PT 536 Progressive Lesions of the CNS PT Implications
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
reading, body orientation, sensory information, language
Brain tumor impairments consistent with the parietal lobe
thinking, speaking, reasoning, problem solving, compassion
Brain tumor impairments consistent with the frontal lobe
vision
Brain tumor impairments consistent with the occipital lobe lobe
coordination, balance, vestibular, attention
Brain tumor impairments consistent with the cerebellum
breathing, temperature, heart rate
Brain tumor impairments consistent with the brainstem
memories, hearing, behavior, emotions
Brain tumor impairments consistent with the limbic system
headaches, seizures, changes in personality/cognition, changes related to elevated ICP
General clinical symptoms associated with a brain tumor
nausea/vomiting, changes in cranial n function, visual changes, alterations of consciousness
signs of increased ICP
worse in morning, better at night, behind eyes, worsens with activity
common themes with headaches associated with brain tumors
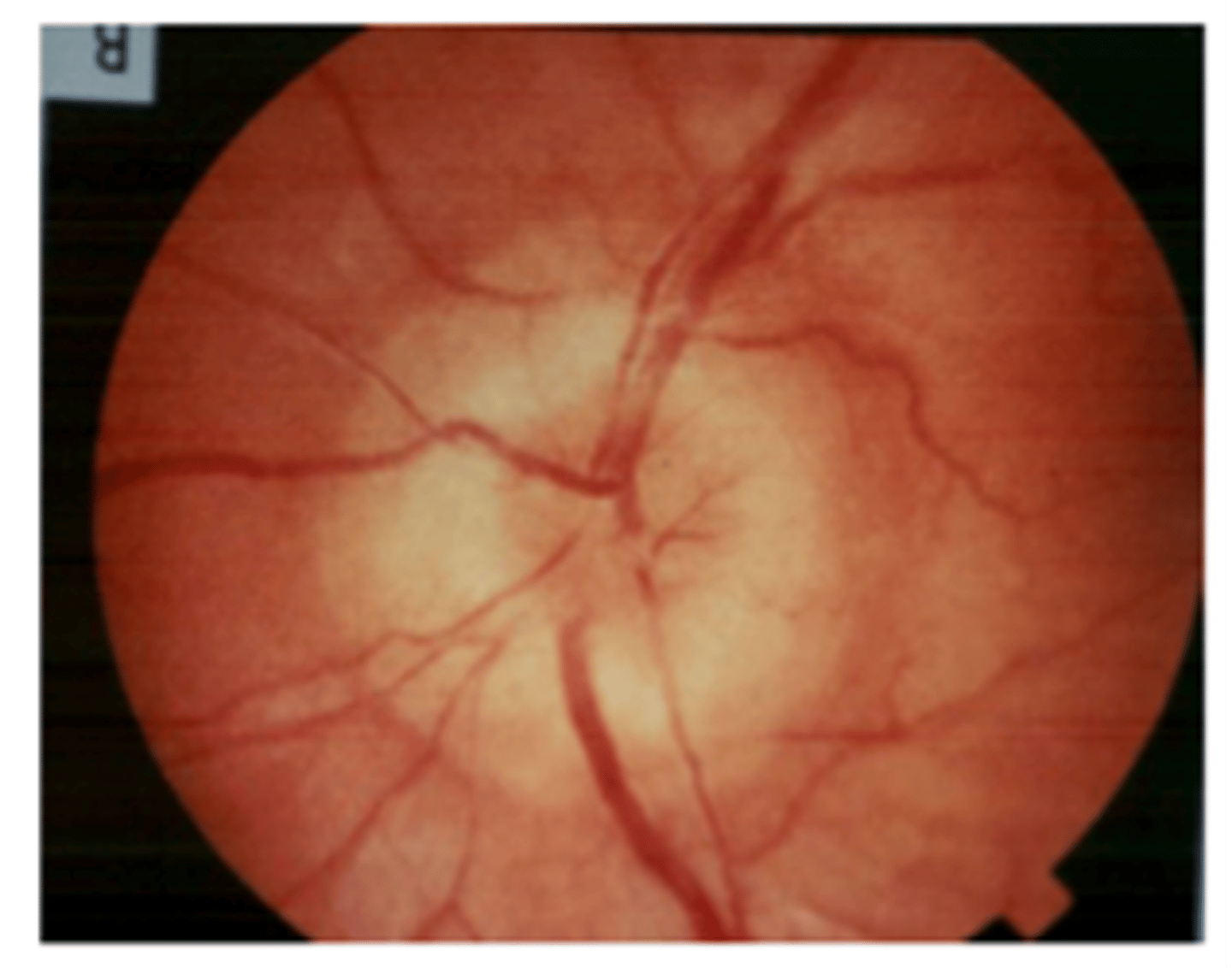
papilledema
swelling of the optic disc, seen in 75% of people with brain tumors
MRI
Most informative diagnostic tool for brain tumors
gadolinium
contrast enhancement used with MRI to distinguish tumors from surrounding area.
