Bio Exam 3 Flashcards
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Phospholipids form a
liquid bilayer, which is like a “lake: in which some proteins float
What is the liquid mosaic model
The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the cell membrane. It states that the membrane is composed of a fluid lipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The lipids can move laterally within the membrane, giving it a fluid nature. The proteins are scattered throughout, creating a mosaic pattern.
definition of mosaic
made of many discrete components
definition of fluid
components can move freely
Membranes are dynamic, meaning
they are constantly forming, transforming, fusing and breaking down
The cell membrane is selectively
permeable
membrane fluidity depends on factors such as,
liquid composition, lipid composition, and temperature
Membrane fluidity is associated with
permeability
Biological membranes are composed of
phospholipids and proteins
Integral membrane proteins are
at least partially embedded in the bilayer
Transmembrane Proteins
some integral proteins are transmembrane proteins, which extend all the way through the phospholipid bilayer
Anchored membrane proteins
covalently attached to fatty acids or other lipids inside the membrane
Peripheral membrane proteins
lack exposed hydrophobic regions, are noncovalently attached to the membrane and do not penetrate the bilayer
Top Hat Question: In a eukaryotic cell, a vesicle carried a protein to the cell membrane where it was inserted into the phospholipid bilayer. The vesicle budded off from the ___ before being inserted into the cell membrane.
a
cis-Golgi
b
Rough ER
c
medial-Golgi
d
Smooth ER
e
trans-Golgi
trans-Golgi
Protein or lipid components of membranes can be modified to have ______ added to them
carbohydrates
Top Hat question: Which of these proteins is most likely to be synthesized in the rough ER? Select all that apply.
a
Insulin a peptide hormone that travels in the bloodstream
b
β-adrenergic receptor which sits in the membrane of heart cells and signals to the cell to contract when bound to extracellular epinephrine
c
Dynein a motor protein that facilitates movement of cilia
d
Actin a component of the actin cytoskeleton
e
Lipase an acid hydrolase enzyme that uses water to break down fat molecules
a
Insulin a peptide hormone that travels in the bloodstream
b
β-adrenergic receptor which sits in the membrane of heart cells and signals to the cell to contract when bound to extracellular epinephrine
e
Lipase an acid hydrolase enzyme that uses water to break down fat molecules
Cell recognition
one cell specifically recognizes and binds to another cell of a certain type
Cell adhesion
the connection between the two cells is stregthened
What involves proteins and carbohydrates at the cell surface
Cell recognition and cell adhesion
What are the two types of cell adhesion
Homotypic: the same molecule sticks out from both cells and bind to each other
Heterotypic: the calls have different proteins that bind together
What are cell junctions
specialized structures comprised of many different proteins that hold cells together
What are tight junctions
a tight seal between cells, ensure directional movement of materials
What are gap junctions
form tunnels so that adjacent cells can communicate by exchanging small molecules, and electrical impulses
What are desmosomes
hold cells together and also allow materials to move around in the intercellular space
What is the ECM
the extracellular matrix - a macromolecule-rich gel outside of cells
What are integrins
one type of adhesion receptor that can facilitate movement by binding and reattaching to the extracellular matrix
The cell membrane is selectively ______
permeable
What is diffusion
the process of random movement of a solute from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
When particles are evenly distributed, they are at ______
equilibrium
Top Hat: The components of a biological membrane that allow it to have fluidity are...
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
integral membrane proteins
b
carbohydrates
c
oligosaccharides
d
peripheral membrane proteins
e
lipids
lipids
Top Hat: A portion of the primary structure of an integral membrane protein is shown here. Which amino acids are most likely to comprise the transmembrane domain?
![]()
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
#1-2
b
#3-17
c
#18-19
d
#1-19
e
Other
#3-17
Top Hat: types of membrane proteins
Review
Which membrane protein type would likely be removed most easily from a cell membrane in a laboratory experiment?
