Unit 1: Digestive System, Cellular Respiration, Tissues, and Organs
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Tissues, Organs, Digestive System, + Cellular Respiration
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
Levels of Organization
1) molecules
2) organelles
3) cells
4) tissue
5) organs
6) organ systems
7) organism
tissue
a group of cells working together
organs
structures composed of multiple tissues working together for 1 function
Organ Systems
multiple organs working together for a specific function
1) different organ systems in organisms interact a lot
Organism
something made up of multiple organ systems
anatomy
the name/identity of something
1) typically organs
physiology
the function of something
1) typically organs
digestive system
takes in food and gets nutrients into the body
respiratory system
exchange gases with the environment
circulatory system
supplies oxygen and nutrients to the whole body
lymphatic/imune system
1) lymphatic: diverts substances to be thoroughly inspected by the body
2) immune: keeps us safe from dangerous foreign bodies.
excretory system
removes waste
endocrine system
maintains homeostasis
nervous system
sends and receives signals from the outside world
integumentary system
body covering (skin)
skeletal system
responsible for movement, support, and protection
muscular system
responsible for movement, support, and protection
reproductive system
sexul reproduction
Tissue Types
1) epithelial
2) Nervous
3) muscle
4) connective
(Edwards Needs Mike Conley)
Epithelial Tissue
linings and coverings
1) does secretion and absorption
2) also protective
3) structures: squamous, cuboidal, columnar and simple or stratified
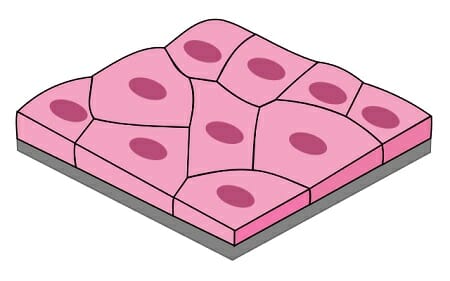
squamous
epithelial tissue with flat cells
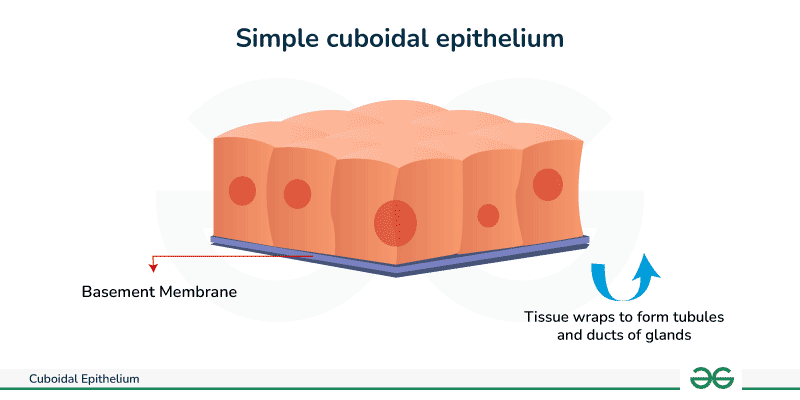
cuboidal
epithelial tissue with cube-like cells
columnar
epithelial tissue with column-like cells

simple tissue
1 layer
1) maximizes diffusion
2) not trying to protect
3) ex: lining of intestine
connective tissues
binds and supports other tissues
1) has many functions (ex: cartilage connects muscles to bones.)
2) contain matrix
3) there are fibrous and loose connective tissues
matrix
non-lining material secreted by cells to help bind and support other cells
1) is how we tell the difference between different connective tissues
fibrous connective tissue
connective tissue with high levels of collagen in matrix but not much elastin.
1) Need have less elastin in order to be tighter
2) two types: tendons and ligaments
tendons
connect muscle to bone
ligaments
connect bone to bone
collagen
makes tissue resistant and resists stretching
elastin
makes tissue more easily stretched
loose connective tissue
connective tissue with lower amounts of collagen and higher amounts of elastin.
