Cold War
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Expansionism
a policy of expansion, especially territorial, by a nation.
Containment
the attempt to thwart another country’s expansionism through means other than direct warfare; eg) Truman Doctrine.
Brinkmanship
the practice of pushing a situation or confrontation to the limit of safety especially to force a desired outcome.
Iron Curtain
a political, military, and ideological barrier that cuts off and isolates an area; in context, one isolating an area under Soviet control.
Espionage
spying to obtain information about the plans and activities of a foreign government or operation.
cold war: distrust between us and USSR caused espionage (ex. great seal of the US had a listening device)
Deterrence
the maintenance of military power for the purpose of discouraging external attack, often nuclear.
Mutually Assured Destruction (MAD)
a doctrine of military strategy and national security in which a full-scale use of nuclear weapons by opposing sides would cause the complete annihilation everyone involved
ICBM
intercontinental Ballistic Missile, is a missile, often nuclear, with a range greater than 5500 km
Non-Proliferation
treaty that stops proliferation (rapid production of specifically nuclear arms);
Détente
the relaxation or easing of strained relations or tensions between nations.
happened after US called back troops in Vietnam war. both russia and us needed to reduce spending
Sphere of Influence
an area under the political influence or interests of one nation that are held to be important.
Proxy War
conflicts where one superpower might fight in another country or provide support to a group which opposes the rival superpower
Kleptocracy
a society or system ruled by people who use their power to steal their country's resources.
Non-Alignment
not allied with other nations; neutral to the Communist and non-Communist blocs.
Cold War (1947 - 1991)
began before WWII ended
US + soviet union were both superpowers and with opposing ideological differences led to hostility and suspicion of each other
Yalta conference
Franklin roosevelt, winston churchill, joseph stalin (US, Britain, USSR) met on Black sea to discuss post WWII europe
made agreements to have USSR enter war against japan after germany was defeated
establish a united nations to replace league of nations
yalta disagreements
stalin wanted polish border moved so soviet territory expanded
fdr and churchill did not support, but couldn’t do anything because ussr had control of area
churchill and fdr agreed to make deal with stalin to allow ussr to keep territory if he did not interfere in the west to put down a communist revolt in greece
how germany was dealt with after war (USSR = weaken economically)
allies believed economic health of Europe depended on vibrant germany so they did not want devastating reparations like treaty of versailles
realpolitik
politics or diplomacy based on practical, rather than ideological or moralistic, premises; “realistic,” but is often used negatively to imply politics that are coercive or amoral.
potsdam conference
meeting between usa, ussr, britain
roosevelt died and truman replaced. clement attlee accompanied churchill
tension between democratic west and communist east emerged
each side wanted to expand spheres of influence
germany divided into zones controlled by britain, france, ussr, usa
all democratic except ussr, and used its area as buffer from the west
Berlin blockade (1948-1949)
one of first international crises of cold war
4 countries occupying germany, soviet union blocked western allies’ railway and road access to berlin. ussr wanted to force western powers to allow soviet zone to start supplying berlin with food and fuel, so they would have control over the city.
allies organized berlin airlift. blockade lifted and resulted in creation of 2 german states.
response to berlin blockade
Allies organized Berlin Airlift where british and american air forces flow 200 000 flights in 1 year to provide 13 000 tons of necessities to people in Berlin. It succeeded and berlin had more deliveries than before via rail. russians were humiliated bc they thought airlifts would fail.
creation of east and west germany
blockade lifted and two seperate german states created.
