Anatomy and Physiology - Bone Anatomy and the Skull
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
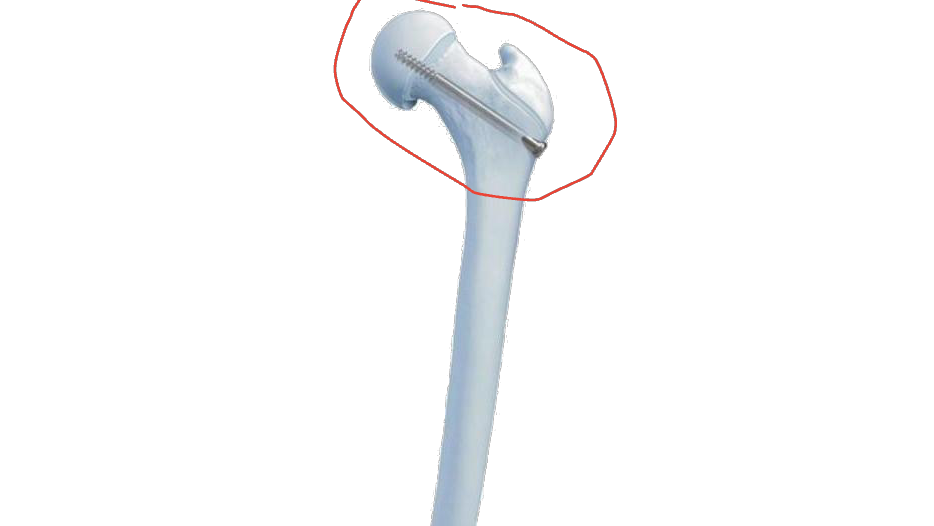
Epiphysis
rounded end of a long bone that forms a joint
both on the distal and proximal ends of the bone
Articular Cartilage
smooth white elastic tissue that covers the end of bones in joints
think of when you eat a chicken and see that white part on the end of the bone, that’s what that is!
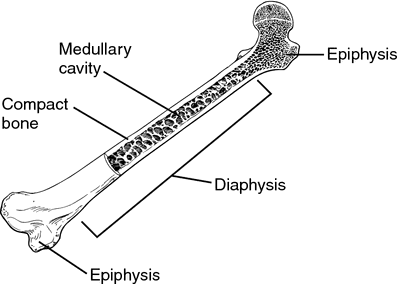
Diaphysis
middle shaft of the bone/central part
Basically everything of the long bone except the ends/epiphysis and articular cartilage
Long bones
LONGER than width, heads at each end
Humerus, femur, metatarsal, phalanges
Short bones
cube shaped and contain higher amounts of spongy bone
_________ and _________ would be an example of short bones.
carpals, tarsals
Flat bone
thinner, flattened, and often curved
thin layers of compact and spongy bone
_______, _________, and ___________ would be an example of flat bones.
Skulls, ribs, sternum
Sesamoid bones
bones embedded in a tendon
The ________ is an example of a sesamoid bone.
patella
Irregular bones
unsual shape and they do not fit another category
The ____________ would be an example of irregular bones.
vertebrae
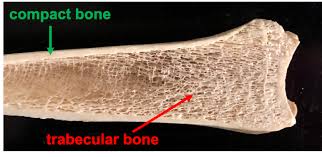
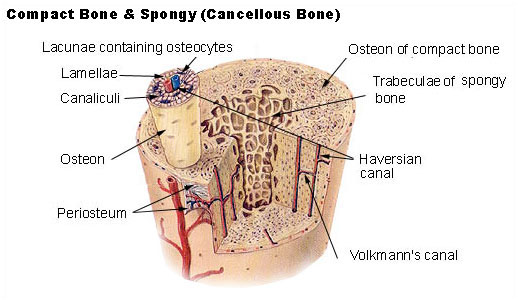
Compact bone
DENSEST part of the bone
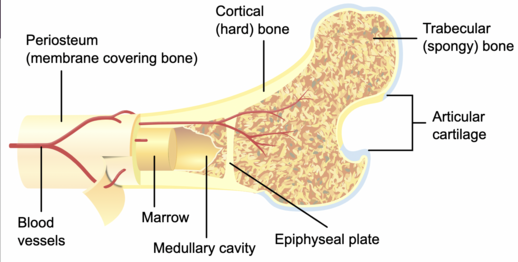
Periosteum
layer of dense tissue that contains blood vessels and sensory neurons
innermost layer of endosteum
Spongy bone
looks like a sponge
it is where bone marrow is
holds stem cells that are able to turn into red blood cells, etc.
