NSC 3361 Exam 1
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
211 Terms
Neuroscience
Study of the nervous system: including the brain, spinal cord, and associated (cranial & spinal) nerves.
deals with the structure and function of the brain, spinal cord, and associated nerves at the molecular, cellular, and system levels
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
temporal lobe
An area on each hemisphere of the cerebral cortex near the temples that is the primary receiving area for auditory information, responsible for language, understanding, and memory
parietal lobe
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position. Responsible for perception, arithmetic, and spelling
medula oblongata
regulates heart rhythm, blood flow, breathing rate
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
motor cortex
an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements
sensory cortex
area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
Hippocrates (460-370 BC)
Father of modern medicine; believed thought & emotion resided in the brain
Descartes (1596-1650)
Mechanistic model: connection between mind & the brain. Father of modern philosophy
Consciousness
defined as the awareness of and the ability to
communicate our thoughts, perceptions, memories, and feelings,
can be altered by drugs —a physiological process.
First drawing of the optic nerve and visual system
Ibn-al Haytham 1027
Phrenology (Franz Gall)
the detailed study of the shape and size of the cranium as a supposed indication of character and mental abilities.
Phineas Gage Case Study
1848, accident -metal piece of iron entered his left cheek, pierced the base of his skull, went through the front of his brain. Damage to his LEFT FRONTAL LOBE provided evidence that the brain affects personality and social behaviors. This study showed that the frontal lobe has a specific function and that many behaviors are localized to this area.
Santiago Ramon y Cajal
first stained neurons in the brain
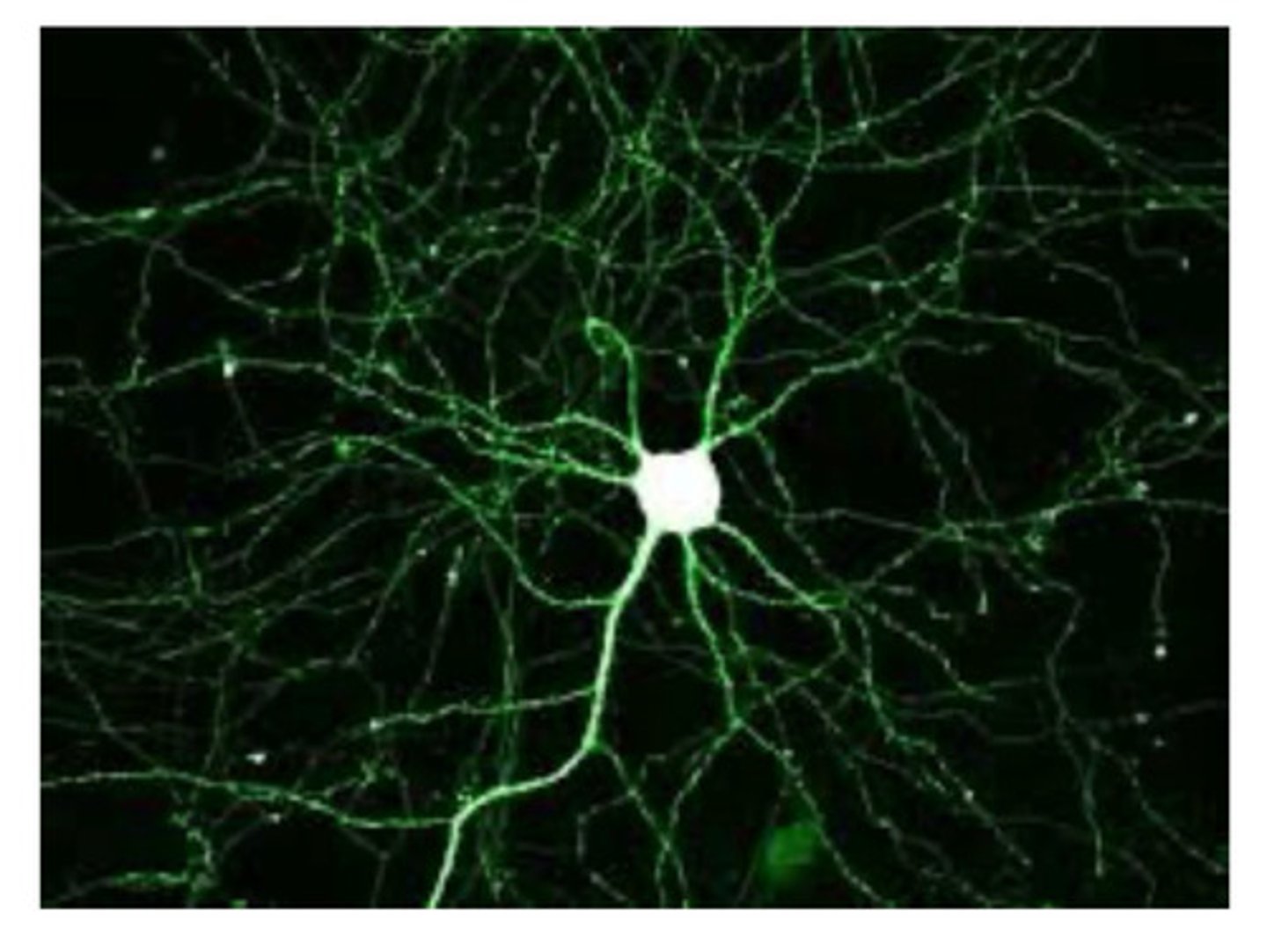
Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)
Fluorescent protein, used to visualize neurons
Patient HM
Developed seizures as the result of a bicycle accident when he was young. Removed hippocampi as a result HM was unable to form new memories. Temporal lobe lesion
Systematic devisions of neuroscience
Molecular, cellular, systems, cognitive, and behavioral
molecular neuroscience
looks at how molecules function within the
neuron and how they enable neurons to communicate with each other
cellular neuroscience
looks at how the neuron itself functions within the nervous system
systems neuroscience
looks at the complex circuits that are formed from a particular set of neurons that serve to perform a common function (for example, vision, auditory, voluntary movement, sensory)
cognitive neuroscience
(cognition; the process by which we come to know) looks at higher order mental processes (thoughts) such as perception and the processing of information related to language, emotion, memory, attention, decision making and consciousness. That is, how the brain (especially the association cortices) processes sensory input to the primary cortices and the behavior that is generated (combining neuroscience and psychology)
behavioral neuroscience
looks at how neural systems work together to produce integrated behaviors
Alzheimer's disease
a PROGRESSIVE and irreversible DEGENERATIVE brain disorder characterized by gradual deterioration of memory, reasoning, language, and, finally, physical functioning. DEMENTIA—>FATAL
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
IMPAIRED: a condition beginning in EARLY CHILDHOOD in which a person shows persistent COMMUNICATION & SOCIAL DEFICITS as well as (RR) RESTRICTED & REPETITIVE BEHAVIORS
cerebral palsy
A MOTOR disorder caused by DAMAGE to the CEREBRUM (before, during, or soon after birth)
Depression
SEVERE disorder of mood, marked by INSOMNIA, LOSS OF APPETITE, feelings of DEJECTION. TMS and deep brain stimulation being used. Meds treat but do not cure.
Stroke
A loss of brain function caused by a disruption of the blood supply. Brain tissue, no O2 for about 20 min neurons will die. CAN LEAD TO PERMANENT sensory, cognitive, or motor deficits.
Epilepsy
Out of control sparks of Action Potential. Seizures, loss of consciousness, and sensory disturbances.
Parkinson's disease
PROGRESSIVE: difficulty initiating movement. PILL-ROLLING TREMOR
multiple sclerosis
myelin sheath destruction. disruptions in nerve impulse conduction. PROGRESSIVE and autoimmune. Weakness, LACK OF COORDINATION & SPEECH DISTURBANCE
Schizophrenia
Positive symptoms (delusion, hallucinations) and negative symptoms (apathy). Severe psychotic illness.
Spinal paralysis
a loss of feeling and movement caused by traumatic DAMAGE TO THE SPINAL CORD
Epigenetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
Neuroplasticity
The brain's neural networks reorganize and grow
New neural connections and pathways are created
The brain adapts to new experiences and learnings
The nervous system
The nervous system is composed of billions of specialized cells and numerous nerves, capable of generating and transmitting information within
the brain as well as between the brain and the rest if the body
neurite
A thin tube extending from a neuronal cell body; the two types are axons and dendrites.
