Pons
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Relations of pons
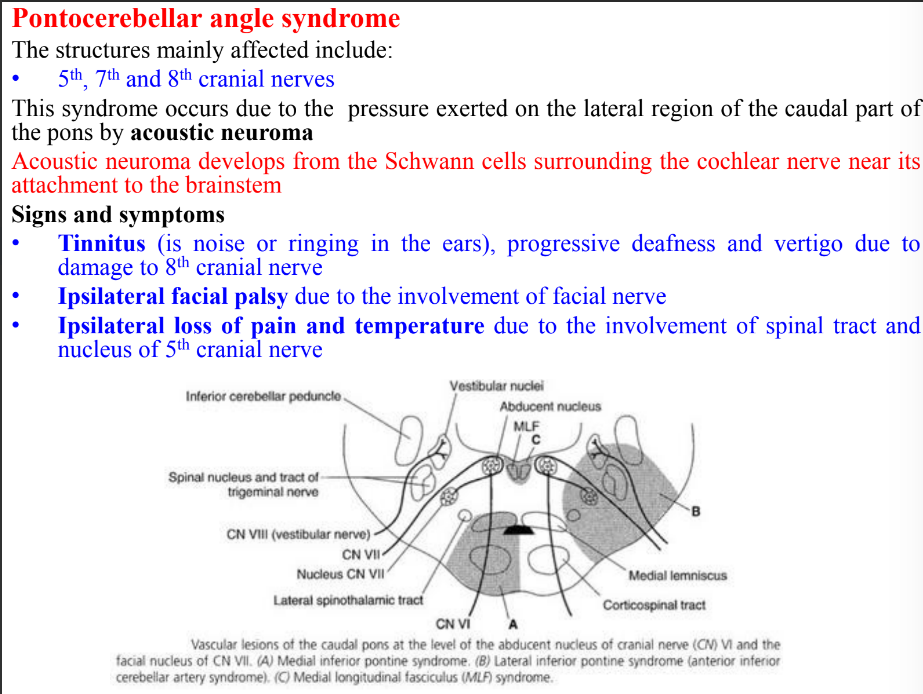
Ventrally related to the clivus by separated from it by meninges, basilar artery and basilar plexus of veins
Laterally connected to the cerebellum by middle cerebellar peduncle
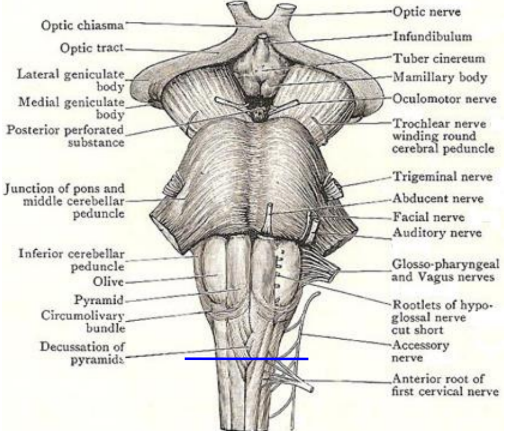
External features
Basilar sulcus
Middle cerebellar peduncle
Motor and sensory root of trigeminal
Ponto-cerebellar fibres
Ponto-medullary junction (attachment of 6th-8th nerves)
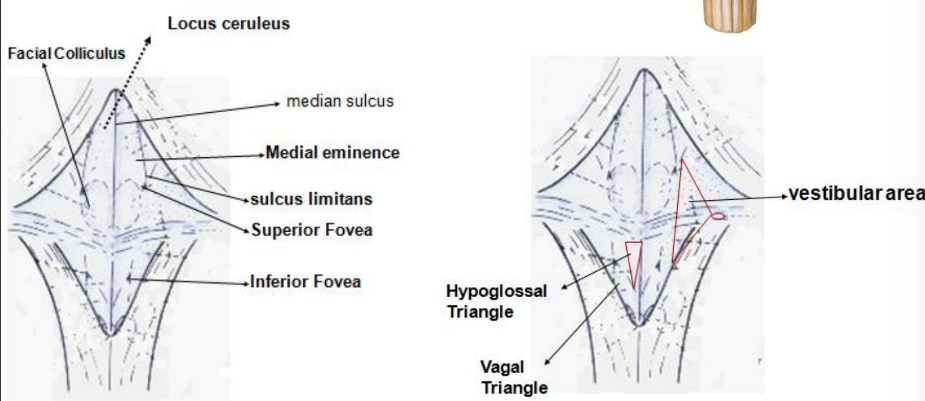
Dorsal surface
Forms 4th floor of ventricle
Facial colliculus
Vestibular area
Locus ceruleus (substantia ferruginea, rich in nor adrenaline)
Has superior border where crus cerebri is attached, inferior border at pontomedullary junction
Internal features
Divided into basilar/ventral part and dorsal/tegmental part
