APUSH Period 5 Key Terms, AP US History: Period 5: 1844-1877, AP US History Period 5 (1844-1877), AP US History Period 5, APUSH Period 5 Terms
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/234
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:05 PM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
235 Terms
1
New cards
Popular Sovereignty
Notion that the sovereign people of a given territory should decide whether to allow slavery. Seemingly a compromise, it was largely opposed by Northern abolitionists who feared it would promote the spread of slavery to the territories.
2
New cards
Fugitive Slave Law
1850. Passed as part of the Compromise of 1850, it set high penalties for anyone who aided escaped slaves and compelled all law enforcement officers to participate in retrieving runaways. Strengthened the antislavery cause in the North.
3
New cards
Uncle Tom's Cabin
Harriet Beecher Stowe's widely read novel that dramatized the horrors of slavery. It heightened Northern support for abolitions and escalated the sectional conflict.
4
New cards
Emancipation Proclamation
1863. Declared all slaves in rebelling states to be free but did not affect slavery in non-rebelling Border States. The Proclamation closed the door on possible compromise with the South and encouraged thousands of Southern slaves to flee to Union lines.
5
New cards
Freedmans' Bureau
1865-1872. Created to aid newly emancipated slaves by providing food, clothing, medical care, education, and legal support. Its achievements were never and depended largely on the quality of local administrators.
6
New cards
Black Codes
1865-1866. Laws passed throughout the South to restrict the rights of emancipated blacks, particularly with respect to negotiating labor contracts. Increased Norhterners' criticisms of President Andrew Johnson's lenient Reconstruction policies.
7
New cards
KKK
An extremist, paramilitary, right-wing secret society founded in the mid-nineteenth century and revived during the 1920s. It was anti-foreign, anti-black, anti-Jewish, anti-pacifist, anti-Communist, anti-internationalist, anti-evolutionist, and anti-bootlegger, but pro-Anglo-Saxon and pro-Protestant. Its members, cloaked in sheets to conceal their identities, terrorized freedmen and sympathetic whites throughout the South after the Civil War. By the 1890s, Klan-style violence and Democratic legislation succeeded in virtually disenfranchising all Southern blacks.
8
New cards
Sharecropping
An agricultural system that emerged after the Civil War in which black and white farmers rented land and residences from a plantation owner in exchange for giving him a certain "share" of each year's crop. Sharecropping was the dominant form of southern agriculture after the Civil War, and landowners manipulated this system to keep tenants in perpetual debt and unable to leave their plantation.
9
New cards
Compromise of 1850
Admitted California as a free state, opened New Mexico and Utah to popular sovereignty, ended the slave trade (but not slavery itself) in Washington D.C., and introduced a more stringent fugitive slave law. Widely opposed in both the North and South, it did little to settle the escalating dispute over slavery.
10
New cards
Kansas-Nebraska Act
1854. Proposed that the issue of slavery be decided by popular sovereignty in the Kansas and Nebraska territories, thus revoking the 1820 Missouri Compromise. Introduced by Stephen Douglass in an effort to bring Nebraska into the Union and pave the way for a northern transcontinental railroad.
11
New cards
Homestead Act
1862. A federal law that gave settlers 160 acres of land for about $30 if they lived on it for five years and improved it by, for instance, building a house on it. The act helped make land accessible to hundreds of thousands of westward-moving settlers, but many people also found disappointment when their land was infertile or they saw speculators grabbing up the best land.
12
New cards
Gettysburg Address