Neurons
a nerve cell; the basic building block/functional units of the nervous system
What 2 major problems impeded the progress of neuroscience
1. Small size of neurons (.01-.05mm)—>compound microscope
2. the ability to view nervous tissue under the microscope —>Fixation and Stains
What 2 stains helped see neuron architecture
1. Golgi
2. Nissl
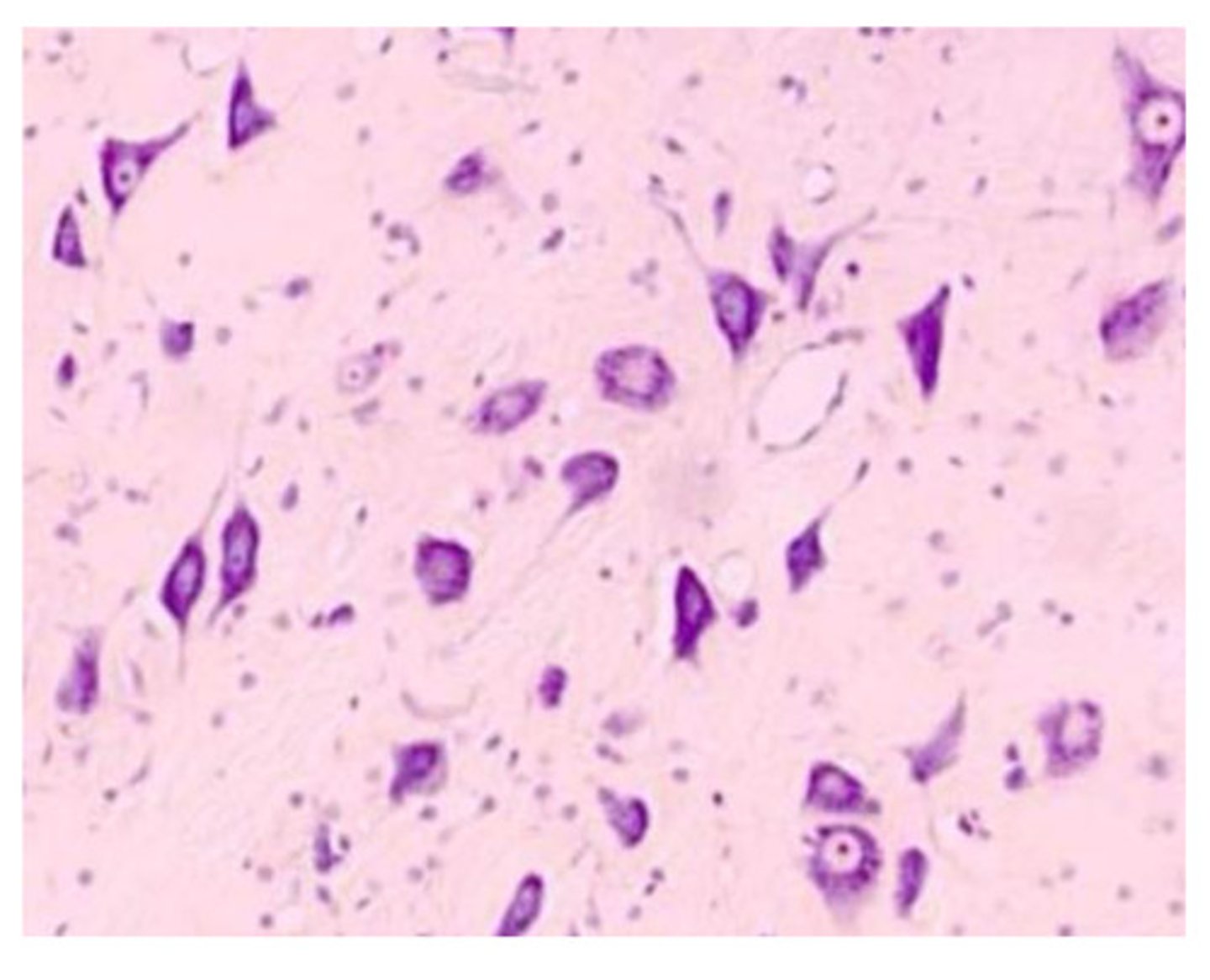
Nissl Stain
-appears purple
-Stains nucleic acids (RNA, DNA) and nissel bodies. -Good for distinguishing neurons from glial cells
Golgi stain
-stains only a few neurons (gold in color)
-stains the entire cell as well as dendrites
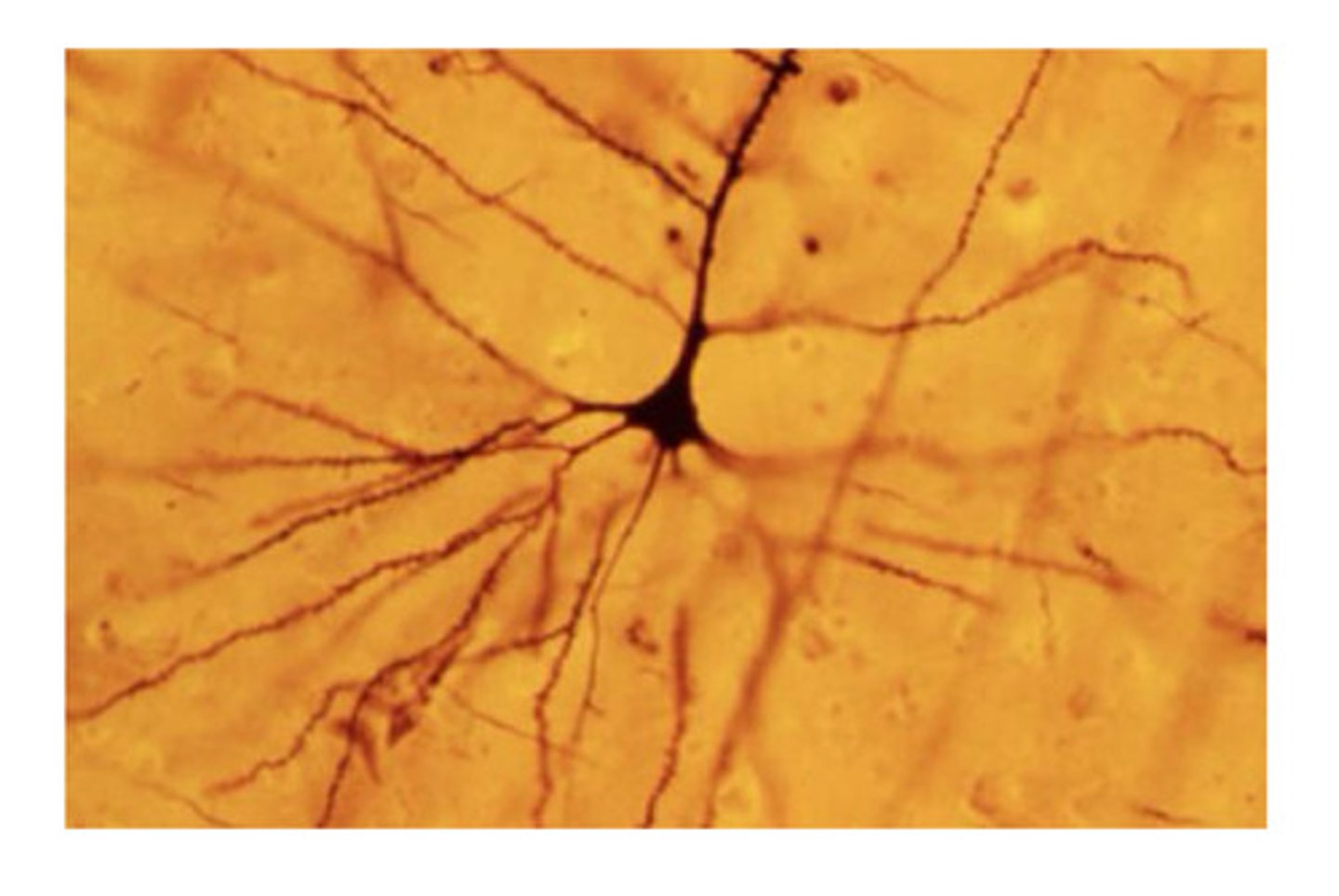
Reticular Theory (Golgi)
Neurons are a part of a continuous, interconnected network. The problem is this theory ignored the synaptic space.
Neuron Doctrine (Ramon y Cajal)
Neurons are discrete, individual cells, signals are transmitted from cell to cell across gaps. The brain is composed of independent cells
Soma
cell body of a neuron
Axon
conducts impulses away from the cell body
Dendrites
Receive synaptic input (from other axon terminals)
2 major intracellular compartments
nucleus (nucleolus & DNA) and cytoplasm
Nucleus
A double membrane bound organelle that contains the genetic material (DNA and some RNA), site of transription, contains nuclear pores
Nucleolus function
Cells RIBOSOME factory, produces ribosomes; the cell's protein synthesis machinery, by transcribing ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes and combining them with proteins to form ribosomal subunits within the nucleus
DNA and RNA
Essential nucleic acids that govern storage, transmission, and expression of genetic information. DNA serves as the hereditary blueprint, while RNA translates this information into proteins, enabling cellular function.
Cytoplasm
contains most of the organelles, cytosol (aqueous part of cytoplasm), and some freely soluble proteins. Site of translation.
cell membranes (plasmalemma)
the semipermeable membrane surrounding the cytoplasm of a cell. Hydrophobic. Intracellular and extracellular environments differ. Has protein pumps and pores, protein composition varies.
Bilayer (5 nm thick)
Major organelles of the cell
(1) nucleolus (2) nucleus (3) ribosome (4) vesicle (5) rough endoplasmic reticulum (6) Golgi apparatus (7) cytoskeleton (8) smooth endoplasmic reticulum (9) mitochondria (10) vacuole (11) cytosol (12) lysosome (13) centriole.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
An extensive membranous network in eukaryotic cells, continuous with the outer nuclear membrane and composed of ribosome-studded (rough ER) and ribosome-free (smooth ER) regions.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
Synthesizes lipids and steroid hormones, detoxifies substances, stores and metabolizes calcium ions (Ca2+).
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
MODIFIES PROTEINS. An endomembrane system covered with ribosomes where many proteins for transport are assembled.
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
Necleotide
Building blocks of DNA & RNA. Molecule made up of sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen base
nuclear pores
structures (holes) in the nuclear envelope that allow passage of certain materials between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm
cell vesicle
A membrane bound sac that contains materials involved in transport of the cell.
Golgi apparatus
Site of post-translational modifications. Protein sorting and packaging.
Lowe Syndrome
Dysfunctional Golgi = no packaging. LOW QUALITY vesicles made in the Golgi apparatus.
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell -site of cellular respiration (needs glucose and O2), organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production.
-Takes pyruvic acid and oxygen from the cytosol for the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain (ETC)
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Energy currency of the cell -synthesized from ADP
Transcription vs. Translation
Transcription copies DNA—>mRNA; translation mRNA synthisizes—>proteins.
Transcription
The process of copying segments of DNA into mRNA for protein synthesis. Occurs ONLY in the nucleus.