AKA cancellous bone
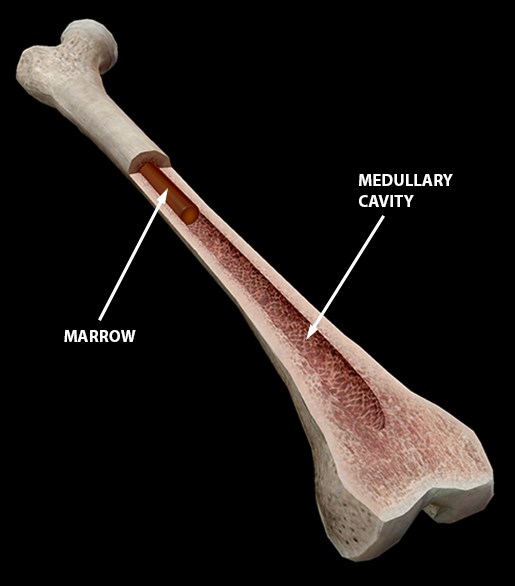
Medullary Cavity
hollow area inside diaphysis
filled with yellow bone marrow
mostly fat cell
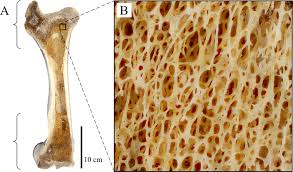
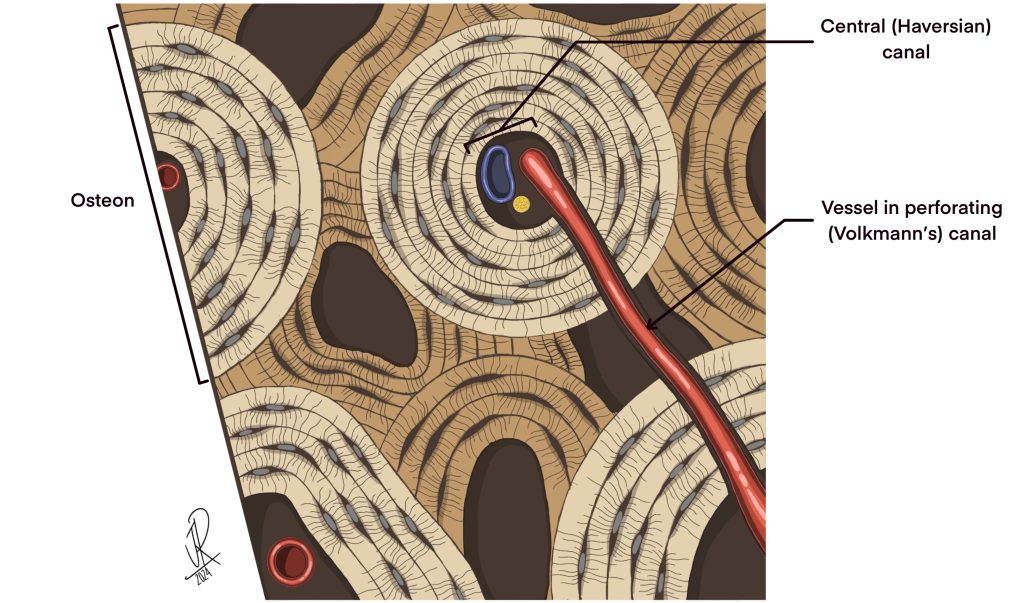
Osteons
circular units
The whole bone area that looks like a circle
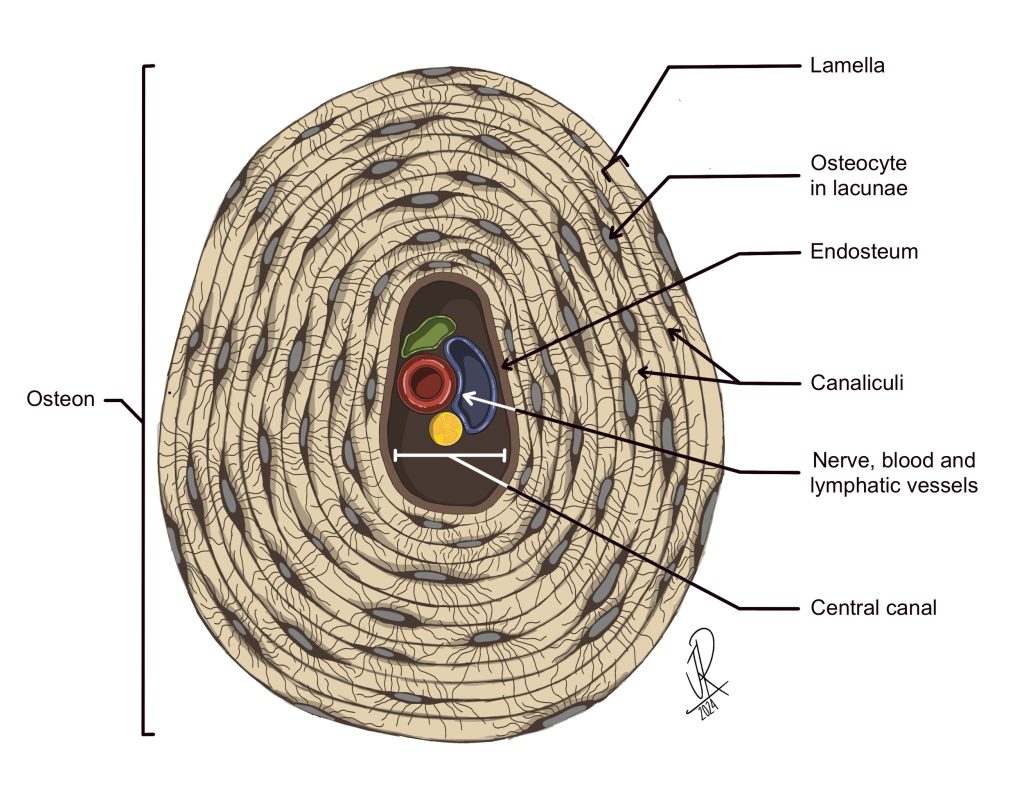
Lamellae
notice how it's not lacunae (lacunae are pits where osteocytes are located)!