1863. Abraham Lincoln's oft-quoted speech, delivered at the dedication of the cemetery at Gettysburg battlefield. In the address, Lincoln framed the war as a means to uphold the values of liberty.
13
New cards
10% Reconstruction Plan
1863. Introduced by President Lincoln, it proposed that a state be readmitted to the Union once 10 percent of its voters had pledged loyalty to the United States and promised to honor emancipation.
14
New cards
13th, 14th, 15th Amendments
13th: Abolished slavery except for criminal punishment.
14th: Gave equal rights and government protection to all men.
15th: Secured suffrage for men.
14th: Gave equal rights and government protection to all men.
15th: Secured suffrage for men.
15
New cards
Radical Republicans
Wanted harsh punishment for the South for the Civil War.
16
New cards
Election of Lincoln
Angered many people in the south who owned slaves because he wanted to end slavery. Won the election of 1860 but did not win the popular vote. South Carolina was happy at the outcome of the election because now it had a reason to secede.11 states in the south seceded and made themselves the Confederacy after the election.
17
New cards
Abolitionist Movement
An international movement that between approximately 1780 and 1890 succeeded in condemning slavery as morally repugnant and abolishing it in much of the world; the movement was especially prominent in Britain and the United States.
18
New cards
Anaconda plan
Union war plan by Winfield Scott, called for blockade of southern coast, capture of Richmond, capture Mississippi River, and to take an army through heart of south
19
New cards
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
(1848) The Mexican government gave up the area of Texas and offered to sell the provinces of California and New Mexico.
20
New cards
The Compromise of 1850
(1850) California as free state, popular sovereignty in Mexican Cession, end of slave trade in DC, fugitive slave law.
21
New cards
The Kansas-Nebraska Act
(1854) Sponsored by Senator Stephen Douglas, this would rip open the slavery debate; and create the territories of Kansas and Nebraska, opened new lands, repealed the Missouri Compromise of 1820, and allowed settlers in those territories to determine if they would allow slavery within their boundaries.
22
New cards
Bleeding Kansas
(1856-1861) A sequence of violent events involving abolitionists and pro-Slavery elements that took place in Kansas-Nebraska Territory. The dispute further strained the relations of the North and South, making civil war imminent.
23
New cards
The Election of 1860
(1860) The United States presidential election of 1860 set the stage for the American Civil War. Hardly more than a month following Lincoln's victory came declarations of secession by South Carolina and other states, which were rejected as illegal by outgoing President James Buchanan and President-elect Lincoln.
24
New cards
The Homestead Act
(1862) Granted 160 acres of government land in the west to any person who would farm it for at least five year.
25
New cards
Black Codes
(1865) Laws denying most legal rights to newly freed slaves; passed by southern states following the Civil War
26
New cards
The Fourteenth Amendment
(1868) This provided equal protection of the law. Representation for any state that withheld voting from African Americans would be reduced.
27
New cards
The Fifteenth Amendment
(1870) Prohibited any state from denying citizens the right to vote on the grounds of race, color, or previous condition of servitude.
28
New cards
The Compromise of 1877
(1877) It withdrew federal soldiers from their remaining position in the South, enacted federal legislation that would spur industrialization in the South, appointed Democrats to patronage positions in the south, appointed a Democrat to the president's cabinet, and allowed Rutherford B. Hayes to win the election. Marked the end of reconstruction.
29
New cards
Manifest Destiny
A notion held by a nineteenth-century Americans that the United States was destined to rule the continent, from the Atlantic the Pacific.