Translation
The process of synthesizing a protein from an mRNA template. Occurs in the ribosomes (cytoplasm or rER)
Path of a protein in a cell
Nucleus/nucleolus, DNA—>transcription to mRNA—>mRNA exits nuclear pore to cytoplasm, attaches to a ribosome—>translation to protein—>enters rER for modification—> transport vesicles with protein pinched of from rER—>transport vesicles fuse with Golgi and release proteins inside—>Golgi processes, sorts, stores, packages—>vesicles containing finished proteins are pinched off from Golgi—>travel to destination (cell membrane)
Cytoskeleton
Cell "railway"; provides shape and support, facilitates transport of molecules, cell division, and movement of cytoplasm and vesicles within the cell.
cytoskeleton structure
microtubules (largest), neurofilaments (midsize), and microfilaments (smallest)
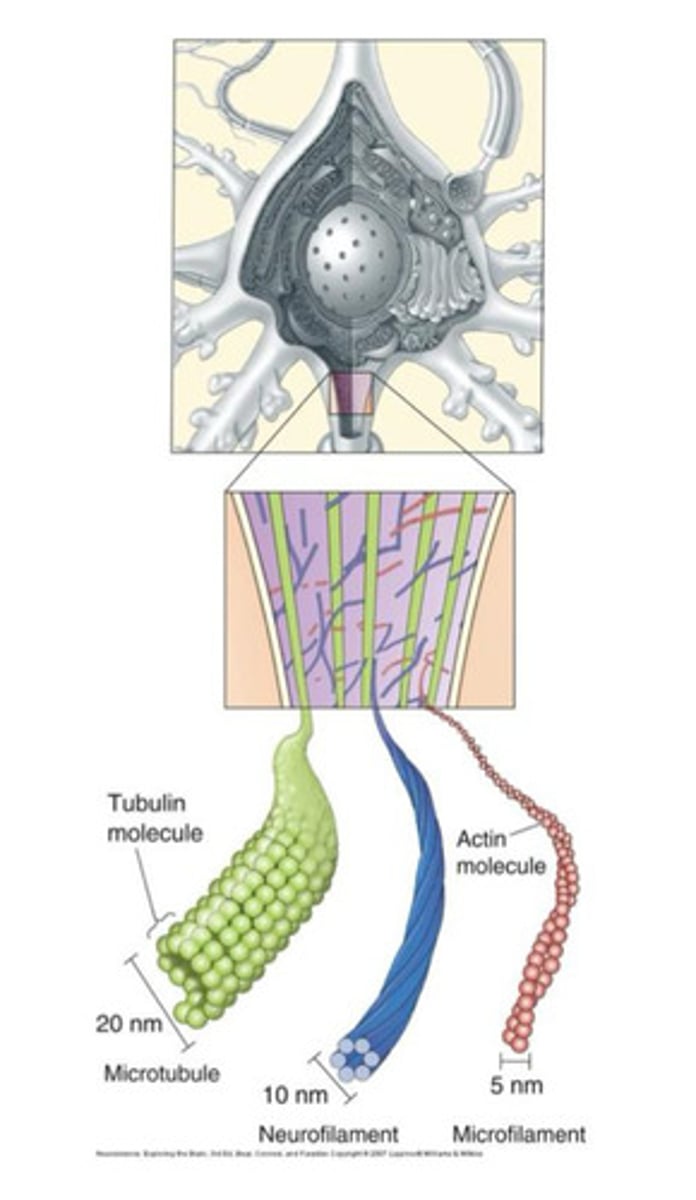
Microtubules
A hollow rod composed of tubulin proteins (20 nm, largest)
Also found in neurites
Axoplasmic transport
Neurofilaments
intermediate filaments found in all cells of the body. Static support structure. Medium diameter (10 nm)
Microfilaments
composed of actin & associated with cell membrane. Smallest (5 nm)
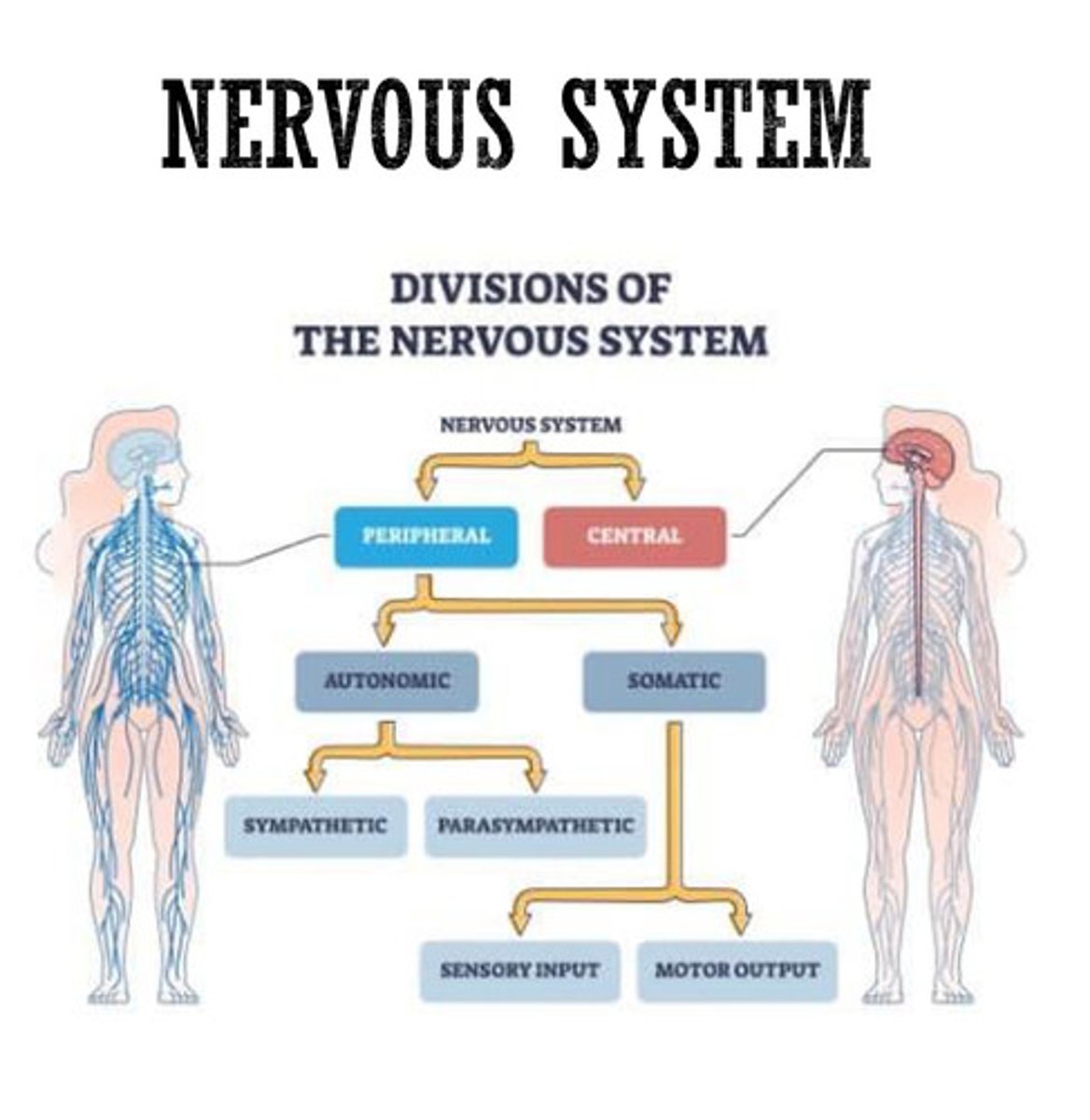
Divisions of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
autonomic and somatic
Autonomic: sympathetic (fight/flight), parasympathetic (rest/digest)
Somatic: sensory input, motor output
autonomic nervous system
sympathetic and parasympathetic
Sypathetic Nervous System
fight or flight: has axons that innervate the sympathetic ganglia (small clusters of neurons outside the CNS)
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest: neurons extend longer distances from the CNS to the parasympathetic ganglia (usually close to the organ they innervate).
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system have _____________ effects on organs due to different ___________.