these are sheets
Canalculi
tiny chanels each osteocyte is connected back to
Osteoclast
dissolve bony matrix
Osteoblast
help build bone
example: “B” for BUILD
Axial Skeleton
everything around the longitudinal (vertical) center plane of body
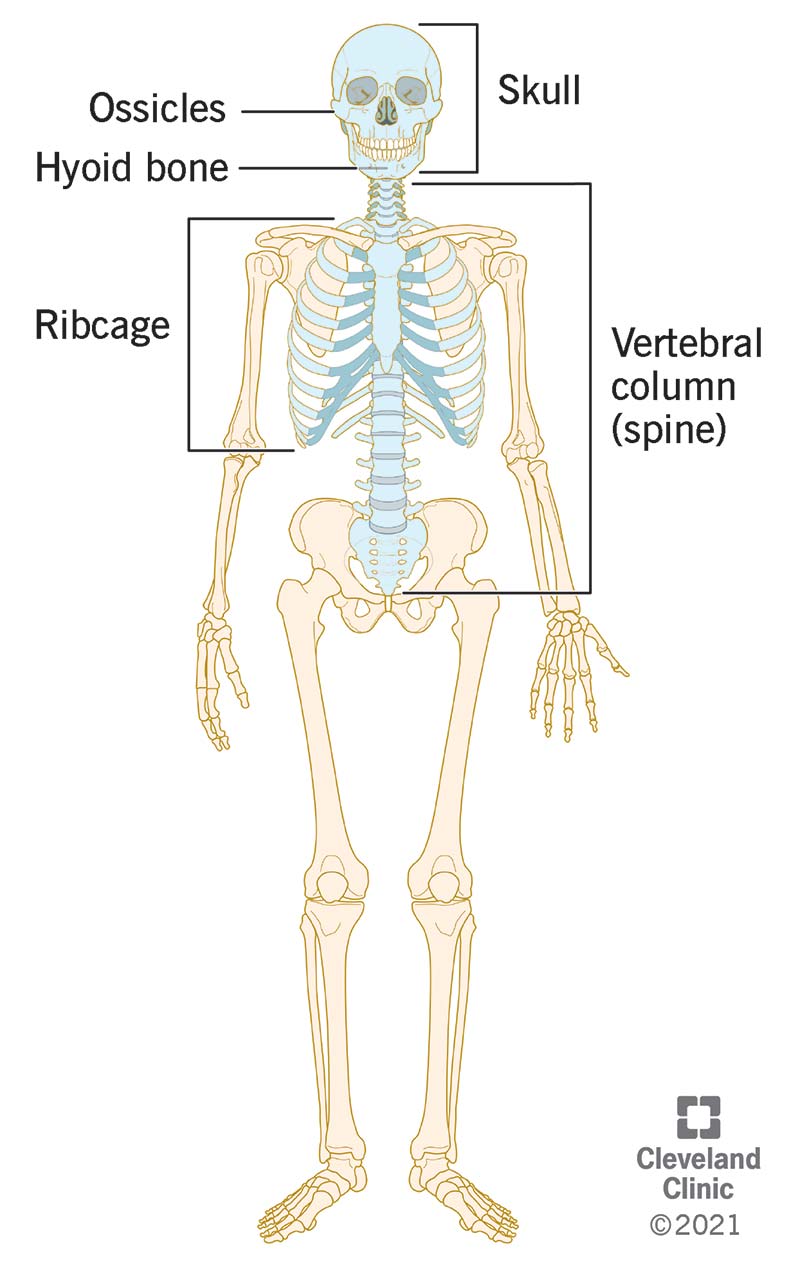
Appendicular Skeleton
includes appendages/extremities: the arms, legs, AND pelvis

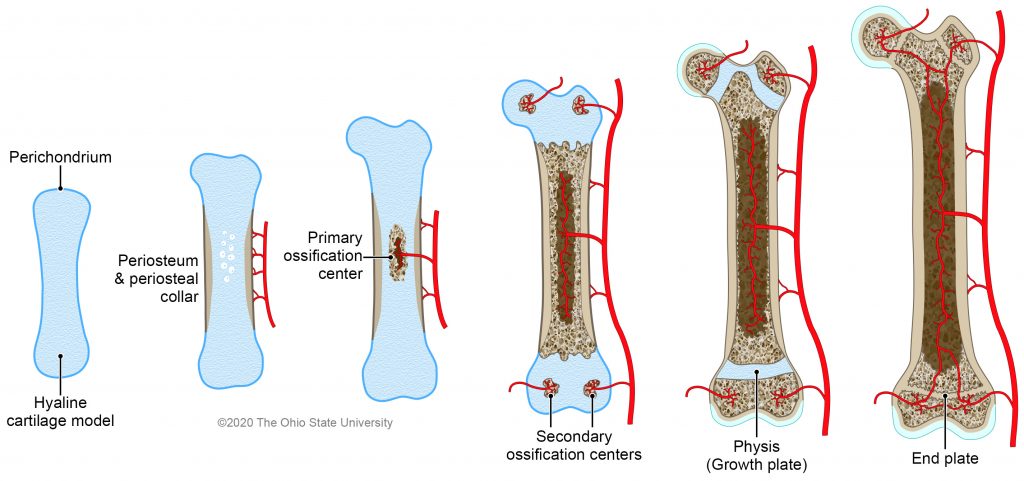
Ossification
the process by which cartilage is being replaced by bone
