Canine Head, Neck, Limb Anatomy
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
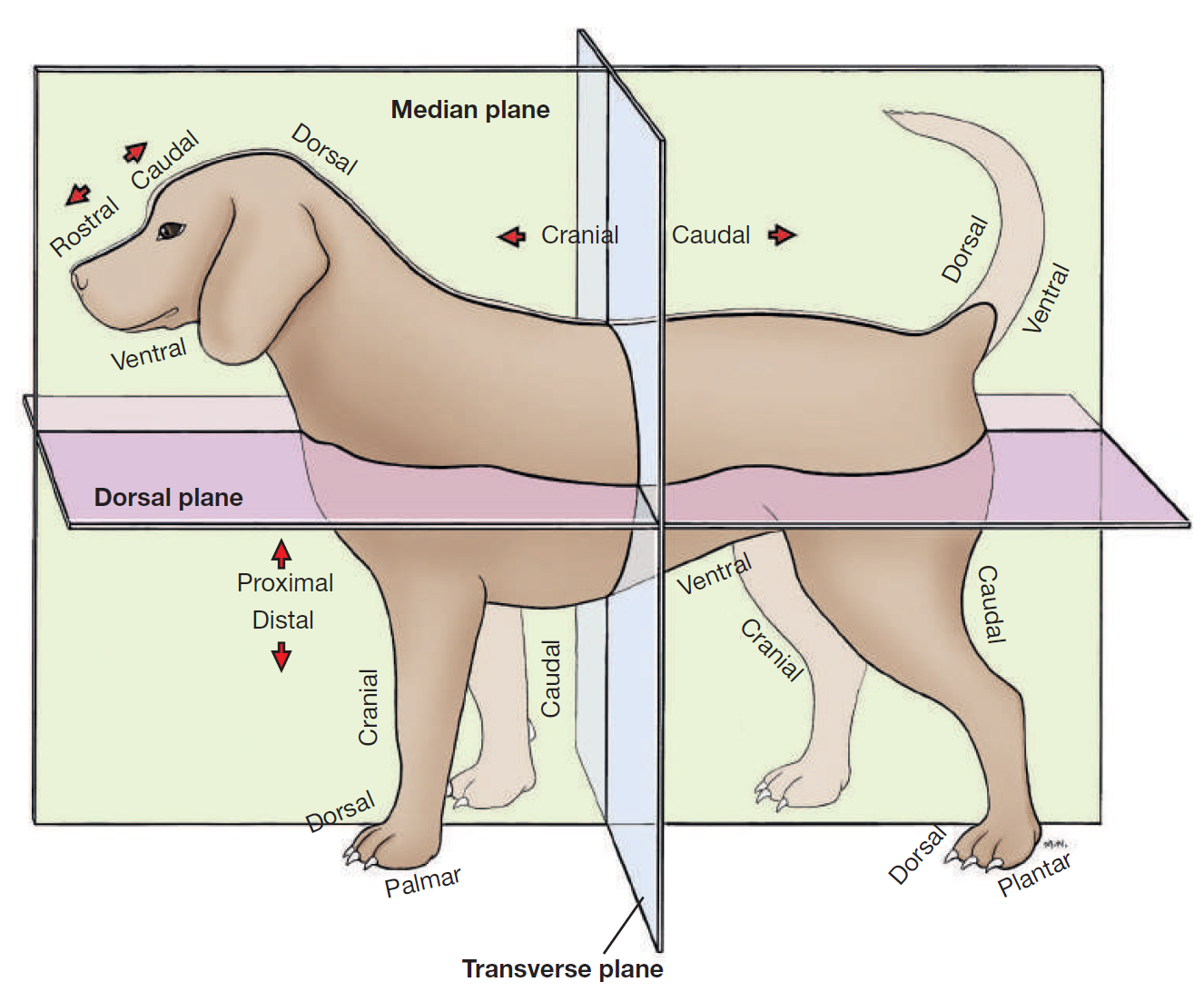
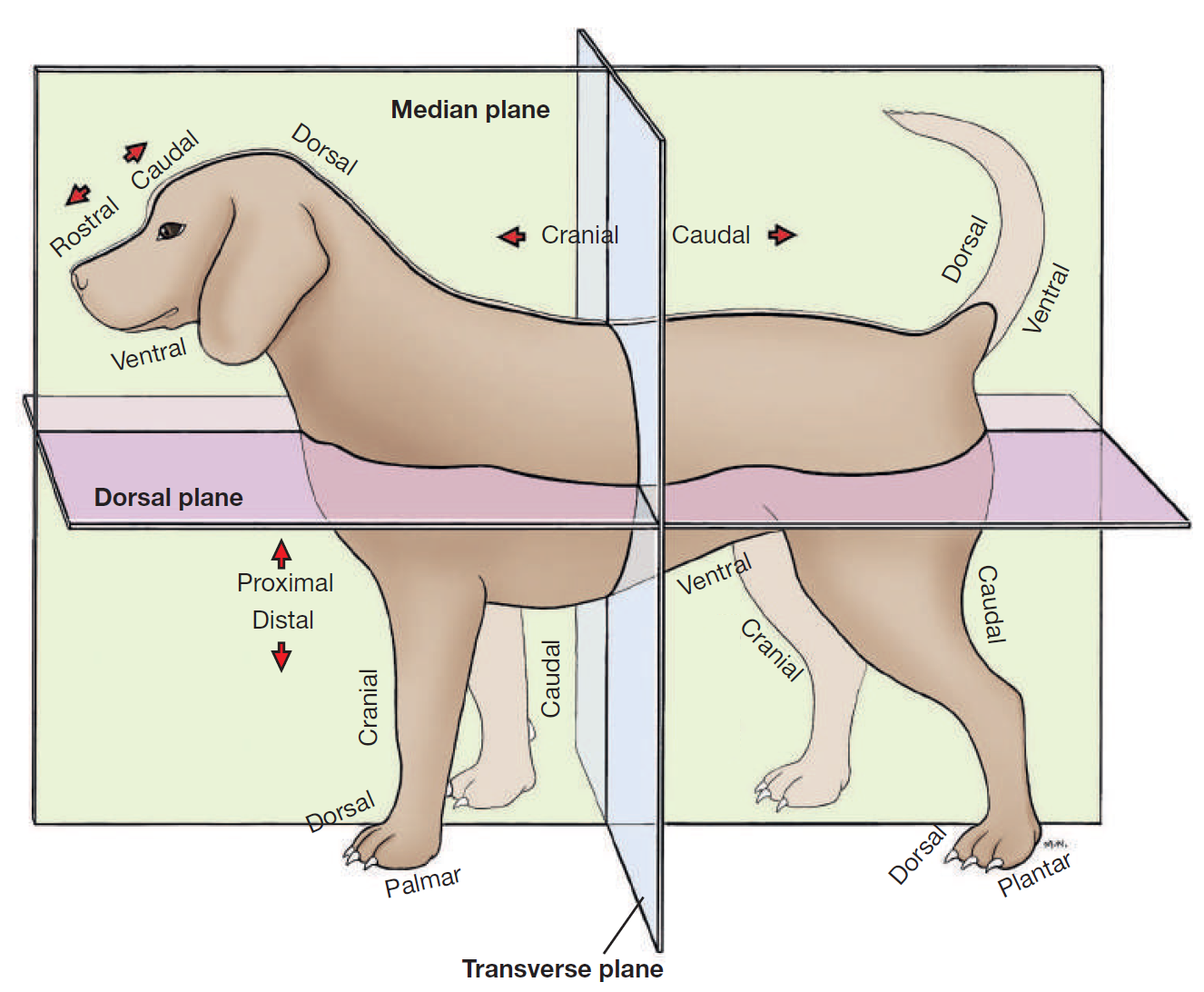
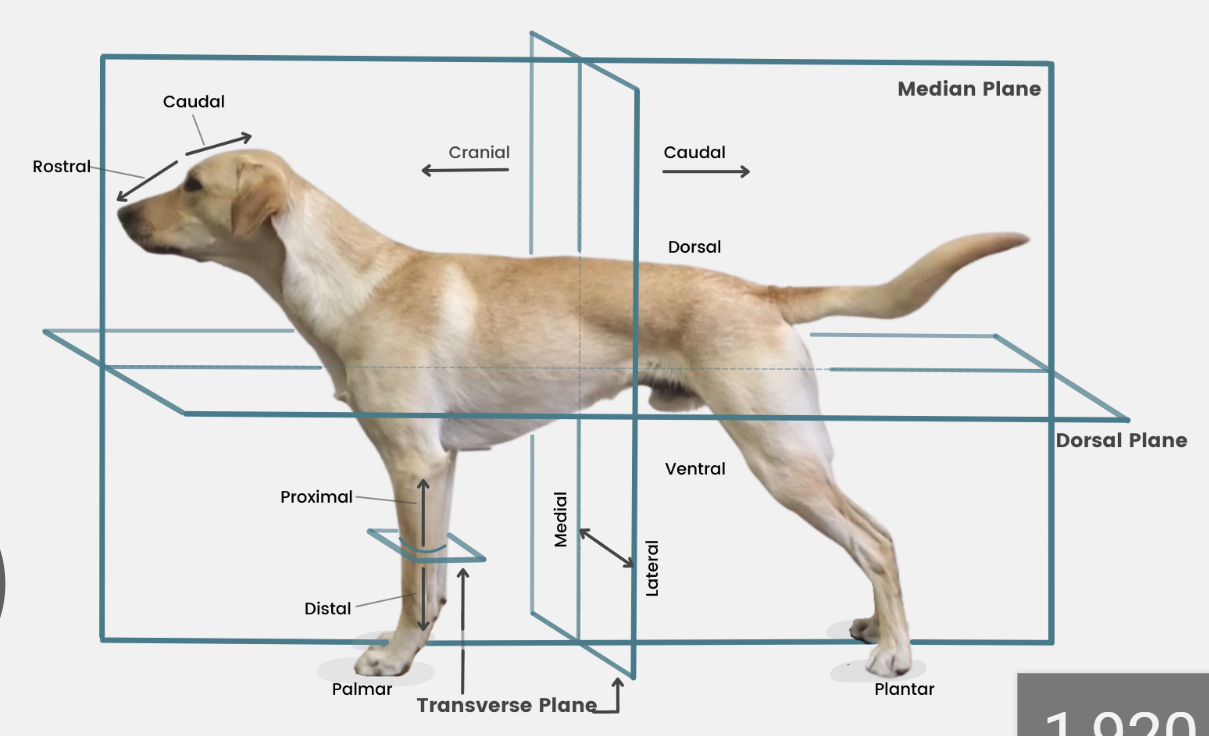
define plane
a surface, real or imaginary, where 2 points can be connected via straight line
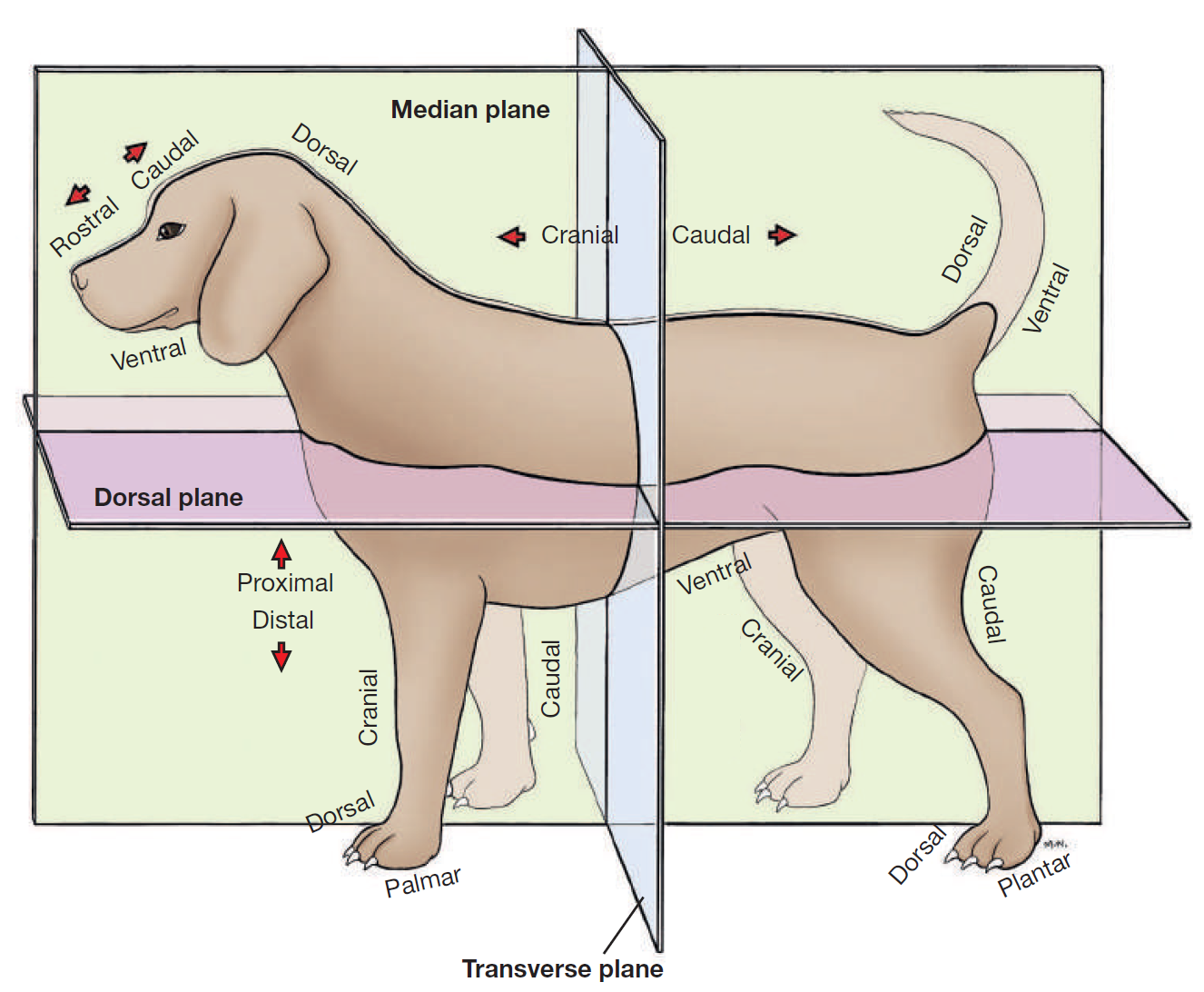
define median plane
