EAC 4: Industrial Electronics Devices
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Q28. Referred to as a bidirectional trigger diode.
a. Triac
b. UJT
c. BJT
d. Diac
d. Diac
Q29. Voltage required to turn on any thyristor.
a. Trigger voltage
b. Breakover voltage
c. Barrier voltage
d. Supply voltage
b. Breakover voltage
Q30. Also known as a four-layer diode.
a. Diac
b. Shockley diode
c. Zener diode
d. FET
b. Shockley diode
Q31. The thyristor counterpart of the unijunction transistor.
a. UJT
b. PUT
c. SBS
d. SCS
b. PUT
Q32. Minimum current required to keep a thyristor “on”.
a. Holding current
b. Trigger current
c. Supply current
d. Collector current
a. Holding current
Q33. A unidirectional three-terminal device, the most popular of thyristors.
a. SCS
b. Triac
c. UJT
d. SCR
d. SCR
Q34. The angle of an AC supply voltage during which an SCR is “off”.
a. Conduction angle
b. Firing delay angle
c. Right angle
d. Off angle
b. Firing delay angle
Q35. Thyristors are most often used as
a. Switches
b. Amplifiers
c. Buffers
d. Decoders
a. Switches
Q36. The total internal series resistance of the UJT.
a. Bulk’s resistance
b. Total resistance
c. Interbase resistance
d. RIS
c. Interbase resistance
Q37. The most popular and typical breakover voltage of a diac.
a. 32V
b. 16V
c. 8V
d. 4V
a. 32V
Q38. The peak voltage of a PUT is
a. VD + VBB
b. VG + VBB
c. VD + VG
d. VBB
c. VD + VG
Q39. A UJT has η = 0.65 and is connected to a 20V supply. What is its VEB1?
a. 12V
b. 13.6V
c. 12.7V
d. 14V
b. 13.6V

Q40. The three-terminal semiconductor device that acts in either direction.
a. Triac
b. SCR
c. Diac
d. SCS
a. Triac
Q41. The "P" in PUT stands for
a. Programmable
b. Performance
c. Peak
d. Post
a. Programmable
Q42. The terminals of a UJT are
a. Gate, Anode, Cathode
b. Anode, Cathode
c. Emitter, Base
d. Emitter, Base1, Base2
d. Emitter, Base1, Base2
Q43. The lowest current that can prevent the transition of a UJT from conduction to blocking region.
a. Switching current
b. Emitter current
c. Valley current
d. Peak current
c. Valley current
Q44. The SCS has how many gate terminals?
a. 0
b. 1
c. 2
d. 3
c. 2
Q45. What device has two terminals connected in inverse-parallel that pass in two directions?
a. Triac
b. Diac
c. Shockley
d. SCR
b. Diac
Q46. What is the breakover voltage of a PUT if it is connected to a 15V supply across the gate terminal?
a. 10.7V
b. 23.7V
c. 15.7V
d. 5.3V
c. 15.7V
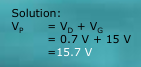
Q47. The gap between the forward blocking region and the forward conduction region.
a. Bandgap
b. Switching region
c. Jump gap
d. Negative resistance region
d. Negative resistance region
Q48. The cathode of the PUT is the counterpart of which terminal in UJT?
a. Anode
b. Base2
c. Emitter
d. Base1
d. Base1
Q49. An electronic switch that has the highest single-device current capacity and can withstand overloads better.
a. Thyratrons
b. Ignitrons
c. SCR
d. Triac
c. SCR
Q50. Group of devices with 4 or more semiconductor layers.
a. Transistors
b. Diodes
c. Thyristors
d. Op-Amps
c. Thyristors
Q51. Identify which of the following is a three-layer device.
a. SCS
b. Diac
c. Triac
d. PUT
b. Diac
Q52. What device can be modeled by a diode and two resistors?
a. BJT
b. Diac
c. SCR
d. UJT
d. UJT
Q53. A junction that is formed by adding controlled amounts of an impurity to the melt during crystal growth is termed as
a. Fused junction
b. Unijunction
c. Alloy junction
d. Doped junction
d. Doped junction
Q54. A triac is a ______.
a. 2 terminal switch
b. 2 terminal bilateral switch
c. 3 terminal unilateral switch
d. 3 terminal bidirectional switch
d. 3 terminal bidirectional switch
Q55. A thyristor equivalent of a thyratron tube is _____.
a. Diac
b. Triac
c. SCR
d. PUT
c. SCR
Q56. Which of the following describes a triac?
a. Conducts when not triggered
b. Conducts when not triggered in both directions
c. Conducts when triggered in one direction
d. Conducts when triggered in both directions
d. Conducts when triggered in both directions
Q57. Minimum anode current to hold a thyristor at conduction.