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
Integral
b
Anchored
c
Transmembrane
d
Peripheral
peripheral
Top Hat: cardiomyocytes
Review
Heart muscle cells beat in unison because of the rapid spread of electrical current through…
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
tight junctions
b
desmosomes
c
gap junctions
d
peripheral membrane proteins
e
neurons
gap junctions
What is concentration
the number of particles in a given volume
What type of substances can cross membranes by diffusion
Liquid-soluble (hydrophobic) substances
Membranes move across a permeable membrane until concentration is ____
equal on both sides
Energy for passive transport comes from the _______
concentration gradient
The rate at which substances diffuse in a solution depends on which factors
Size and mass, temperature, density of the solution, concentration gradient in the system, area across which a substance diffuses and the distance it diffuses
Water diffuses across a membrane in a process called
osmosis
Isotonic
equal solute concentration inside and outside the cell
Hypotonic
lower solute concentration outside the cell
Hypertonic
higher solute concentration outside the cell
Passive Transport
does not require energy input and transports substances down a concentration gradient
In a cell water moves across the membrane through channel proteins called ____
aquaporins
What are ion channels?
integral membrane proteins that have hydrophilic pores
most are gated can be open or closed to ion diffusion
The gate opens when the protein is stimulated to change conformation
change in shape can be stimulated by the binding of a chemical signal (ligand)
What are carrier proteins
transport polar molecules, such as glucose, across membranes in both directions
Active transport
