Molecular Genetics Lecture 11 - Non-coding RNAs
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What is a coding RNA?
mRNA which codes for polypeptides/proteins
What is a non-coding RNA?
transcribed into RNA but not translated into proteins
What are small non-coding RNA (<200 nt)?
microRNA (miRNA), small interfering RNA (siRNA), crRNA
What are long non-coding RNAs (>200 nt)?
IncRNA
What do non-coding RNAs regulate?
gene expression at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels
What are MicroRNA (miRNA) and small-interfering RNA (siRNA)?
small regulatory RNAs
What is the function of MicroRNA (miRNA) and small-interfering RNA (siRNA)?
regulate the expression and degradation of mRNAs
What is CRISPR RNA (crRNA)?
small regulatory RNA found in prokaryotes that guide endonuclease to foreign DNA and some CRISPR-Cas systems can target RNA
What is the function of CRISPR RNA (crRNA)?
genome defense
What are the functions of small interfering RNA (siRNA)?
genome defense, involved in the suppression of exogenous RNA sequences especially from viruses by RNA interference (RNAi)
What is the function of RNA interference (RNAi)?
tool in gene therapy used to control gene expression
What is the function of MicroRNA (miRNA)?
regulates endogenous gene expression
The human genome contains about _____ miRNA loci
2600
What human diseases do miRNAs implicit?
cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s
How are miRNA and siRNA used as tools in functional genomic studies?
used to silence genes to understand gene function
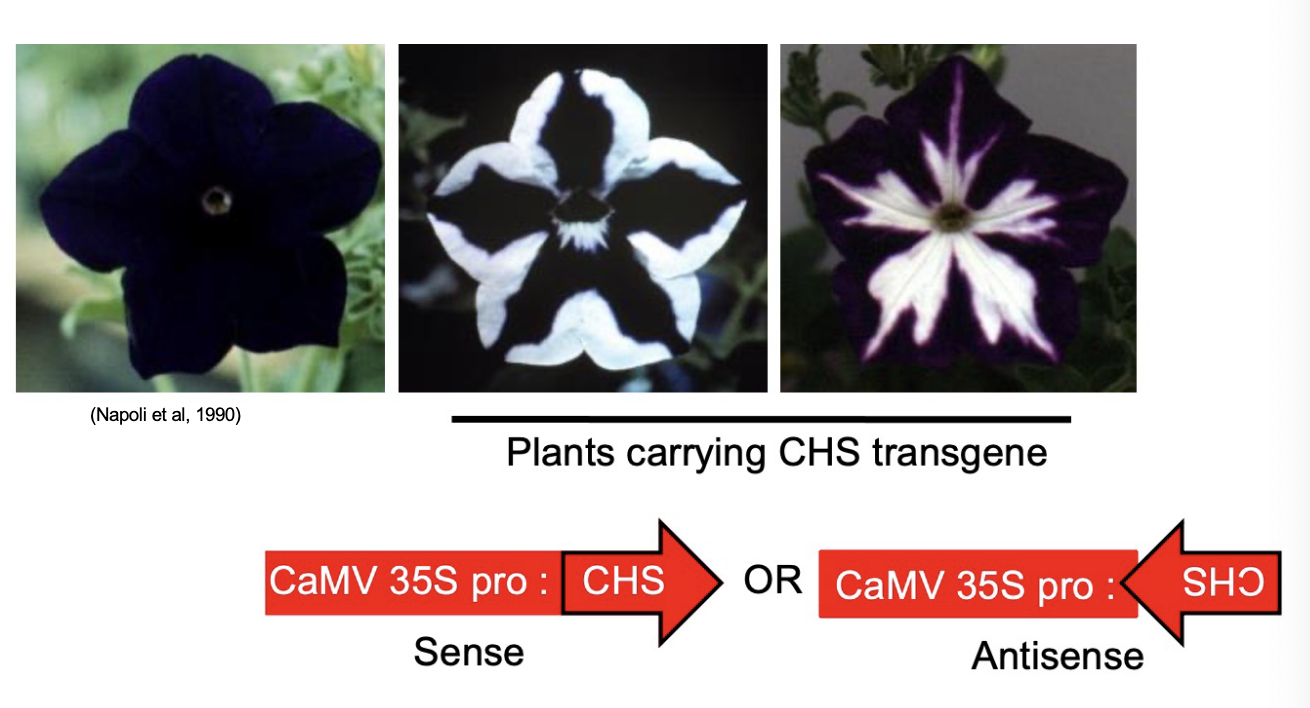
What is the name of the enzyme that is at the start of the biosynthetic pathway for anthocyanins?
