Princeton Review AP Environmental Science Chapter 4
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
solid earth
earth's solid, rocky outer shell
lithosphere
a thin, rigid layer of rock that serves as the earth's outer shell, of which interacts the most with the other spheres
atmosphere
the envelope of gases that surrounds earth; held close to the earth by the force of gravity
hydrosphere
earth's oceans and freshwater bodies
pedosphere
the outermost layer of the Earth that is composed of soil (more commonly known as soil)
geologic time scale
a record of the geologic events and life forms in Earth's history
inner core
solid inner sphere that contains mostly nickel and iron; it is solid to the tremendous pressure of overlying matter
outer core
semi-solid outer sphere comprised mostly of iron, nickel and some lighter elements; semi-solid due to low pressure
mantle
the layer of mostly solid rock flowing rock between the crust and the core
asthenosphere
a layer of slowly moving flowing rock, over which the tectonic plates move
crust
the solid surface of the earth (above the asthenosphere)
Pangea
a supercontinent formed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras, of which encapsulated all land material on earth
tectonic plates
the several large pieces of lithosphere that move slowly over the mantle of the earth (about 1 dozen: 6 continental and 6 oceanic)
plate boundaries
the edges of tectonic plates
Nazca Plate
plate that consists of only oceanic crust
convergent boundary
