physics paper 1
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Define the term power
Rate at which energy is transferred or work is done.
mA → A
%1000
Km→m
X 1000
Cm→m
%100
nm→m
%10x*-9
ŲA→ A
%10*-6
MJ→J
X 10*6
GJ→J
X10*9
Power units
Watts
Kinetic energy units
Joules
Gravitational potential energy unit
Joules
Weight units
Kg
Work done units
Joules
Hight units
Metres
Mass units
Kg
Gravity units
N/kg
Speed units
m/s
Define the term density
The mass per unit volume of a material
Units of density
Kg/m3
Define upthrust
The upward force exerted by a fluid on an object submerged in it.
Define internal energy
The sum of the kinetic energy and potential energy of all the particles
Why doesn’t the temperature change when substances are changing state?
Because energy is used to either break or make bonds so it stays constant.
Units of specific latent heat
J/kg
What is latent heat
The energy needed to change the state of 1kg of a substance without changing temp.
What is the latent heat of fusion
Energy needed to melt/freeze
What is latent heat of vapourisation
Energy needed to evaporate/condense.
What is Brownian motion
When larger particles are moved randomly because other particles bump into it and push it around. In fluids .
Define pressure
The force acting on a surface per unit area
What happens to pressure when temp. Increases
Particles gain kinetic energy which means they move faster and collide more frequently with the container walls and with more force making the pressure increase.
What happens to pressure as volume increases
Pressure decreases as it is inversely proportional. Because the particles have less space to move around so there are more frequent collisions with the container walls.
What is the specific heat capacity
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of the sun stance by 1*c
Units units for specific heat capacity
J/kg*c
What is a conduction
The transfer of heat by particles colliding with each other
What makes a good insulator
Any material with air trapped in it e.g. feathers , polystyrene
5 ways to insulate houses
1) have a cavity wall filled with foam or trapped air.
2) carpets /underlay
3) draught excluders
4) double glazing- traps gas’s between glass
5)loft insulation-fibre glass ,reflects IR
How to calculate payback time
Payback time = insulation cost / annual saving
Describe the greenhouse effect
1)short wave radiation from the sun comes into earths atmosphere
2)earth emits long wave radiation
3) gases in the atmosphere trap some outgoing long wave radiation-heating the atmosphere.
4) some long wave radiation leaves the atmosphere.
What can you measure levels of radioactivity with
Geiger counter
Units of radioactivity
Sieberts
Define background radiation
Radiation that is always present around us , very low levels.
Where does background radio come from
Rocks underground
Cosmic rays From space
Food& drink
Medical resources like x-rays
Advantage of using natural gas instead of coal
Doesn’t release sulfur dioxide so doesn’t cause global dimming , acid rain.
Definition of an isotope
Elements with the same number of protons and different numbers of neutrons
Features of radioisotopes
Heavy,unstable
Decay to become more stable by emitting radioactivity particles.
Who discovered radioactivity
Henry Becquerel and Mary Curie
what was JJ. Thompsons atom model
Plum pudding - positive body whithe negative electrons embedded randomly. It don’t have free space
What was Earnest Rutherford atom model
Alpha scattering experiment. Fired alpha particles at a gold sheet , discovering the nucleus is a dense ,positive mass at the centre of the particle with mostly empty space around it .1/8000 alpha particles were deflected instead of going through
Bohrs particle model
Had electron shells orbiting the nucleus .shells were at set distances from the nucleus.
Define irradiation
When an object is exposed to ionising radiation. The object does not become radioactive.
Define ionisation
Any process which atoms become charged
Define contamination
The unwanted presence of materials containing radioactive atoms on other materials. This is due to the decay of the contaminating atoms.
Mass of alpha
Heavy
Speed of alpha
Slow
What is alpha stopped by
A few centimetres of air
Paper
Skin
Charge of alpha
+
Ionising strength of alpha
Highly ionising
Source that emits alpha
Americium
Mass of beta
Light
Speed of beta
Fast
What is beta stopped by
1m air
3mm aluminium
Charge of beta
-
Ionising strength of beta
Medium
What does beta do to magnetic fields
Strongly deflects them
What is beta emitted by
Strontium
What is gamma emitted by
Colbalt
Mass of gamma
0
Speed of gamma
Speed of light - 3×10*8
What is gamma stopped by
3cm lead
1m concrete
Charge of gamma
Neutral
Ionising strength of gamma
Weak
How to be safe handling ionising radioactive sources
Use to tongs
Wear a lead lined apron
Don’t point the source at someone
Limit dose/contact
Hazard symbols
Symbol for alpha decay
🐠
Symbol for beta decay
0
-1. ẞ
Gamma decay
0
Y
Define half-life
The time it takes for half of the radioisotopes/ radioactive nuclei to decay.

