Review of Nuclear Medicine Technology, 5th Edition
1/799
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
800 Terms
1 Before tracer administration, all of the following preparations are required for a 77-year-old woman referred for total-body bone imaging except:
a. removing attenuating materials from the patient
b. answering the patient’s questions
c. ruling out pregnancy
d. explaining the procedure to the patient
e. swab the injection site with alcohol
a. removing attenuating materials from the patient
2. Which of the following structures normally appear as areas of increased activity on the bone images of children?
a. diaphyses of the long bones
b. breast tissue
c. lumbar spine and cranium
d. costochondral junctions and epiphyseal plates
e. metatarsals
d. costochondral junctions and epiphyseal plates
3. If tracer concentration is visualized in the skeleton, stomach, thyroid, and salivary glands on a bone image, the most likely explanation for these findings is that:
a. patient was imaged too soon after tracer administration
b. patient's renal function is compromised
c. radiopharmaceutical contained excess free [Tc-99m] pertechnetate
d. incorrect radiopharmaceutical was administered
e. radiopharmaceutical contained excess free [F-18] sodium fluoride
c. radiopharmaceutical contained excess free [Tc-99m] pertechnetate
4. For interpretation of nuclear medicine lung images, a chest x-ray is required to:
a. rule out possible causes of the patient's symptoms
b. determine cardiac size
c. rule out previous lung surgery
d. rule out a pulmonary embolus
e. rule in a pulmonary embolus
a. rule out possible causes of the patient's symptoms
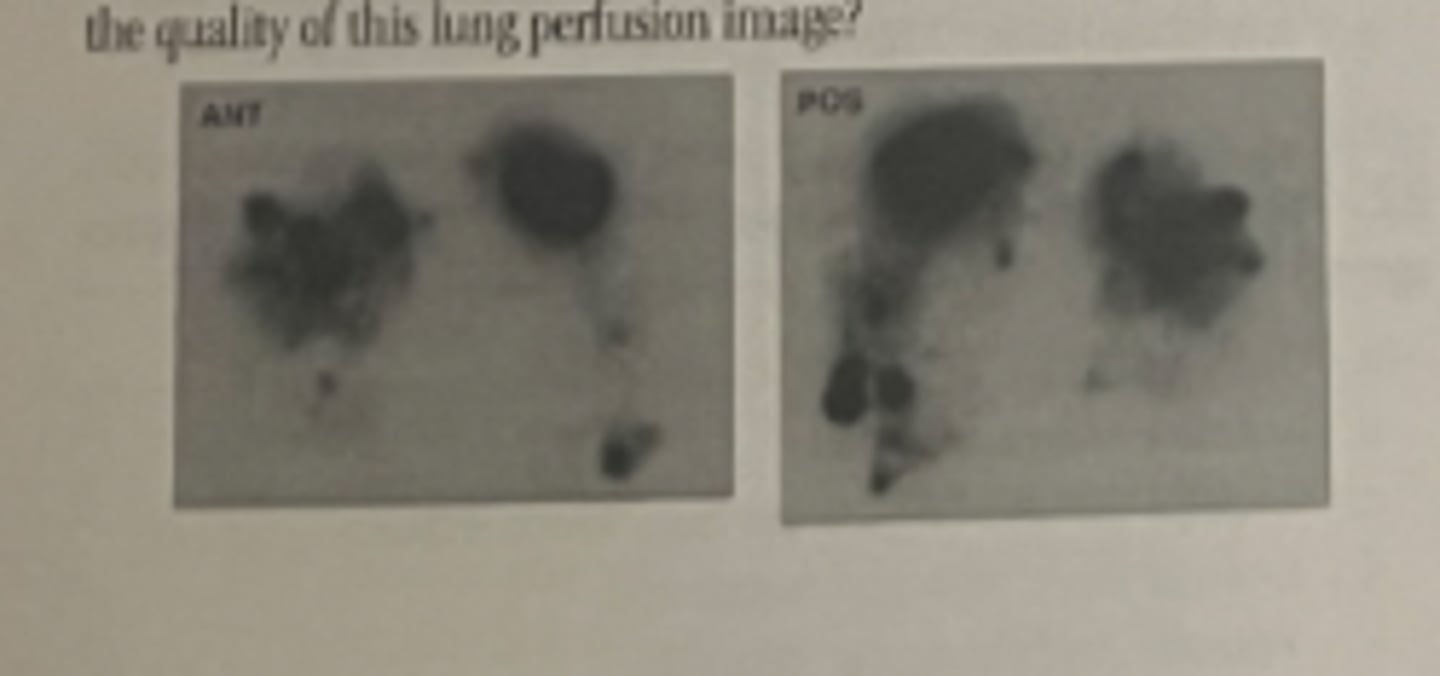
5. The image shown here was obtained after the administration of [Tc-99m] MAA. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the quality of this lung perfusion image?
a. The image shows lung pathology
b. There is radioactive contamination on the patient's skin or the camera detector
c. Blood clotted to MAA particles was injected intravenously
d. Too many MAA particles were administered to the patient
e. A left to right shunt occurred in the heart
c. Blood clotted to MAA particles was injected intravenously
6. The purpose of a charcoal filter in a xenon delivery unit is to absorb:
a. bacteria
b. carbon dioxide
c. xenon gas
d. moisture
e. oxygen
c. xenon gas
7. Radionuclide venography may be performed with which of the following radiopharmaceuticals?
a. [Tc-99m] pentetate
b. [Tc-99m] pertechnetate
c. [Tc-99m] exametazime
d. [Tc-99m] mebrofenin
e. [Tc-99m] MAA
e. [Tc-99m] MAA
8. If ectopic thyroid tissue is suspected, the technologist can expect to find it most commonly in which of the following areas?