a plate boundary in which two plates are pushed toward and into each other; one slides beneath the other and is pushed deep into the mantle
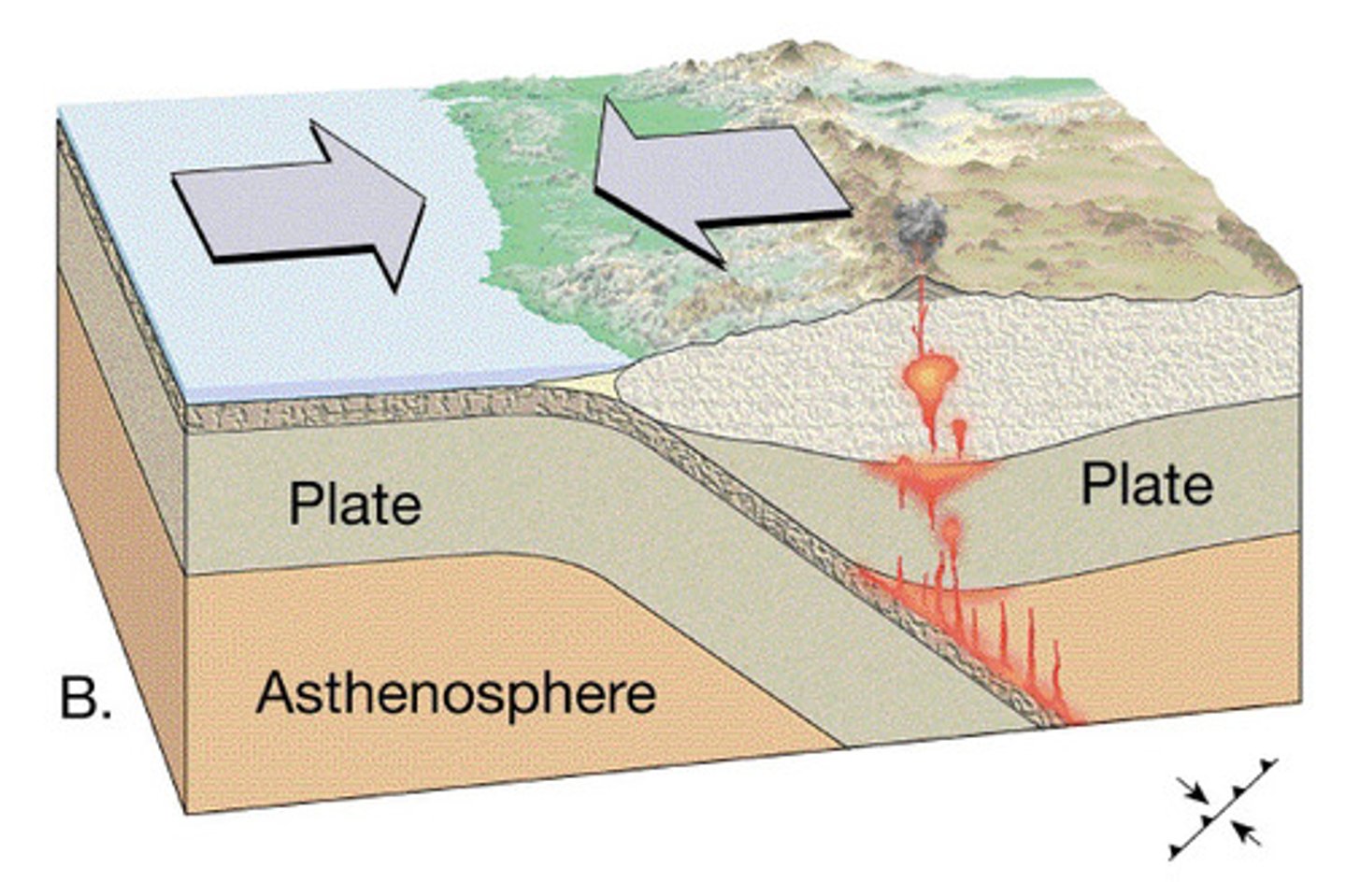
divergent boundary
a plate boundary in which two plates move away from each other; creates a gap between plates that may be filled with rising magma, which- once cooled- forms new crust
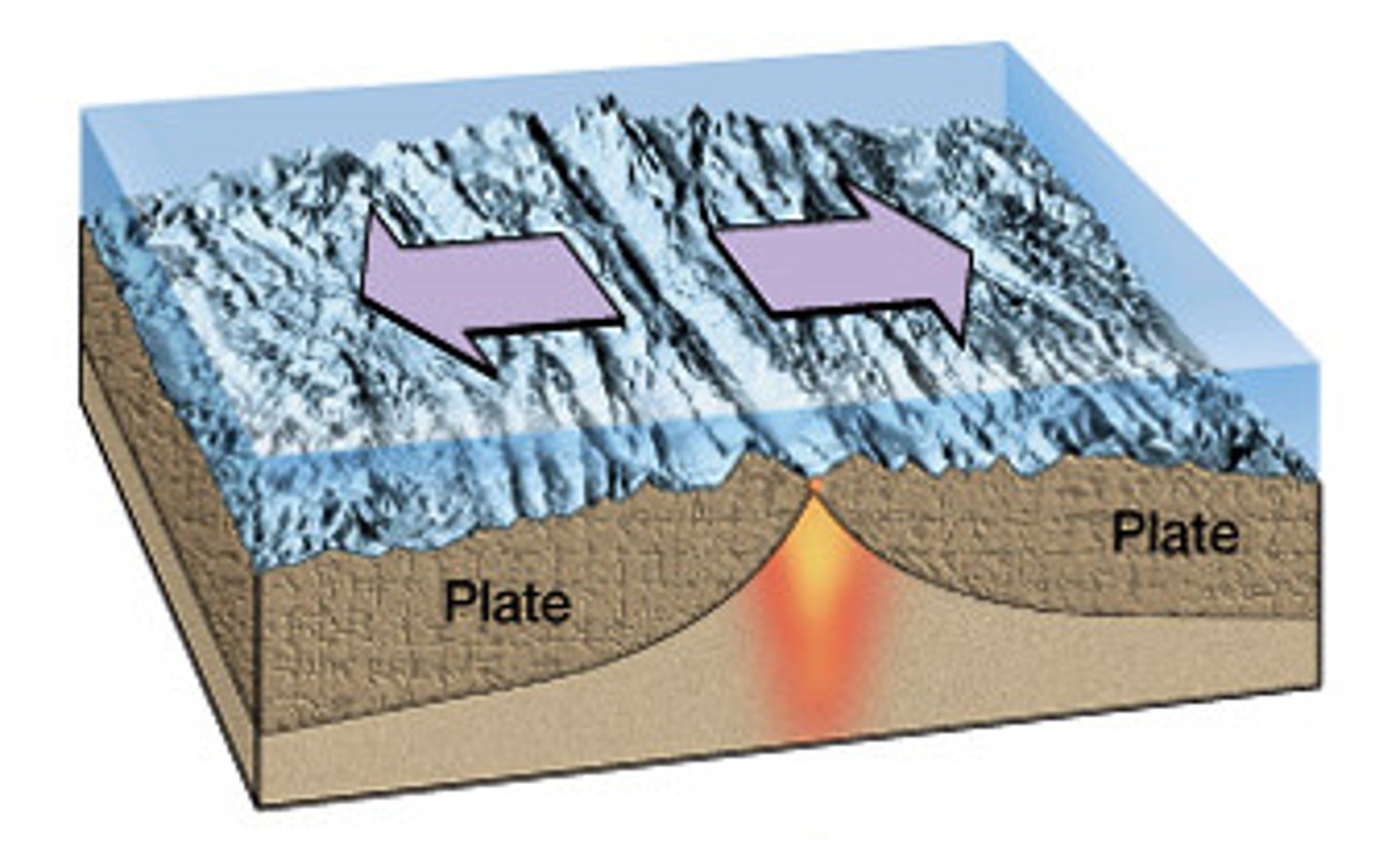
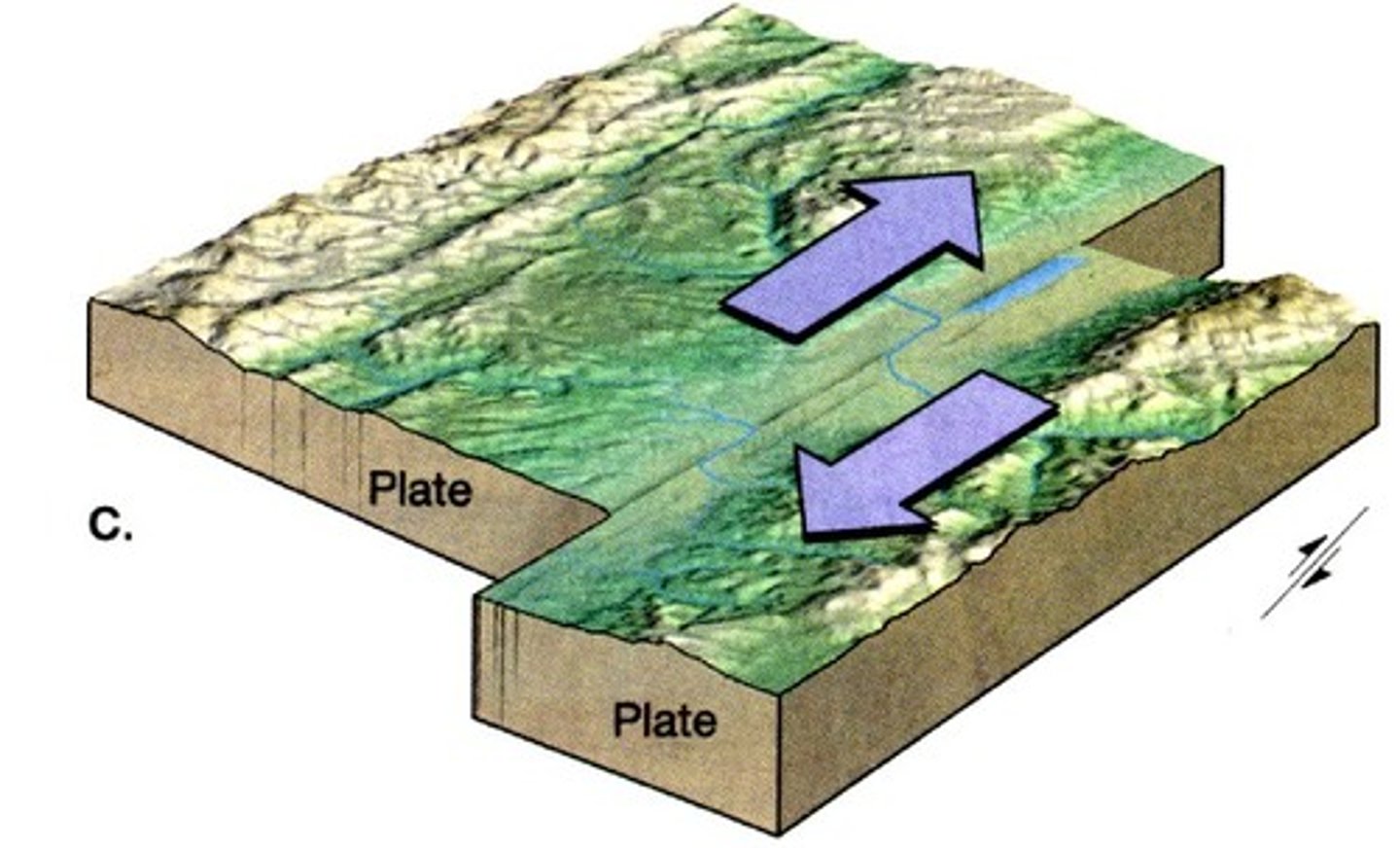
transform fault boundary
a plate boundary in which two plates slide against each other in opposite directions
subduction
a heavy ocean plate is pushed below the other plate and melts as it encounters the hot mantle (occurs with ocean-continent convergence and ocean-ocean convergence)
orogeny
the uplifting of plates that form large mountain chains as they crunch into each other(occurs with continent-continent convergence)
volcanoes
mountains formed by pressure from magma rising from earth's interior
active volcanoes
volcanoes that are currently erupting or have erupted within recorded history (past 10,000 years)
dormant volcanoes
volcanoes that have not been known to erupt in recorded history (past 10,000 years)
extinct volcanoes
volcanoes that will probably not erupt again
subduction zones
occur at convergent boundaries between oceanic and continental plates (occasionally between two oceanic plates); subjecting plate is recycled into new magma, which rises through the overlying plate to create volcanoes inland
rift valleys