1) stretchier
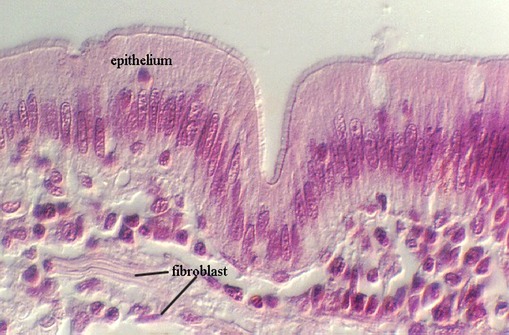
muscles
responsible for movement
1) three muscle types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac
(Steph Curry Sweeps)
skeletal muscle
Muscle connected to the bone
1) under voluntary control
1) has contractile units (sarcomeres) responsible for striations (the stripes)
2) activation of a single part contracts the whole fiber (moves as a unit)
4) strong
5) structure is extremely regular; easier to move as one
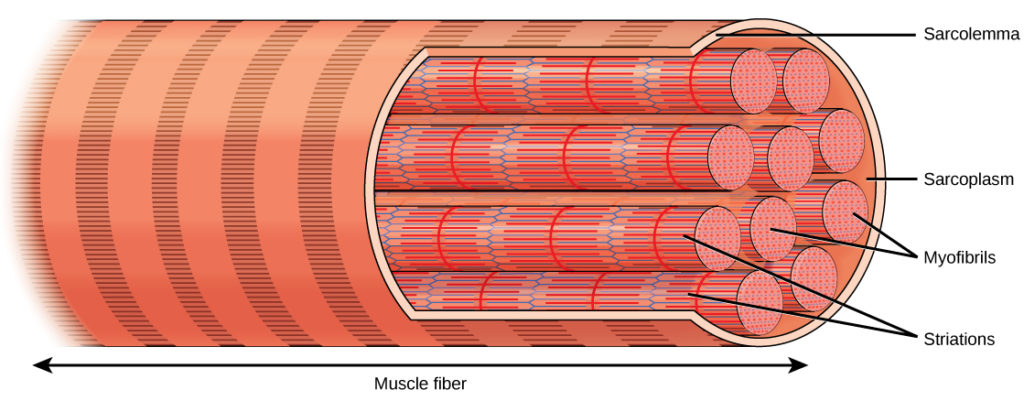
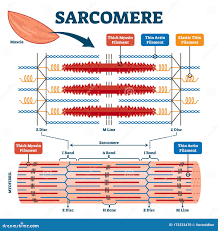
sarcomere
contractile units of muscles
1) responsible for striations
smooth muscle
on walls of digestive tract, bladder, arteries, etc.
1) has sarcomeres under the plasma membrane (non-visible)
2) contraction is weaker but can be sustained for longer
3) like a smooth, elastic sheet
4) no striations
5) not voluntarily controlled
cardiac muscle
surrounds the ykw
1) responsible for pumping
2) has sarcomeres and striations
3) branched for transmission and signaling
4) shorter but stronger
nervous tissue
senses stimuli and transmits info from 1 part to another
1) has long extensions that help it do that
2) ex: nuerons and glial
neurons
nervous cells responsible for the transmission of info; communication network
1) can be very long
glial cells
surround + support neurons
Digestive System
organ system responsible for ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination
Ingestion
getting food into the body
digestion
breaking down polymers into monomers
1) has 2 parts: mechanical and chemical digestion.