a. in the brain
b. in the skull
c. in the nasopharynx
d. in the mediastinum
e. behind the optic nerve
d. in the mediastinum
9. During parathyroid imaging, images of the chest as well as the neck are obtained to:
a. correct the image series for patient motion
b. visualize substernal thyroid tissue
c. visualize ectopic parathyroid tissue
d. diagnose hyperparathyroidism
e. to localize the parathyroid
c. visualize ectopic parathyroid tissue
10. When performing a gated equilibrium cardiac study, which of the following anatomical views best separates the right and left ventricles?
a. left lateral
b. left anterior oblique
c. left posterior oblique
d. anterior
e. posterior
b. left anterior oblique
11. In preparation for a [Tl-201] stress test, patients are instructed to fast to:
a. prevent gastrointestinal upsets during exercise
b. minimize tracer uptake in the gastrointestinal tract
c. enhance myocardial tracer uptake
d. standardize test conditions among patients
e. prevent redistribution of the tracer
b. minimize tracer uptake in the gastrointestinal tract
12. Which of the following agents used for pharmacologic stress testing remains in the plasma for the greatest length of time?
a. dobutamine
b. adenosine
c. nitroglycerin
d. dipyridamole
e. regadenoson
d. dipyridamole
13. SPECT liver imaging with [Tc-99m] sulfur colloid is performed how soon after tracer administration?
a. immediately
b. 10-15 min
c. 30-45 min
d. 1-2 hr
e. 3-4 hr
b. 10-15 min
14. Significantly increased serum bilirubin levels will most likely cause which of the following to be visualized on hepatobiliary images?
a. kidneys
b. colon
c. lungs
d. spleen
e. pancreas
a. kidneys
15. Localization of a Meckel's diverticulum can be accomplished with which of the following radiopharmaceuticals?
a. [Ga-67] citrate
b. [Tc-99m] pentetate
c. [Tc-99m] MAA
d. [Tc-99m] sulfur colloid
e. [Tc-99m] pertechnetate
e. [Tc-99m] pertechnetate
16. In infants, 24 hr images are sometimes performed over what area to demonstrate gastroesophageal reflux?
a. nasopharynx
b. lung fields
c. stomach
d. upper small intestine
e. lower esophagus
b. lung fields
17. Effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) is measured with which of the following radiopharmaceuticals?
a. [Tc-99m] pentetate
b. [Tc-99m] disofenin
c. [Tc-99m] medronate
d. [Tc-99m] mertiatide
e. [Tc-99m] exametazime
d. [Tc-99m] mertiatide
18. Evaluating the quality of a bolus injection is best accomplished by which of the following techniques?
a. generating a time-activity curve for the superior vena cava
b. calculating the cardiac transit time
c. determining the heart to lung ratio
d. imaging the injection site for residual activity
e. visually inspecting the bolus
a. generating a time-activity curve for the superior vena cava
19. Which of the following is/are not normally visualized on a Ga-67 image acquired 72 hr after tracer administration?
a. nasopharynx
b. lacrimal glands
c. kidneys
d. liver
e. sternum
c. kidneys
20. Which of the following statements about “transmission-based precautions” is false?
a. These precautions are applied when a patient is known to be infected with a communicable disease
b. These precautions replace “Standard precautions.”
c. These precautions include guidelines for airborne- and droplet-borne diseases
d. These precautions include guidelines for contact transmitted diseases
e. These precautions must be implemented in the case of diseases such as varicella, tuberculosis, and mumps
b. These precautions replace "Standard precautions."
21 Which of the following statements about pentetreotide is true?
a. It exhibits no human antimurine antibody (HAMA) effect
b. It is a labeled antibody
c. It is a labeled antigen
d. It is excreted exclusively through the kidneys
e. It is labeled with [Tc-99m]
a. It exhibits no human antimurine antibody (HAMA) effect
22. The purpose of using acetazolamide in conjunction with a brain agent is to:
a. Tranquilize the patient
b. Localize brain tumors
c. Localize the area of the brain from which seizures arise
d. Evaluate cerebrovascular hematoma
e. Evaluate cerebrovascular ischemia
e. Evaluate cerebrovascular ischemia
23. The technologist’s responsibilities during tracer administration for a cisternogram include:
a. Ensuring that personnel and the surroundings are not contaminated with radioactivity
b. Obtaining consent to perform the procedure
c. Delivering antihistamines for any adverse reactions to the procedure
d. Testing the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid
e. Performing the lumbar puncture
a. Ensuring that personnel and the surroundings are not contaminated with radioactivity
24. Sodium phosphate ³²P may be used to treat which of the following conditions?
a. Liver metastases
b. Lupus
c. Rheumatoid arthritis
d. Malignant effusions
e. Polycythemia vera
e. Polycythemia vera
25. Supersaturated potassium iodide solution may be administered to the patient for therapy with which of the following radiopharmaceuticals?
