Costal landscapes in the UK
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
define mechanical weathering
The breakdown of rock without changing its chemical composition
Give an example of mechanical weathering and explain it
Freeze-thaw weathering
It happens when the temperature alternate above and below zero Celsius
Water enters rocks that has cracks e.g granite
When the water freezes it expands which puts pressure on the rock
When the water thaws it contacts which releases the pressure on the rock
Repeated freezing and throwing widen the crack and caused the rock to break up
define chemical weathering
Is the breakdown of rock by changing its chemical composition
Give an example of chemical weathering and explain it
Carbonation
which happens in warm and wet conditions
Rainwater has carbon dioxide dissolved in it, which makes a weak carbonic acid
Carbonic acid reacts with the rock that contains calcium carbonate e.g carboniferous limestone so the rocks are dissolved by rainwater
define mass movement
When material falls down a slope
How does mass movement happen?
Mass movement happens when the force of gravity acting on the slope is greater than the force supporting it, causing the coast to retreat rapidly.
It is more likely to happen when:
the material fills with water, and the water acts as a lubricant
water makes the material heavier
When the material shifts, it can
create a scarp (a steep cut in the side of the slope)
Define deposition
dropping of material
define swash and backwash
Swash = water moving up the beach
Backwash = water moving down the beach
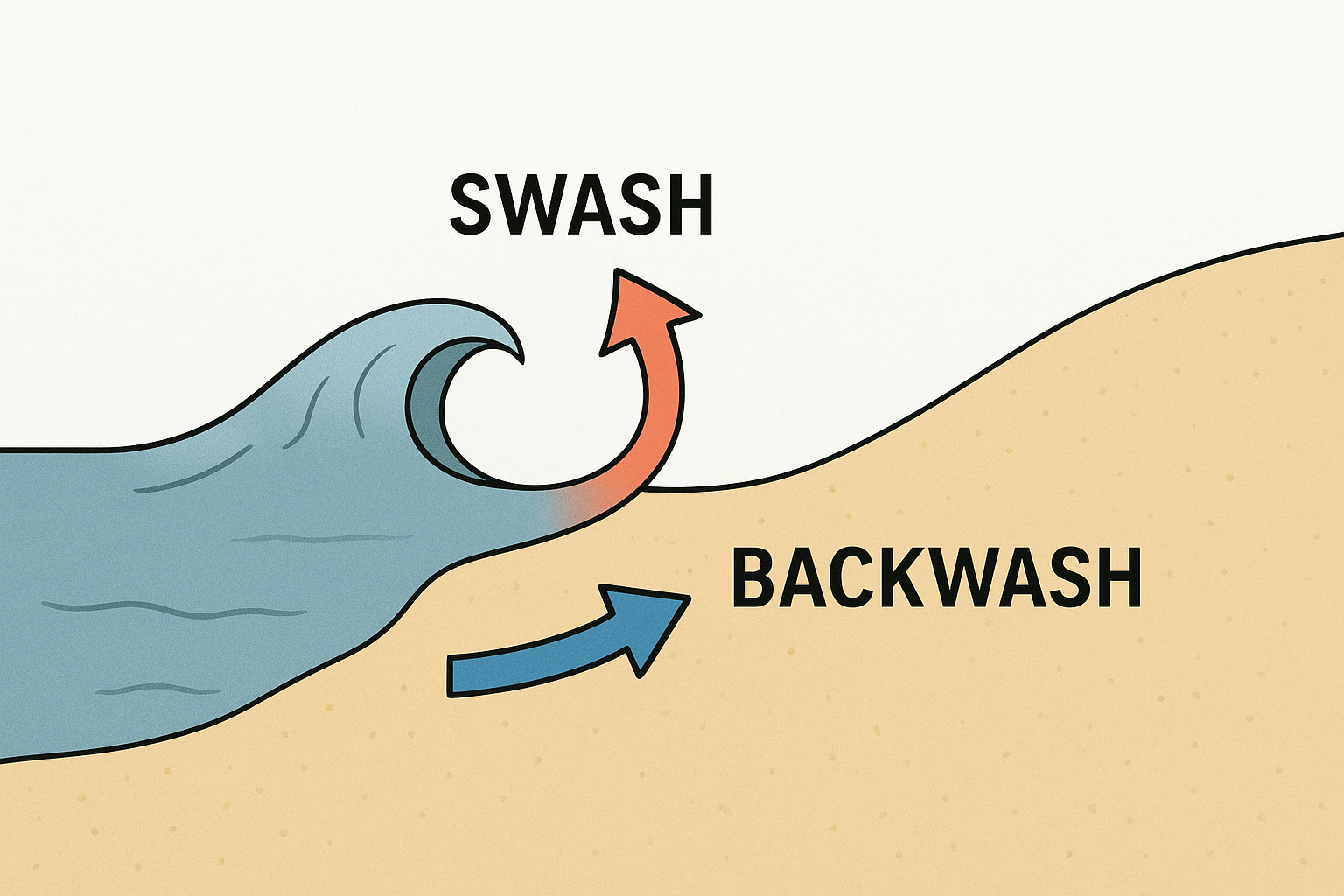
Can waves only be destructive?
