Active vs Passive Transport
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
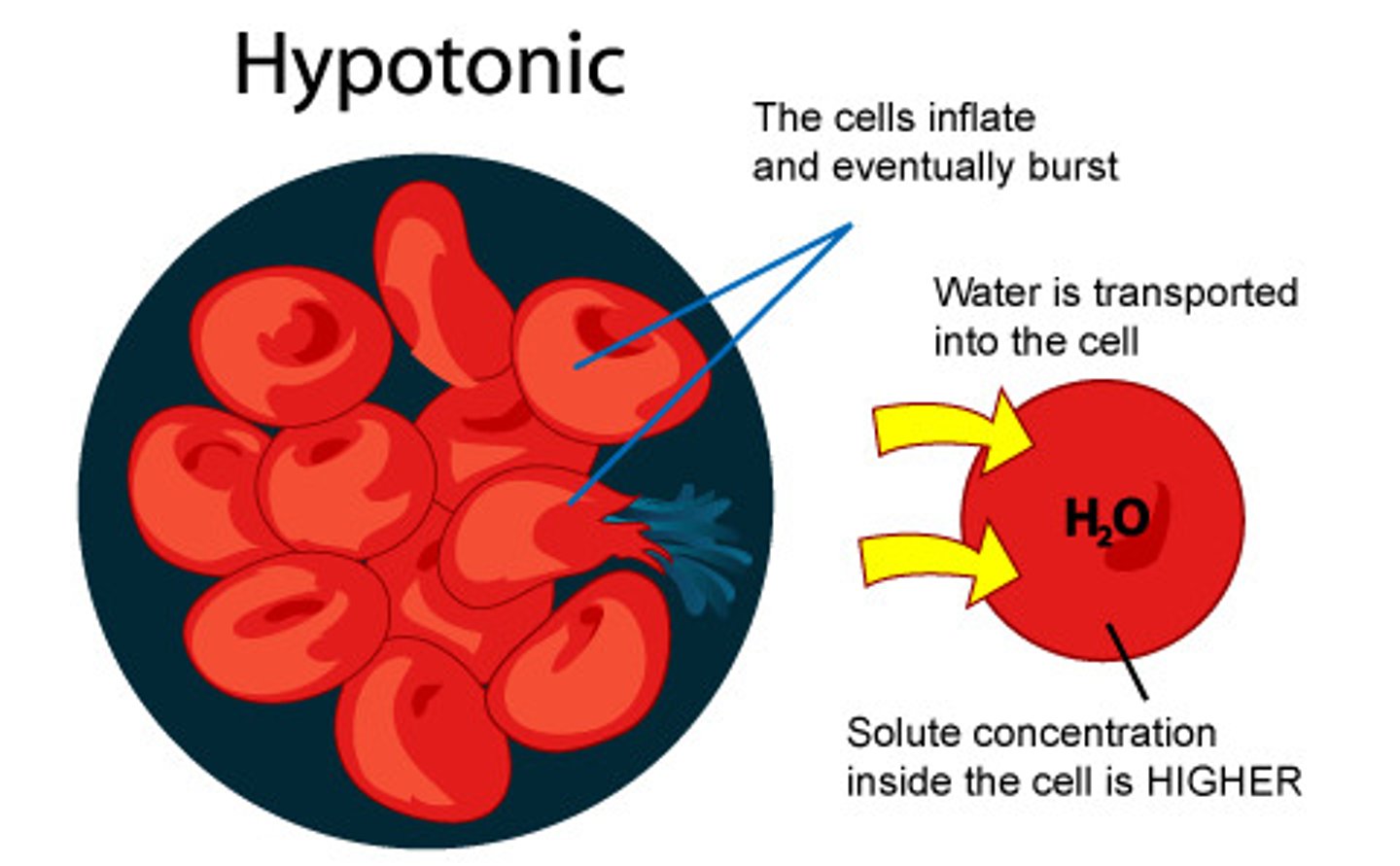
hypotonic environment
water moves into the cell from high to low to try to reach equilibrium in this type of solution
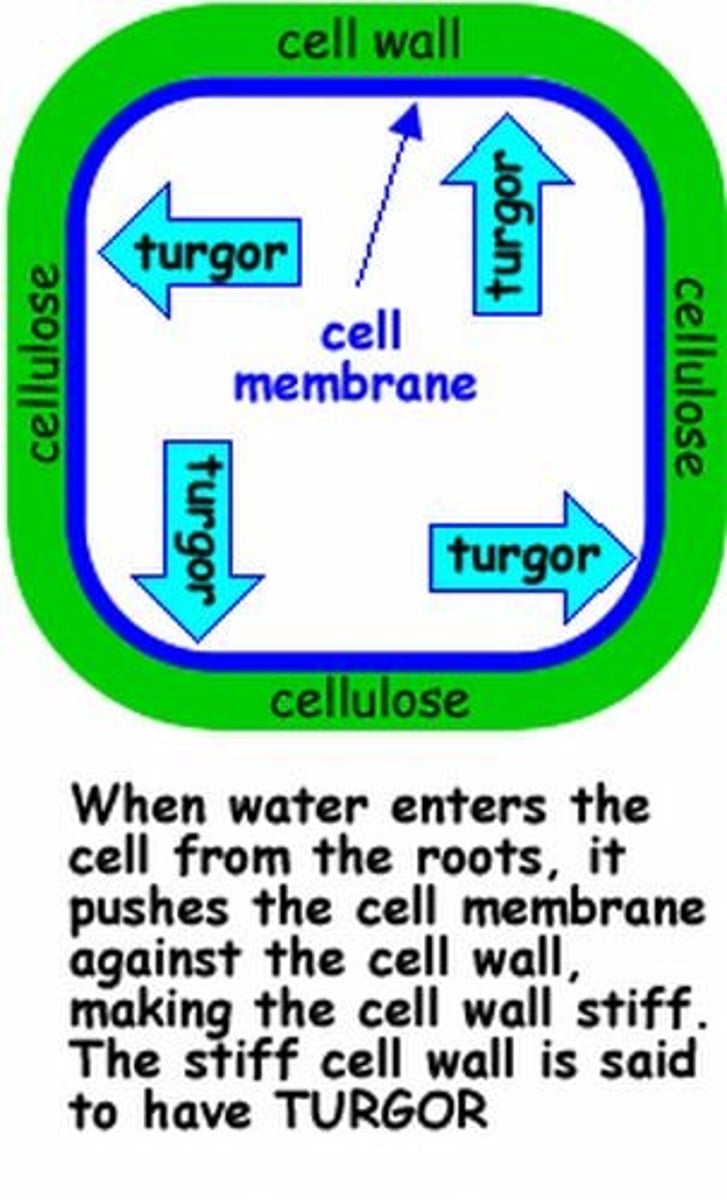
turgor pressure
the pressure the central vacuole puts on the cell membrane and cell wall of a plant cell when it takes up more water and expands
osmosis
water moves from high to low through the cell membrane