divides head/body/limb into right and left halves
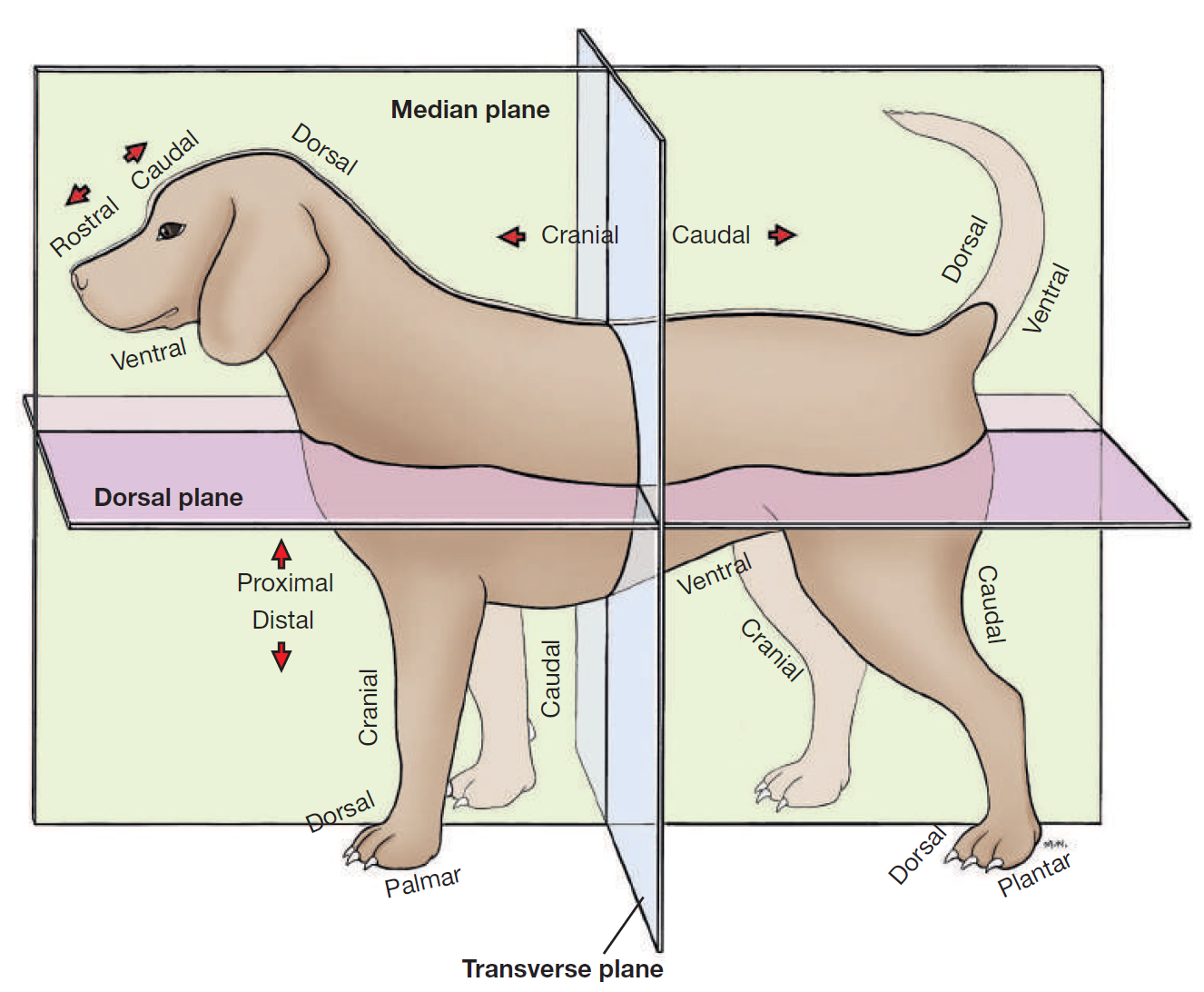
define dorsal
toward/near upper surface of head/body/tail
or it means upper/front surface of carpus, tarsus, metapodium, & digits on limbs
opposite to supporting surface when standing/paw pad
opposite ventral
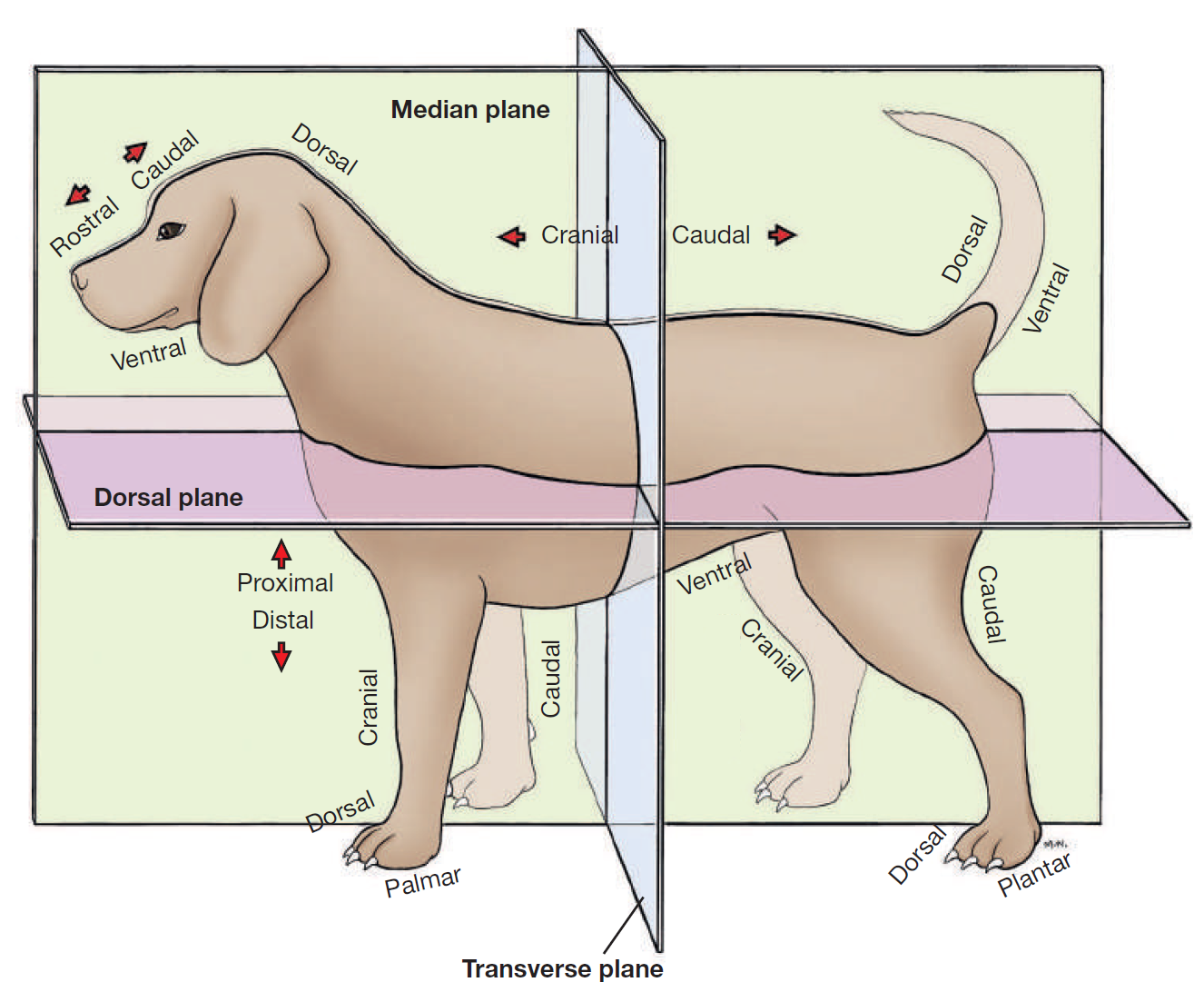
define ventral