30
New cards
Texas Annexation
1845. Originally refused in 1837, as the U.S. Government believed that the annexation would lead to war with Mexico. Texas remained a sovereign nation. Annexed via a joint resolution through Congress, supported by President-elect Polk, and approved in 1845. Land from the Republic of Texas later became parts of NM, CO, OK, KS, and WY.
31
New cards
Oregon Trail
2000 mile long path along which thousands of Americans journeyed to the Willamette Valley in the 1840's.
32
New cards
California Gold Rush
1849 (San Francisco 49ers) Gold discovered in California attracted a rush of people all over the country and world to San Francisco; arrival of the Chinese; increased pressure on federal government to establish a stable government

33
New cards
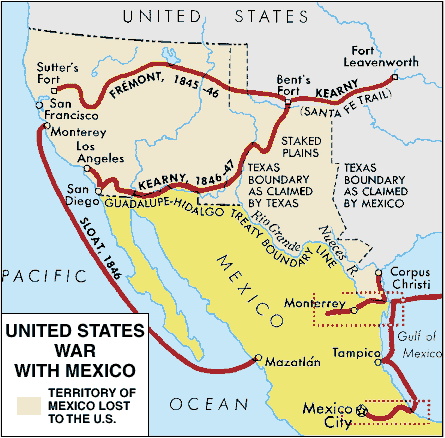
Mexican American War
1846 - 1848 - President Polk declared war on Mexico over the dispute of land in Texas. At the end, American ended up with 55% of Mexico's land.
34
New cards
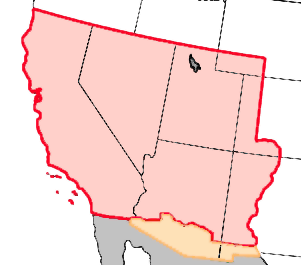
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
(1848) treaty signed by the U.S. and Mexico that officially ended the Mexican-American War; Mexico had to give up much of its northern territory to the U.S (Mexican Cession); in exchange the U.S. gave Mexico $15 million and said that Mexicans living in the lands of the Mexican Cession would be protected
35
New cards
popular sovereignty
A belief that ultimate power resides in the people.
36
New cards
Kansas Nebraska Act
1854 - Created Nebraska and Kansas as states and gave the people in those territories the right to chose to be a free or slave state through popular sovereignty.

37
New cards
Free "Soiler"
People who opposed expansion of slavery into western territories

38
New cards
Republican Party
1854 - anti-slavery Whigs and Democrats, Free "Soilers" and reformers from the Northwest met and formed party in order to keep slavery out of the territories
39
New cards
secession
Formal withdrawal of states or regions from a nation
40
New cards
Uncle Tom's Cabin
Written by Harriet Beecher Stowe in 1853 that highly influenced England's view on the American Deep South and slavery. A novel promoting abolition. intensified sectional conflict.
41
New cards
Sectionalism
Loyalty to a region
42
New cards
John Brown's Raid
Began when he and his men took over the arsenal in Harpers Ferry, Virginia, in hopes of starting a slave rebellion.

43
New cards
Robert E Lee
Confederate general who had opposed secession but did not believe the Union should be held together by force

44
New cards
Gettysburg
A large battle in the American Civil War, took place in southern Pennsylvania from July 1 to July 3, 1863. The battle is named after the town on the battlefield. Union General George G. Meade led an army of about 90,000 men to victory against General Robert E. Lee's Confederate army of about 75,000. Gettysburg is the war's most famous battle because of its large size, high cost in lives, location in a northern state, and for President Abraham Lincoln's Gettysburg Address.

45
New cards
Ulysses S Grant
an American general and the eighteenth President of the United States (1869-1877). He achieved international fame as the leading Union general in the American Civil War.

46
New cards
habeas corpus
Constitutional protection against unlawful imprisonment

47
New cards
martial law
rule by the army instead of the elected government

48
New cards
Lincoln 1st Inaugural Address
Lincoln tries to appease the south and avoid war
49
New cards
Gettysburg Address
A 3-minute address by Abraham Lincoln during the American Civil War (November 19, 1963) at the dedication of a national cemetery on the site of the Battle of Gettysburg

50
New cards
Lincoln 2nd Inaugural Address
"with malice toward none, and charity for all"
51
New cards
Presidential Reconstruction
President's idea of reconstruction : all states had to end slavery, states had to declare that their secession was illegal, and men had to pledge their loyalty to the U.S.