occur at divergent boundaries, usually between two oceanic plates; new ocean floor is formed as magma fills in the gap between separating plates (magma rising from the rift valleys is made of basaltic materials and forms pillow lava upon contact with cold water (may also occur between continental plates- Mt. Kilimanjaro)
hot spots
places where molten material from the mantle reaches the lithosphere; do not form at plate boundaries, but rather form in the middle of tectonic plates in locations where columns of unusually hot magma melt through the mantle and weaken the earth's crust
shield volcanoes
have a broad base with gentle slopes; generally form over oceanic hot spots and usually have mild eruptions with slow lava flow (when water enters the flow, they may be explosive with the forming of pyroclastic flows)
pyroclastic flow
a fluidized mixture of hot ash and rock
composite volcanoes
have a broad base and are tall with gentle slopes; formed at subduction zones and are associated with violent eruptions that eject lava, water, and gases as superheated ash and stones
cinder volcanoes
(MOST COMMON TYPE OF VOLCANO) small, short, and steeply sloped cones; form when molten lava erupts and cools quickly in the air, hardening into porous rocks (cinders) that fracture as they hit earth's surface; generally form near other types of volcanoes
lava domes
small and short with steep slopes and a rounded top; formed from lava that is too viscous to travel far but instead hardens into a dome shape; often occurs near or inside other types of volcanoes
earthquakes