no as waves can be destructive and constructive
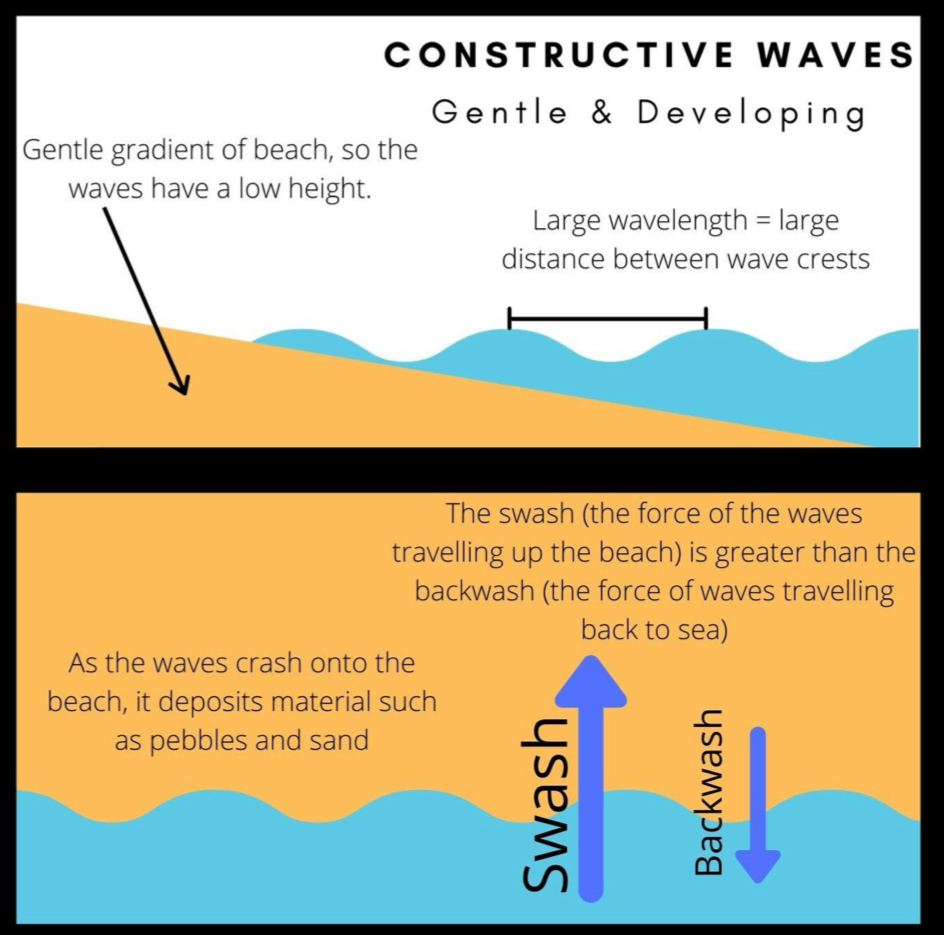
What are the characteristics needed for a destructive wave?
High frequency
high and steep waves
the backwash is more powerful than their swash so material is removed

What are the characteristics needed for a constructive wave?
low frequency
low and long waves
swash is more powerful than the backwash the material is deposited
What are the three processes of erosion waves use to wear away the coast?
