04. Pulse Code Modulation
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
pulse code modulation (PCM)
It is essentially analog-to-digital conversion of a special type where the information contained in the instantaneous samples of an analog signal is represented by digital words in a serial bit stream.
instantaneous samples
PCM is essentially analog-to-digital conversion of a special type where the information contained in the____ of an analog signal is represented by digital words in a serial bit stream.
TRUE
PCM is relatively inexpensive digital circuitry that may be used extensively.
PCM
It is derived from all types of analog sources that may be merged with data signals and transmitted over a common high-speed digital communication system.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] In long-distance digital telephone systems requiring repeaters, a clean PCM waveform can be regenerated at the output of each repeated, where the input consists of a noisy PCM waveform.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] The noise performance of a digital system can be superior to that of an analog system.
appropriate coding techniques
The probability of error for the system output can be reduced even further by the use of _____.
sampling
quantizing
encoding
3 Basic Operations of PCM Signal (HINT: SQE)
flat-top PAM signal
Sampling operation generates a ______.
quantizing operation (quantization)
It approximates analog values by using a finite number of levels.
approximates
Quantizing operation _____ analog values by using a finite number of levels.
uniform quantizer
quantization error
quantized PAM signal output
3 Steps of Quantizing Information (HINT: UQQ)
quantized PAM signal
PCM signal is obtained from the _______ by encoding each quantized sample value into a digital word.
sampling
quantization
encode
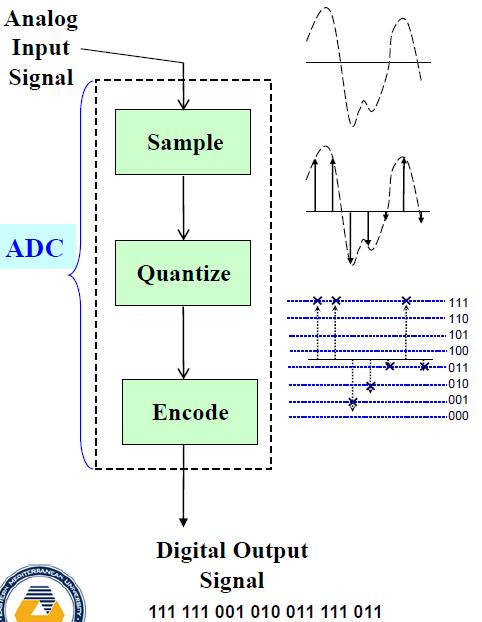
3 Functions of Analog-to-digital Converter (ADC)
sampling
This make the signal discrete in time.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] If the analog input has a bandwidth of W Hz, then the minimum sample frequency such that the signal can be reconstructed without distrotion.
W Hz
If the analog input has a bandwidth of ____, then the minimum sample frequency such that the signal can be reconstructed without distrotion.
quantization
This makes the signal discrete in amplitude.
quantization
This rounds off to one of q discrete levels.
encode
It maps the quantized values to digital words that are v bits long.
v bits long
It maps the quantized values to digital words that are _____.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] If the Nyquist sampling theorem is satisfied, then only quantization introduces distortion to the system.
analog-to-digital conversion
continuous in amplitude
The output of a sampler is still ______.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] Each sample can take on any value
infinite
The number of possible values in sampling is _____.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] To transmit as a digital signal, we must restrict the number of possible values.
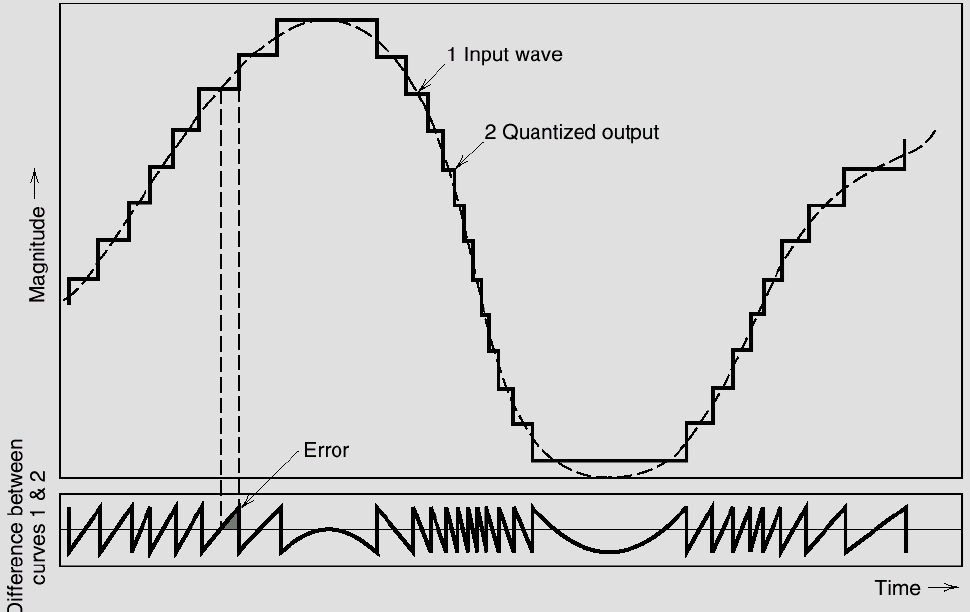
quantization
It is the process of “rounding off” a sample according to some rule.