federal republic of germany (west) was controlled by western allies
german democratic republic (east germany) was to be communist and controlled by the ussr
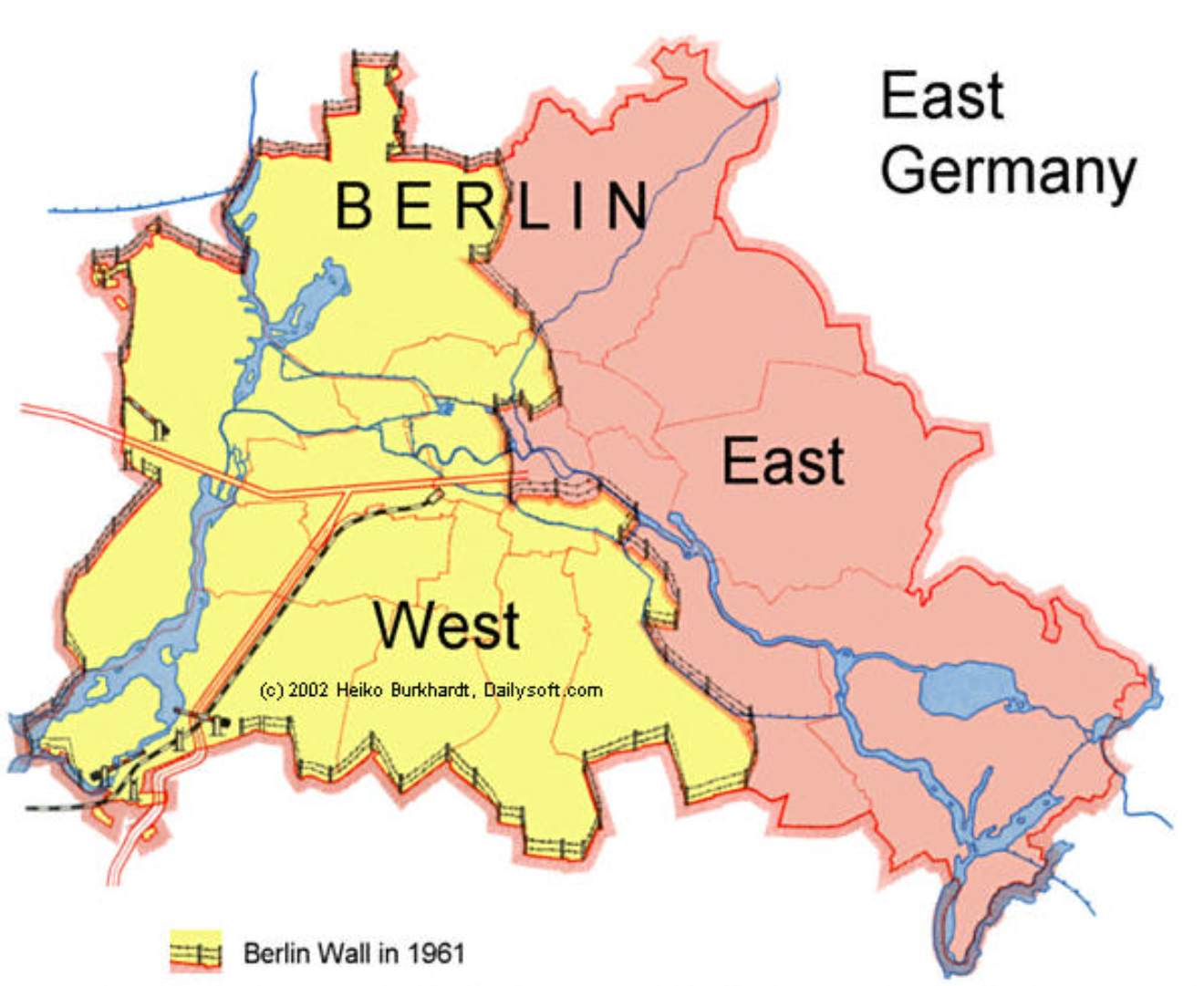
Berlin Wall
after WWII berlin was divided in four sectors. American, British, French sector: western system, Soviet sector: communist system in east
berlin wall constructed around west berlin, protected by NATO to keep berlin citizens from crossing border between east and west berlin. truman believed domino theory so he created truman doctrine. marshall plan followed (USSR had something similar, Moltov plan)
Truman Doctrine
introduced idea that if US let one country fall to communism, all neighboring countries would follow (domino theory). truman said cold war was a choice between freedom and oppression, and the US was obliged to get involved.