the result of vibrations caused by sudden moving of stress overcoming a locked fault deep in the earth that release stored energy; mainly occur at transform boundaries
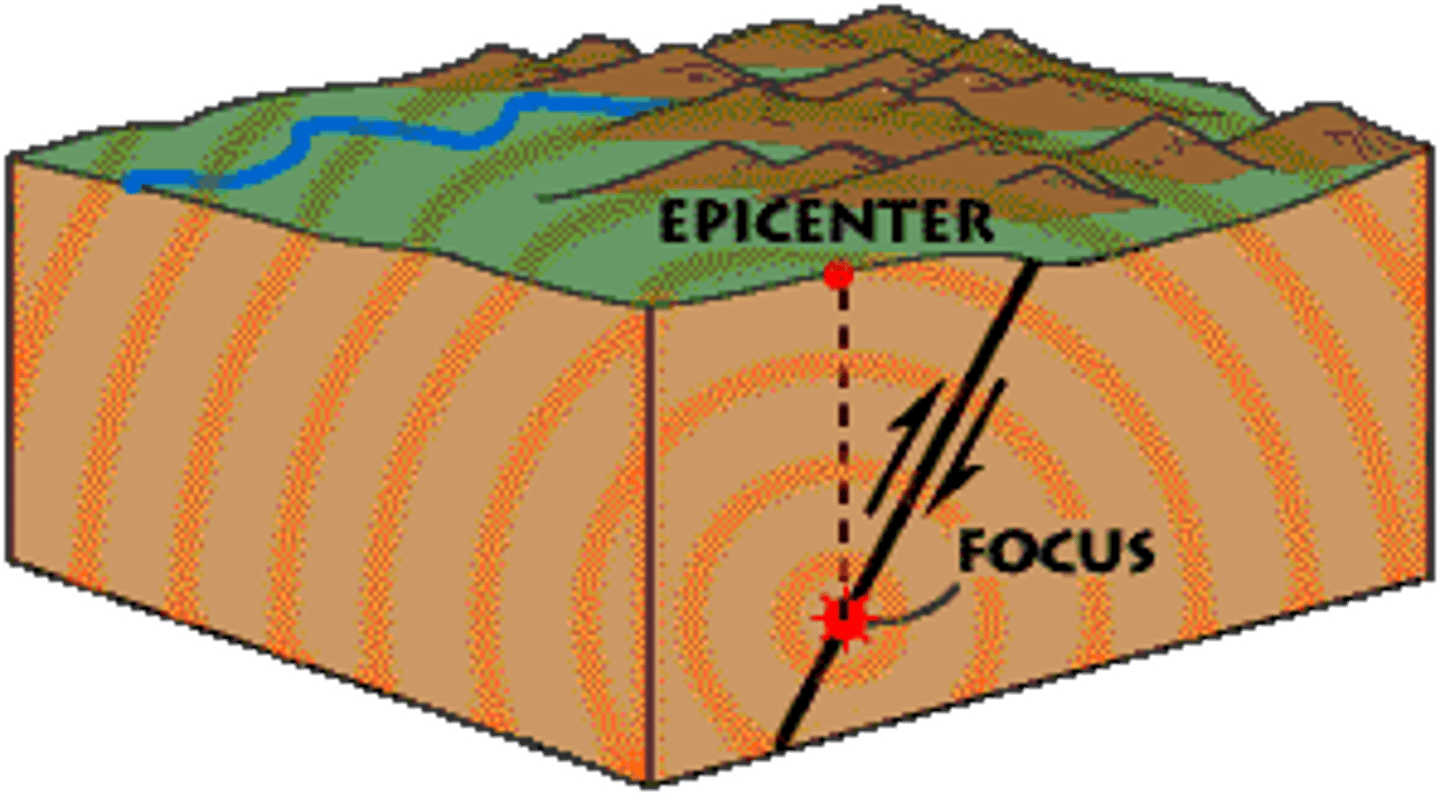
focus
the location at which the earthquake happens within the earth
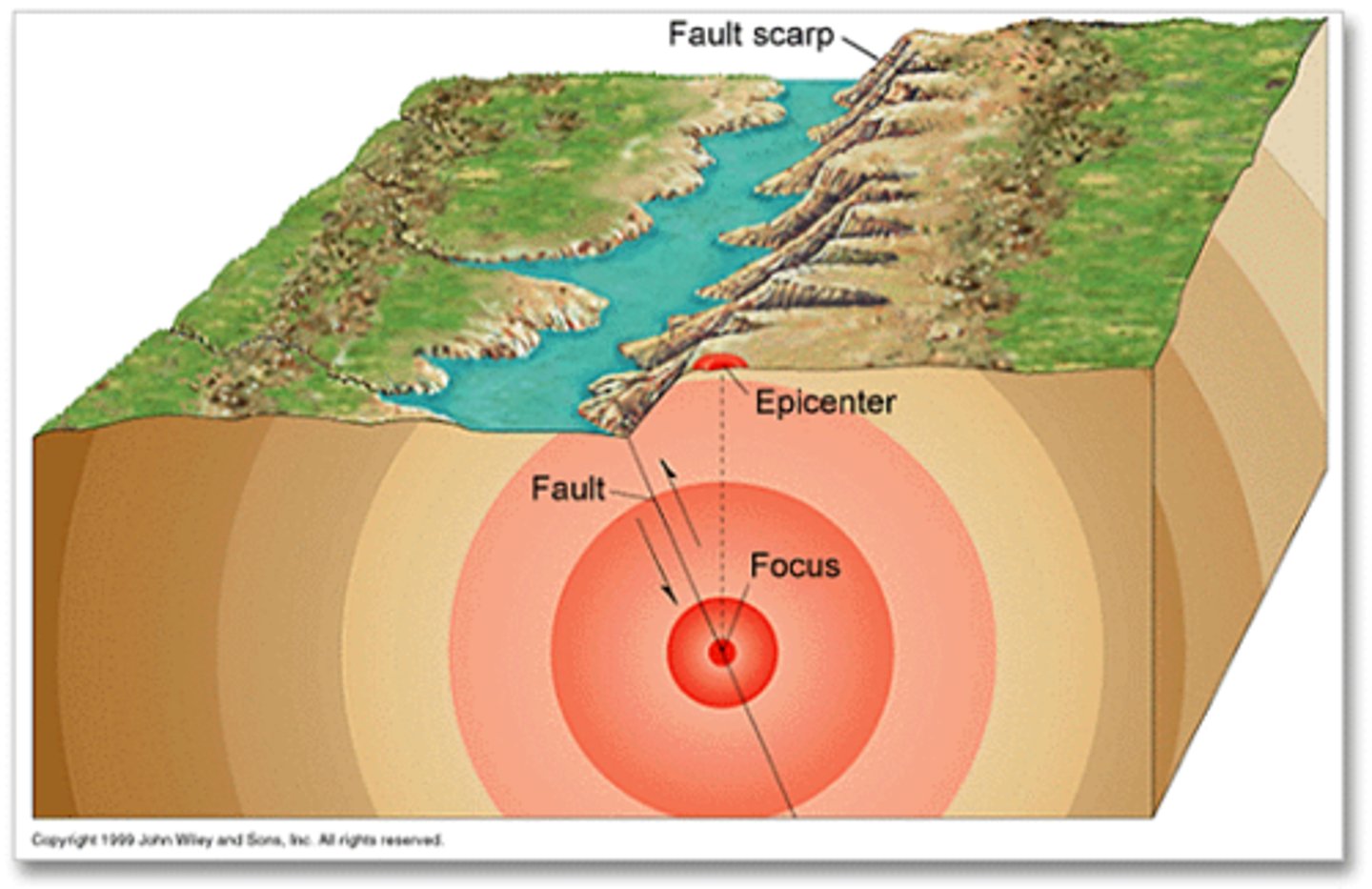
epicenter
the point on the Earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake; the initial surface location of the earthquake on earth
seismograph
an Instrument that measures the size or magnitude of earthquakes; devised by Charles Richter
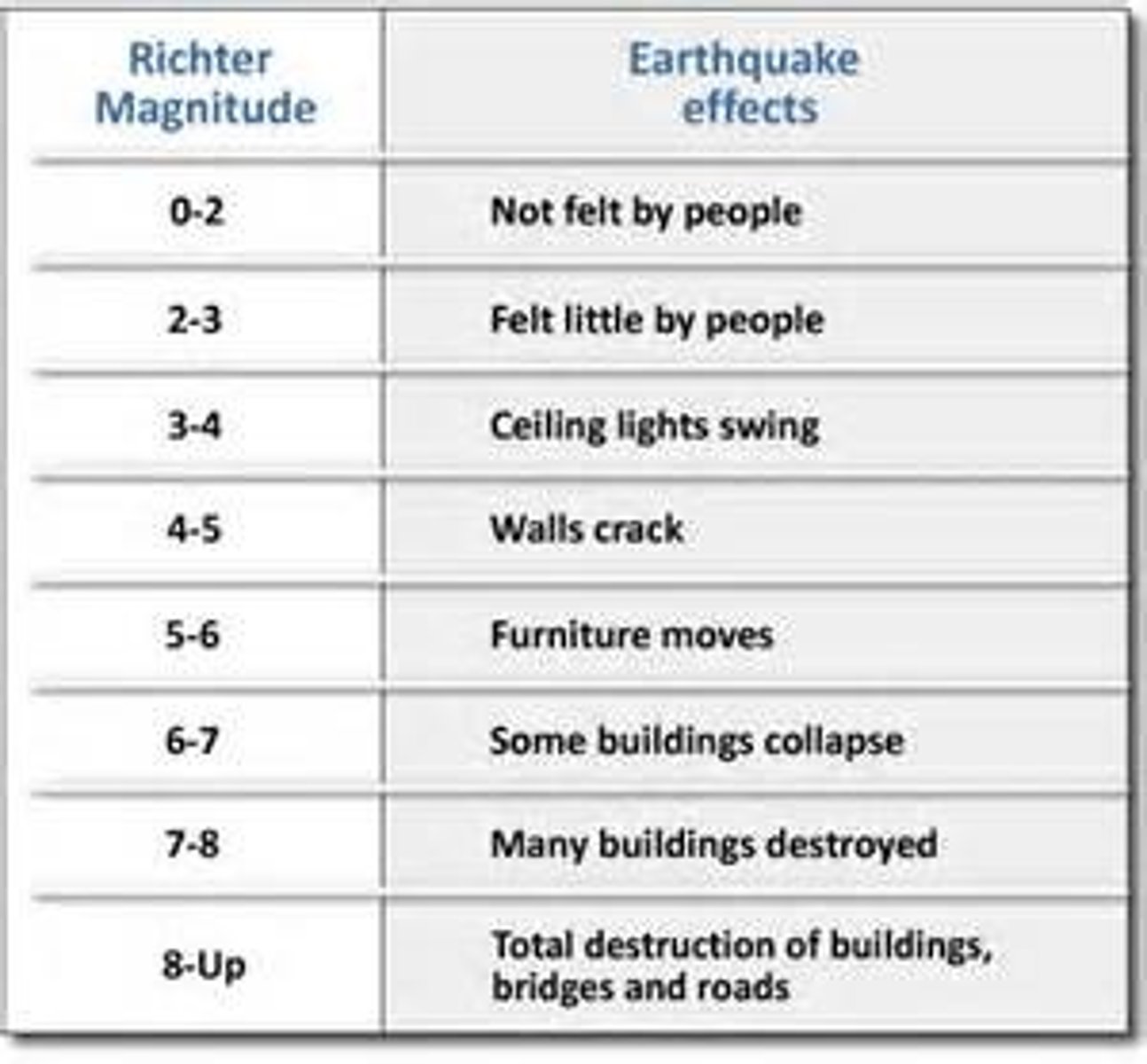
Richter Scale
measures the amplitude of the highest S-wave of an earthquake; values range from 0-9, although there is theoretically no maximum value; each increase in the scale corresponds to an increase of approximately 33 times the energy of the previous number
tsunamis
very large waves or chains of waves caused by the movement of the earth during an earthquake or volcanic eruption, which can be very detructive
rock cycle
the series of processes that change one type of rock into another type of rock
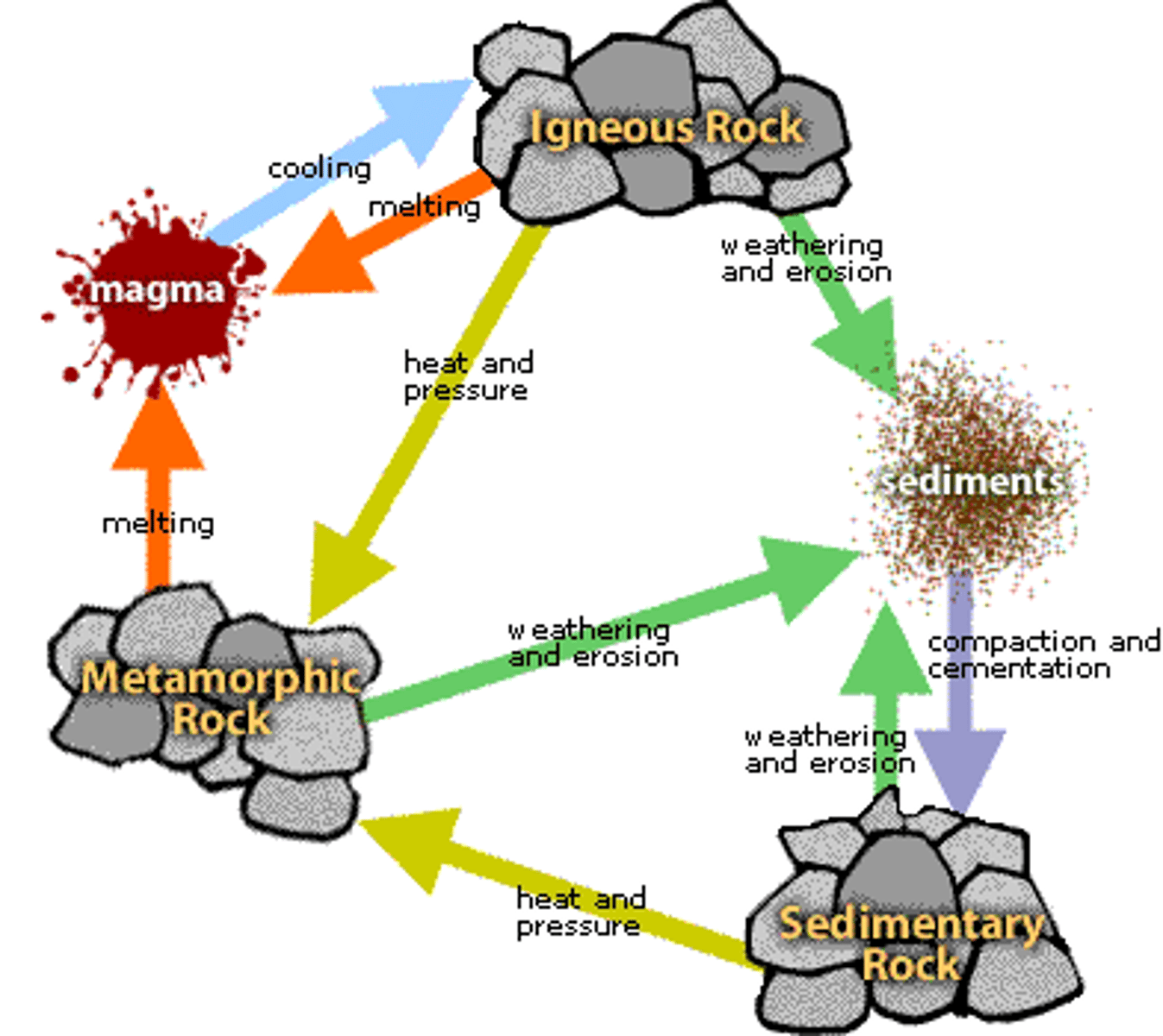
igneous rock
results when rock is melted (by heat and pressure below the crust) into a liquid and then solidifies when cooled (ex. basalt)
magma
molten rock
sedimentary rock
formed as sediment (eroded rocks and the remains plants and animals) builds up and is compressed; can form underwater when sediments or dissolved minerals deposit on a stream bed or ocean floor; become compressed as more material is deposited and then cemented together (ex. limestone)