Hydraulic power - waves crashed against a rock and compress the air in the cracks. This puts pressure on the repeated compression widen the crack and causes bits of rock to break off
Abrasion - eroded particles in water scrape and rub against rock removing small pieces
Attrition - eroded particles in the water collide break into small pieces and become more rounded
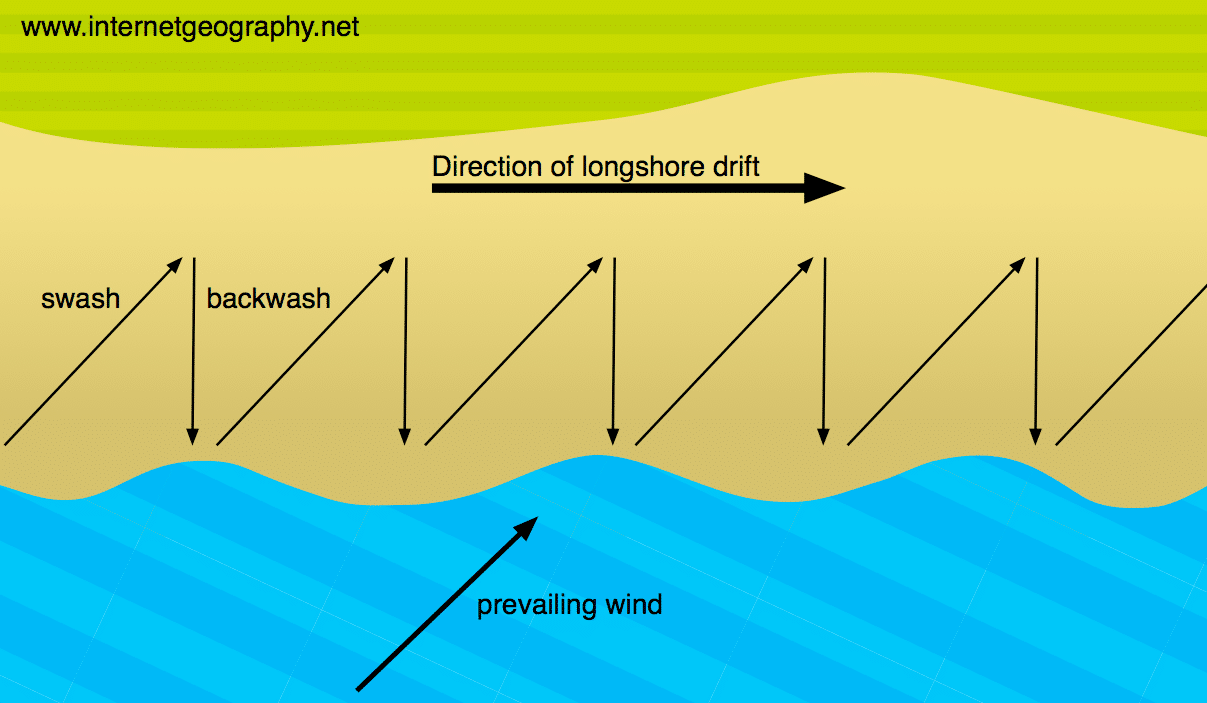
How can material be transported along the coast?
By longshore drift
Describe the process of longshore drift
Waves follow the direction of the prevailing wind
They usually hit the coast at an oblique angle
The swash carries material up the beach in the same direction as the waves
The backwash, then carries material down the beach at right angles back towards the sea
Overtime materials zigzags along the coast
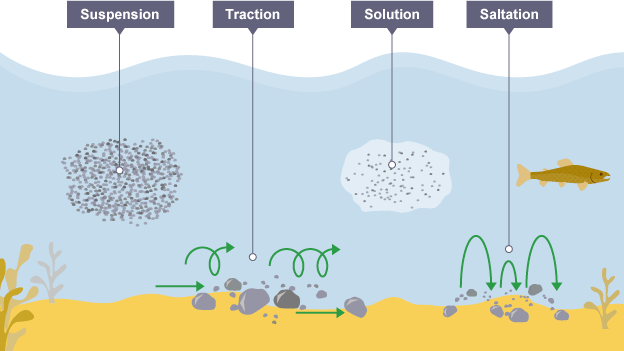
What are the four processes of transportation?
Traction - large particles like boulders are pushed along the sea bed by the force of water
Suspension - small particles like silt and clay are carried along in the water
Saltation - pebble sized particles are bounced along the sea bed by the force of water
Solution - soluble materials dissolve in the water and are carried along
What are the two types of coastlines?
Concordant - the alternating band of hard and soft rock are parallel to the coastline
Discordant - made up of alternating bands of hard and soft rock at right angles to the coast
Characteristics and formation of landforms resulting from erosion
Headlands and bays
cliffs and wave cut platforms
cave arches and stacks
How does rock type geological structure influence the erosional landforms that develop on a coast line?
Hard rocks like granite take a long time to erode, while softer rocks like sandstone erode more quickly.
Rocks with lots of joints and faults erode faster.