toward/near supporting surface of head/neck/thorax/tail
NEVER USE FOR LIMBS
opposite dorsal
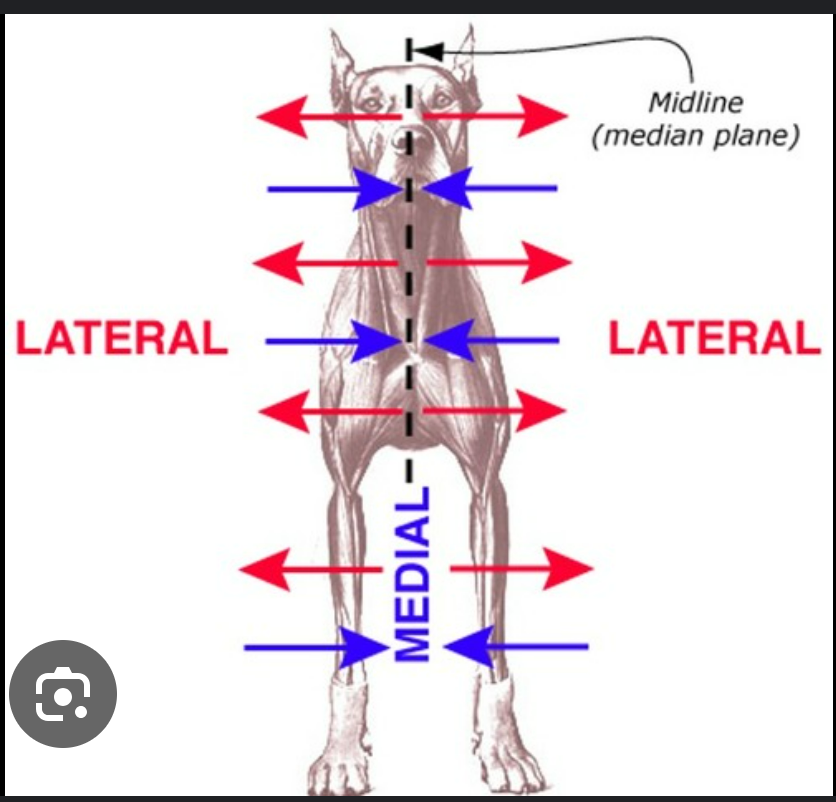
define medial
toward/near median plane
opposite lateral
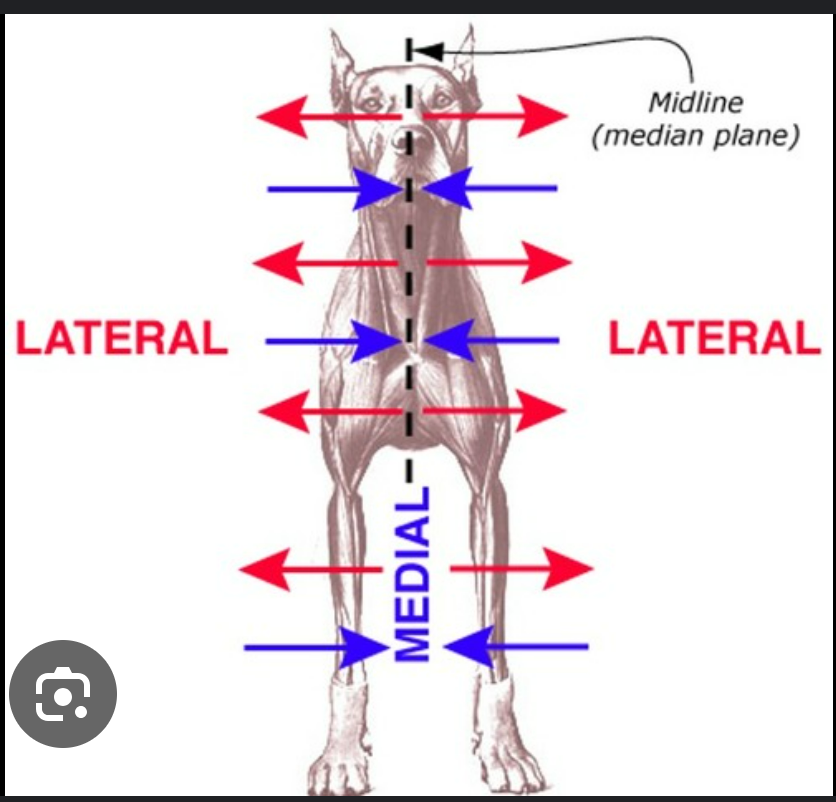
define lateral
away/far from median plane
opposite medial
define cranial
toward/near head
or it means proximal to carpus/tarsus on limbs