CT
diagnostic tool that only really detects larger tumors or things associated with tumors like hydrocephalus or herniation of the brainstem
PET scans
used to estimate boundaries of a tumor as well as track how fast a tumor is growing
fluorodeoxyglucose
radiopharmaceutical used in PET scanning
surgery, radiation, chemotherapy
3 main treatments for primary brain tumors
surgery
usual initial step to tx brain cancer if it is large enough
corticosteroids
given to patients after surgery to remove brain tumor in order to reduce swelling in the brain
radiation
treatment following the removal of a tumor to reduce the risk that the tumor will come back
stereotactic radiosurgery
use of a specialized instrument to locate and treat targets in the brain
"it depends"
prognosis for brain tumors
70%
1 year survival rates for grade 3 glioblastomas
50%
1 year survival rates for grade 4 glioblastomas
40%
2 year survival rates for grade 3 glioblastomas
15%
2 year survival rates for grade 4 glioblastomas
10-20%
5 year survival rates for grade 3 glioblastomas
rare
5 year survival rates for grade 4 glioblastomas
worse for metastatic
prognosis for metastatic brain tumors versus primary brain tumors
encourage mobility but;
pts may have weakness, paralysis, decreased sensation, and pain as well as limitation in daily activities
PT considerations for patients with brain tumors (metastatic and primary)
family training, home mobility for as long as possible
if an individual with a brain tumor has a poor prognosis, what should PT focus on?