Half life

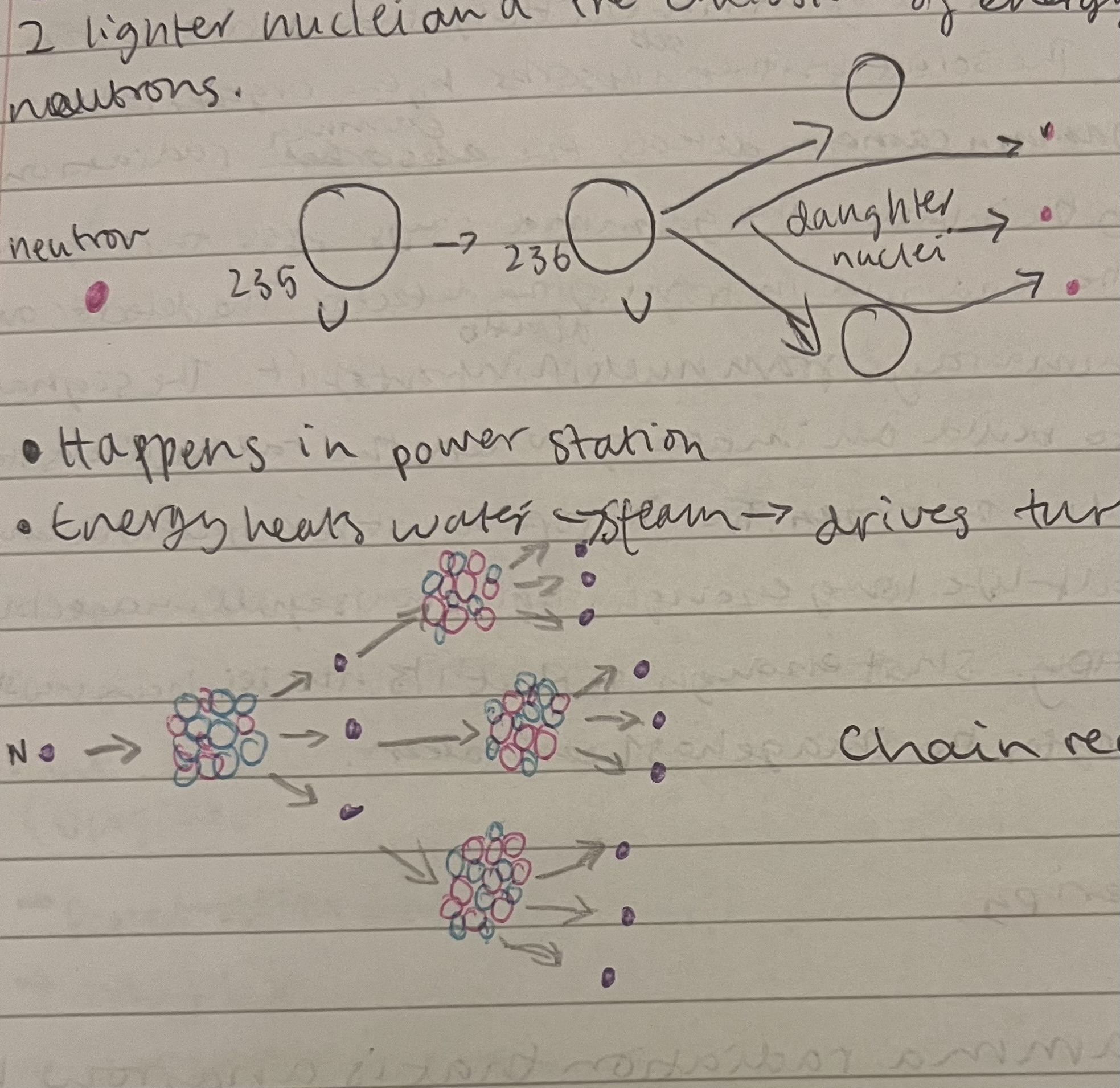
Nuclear fission
The splitting of a heavier nucleus into 2 lighter nuclei and the emitting of energy and 2/3 neutrons.
Happens in power stations , chain reaction .