a. [¹³¹I]Iodinated human serum albumin
b. [¹³¹I]Chloride
c. [¹³¹I]Sodium iodide
d. [¹³¹I]Tositumomab
e. [¹³¹I]Chloride
d. [¹³¹I]Tositumomab
26. The first step that a technologist should initiate in a safe environment when an adult patient is determined to be unresponsive is to:
a. Perform chest compressions
b. Establish an airway
c. Check for a carotid pulse
d. Call for help
e. Perform rescue breathing
d. Call for help
27. [¹¹¹In]Pentetreotide should not be administered through an intravenous line containing:
a. Water
b. A total parenteral nutrition mixture
c. Dextrose
d. Glucose
e. 0.9% Sodium chloride
b. A total parenteral nutrition mixture
28. Dual-isotope gastric emptying studies use which of the following radiopharmaceuticals for each phase of gastric emptying:
Liquid phase:
a. [¹¹¹In]Pentetate
b. [¹¹¹In]Pentetreotide
c. [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Sulfur colloid
d. [²⁰¹Tl]Thallous chloride
e. [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Pentetate
Solid phase:
a. [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Sulfur colloid
b. [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Sulfur colloid
c. [¹¹¹In]Pentetate
d. [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Sestamibi
e. [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Sulfur colloid
a. [¹¹¹In]Pentetate ; [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Sulfur colloid
29. Proper placement of a urine collection bag includes:
a. Placing it across the patient's lower legs to keep it near the level of the bladder
b. Placing it on the stretcher near the patient's feet so it is out of the field of view of the camera
c. Discharging the urine collection bag must be done before the exam begins
d. Hanging it from an IV pole and raising it above the level of the bladder
e. Hanging it from the imaging table so it is lower than the level of the bladder
e. Hanging it from the imaging table so it is lower than the level of the bladder
30. Which of the following radiopharmaceuticals can be used to assess vesicoureteral reflux by the indirect method:
a. [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Pertechnetate
b. [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Sulfur colloid
c. [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Pentetate
d. [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Mertiatide
e. [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Albumin
c. [⁹⁹ᵐTc]Pentetate
31. If 0.02 µg/kg of cholecystokinin is needed for a hepatobiliary study, what volume needs to be drawn for a 175 lb patient with a solution of 10 µg/mL available to draw from:
a. 0.115 mL
b. 0.129 mL
c. 0.140 mL
d. 0.149 mL
e. 0.159 mL
e. 0.159 mL
32. Parenteral administration of a drug or radiopharmaceutical would include all of the following routes except:
a. Oral
b. Intramuscular
c. Subcutaneous
d. Intravenous
e. Intrathecal
a. Oral
33. The red cell survival test is most often performed on a patient with suspected:
a. Hemolytic anemia
b. Intestinal malabsorption
c. Iron deficiency anemia
d. Pernicious anemia
e. GI bleed
a. Hemolytic anemia
34. A technologist confirms a referring physician's request for a nuclear medicine procedure for a hospitalized patient by:
a. asking the floor nurse
b. telephoning the patient's physician for confirmation
c. locating the order for the test in the patient's medical record
d. conferring with the nuclear medicine physician
e. asking the patient why s/he came to the nuclear medicine department
c. locating the order for the test in the patient's medical record
35. Which type of collimator should be used for organ counting during a red cell sequestration study:
a. low-energy, high-sensitivity parallel hole
b. high-energy, low-resolution parallel hole
c. pinhole
d. flat field
e. converging
d. flat field
36. If a plasma volume has been determined to be 15L, which of the following events has most likely occurred:
a. completion of a satisfactory study
b. overhydration of the patient
c. dehydration of the patient
d. patient did not fast for the study
e. infiltration of the tracer
e. infiltration of the tracer
37. A biohazard warning label would be found on all of the following except:
a. contaminated sharps container
b. refrigerator containing potentially infectious material
c. receptacle for contaminated laundry
d. unit of blood released for clinical use
e. uncontaminated sharps container
d. unit of blood released for clinical use
38. The total blood volume may be calculated by dividing the plasma volume measured with labeled albumin by the:
a. hematocrit
b. plasmacrit
c. corrected hematocrit
d. corrected plasmacrit
e. hemoglobin
d. corrected plasmacrit
39. If radioactivity in the circulation from a previous nuclear medicine test is unaccounted for, results of a plasma volume determination will be:
a. falsely decreased
b. falsely elevated
c. positive
d. impossible to predict
e. unaffected
a. falsely decreased
40. The recommended amount of captopril to be given orally an hour before renal imaging in a hypertension study is:
a. 10-15 mg
b. 15-20 mg
c. 25-50 mg
d. 55-100 mg
e. 105-110 mg
c. 25-50 mg
41. Imaging with [In-111] pentetreotide routinely includes what area(s) of the body:
a. head and chest
b. chest
c. abdomen
d. head to upper femurs
e. lower extremities
d. head to upper femurs
42. A patient scheduled for scintimammography has symptoms involving her left breast. Which of the following sites is the best choice for injection of the radiopharmaceutical:
a. subcutaneous in the left breast
b. right carotid artery
c. right antecubital area
d. left hand
e. left carotid artery
c. right antecubital area
43. Based on the net counts data shown here: Right lung: 175,362, Left lung: 325,672. What is the percentage perfusion to the right lung:
a. 30%
b. 35%
c. 54%
d. 65%
e. 77%
b. 35%
44. If 375 mCi of [Tc-99m] are present on the column of a Mo-99/Tc-99m generator, and after elution, 342 mCi [Tc-99m] are assayed in the elution vial, the approximate elution efficiency of the generator is:
a. 110%
b. 91%
c. 33%
d. 11%
e. 5%
b. 91%
45. 250 kilobecquerels are equivalent to how many microcuries:
a. 0.25 µCi
b. 0.55 µCi
c. 6.76 µCi
d. 9.25 µCi
e. 10.35 µCi
c. 6.76 µCi
46. If a ⁹⁹Mo/⁹⁹ᵐTc generator is eluted on Monday at 0600, the maximum ⁹⁹ᵐTc activity could next be eluted at what time?
a. 0600 on Tuesday
b. 1200 on Monday
c. 1800 on Monday
d. 0600 on Wednesday
e. 1200 on Tuesday
a. 0600 on Tuesday
47. According to the NRC, ⁹⁹Mo contamination in ⁹⁹ᵐTc eluate must be measured how often?
a. weekly
b. daily
c. only after the first elution
d. yearly
e. after each elution
c. only after the first elution
48. If these results shown were obtained when ⁹⁹ᵐTc eluate was assayed for ⁹⁹Mo breakthrough at 0600, immediately after elution:
⁹⁹Mo: 10 µCi
⁹⁹ᵐTc: 416 mCi
which of the following statements about this elution at 1700 is true?
a. The eluate should not be used to label compounds with ⁹⁹ᵐTc.
b. The eluate does not contain sufficient ⁹⁹ᵐTc activity.
c. The eluate does not contain sufficient ⁹⁹Mo activity.
d. The eluate may be not administered to patients.
e. The eluate may be administered to patients.
e. The eluate may be administered to patients.
49. A technologist performs an aluminum ion breakthrough test on ⁹⁹ᵐTc eluate and obtains the following results: When the indicator paper is spotted with aluminum ion solution, a faint red color is observed, but when the paper is spotted with eluate, no color change is observed. These results indicate:
a. absence of radionuclidic impurities in the eluate
b. absence of free [⁹⁹ᵐTc]pertechnetate
c. the aluminum ion concentration in the eluate is below the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) limit
d. the aluminum ion solution contains less aluminum than the eluate
e. the eluate should be discarded
c. the aluminum ion concentration in the eluate is below the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) limit
50. All of the following procedures may be performed with [⁹⁹ᵐTc]sulfur colloid except:
a. gastric-emptying study
b. gastroesophageal reflux study
c. gastrointestinal-bleeding localization
d. Meckel's diverticulum localization
e. bone marrow imaging
d. Meckel's Diverticulum
51. Based on the day's clinic schedule shown here:
Patient A - Thyroid uptake and image
Patient B - Therapy for hyperthyroidism
Patient C - Cisternogram
the technologist should prepare or order which of the following radiopharmaceuticals?
a. [¹³¹I]sodium iodide, [¹²³I]sodium iodide, and [¹¹¹In]pentetate
b. [¹³¹I]oxine and [¹³¹I]sodium iodide
c. [¹³¹I]sodium iodide, [⁹⁹ᵐTc]sulfur colloid, [⁹⁹ᵐTc]macroaggregated albumin
d. [¹³¹I]sodium iodide and [¹¹¹In]chloride
e. [¹³¹I]human serum albumin, [¹³¹I]sodium iodide, and [⁹⁹ᵐTc]pertechnetate
a. [¹³¹I]sodium iodide, [¹²³I]sodium iodide, and [¹¹¹In]pentetate
52. If an MAA kit must be reconstituted with 3.5 mL of [⁹⁹ᵐTc]pertechnetate, what are the consequences if only 2.0 mL are added to the kit?
a. Patients will receive more MAA particles per milliliter of [⁹⁹ᵐTc]MAA.
b. Patients will receive more pertechnetate per milliliter of reconstituted patient dose.
c. Patients will receive the recommended number of particles if the correct activity is administered.
d. The perfusion lung images will have the appearance of decreased tracer uptake.
e. Patients will receive fewer MAA particles per milliliter of [⁹⁹ᵐTc]MAA.
a. Patients will receive more MAA particles per milliliter of [⁹⁹ᵐTc]MAA.
53. Reconstituted "cold" pyrophosphate is administered to the patient in which red blood cell labeling method(s)?
a. in vitro method
b. both the in vivo method and the modified in vivo method
c. modified in vivo method
d. both the in vitro method and the in vivo method
e. in vivo method
b. both the in vivo method and the modified in vivo method
54. Which of the following radiopharmaceutical kit formulations is light-sensitive?
a. sestamibi
b. oxidronate
c. mertiatide
d. exametazime
e. pertechnetate
c. mertiatide
55. When performing radiochromatography on a radiopharmaceutical sample, the solvent front is located 8.5 cm from the origin and the radiochemical impurity is at the origin. What is the Rf value of the radiochemical impurity?
a. -0.5
b. 0
c. 1.0
d. 8.5
e. 0.85
b. 0
56. According to the USP, most 99mTc-labeled radiopharmaceuticals should have a radiochemical purity of at least what percentage to be administered to patients?
a. 98%
b. 95%
c. 90%
d. 88%
e. 85%
c. 90%
57. A technologist must administer 8 mCi of [99mTc]mebrofenin to a patient at 1100, on the basis of this vial label information:
- Calibration: 1700, August 4
- Total activity: 120 mCi
- Total volume: 20 mL
- Concentration: 118 mCi/20 mL
- Expiration: 0500, August 5
What volume of [99mTc]mebrofenin should be administered to the patient?