a. Trigger
b. Maintaining current
c. Holding current
d. Threshold voltage
c. Holding current
Q58. General term for semiconductor devices primarily used as switches.
a. Shockley
b. Thyratron
c. Thyristor
d. Relay
c. Thyristor
Q59. A two-terminal, unidirectional thyristor.
a. DIAC
b. Shockley
c. TRIAC
d. Diode
b. Shockley
Q60. A thyristor is basically ______.
a. PNPN device
b. A combination of diac and triac
c. A set of SCRs
d. A set of SCR, diac and triac
a. PNPN device
Q61. What is the PNPN device with two gates?
a. Diac
b. Triac
c. SUS
d. SCS
d. SCS
Q62. Which device incorporates a terminal for synchronizing purposes?
a. Diac
b. Triac
c. SUS
d. SCR
c. SUS
Q63. An SCR is a _______.
a. Unijunction device
b. Device with three junctions
c. Device with four junctions
d. Device with two junctions
b. Device with three junctions
Q64. A thyristor can be turned off
a. By reducing the anode current below the holding current value
b. By reversing the anode voltage
c. Either a or b
d. Both a and b
d. Both a and b
Q65. Minimum duration of pulse triggering system for thyristors is ________.
a. At least 10 microseconds
b. At least 30 milliseconds
c. At least 10 milliseconds
d. At least 1 second
a. At least 10 microseconds
Q66. A device that cannot be triggered by voltage of either polarity is ________.
a. Diac
b. Triac
c. SCS
d. All of the above
c. SCS
Q67. Technically, what does dicing mean?
a. Process of joining two diacs
b. Circuit of reducing noise
c. Device for reducing magnetic and radio interference
d. Process of breaking the silicon slice into chips
d. Process of breaking the silicon slice into chips
Q68. The term used to describe the process whereby two transistors with positive feedback are used to simulate the action of the thyristor.
a. Arcing
b. Latching
c. Damping
d. Switching
b. Latching
Q69. It is the minimum anode current to hold a thyristor at conduction.
a. Trigger
b. Maintaining current
c. Holding current
d. Threshold voltage
c. Holding current
Q70. Electron tube containing mercury functioning as a rectifier.
a. Thyratron
b. Ignitron
c. Thyrector
d. SCR
b. Ignitron
Q71. How do you stop the conduction during which the SCR is also conducting?
a. Remove voltage gate
b. Increase cathode voltage
c. Interrupt anode current
d. Reduce gate current
c. Interrupt anode current
Q72. A series RC connected in parallel with an SCR to eliminate false triggering is the _______.
a. Crowbar
b. Snubber
c. Varistor
d. Eliminator
b. Snubber
Q73. Which are the three terminals of a TRIAC?
a. Gate, anode1 and anode2
b. Gate, source and sink
c. Base, emitter and collector
d. Emitter, base1 and base2
a. Gate, anode1 and anode2
Q74. The term used to describe the process whereby two transistors with positive feedback are used to simulate the action of the thyristor.
a. Arcing
b. Latching
c. Damping
d. Switching
b. Latching
Q75. The minimum emitter-to-base voltage to trigger the UJT is the ________.
a. Forward breakover voltage
b. Trigger
c. Breakdown voltage
d. Peak voltage
d. Peak voltage
Q76. The ratio of the emitter to base1 resistance to the interbase resistance of a UJT is called ________.
a. Aspect ratio
b. Current gain
c. Voltage gain
d. Intrinsic standoff ratio
d. Intrinsic standoff ratio
Q77. For a UJT, it is the region between the peak and valley points as seen in its characteristic curve.
a. Active region
b. Negative resistance region
c. Trigger region
d. Saturation region
b. Negative resistance region
Q78. This device is two zener diodes connected back-to-back in series and is used to support voltage surges and transients.
a. Thyristor
b. Varactor
c. Thyrector
d. Phanatron
c. Thyrector
Q79. Refers to the number of degrees of an AC cycle during which the SCR is turned on.
a. Conduction angle
b. Firing delay angle
c. Induction angle
d. ON angle
a. Conduction angle
Q80. A four-element solid-state device that combines the characteristics of both diodes and transistors.
a. Varactor
b. Zener diode
c. Tunnel diode
d. SCR
d. SCR
Q81. Electron tube equivalent to solid state SCR.
a. Triode
b. VTVM
c. CRT
d. Thyratron
d. Thyratron
Q82. Find the two stable operating conditions of an SCR.
a. Conducting and non-conducting
b. Oscillating and quiescent
c. NPN conduction and PNP conduction
d. Forward conducting and reverse conducting
a. Conducting and non-conducting
Q83. How do you stop conduction during which SCR is also conducting?