“I believe that it must be the policy of the United States to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressures.”
Marshall Plan
direct result of truman doctrine. $13 billion to provide aid money to countries in europe devastated by the war regardless if communist or democratic
economic reforms that embraced capitalism and sought to defeat appeal of communism
space race
superpowers sought to get upper hand politically, geographically and militarily and wanted dominance in outer space. soviet union was successful early on: first nation to put satellite in space, launch a man into orbit, put a woman in space, land unmanned spaceship on moon
dissident
disagreeing especially with an established religious or political system, organization, or belief
First red scare
as WWI ended, there was a rise in labour tensions and domestic unrest with soldiers returning to workforce.
american gov saw threat of communist revolution in the actions of organized labour and wanted to suppress this radicalism.
palmer raids → mitchell palmer (US attorney general)launched a series of illegal searches, arrests, and deportations of supposed Communists
cold war tensions
relationship between US and USSR deteriorated as WWII concluded because of ideological differences on economics and political spheres of influence
Berlin Blockade, successful rise of communism in china, soviet acquisition of the atomic bomb, korean war: heightened tensions between east and west
Joseph McCarthy
McCarthy began investigations and hearings to expose supposed communist infiltration of various areas of US government
Senator Joseph McCarthy led a campaign to root out communists in the US government and society through aggressive investigations and accusations. (second red scare) People feared him, even the president, because he had a radically supportive mob that would believe whatever he said. (1954) The Senate voted to formally denounce McCarthy, and his influence would continuously weaken from there. “We will not walk in fear.”
House Un American Activities Committee (1938 - 1975)
used subpoena power and called citizens to testify in high profile hearings before congress
intimidating atmosphere produced dramatic but questionable revelations about communists infiltrating American institutions and subversive actions by well known citizens
HUAC contreversial tactics contributed to fear, distrust and repression during anticommunist hysteria
late 1950s, HUAC influenced declined and dispanded in 1975
domino theory
if one nation becomes Communist-controlled the neighboring nations will also become Communist-controlled
hollywood ten
10 members of hollywood industry denounced HUAC tactics and they received jail sentences and were banned from working for major hollywood studios.
Edward R Murrow
co-produced an investigative news program called “See It Now:” in 1954, he produced an expose on McCarthy’s tactics and falsehoods, helping to turn citizens against McCarthyism.
in 1954, senate voted to censure McCarthy and his influence on public discourse waned.
jim crow laws
Following the 13th amendment to the American constitution, which abolished slavery, racism remained prominent through the Jim Crow laws, which legalized many manners of segregation.
They became prominent in the late 1800s and lasted until the mid 1960s, especially due to the racist power held by Southern politicians.
mccarthyism
movement to uncover and persecute those with perceived ties to communism, and divided americans along ideological and political lines.
NAACP
The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People desired to overturn the laws maintaining segregation in schools.
Matrin Luther King Jr was an executive and lead a demonstration to oppose segregation on buses
Little rock nine
The Little Rock Nine were a group of nine black students meant to attend a previously all-white school in Little Rock, but faced resistance from white residents in Arkansas.
The National Guard was called to prevent violence, turning the nine students away, but the students were eventually allowed in with President Eisenhower’s use of the Guard in classrooms.
Montgomery Bus Boycott
(1950s) NAACP were involved in desegregating public transit, which in the early 50s was enforced by the Supreme Court, but southern states would continue segregation anyway.
(1955) Rosa Parks was arrested after refusing to give her bus seat to a white man in Alabama.
Martin Luther King Jr. organized protests against transit segregation with civil rights activists, resulting in a year-long “bus boycott,” leading to the Supreme Court declaring transit segregation unconstitutional.