Chalcone synthase (CHS)
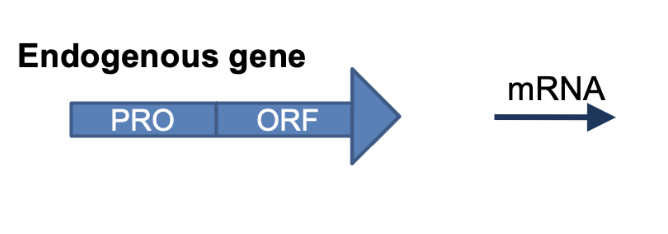
What is the result of this?
regular amount of anthocynanin pigment proteins translated
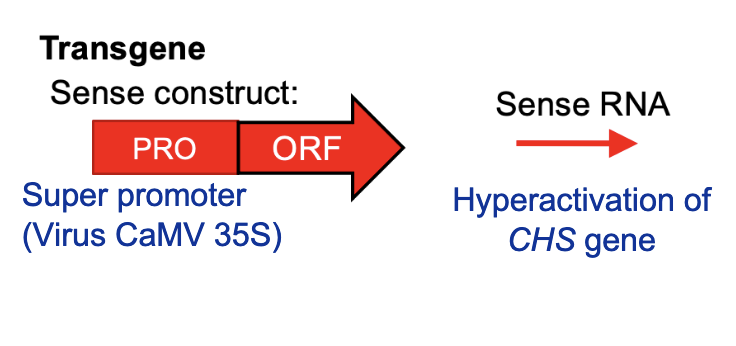
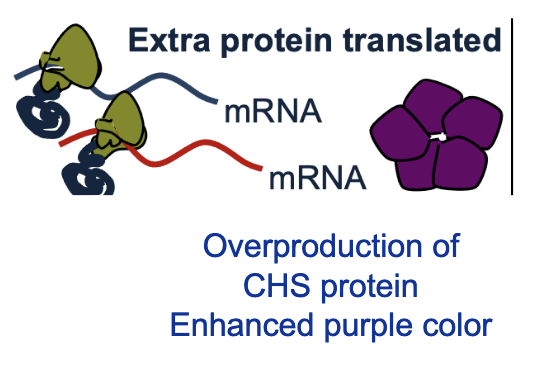
What is the result of this?
Extra protein translated, overproduction of CHS protein, enhanced purple color
Both sense and antisense sequences of the CHS gene cause ______
reduced pigmentation
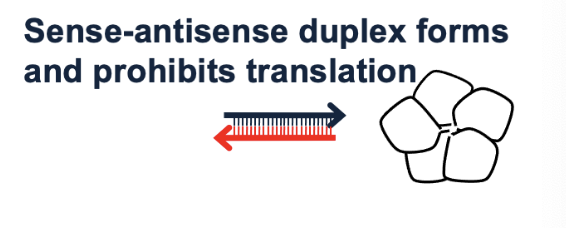
Co-suppression is caused by ____ ____
small RNAs

What is the result of this?