functional interventions, prior level of function and exercises
if an individual with a brain tumor has a high survival rate, what should PT focus on?
3x/week for 30-60 moderate to vigorous exercise
for most outcomes, what would the recommended dose of exercise be for patients with cancer when only doing aerobic exercises?
meningitis
inflammation of the meninges of the brain and spinal cord
neck stiffness, headache, high fever
top 3 clinical symptoms of meningitis
high pitched cry and neck stiffness
common way to recognize meningitis in babies
photophobia, nausea/vomiting, confusion and altered mental state
3 advanced symptoms of meningitis
jolt of accentuation of headache (JAH)
headache increased when patient rotates the head two or three times in a second
OUT
Is JAH better for ruling OUT or ruling IN meningitis ?
Kernig's sign, Brudzinski sign
two clinical signs that are good for ruling IN meningits
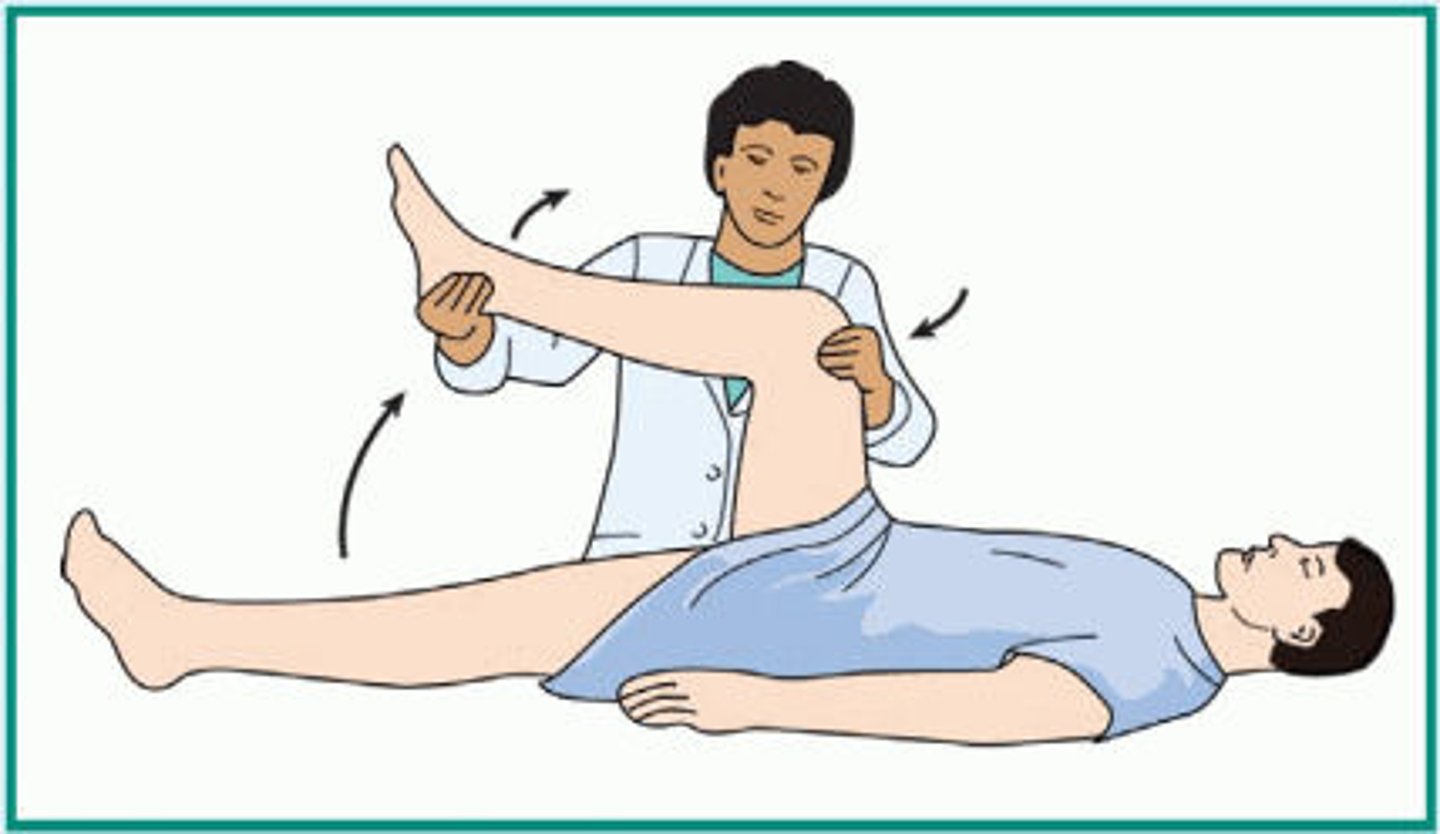
Kernig's sign
a diagnostic sign for meningitis marked by the person's inability to extend the leg completely when the thigh is flexed upon the abdomen and the person is sitting or lying down
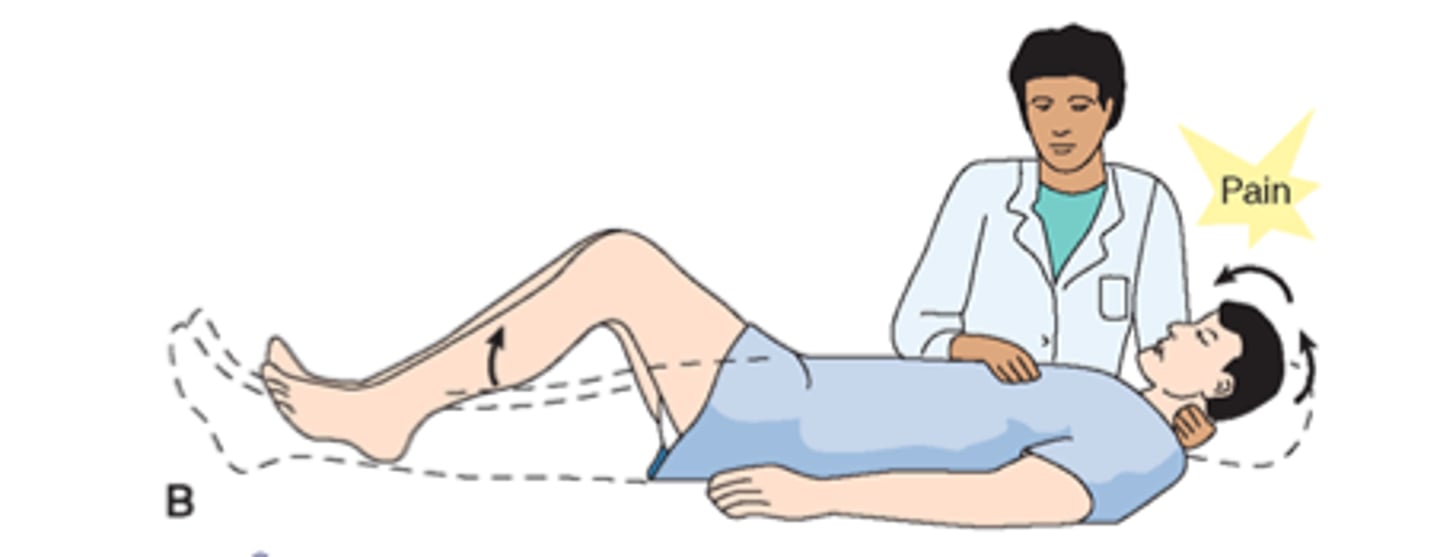
brudzinski's sign
pain with resistance and involuntary flex of hip/knee when neck is flexed to chest when lying supine
lumbar puncture CSF
best diagnostic to confirm meningitis
gram stain
test taken at the same time as a lumbar puncture due to faster results
potentially - may need to rule out tumors, strokes, etc
is it necessary to perform an MRI or CT on an individual with suspected meningitis?