opposite caudal
replaced by rostral on head
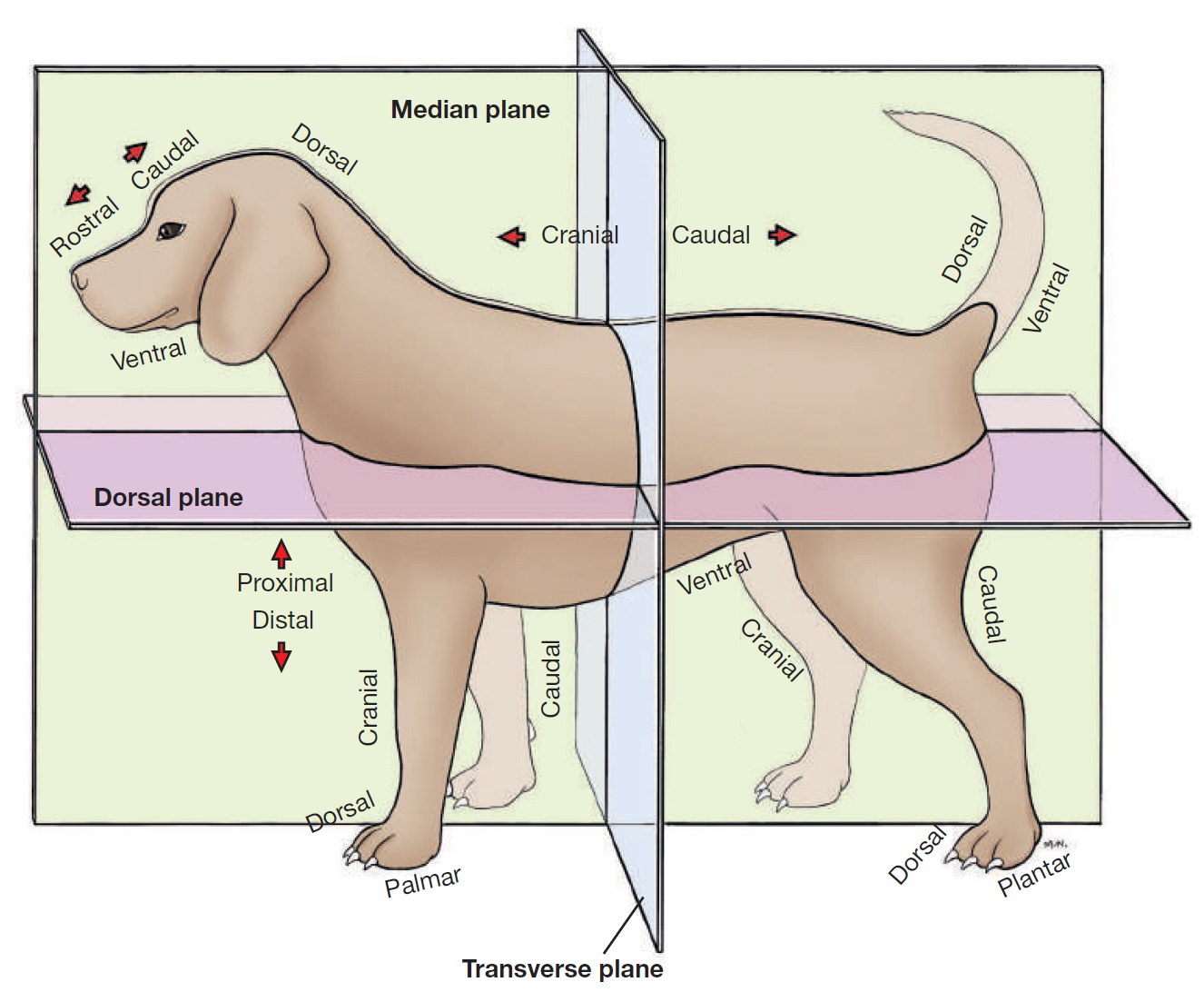
define rostral
toward/near nose
APPLIES TO HEAD ONLY
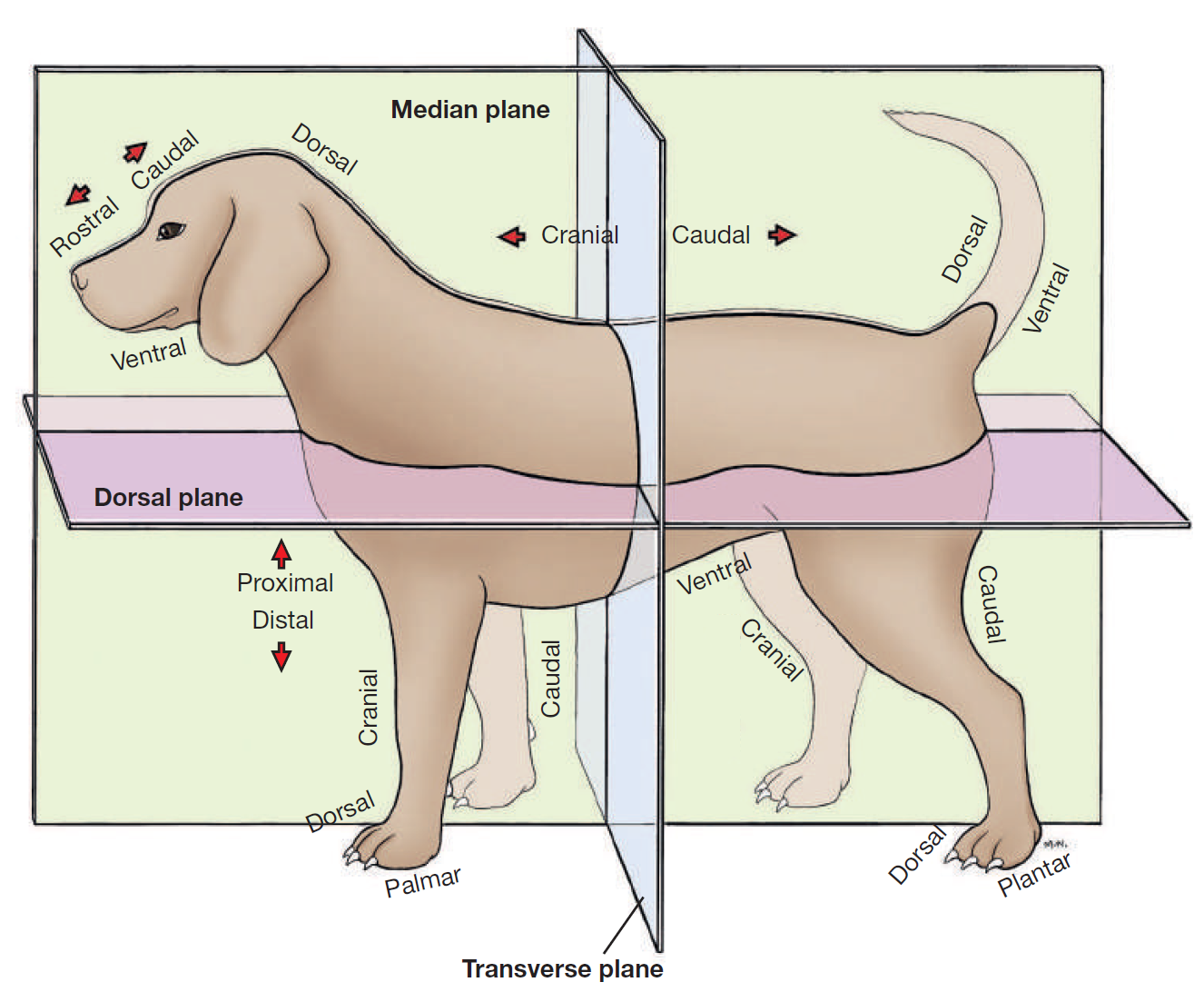
define caudal
toward/near tail
opposite cranial
defina internal/inner
close to/in direction of/the center of a hollow organ/body cavity/structure
opposite external