Has carbon control rods which absorb neutrons to stop chain reactions
Nuclear fusion
The joining together if light nuclei to make a heavy nucleus. Hydrogen+hydrogen=helium
Happens in stars needs a high pressure and high temp.
What happens to mass after fusion
It is less than the individual nuclei added together before. Some mass is converted into energy.
Is nuclear power a fossil fuel
No
Is nuclear power non-renuable
Yes
Compare fission and fusion
Fission- splitting of nuclei , neutron needed to start it, happens in nuclear power stations , produces a lot of energy, produces radioactive waste, no CO2 produced , produces gamma radiation.
Fusion- joining id 2 nuclei to form a new nucleus, needs 1000*c and high pressure, happens in stars, produces even more energy, no harmful products, no CO2 produced, produces gamma radiation.
What do opposite charges do
Attract
What do like charges do
Repel
What happens if you make friction between 2 insulators
Electrons can be transferred onto or off an object causing a build up of static charge.
What happens if I rub a polythene rod with a cloth
The rod is negatively charged
The cloth is positively charged
What happens if I rub a Perspex rod and a cloth
Cloth becomes negatively charged
Rod becomes positively charged
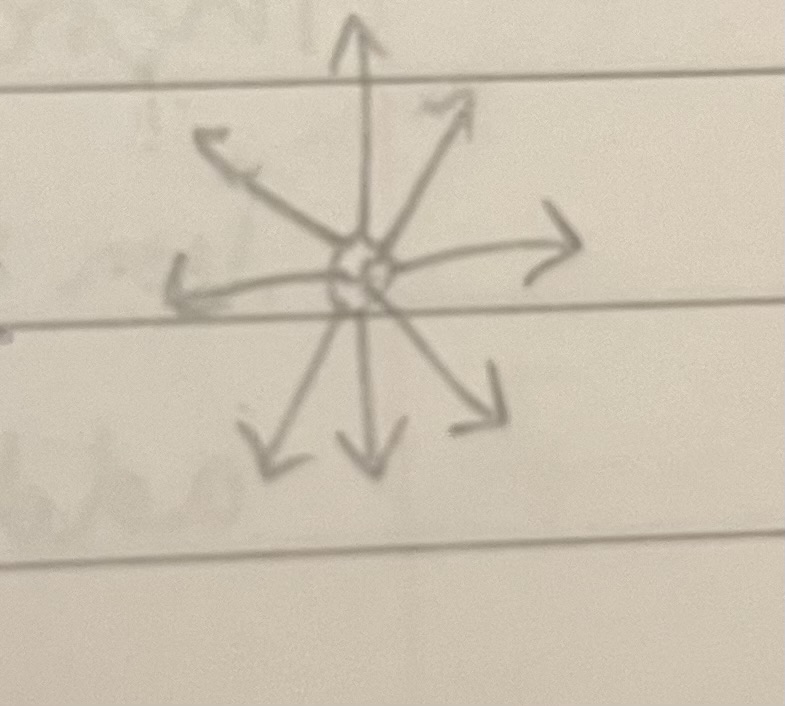
How do electric field lines look in positive charge
Lines from all sides of the ball with arrows facing away from it
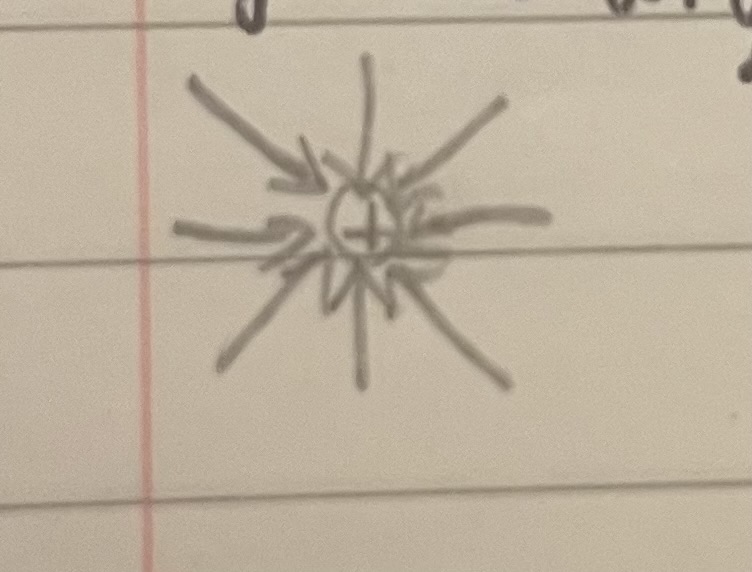