metamorphic rock
formed as a great deal of pressure and heat produces physical and/or chemical in existing rock (existing rock could have originally been igneous, sedimentary, or another metamorphic rock); occurs as sedimentary rocks sink deeper into the earth and are heated by the high temperatures found in the earth's mantle (ex. shale)
troposphere
extends from earth's surface to 12km at poles and 20 km at equator; where all of the weather that we experience takes place; contains 99% of all of atmosphere's water vapor and clouds; gases well mixed as it gets colder with altitude; densest atmospheric layer (contains 75-80% of earth's atmospheric mass)
greenhouse effect
the trapping of the sun's warmth in a planet's lower atmosphere due to the greater transparency of the atmosphere to visible radiation from the sun than to infrared radiation emitted from the planet's surface
air
78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and remaining 1% greenhouse gases
tropopause
a layer atop the troposphere that acts as a buffer between the troposphere and the stratosphere; where the jet streams travel
stratosphere
atmospheric layer directly above the troposphere that extends 20-50km above earth's surface; gases not well mixed; temperatures increase with distance from earth; less dense and drier than troposphere
ozone (O3)
exists in the lower half of the stratosphere; traps the heat energy radiation of the sun, holding some of the heat and protecting the troposphere and earth's surface from this radiation
S-wave
(shear wave) a seismic body wave that shakes the ground up and down or side to side, perpendicular to the direction the wave is moving
wave
a disturbance that transfers energy from one place to another
mesosphere
atmospheric layer between the stratosphere and the thermosphere; extends about 80km above earth's surface; the area where meteors usually burn up; temperatures decrease to the atmosphere's coldest point at the top of this layer (-90 degrees C)
thermosphere
atmospheric layer between the mesosphere and the exosphere; extends from 80-500 km above earth; gases very thin (rare); where the auroras occur
exosphere
furthest layer of the atmosphere; 10,000 km and beyond above earth; thinnest concentration of gases; where human-made satellites orbit (as well as in the upper thermosphere)
ionosphere
not a distinctive layer; dispersed throughout the upper mesosphere, the thermosphere, and the lower exosphere; comprises regions of ionized gases that absorb most of the energetic charged particles from the sun- the protons and electrons of solar wind; reflects radio waves- makes long-distance radio communication possible
weather
the day-to-day properties such as wind speed and direction, temperature, amount of sunlight, pressure, and humidity
climate
weather patterns that are constant over many years (30 years or more) (TWO MOST IMPORTANT ARE AVERAGE TEMPERATURE AND AVERAGE PRECIPITATION AMOUNTS!!!)
