GY 100 lab final
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
ecological footprint
measures the amount of land and water required to sustain the people in a given area
population change equation
= (Births + Immigration) - (Deaths + Emigration)
population increase factors
high fertility rate
immigration
population decrease factors
emigration
high death rate
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
The rate at which producers capture and store chemical energy as biomass
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
The amount of biomass available for herbivores, calculated as GPP minus the energy used by producers for respiration
NPP for temperate forest
1200g/m2/yr
NPP=
𝐺𝑃𝑃−R
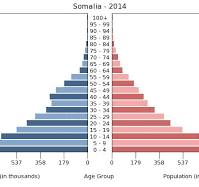
rapid growth
found in developing nations with a high birth rate
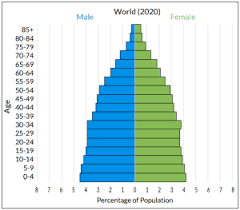
near-zero growth
found in developed countries with a low birth rate and longer lifespans
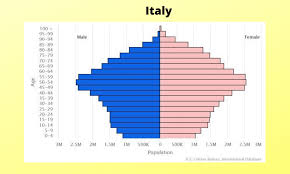
negative growth
found in developed countries like China with a low population of young people
climate
long-term atmospheric patterns
30 or more years
weather
short-term conditions
species richness
a measure of biodiversity that simply counts the number of different species present in a specific area, without considering their population sizes
species richness equation
=TS/A
TS (total number of species)
A (total area)
generalist species
an organism that can live in a wide range of environmental conditions and use a large variety of resources
specialist species
has a narrow ecological niche, meaning it has specific and limited requirements for survival, such as a particular food source or habitat
Key indicators of water quality
Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
pH levels
Nitrates and Ammonia
Fecal Coliforms
natural greenhouse effect
a process where Earth's atmosphere traps some of the sun's energy, warming the planet to a habitable temperature