4.3 Genetic diversity can arise as a result of mutation or during meiosis
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is a gene mutation?
● A change in the base sequence of DNA (on chromosomes)
● Can arise spontaneously during DNA replication (interphase)
What is a mutagenic agent?
A factor that increases rate of gene mutation, eg. ultraviolet (UV) light or alpha particles.
Explain how a mutation can lead to the production of a non-functional protein or enzyme
1. Changes sequence of base triplets in DNA (in a gene) so changes sequence of codons on mRNA
2. So changes sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide
3. So changes position of hydrogen / ionic / disulphide bonds (between amino acids)
4. So changes protein tertiary structure (shape) of protein
5. Enzymes - active site changes shape so substrate can’t bind, enzyme-substrate complex can’t form
Explain the possible effects of a substitution mutation
1. DNA base / nucleotide (pair) replaced by a different base / nucleotide (pair)
2. This changes one triplet so changes one mRNA codon
3. So one amino acid in polypeptide changes
○ Tertiary structure may change if position of hydrogen / ionic /
disulphide bonds change
OR amino acid doesn’t change
○ Due to degenerate nature of genetic code (triplet could code for same amino acid) OR if mutation is in an intron so removed during splicing
Explain the possible effects of a deletion mutation
1. One nucleotide / base (pair) removed from DNA sequence
2. Changes sequence of DNA triplets from point of mutation (frameshift)
3. Changes sequence of mRNA codons after point of mutation
4. Changes sequence of amino acids in primary structure of polypeptide
5. Changes position of hydrogen / ionic / disulphide bonds in tertiary
structure of protein
6. Changes tertiary structure / shape of protein
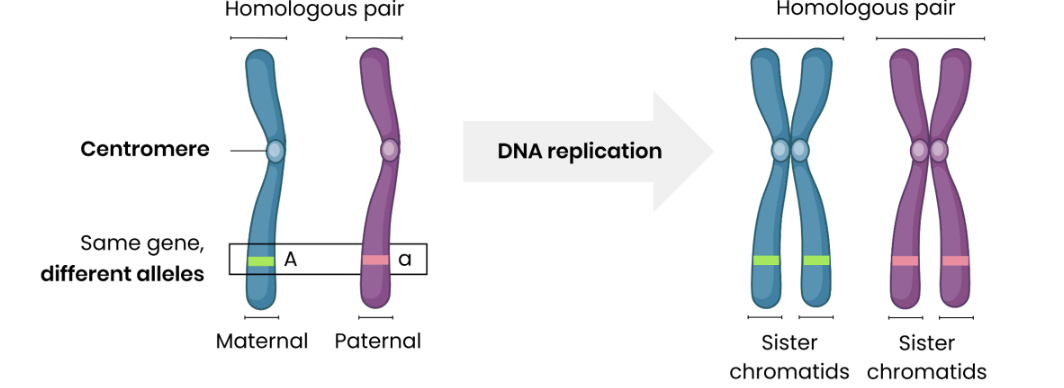
Describe features of homologous chromosomes
Same length, same genes at same loci, but may have different alleles.
Describe the difference between diploid and haploid cells
● Diploid - has 2 complete sets of chromosomes, represented as 2n
● Haploid - has a single set of unpaired chromosomes, represented as n
Describe how a cell divides by meiosis
In interphase, DNA replicates → 2 copies of each chromosome (sister chromatids), joined by a centromere
1. Meiosis I (first nuclear division) separates homologous chromosomes
○ Chromosomes arrange into homologous pairs
○ Crossing over between homologous chromosomes
○ Independent segregation of homologous chromosomes
2. Meiosis II (second nuclear division) separates chromatids
● Outcome = 4 genetically varied daughter cells
● Daughter cells are normally haploid (if diploid parent cell)
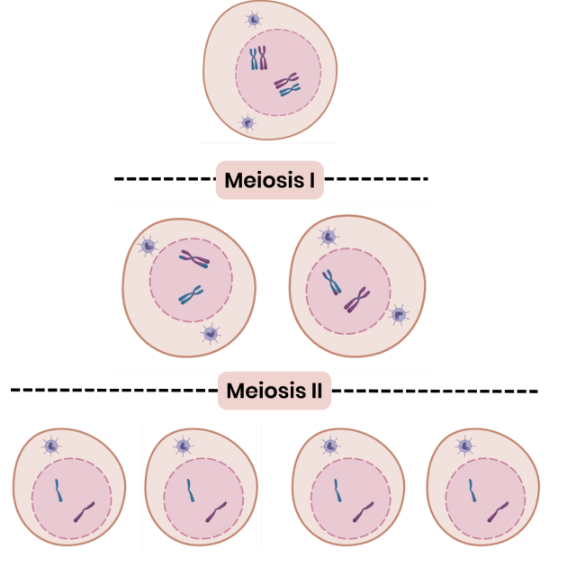
Draw a diagram to show the chromosome content of cells during meiosis
You should be able to complete diagrams showing the chromosome contents of cells after the first and second meiotic division, when given the chromosome content of the parent cell.
