RADT W4 Xray Films and Radiation Characteristics
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What are the 4 components of a Dental X-ray Film?
Film base → provides support for emulsion and strength
Adhesive Layer → attaches emulsion to the base
Film Emulsion → radiation absorption layer
Protective layer → protects emulsion from damage
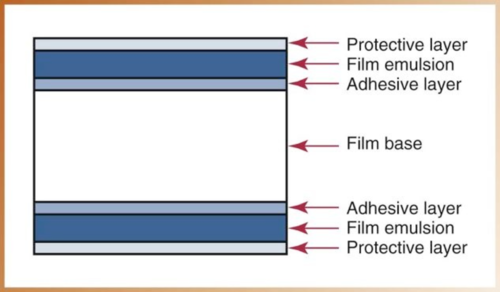
What colour is the film base? Why?
Slight blue tint which is necessary for xray image quality
What does the film emulsion consists of? What is the fx of each?
Gelatin → suspense the crystals over the film base so film processing solution can react with crystals
Silver Halide Crystals → Absorbs radiation during x-ray exposure and store energy from radiation
*Halide is sensitive to light or radiation
Define Latent Image
Latent image is the invisible image on the emulsion that is formed from the stored energy within the silver halide crystals
What are the 3 types of dental x-ray films?
Intraoral → PA, BW, Occlusal
Extraoral → Pano, Cephalometric
Duplicating
When are Size 3 films used for BW?
For adults posterior teeth when 8’s are present
Describe Occlusal films
Largest intraoral film
4x size 2
Used to examine the max and mand arch.
Film speed is determined by…(3)
Size of silver halide crystals
Thickness of Emulsion
Radiosensitive dyes
Larger crystals = faster film
faster film = less radiation exposure
What are the 6 components of the Intraoral Film Packet?
Identification dot → on the film
Paper film wrapper → surrounds film and helps protect film from light
Lead Foil → found behind the film shielding film from scatter which results in FILM FOG
Outerpackage wrapping → vinyl or paper wrapper; protects film from light and saliva
Tube side → solid white and has ID dot
Label Side → flap used to open the film packet

What are the 2 types of Extraoral Film Type?
Screen films
Nonscreen films
Describe Screen films
need a screen for exposure
place between 2 special intensifying screens in a cassette
Less radiation required to exposure film
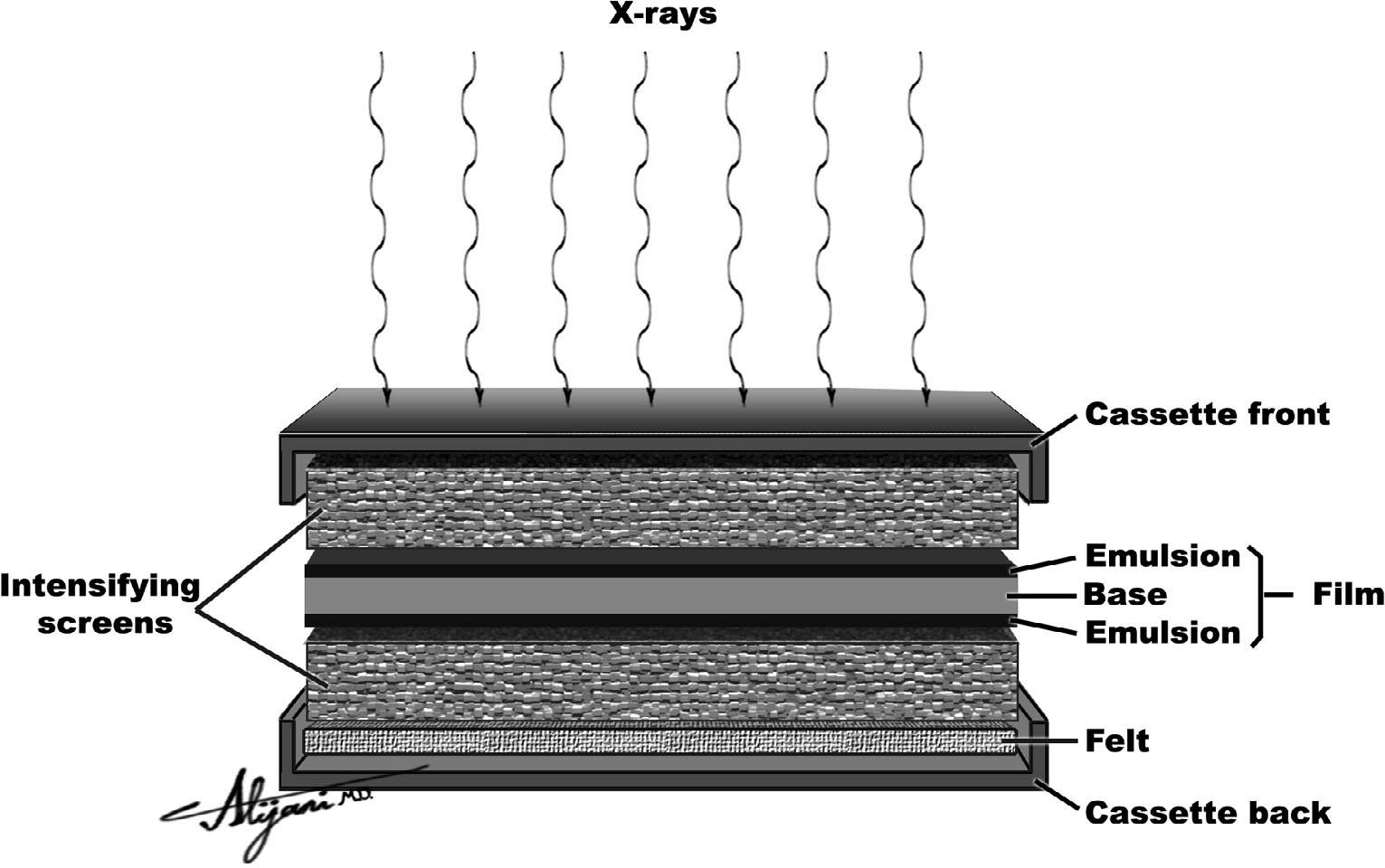
Describe the Intensifying screens of Screen Films
Smooth plastic sheet coated with tiny fluorescent crystals (phosphors)