Different, neurotransmitters
somatic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. Enables voluntary actions to be undertaken due to its control of skeletal muscles; SENSORY input & MOTOR output
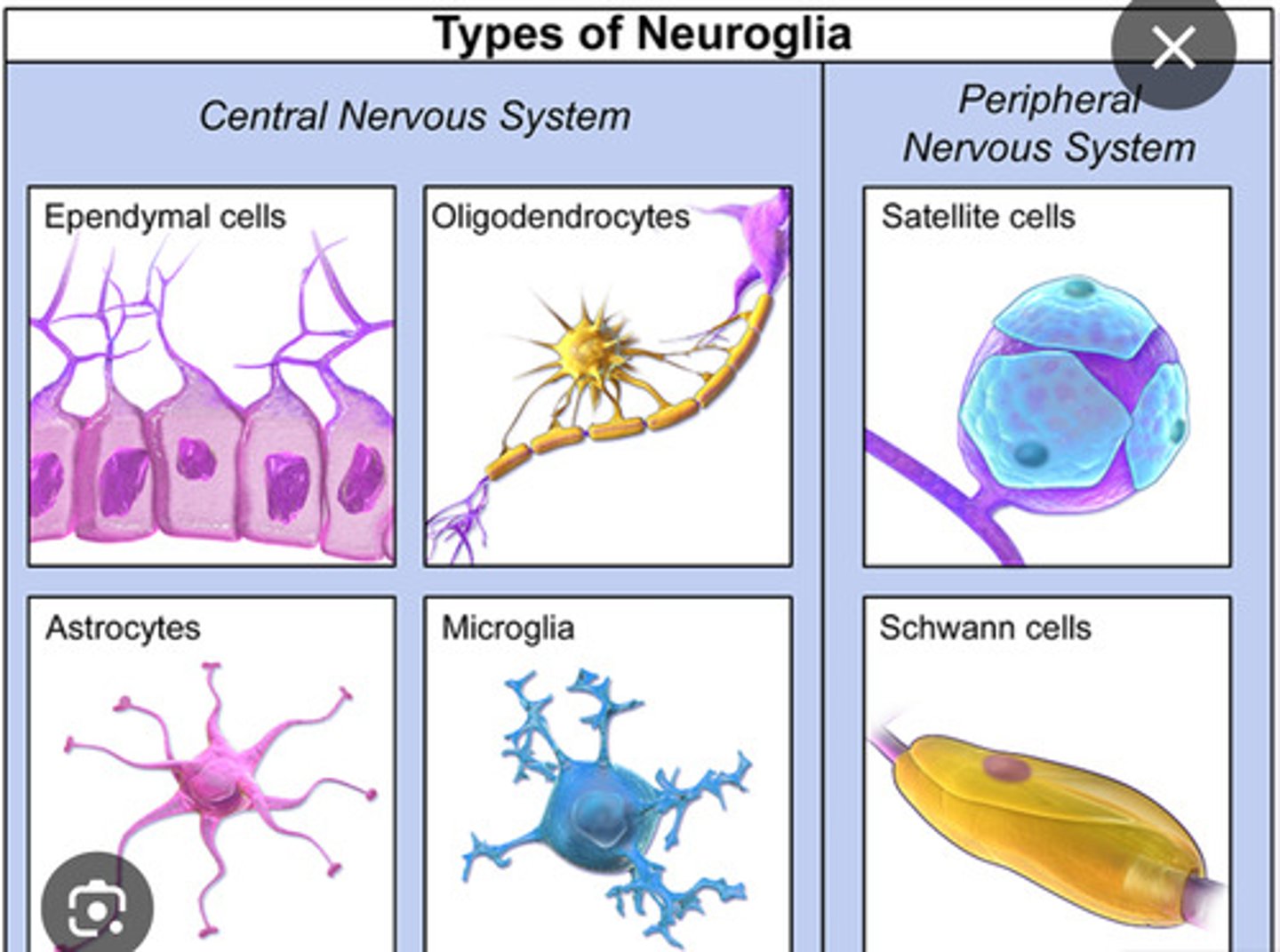
2 types of brain cells
neurons and glia
glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons by providing raw material, chemical signals, and structure, and also participate in information processing
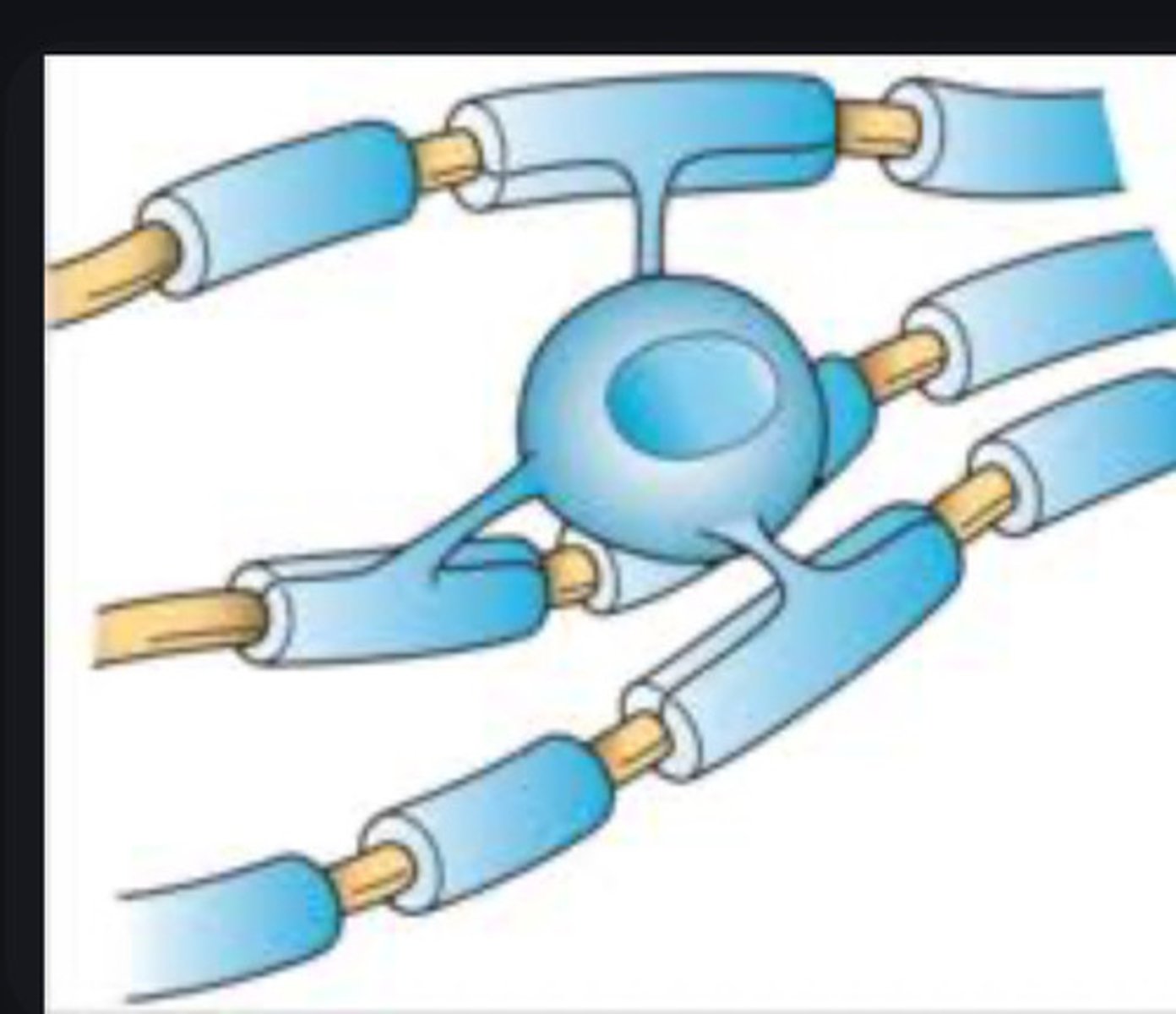