mechanical digestion
separating food into chunks; big chunks → little chunks
chemical digestion
hydrolysis/the chemical separation of polymers into monomers (H2O is required)
1) required for absorption to occur
absorption
actually taking in the monomers
elimination
disposing of the waste (pooping)
protease
enzymes that digest proteins
amylases
enzymes that digest polysaccharides
nucleases
enzymes that digest nucleic acids
lipases
enzymes that digest fatty acids
1) fats start digestion the latest out of all of the enzymes because are digested in the small intestine
mouth/teeth
1) do mechanical digestion
salivary glands
1) produce saliva and enzymes for chemical digestion
2) mostly produce amylases
saliva
the beginning of polysaccharide digestion
pharynx
entrance to the respiratory system and the tubular section of the digestive system
epiglottis
the flap over the trachea
1) opens and closes to allow air in
esophagus
transport food from the pharynx to the stomach
stomach (structure)
does chemical and mechanical digestion
1) includes the cardiac sphincter, gastric sphincter, and duodenum (kinda)
cardiac sphincter
closes at the top of the stomach
1) keeps acid in the stomach
gastric sphincter
closes at the bottom of the stomach
1) keeps acid in the stomach
duodenum
the start of the small intestine
1) transports chyme from the stomach to the small intestine
liver
secretes bile
bile
emulsifies fats to aid digestion (helps them mix with digestive liquids)
1) also neutralizes chyme
gall bladder
stores bile
pancreas
1) produces digestive enzymes
2) produces pancreatic juice
3) produces hormones
small intestine
does chemical digestion absorption
1) has chemicals and enzymes from the liver/+ pancreas and from its epithelial tissue
2) has a lot of length/surface area to maximize absorption
3) absorbs nutrients into blood and the lymphatic system
nutrients absorbed by blood
monosaccharides, amino acids, and nucleotides
nutrients absorbed by lymphatic system
fatty acids
structure of the small intestine
1) extremely long to increase surface area for absorption and time for chemical digestion
2) has many folds to increase surface area per section of the lining
3) has villi and microvilli
villi
finger-like projections/units of absorption on the folds of the small intestine
1) has its own blood supply and lymphatic system
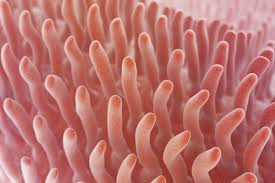
microvilli
mini villi on the villi
large intestine
reabsorbs water and is a bacteria microbiome
1) called the “large” intestine because is greater in diameter
2) made up of the ascending, transverse, and descending colon.
3) hosts a lot of bacteria; most of it is helpful for us. 700+ species
3) distributes water back into the blood stream
bacteria in the large intestine
1) facilitates chemical digestion
2) synthesizes vitamins (ex: vitamin K)
3) have many other functions
4) dangerous if the balance is off
stomach (function)
for the digestion of proteins
1) proteins are difficult to digest because of the tertiary structure/2nd folding + peptide bonds are hard to break
2) secrets pepsin (enzyme) and HCl acid (strong)
chyme
patrially digested food
self digestion (explanation)
1) HCl acid is really strong, so the stomach needs to protect itself
2) the stomach s made of proteins but also digests proteins, so could potentially eat itself
structures to prevent self digestion
1) sphincters
2) mucus
3) hormone gastrin
4) (bonus) epithelium constantly replaces itself through mitosis
sphincters
close to stop stomach acid from escaping
mucus
basic (pH) snot-like structure produced by the stomach for protection
hormone gastrin
regulates acid release
1) makes sure acid is only being produced when food is being consumed
2) has negative feedback loop (stops producing if there’s enough)
3) produced by the stomach for the stomach
parietal cells
cells in the stomach lining that produce HCl
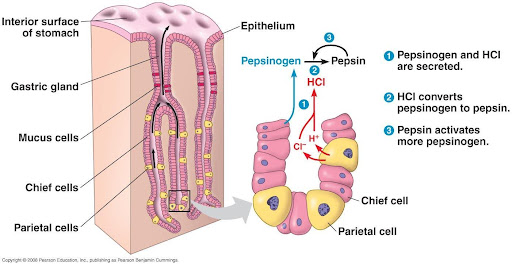
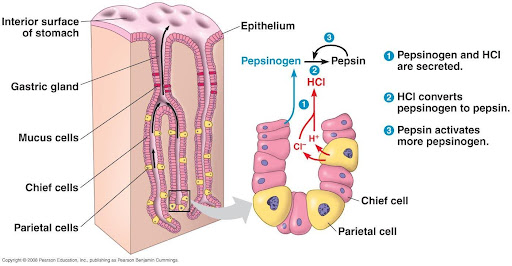
chief cells
cells in the stomach lining that produce pepsinogen
pepsinogen
the inactive form of pepsin
1) becomes pepsin when in contact with HCl
pepsin
a protease found in the stomach
1) breaks down proteins
gastric glands
glands in the stomach lining that produced hormone gastrin
Stomach Acid
HCl
1) softens food
2) denatures proteins for easier digestion
3) activates pepsinogen (optimal range turns it into pepsin)
4) kills bacteria on food
rectum
last part of the large intestine where things are stored until releasing fecal matter.
apendix
the vestigial structure at the start of the large intestine
cellular respiration
what cells do after you breath in oxygen during respiration
1) powers cells
2) is an exergonic reaction performed by the mitochondrion
3) part of energy from glucose and oxygen is harnessed to activate ATP; other part is stored.