requires energy to move substances against a concentration and/or electrical gradient
The energy for active transport comes from
ATP hydrolysis, which releases energy
Active transport involves three proteins. What are they?
Uniporter: moves on substance in one direction
Symporter: moves two substances in one direction
Antiporter: moves two substances in opposite directions
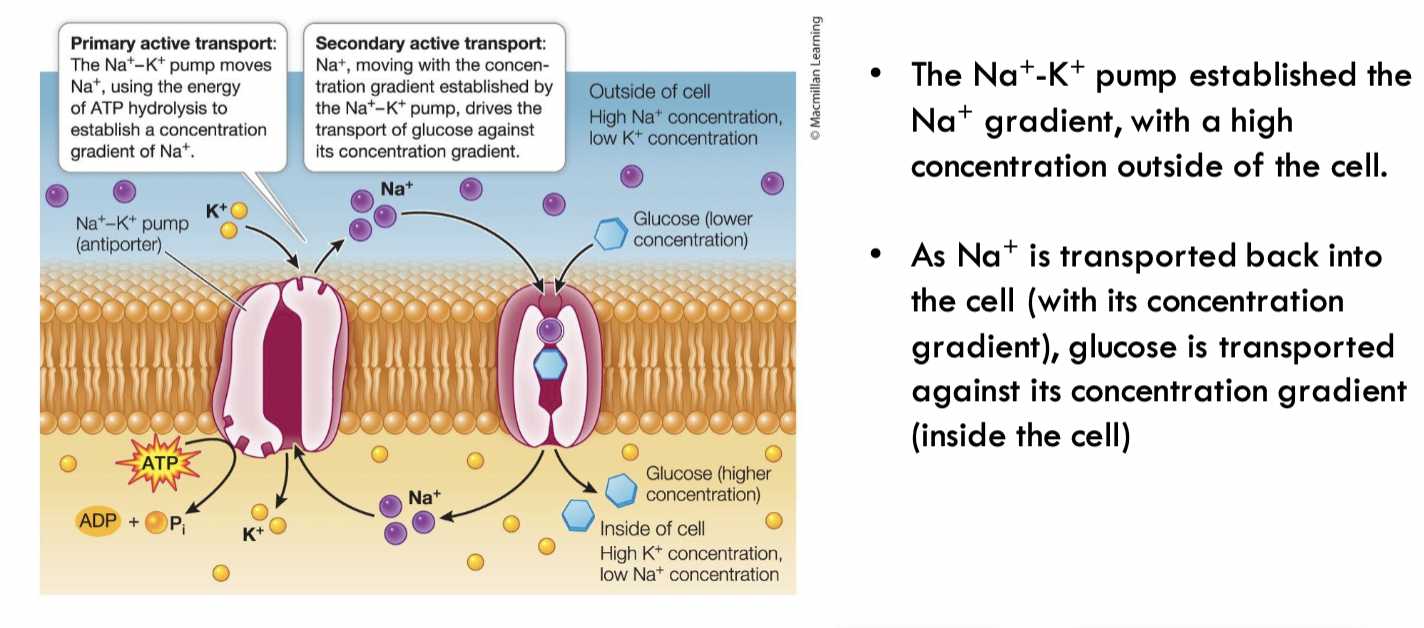
Primary active transport
requires direct hydrolysis of ATP to drive movement of specific ions against their concentration gradients
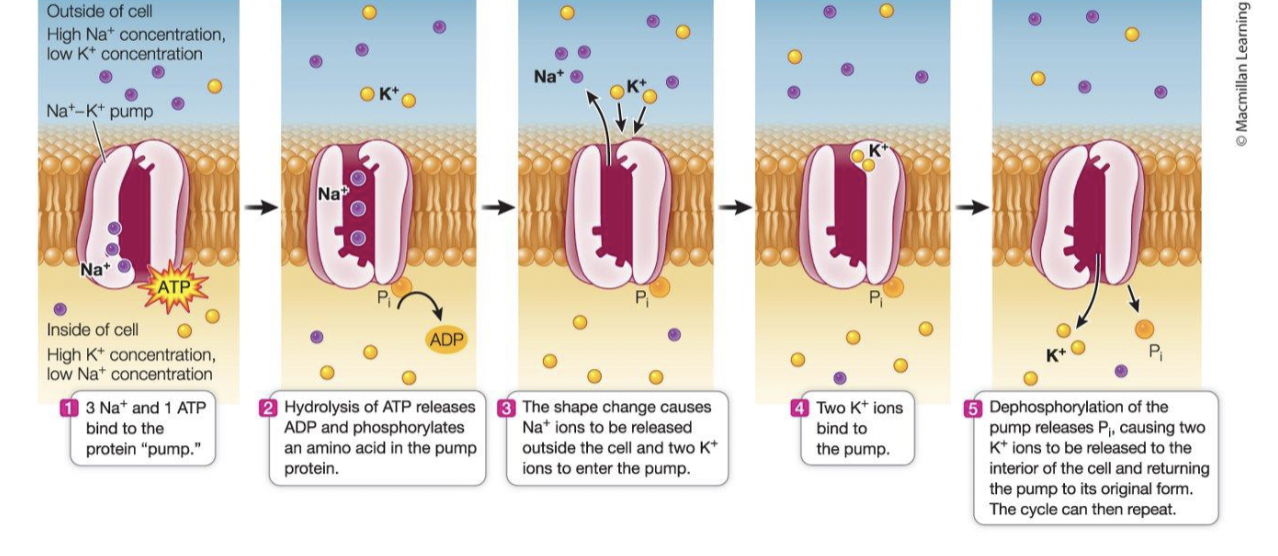
Secondary active transport
energy comes from an ion concentration gradient that is established by primary active transport
Eukaryotic cells may take up and release fluids, large molecules, and smaller cells via
endocytosis
What is phagocytosis?
molecules or entire cells are engulfed
What is pinocytosis?
a vesicle forms to bring small dissolved substances or fluids into a cell
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
molecules at the cell level service recognize and trigger uptake of specific molecules
Top Hat: Which statement about diffusion is true?
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
The concentration gradient of a solute depends on the size of the molecule.
b
Equilibrium in a solution is the end point of diffusion.
c
The net movement of particles depends on the temperature of the solution.
d
Diffusion is most efficient over long distances.
e
Diffusion can reduce selective permeability of a membrane.
B
rate of diffusion
Review
You are monitoring the diffusion of a molecule across a membrane. Of the options listed below, the fastest rate of diffusion would result from an internal concentration of ____ µM and an external concentration of ____ µM.