1. Oligodendrocytes
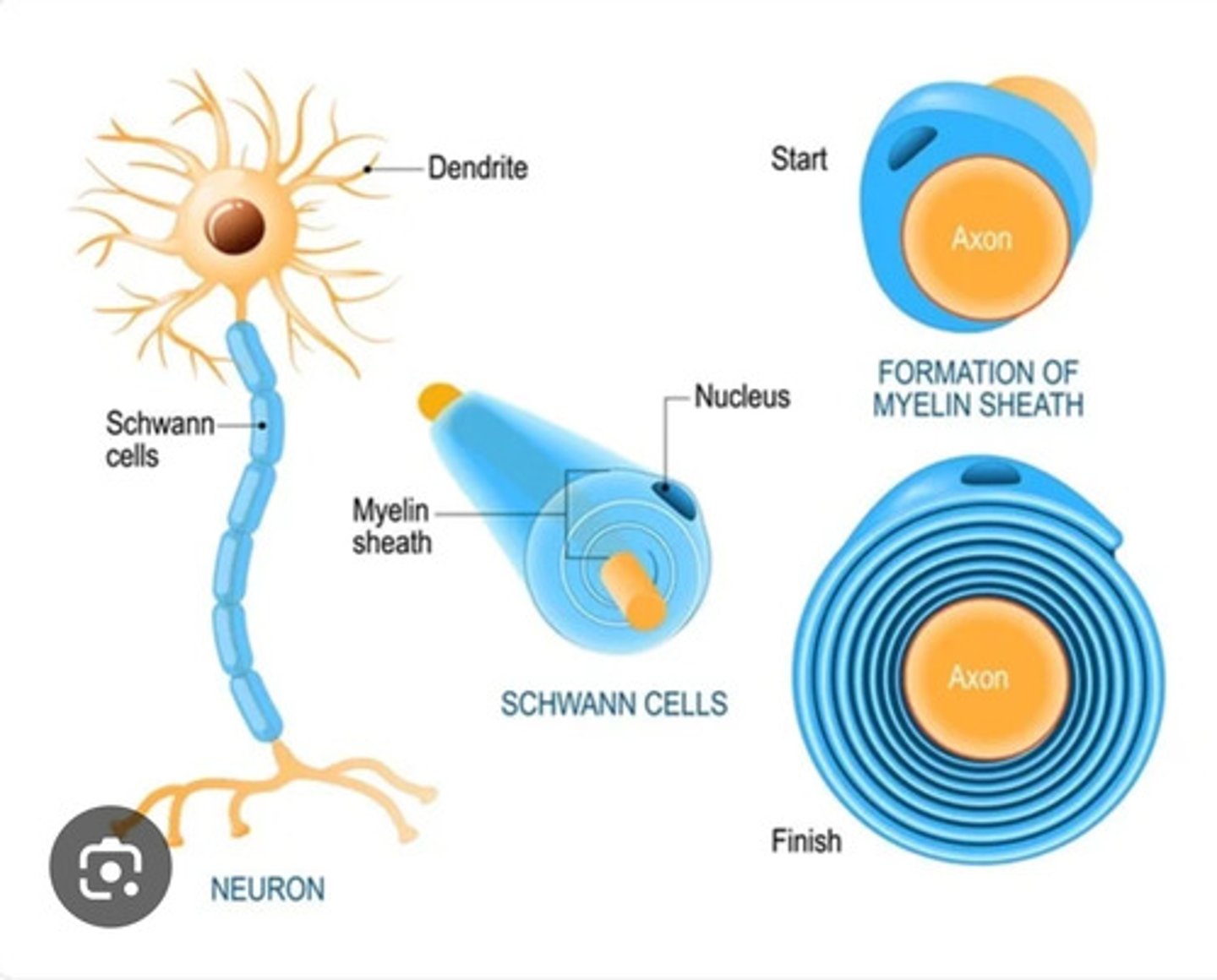
2. Schwann cells
3. Astrocytes
4. Microglial cells
5. Ependymal
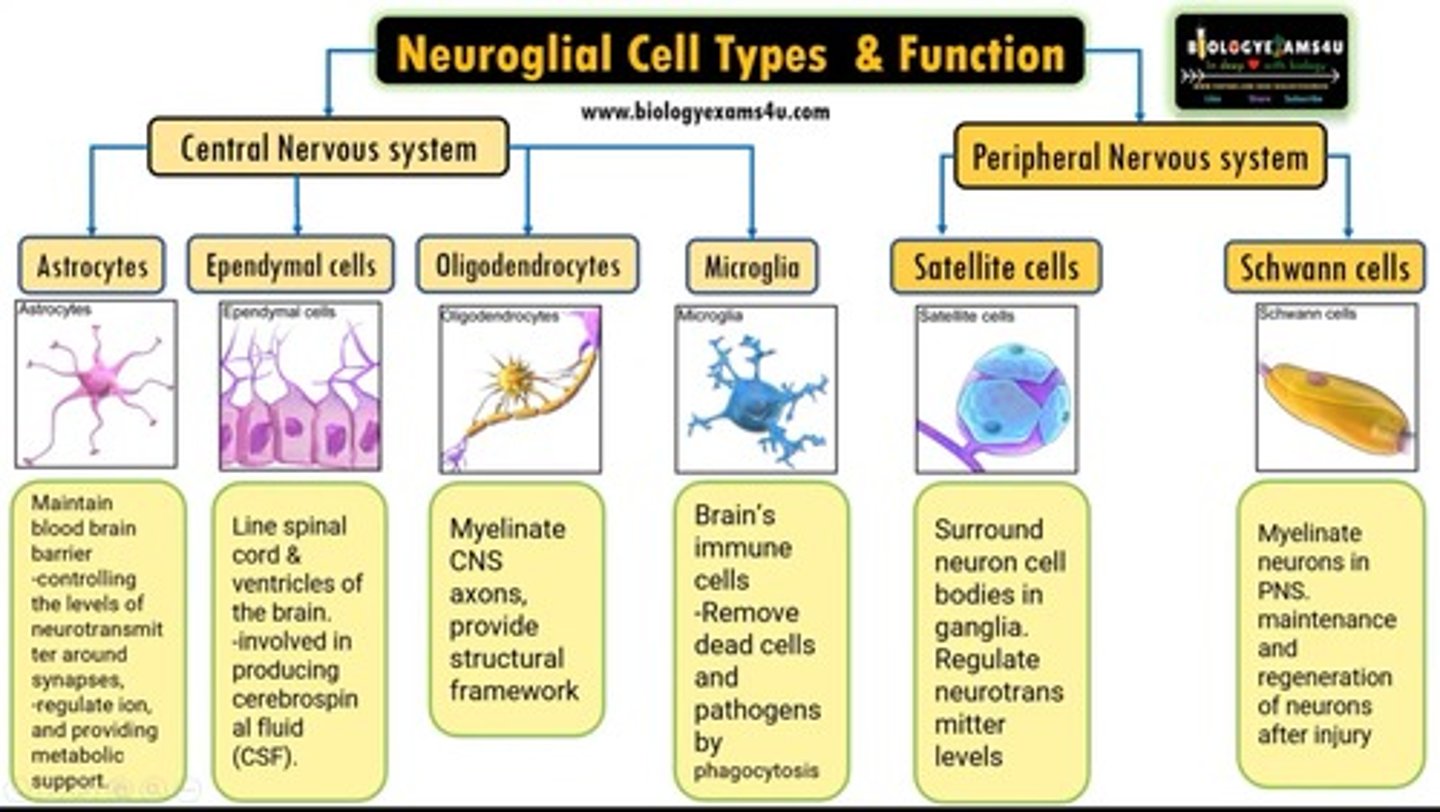
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheaths in the brain and spinal cord. One cell wraps multiple sheaths
Schwann cells (PNS)
Provide myelin insulation to neurons outside the brain and spinal cord, in PNS
Astrocytes
Forms and regulates the blood-brain barrier