meteorologists
scientists who study weather and climate
convection currents
vertical air flow caused by heat energy being transferred to the atmosphere by radiation heating, where it expands, becomes less dense, and rises
horizontal air flow
cool air that flows along earth's surface to occupy the area vacated by warm air; one way that surface winds are created
dew point
the temperature at which water vapor condenses into liquid water
precipitation
any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface (can be frozen or liquid)
convection cell
a circular pattern of air rising, air sinking, and wind
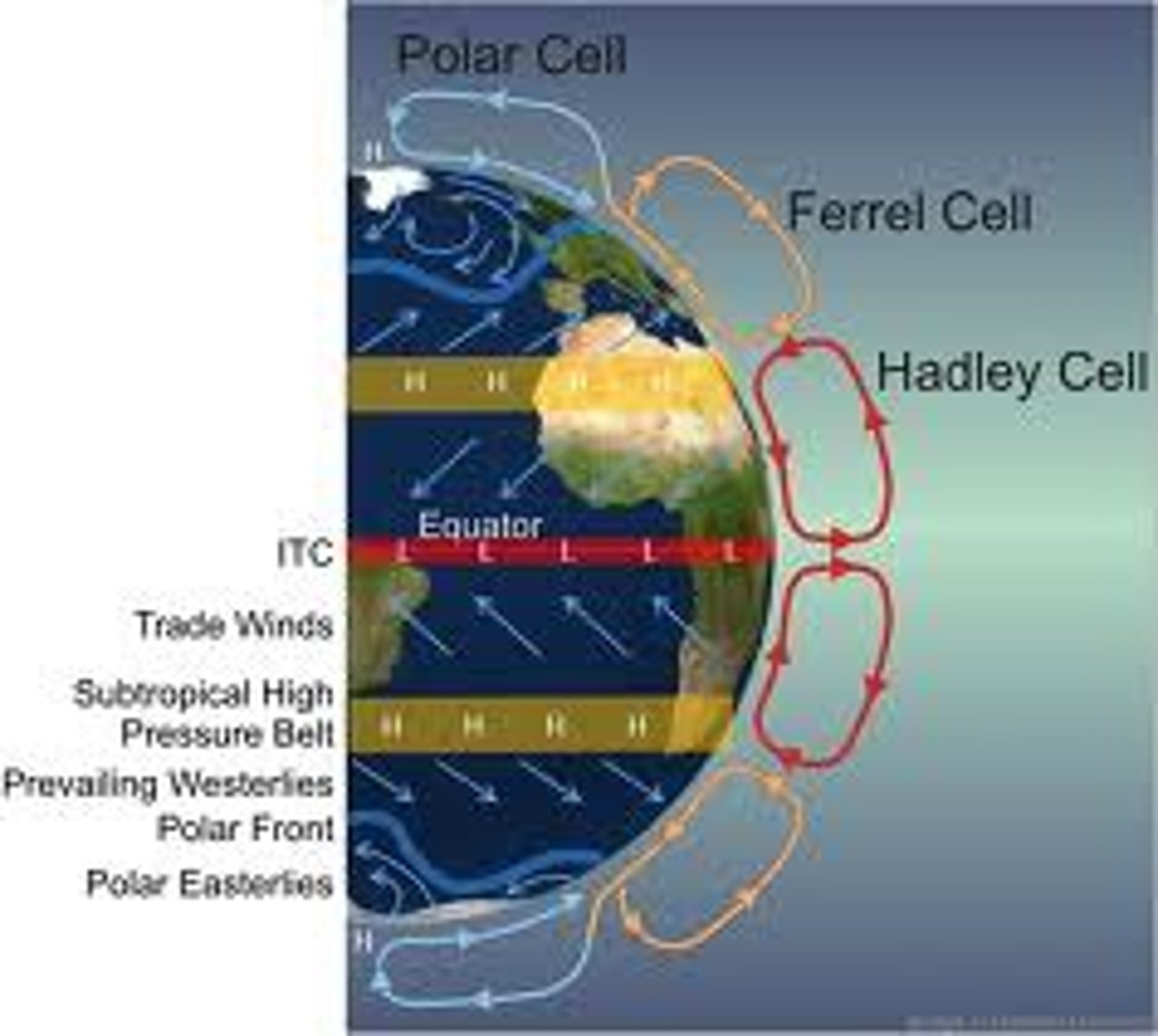
Hadley cells
a large-scale atmospheric convection cell in which air rises at the equator and sinks at medium latitudes, typically about 30° north or south
insolation
the amount of solar radiation that reaches a given area
revolution
trip around the sun (in terms of earth)
rotation
the spinning of earth on its axis (in terms of earth)
axis
an imaginary line about which a body rotates (earth's axial tilt is 23.5 degrees)
albedo
the percentage of incoming sunlight (insolation) reflected from a surface; lower the albedo- more solar radiation absorbed; albedo of 0- no reflection of all incoming radiation; albedo of 1- reflection of all incoming radiation
wind
air that's moving as a result of the unequal heating of earth's atmosphere; moves heat, moisture, soil, and pollution around the planet
trade winds
prevailing winds that blow from east to west from 30 degrees latitude to the equator in both hemispheres; 11-13 mph; caused by surface currents of the Hadley cells; steady and somewhat predictable patterns
northeast trade winds
trade winds that blow from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere
southeast trade winds
trade winds that blow from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere
westerly
a type of moving air mass that results from air being deflected south and west in the northern hemisphere and north and west in the southern hemisphere near the equator (Coriolis effect) (COMES FROM THE WEST NOT THE EAST)
Ferrel cell
movement of air that accounts for westerlies; opposite of Hadley cells but has same thermodynamic principles
Polar easterlies
cold winds that blow from the east to the west near the North Pole and South Pole; formed by the Coriolis effect
Coriolis effect
causes moving air and water to turn left in the southern hemisphere and turn right in the northern hemisphere due to Earth's hemisphere
horse latitudes
regions of high pressure and gentle winds at about 30 degrees north and south latitude; subsiding dry air and high pressure results in weak winds
doldrums
region 5 degrees north and south of the equator with relatively still air due to it constantly rising rather than blowing
Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)
an area of Earth that receives the most intense sunlight; where the ascending branches of the two Hadley cells converge; the area containing the doldrums
jet stream
high-speed currents of wind that occur in the tropopause that have a large influence on local weather patterns
monsoons
seasonal winds that are usually accompanied by very heavy rainfall.; occur when land heats up and cools down more quickly than water does; hot air rises from heated land, creating a low-pressure system; rising air quickly replaced by cooler moist air that flows from over ocean surface; moisture carried is released in steady seasonal rainfall as air rises over land and cools
lake effect
small-scale monsoon effect in which air moves in from lake, creating a breeze; reverse occurs at night: land cools more quickly than water- air over lake rises; air mass from land moves over lake to replace rising air, creating a breeze
rain shadow effect
precipitation falls on the windward side of a mountain range, resulting in lush vegetation & a warm, moist climate on one side, but a desert area on the leeward side (ex. Olympic rainforest in Washington state)
hurricanes
tropical storms with wind speeds greater than 120 km/hr; rotating winds remove water vapor from ocean's surface, and heat is released as water vapor condenses- contributes to faster wind speeds (called this in the Atlantic Ocean)
typhoons/cyclones
hurricanes in the Pacific Ocean
Southern Oscillation
a reversal of airflow between normally low atmospheric pressure over the western Pacific; the cause of El Nino
El Nino
an irregularly occurring and complex series of climatic changes affecting the equatorial Pacific region that appears every 3-7 years, characterized by the appearance of unusually warm, nutrient-poor water off northern Peru and Ecuador, typically in late December.