March on Washington
(1963) The March on Washington was a political rally moving from the Washington Monument to the Lincoln Memorial, where King Jr. delivered the famous “I Have A Dream” speech.
Broadcast on television, heavy police personnel were deployed, expecting violence, but the large protest ended peacefully.
Civil Rights Act of 1964
(1964/65) The passing of the Civil Rights Act and Voting Rights Act ensured liberal values supposedly presented in the constitution now applied to all citizens.
(1970) The Supreme Court had declared all forms of segregation unconstitutional and support for legal segregation had largely dissolved to radical and select political groups.
Formal racial discrimination was illegal in schools, on transit, in businesses, the military, civil services and government.
How did the Marshall Plan reinforce the policy of containment?
Marshall Plan was still derived from the Truman Doctrine - any country that accepted aid from the United States was put under pressure to embrace Western economics. They had to undergo an economic assessment and participate in a unified European economy. so soviet satellite states rejected marshall plan because it was incompatible with soviet ideology
What was the Communist response to the Marshall Plan?
The USSR released their own program, dubbed the Molotov Plan, open to East European countries under their influence. This involved bilateral trade agreements which consolidated the economy of many East European countries.
What were the reasons that precipitated the Berlin Blockade in 1948?
Following WWII, Germany was split into a capitalist West and communist East. The USSR viewed the thriving capitalist economy in the East as a threat to the USSR and West Germany communist way of life, so on June 24, 1948, Stalin blocked all roads, rails, and canals into East Germany.
What was the reason for the construction of the Berlin Wall?
The West Germans claimed the wall was to prevent the flow of East Germans into the West, where there was NATO protection and economic opportunities. From the Eastern perspective, they claimed that the wall was to prevent Western aggression.
resistance to the constraints of the Iron Curtain under Soviet-dominated communism.
1956 Hungarian Revolution - Hungarian people revolted against their Stalinist government and formed their democratic government. This was later undone by Soviet forces.
Spring 1968 Prague - Alexander Dubeck came to power and reformed oppressive aspects of government. This was later undone by Soviet forces.
1955 Yugoslavia - Josip Ttito was a Yugoslavian leader and was the first and only socialist leader to reject Stalin’s ideals. he made Yugoslavia a founding member of the Non-Aligned movement as well as improving relationships with the West.
Bay of Pigs
a failed 1961 invasion of Cuba by US-backed Cuban exiles, leading to increased support for Fidel Castro and strained US-Cuba relations.
failed due in part to poor planning, inadequate support from the US military, and the false assumption that rebels in Cuba would be motivated by the attack to rise against Castro. The failed invasion served to increase the popularity of Castro, to generate greater suspicion and mistrust of the United States, and to solidify Cuba’s military, political, and economic relationships with the Soviet Union.
How did the Cuban Missile Crisis result in a period of détente after the crisis?
The cost of escalating tensions was too great and there were compelling reasons to ease tensions, such as:
The USSR was spending billions of dollars on the arms race and it was unsustainable.
Better relationships with the US would open up more trade opportunities.
Americans wanted to send more money on social programs and on the Vietnam War which was hard with the costs of the arms race.
salt
Strategic Arms Limitation Talks - talks that took place in 1969 between the US and Soviet Union and resulted in a 1972 agreement to limit the number of missiles acquired, armed, and aimed by the two countries. during period of detente
Iran Contra Affair
The Iran-Contra affair involved the Reagan administration secretly funding Nicaraguan Contras, aiming to counter leftist influence in Central America. To bypass legal restrictions, they used the National Security Council to sell weapons to Iran, funnelling the proceeds to the Contras. The scandal erupted when exposed by a Lebanese magazine, sparking international outrage
Julius & Ethel Rosenberg
Convicted of espionage for supplying the Soviet Union with important American documents about military weaponry; were executed by electric chair in 1953.
Why did Salvador Allende lose power in Chile in 1973?