a. 1.1 mL
b. 0.92 mL
c. 0.68 mL
d. 0.52 mL
e. 0.45 mL
a. 1.1 mL
58. A technologist must administer 37 MBq [201Tl]thallous chloride at 1000 on February 16. On the basis of this vial label information:
- Calibration: 1200, February 14
- Total activity: 222 MBq
- Total volume: 4.0 mL
- Concentration: 55.5 MBq/mL
- Expiration: 1200, February 17
What volume should be administered to the patient?
a. 1.0 mL
b. 0.96 mL
c. 0.84 mL
d. 0.44 mL
e. 0.23 mL
a. 1.0 mL
59. A technologist needs 4 mCi [201Tl]thallous chloride at 0800 on June 29th. The label on the radiopharmaceutical vial contains this information:
- Total activity: 10.0 mCi
- Total volume: 5 mL
- Assay: 1200, July 1
What volume is required to obtain the necessary activity on June 29?
a. 3.6 mL
b. 1.35 mL
c. 0.74 mL
d. 0.28 mL
e. 0.13 mL
b. 1.35 mL
60. Which radiopharmaceutical is used to label red blood cells with 99mTc?
a. 99mTc-albumin
b. 99mTc-pertechnetate
c. 99mTc-sulfur colloid
d. 99mTc-pyrophosphate
e. 99mTc-exametazime
b. 99mTc-pertechnetate
61. Which of the following radiopharmaceuticals is used to label white blood cells with 99mTc?
a. 99mTc-bicisate
b. 99mTc-sulfur colloid
c. 99mTc-pertechnetate
d. 99mTc-sestamibi
e. 99mTc-exametazime
e. 99mTc-exametazime
62. When 99mTc-exametazime is used to label white blood cells, which of the following reagents is omitted from its preparation?
a. 99mTc-pertechnetate
b. 0.9% sodium chloride
c. heparin
d. methylene blue stabilizer
e. ACD solution
d. methylene blue stabilizer
63. If a 4 millicurie vial of [201Tl]thallous chloride is the prescribed unit dosage, which of the following dose calibrator measurements, according to the NRC, verifies that a dosage within acceptable limits has been dispensed into the syringe?
I. 3.5 mCi
II. 4.0 mCi
III. 4.3 mCi
IV. 4.5 mCi
a. I only
b. II only
c. II or III only
d. I, II, or III only
e. I, II, III, or IV
e. I, II, III, or IV
64. In labeling red blood cells with radiochromium, the correct order of components to be added to the vial is:
a. radiochromium, ACD, patient blood, ascorbic acid
b. radiochromium, patient blood, ascorbic acid
c. radiochromium, ascorbic acid, patient blood
d. patient blood, radiochromium, ascorbic acid
e. ascorbic acid, radiochromium, patient blood
d. patient blood, radiochromium, ascorbic acid
65. If a unit dosage of [Tc-99m] MAA contains 148 MBq and 325,000 particles in 0.75 mL at 1,000, approximately how many particles will be contained in 148 MBq at 1,600?
a. 162,500
b. 325,000
c. 433,333
d. 522,000
e. 650,000
e. 650,000
66. If a unit dosage contains 4.5 mCi in 1.2 mL, how many mL must be removed so 3.5 mCi remain in the syringe?
a. 0.93 mL
b. 0.78 mL
c. 0.27 mL
d. 0.13 mL
e. 0.02 mL
c. 0.27 mL
67. A radiopharmaceutical kit must be reconstituted to contain 30 mCi in 5 mL, and the eluate has 350 mCi in 7 mL. How much preservative-free saline must be added?
a. 0.6 mL
b. 4.4 mL
c. 4.9 mL
d. 5.2 mL
e. 6.0 mL
b. 4.4 mL
68. What is the minimal centrifugation time needed if a protocol specifies 5000 g for 5 min, but the maximum RCF available is 2500 g?
a. 2 min
b. 2.5 min
c. 7.5 min
d. 10 min
e. 12.5 min
d. 10 min
69. According to the NRC, imaging rooms should be posted with which sign?
a. No posting is required
b. "Caution: No Food or Drink"
c. "Caution: Radiation Area"
d. "Caution: Radioactive Materials"
e. "Caution: High Radiation Area"
d. "Caution: Radioactive Materials"
70. Which of the following exposure rates indicates a Category III DOT label is required for a package of radioactive material?
Surface (mR/hr) 1m (mR/hr)
a. 76 5.5
b. 56 3.5
c. 22 0.9
d. 1.5 1.0
e. 0.5 None
b. 56 3.5
71. A point source produces 30 mR/hr at 15 cm. What is the exposure rate at 40 cm?
a. 4.2 mR/hr
b. 8.5 mR/hr
c. 11.2 mR/hr
d. 22.0 mR/hr
e. 25.0 mR/hr
a. 4.2 mR/hr
72. If the HVL (half-value layer) for I-131 in lead is 0.3 cm, what thickness is required to reduce 12 mR/hr to less than 2 mR/hr?
a. 0.3 cm
b. 0.6 cm
c. 0.75 cm
d. 0.9 cm
e. 1.2 cm
d. 0.9 cm
73. A patient receives a unit dose of Sr-89 chloride intended for another patient. What is the correct regulatory response?
a. No NRC report is needed due to low dose
b. Not a medical event, but record it internally
c. Report to supervisor and authorized user only
d. No report needed if below dose threshold
e. Must be reported to NRC as a medical event
e. Must be reported to NRC as a medical event
74. According to NRC regulations, the annual occupational dose limit to the eye is:
a. 150 mSv
b. 100 mSv
c. 85 mSv
d. 50 mSv
e. 5 mSv
a. 150 mSv
75. A vial of ¹³¹I has been decayed in storage for 2 months. When the vial is monitored with a survey meter, the reading is twice the background radiation level. What should the technologist do next?
a. Remove any radiation symbols from the vial, then dispose of it.
b. Perform a wipe check.
c. Return the vial to storage.
d. Vent the radioactivity left in the vial into a fume hood.
e. Dispose of the vial as biohazardous waste.
c. Return the vial to storage.
