Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
alcohol
An organic compound containing a hydroxyl group, -OH
What are the examples of alcohols?
methanol
ethanol
propanol
butanol
functional group
An atom, or group of atoms, that determines the main chemical properties of an organic compound.
What’s alcohol functional group?
OH
Methanol
CH3OH
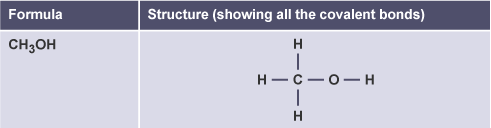
Ethanol
C2H5OH
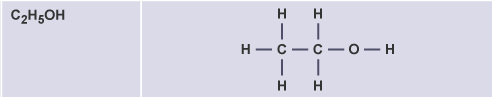
Propanol
C3H7OH
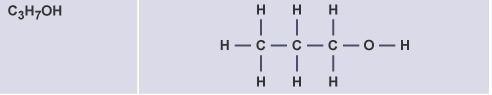
Butanol
C4H9OH
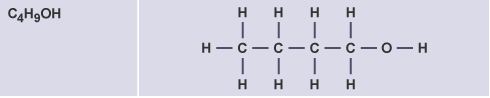
By what process is ethanol produced?
fermentation
Equation for fermentation
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
Uses alcohols
fuels - burn well
solvents - water soluble
alcoholic drinks - ethanol
Solubility in water (alcohols)
alcohols with the shortest hydrocarbon chains, eg methanol, ethanol or propanol mix easily to produce a solution
Solubility decreases as the length of the alcohol molecule gets longer
Butanol is less soluble than propanol may not mix easily
forms neutral solution
Reaction with sodium (alcohol)
forms hydrogen
Oxidation of alcohols
The alcohols can also be oxidised without combustion to produce carboxylic acids
forms carbon dioxide and water
Carboxylic acid
A homologous series of compounds that contain the carboxyl functional group, -COOH.
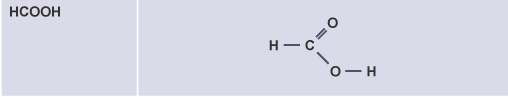
Methanoic acid
HCOOH
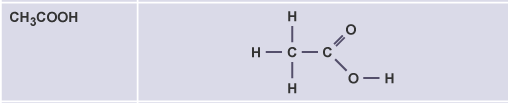
Ethanoic acid
CH3COOH
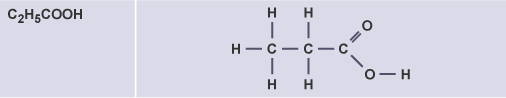
Propanoic acid
C2H5COOH
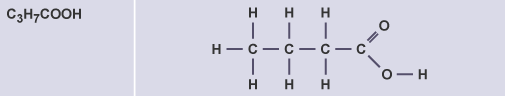
Butanoic acid
C3H7COOH
Properties of carboxylic acids
dissolve in water to form acidicsolutions with pH values less than 7
react with metals to form a salt and hydrogen
react with bases to form a salt and water
react with carbonates to form a salt, water and carbon dioxide
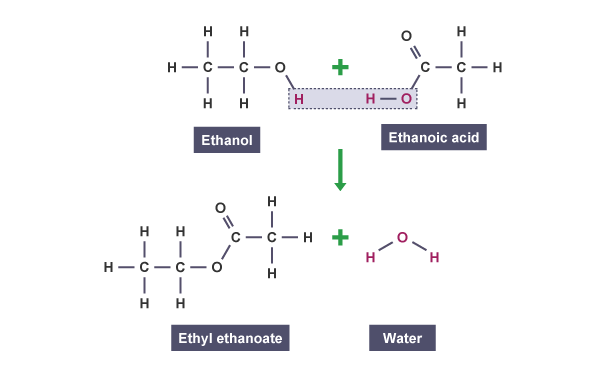
Carboxylic reaction with alcohols
react with alcohols to make esters
Esters contain the functional group -COO-.
alcohol + carboxylic acid → ester + water
Strength of carboxylic acids
Weak acids
don’t contain many hydrogen ions compared with a solution of a strong acid with the same concentration
pH of a weak acid will be higher than the pH of a strong acid