quantization error
uniform quantizers
Most ADCs use ______.
equally spaced apart
In uniform quantization, the quantization levels are _____.
uniform quantizers
They are optimal when the input distribution is uniform. When all values within the dynamic range of the quantizer are equally likely.
dynamic range
Uniform quantizers are optimal when all values within the _______ of the quantizer are equally likely.
sampling timing
quantized 5-level
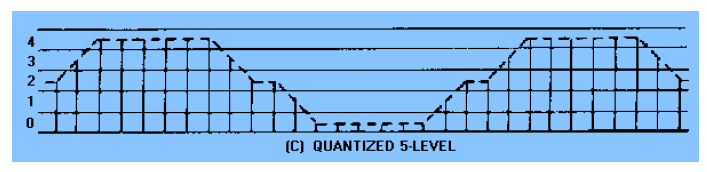
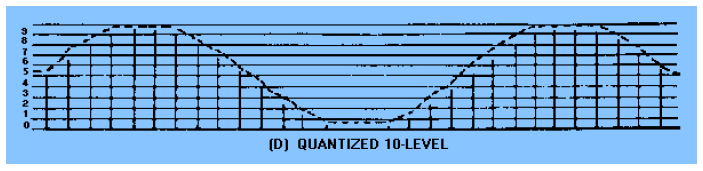
quantized 10-level
33 bits
How many bits were used to encode a signal?
M possible signal levels
The output of the quantizer is one of __________.
n-bit binary word
If we want to use a binary transmission system, then we need to map each quantized sample into an _________.
M = 2n
Formula in Finding Quantization/Signal Levels
n = log2(M)
Formula to find the n-bit binary word.
encoding
It is the process of representing each quantized sample by a v bit code word.
one-on-one
In encoding, the mapping is _____ so there is no distortion introduced by encoding.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] Some mappings are better than others.
gray code
This gives the best end-to-end performance.
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] The weakness of Gray codes is poor performance when the sign bit (MSB) is received in error.
most significant bit (MSB)
the sign bit is also known as the _____.
one bit position
With gray codes, adjacent samples differ only in _____.
number of quantization levels
In M = 2n, M is the?
number of bits per sample
In n = log2(M), n is the?
counting or ramp (Maxim ICL7126 ADC)
serial or successive approximation (AD 570)
parallel or flash encoders (CA3318)
3 Popular Techniques Used to Implement ADC Encoding Operation (HINT: CSP)
Maxim ICL7126 ADC
example of an ADC in counting or ramp
AD 570
example of a serial or successive approximation
CA3318
example of a parallel or flash encoders
to generate PCM word
What is the objective of practical PCM circuits?
serialized
Parallel digital output obtained needs to be _____ before sending over a 2-wire channel.
parallel-to-serial converters
Serializing parallel digital output is accomplished by _____.
Serial Input-Output (SIO) chip
example of a parallel-to-serial converter
UART
USRT
USART
Examples of Serial Input-Output Chips (HINT: 3Us)
TRUE
[TRUE or FALSE] The spectrum of the PCM signal is not directly related to the spectrum of the input signal.
bandwidth
The _____ of (serial) binary PCM waveforms depends on the bit rate R and the waveform pulse shape used to represent the data.
R = nfs
formula for bit rate R
number of bits in the PCM word (M=2^n)
In R = nfs, what does n represent?
sampling rate
In R = nfs, what does fs represent?
BPCM(min) = R/2 = nfs/2
For no aliasing case (fs≥2B), the minimum bandwidth of PCM is?