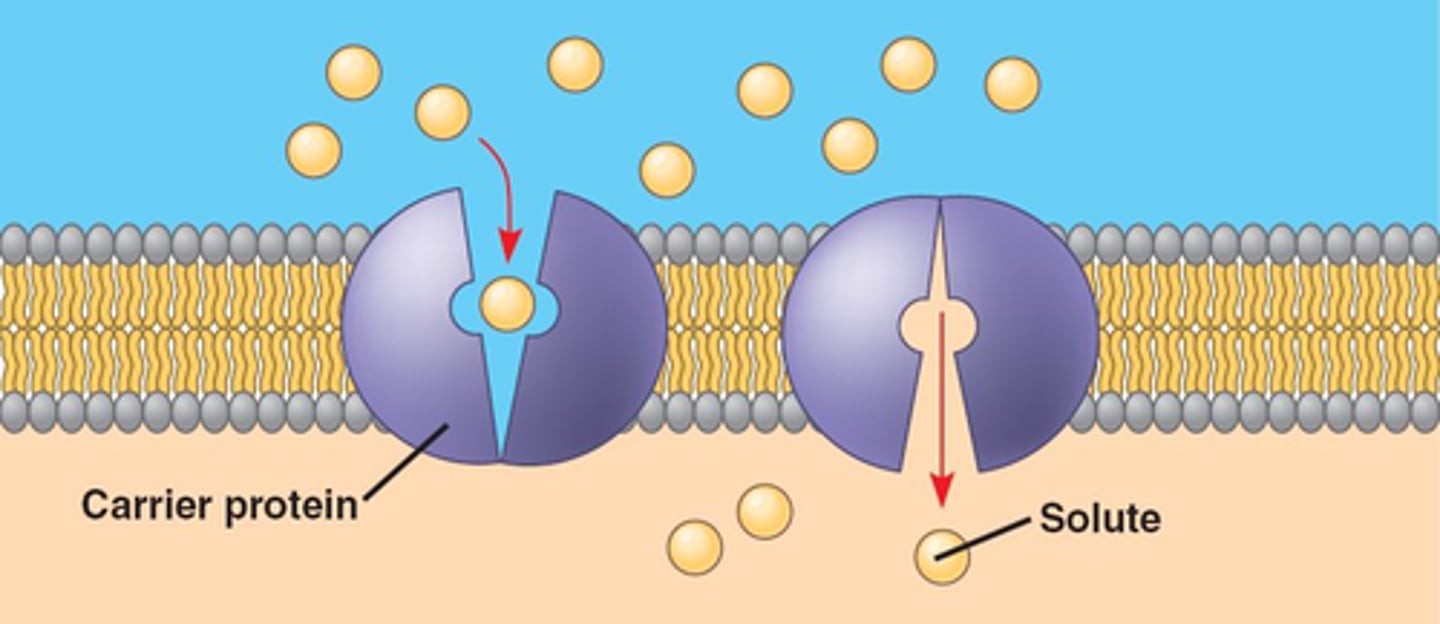
facilitated diffusion
the movement of molecules through proteins in a cell membrane from high to low concentration.
equilibrium
a state of having the same concentration of a substance when comparing two areas such as in and out of a cell
diffusion
movement of molecules from high to low through the phospholipid bilayer
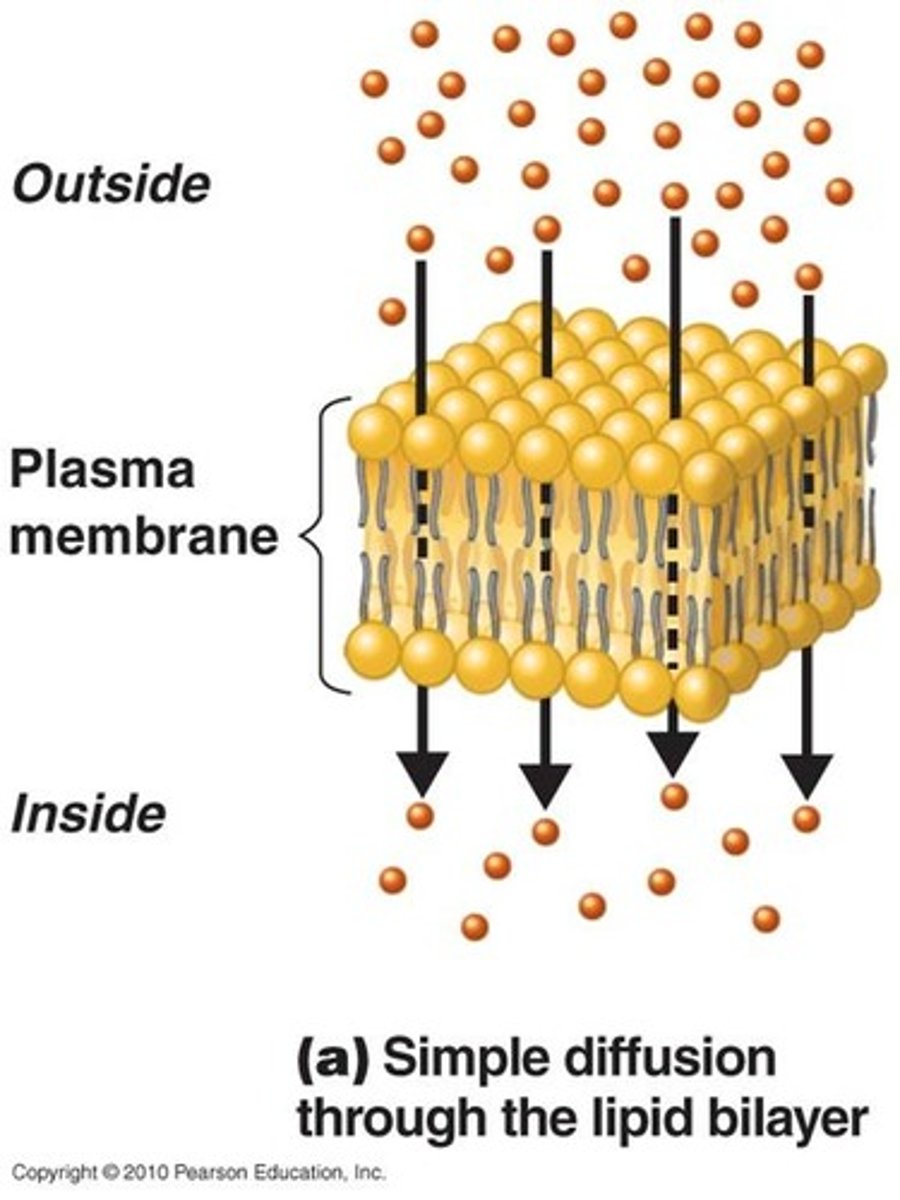
small nonpolar substances
can move from high to low through a membrane by the process of diffusion