Nixon authorized millions of dollars for the CIA to create political instability in Chile to unseat Allende. On September 11, 1973, Allende died during a military coup led by Augusto Pinochet who ruled the country as a dictator who implemented free market capitalist economic policies.
u2 incident (1960)
In the 1950’s, the American government set up a base in Pakistan from which surveillance missions were flown over Soviet territory. A U-2 plane piloted by Gary Powers was shot down after he was caught taking pictures of Soviet uranium plants. The Americans lied and said a weather research aircraft had gone off course and was missing. That was embarrassing because the Soviets admitted to having captured Powers and his plane was nearly still intact, and the Americans were publicly caught lying. Because of this, the East-West summit was cancelled which left American-Soviet relationships at an all time low.
What was Edward R. Murrow’s argument in his denunciation of Senator Joseph McCarthy?
He believed that living in fear would lead to failure and McCarthyism stemmed from a place of fear. They had to stand up just as their ancestors did and take responsibility for their actions instead of fearing one another
What effect did McCarthyism have on liberalism in the United States in the early 1950s?
McCarthyism was the illiberal stifling of the freedom of speech and belief through fear and suspicion. This led to the suppression of liberal thought and the shutting down of civil liberals. The anti-leftist era of the 1950s shifted the United States to the right which also assisted in the marginalization of liberal policies. People were forced to change their own beliefs for the sake of fear and it led to thought monolithism within a liberal institution.
John F Kennedy
modern liberal. won presidential election over nixon. opposed colonial empires and increased financial aid to underdeveloped countries. social welfare, civil rights, education, liberalized US. peace corps (americans volunteer to help underdeveloped nations)
who was president during cuban missile crisis
john f kennedy and with Khrushchev they ended the mutual brinkmanship through peace negotiations over each of their nuclear assembly sites.
Nikita Krushchev
supported stalin and was adviser. secret speech → denounced stalin’s purges, de-stalinized soviet union (less repressive soviet union). allowed freedom in arts but ordered an attack when Doctor Zhivago (didn’t support the left) was published when he denied publication. founded academic towns like oxford.
Martin Luther King Jr
liberal pastor and activist of civil rights movement. wrote books, articles, and spoke. directed march of 250 000 people in washington dc where he delivered his address “I have a dream” which led to civil right legislation passed in US. was awarded 5 degrees, man of the year, and nobel peace prize.
Lenoid Brezhnev
Kruschev was ousted from power by radical communists who instated brezchev which led to re-stalinization. invaded Czechoslovakia, warfare in people’s republic in China. Brezhnev doctrine. With Nixon, they improved relations and created joint united states-soviet space program
Brezhnev doctrine
any threat to socialist/communist rule in any state of the soviet controlled section of Eastern Europe was a threat to all communism.. truman doctrine inversed.
Mikhail Gorbachev
first party secretary of stavropol to reorganize collective farms, improve working conditions and expand farmer land. introduced glasnost and perestokia. the press in soviet union became less controlled and he was open to criticism and input to improve economic production. economic policy created shortages of food supplies. democratization.
glasnost and perestrokia
Gorbachev’s polivies. openess (freedom of speech) and restructuring
Boris Yeltsin
member of communist party and appointed by gorbachev to reorganize party central committee and became mayor. supported gorbachev’s reforms. when radical communists tried to overthrow gorbachev, he influenced demostrations and forced coup leaders to flee. power shifted to yeltsin and there was more opposition to his leadership so he resigned.
Vladmir Putin
was intelligence officer for KGB. after yeltsin re4signed, he became pres of russian federation. attempted to reconstruct country with grand bargain with russian oligarchs, where they maintained power if they supported putin. slashed taxes to benefit big businesses and renationallized key sectors of economy. moves to consolidate power for kleptocracy. (appointed favoured governors and silenced opposition) banned promotion of lgbtq rights. Waged war against Chechen separatists, annexed the Crimean peninsula, supported separatists in the Ukraine and propped up Bashar al-Assad’s government in Syria.
alger hiss
A U.S. state department official accused of espionage during the Second Red Scare, but he was only convicted for perjury.