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
5; 60
b
35; 40
c
50; 40
d
50; 50
e
100; 120
A
osmosis
Review
Solution X is hypotonic relative to solution Y if…
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
X has a solute concentration that is lower than the solute concentration of Y.
b
Y has a greater volume of fluid than X.
c
X and Y have equal amounts of solute but Y has a greater volume of fluid.
d
X has a solute concentration that is higher than the solute concentration of Y.
e
X and Y have equal volumes of fluid but X has a greater amount of solute.
A
If a cell has an increased need for a particular molecule already present in a higher concentration within the cell than in the extracellular fluid, the cell might use active transport, which usually moves molecules
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
in the same direction as diffusion moves them.
b
in a direction opposite to the one in which diffusion moves them.
c
in a direction that tends to bring about equilibrium.
d
toward higher pH.
e
from inside to outside the cell.
B
What is signal transduction?
Definition: Signal transduction is the process by which cells convert external signals into specific cellular responses.
Importance: It plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including cell growth, development, and immune response.
Steps: Signal reception, signal transduction, and cellular response.
Signaling molecules: Hormones, neurotransmitters, growth factors, and cytokines.
Key components: Receptors, second messengers, protein kinases, and transcription factors.
Examples: cAMP, MAPK, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.
Regulation: Feedback loops, cross-talk, and desensitization mechanisms.
Diseases: Dysregulation of signal transduction can lead to cancer, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
All cells process information from the environment when a _____ binds to a ______
ligand, receptor
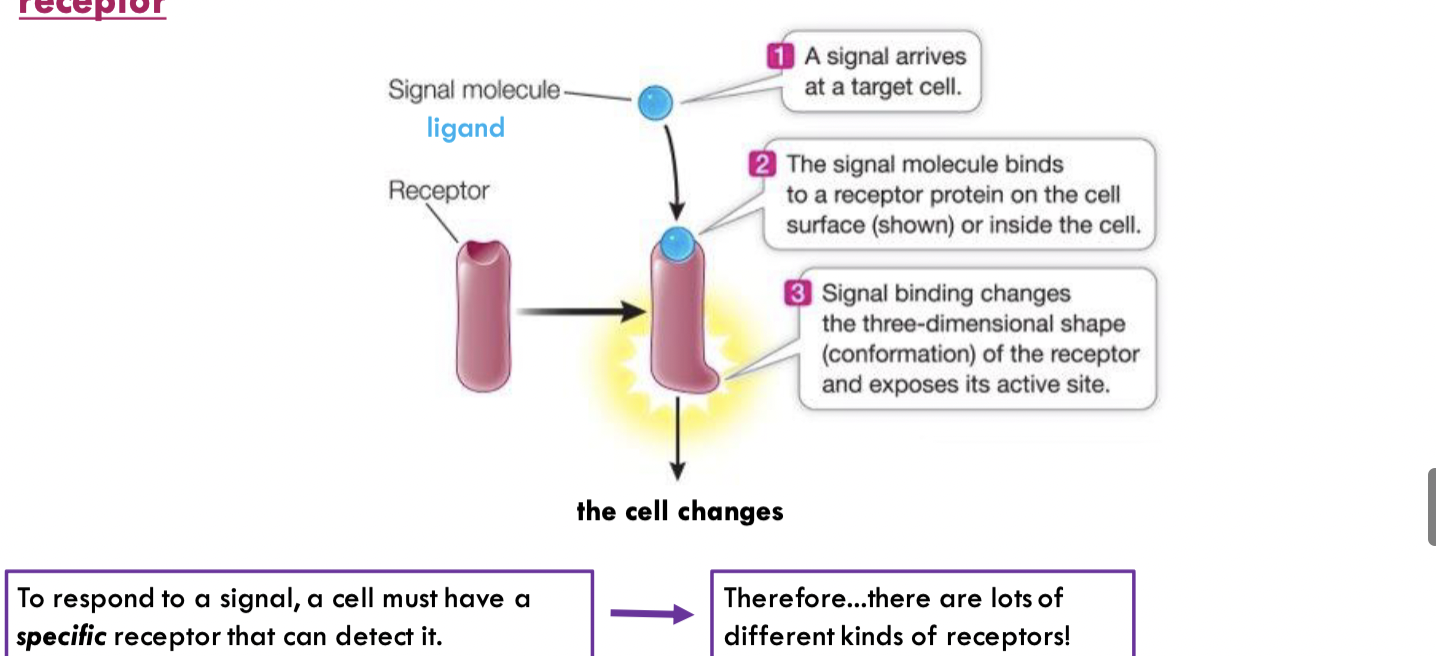
Justacrine signals
bind to adjacent cells in contact with the secreting cells
Autocrine signals
bind to the receptors on the cell that secretes them
Paracrine signals
bind to receptors on nearby cells m
What are hormones
signals that travel to distant cells, often using the circulatory system
Ion channel linked receptors
allows ions to enter or leave a cell
signal binding results in a change in share of the channel protein. This results in the channel opening.
