1c and 1d EXAM #1 patho
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
edema
excessive accumulation of fluid in the interstitial spaces
localized edema
due to trauma or around an organ (i.e. sprained ankle)
-negative pitting edema
generalized edema
uniform distribution of fluid (i.e. right sided congestive heart failure)
-positive pitting edema
capillary hydrostatic pressure CHP
pushes fluid out of capillary
capillary osmotic pressure COP
pulls fluid into capillary (albumin attracts water)
what happens to Capillary Hydrostatic pressure during edema?
It goes up, which increases blood volume and blood pressure as well
what happens to capillary osmotic pressure during edema?
it goes down, not absorbing enough fluid back into capillaries (hypoproteinemia)
what effect does histamine have on capillary permeability
easier to filter (more pores/exits), no change in pressure
two common causes of edema
hypertension and congestive heart failure
Left sided CHF
congestion in lungs (pulmonary edema)
Right sided CHF
congestion in the body (pitting edema, fluid congests in vena cava)
ascites
accumulation of fluid in peritoneal space
MCC: liver failure
patho of ascites
low albumin means low COP reabsorption which means edema
Anti Diuretic Hormone effect
NO PEEING, water reabsorption in kidney
Aldosterone Hormone effect
kidney reabsorbs sodium from pee, water follows sodium and excretes potassium. Less water loss
ADH and Aldosterone released because of
low BV and low BP triggers release of these hormones.
goal is to increase BV and BP and less water loss
ANP and BNP released because
high blood volume and high blood pressure
goal is to decrease blood pressure and blood volume and increase water loss
ANP and BNP effect
kidney secretes salt into urine and water will follow, more water loss
when does the kidney release renin for RAAS
low blood volume
low blood pressure
low sodium levels
effect of RAAS
increase blood volume/pressure
increase Antidiuretic hormone/ aldosterone
less urine output
SIADH (syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion)
-too much ADH
-less urine output/ low volume
-higher concentrated urine
-lower concentrated blood
DI (Diabetes Insipidus)
-too little ADH
-high urine output
-low urine concentration
-high blood concentration (hyperglycemia)
causes and S/S of SIADH
MCC: idiopathic
brain trauma, cancer, medication SE
S/S: fatigue, confusion, lethargy
causes and S/S of DI
pituitary tumor, kidney damage, medication SE
S/S: excessive thirst and urination (polyuria/polydipsia)
dehydration S/S
Hypotension and tachycardia, decreased urine output, increased urine concentration, increased blood concentration
sodium characteristics
-major cation outside of the cell
-maintain tonicity (cell size) of ECF
-facilitate nerve conduction
Na effect in hypertonic alteration for cells
Low water levels inside cell, High sodium levels outside of cell
Water escapes cell to follow ECF Na and cell shrinks
Na effect in hypotonic alteration for cells
High water levels inside cell, low sodium levels outside cell
Water rushes inside cell to follow gradient of Na
