Module 14 Notes: Aggregate Expenditure Multiplier
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
aggregate expenditure equals the sum of-
consumption expenditure, C, investment, I, government expenditure on goods and services, G, and net exports, NX.
Autonomous expenditure does not respond to-
changes in real GDP and induced expenditure does respond to changes in real GDP.
Consumption plans are influenced by many factors other than disposable income. The more important influences are
Real interest rate
Wealth
Expected future income
Many factors influence U.S. imports, but in the short run, one factor dominates:
U.S. real GDP.
When autonomous expenditure (investment, government expenditure, or exports) increases-
aggregate expenditure and real GDP also increase.
The change in equilibrium expenditure also equals-
the change in real GDP
The marginal tax rate determines-
the extent to which income tax payments change when real GDP changes.
The larger the marginal tax rate, the smaller are the changes in-
disposable income and real GDP that result from a given change in autonomous expenditure.
When the price level falls, other things remaining the same, aggregate planned expenditure increases and equilibrium expenditure increases. The reason is that a change in the price level changes the-
buying power of money, the real interest rate, and the real prices of exports and imports
Autonomous expenditure is
the sum of the components of aggregate expenditure that real GDP does not influence directly.
Induced expenditure is
the sum of the components of aggregate expenditure that real GDP influences.
Consumption expenditure varies with
disposable income and real GDP and depends on the marginal propensity to consume.
Imports vary with real GDP and
depend on the marginal propensity to import.
Actual aggregate expenditure equals real GDP, but when aggregate planned expenditure differs from real GDP-
firms have unplanned inventory changes.
If aggregate planned expenditure exceeds real GDP _________________. If real GDP exceeds aggregate planned expenditure, _______________.
firms increase production and real GDP increases; firms decrease production and real GDP decreases.
Real GDP changes until-
aggregate planned expenditure equals real GDP.
When autonomous expenditure changes, equilibrium expenditure changes by a larger amount:
There is a multiplier
The multiplier is greater than 1 because
a change in autonomous expenditure changes induced expenditure.
The larger the marginal propensity to consume-
the larger is the multiplier.
The AD curve is
the relationship between the quantity of real GDP demanded and the price level when all other influences on expenditure plans remain the same.
The quantity of real GDP demanded on the AD curve is
the equilibrium real GDP when aggregate planned expenditure equals real GDP.
From the circular flow of expenditure and income aggregate expenditure is the sum of-
Consumption expenditure, C
Investment, I
Government expenditure on goods & services, G
Net Exports, NX
Aggregate expenditure =
C+ I + G + NX
Aggregate planned expenditure is-
sum of the spending plans of households, firms, & governments
planned consumption expenditure, plus planned investment, plus planned government expenditure, plus planned exports, minus planned imports
sum of induced expenditure and autonomous expenditure
We divide aggregate expenditure plans into-
Autonomous expenditure & Induced expenditure
Autonomous expenditure is
the components of aggregate expenditure that do not change when real GDP changes
Autonomous expenditure equals
investment, plus government expenditure, plus exports, plus the components of consumption expenditure and imports that are not influenced by real GDP.
Induced expenditure is
the components of aggregate expenditure that change real GDP changes
Induced expenditure =
consumption expenditure minus imports (excluding the elements of consumption expenditure and imports that are part of autonomous expenditure).
Consumption function is
the relationship between consumption expenditure and disposable income, other things remaining the same
Disposable income is-
aggregate income (GDP) minus net taxes.
Net taxes are
taxes paid to the government minus transfer payments received from the government.
The Marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is
the fraction of a change in disposable income that is spent on consumption.
MPC =
Change in consumption expenditure/ change in disposable income.
The other influences on consumption plans are:
The real interest rate
Wealth
Expected future income
When the real interest rate falls,
consumption expenditure increases and saving decreases
When the real interest rate rises,
consumption decreases and saving increases
When wealth or expected future income increases,
consumption expenditure increases
When wealth or expected future income decreases,
consumption expenditure decreases
Consumption expenditure increases when
disposable income increases
Disposable income = aggregate income— real GDP — minus net taxes,
so disposable income and consumption expenditure increase when real GDP increases
We use this link between consumption expenditure and real GDP to-
determine equilibrium expenditure
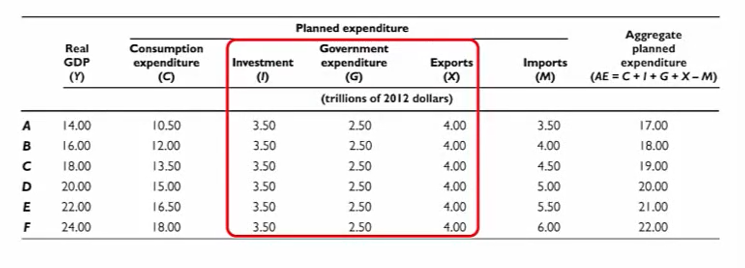
Investment, government expenditure, and exports, which are
components of autonomous expenditure, are the same at all levels of real GDP.