Ex: the acetylcholine receptor
The signal is acetylcholine
When the channel is open, sodium ions enter the cell
Protein kinase receptors
catalyze phosphorylation of themselves and/or other proteins to change their shapes and functions
Ligand binding to a G protein-coupled receptor activates a
a protein called a G protein
Both primary and secondary active transport
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
generate ATP.
b
are based on passive movement of Na+ ions.
c
include the passive movement of glucose molecules.
d
use ATP directly.
e
can move solutes against their concentration gradients.
E
Endocytosis
Review
An important difference between phagocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis is that
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
in phagocytosis, the membrane forms coated vesicles.
b
vesicles do not form in receptor-mediated endocytosis.
c
dissolved substances can be taken up by phagocytosis.
d
receptor-mediated endocytosis is more specific.
e
macromolecules can enter through receptor-mediated endocytosis.
D
Classification of ACh
Review
Acetylcholine (ACh) is a molecule released by a neuron. That ACh diffuses across the extracellular space to a nearby neuron, where it binds and initiates a response. How would you classify acetylcholine?
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
Juxtacrine signal
b
Paracrine signal
c
Hormone
d
Temporal signal
e
Autocrine signal
B
General signal transduction
Review
Which is the correct order of the steps in a generalized signal transduction pathway?
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
Signal molecule activates target cell → target cell binds to receptor → receptor is activated
b
Signal molecule is secreted by nearby cell → signal molecule enters cell → signal activates receptor
c
Signal molecule enters nucleus → signal molecule binds to DNA → transcription of specific genes occurs
d
Signal molecule binds to receptor → molecules within cell transduce signal → cell responds
D
in the brain _____ binds to its _____ to inhibit wakefulness
adenosine, receptor
When an _____ binds to a receptor, it has the same effect as the natural ligand
agonist
When an ______ binds to a receptor, it prevents the ligand from binding and does not trigger a response
antagonist
Intracellular receptors
respond to signals that can cross the cell membrane
many are transcription factors
Transcription factors change the expression of genes in a cell
What are the three kinds of eukaryotic membrane receptors
Ion channel linked receptors - ligand binding allows ions to enter or leave a cell
protein kinase receptors - ligand binding activates a protein kinase cascade, which can lead to short-or-long term responses in the cell
G protein coupled receptors - ligand binding activates the production of a secondary messenger, which can lead to short-or-long term responses in the cell
A protein kinase cascade can amplify an intracellular signal by…
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
opening gap junctions to allow diffusion of signals from neighboring cells.
b
using nitric oxide to quickly diffuse into cells, amplifying the response.
c
using transcription factors to increase gene expression.
d
activating one kinase molecule that can then trigger the activation of many proteins.
D
After a ligand binds to a G protein coupled receptor and activates a G protein, what happens next?