septicemia
bacteria in blood that cause extremely cold hands and feet, limb pain, and mottled skin; IMMEDIATE REFERRAL
MEDICAL EMERGENCY
• Appropriate antibiotic and steroids
• Antibiotic therapy immediately
• Dexamethasone
Treatment for Bacterial Meningitis
decrease inflammation/swelling in the SA space
Purpose of dexamethasone in bacterial meningitis treatment
supportive treatments, corticosteroids reduce morality
Treatment for viral Meningitis
control ICP
general treatment consideration for meningitis
fatal 5-25%, neurologic sequelae 75%
Prognosis for bacterial meningitis
cardiorespiratory failure, sepsis
specific complication seen in 40% of bacterial meningitis cases
blindness, permanent hearing loss, developmental impairments, hydrocephalus, hemiparesis, tetraparesis
long term bacterial meningitis impairments seen in children
age, health
prognosis for bacterial meningitis depends on what two factors?
generally okay
prognosis for viral meningitis
hearing
sometimes, those with viral meningitis will have these impairments which will typically resolve after time
severe disturbance of consciousness, intracranial swelling, cerebral hemorrhage, PNA, age over 60 (death occurring 2 weeks after diagnosis)
indicators of poor prognosis for meningitis
Encephalitis
viral invasion or hypersensitivity initiated by a virus
False
True or False? Viral meningitis typically has more serious symptoms than encephalitis.
ticks & mosquitos (West Nile, Lyme), Herpes Simplex Virus
Common sources of encephalitis
brainstem, thalamus, cerebella
West Nile virus attacks neurons in what part of the brain?
limbic, frontal, temporal
Herpes Simplex virus attacks neurons in what part of the brain?
headache, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness if untreated
General symptoms of encephalitis
paresis, aphasia, ataxia, seizures, hallucinations, memory issues
Neurologic signs/symptoms that accompany encephalitis
look at CSF, MRI
How so we diagnose encephalitis
IgM antibodies, viral particles
what will be found in CSF when an individual has encephalitis?
cerebral swelling, vascular damage, activity in brain tract
what will MRI show for encephalitis?
only show damage until damage is already severe
Why are CT scans not good for diagnosing encephalitis?
"it depends"
Treatment for encephalitis
supportive care (swelling, inflammation management, mosquito control)
Most common encephalitis treatment
Acvclovir
Medication that decreases effects of encephalitis causes by herpes simplex virus
Pro: helps with swelling
Cons: lowers body's immune response, harder to fight infection
pros and cons of using corticosteroids to treat encephalitis
"it depends"
Prognosis of Encephalitis
10-50%
Overall recovery of encephalitis
excellent
Recovery from Mumps Encephalitis
moderate/good
prognosis of west nile virus
fatal 10-20%, remaining neurologic involvement in 50%
prognosis of herpes simplex encephalitis
ataxia, myoclonic jerks, weakness and paralysis, cognitive impairments, emotional disturbances, sleep abnormalities, hallucinations
Clinical symptoms of prion disease
sporadic, inherited, acquired by infection
three types of prion disease
apathy, anxiety, mood changed, decreases ability to want to eat, ability to concentrate
Early symptoms of prion disease
expression of apprehension
constant symptom of prion disease
Postmortem Examination, Western Blot
Diagnosis of prion disease
none, supportive only
Treatment for prion diseases
fatal within 6-12 months
Prognosis of prion disease
early mobility, awareness of lines and tubes, vital sign monitoring, comfort measures
PT implications for progressive lesion patients in the ICE
hospice care
care provided for the dying in institutions devoted to those who are terminally ill
palliative care
supportive medical and nursing care that keeps the patient comfortable but does not cure the disease
Glasgow coma scale
if a patient presents with altered levels of consciousness, what can be used to evaluate the patient?
isolation protocols must be followed, monitor vitals, ID potential infectious agents and ask for referral
Safety considerations for the infectious disorders