Lyndon B Johnson
vice pres to JFK and succeeded him as president. campaign of “The Great Society” built on aid to education, social safety nets, attack on disease and urban renewal.
Gulf of Tonkin resolution
allowed Lyndon b Johnson to further involve america in the vietnam war.
Ronald Reagan
neoconservative U.S. president in the 80s, responsible for the reignition of the Cold War: billions of dollars spent on military operations around the world.
Korean War (1950-1953)
WWII divided Korea into communist northern half and american occupied southern half. war began when north korean army backed with soviet supplies crossed 38th parallel and invaded non-communist south korea. US, fuelled by politics of truman doctrine intervened to fight North Korean army through an “official” UN peacekeeping operation which was influenced by american interests. China backed north korea and was scared a victorious US would then war with china. many countries would take sides to further their political values, leading to proxy war. Truman wanted to end war fast, but US contined to bomb north korea (wanted to intimidate them into suing for peace). after Eisenhower became president, stalemate became permanent through signing an armstice that returned korea to its territories before the war.
war and outcome did not lessen cold war tension.
Cuban Missile crisis (1962)
US before crisis had nuclear missile base in Turkey with intent to intimidate Russia. With fidel Castro as the leader, cuba led a communist revolution against its government.
failed invasion at bay of pigs influenced castro to strike a deal with soviet union
kruschev and castro worked to make a soviet nuclear missile base in cuba, with missiles pointed at US
U2 plane took pic of soviet sites being assembled so US gov knew about nuclear threat
US made naval blockade to prevent soviet ships from reaching and delivering supplies to cuba as tensions rose
with fear of total nuclear war, Kennedy and Khrushchev directly communicated and negotiated hesitant peace
both parties removed missiles from cuba and turkey and communication remained. tension and fear was still high so missile numbers were high
US and soviet union signed test-ban treaty preventing above ground nuclear testing
warsaw pact
collective defense treaty between soviet union and seven eastern bloc socialist republics, aligned Eastern and Central Europe with communism.
blockade
an act or means of sealing off a place to prevent goods or people from entering or leaving.
desegregation
the ending of a policy of racial segregation
the great society
The West Germans claimed the wall was to prevent the flow of East Germans into the West, where there was NATO protection and economic opportunities. From the Eastern perspective, they claimed that the wall was to prevent Western aggression.
Civil Rights Movement
after 13th amendment which abolished slavery, racism was still prominent with jim crow laws which legalized segregation
NAACP overturned the laws that maintained segregation in schools
President Eisenhower was sympathetic to south but upheld desegregation
Little rock nine, rosa parks
Martin luther King jr organized protests against transit segregation (year long bus boycott leading to supreme court declaring transit segregation unconstitutional)
March on Washington
civil rights act + voting rights act: liberal values in constitution applied to all citizens
supreme court declared all forms of segregation unconstitutional (1970)
Rosa Parks
arrested for refusign to give her bus seat to a white man in Alabama
segregation
separation of people into racial or other ethnic groups in daily life. can involve the spatial separation, and mandatory use of different institutions, such as schools and hospitals by people of different races
Vietnam War (1955-1975)
Vietnam, previously controlled by France, was separated when uprising removed French in the North
Ho Chi Minh led communist group, the Viet Cong, formed in North Vietnam
US thought they need to intervene due to domino principle (limit spread of communism)
began as a proxy war developing over 20 years and resulted in illiberal military conscription in the states that could be avoided by the rich, so the lower class and minority groups were targeted.