Basilar or ventral part
Occupied by longitudinal and transverse fibres
Longitudinal fibres made up of corticospinal, corticobulbar and corticopontine
Transverse fibres are axons from pontine nuclei (pontocerebellar)
Nuclei pontis
Tegmental part
Presence of salivatory nuclei, cranial nuclei (6th-8th) and reticular formation
Features at levels
At lower level of facial colliculus
At level of upper pons
The tegmental part differs in the upper and lower part but the basilar part continuous throughout
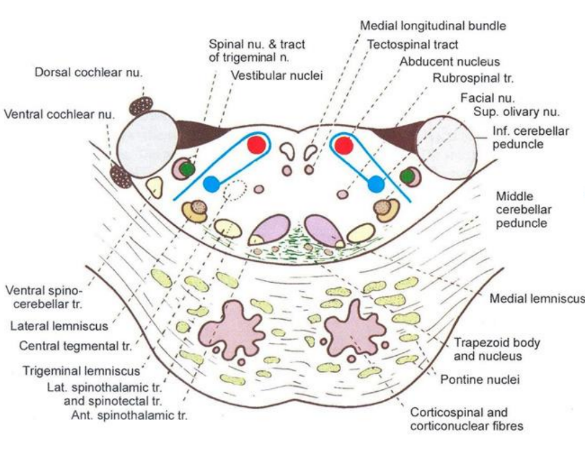
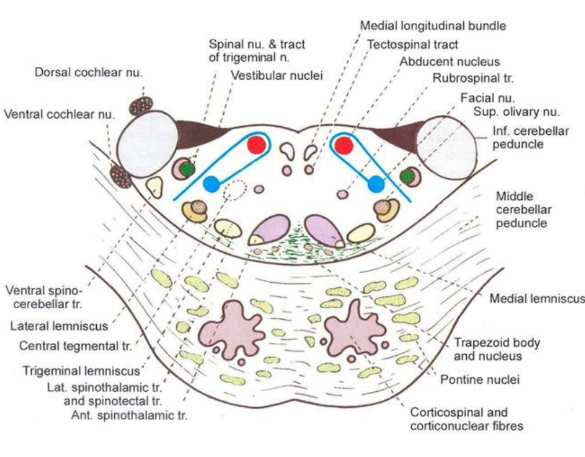
Transverse section at the level of the facial colliculus
Medial lemniscus
Spinal lemniscus (carry contralateral pain and temperature)
Trigeminal lemniscus (convey pain and thermal from face)
Lateral lemniscus (concerned with hearing, formed by contralateral ventral & dorsal cochlear nuclei and contralateral & ipsilateral fibres from trapezoid body and superior olivary complex )