Hyponatremia causes
low salt intake
high water intake (water intoxication)
SIADH (high ADH)
Hypernatremia causes
high salt intake
low water intake (dehydration)
Diabetes Insipidus (low ADH)
hypersecretion of Aldosterone
S/S of hyponatremia
lethargy, hyporeflexia
S/S of hypernatremia
restlessness, hyperflexia
Osmolality
concentration of stuff in the blood
Na:H20 is homeostasis
Hypertonic solution and causes
concentrated blood
(hypernatremia, decreased water intake/ increased water loss, Diabetes insipidus)
Hypotonic solution and causes
diluted blood
(hyponatremia, increased water intake or decreased water loss, SIADH)
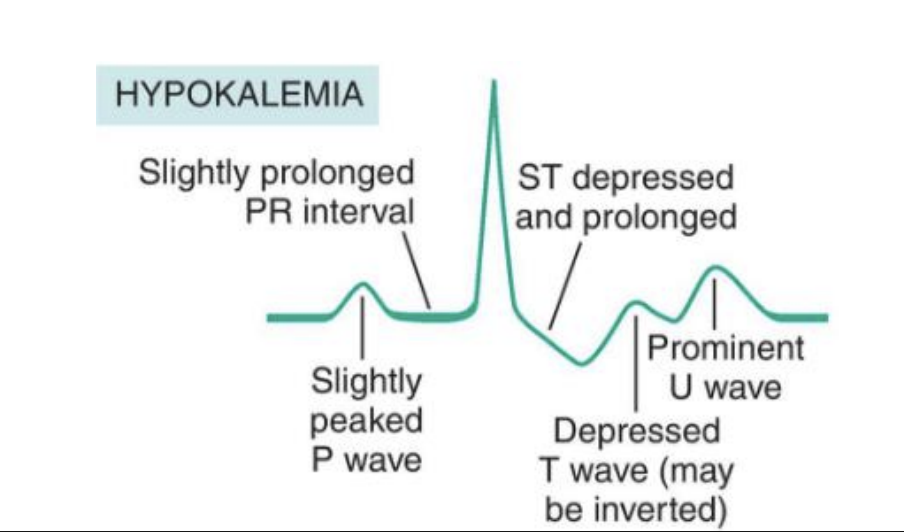
Hypokalemia causes
Reduced intake of K+ potassium (elderly, alcoholism, anorexia)
Increased entry of K+ into cells (alkalosis, too much insulin)
Increased loss of body K+ (vomitting,diarrhea)
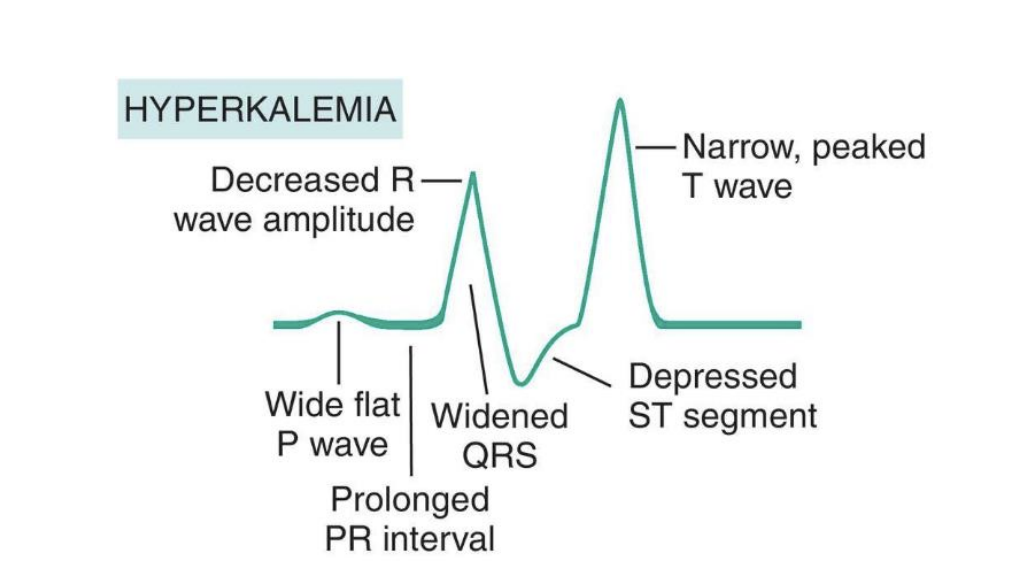
Hyperkalemia causes
Increased intake of K+
Increased exit of K+ from cells (acidosis, trauma,insulin deficiency)
Decreased renal excretion of K+ (renal failure, low aldosterone)
S/S hypokalemia
muscle weakness, cramps
EKG (inverted/flattened T wave, prominent U wave)
S/S hyperkalemia
muscle weakness, spasticity
EKG (wide QRS w/ Tall peaked T waves)
why do those with hypokalemia experience muscle cramps/weakness?
potassium helps move calcium out of the cell allowing muscle to relax
what are the three states extracellular calcium exists?
Ionized Ca2+ (50%) = Free and available (active form)
Protein bound calcium (41%) - mostly albumin (helps maintain homeostasis of calcium
Hypokalemia pH level relations
high pH, low H+, low K+
Hyperkalemia pH level relations
low pH, high H+, high K+
relation between hydrogen and calcium
low hydrogen = low calcium
high hydrogen = high calcium
calcitriol (active form of Vit D3)
activated in kidney
Ca2+ absorption in GI
Ca2+ reabsorption in Kidney
Enhanced bone mineralization
Vitamin D and calcium relation
Vitamin D helps absorb calcium in GI tract
kidney failure linked to hypocalcemia
Can’t activate Vit-D3, low calcium absorption in GI, low Calcium reabsorption in kidney = hypocalcemia
relation of PTH and Calcium
PTH will be secreted to increase Calcium levels
How does PTH regulate Calcium levels
@ Kidney (calcium reabsorption and Vitamin D activation)
@ Bone (break down bone/osteoclast activity)
what is released when blood calcium levels are too high?
Calcitonin (tone Ca2+ down)
What are the main roles of calcium and sodium in the body?
Calcium helps with muscle contraction and nerve function; sodium helps with nerve impulses and fluid balance.
How does calcium affect sodium movement in cells?
High calcium levels can inhibit or slow sodium entry into cells (decreased excitability)
What happens to nerve and muscle cells when calcium is low?
Low calcium allows more sodium into cells (increased excitability)
How are hypocalcemia and pseudohypernatremia linked in lab testing?
Both can result from abnormal blood protein or fat levels, causing false low calcium or false high sodium readings due to lab artifacts.