define external/outer
away from center of a hollow organ or structure
opposite internal
define superficial
near surface of the body/solid organ
opposite deep
define deep
near center of body/solid organ
opposite superficial
define proximal
near the main mass or origin
or near the attached end of limbs/tail
opposite distal
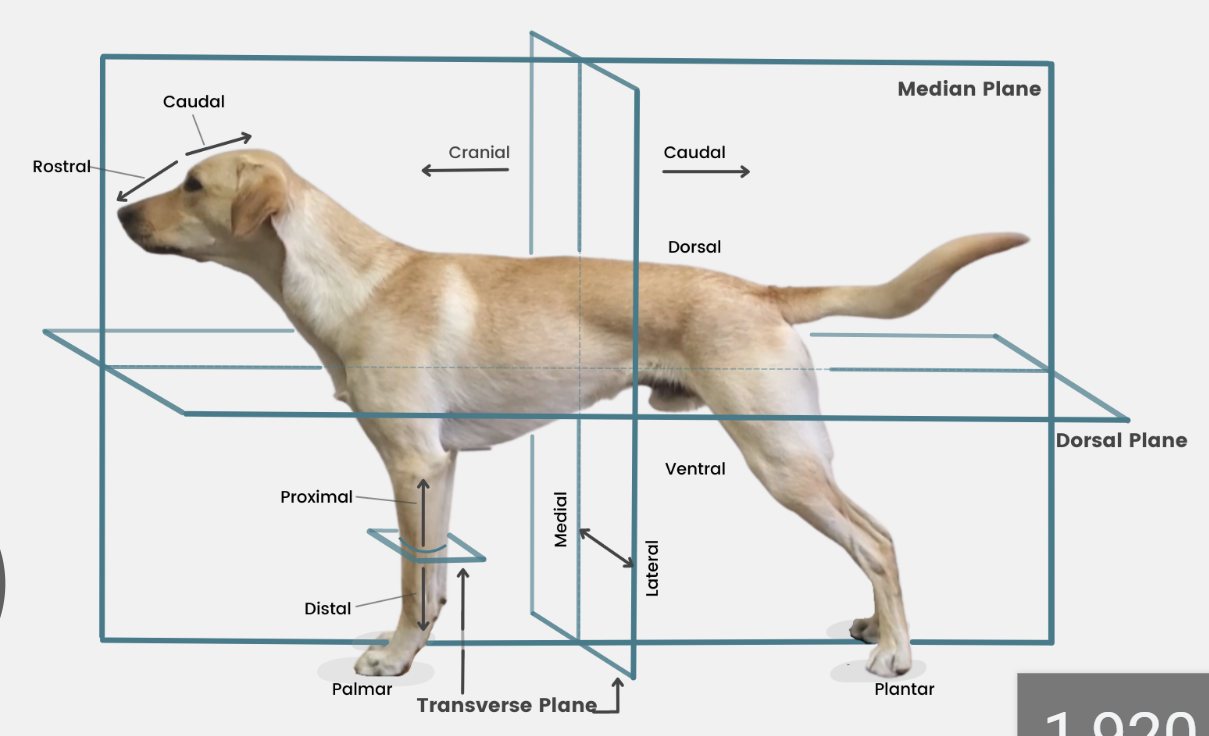