large or polar susbtances
can move from high to low through a membrane by the process of facilitated diffusion
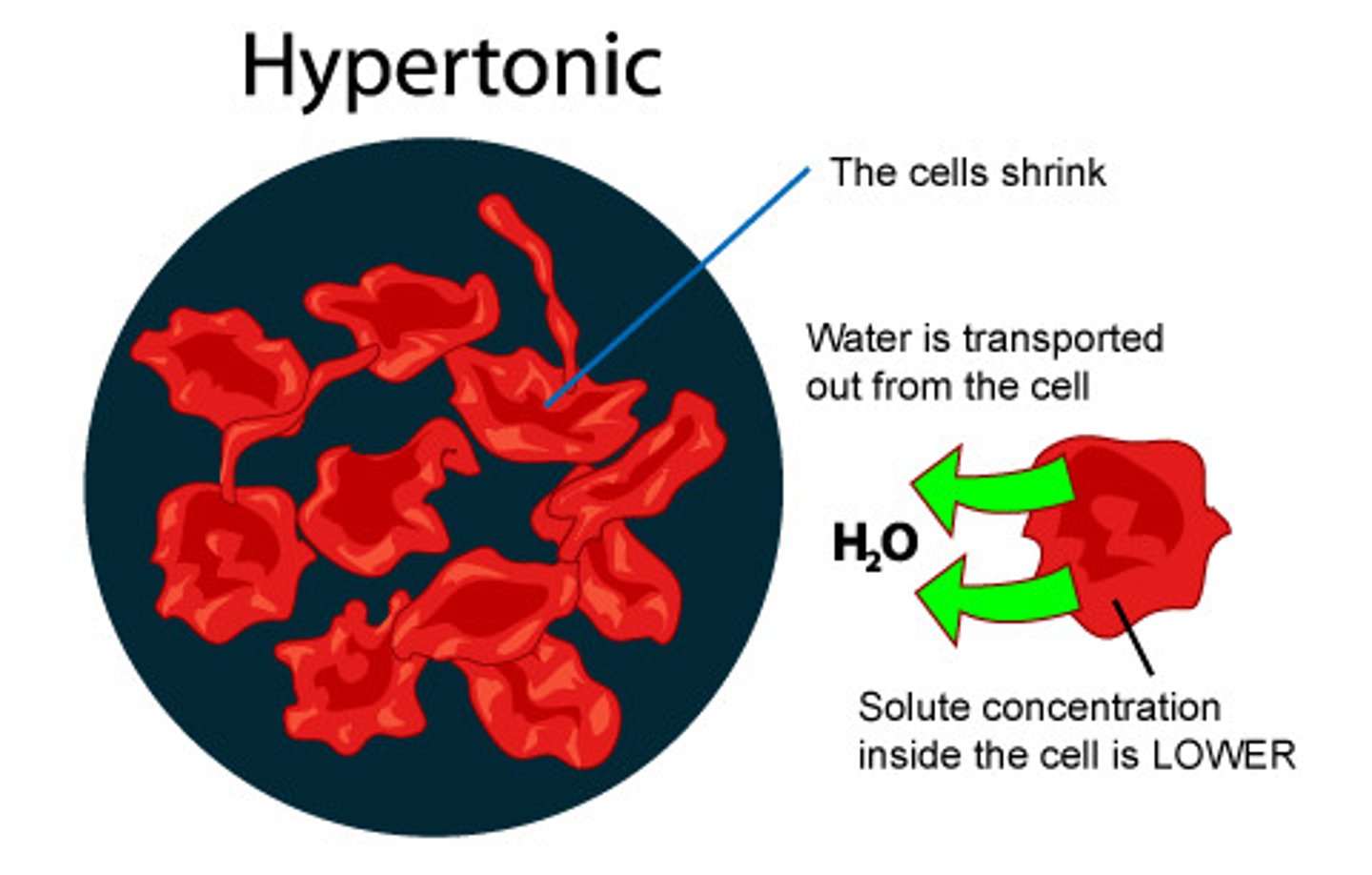
hypertonic environment
water flows out of a cell to try to reach equilibrium in this solution
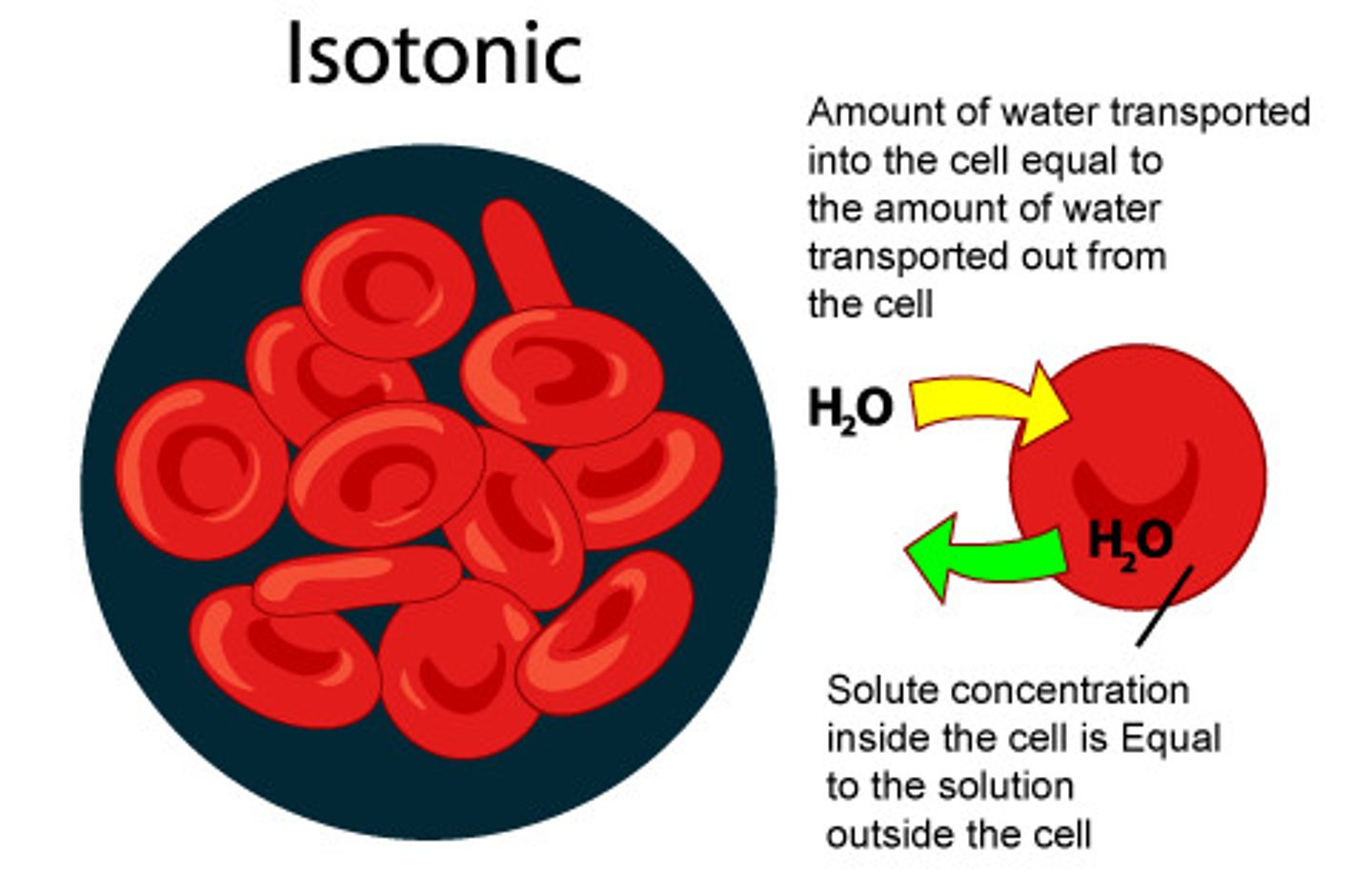
isotonic environment
water flows in/out of a cell because it is at equilibrium
ideal environment for plant cells
hypotonic environment because turgor pressure increases