52
New cards
Radical Reconstruction
Reconstruction strategy that was based on severely punishing South for causing war

53
New cards
Black Codes
Laws denying most legal rights to newly freed slaves; passed by southern states following the Civil War

54
New cards
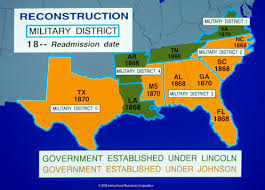
Military Reconstruction Act
1867; divided the South into five districts and placed them under military rule; required Southern States to ratify the 14th amendment; guaranteed freedmen the right to vote in convention to write new state constitutions
55
New cards
Reconstruction Amendments
13th: abolished and continues to prohibit slavery and involuntary servitude, 14th: secured the rights of former slaves after reconstruction, 15th: prohibits each government in the United States to prevent a citizen from voting based on their race

56
New cards
Freedmen's Bureau
1865. help former black slaves after civil war
Organization run by the army to care for and protect southern Blacks after the Civil War
Organization run by the army to care for and protect southern Blacks after the Civil War

57
New cards
Compromise of 1877
Ended Reconstruction. Republicans promise 1) Remove military from South, 2) Appoint Democrat to cabinet (David Key postmaster general), 3) Federal money for railroad construction and levees on Mississippi river
58
New cards
Election of 1876
Ended reconstruction because neither candidate had an electoral majority. The Democrat Sam Tilden loses the election to Rutherford B Hayes, Republican, was elected, and then ended reconstruction as he secretly promised.

59
New cards
KKK
Stands for Ku Klux Klan and started right after the Civil War in 1866. The Southern establishment took charge by passing discriminatory laws known as the black codes. Gives whites almost unlimited power. They masked themselves and burned black churches, schools, and terrorized black people. They are anti-black and anti-Semitic.
60
New cards
carpetbagger
A northerner who went to the South immediately after the Civil War; especially one who tried to gain political advantage or other advantages from the disorganized situation in southern states

61
New cards
scalawag
A derogatory term for Southerners who were working with the North to buy up land from desperate Southerners

62
New cards
sharecropper
A person who works fields rented from a landowner and pays the rent and repays loans by turning over to the landowner a share of the crops.