sense-antisense duplex forms and prohibits translation
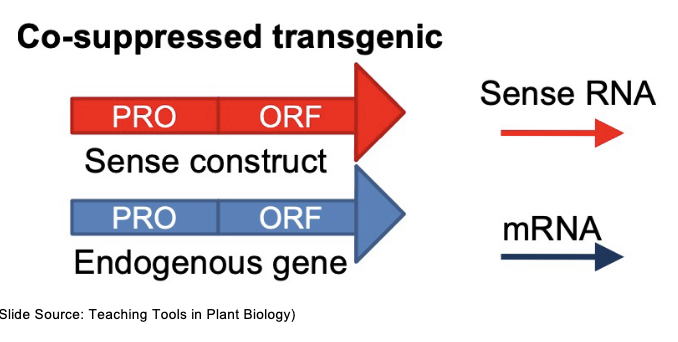
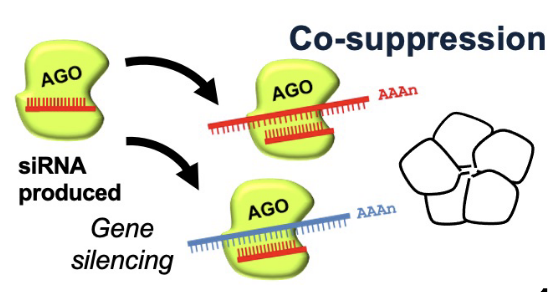
What is the result of this?
co-suppression
What is the major discovery of RNA interference in C. elegans when sense, antisense or double-stranded RNAs that are homologous to the unc-22 gene were introduced into C. elegans?
the silencing of the unc-22 gene causes loss of muscle control
What does ‘unc’ stand for in unc-22 gene?
uncoordinated
What happens when the unc-22 gene is silenced in C. elegans?
causes loss of muscle control
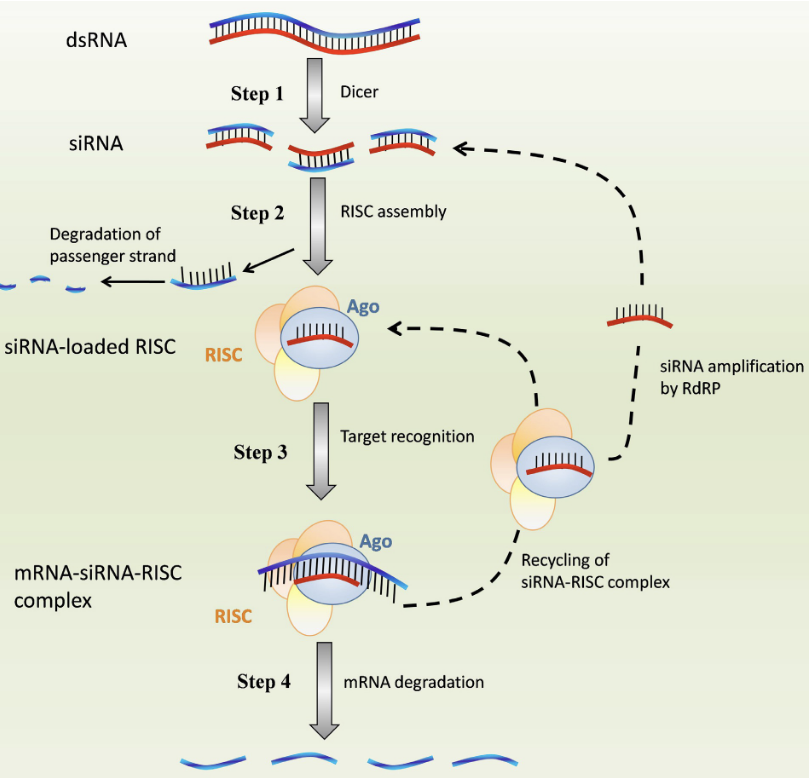
What is the first step of Mechanisms of RNA interference by siRNA?