In the example shown:
● Parent cell has 4 chromosomes = 2 homologous pairs
● These appear as X shapes due to DNA replication
Explain why the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis
Homologous chromosomes are separated during meiosis I (first division).
Explain how crossing over creates genetic variation
● Homologous pairs of chromosomes associate / form a bivalent
● Chiasmata form (point of contact between (non-sister) chromatids)
● Alleles / (equal) lengths of (non-sister) chromatids exchanged between chromosomes
● Creating new combinations of (maternal & paternal) alleles on chromosomes
Explain how independent segregation creates genetic variation
● Homologous pairs randomly align at equator → so random which chromosome from each pair goes into each daughter cell
● Creating different combinations of maternal & paternal chromosomes / alleles in daughter cells
Other than mutation and meiosis, explain how genetic variation within a species is increased
● Random fertilisation / fusion of gametes
● Creating new allele combinations / new maternal and paternal chromosome combinations
Explain the different outcomes of mitosis and meiosis
1. Mitosis produces 2 daughter cells, whereas meiosis produces 4 daughter cells
○ As 1 division in mitosis, whereas 2 divisions in meiosis
2. Mitosis maintains the chromosome number (eg. diploid → diploid or haploid → haploid) whereas meiosis halves the chromosome number (eg. diploid → haploid)
○ As homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis but not mitosis
3. Mitosis produces genetically identical daughter cells, whereas meiosis produces genetically varied daughter cells
○ As crossing over and independent segregation happen in meiosis but not mitosis
Explain the importance of meiosis
● Two divisions creates haploid gametes (halves number of chromosomes)
● So diploid number is restored at fertilisation → chromosome number maintained between generations
● Independent segregation and crossing over creates genetic variation
How can you recognise where meiosis and mitosis occur in a life cycle?
● Mitosis occurs between stages where chromosome number is maintained
○ Eg. diploid (2n) → diploid (2n) OR haploid (n) → haploid (n)
● Meiosis occurs between stages where chromosome number halves
○ Eg. diploid (2n) → haploid (n)
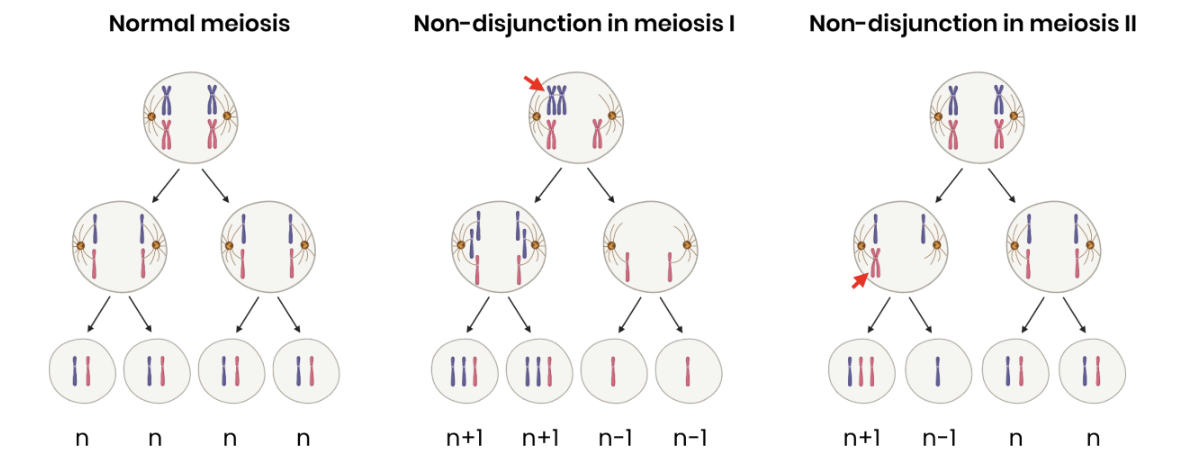
Describe how mutations in the number of chromosomes arise
● Spontaneously by chromosome non-disjunction during meiosis
● Homologous chromosomes (meiosis I) or sister chromatids (meiosis II) fail to separate during meiosis
● So some gametes have an extra copy (n+1) of a particular chromosome and others have none (n-1)
Suggest how the number of possible combinations of chromosomes in daughter cells following meiosis can be calculated
2^n where n = number of pairs of homologous chromosomes (half the diploid number)
Suggest how the number of possible combinations of chromosomes
following random fertilisation of two gametes can be calculated
(2^n)²
2 where n = number of pairs of homologous chromosomes (half the diploid number)