63
New cards
Morehouse College
Founded in Atlanta in 1867 for black education for professional careers such as lawyers, ministers, and educators.
64
New cards
peculiar institution
..., southern euphemism for slavery
65
New cards
John C. Calhoun
..., South Carolina Senator - advocate for state's rights, limited government, and nullification
66
New cards
Harriet Tubman
..., United States abolitionist born a slave on a plantation in Maryland and became a famous conductor on the Underground Railroad leading other slaves to freedom in the North (1820-1913)
67
New cards
Sojourner Truth
..., United States abolitionist and feminist who was freed from slavery and became a leading advocate of the abolition of slavery and for the rights of women (1797-1883)
68
New cards
Fredrick Douglas
..., former slave + abolitionist, stood up for his beliefs, fought for womens + blacks rights, runaway slave, newspaper-the north star
69
New cards
Sarah and Angelina Grimke
..., Quaker sisters from South Carolina who came north and became active in the abolitionist movement; Angelina married Theodore Weld, a leading abolitionist and Sarah wrote and lectured on a variety of reforms including women's rights and abolition.
70
New cards
Nat Turner's Rebellion
..., Rebellion in which Nat Turner led a group of slaves through Virginia in an unsuccessful attempt to overthrow and kill planter families
71
New cards
Declaration of Sentiments
..., declared that all "people are created equal"; used the Declaration of Independence to argue for women's rights
72
New cards
Underground Railroad
..., abolitionists secret aid to escaping slaves
73
New cards
James K. Polk
..., president in March 1845. wanted to settle oregon boundary dispute with britain. wanted to aquire California. wanted to incorperate Texas into union.
74
New cards
Bear Flag Republic
..., aka the California republic; the result of a revolt by Americans on June 14, 1846, in the town of Sonoma against the authorities of the Mexican province of California; the Republic lasted less than a month. The republic eventually became the present-day state of California.
75
New cards
Wilmot Proviso
..., Bill that would ban slavery in the territories acquired after the War with Mexico
76
New cards
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
..., Treaty that ended the Mexican War, granting the U.S. control of Texas, New Mexico, and California in exchange for $15 million
77
New cards
Oregon Trail
..., pioneer trail that began in missouri and crossed the great plains into the oregon country
78
New cards
Harriet Beecher Stowe
..., United States writer of a novel about slavery that advanced the abolitionists' cause (1811-1896)
79
New cards
George Fitzburgh
..., says slavery in South is better than wage slavery in North
80
New cards
John Brown
..., abolitionist who was hanged after leading an unsuccessful raid at Harper's Ferry, Virginia (1800-1858)
81
New cards
apologists
..., Christian thinkers who defended slavery and explained its "positive good" through Christian beliefs
82
New cards
Free-soil party
..., Formed in 1847 - 1848, dedicated to opposing slavery in newly acquired territories such as Oregon and ceded Mexican territory.
83
New cards
49ers
..., People who rushed to california in 1849 for gold.
84
New cards
Republican Party
..., the younger of two major political parties in the United States
85
New cards
Confederate States of America
..., a republic formed in February of 1861 and composed of the eleven Southern states that seceded from the United States
86
New cards
Gadsden Purchase
..., purchase of land from mexico in 1853 that established the present U.S.-mexico boundary
87
New cards
Fugitive Slave Law
..., Enacted by Congress in 1793 and 1850, these laws provided for the return of escaped slaves to their owners. The North was lax about enforcing the 1793 law, with irritated the South no end. The 1850 law was tougher and was aimed at eliminating the underground railroad.
88
New cards
The Compromise of 1850
..., Slavery becomes outlawed in Washington D.C., California is admitted as a free state, and Utah and New Mexico will determine whether slavery is allowed through popular sovereignty. Also, the Fugitive Slave Law is passed.
89
New cards
The Kansas-Nebraska Act
..., 1854; sponsored by Senator Stephen Douglas, this would rip open the slavery debate; and create the territories of Kansas and Nebraska, opened new lands, repealed the Missouri Compromise of 1820, and allowed settlers in those territories to determine if they would allow slavery within their boundaries.
90
New cards
Dred Scott v. Sanford
..., Supreme Court case that decided US Congress did not have the power to prohibit slavery in federal territories and slaves, as private property, could not be taken away without due process - basically slaves would remain slaves in non-slave states and slaves could not sue because they were not citizens
91
New cards
Bleeding Kansas
..., A sequence of violent events involving abolitionists and pro-Slavery elements that took place in Kansas-Nebraska Territory. The dispute further strained the relations of the North and South, making civil war imminent.
92
New cards
Harper's Ferry
..., John Brown's scheme to invade the South with armed slaves, backed by sponsoring, northern abolitionists; seized the federal arsenal; Brown and remnants were caught by Robert E. Lee and the US Marines; Brown was hanged
93
New cards
popular sovereignty
..., The doctrine that stated that the people of a territory had the right to decide their own laws by voting. In the Kansas-Nebraska Act, popular sovereignty would decide whether a territory allowed slavery.
94
New cards
Robert E. Lee
..., Confederate general who had opposed secession but did not believe the Union should be held together by force
95
New cards
Ulysses S. Grant
..., an American general and the eighteenth President of the United States (1869-1877). He achieved international fame as the leading Union general in the American Civil War.
96
New cards
Abraham Lincoln
..., 16th President of the United States saved the Union during the Civil War and emancipated the slaves; was assassinated by Booth (1809-1865)
97
New cards
John Wilkes Booth
..., was an American stage actor who, as part of a conspiracy plot, assassinated Abraham Lincoln, the 16th President of the United States, at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C. on April 14, 1865.
98
New cards
Copperheads
..., northern democrat who advocated making peace with the Confederacy during the Civil War
99
New cards
New York Draft Riots
..., July 1863 just after the Battle at Gettysburg. Mobs of Irish working-class men and women roamed the streets for four days until federal troops suppressed them. They loathed the idea of being drafted to fight a war on behalf of slaves who, once freed, would compete with them for jobs.
100
New cards
Bull Run
..., either of two battles during the American Civil War (1861 and 1862)