CARTILAGE —> BONE
this happens as babies grow older, their cartilage is being turned into bone
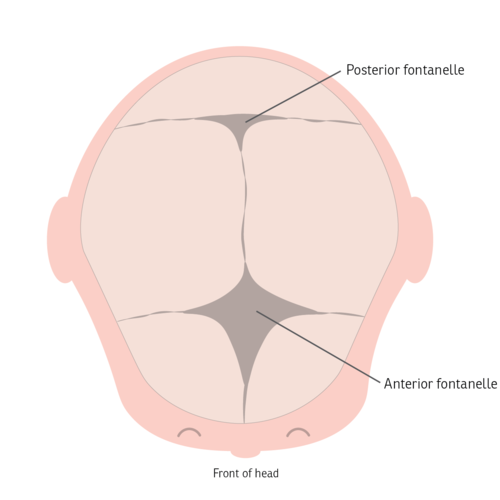
Fontanelles
wider structures found in the fetal skull
allow share to change during birth
close within 1st 2 years of living
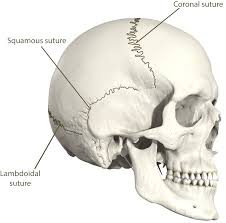
Sutures
dense fibrous tissue located in the skull
looks zig-zag like
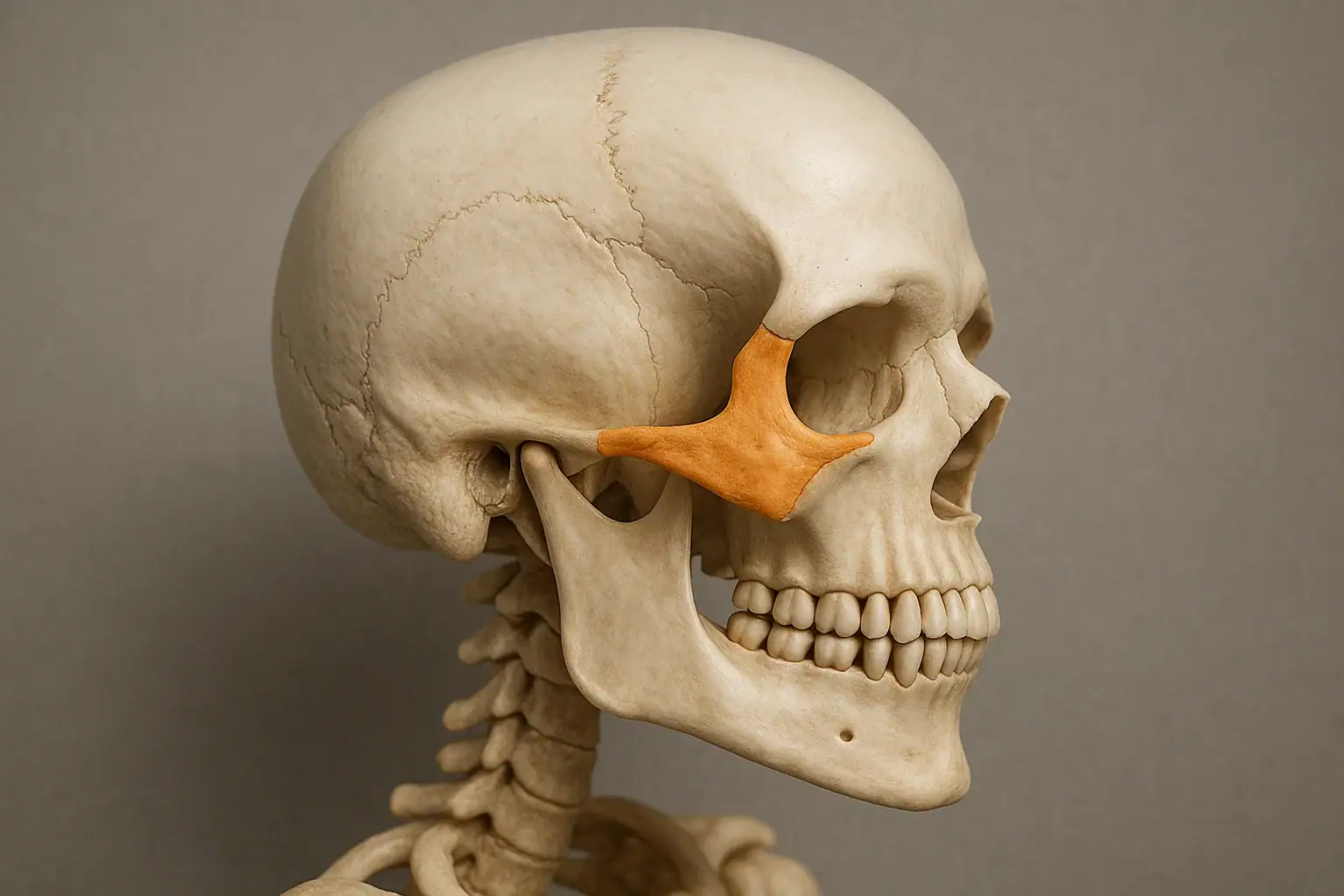
Zygomatic
also known as cheek bones