define distal
away from main mass or origin
or free end of limbs/tail
opposite of proximal
define radial & tibial
radial: on the side of the antebrachium/forearm where the radius is
tibial: same but for back leg/crus where tibia is
define ulnar & fibular
ulnar: on the side of the antebrachium/forearm where the ulna is
fib: same but for back leg/crus where fibula is
define palmar
SPELLING
part of FOREPAW where pads are
surface that touches the ground when animal stands
corresponding surface of metacarpus and carpus
opposite dorsal surface (top of paw)
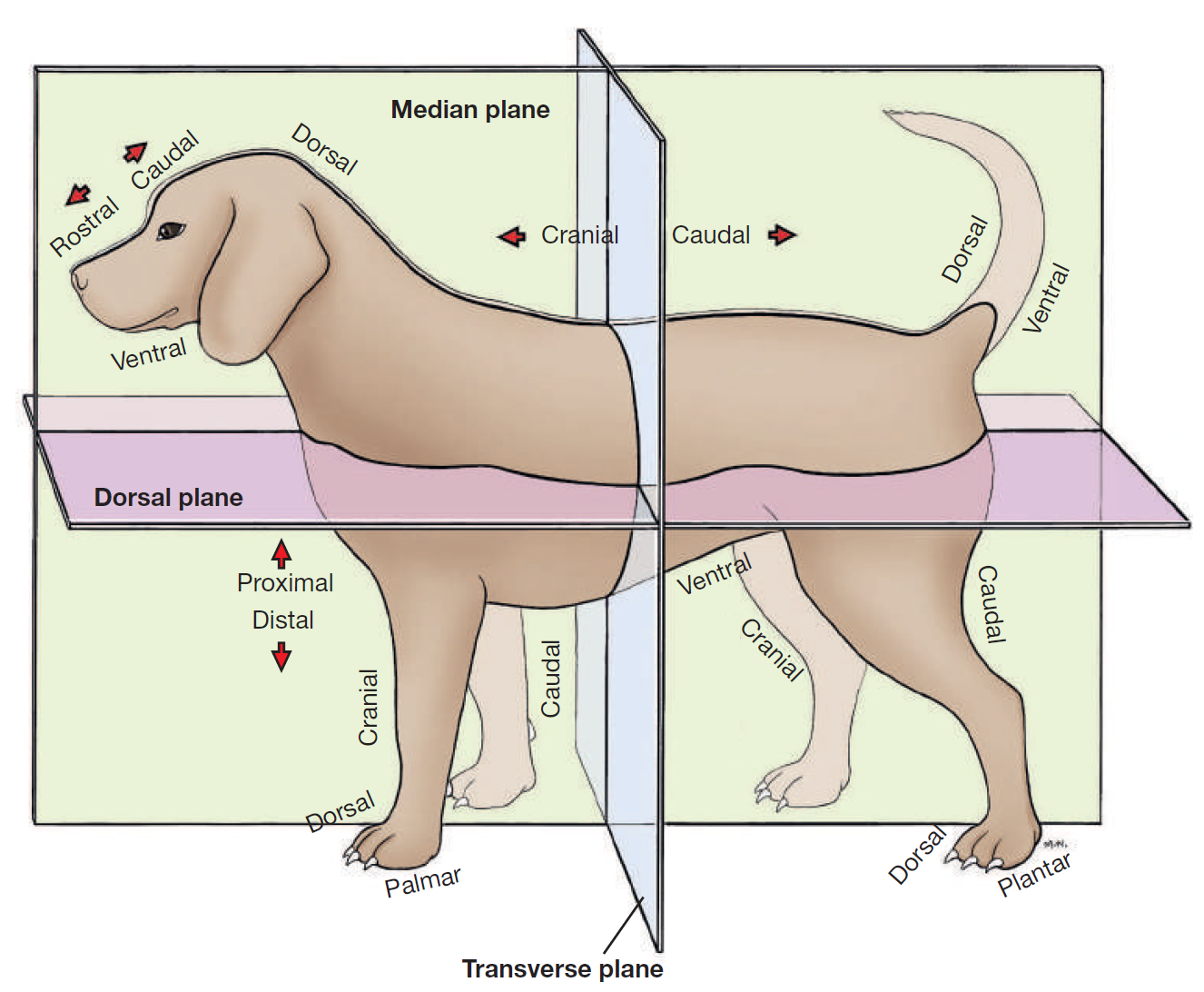
define plantar
SPELLING
part of HINDPAW where pads are
surface that touches ground when animal stands
