Biology Topic 1: Cell Biology
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are eukaryotic cells?
Cells with a nucleus containing DNA. Examples include animal and plant cells.
List three organelles found in animal cells and describe their function.
Nucleus: Contains DNA coding for proteins.
Cytoplasm: Site of chemical reactions and contains enzymes.
Mitochondria: Site of aerobic respiration, providing energy.Ribosomes: Synthesize proteins.
Compare the structure of a prokaryotic cell with a eukaryotic cell. (4 marks)
Prokaryotic cells: Smaller, no nucleus, DNA in a circular strand, may have plasmids.
Eukaryotic cells: Larger, nucleus present, DNA enclosed within the nucleus.
Both have a cell membrane and cytoplasm.
What is cell differentiation, and why is it important?
The process where cells develop specific Functions to perform particular functions. It is important for creating specialized tissues and organs.
Explain how a sperm cell is adapted for its function.
Streamlined head and long tail for swimming.
Many mitochondria provide energy for movement.
Acrosome contains enzymes to penetrate the egg.
The sperm cell has a streamlined head and long tail for efficient swimming, numerous mitochondria for energy production, and an acrosome filled with enzymes to help penetrate the egg's outer layer.
Suggest why nerve cells have a long axon and many dendrites. (2 marks)
Long axon allows impulses to travel long distances.
Dendrites form connections with other nerve cells for communication.
What is the maximum magnification of a light microscope?
Approximately ×2000.
Calculate the magnification if the image size is 5 mm and the object size is 0.02 mm.
Magnification = Image size ÷ Object size = 5 ÷ 0.02 = ×250.
Explain one advantage of using an electron microscope over a light microscope. (1 mark)
An electron microscope has a higher resolution, allowing for detailed images of sub-cellular structures.
Why must inoculating loops be sterilized before use?
To kill unwanted microorganisms and prevent contamination.
Design an experiment to test the effectiveness of different antibiotics on bacterial growth.
Soak paper discs in different antibiotics.
Place discs on agar gel spread with bacteria.
Incubate plates at 25°C for 48 hours.
Measure the zone of inhibition for each disc.
Why is it important to not completely seal a Petri dish with tape? (1 mark)
To prevent anaerobic bacteria from growing, which could be harmful.
What is mitosis?
A type of cell division produces two identical daughter cells for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction.
Describe what happens to chromosomes during mitosis.
Chromosomes replicate and form X shapes during interphase.
They align at the equator.
Chromatids are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell.
Two nuclei form, and the cell divides.
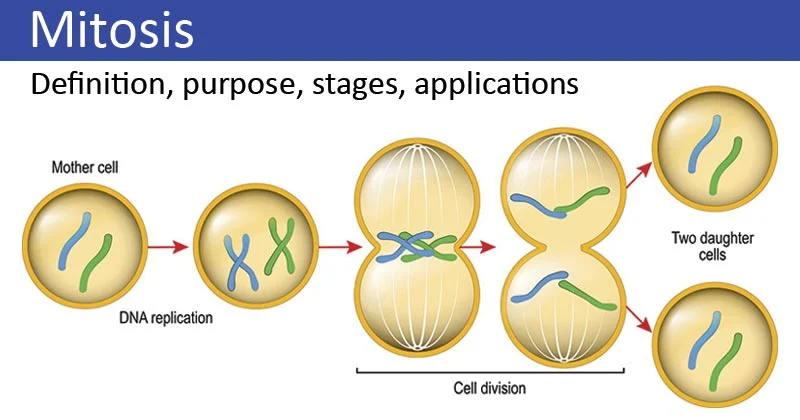
Why is mitosis important in multicellular organisms? (2 marks)
Ensures identical cells for growth and repair.
Vital for asexual reproduction to produce genetically identical offspring
What are the three types of stem cells?
Embryonic stem cells: Can become any cell type.
Adult stem cells: Found in bone marrow; produce limited cell types (e.g., blood cells).
Meristem cells: Found in plants; can differentiate into any plant cell.
Explain how stem cells can be used in medicine.
Replace damaged cells (e.g., nerve cells in spinal injuries).
Therapeutic cloning can produce genetically identical tissues, reducing rejection risk.
Research to treat diseases like diabetes.
Evaluate the use of embryonic stem cells in medical research. (6 marks)
Advantages: Can treat diseases, use unwanted embryos, reduce organ rejection.
Disadvantages: Ethical concerns about embryo destruction, risk of uncontrolled differentiation, and infection.
Conclusion: Balancing potential benefits against ethical concerns is crucial.
What is osmosis?
The movement of water from a high water potential to a low water potential through a partially permeable membrane.
Predict what happens to an animal cell placed in a hypotonic solution.
Water enters the cell by osmosis, causing it to swell and potentially burst.
Describe two adaptations of the alveoli for efficient gas exchange. (2 marks)
Large surface area increases the rate of diffusion.
Thin walls provide a short diffusion pathway.
Explain how active transport is used in root hair cells.
Root hair cells absorb mineral ions from the soil, moving them from a lower to a higher concentration using energy from respiration.
Compare diffusion and active transport. (3 marks)
Diffusion: Passive, down a concentration gradient.
Active transport: Requires energy, against a concentration gradient.
Both involve the movement of substances across membranes.