a. Remove voltage gate
b. Increase cathode voltage
c. Interrupt anode current
d. Reduce gate current
c. Interrupt anode current
Q84. When an SCR is triggered or on conducting, its electrical characteristics are similar to what other solid-state device (as measured between its cathode and anode)?
a. The junction diode
b. The varactor diode
c. The tunnel diode
d. The hot carrier diode
a. The junction diode
Q85. Which of the following does not have a base terminal?
a. UJT
b. PNP
c. SCR
d. NPN
c. SCR
Q86. A series RC circuit that is connected in parallel with an SCR to eliminate false triggering.
a. Crowbar
b. Snubber
c. Varistor
d. Eliminator
b. Snubber
Q87. A circuit that protects a sensitive circuit from a sudden increase in supply voltage.
a. Crowbar
b. Snubber
c. Varistor
d. Eliminator
a. Crowbar
Q88. A two-terminal, bidirectional thyristor.
a. DIAC
b. Shockley
c. TRIAC
d. Diode
a. DIAC
Q89. A DIAC is equivalent to inverse parallel combination of
a. Shockley diodes
b. Schottky
c. BJT
d. SCRs
a. Shockley diodes
Q90. A TRIAC is equivalent to inverse parallel combination of
a. Shockley
b. Schottky
c. BJT
d. SCRs
d. SCRs
Q91. Which are the three terminals of a TRIAC?
a. Gate, anode1 and anode2
b. Gate, source and sink
c. Base, emitter and collector
d. Emitter, base1 and base2
a. Gate, anode1 and anode2
Q92. Which device can be modeled by a diode and two resistors?
a. BJT
b. DIAC
c. SCR
d. UJT
d. UJT
Q93. The minimum emitter to base1 voltage to trigger the UJT.
a. Forward breakover voltage
b. Trigger
c. Breakdown voltage
d. Peak voltage
d. Peak voltage
Q94. The ratio of the emitter to base1 resistance to the interbase resistance of a UJT.
a. Aspect ratio
b. Current gain
c. Voltage gain
d. Intrinsic standoff ratio
d. Intrinsic standoff ratio
Q95. For UJT, it is the region between the peak and valley points.
a. Active region
b. Negative resistance region
c. Trigger region
d. Saturation region
b. Negative resistance region
Q96. Typical breakover voltage of an SBS.
a. 2V
b. 4V
c. 8V
d. 16V
c. 8 V
Q97. The trigger current is applied to the…
a. Anode
b. Gate
c. Cathode
d. Base
b. Gate
Q98. The region where breakover voltage of the SBS drops to 1V instantaneously.
a. Falldown region
b. Fallback region
c. Breakback region
d. Breakdown region
c. Breakback region
Q99. The ratio of RB1 and RBB is called
a. Intrinsic standoff ratio
b. Reuber’s ratio
c. Common mode rejection ratio
d. Cat’s ratio
a. Intrinsic standoff ratio
Q100. It is a system in which a precise movement of a large load is controlled by a relatively weak control signal.
a. Synchro
b. Servo
c. Gyro
d. Motor
d. Motor
Q101. It is the name given to the electrical output of the control transformer.
a. Error signal
b. Correct signal
c. Differential signal
d. Error-free signal
a. Error signal
Q102. In a servo system, there are series of overshoots which are known as ______.
a. Eating
b. Climbing
c. Hunting
d. Resting
c. Hunting
Q103. This principle stabilizes a system to minimize the problem of overshoot.
a. Clamping
b. Fanning
c. Damping
d. Lagging
c. Damping
Q104. It is the property of gyro causing it to tilt in a direction perpendicular to the direction of any outside force.
a. Recession
b. Tecession
c. Precession
d. Postsession
c. Precession
Q105. It is the tendency of a spinning wheel to remain in fixed position in space.
a. Mobility
b. Rigidity
c. Accuracy
d. Alternativity
b. Rigidity
Q106. A universally mounted gyro has how many gimbals?
a. One
b. Two
c. Three
d. Four
b. Two
Q107. In what direction will a gyro precess in response to an outside force?
a. Perpendicular to the force
b. Perpendicular to the spin axis
c. Parallel to the force
d. Parallel to the spin axis
a. Perpendicular to the force
Q108. How many degrees of freedom does a rate gyro usually have?
a. One
b. Two
c. Three
d. Four
a. One
Q109. What gyro characteristic provides the basis for the operation of rate gyro?
a. Decision
b. Precession
c. Weight
d. Spin
b. Precession
Q110. What is defined as a device that gives an indication, usually in the form of a voltage, that is proportional to the acceleration to which it is subjected?
a. Inertia meter
b. Accelerometer
c. Speedometer
d. Voltmeter
b. Accelerometer