Viet cong knew the terrain better than American troops, we warfare was messy and brutal
more weapons were dropped in Vietnam than entirety of WWII, many traps were deployed by viet cong
Americans used chemical warfare
Due to rise in accessibility in video technology in US, citizens could see documentation which fueled anti-war movements that turned many against actions of the states
Nixon administration would informally war with Cambodia to disrupt viet cong’s supplies and intimidate them, but this destabilized the country which then became fascist state
ended with American loss and communist victory. escalated tension with soviet union and communism, as well as internal instability against American gov
anti war movement
During vietnam war, Due to rise in accessibility in video technology in US, citizens could see documentation which fueled anti-war movements that turned many against actions of the states
watergate scandal (1972-1974)
to be reelected, nixon said he wanted to end the war, but his actions proved otherwise
during time of political volatility due to vietnam war, nixon formed governmental fundraising organization called committee for the reelection of the president
political opponents called crp, creep, because crp engaged in espionage and sabotage to benefit nixon
CRP sent burglars to watergate (headquarters of opposing democratic party) to steal documents and bug communications
they were forced to return after first attempt failed which led to security guard discovering the twice taped over doors
guard found high tech equipment and number going to white house, so he called police
during scandal, nixon and his inner circle attempted an illiberal, illegal cover up, but reporters from washington post investigated, including hiring a spy
they are blocked as much as possible from white house but their work leads to government intvestigations of watergate that led back to nixon and white house
nixon resigns after he is outed for scandal and is nearly impeached, he tries to restore repuation and defend himself but he fails.
ford becomes president after and then jimmy carter is elected.
non aligned movement
international organization of states who consider themselves not formally aligned with or against the west or soviets.
Many countries that had a history of European imperialism wanted to step away from the superpower spheres of influence.
Bandung Conference started it
bandung conference
started non aligned movement where 29 african and asian countries met to promote economic and cultural co-operation and oppose colonialism by the superpowers.
canada in cold war
was founding member of NATO and contributed to defense of south korea in korean war
canada constructed NORAD and DEW line
NORAD
north american aerospace defence command
cosntructed by canada and is a united air defense system on Canada’s northern shores, with the States.
DEW Line
distant early warning line
part of NORAD, which would give an early warning to america of incoming missiles from soviet union
iran contra affair (1981-1986)
new reagan administration, led by neoconservative republican ronald reagan, saw nicaraugua as communist, so US gov security agencies funneled weapons and money to the contras, a nicaraguan rebel group
congress passed legislation to embargo support of the contras via government agencies
Reagan avoided these restrictions by using an agency not named in the legislation, national security council, which would secretly obtain funds by illegally selling weapons to moderates in the iranian gov
wanted to get american hostages in lebanon released
embargo
an official ban on trade or other commercial activity with a particular country.
blacklist
a list of people or things that are regarded as unacceptable or untrustworthy and should be excluded or avoided.
ex. hollywood ten were blacklisted from hollywood
viet cong
communist group in vietnam war
NATO
a military alliance designed to defend member countries, including the U.S., Canada, Britain, and France (for a while) against attack from the Soviet Union and its allies.
superpower
a very powerful and influential nation (used especially with reference to the US and the former Soviet Union when these were perceived as the two most powerful nations in the world).
civil disobedience
the refusal to comply with certain laws or pay taxes, as a peaceful form of political protest.
united nations
an international organization founded in 1945; its goals are to maintain international peace, develop relations among nations, and achieve cooperation.
UN security council
The board of the UN responsible for maintaining international security, often involved during international conflicts.
Satellite State
a country that is formally independent but under heavy influence or control from another country.
de-stalinization
Policy of eradicating the influence of Stalin's rule in the Soviet Union, initiated by Khrushchev in the mid-1950s to denounce Stalin's actions.
re-stalinization
Re-Stalinization refers to the resurgence of Stalinist policies and practices after a period of destalinization. Lenoid Brezhnev initiated.
fallout shelter
a building or other structure designed to protect people from radioactive fallout after a nuclear explosion.
hot war
troops and battles in direct conflict