ideal environment for animal cells
isotonic environment - the cell will neither have a net gain or net loss of water
concentration gradient
the differences in concentration of a substance when comparing two areas

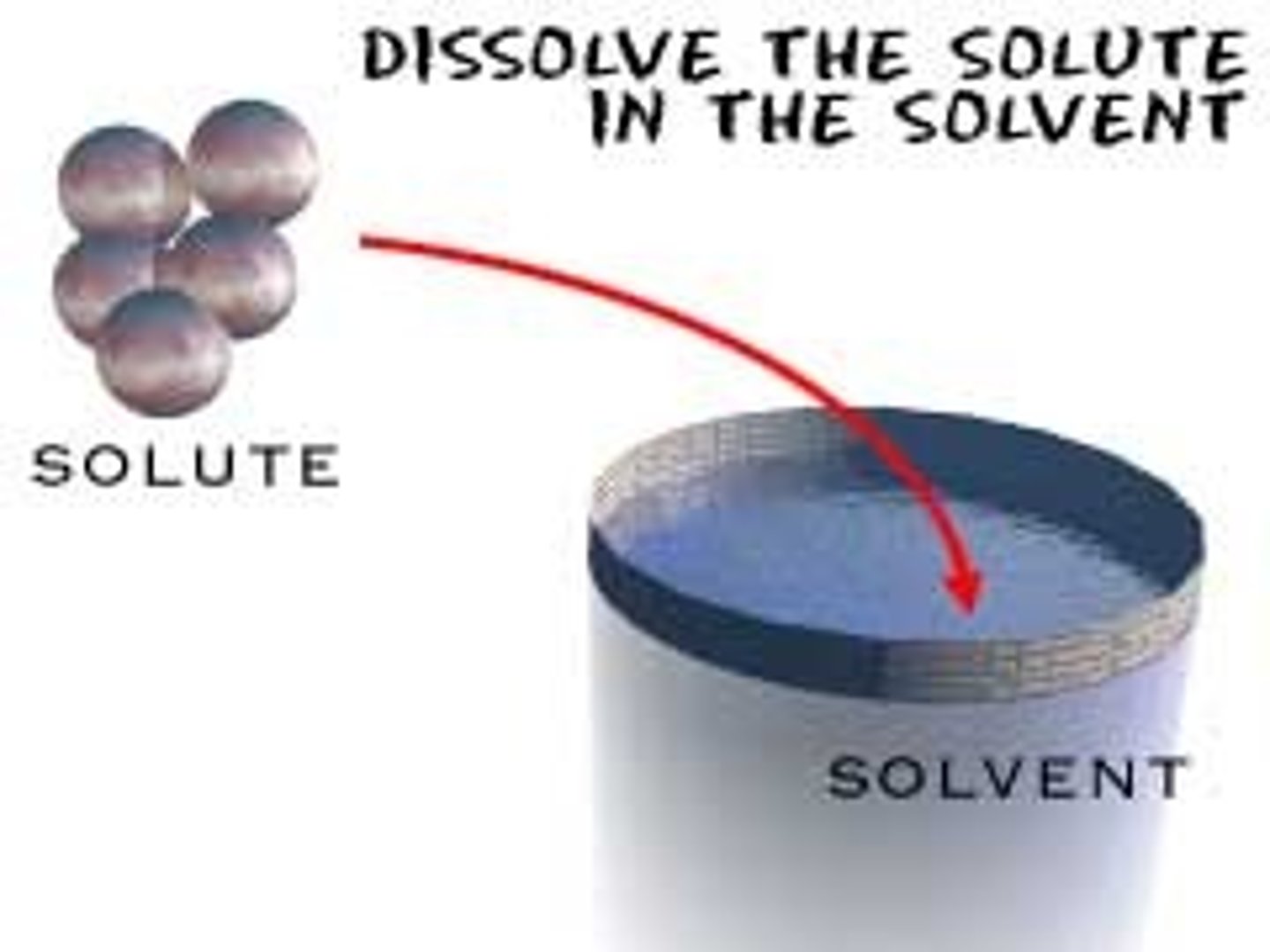
solute
the material being dissolved by the solvent

solvent
the material doing the dissolving
passive transport
a type of transport characterized by the movement of molecules down a concentration gradient (high to low) and no energy is needed.