Electric field lines on a negative ball
Lines with arrows pointing inwards
Draw a diode
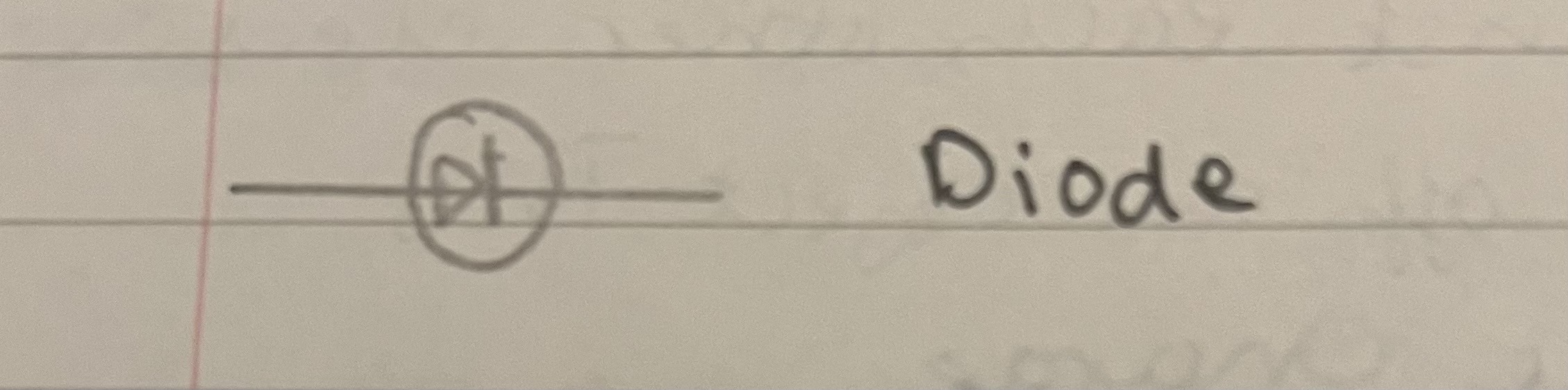
Draw a resistor
Plain box
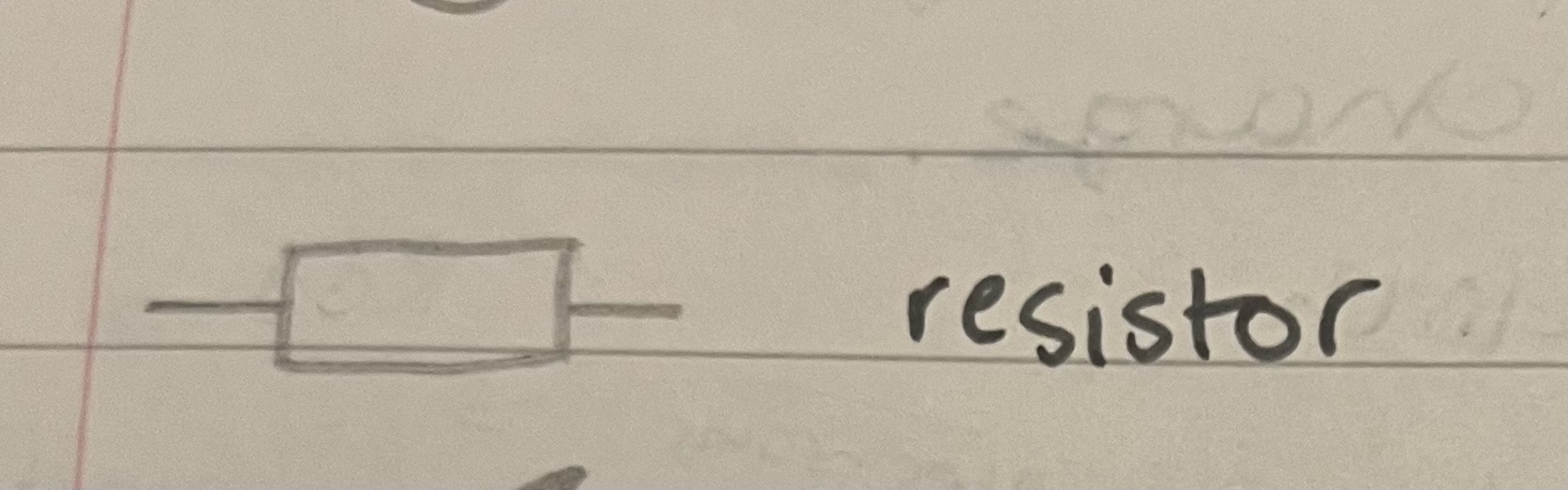
Draw a variable resistor
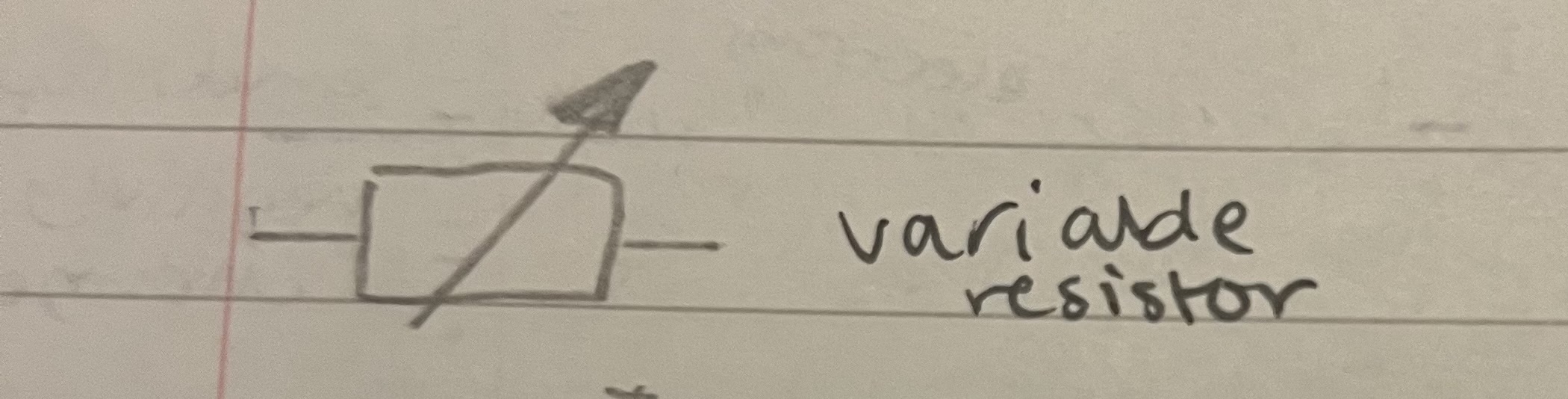
Draw a light emitting diode
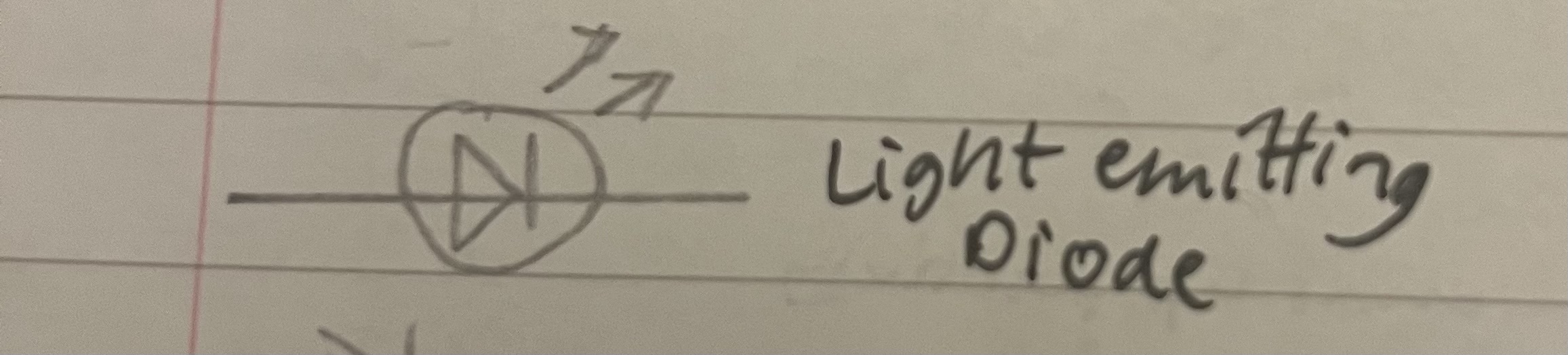
Draw a light depended resistor

Where do you add an ammeter to a circuit
In series
Where do you add a voltmeter in a circuit
In parallel
What happens to a bulb if you increase the potential difference in parallel
Gets brighter
Define current
A flow of charge
What is conventional current
First belief of electricity - positive to negative
Current in series
Equal everywhere
TotalA = A1 =A2