4.5 Web Filtering
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Content Filtering
Allows organizations to control what web content users can access by filtering data within web pages.
Often referred to as URL filtering or website category filtering
At home, similar tools are called parental controls
Can block or allow content based on specific rules
Restrict access to inappropriate or dangerous sites.
Sometimes helps prevent sensitive data from leaving the network
Some filters are specifically used to block known-malicious websites containing malware or viruses.
URL Scanning
A type of content filtering that allows or blocks websites based on their Uniform Resource Locator (URL).
Also known as a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI)
Can allow or block specific sites by adding them to an allow list or block list.
Often categorize URLs—such as auction, hacking, malware, or recreation—for easier management
Effective for controlling browser content, though users can access data through other means.
Commonly built into next-generation firewalls
Agent Based
Installed directly on users' devices, allowing URL filtering to occur regardless of the user’s location or network.
Function even when users are remote or traveling
Firewall-based filtering, which only works when traffic passes through a specific firewall
Are centrally managed
Each device must regularly receive updates to ensure it has the latest URL categories
Proxies
Acts as an intermediary between users and external networks, controlling the flow of web traffic.
Receives user requests and then makes those requests itself to the internet.
Evaluates the responses before forwarding content to the user’s device.
Allows more than just filtering of URLs—it can cache web pages to speed up repeat requests and provide access control, limiting internet access based on user identity or device IP address
Types of Proxies
An explicit proxy requires the client (such as a web browser) to be manually configured with the proxy’s IP address and port number. The application knows it must send requests through the proxy.
In contrast, a transparent proxy (also called an implicit proxy) intercepts network traffic automatically, without the client’s knowledge or configuration.
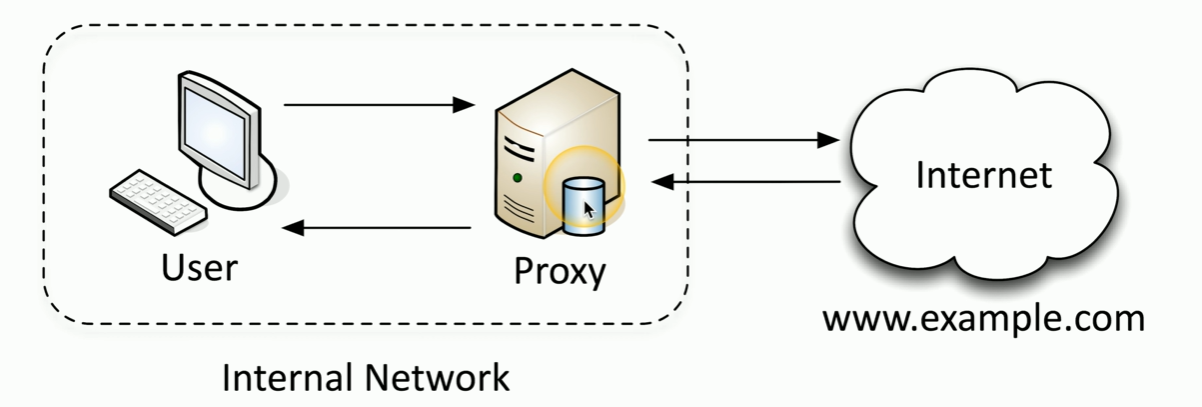
Forward Proxy
A proxy that we would install specifically for users to gain access to the internet.
Sometimes you’ll see it referenced as an internal proxy.
The user and the proxy are in the internal network of the organization.
Block Rules
Block access based on fully qualified domain names (FQDNs) or by website category.
You can create specific rules, such as allowing *.professormesser.com
Or use predefined categories like educational, gambling, or government.
Most filters support over 50 categories, enabling granular control.
For example, educational sites might be allowed, home and garden sites allowed but logged, and gambling sites completely blocked.
Reputation
Sites are rated as trustworthy, low risk, medium risk, suspicious, or high risk.
Filters can automatically scan and assign based on site content, but admins can also manually override these ratings.
You might block all high-risk sites while allowing trustworthy ones, giving you fine-tuned control over what users can access.
DNS Filtering
Blocks access to malicious or inappropriate content by intercepting DNS lookups
When a user requests a domain, checks if it’s on a blocklist.
If so, it withholds the IP or returns a safe default, preventing the connection
Helps stop malware from reaching command-and-control servers.