located behind eyes or next to eyes, depending on view
Mandible
also known as your jaw bone
largest and strongest bone of face
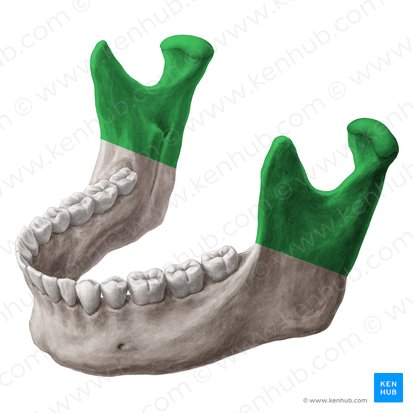
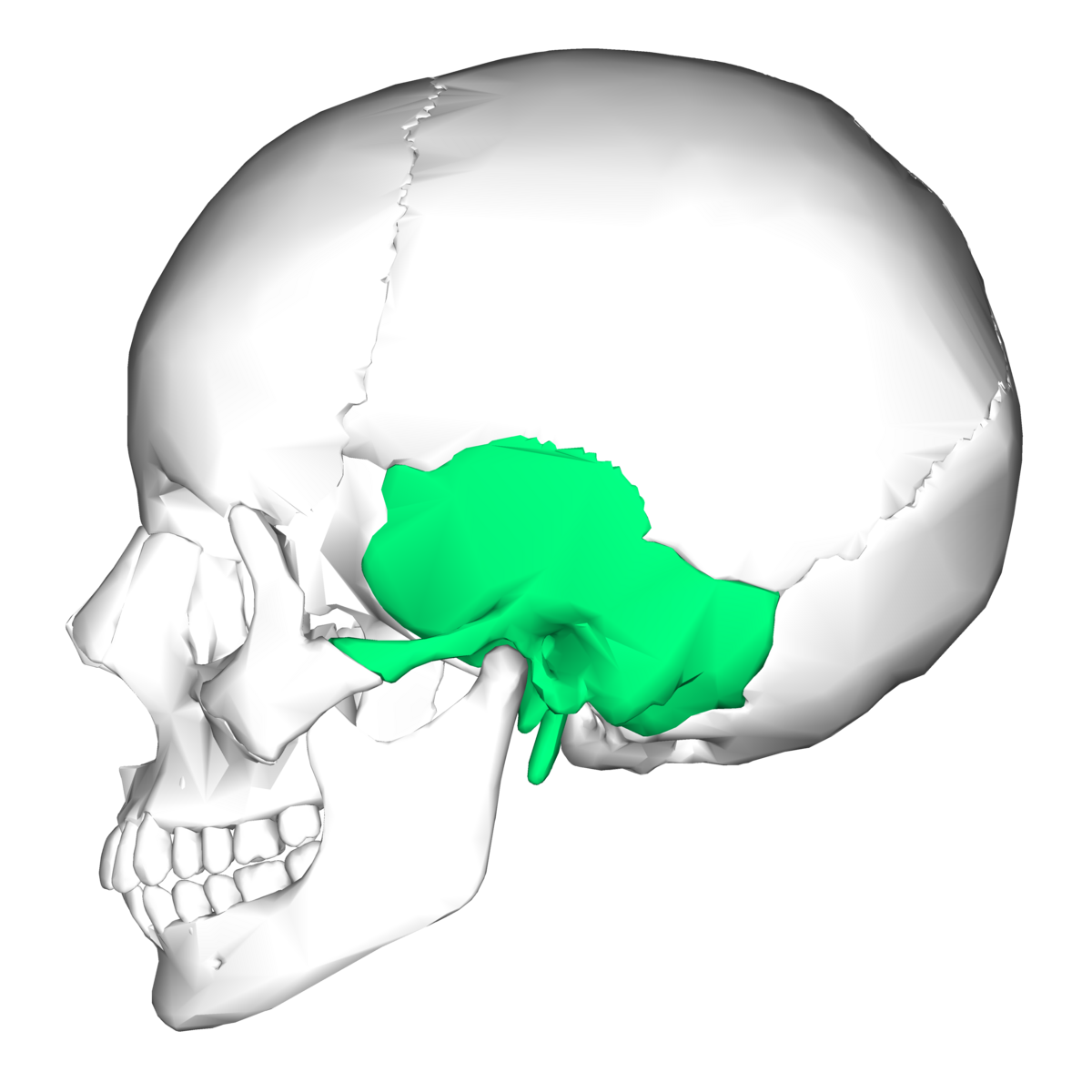
Sphenoid
butterfly or bat shaped bone
located behind the nose area and eyes
from side profile near the holes of the ear in the skull
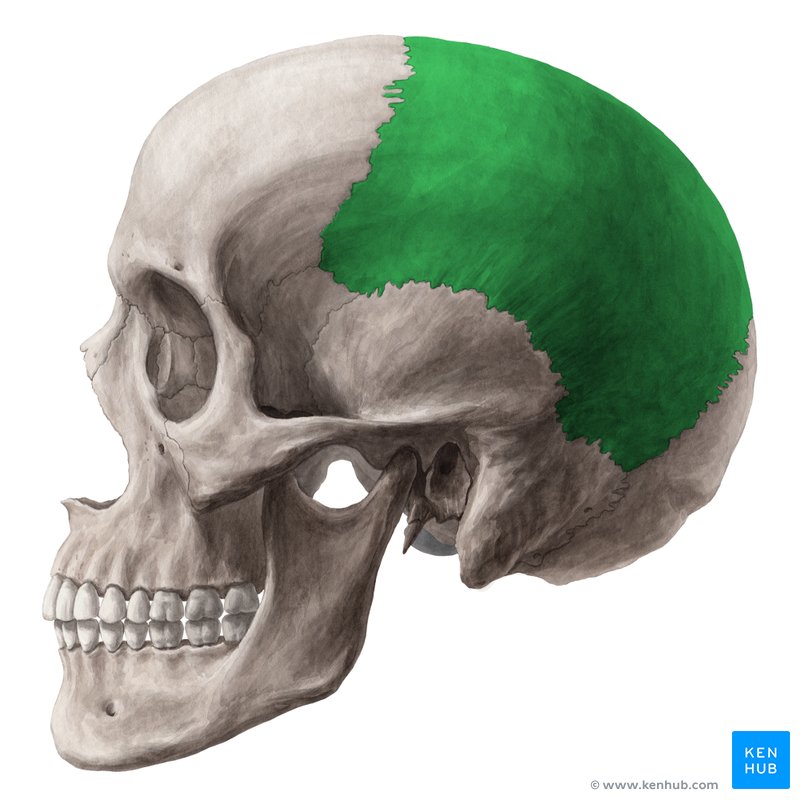
Parietal
located on the top section of the head
although still further back then the frontal lobe