The active G protein activates an effector protein
G proteins are active when bound to ____
GTP
What is cAMP
a second messenger that amplifies and distributes a signal. cAMP is produced from ATP be effector protein adenylyl cyclase.
Second messengers are…
signaling molecules that increase in concentration inside a cell in response to a signaling molecule that binds at the surface
amplify the signal in a signal transduction pathway
What is happening in the photo
cAMP relays and amplifies the signal coming from Epinephrine by activating Protein Kinase A
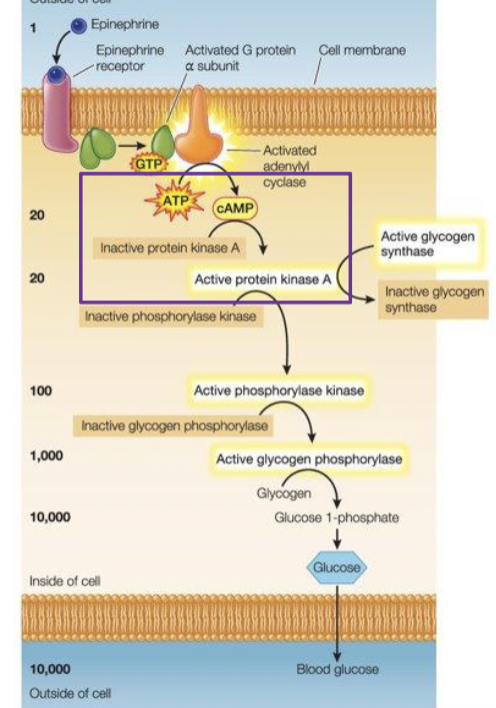
Protein Kinase A is activated by…
high concentration of cAMP
Examples of second messengers
cAMP - produced by Adenylyl cyclase following GCPR activation, increase in cAMP concentration can activate PKA
IP3 and DAG - produced by Phospholipase C following GCPR activation
Ca2+ - release into the cytosol following GPCR activation, can help activate PKC
Nitric Oxide - produced following activation of the acetylcholine receptor
IP3 and DAG are…
second messengers made from the phospholipids in the cell membrane
Hydrolysis of PIP2 by…
Phospholipase C makes IP3 and DAG
IP3 binds to and activates a _____
Ca2+ channel in the ER membrane, which release stores of Ca2+ from the ER into the cytosol
Increased Ca2+ helps activate…
Protein Kinase C (PKC)
Ca2+ bound PKC binds to DAG, which
fully activates it
What is nitric oxide
a second messenger that acts between acetylcholine and the relaxation of smooth muscle in blood vessels
What are the three ways that cells respond to signals
opening ion channels, changing enzyme activity, differential gene expression
How are signal transduction pathways turned off?
GTPases can hydrolyze GTP into GDP, which inactivates the G protein or second messengers can be degraded
When is a signal tranduction pathway not regulated properly
when a signal transduction pathway is not activated or inactivated correctly
A ligand binds to the membrane receptor...
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
inside the cell.
b
outside the cell.
c
Both A and B can be true.
d
Neither A nor B are ever true.
B
Antagonists differ from agonists because they...
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
trigger a response from the receptor.
b
trigger a response more slowly than agonists.
c
trigger a response more quickly than agonists.
d
do not trigger a response from the receptor.
D
Which of these is directly activated by a hormone binding to a GPCR?
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
The effector protein
b
Adenylyl cyclase
c
The G protein
d
A protein kinase
e
cAMP
C
When the G protein is active, ___ has been replaced by ____.
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
GTP; GDP
b
GDP; GTP
c
cAMP; GTP
d
GTP;cAMP
B
Adenylyl cyclase is then activated by...
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
being phosphorylated by a kinase.
b
the creation of cAMP from ATP.
c
the creation of GTP from GDP.
d
the active G protein.
D
When adenylyl cyclase is activated and undergoes a conformational change, it will...
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
make ATP from cAMP.
b
make cAMP from ATP.
c
make ADP from ATP.
d
make ATP from ADP.
B