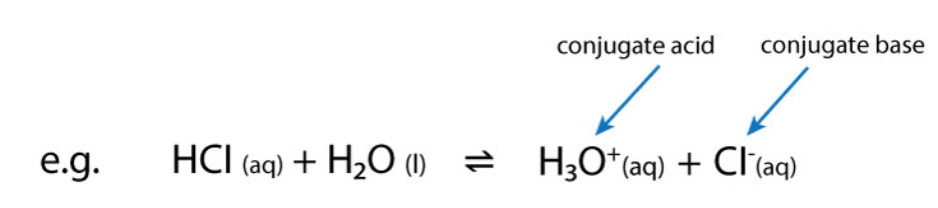
What is Ka?
The equilibrium constant for acids.
Ka= [H(aq)+][A(aq)−] / [HA(aq)]
What does the Ka value of a weak acid suggest?
The degree of dissociation- the higher the Ka, the stronger the acid.
What is the ionic product of water?
Kw=[H+][OH−]
Kw has a value of 1×10−14 mol2 dm−6 (at 298 K).
What can be said about the concentration of H+ ions and OH- ions in pure water?
The concentrations are equal.