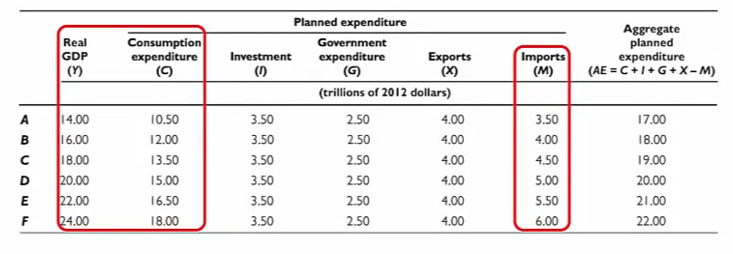
A higher level of GDP brings
higher levels of consumption expenditure and imports
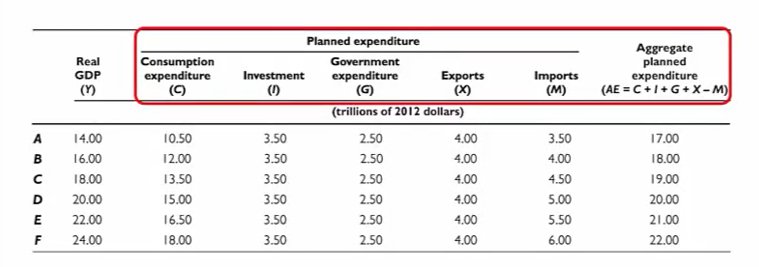
To find aggregate planned expenditure, AE, we the planned levels of
C, I, G, and X and subtract M
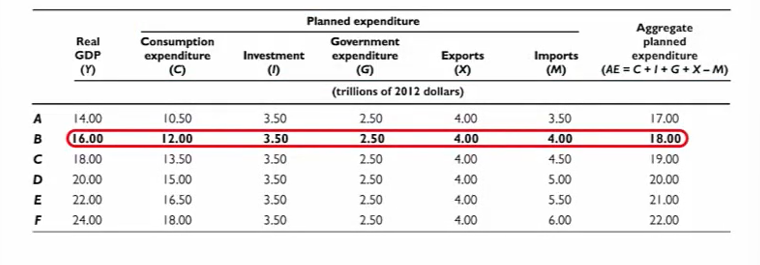
For example if real GDP is $16 trillion, aggregate planned expenditure is equal to
($12.00 + $3.50 + $2.50 + $4.00 - $4.00) trillion, which = $18.00
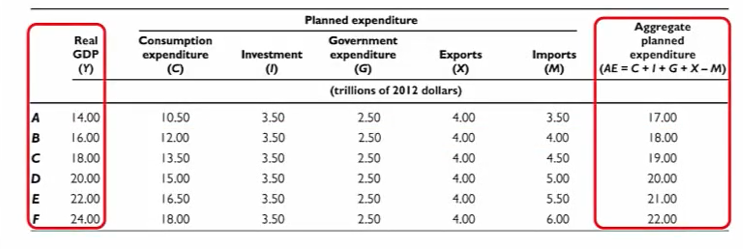
The aggregate planned expenditure curve, or AE curve is
a graph of aggregate planned expenditure of each level of real GDP
Equilibrium expenditure is
the level of aggregate expenditure when aggregate planned expenditure = real GDP
Equilibrium expenditure = the real GDP at which
the AE curve intersects the 45 degree line
At equilibrium expenditure, production plans and spending plans-
agree, and there is no reason to change production or spending
But when aggregate planned expenditure and actual aggregate expenditure are
unequal, production plans and spending plans are misaligned, and a process of convergence toward equilibrium expenditure occurs
When aggregate planned expenditure is less than real GDP
firms cut production. Real GDP decreases
When GDP decreases -
aggregate planned expenditure decreases
But real GDP decreases by more than planned expenditure
so eventually the gap between planned expenditure and actual expenditure closes.
When aggregate planned expenditure exceeds real GDP
firms increase production. Real GDP increases.