Generation of siRNA: Dicer endonuclear cleaves dsRNA into 21-23 bp siRNA
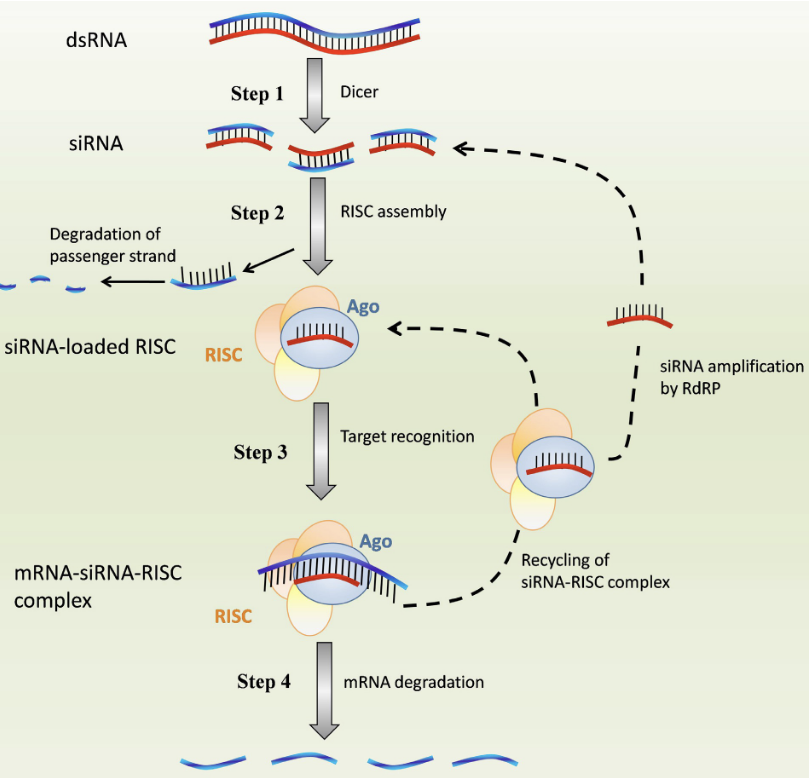
What is the second step of Mechanisms of RNA interference by siRNA?
RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) assembly: passenger strand is removed by Argonaute (Ago) and guide strand of siRNA is loaded into the RISC complex
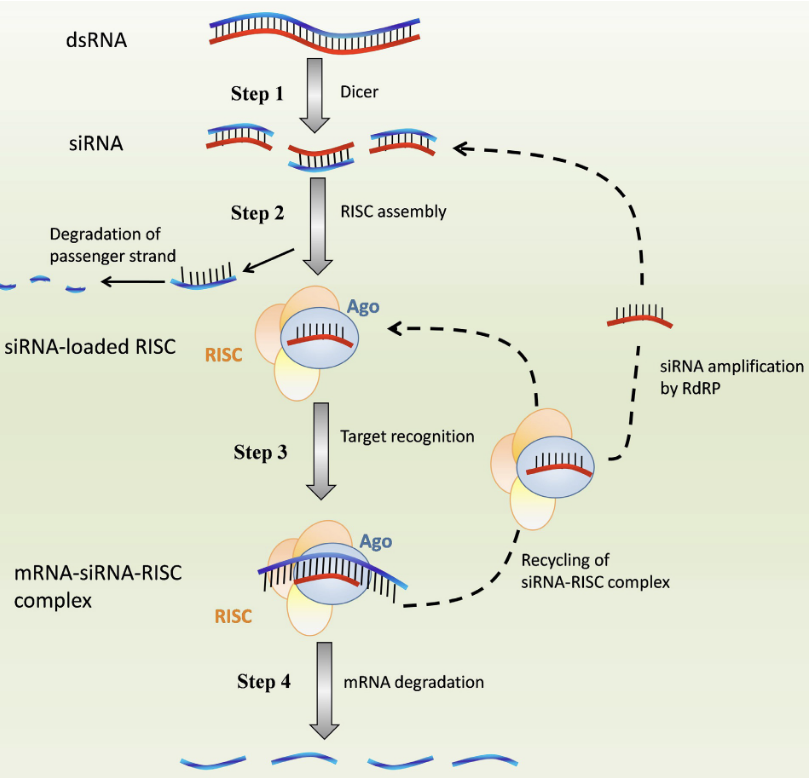
What is the third step of Mechanisms of RNA interference by siRNA?