Phosphors emit blue/green light when exposed to x-rays
How are Nonscreen Films different to Screen films? Why are they not used in dentistry?
Nonscreen films do not require intensifying screen for exposure.
Film is directly expoused to xrays
Emulsion on the film is sensitive to x-rays rather than fluorescent light
Not used in dentistry because it requires more exposure time vs screen films
Why is the cassette important for Screen Films?
They are light-tight allowing sharper images to be produced
What are duplicating films?
Duplicating film is a specialized type of X-ray film used to create exact copies of original radiographs (X-ray images).
films may need to be duplicated for insurance companies, referrals to specialists, teaching aid, etc.
The emulsion side of a duplicated film must be…
contacting the radiograph during duplicating process.
There is only one emulsion side on duplicating films.
How should unexposed films be stored?
50-70F, cool dry place
What controls the QUALITY of the central ray?
kVp = kilovoltage peak
higher kvp = more penetrating power, shorter wavelength
kV regulates speed and energy of electrons
What is the kVp range used in dental radiography?
65-100 kV
60-70 kV for digital
higher kV is used for areas that are thick or dense
Density of a radiograph is affected whenebver there is a change in …?
kVp or mA, and exposure time.
higher kVp/mA = increased density = darker films.
more electrons = darker films
Define Contrast in relation to Radiography
Contrast is how sharply dark and light areas are differentiated or separated on an image.
aka difference in density
low kVp = high contrast = black and white
high kVp = low contrast = many shades of grey
Exposure time is measured in ___ rather than in ___. Why?
measured in impulses rather than a continuous stream
because xrays are created in a series of bursts
1 impulse every 1/60th of a second =60 impulses per second
inverse relationship w kVp
ex. if kVp decreases, exposure time increases
How do we increase the amount of electrons ?
increasing mA = increase temperature = more electrons released from cathode
mA range 7-15 mA
What is the relationship between mA and exposure time?