76. According to the NRC, wipe tests of areas where radiopharmaceuticals are prepared or administered must be performed:
a. on a reasonable schedule
b. every day on which radiopharmaceuticals are used
c. weekly
d. only if contamination occurs
e. monthly
a. on a reasonable schedule
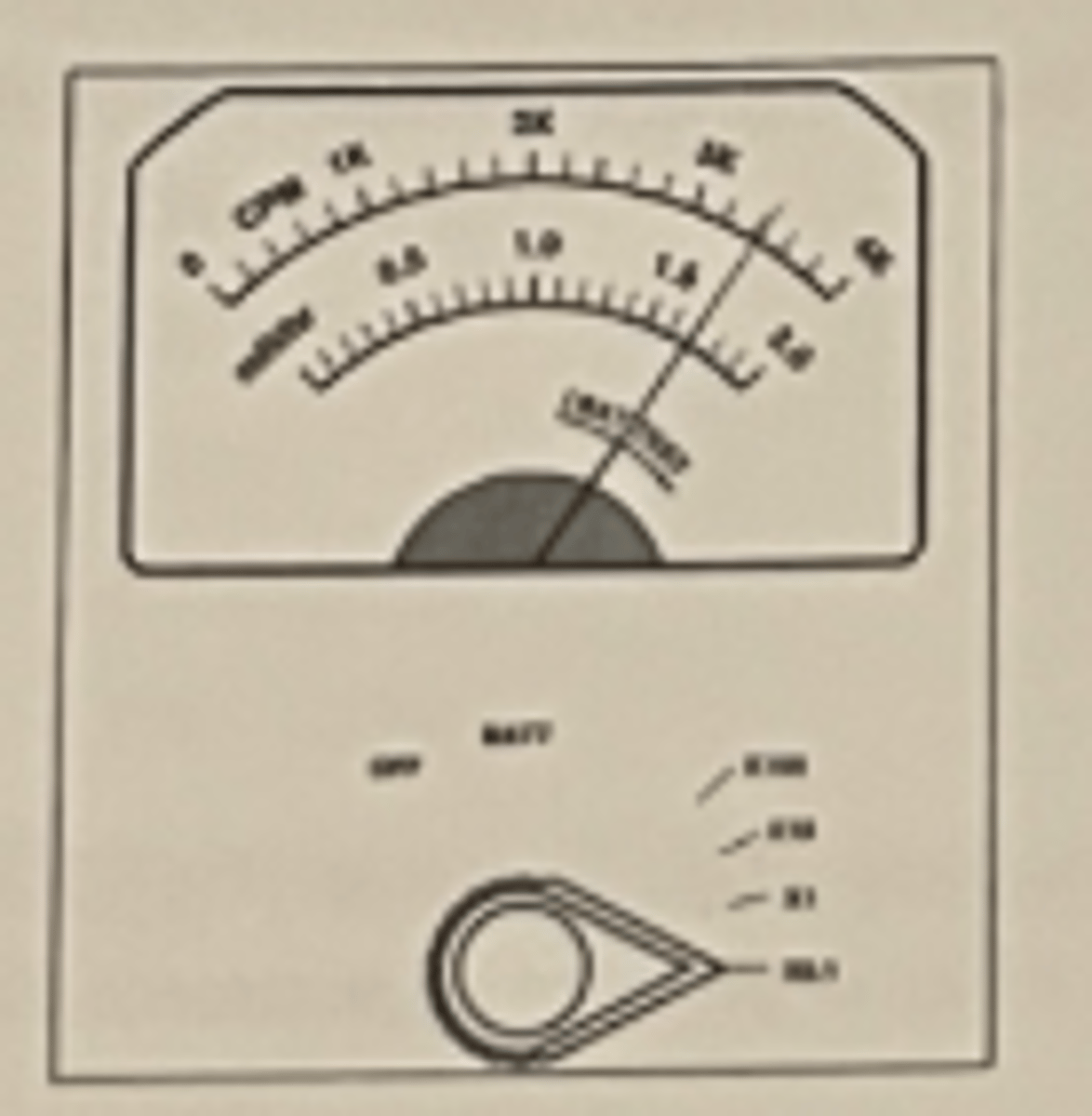
77. What is the measured exposure rate shown on the diagram of the G-M meter depicted here?
a. 0.017 mR/hr
b. 0.17 mR/hr
c. 1.7 mR/hr
d. 17 mR/hr
e. 170 mR/hr
b. 0.17 mR/hr
78. When opening packages containing radioactive material, which of the following steps should be performed first?
a. Perform a survey using Geiger counter.
b. Wipe-test the package receiving area.
c. Put on disposable gloves.
d. Wipe-test the package for contamination.
e. Verify the package contents against the packing slip.
c. Put on disposable gloves.
