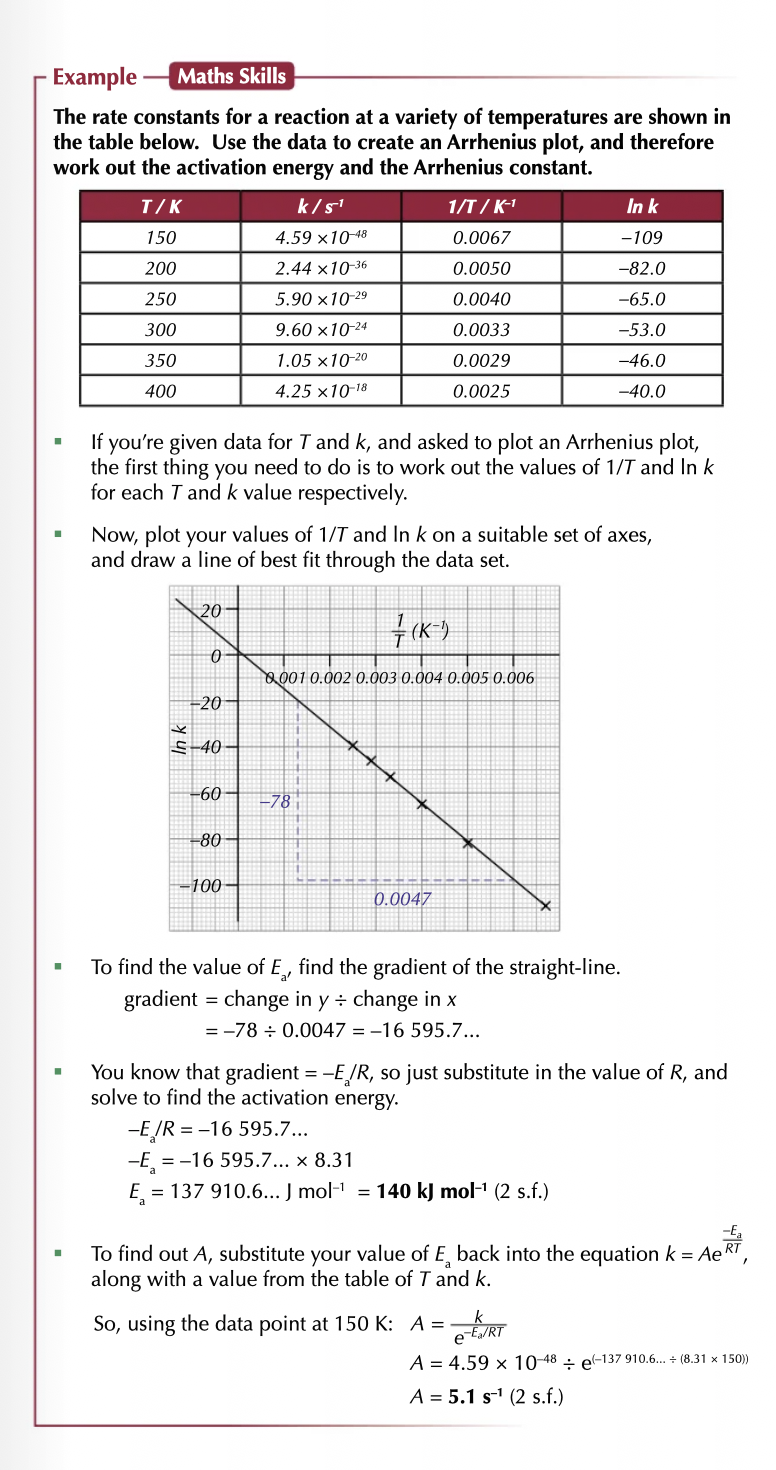
Arrhenius equation
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What is the Arrhenius equation?
box) shows how the rate constant (k) varies with temperature (T)) and activation energy
(Ea) the minimum amount of kinetic energy particles need to react).
What is the equation ?