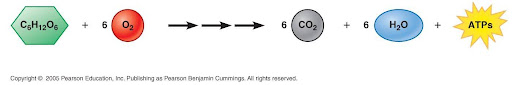
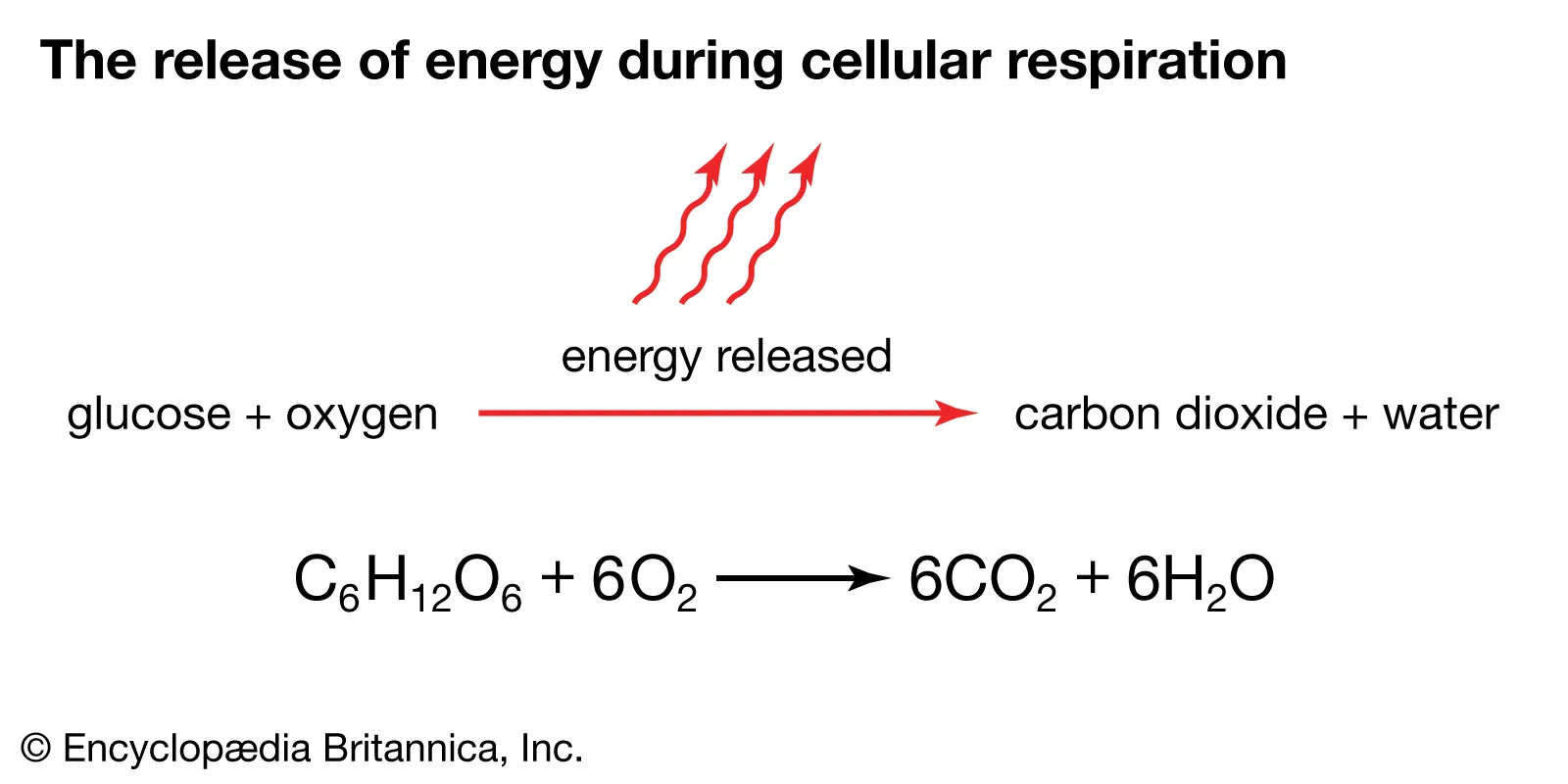
aerobic cellular respiration
cellular respiration that requires oxygen
1) glucose (C6H12O6) + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP (look at photo)
2) ATP released because it’s an exergonic reaction
glucose release energy
1) 60% heat
2) 40% ATP
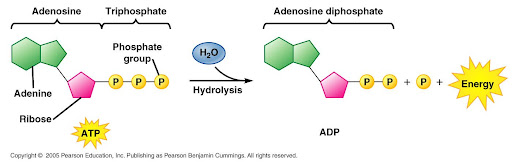
ATP
released by breaking bonds between the 2nd and third phosphate groups of a nucleotide
1) ATP hydrolysis produces ADP and P; ADP phosphorylation produces ATP
2) used for movement, active transport, endergonic reactions, and growth
3) is used and reused by the cell
glucose
C6H12O6
1) one glucose molecule can get roughly 32 ATP through cellular respiration
cellular respiration steps
1) glycolysis
2) citric acid/krebs cycle
3) Electron Transportation Chain/Oxidative Phosphorylation/chemiosmosis
glycolysis
the first stage of cellular respiration
1) occurs in the cytoplasm