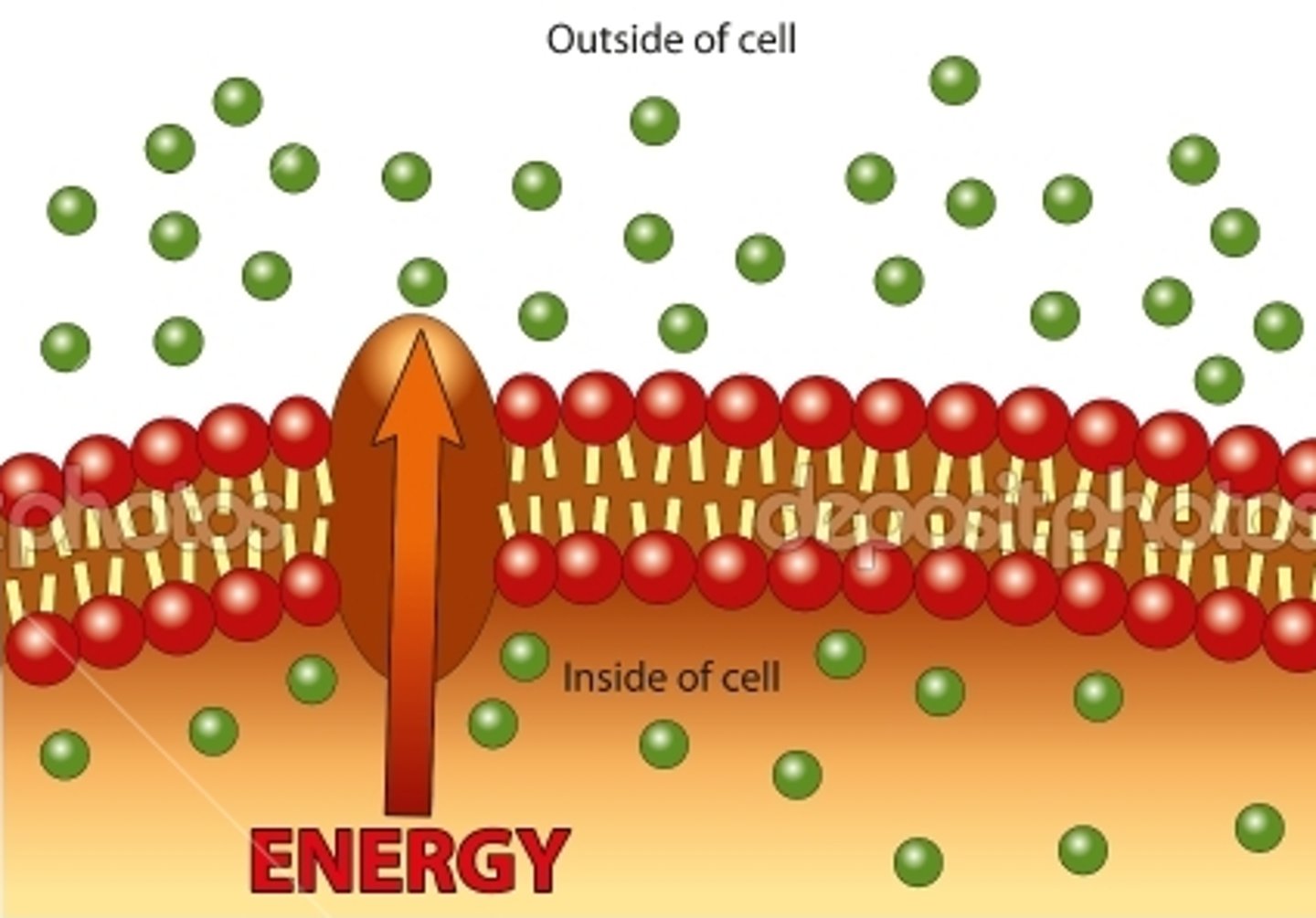
active transport
a type of transport characterized by the movement of molecules against the concentration gradient (low to high) so energy IS NEEDED
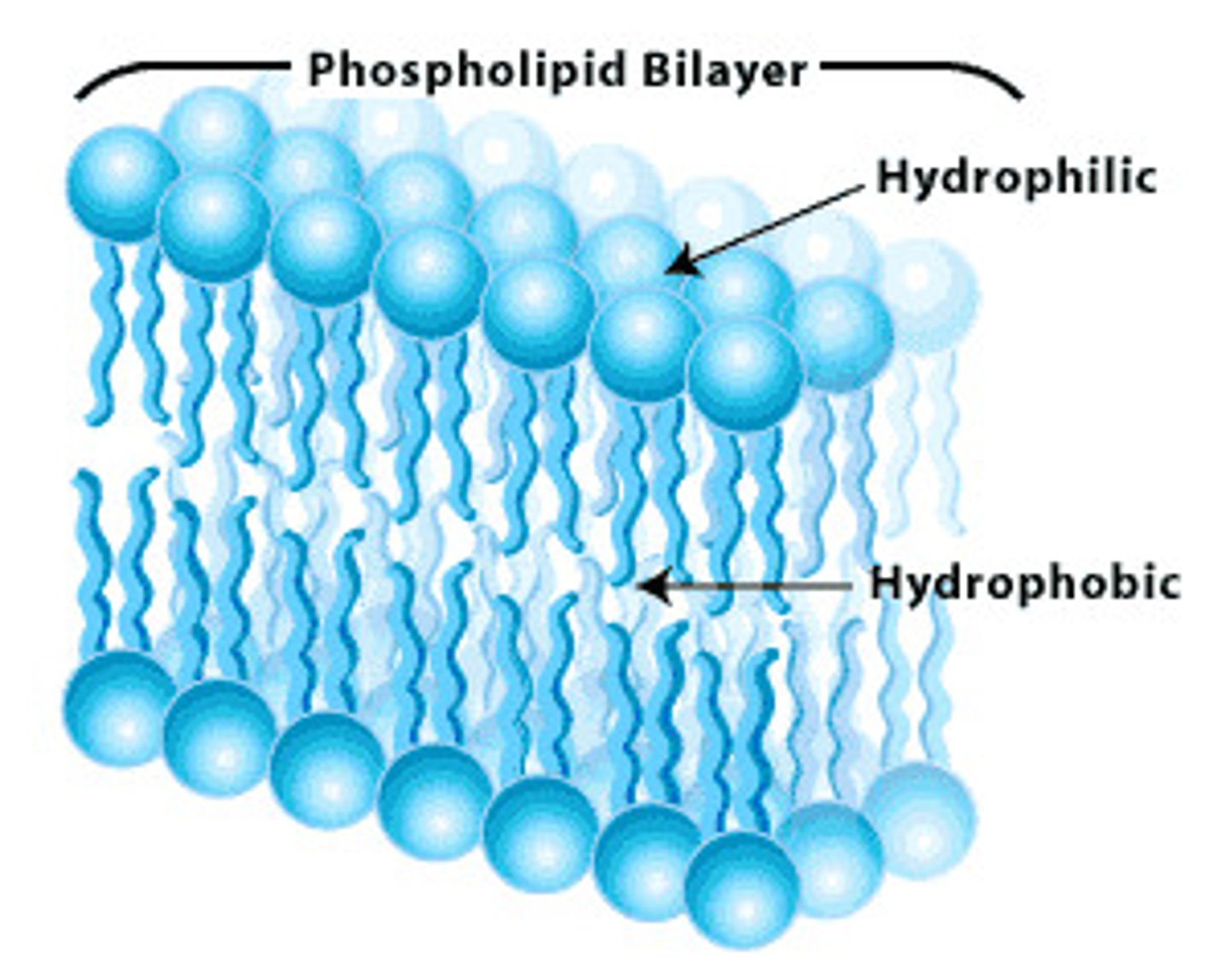
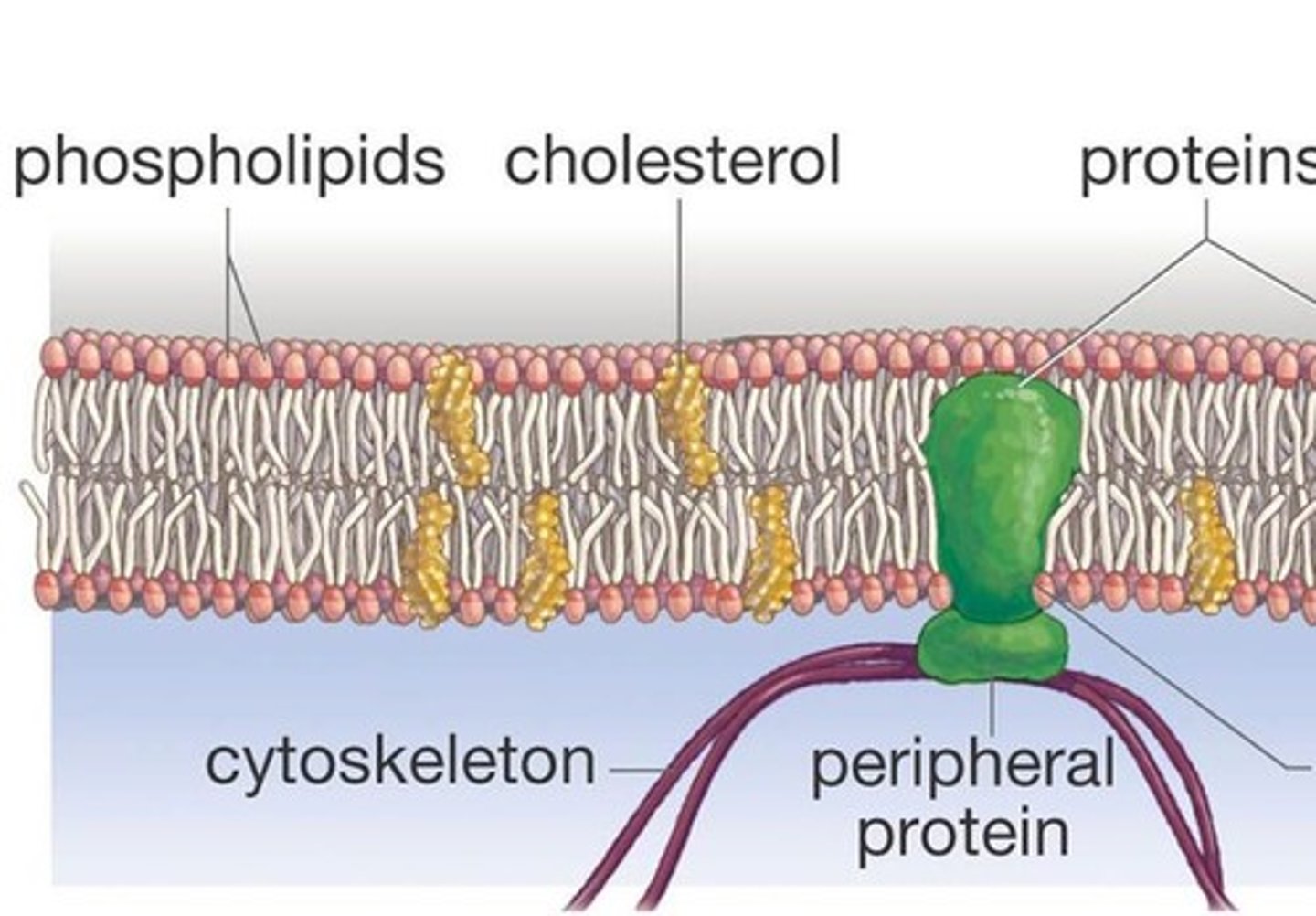
phospholipid bilayer