S/S of hypocalcemia
Hyperreflexia
Tetany (Paresthesias/tingling of lips, tongue, fingers, feet)
intermittent muscle spasms, convulsions/seizures
Trousseau sign (BP wrist flex)
Chvostek’s sign (tapping and twitching of face)
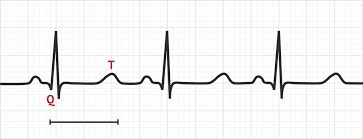
what does a hypocalcemia EKG look like?
Long QT interval
Hypercalcemia S/S
painful bones
kidney stones (calcium stones)
abdominal groans (pains)
thrones (polyuria, dehydration)
psychiatric overtones (acting different)
arrhythmias, hyporeflexia, muscle weakness
causes of hypocalcemia
hypoparathyroidism, Vit D deficiency, malabsorption/nutritional deficiency
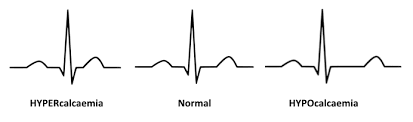
what does a hypercalcemia EKG look like
short ST segment
causes of hypercalcemia
hyperparathyroidism, calcium antacid abuse (tums), bone metastasis (cancer spread to bone), PTH producing tumors
Acidosis (high H+, low pH) S/S
decreased excitability of CNS (headache, lethargy, confusion)
hyperkalemia
hypercalcemia
pseudohyponatremia
Alkalosis (low H+, high pH) S/S
over excitability of CNS (restlessness, confusion, convulsions)
Hypokalemia
Hypocalcemia
Pseudohypernatremia
acid
CO2
base
HCO3 (chemical buffer)
metabolic acidosis (uncompensated)
retention of too much H+
low pH and low HCO3
metabolic alkalosis (uncompensated)
loss of too much H+
high pH and high HCO3
hyperventilation
exhale more CO2
high pH = alkalosis
hypoventilation
exhale less CO2
low pH = acidosis
respiratory acidosis (uncompensated)
because of hypoventilation
low pH and high CO2
respiratory alkalosis (uncompensated)
because of hyperventilation
high pH and low CO2
Metabolic acidosis compensation
hyperventilation, lungs blow off more CO2
low pH, low HCO3, low CO2
Metabolic alkalosis compensation
hypoventilation, lungs blow off less CO2
high pH, high HCO3, high CO2
respiratory acidosis compensation
kidney secretes more H+ and absorbs more HCO3
low pH, high HCO3, high CO2
respiratory alkalosis compensation
Kidney reabsorbs more H+ and secretes more HCO3
high pH, low HCO3, low CO2
How is Acidosis linked with Hyperkalemia?
high H+ levels and low pH levels
excess H+ moves into cell, kicks K+ out of cell
How is Alkalosis linked with Hypokalemia?
low H+ levels and high pH levels
H+ moves from IC —>EC in exchange for K+
How does Alkalosis affect calcium
Alkalosis causes binding of Ca++ to albumin, less free Ca++ in the blood (hypocalcemia=tetany)
S/S Acidosis high H+ and low pH
Hyperkalemia, Pseudohyponatremia, Hypercalcemia (muscle weakness, hyporeflexia, psychiatric overtones), decreased excitability of CNS
S/S Alkalosis low H+ and high pH
Hypokalemia, Hypocalcemia, Tetany, Hyperreflexia, over excitability of CNS
Respiratory Alkalosis causes (low pCO2, high pH)
Hyperventilation, hypoxemia, hypermetabolism, anemia, hyperthyroidism, hysteria
Metabolic alkalosis causes (high HCO3 and high pH)
Acid loss (loss of stomach acid, vomiting, antacids), hypokalemia
Respiratory acidosis causes
Hypoventilation (decreased depth of breathing), Drugs that depress the respiratory centers, and other problems that may effect breathing
Metabolic Acidosis
Shock, Diabetic KetoAcidosis (DKA), Lactic Acidosis (anaerobic metabolism/shock)
Metabolic Acidosis High Anion Gap causes
Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Lactic Acidosis (shock)
Metabolic Acidosis Normal Anion Gap
Diarrhea
Anion Gap equation (only use for metabolic acidosis)
Anion Gap = Na - (HCO3 + Cl)
Normal 10-12
High > 12
What does the body make when fasted and metabolizing fatty acids?
Ketone bodies
(Fed state and high glucose) body’s response:
Insulin released:
Glycolysis, lowers glucose levels (energy used)
Glycogenesis, lowers glucose levels (store excess glucose not used)
(Fasted state and low glucose) body’s response:
gluconeogenesis, highers glucose levels
glycogenolysis, highers glucose levels (break down sugar to be released)
why gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis hurt those with Type 1 Diabetes
No insulin. sugar cannot get into cells.
“fasting state”, high blood sugar already, and liver increases sugar levels even more, when the problem is just with insulin
levels in Diabetes Ketoacidosis
high Ketones, high H+, low pH, high glucose