But Real GDP increases by more than
the increase in planned expenditure
Eventually the gap between ____________ and __________ is closed.
planned expenditure, actual expenditure
The multiplier is
the amount by which a change in autonomous expenditure is magnified or multiplied to determine the change in equilibrium expenditure and real GDP that it generates.
A change in autonomous expenditure brings a larger change in aggregate expenditure because-
it induces a change in consumption expenditure.
The magnitude of the multiplier is influenced by the
marginal propensity to consume — the MPC
The change in real GDP (△ Y) equals the change in
consumption expenditure (△ C) plus the change in investment (△I)
Step 1: △ Y = △ C + △ I but the change in consumption expenditure is determined by the change in-
Step 1: Real GDP and the marginal propensity to consume.
Step 2: △ C = MPC x △ Y But the change in consumption expenditure is determined by the change in
Step 2: real GDP and the marginal propensity to consume.
Step 3: To get △ Y =
MPC x △ Y + △I
Step 4: (1- MPC) x △ Y =
△I
Step 5: △ Y =
△I/ (1-MPC)
Step 6: △ Y /△I =
1/(1-MPC)
So when the MPC is 0.75, the multiplier is
△ Y /△I = 1/(1-0.75) = 1/0.25 = 4
Imports and income taxes make the
multiplier smaller
Imports make the multiplier smaller because
only expenditure on U.S. -made goods and services increases U.S. real GDP
Income taxes make the multiplier smaller because
when real GDP increases, income tax payments increase and disposable income increases by less than the increase in real GDP.
The marginal propensity to consume, the marginal propensity to import, and the marginal tax rate-
determine the multiplier
Their combined influences determines the
slope of the AE curve
The general formula for the multiplier is
△Y/△I = 1/(1- Slope of AE curve)
The AE curve is
the relationship between aggregate planned expenditure & real GDP all other influences on expenditure plans remain the same
A movement along the AE curve arises-
from a change in real GDP
The AD curve is
the relationship between quantity of real GDP demanded and the price level when all other influences on expenditure plans remain the same
A movement along the AD curve arises from
a change in the price level
Equilibrium expenditure depends on
the price level
When the price level changes, other things remaining the same, ______ ______ changes and _____ ______ changes.
aggregate planned, equilibrium expenditure
Aggregate planned expenditure changes because
a change in the price level changes the buying power of net assets, the real interest rate, and the real prices of exports and imports
When the price level changes-
the AE curve shifts
Formula: Marginal propensity to import =
change in imports/ change in real GDP
Formula: Multiplier =
change in equilibrium expenditure/ change in autonomous expenditure
General formula for the multiplier is
Multiplier = △Y/△I = 1/ (1 - Slope of AE curve)
marginal propensity to import
the fraction of an increase in real GDP that is spent on imports.
Equilibrium expenditure
occurs when aggregate planned expenditure equals real GDP.
Aggregate planned expenditure is the sum of planned _____.
D. consumption expenditure, investment, government expenditure, and exports minus imports
The consumption function is the relationship between consumption expenditure and _____, other things remaining the same.
A. disposable income
If disposable income increases from $4 trillion to $7 trillion, consumption expenditure increases from $3.5 trillion to $5.5 trillion, and nothing else changes, the marginal propensity to consume is _____.
C. 0.67
If real GDP increases by $2 million and potential GDP increases by $3 million and the marginal propensity to import is 0.2, by how much do imports change?
A. Imports increase by $400,000
Equilibrium expenditure is the level of aggregate expenditure that occurs when aggregate _____ equals _____.
C. planned expenditure; real GDP
A multiplier is the amount by which a change in any component of _____ is magnified or multiplied to determine the change in _____ and _____ that it generates.
B. autonomous expenditure; equilibrium expenditure; real GDP
The marginal tax rate is the fraction of a change in _____ that is paid in _____ - the change in _____ divided by the change in _____.
C. real GDP; income taxes; tax payments; real GDP
The consumption function shows how an increase in _____- influences ______.
C. disposable income; consumption expenditure
The marginal propensity to consume tells us by how much ______ changes when _______ changes.
D. consumption expenditure; disposable income
The components of induced expenditure are .
A. consumption expenditure, government expenditure, and exports
The aggregate planned expenditure curve increases.
A. slopes upward because induced expenditure increases as income
If real GDP _______ planned expenditure, the economy converges to equilibrium expenditure because inventories _______ and firms increase production.
C. is less than; are run down
The multiplier equals ______ divided by ______
B. 1; (1 - Slope of the AE curve)