Provides neuronal support: allows neuron to get nutrients and oxygen from blood vessels
STAR shaped; stretch around and between neurons and blood vessels, secrete chemicals
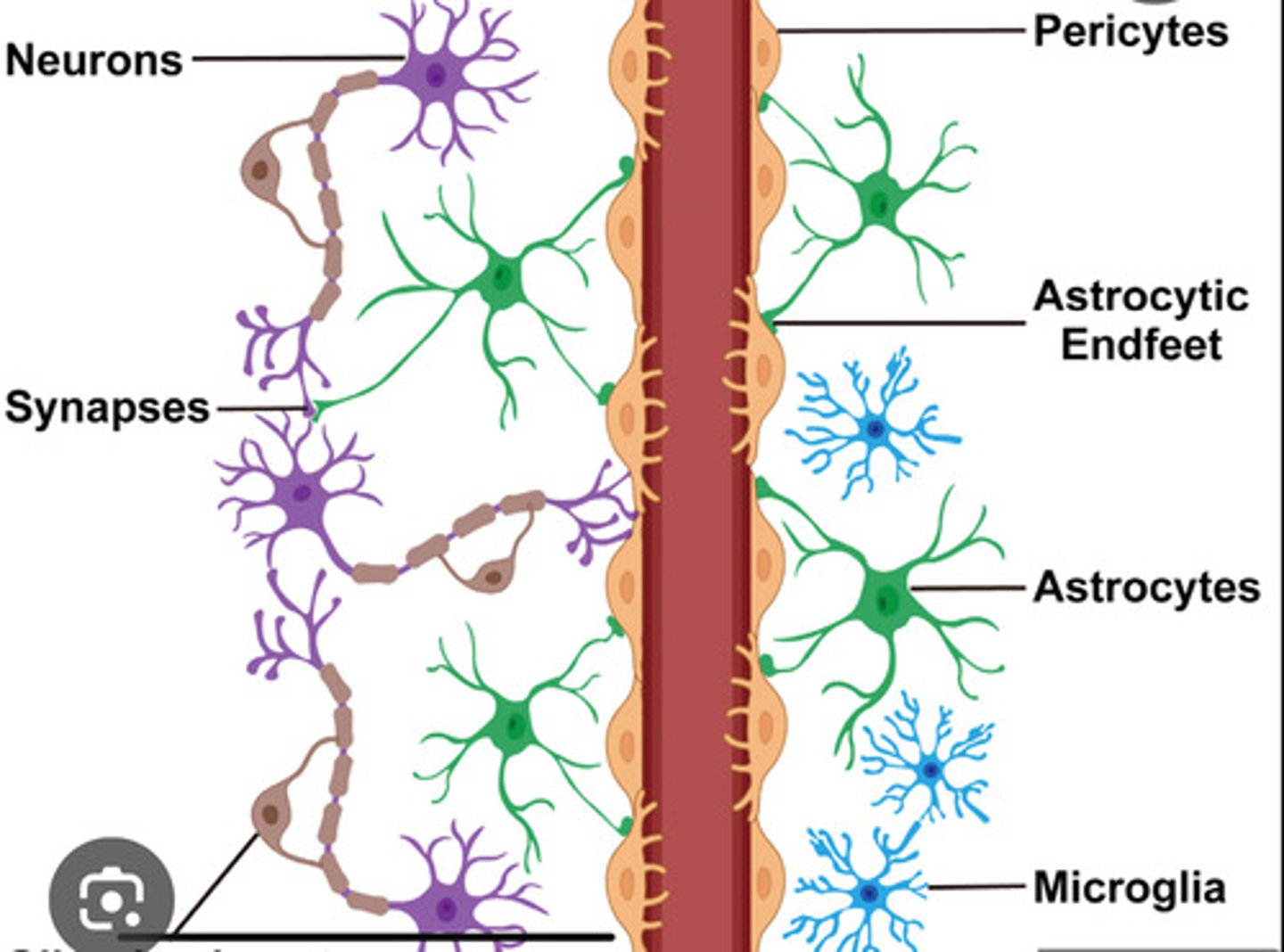
Microglial cells (CNS)
immune function; digest debris, kills bacteria
Tiny and mobile
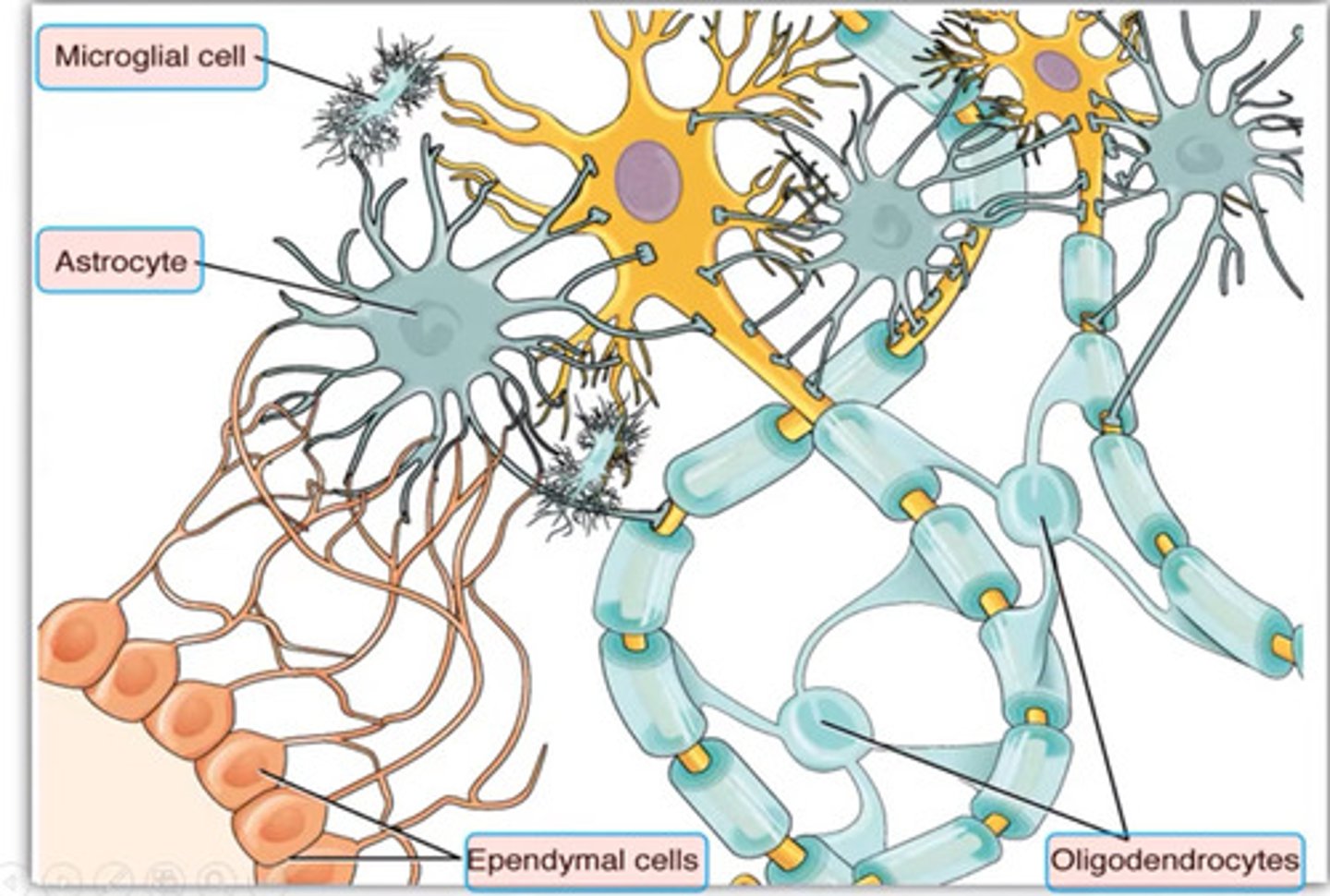
ependymal cells
produce cerebrospinal fluid (glial)
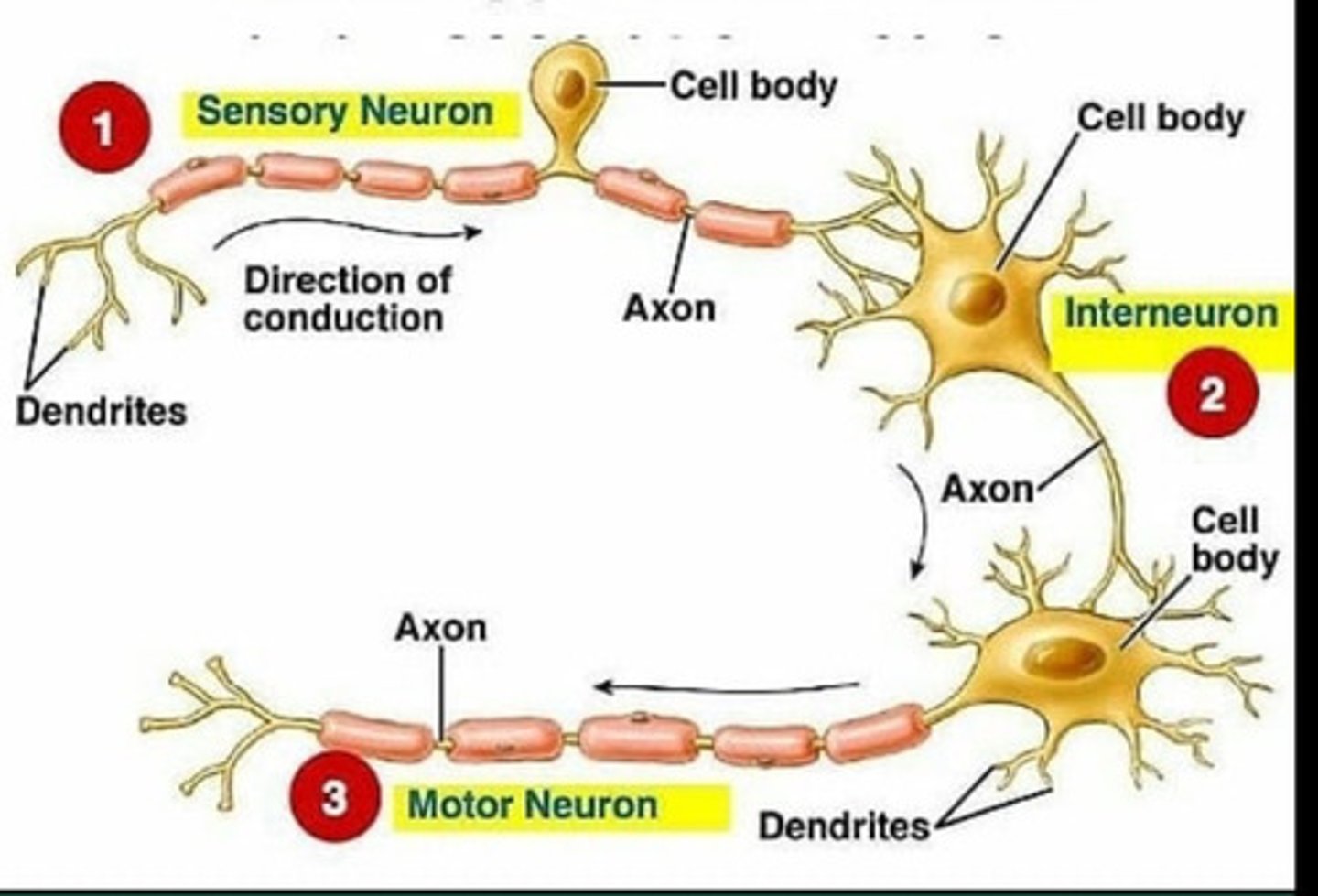
types of neurons
Shape: multipolar, bipolar, unipolar
Function: motor, sensory, interneurons