2) universal. Pretty much every organism can use it b/c so basic (argument for common ancestor)
3) doesn’t need oxygen
4) requires ATP to occur but produces more than used
5) does substrate-level phosphorylation (adds electrons)
6) produces CO2
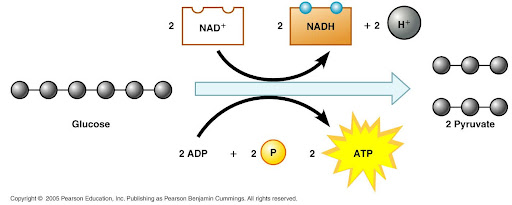
what goes into glycolysis
glucose, 2ADP+2P, 2NAD+, as well as the required 2ATP
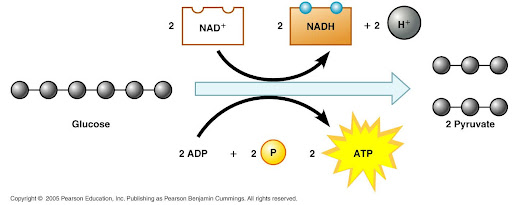
what comes out of glycolysis
2 pyruvate, 4 ATP, and 2NADH
1) NAD+ becomes NADH because once an electron is added to that plus charge, it becomes hydrogen (one proton, one electron)
NAD+
dinucleotide
1) has 1 hydrogen at top
2) NADH has 2 H’s at the top
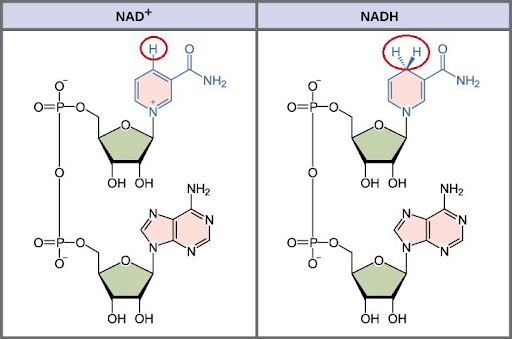
NADH
electron carrier produced by glycolysis
1) carries the high energy electrons from glycolysis to the ETC
citric acid/krebs cycle
the second stage of cellular respiration
1) finishes the breakdown of glucose into CO2
2) occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
3) produces lot of electron carriers
4) requires oxygen
5) net yields 2 ATP