the main component of the cell membrane
carbohydrates
stick out of the cell membrane that acts as a name tag for a cell or used for cell to cell communication
semipermeable
the idea that the cell membrane easily lets some materials pass through it but not others
cholesterol
embedded in between the phospholipids to keep the cell membrane more fluid-like
homeostasis
the characteristic of life that the cell membrane helps the cell to achieve
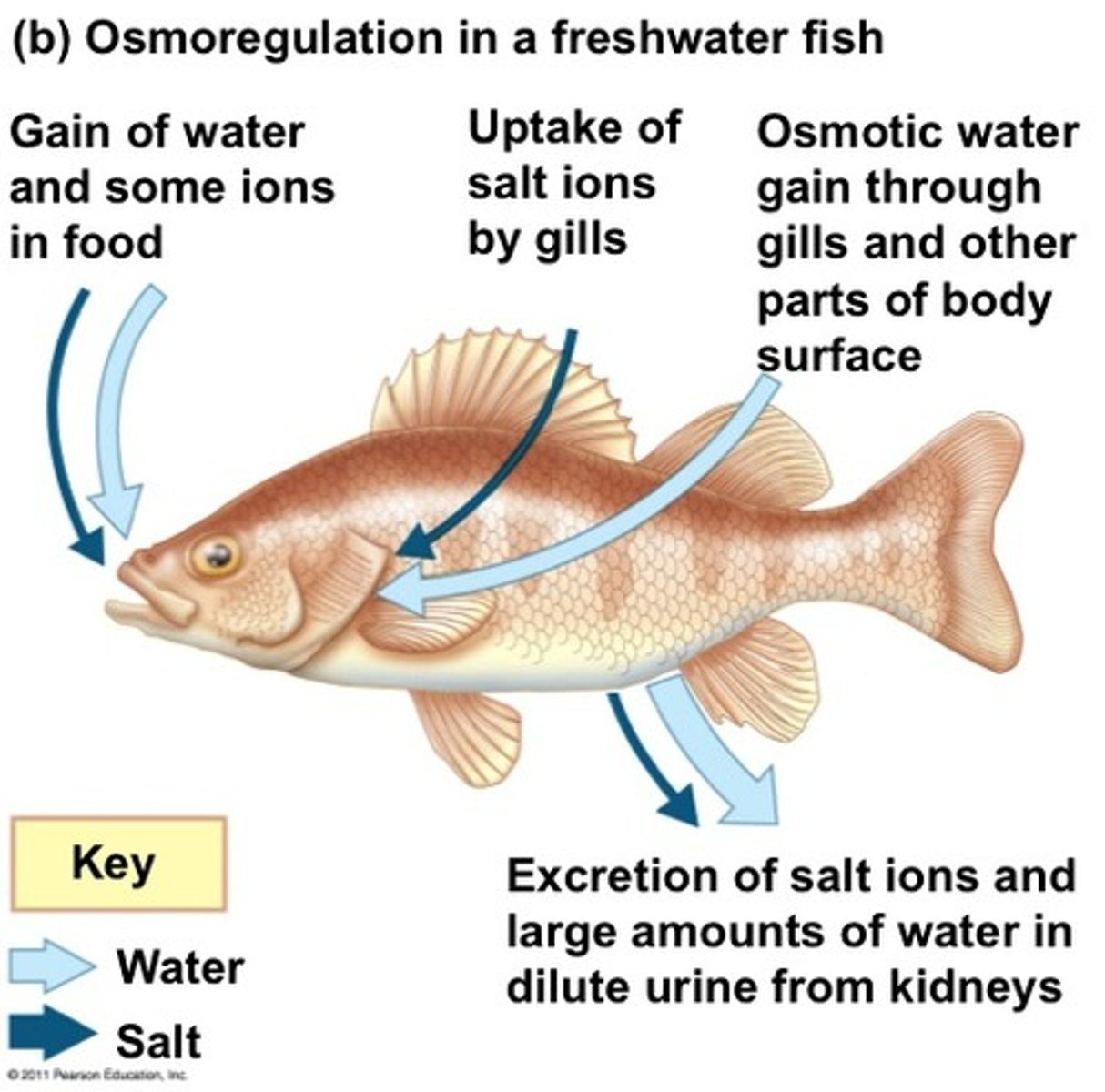
osmoregulation
the process of controlling the amount of water within a living organism; in humans the kidney has an important role in this.