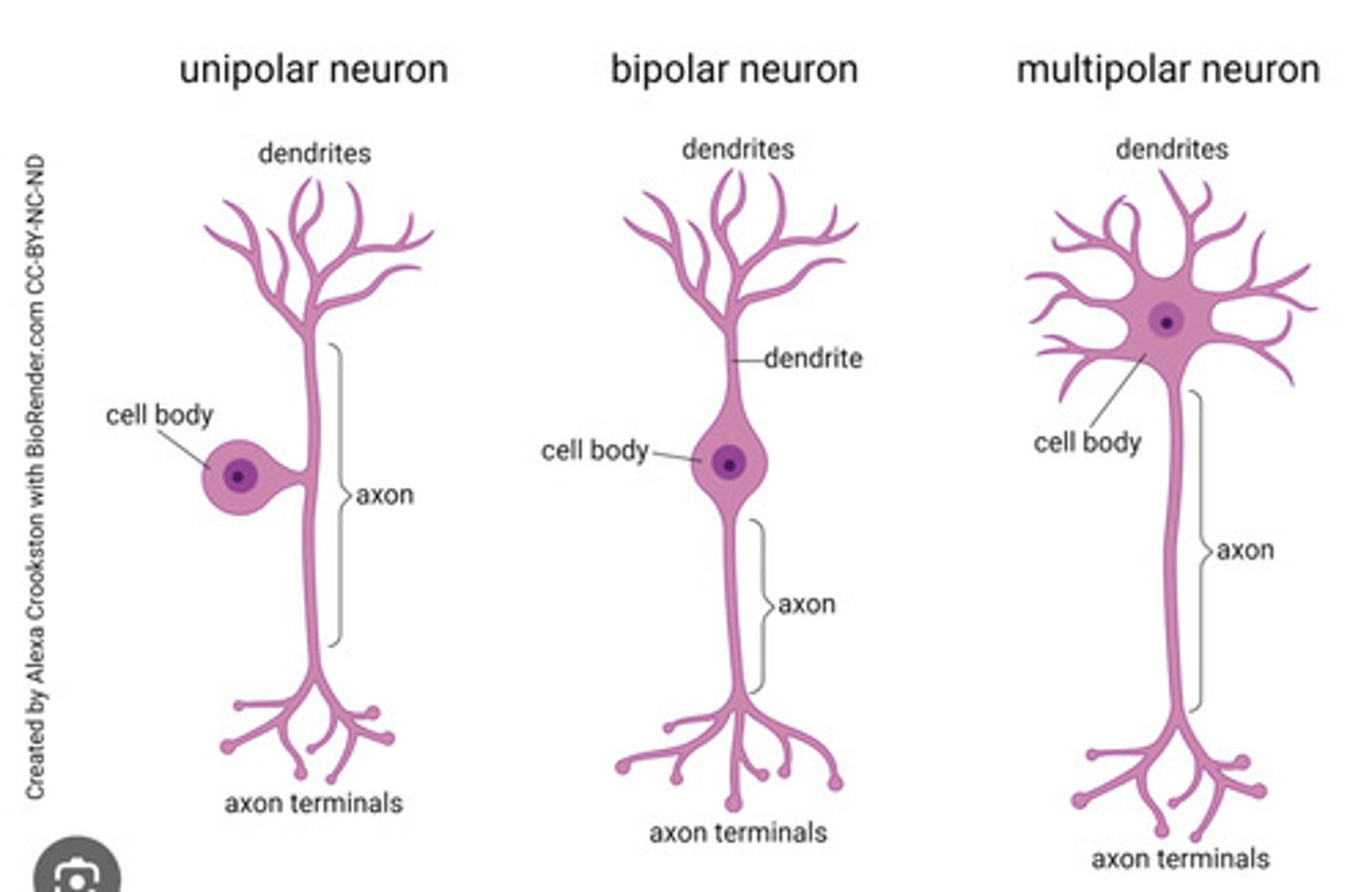
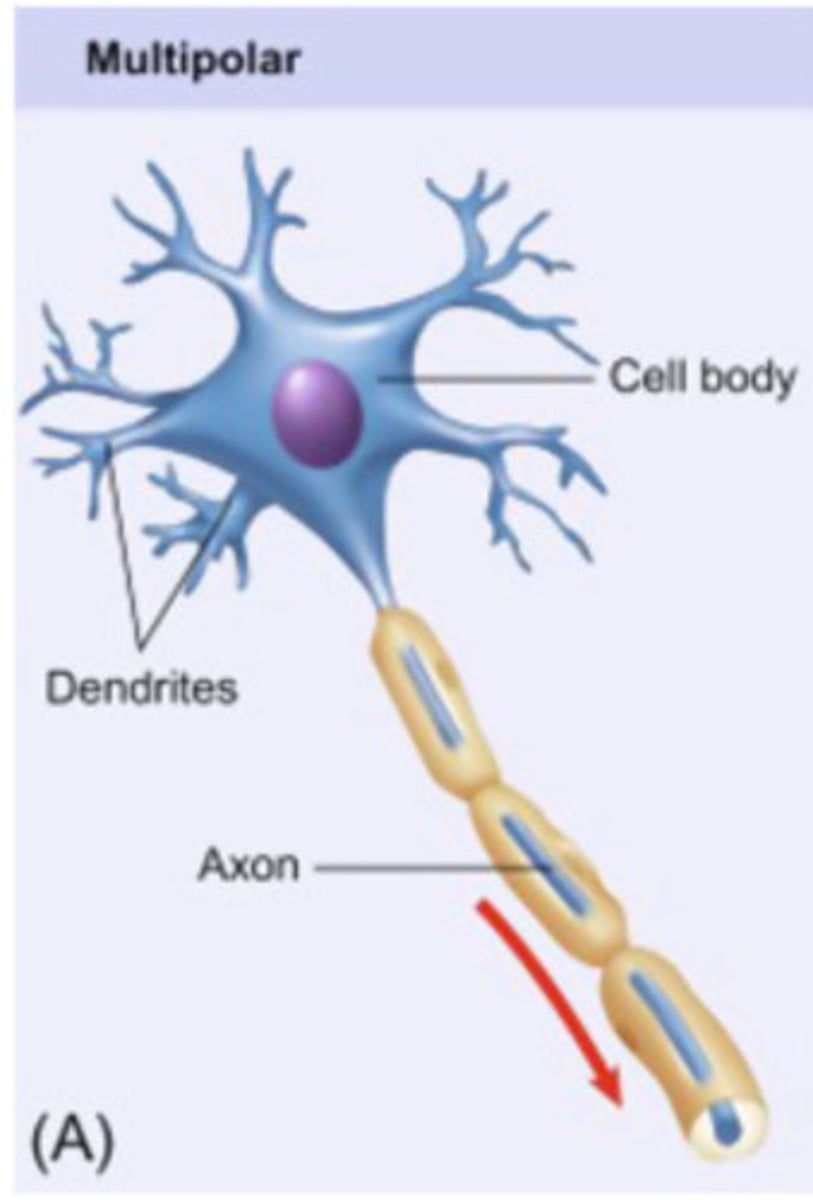
mulipolar neurons
single axon with many dendrites
most common neurons in CNS
examples: spinal motor neurons, pyramidal cells, and Purkinje cells of the cerebellum
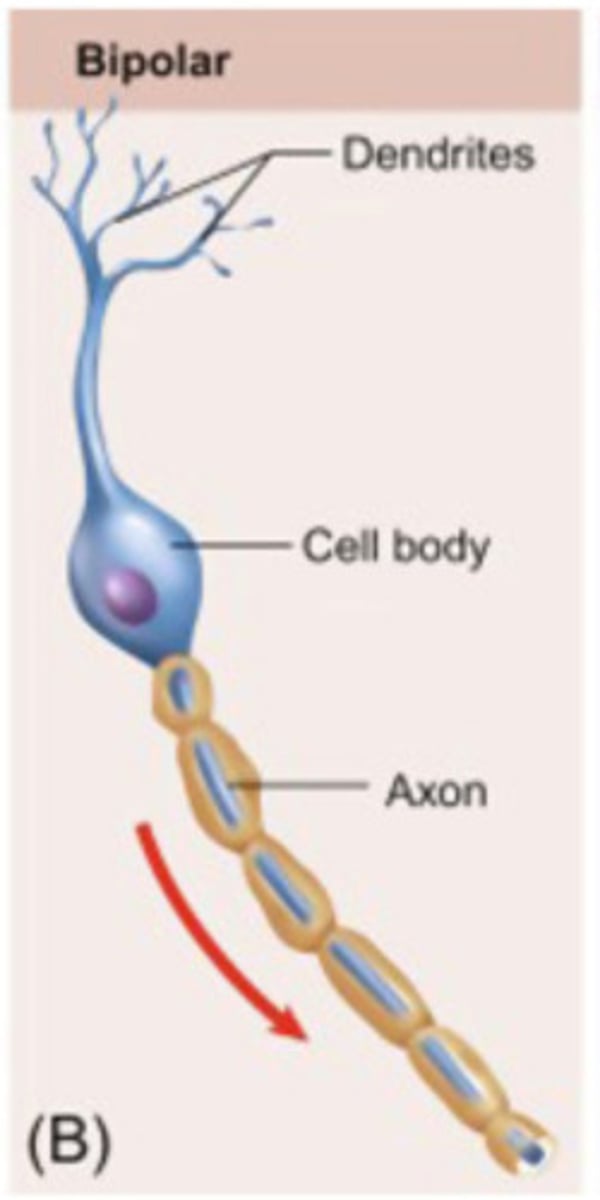
bipolar neurons
One axon and one dendrite; found in retina.
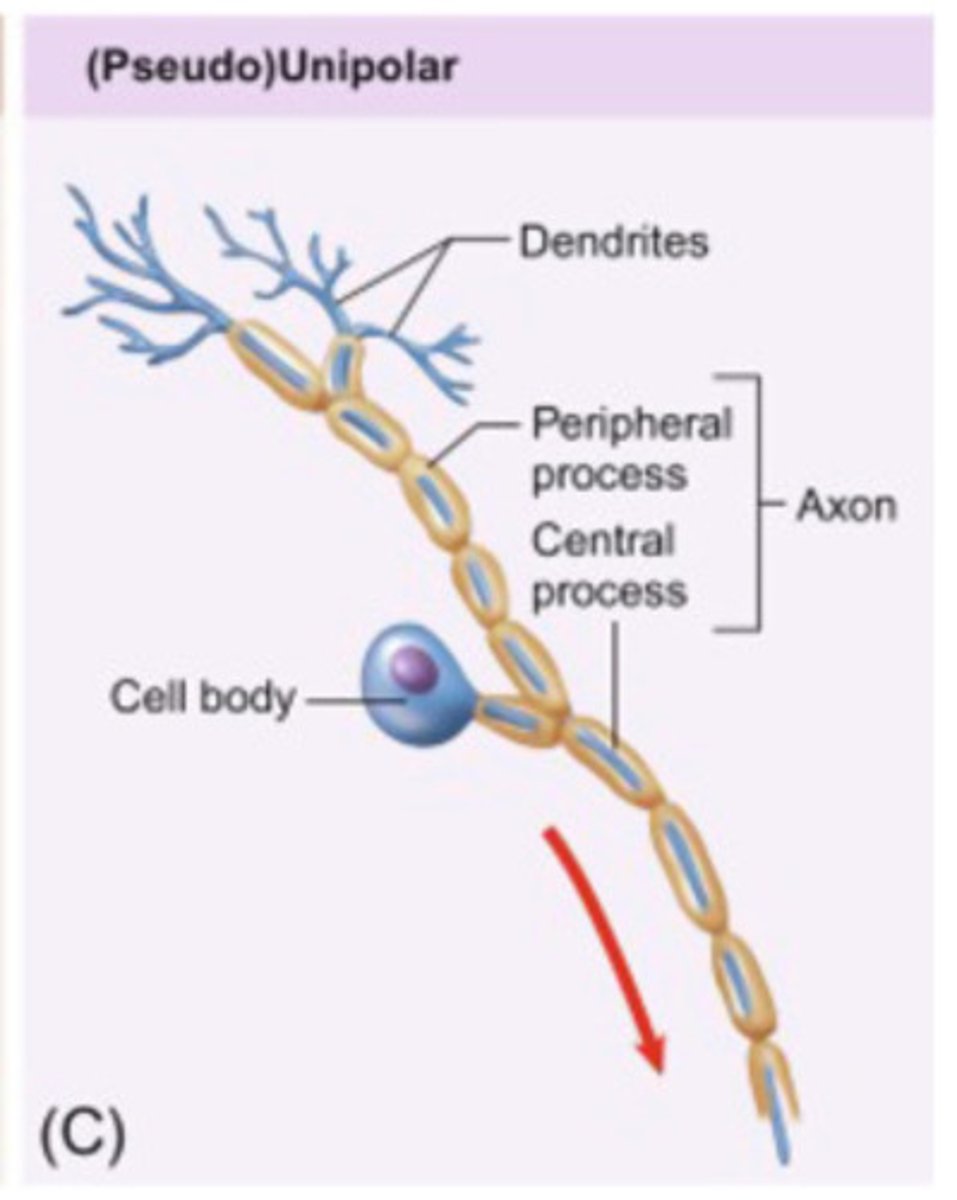
unipolar neuron
a single extension branches in two directions, forming an input zone and an output zone.