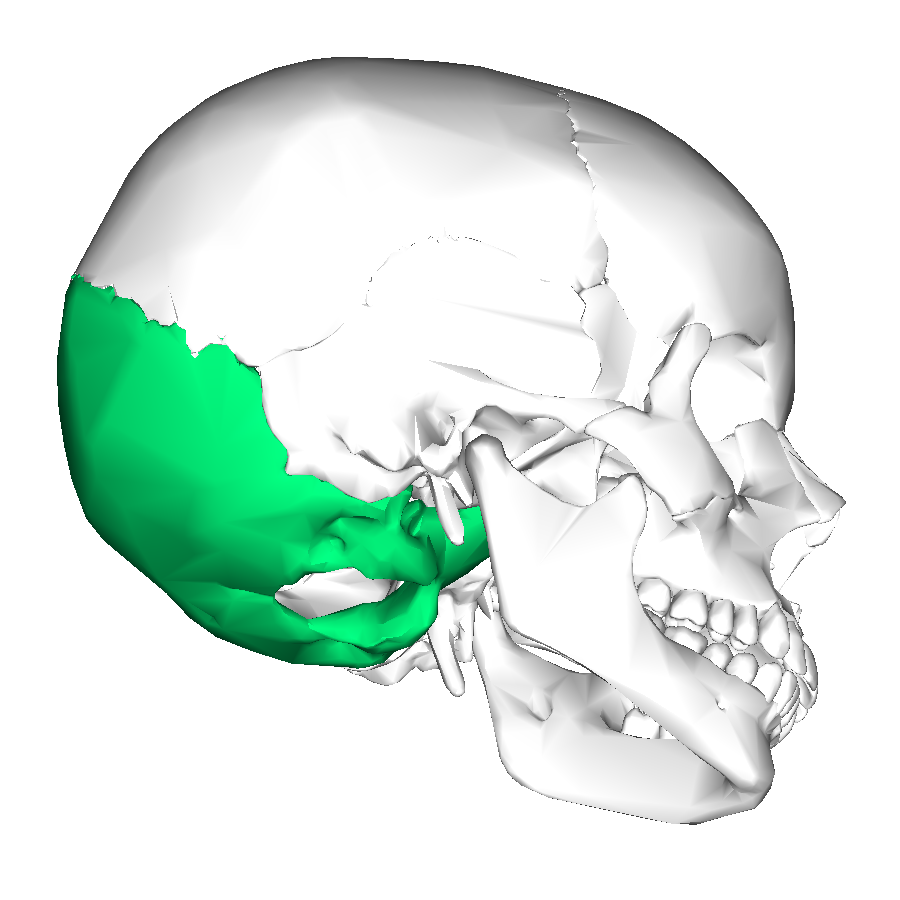
Occipital
located at the very back of the head
parallel to where the eye placement is
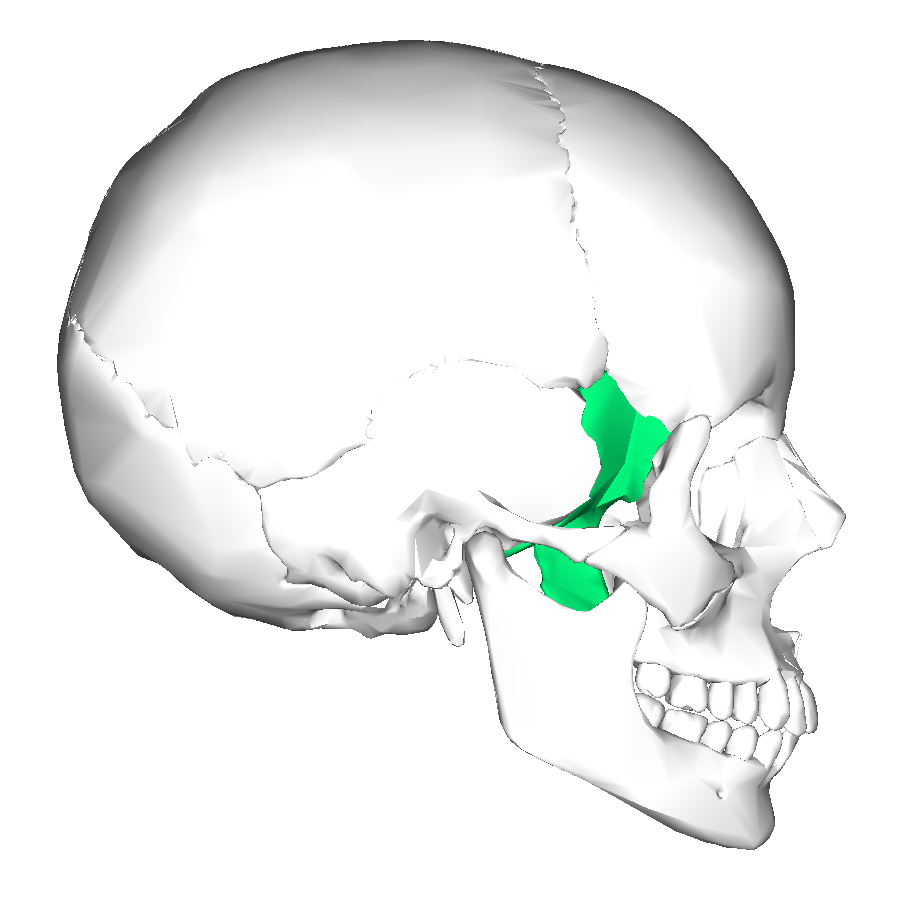
Temporal
located behind ears and sphenoid area
near temples
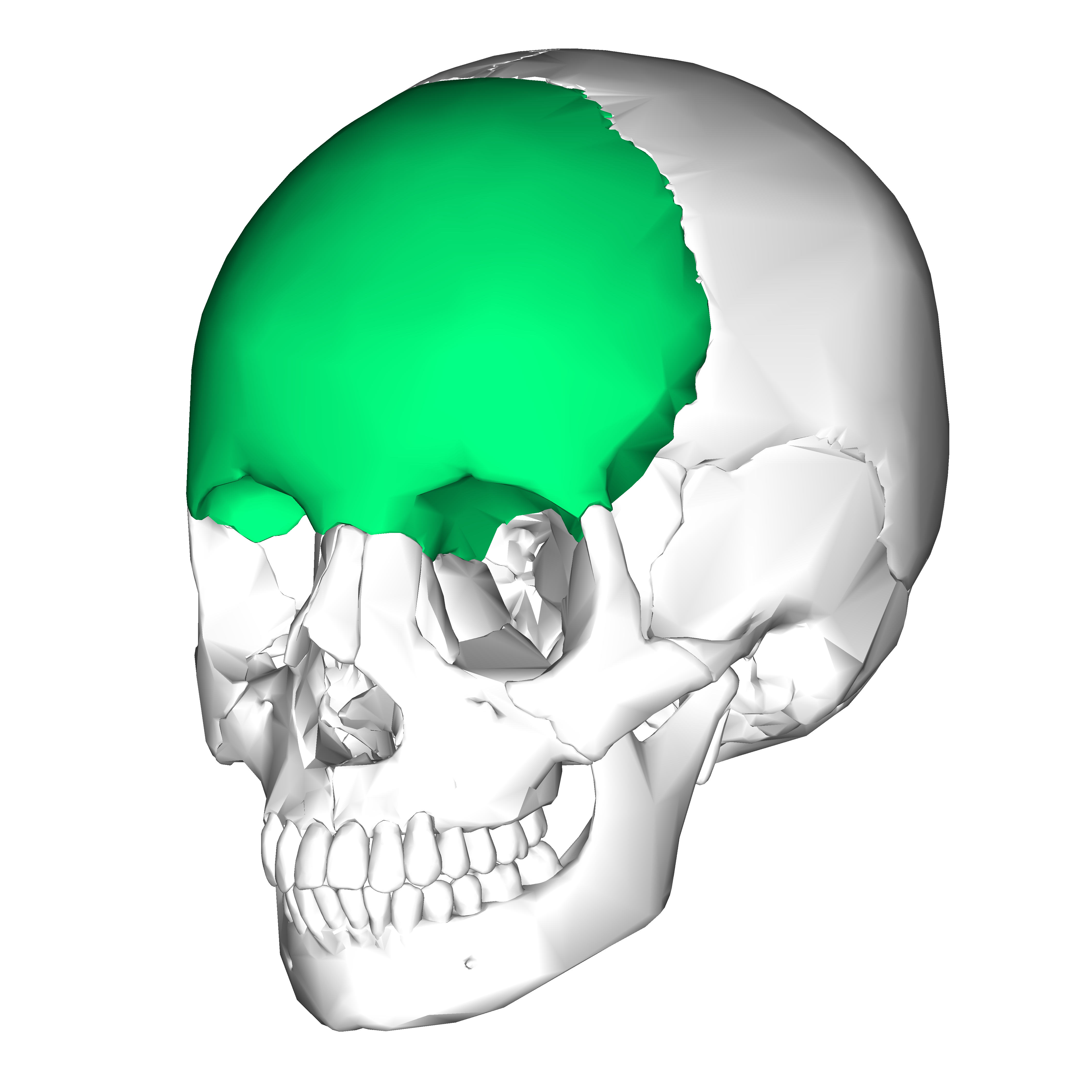
Frontal lobe
located at the top front of the skull
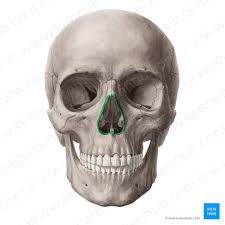
Nasal
holes where cartilage for the nose would be located
under the eye sockets