79. During cleanup of a radioactive spill, decontamination of the area must continue until wipe checks reveal that:
a. The exposure rate of the area is less than 3 mRem/hr.
b. The exposure rate of the area cannot be distinguished from background activity.
c. The contamination is reduced to a small area.
d. No one would receive the maximum allowable total effective dose equivalent (TEDE) if he/she remained in the area.
e. No more contamination can be removed from the area.
e. No more contamination can be removed from the area.
80. Personnel must wear a radiation monitoring device during work hours if they are:
a. exposed to radiation at any time during work hours
b. exposed to radiation above background levels
c. likely to exceed 10% of the annual maximum allowable occupational exposure
d. likely to exceed the annual maximum allowable occupational exposure
e. a radiologic technologist
c. likely to exceed 10% of the annual maximum allowable occupational exposure
81. A patient can be released after receiving a therapeutic radiopharmaceutical if no other individual is likely to receive an exposure dose from being exposed to the patient, exceeding how many Rems?
a. 0.5 Rem
b. 1.0 Rem
c. 2.5 Rem
d. 5.0 Rem
e. 7.0 Rem
a. 0.5 Rem
82. If a source of radioactive contamination produces an exposure rate of 3 mR/hr, how long will it take for the exposure rate to drop to a background exposure rate of 0.05 mR/hr?
a. 5 half-lives
b. 6 half-lives
c. 7 half-lives
d. 8 half-lives
e. 9 half-lives
b. 6 half-lives
83. According to the NRC, records of surveys must be retained for how many years?
a. as long as the facility's license is in effect
b. 7 years
c. 5 years
d. 4 years
e. 3 years
e. 3 years
84. Which of the following materials is recommended for shielding syringes containing positron-emitting radionuclides?
a. lead
b. tungsten
c. gold
d. steel
e. plastic-lined lead
b. tungsten
85. If a nuclear medicine technologist needs a diagnostic x-ray, how should this exposure be included in his/her occupational exposure record?
a. The technologist should wear his/her radiation dosimeter during the x-ray examination.
b. The exposure from the x-ray examination must not be included in the occupational exposure record.
c. The RSO will supply a separate dosimeter for the technologist to wear during the x-ray examination.
d. A pocket dosimeter should be used.
e. The RSO will estimate the probable exposure and add it to the technologist's permanent record
b. The exposure from the x-ray examination must not be included in the occupational exposure record.
86. According to the standard of practice, if the results of a dose calibrator geometric variation test demonstrate that the measured values exceed the values by 12-15%, the technologist should:
a. Replace the instrument.
b. Use a correction factor to determine true activities.
c. Perform a chi-square analysis.
d. Use the actual dose calibrator activity readings.
e. Have the instrument repaired.
b. Use a correction factor to determine true activities.
87. A technologist measures a ⁵⁷Co standard in a dose calibrator on the following settings—⁵⁷Co, ⁶⁰Co, ¹²⁵I, ¹³¹I, and ⁹⁹ᵐTc—and then calculates the percentage difference between the calculated and measured activities. The technologist is assessing:
a. constancy
b. chi-square analysis
c. linearity
d. geometric variation
e. accuracy
a. constancy
88. A ⁶⁵Cs reference standard is counted daily with a scintillation spectrometer, using the same gain, window, and high voltage setting. On the basis of these data:
Date Net counts per minute
July 15 12,555
July 16 12,534
July 17 12,613
July 20 10,678
On July 20, the technologist should:
a. Use the spectrometer for clinical studies.
b. Arrange for repair of the instrument.
c. Change the gain setting.
d. Change the fine gain setting.
e. Recalibrate the operating voltage.
e. Recalibrate the operating voltage.
89. According to the standard of practice, how often should dose calibrator linearity testing be performed?
a. annually
b. quarterly
c. monthly
d. daily
e. hourly
b. quarterly
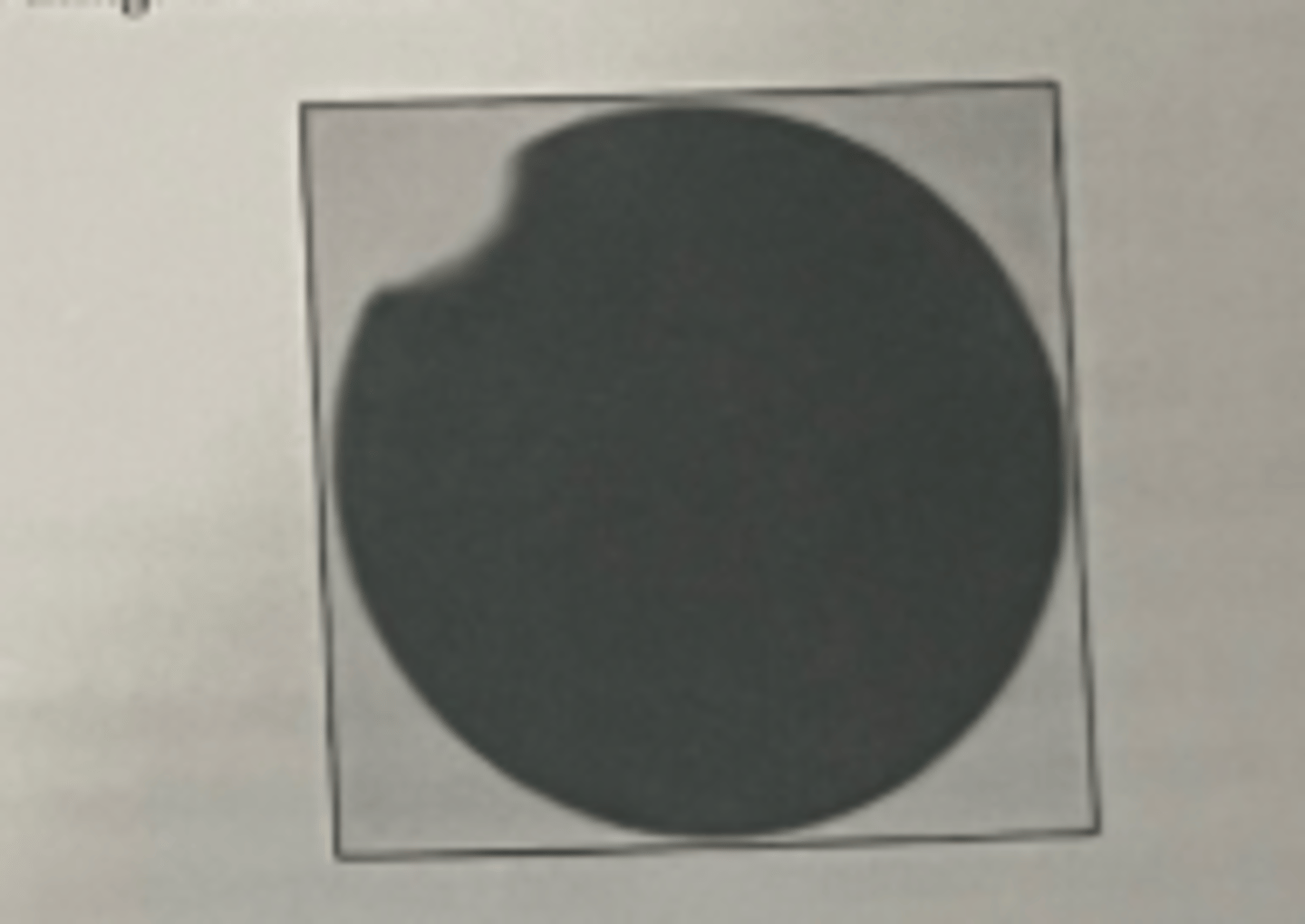
90. To repair the non-uniformity demonstrated on the intrinsic uniformity image shown here, the service engineer will need to:
a. Replace the crystal.
b. Redo reference map calibration.
c. Repair the collimator.
d. Replace a photomultiplier tube.
e. Replace the x,y localization board.
d. Replace a photomultiplier tube.

91. Which of the following sources is the most appropriate for assessing dose calibrator constancy?
a. ⁵⁷Co
b. ⁶⁰Co
c. ¹³¹I
d. ¹²⁵I
e. ⁹⁹ᵐTc
a. ⁵⁷Co
92. Which of the following statements about the effect of the filter cut-off frequency is true?
a. The lower the cutoff frequency, the smoother the image.
b. The higher the cutoff frequency, the noisier the image.
c. Adjusting the cutoff frequency will not affect image appearance.
d. The cutoff frequency cannot be adjusted after the image has been acquired.
e. The lower the cutoff frequency, the noisier the image.
e. The lower the cutoff frequency, the noisier the image.
93. Temporal resolution is related to which of the following acquisition parameters?
a. percentage energy window
b. matrix size
c. framing rate
d. collimator
e. crystal size
c. framing rate
94. It would be appropriate to apply temporal smoothing in which of the following studies?
a. gated-equilibrium cardiac function study
b. SPECT study of the brain
c. SPECT study of the liver
d. thyroid image
e. whole-body bone image
a. gated-equilibrium cardiac function study
95. If an image is acquired into a 128 × 128 matrix on a scintillation camera with a 350 mm diameter field of view, what are the dimensions of each pixel?
a. 2.73 × 2.73 mm
b. 3.14 × 3.14 mm
c. 592 × 592 mm
d. 6.51 × 6.51 mm
e. 7.83 × 7.83 mm
a. 2.73 × 2.73 mm
96. Which of the following instruments should be used to determine whether all removable contamination has been eliminated?
a. Geiger-Mueller counter
b. well counter
c. dose calibrator
d. uptake probe
e. cutie pie (ionization chamber)
b. well counter
97. Which of the following matrix sizes and acquisition modes would be most appropriate for a blood flow study of the feet?
a. 64 × 64 word
b. 64 × 64 byte
c. 256 × 256 byte
d. 256 × 256 word
e. 512 × 512 byte
b. 64 × 64 byte
98. A daily uniformity flood for a scintillation camera should contain a minimum of how many counts?
a. 10,000
b. 1-2 million
c. 3-5 million
d. 6-10 million
e. 20-30 million
c. 3-5 million
99. As a pinhole collimator is moved farther away from the thyroid, how will it affect the image?
a. The gland will appear larger.
b. The image will be flipped.
c. The gland will appear smaller.
d. There is no change in size or orientation.
e. Right and left are reversed.
c. The gland will appear smaller.
100. During geometric variation testing of a dose calibrator, activity in a 1 mL syringe measures 253 µCi when the expected reading is 212 µCi. Which of the following correction factors should be applied to the measured reading?
a. 2.33
b. 4.1
c. 1.19
d. 0.84
e. 0.51
d. 0.84