Formation of mRNA-siRNA-RISC complex: guide siRNA binds to the target mRNA via complementary base pairing
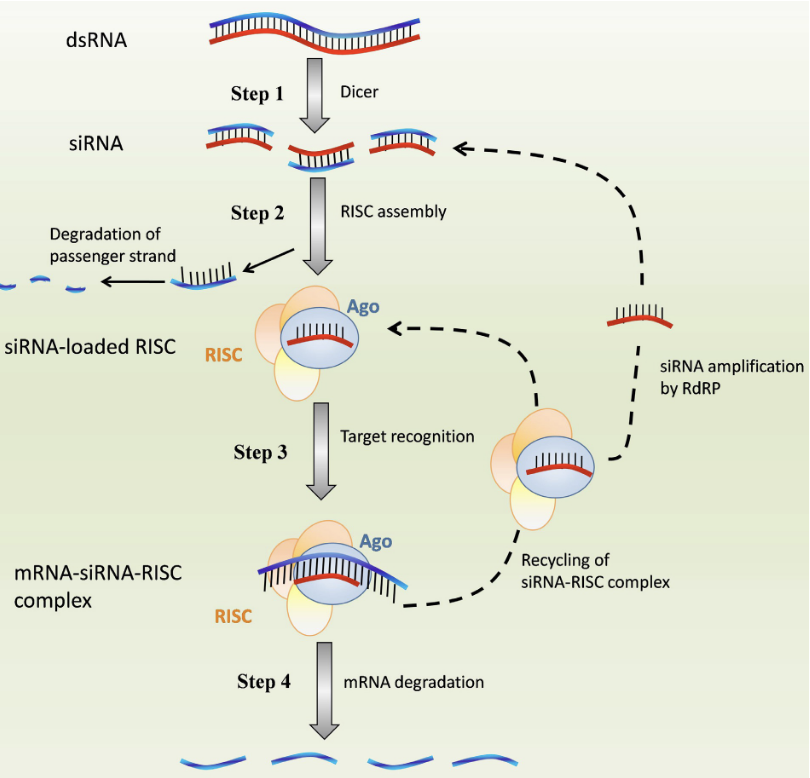
What is the fourth/last step of Mechanisms of RNA interference by siRNA?
mRNA degradation: Ago protein cleaves mRNA which silences the target gene
What process silences transposons?
RNA inference
What is DNA methylation induced by?
small RNAs
What are the three major steps of silencing transposons?
RNAi: activates RNAi pathway, generates siRNA, siRNA degrades mRNA
RNA-dependent DNA methylation
Histone methylation (H3K9me2) and formation of heterochromatin
Transposon is completely silenced
What are the 7 steps of Biogenesis and gene regulation by microRNA (miRNA)?
Generation of precursor microRNA (premiRNA): RNA polymerase transcribes miRNA gene —> pri-mRNA
Processing of pri-mRNA: Ribonuclease III Drosha cleaves pri-mRNA into 70 bp precursor mRNA (Pre-mRNA)
Transport pre-mRNA to a cytoplasms via Ran GTP and Exportin 5 proteins
Generation of 22 bp miRNA: miRNA duplex by Dicer enzyme and removal of passenger strand in miRNA duplex by Ago protein
Generation of mature guide miRNA and RISC assembly including Ago protein
mRNA cleavage: Ago cleaves mRNA if guide miRNA sequences are perfectly complementary to the target
Transcriptional repression: imperfect complementary of miRNA to target mRNA —> inhibition of translation