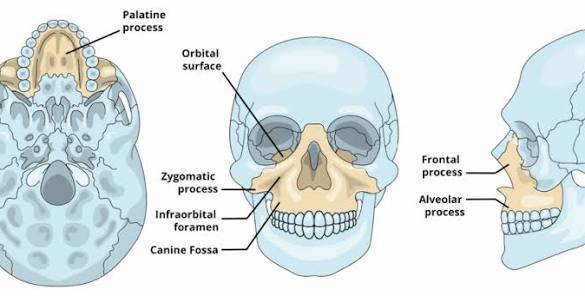
Maxilla
central bone that helps support the teeth
part of the upper face
Foramem Magnum
hole in base of skull
spinal cord passes through here
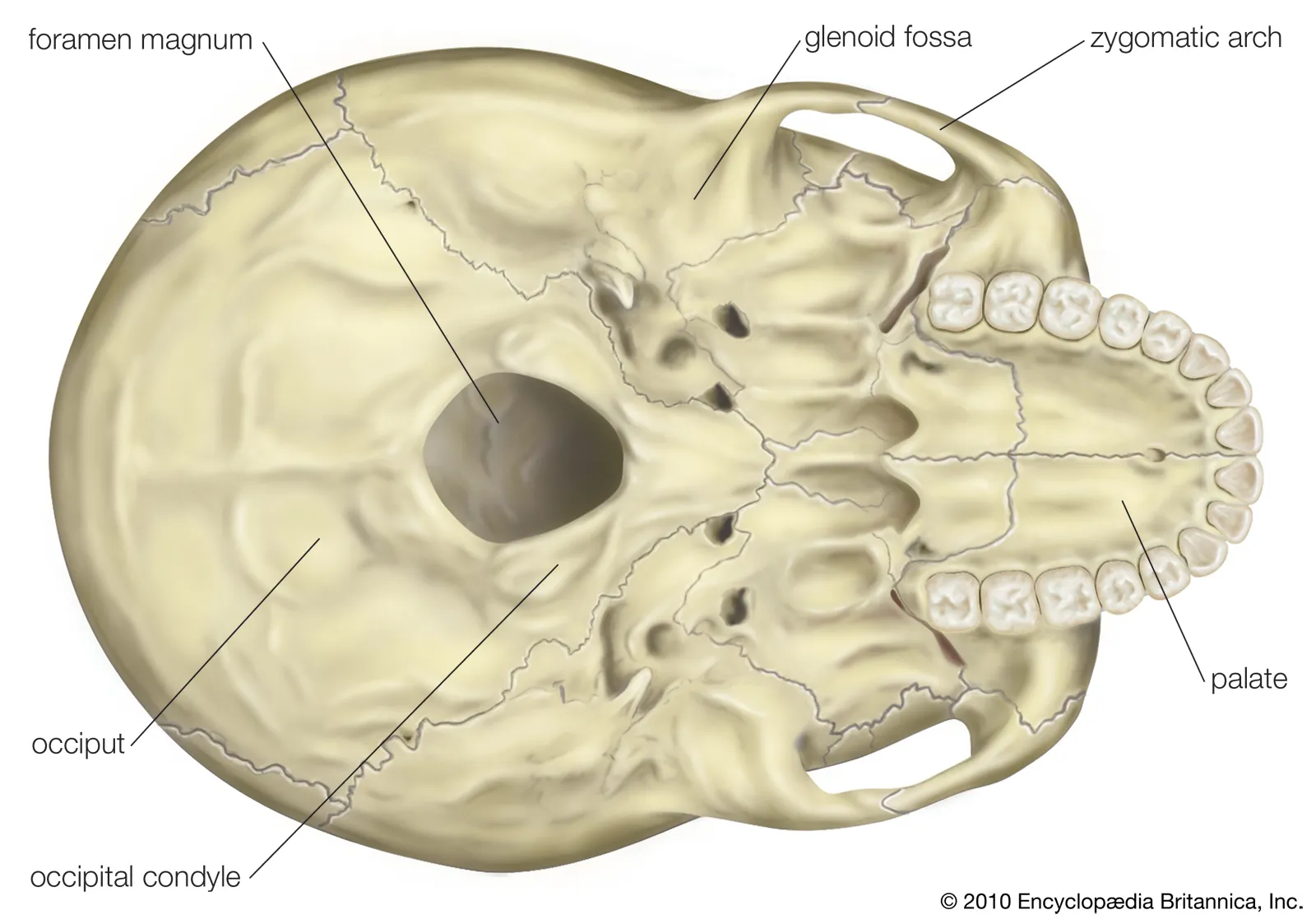
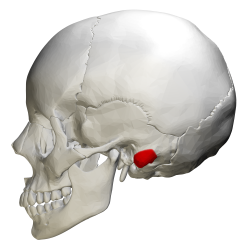
Mastoid process
bony projection located behind the ear
can see best when the skull is placed from bottom facing up (the view where the foramen magnum is present)
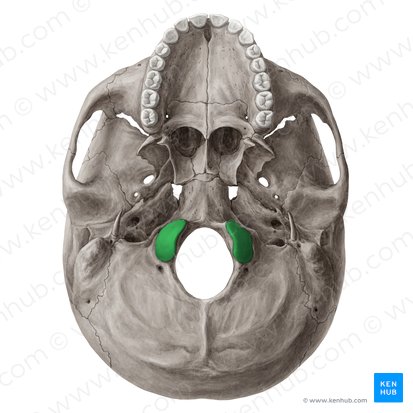
Occipital condyle
rounded knobs on the underside of occipital bone that forms a joint
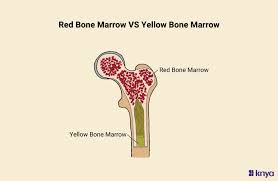
Red Bone Marrow
produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
made of spongy tissue
in young children all bone marrow is red, and then in adults its mainly inside flat bones
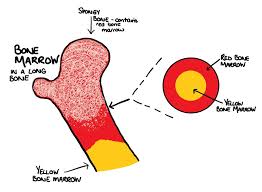
Yellow Bone Marrow
mainly produces adipose
mainly located in MEDULLARY cavities of long bones