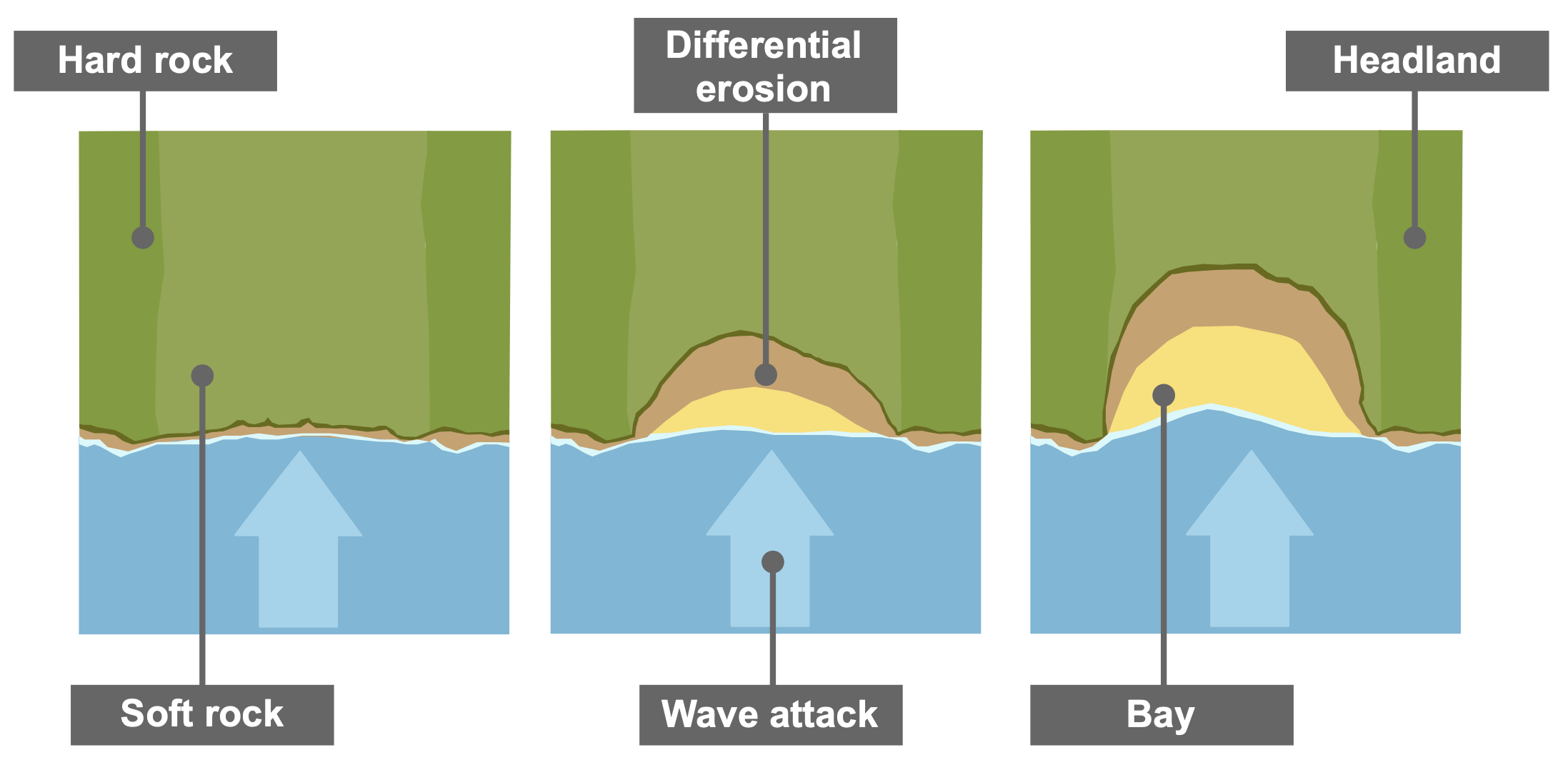
How are headlands and bays formed?
Headlands and bays form along discordant coastlines, where bands of rock run at right angles to the coast. The less-resistant rock erodes faster through processes such as hydraulic action and abrasion, forming bays with gentle slopes. The more-resistant rock erodes more slowly and therefore sticks out into the sea as a headland with steep sides. Over time, differential erosion creates a coastline with alternating headlands and bays.
How are caves formed?
Waves crash into the headlands and enlarge the cracks mainly by hydraulic power and abrasion. Repeated erosion and enlargement of the cracks causes a cave to form.
How does a cave become an arch?
Continued erosion deepens the cave until it breaks through the headland to form an arch.
How is a stack formed?
Erosion continues to wear away the rock supporting the arch, until it eventually collapses which forms a stack an isolated rock that’s separate from the headland
Describe the formation of a wave cut platform
Waves cause most erosion at the foot of the cliff, forming a wave-cut notch which is enlarged over time.
Repeated erosion causes the rock above the notch to become unstable and eventually collapse.