The rate constant and activation energy
As the activation energy, Ea gets bigger what happens to rate constant ?
As the activation energy, Ea gets bigger, Rate constant gets smaller.
Few reactant particles will have sufficient energy to react in a reaction with a high activation energy. Therefore, the reaction will only occur in a small number of collisions and at a slow rate.
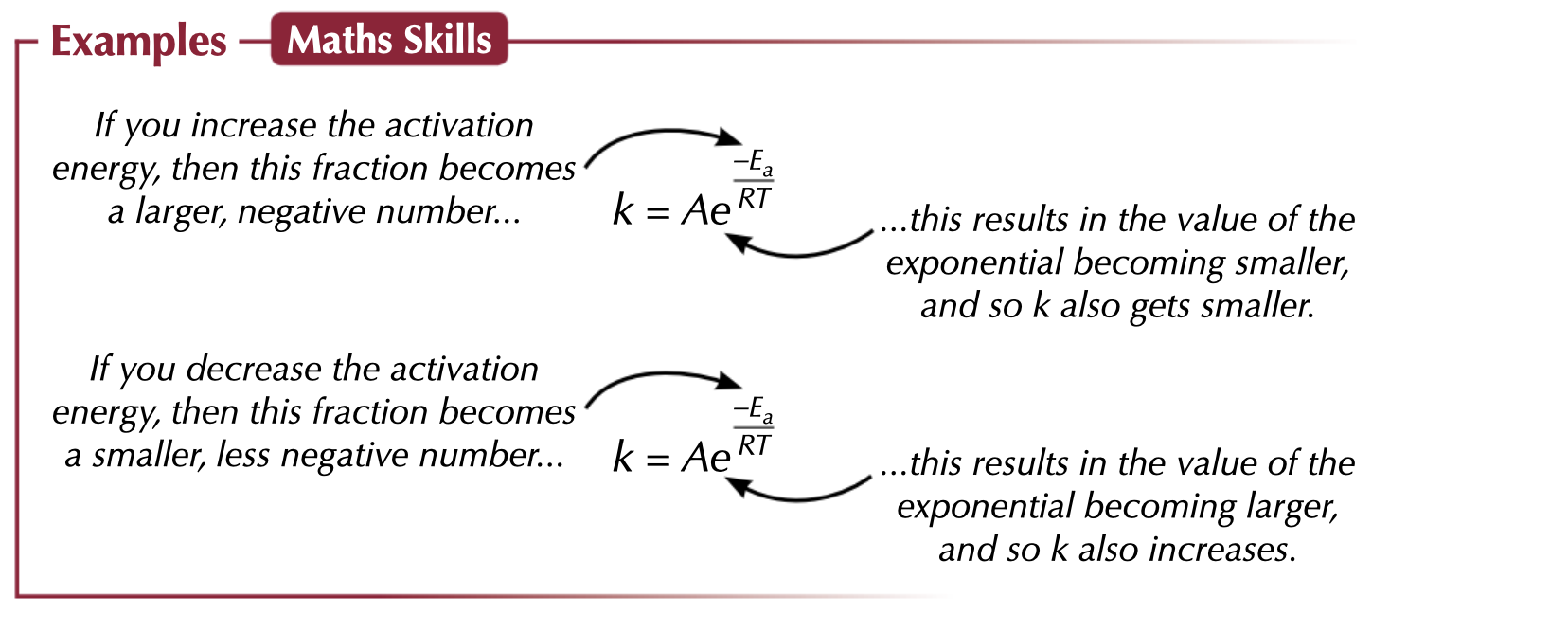
The rate constant and temperature
The equation also shows that as the temperature rises, k increases.
Higher temperatures
mean reactant particles move around faster and with more energy so they're more likely to collide and more likely to collide with at least the activation energy, so the reaction rate is higher.
re-arrange to find Ea
Ea= (In (A) - In (k)) x RT
A=) Arrhenius constant
k) rate constant

re-arrange to find temperature

Arrhenius Plot using y = mx+c
m = Ea/ R
x = 1/t c
c = Arrhenius constant