La Nina
a cooling of the ocean surface off the western coast of South America, occurring periodically every 4 to 12 years and affecting Pacific and other weather patterns (nutrient-rich waters)
ENSO
El Niño Southern Oscillation, alterations of atmospheric conditions that lead to el niños or la niñas
3.5
ocean salinity
freshwater
water that contains only minimal quantities of dissolved salts; ultimately comes from precipitation of atmospheric water vapor that reaches inland lakes, rivers, and groundwater directly or by melting of ice
watershed
the land area that drains into a particular stream; drainage basin
headwaters
the source of a stream or river
deltas
the triangle-shaped deposit of sand and sediment that occurs where a river flows into an ocean
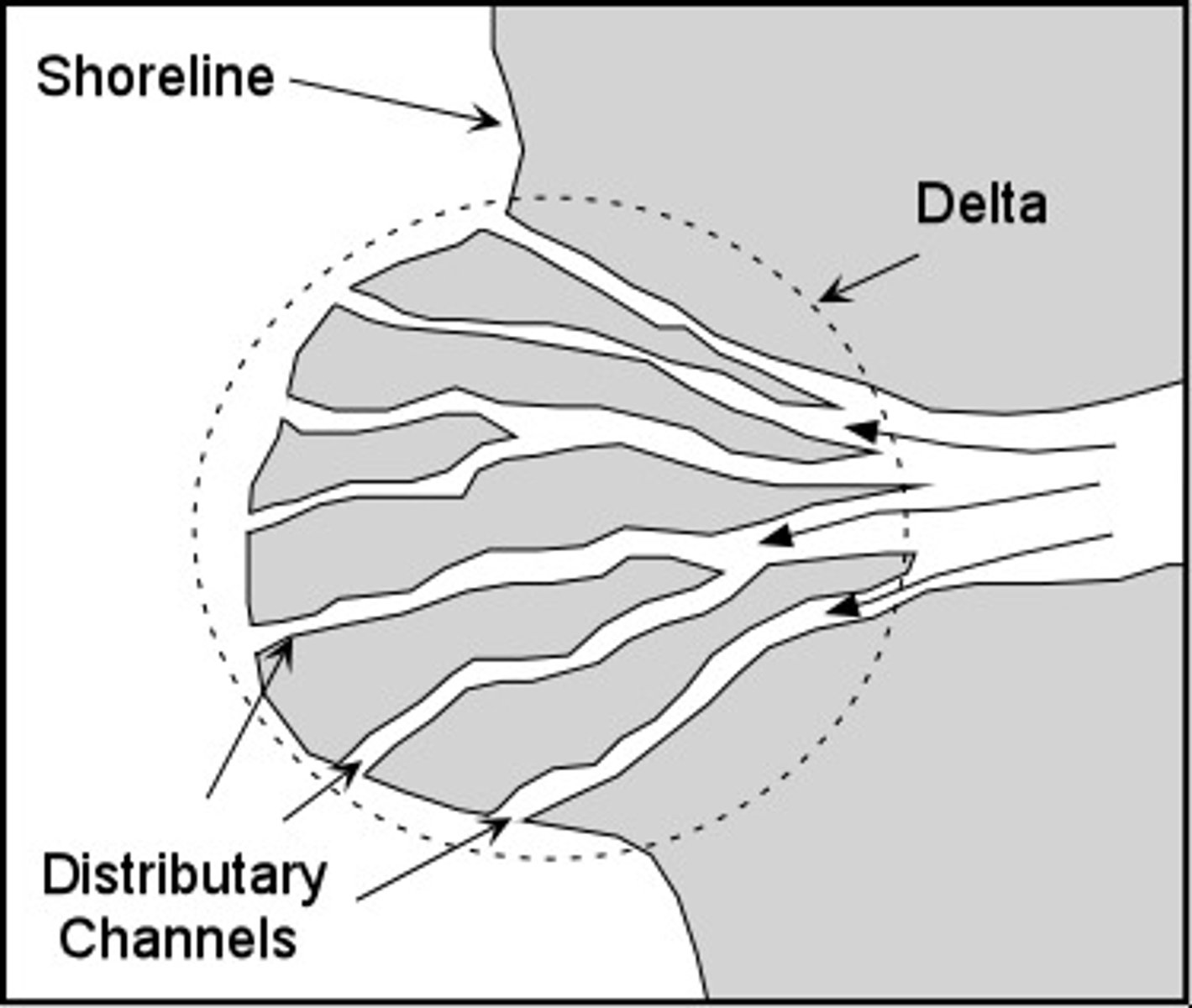
estuaries
sites where the "arm" of the sea extends inland to meet the mouth of a river; often rich with many types of plant and animal species due to water's high concentration of nutrients and sediments; shallow with warm water (ex. saltwater marshes, mangrove forests, inlets, bays, and river mouths)
epilimnion
the uppermost and most oxygenated layer of freshwater
hypolimnion
the lower, colder, and denser layer of freshwater
thermocline
the line of demarcation between two layers of water to rise
littoral zone
begin with very shallow freshwater at shoreline and ends at depth at which rooted plants stop growing; many plants and animals that receive abundant sunlight