The collapsed material is washed away, and a new wave-cut notch begins to form.
After repeated collapses, the cliff retreats, leaving a wave-cut platform.
Characteristics and formation of landforms resulting from deposition
Beaches
Sand dunes
Spit and bars
describe how a sand beach is formed?
Sand beaches are created by low energy waves and are flat and wide sand particles are small so the weak backwash can move them down the beach creating a long gentle slope
Describe how a shingle beach is formed
Single beaches are created by high energy waves and a steep and narrow sand particles are washed away but largest shingle is left behind the shingle particles built up to create a steep slope
Describe how spits are formed
Spits form at sharp bends in the coastline.
Longshore drift transports sand and shingle past the bend and deposits it in the sea.
Strong winds and waves can curve the end of the spit, forming a recurved end.
The area behind the spit is sheltered from waves, so material accumulates and plants are able to grow.
Over time, the sheltered area can become a mudflat or salt marsh.
Describe how bars are formed
A bar forms on a spit joins two headlands together
The bay between the headlands get cut off from the sea
This means a lagoon can form behind the bar
Offshore bars can form if the coast has gentle slope
friction with sea beds causes waves to slow down and put settlement offshore creating a bar that is not connected to the coast
Describe how sand dunes are formed
Sand dunes form when sand deposited by longshore drift is move up the beach by the wind.
Obstacles (e.g. driftwood, plants) cause wind speed to decrease, so sand is deposited and forms small embryo dunes.
Embryo dunes are colonised by plants (e.g. marram grass). The roots of vegetation help stabilise the sand, allowing more sand to accumulate. This creates fore dunes, which develop into mature dunes. New embryo dunes form in front of the older, stabilised dunes.
Dune slacks (small pools) can form in the hollows between dunes.
How can coastlines be managed
By hard + soft engineering and managed retreat
Define hard engineering
man-made structures built to control the flow of sea and reduce flooding and erosion
Define soft engineering
schemes set up using knowledge of the sea and its processes to reduce the effects of flooding and erosion erosion
Four examples of hard engineering
Sea wall
Gabions
Rock armour
Groynes
Sea wall give the description and advantages + disadvantages
Description
A wall made out of material like concrete that reflects waves back to sea
Advantage
It prevents erosion of the coast. It also acts as a barrier to prevent flooding.
Disadvantage
It creates a strong backwash that erodes under the wall and is expensive to build and maintain
Gabions give the description and advantages + disadvantages
Description
A wall of wire cage is filled with rocks usually built at the foot of cliffs
Advantage
absorb wave energy and so reduce erosion they are cheap and easy to build
Disadvantage
they are ugly to look at and the wire cages can corrode over time
Rock armour give the description and advantages + disadvantages
Description
boulders that are piled up along the coast it’s also sometimes called riprap
Advantage
it absorbs wave energy reducing erosion and flooding it’s a fairly cheap defence
Disadvantage
boulders can be moved around by strong waves so they need to be replaced
Groynes give the description and advantages + disadvantages
Description
wooden or stone fences that are built at right angles to the coast they trap material transported by longshore drift
Advantage
they create wider beaches which slow the waves this gives greater protection from flooding and erosion. They’re a fairly cheap defence.
Disadvantage
they starve beaches further down the coast of sand making them narrower beaches which don’t protect the coast very well leading to greater erosion
two examples of soft engineering
Beach nourishment and reprofiling
Dune regeneration
Beach nourishment and reprofiling give the description and advantages + disadvantagessand
Description
Sand and shingle from elsewhere (e.g seabed) all from lower down the beach that added to the upper part of beaches
Advantage
It creates wider beaches which slow the waves this give greater protection from the flooding and erosion
Disadvantage
Taking material from the sea that can kill organisms like sponge and coral it’s a very expensive defence. It has to be repeated
Dune regeneration give the description and advantages + disadvantages
Description
Creating or restoring sand dunes by nourishment or by planting vegetation to stabilise the sand
Advantage
Dunes create a barrier between land and sea and absorb wave energy, prevent flooding and erosion. stabilisation is cheap
Disadvantage
The protection is a limited to a small area. Nourishment is very expensive
Managed retreat give the description and advantages + disadvantages
Description
Removing current defences and allowing the sea to flood the land behind
Advantage
Overtime the land will become marshland which then protects the land behind it from flooding erosion. It’s cheap and easy. It doesn’t need maintaining the marshland can also create new habitats for plants and animals.
Disadvantage
can cause conflicts e.g flooding farm line affects the livelihood of farmers and saltwater can have a negative effect on existing ecosystems