inversely related
if mA increases , expsure time decreases
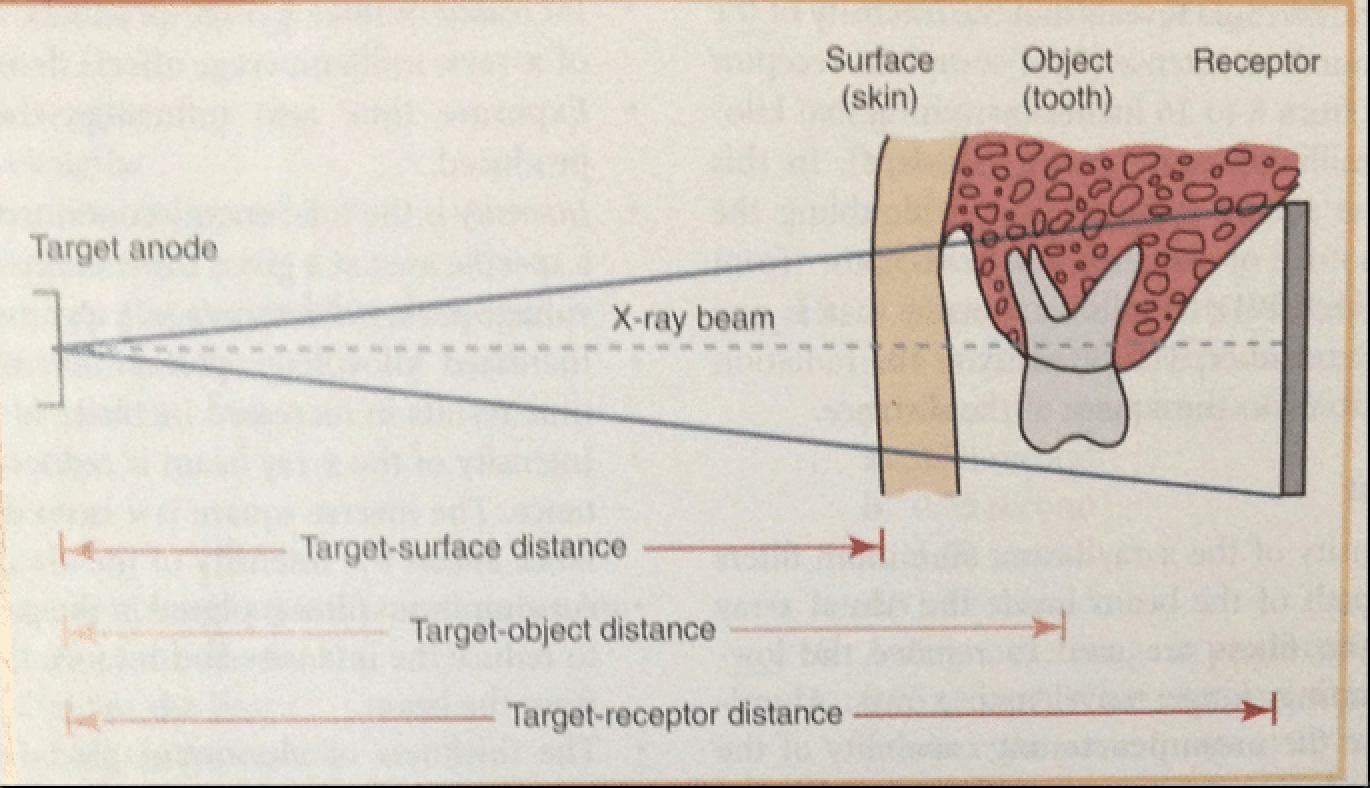
What are the 4 distances thaat must be taken into consideration when exposing a dental radiograph?
Target-Surface distance → distance between xray source and client skin
Target-object distance → distance between xray source and tooth
Target-Receptor distance → distance between xray source and film receptor
Object-film distance → distance between object and the film
If the distance between the xray tube ____ the intensity of the xray beam decreases. What is the name of this relationship?
increases; more distance, less intense
Inverse Square Law = relationship between distance and intensity
think of a flashlight on a wall
What is the definition of Inverse sqaure law.
The intensity of the radiation is inversely proportional to the SQUARE of the distance from the source of radiation
Formula:
original intensity/new intensity = new distance²/original distance ²
How do we reduce the intensity of the xray beam?
with a half-value layer = aluminum filter
placed in the path of the beam inside tube head to filter out the less penetrating, long wavelength radiation.