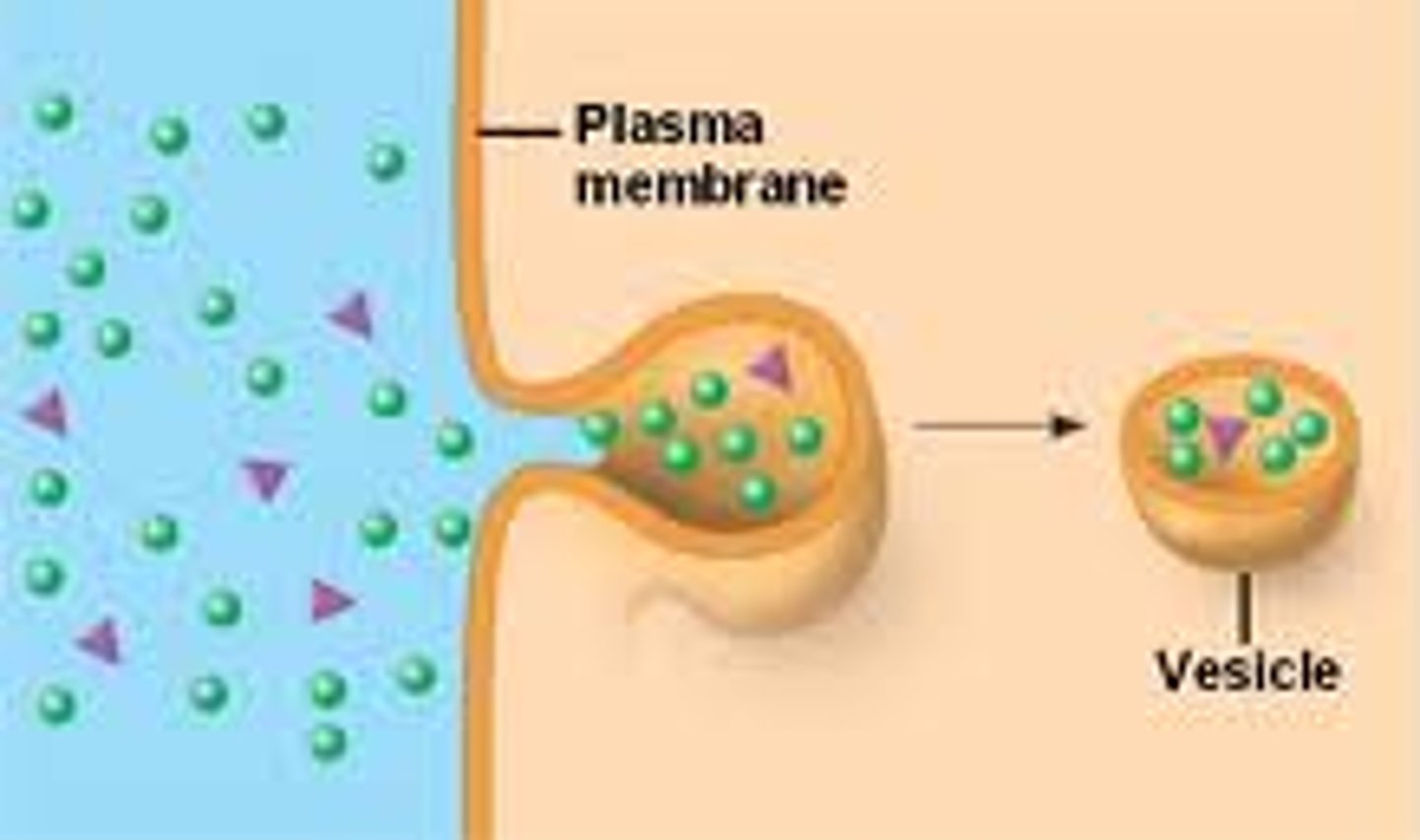
endocytosis
transport of very large materials into the cell through a vesicle

pinocytosis
transport of large amount of liquid into the cell by using a vesicle
phagocytosis
transport of large solid material into the cell by using a vesicle
exocytosis
transport of large materials out of the cell through a vesicle
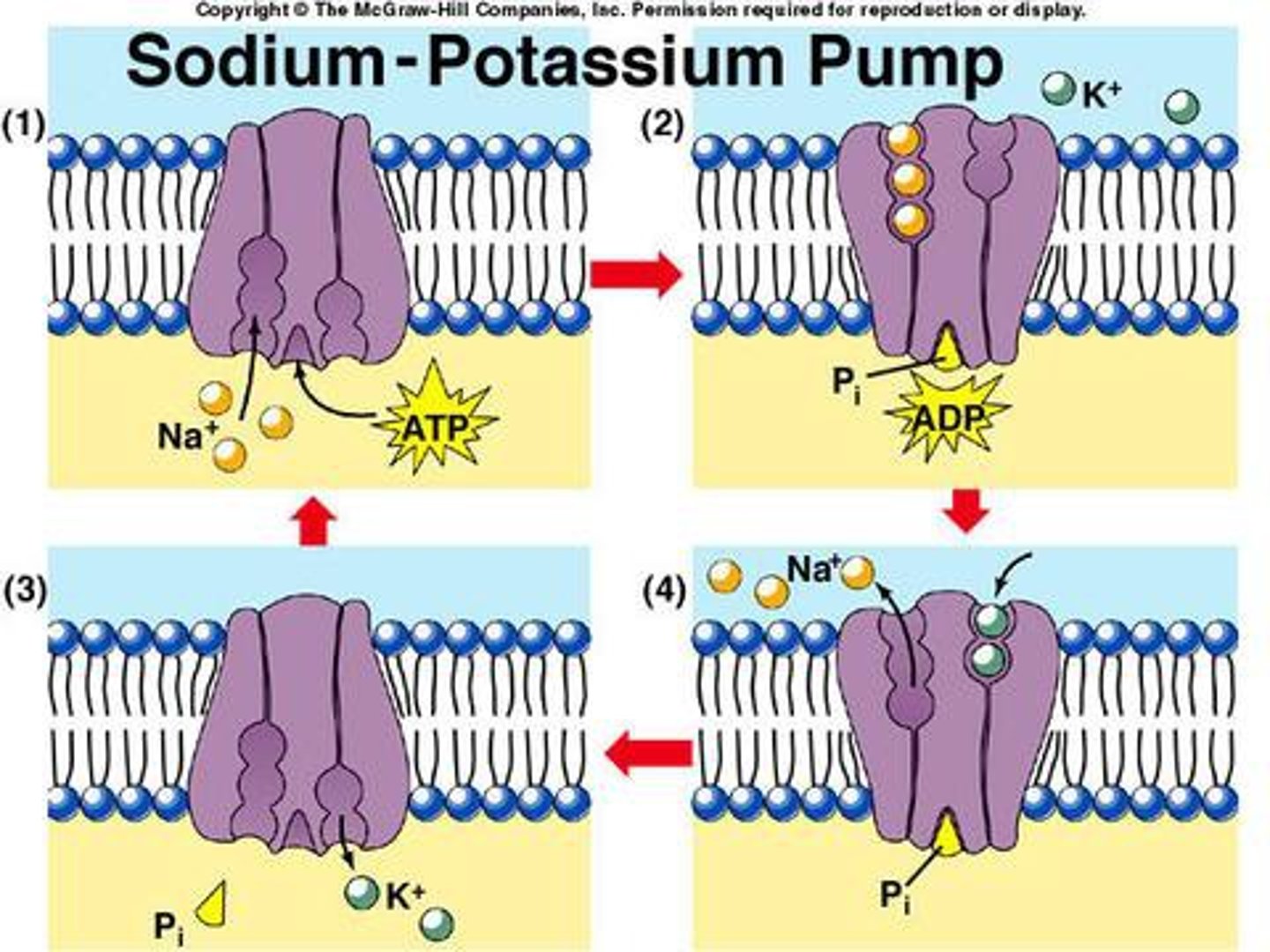
sodium potassium pump
an example of active transport where 3 sodium are pumped out where concentration is high and 2 potassium are pumped in where concentration is high