Often seen in sensory neurons
blood-brain barrier
protective membrane that prevents toxins and pathogens in blood from reaching the central nervous system. The BBB is made up of endothelial cells, tight junctions, astrocytes, and basement membranes. To pass should be lipophilic (non-polar)
motor neurons (efferent)
[exit] communication sent from brain to the body; stimulates muscles. Large and have long axons. Smooth muscle and skeletal
![<p>[exit] communication sent from brain to the body; stimulates muscles. Large and have long axons. Smooth muscle and skeletal</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9886a337-1064-4cee-903a-11cbd116d64d.jpg)
sensory neurons (afferent)
respond to environmental stimuli, such as light, odor, or touch. Have various shapes. All senses
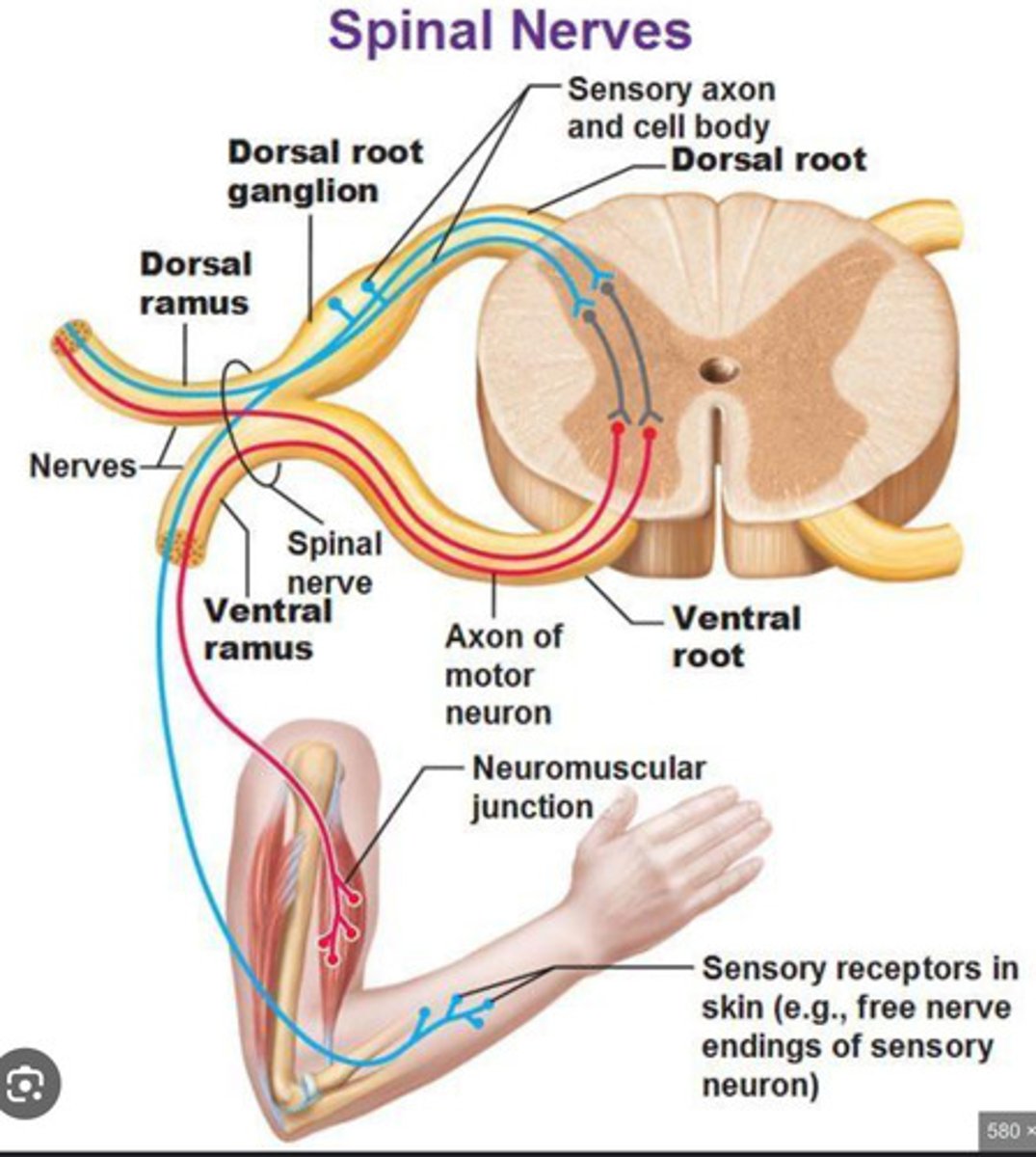
Interneurons
receive/analyze input from one set of neurons and send/communicate with other neurons
pyramidal neurons
cerebral cortex
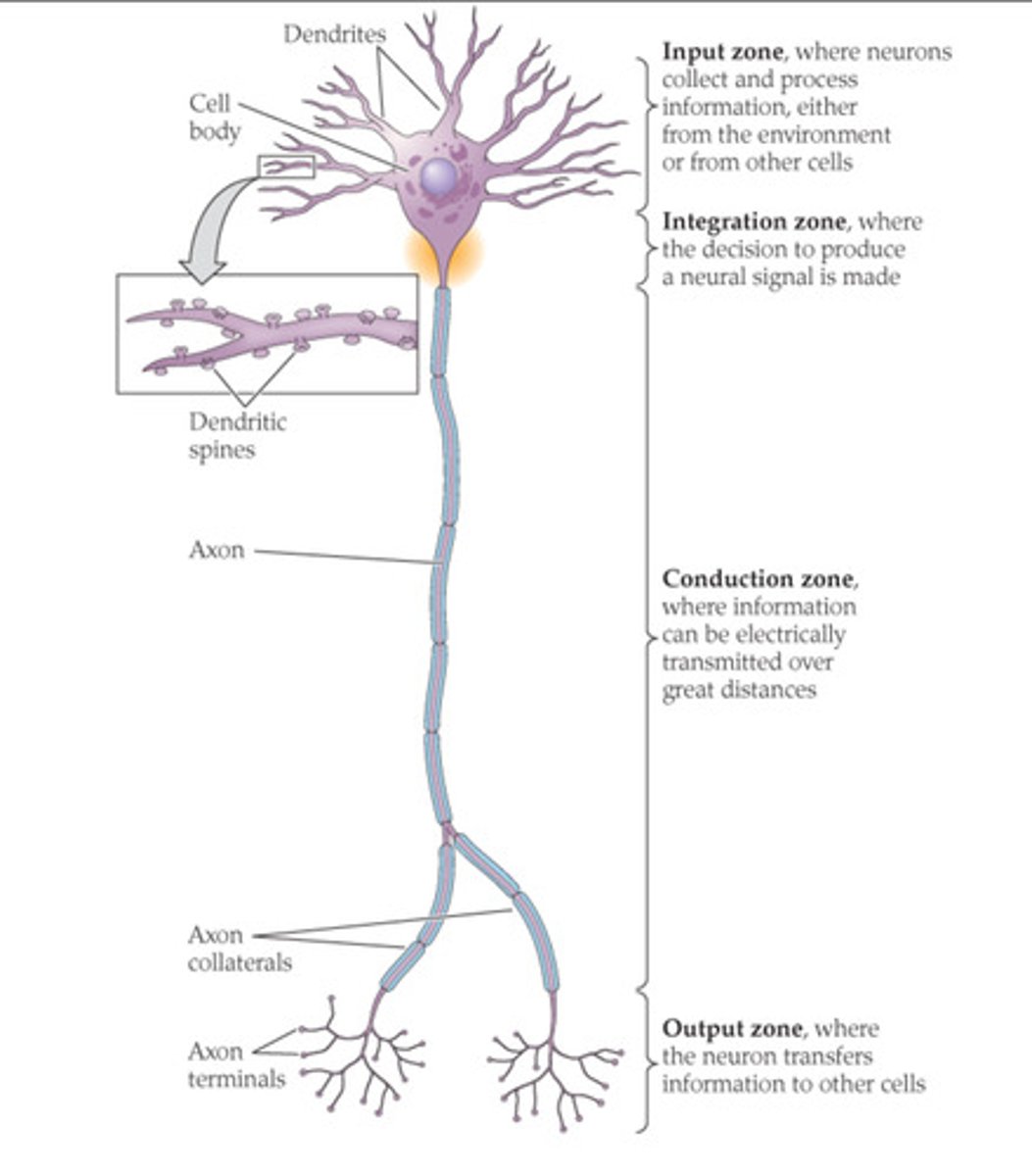
Functional zones of a neuron
Input zone: dendrites- receives signals
Integration zone: cell body (soma)
Conduction zone: axon - carries electrical signals
Output zone: axon terminals
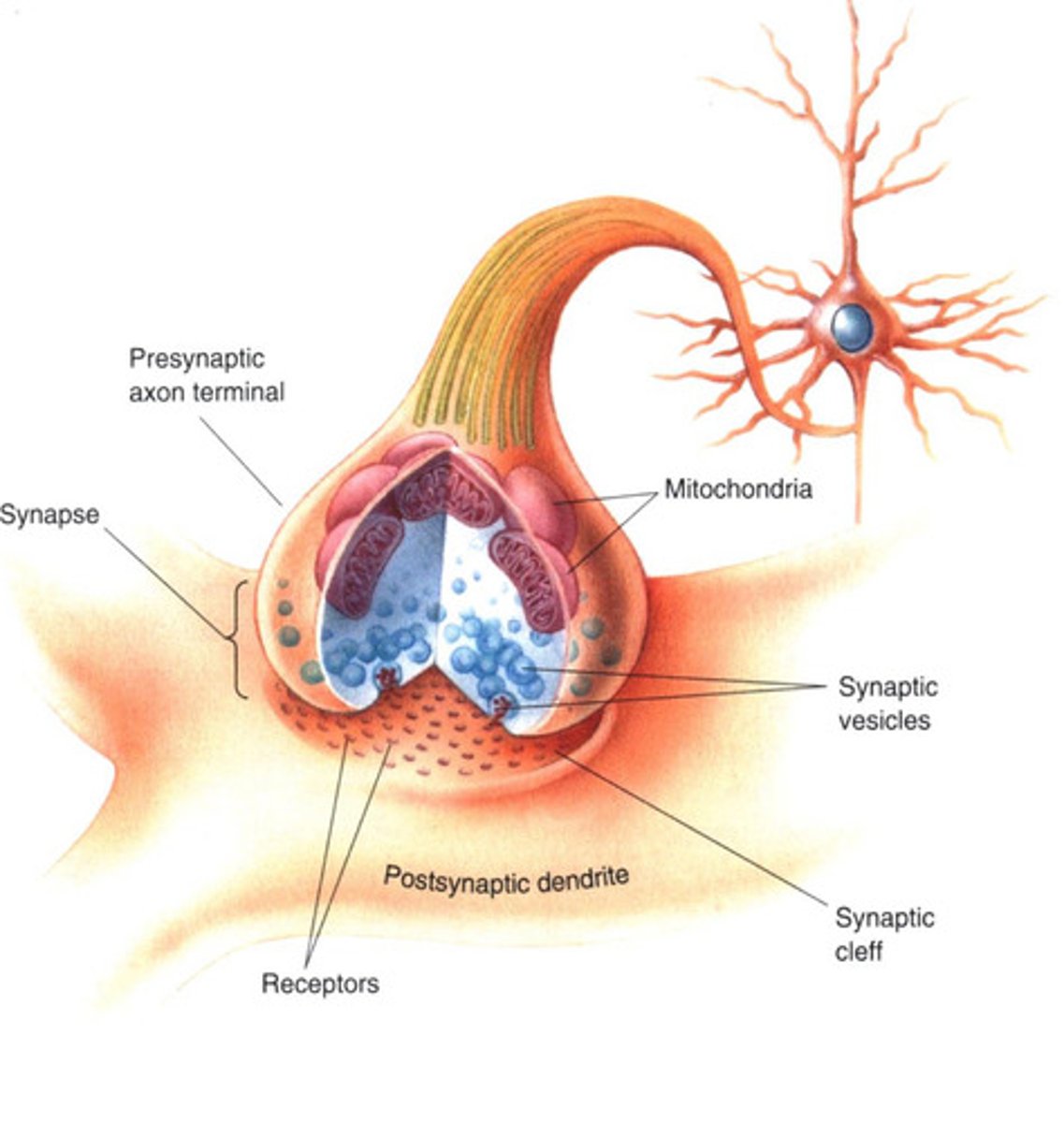
input zone of neuron
receives information from other cells through dendrites