Superior olivary nucleus composed of principal superior olivary nucleus, accessory and retro-olivar
Nucleus solitarius
Nucleus of spinal tract of trigeminal nerve
Motor nucleus of facial nerve
(Neurobiotaxis-migration of motor nucleus of VII towards spinal nucleus of V)
Medial longitudinal bundle
Tectospinal tract
Ventral and dorsal cochlear nuclei (line in inferior cerebellar peduncle)
Vestibular nuclei
Abducent nuclei
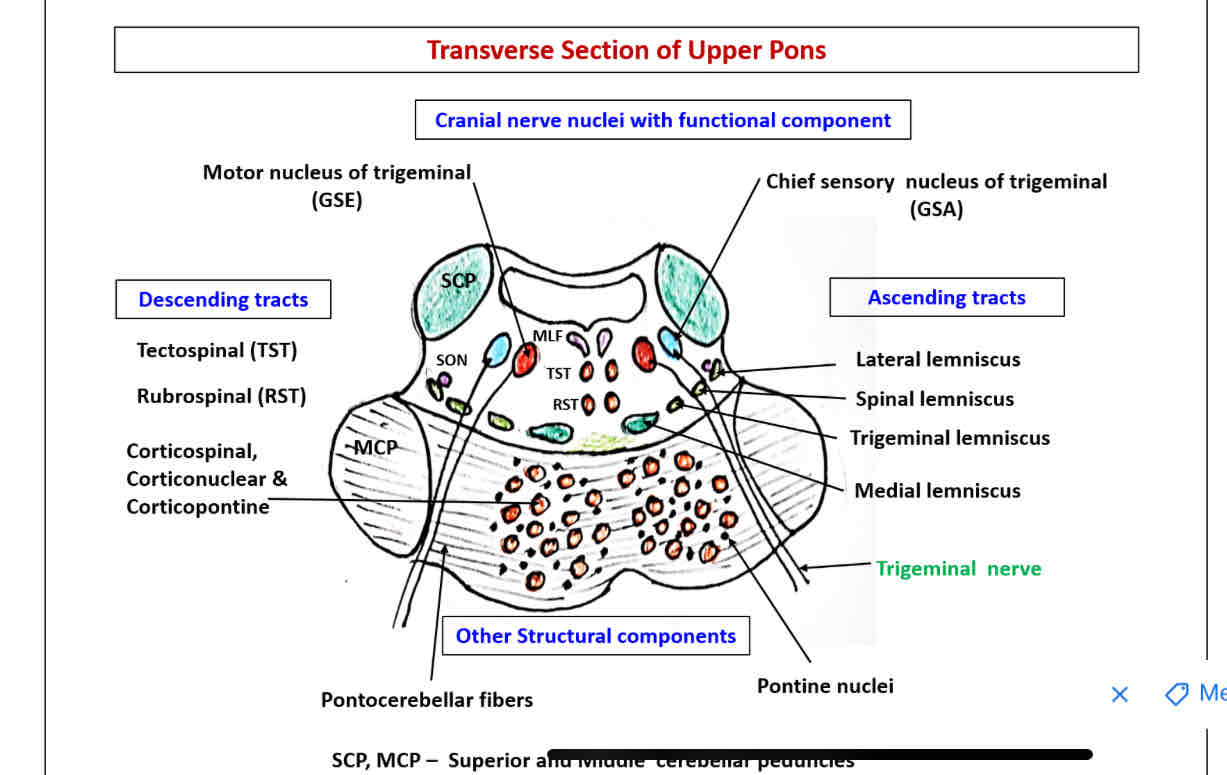
Cross section at upper level of pons
Superior cerebellar peduncles
Medial longitudinal bundle
Blood supply
Numerous pontine branches from basilar artery
Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
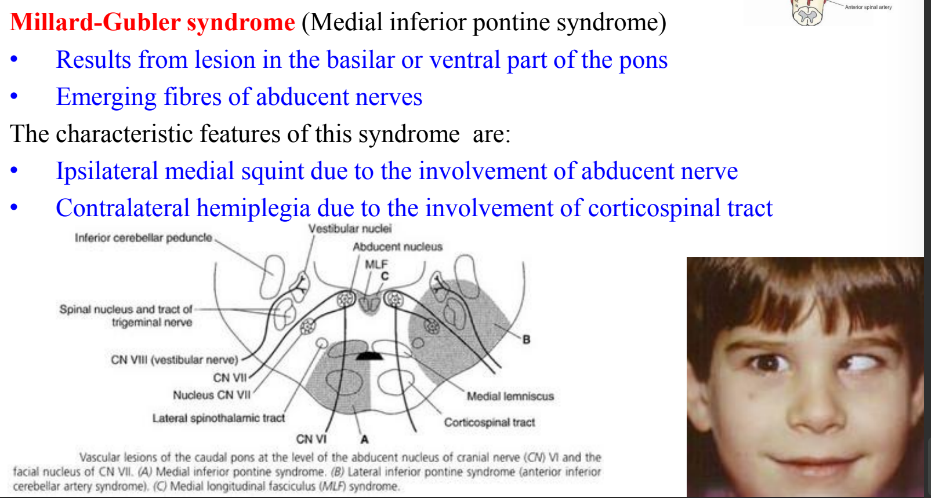
Millard Gubler syndrome (medial inferior pontine syndrome)
Pontocerebellar angle syndrome