corresponding surface of metatarsus and tarsus
opposite dorsal surface (top of paw)
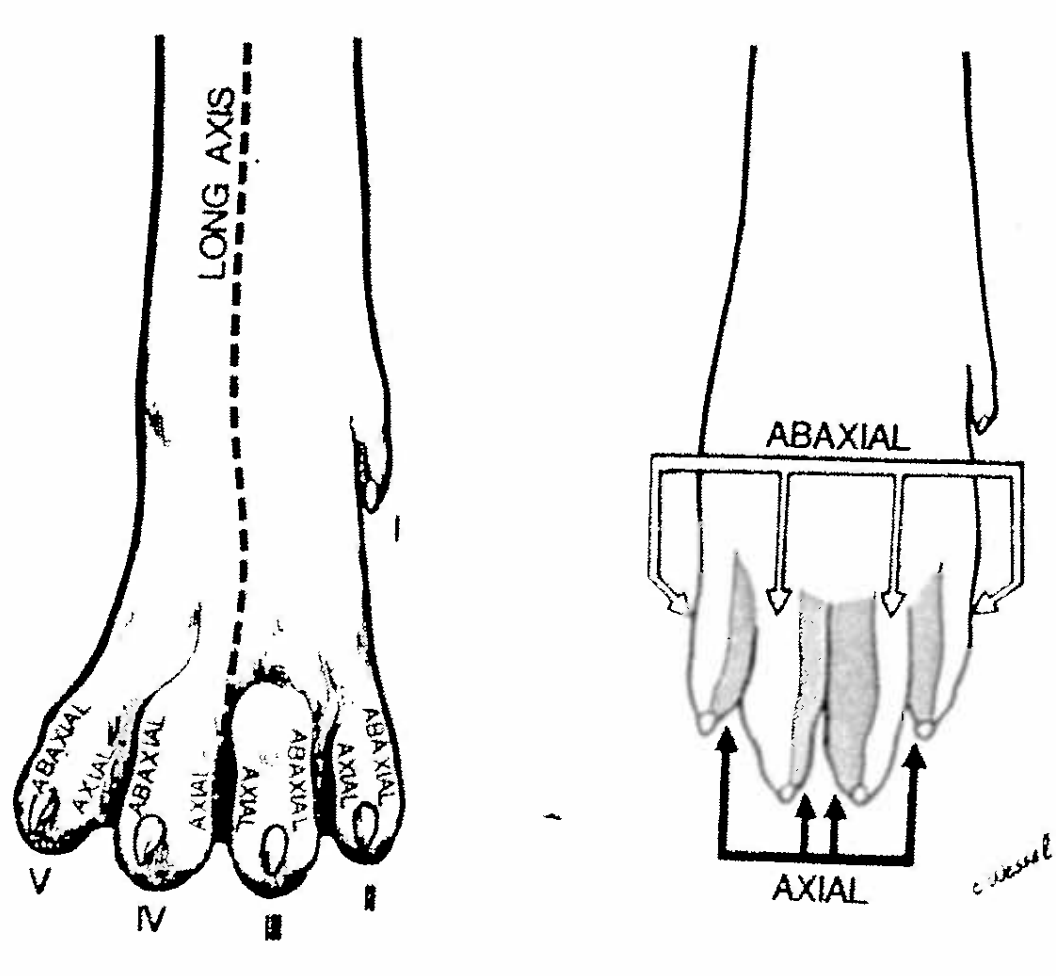
define axis
the central line of the body or any of its parts
define axial & abaxial
of, pertraining to, relative to the axis
or in cows the axis of the limb passes through the middle…
axial surface of the digit faces the axis
abaxial faces away
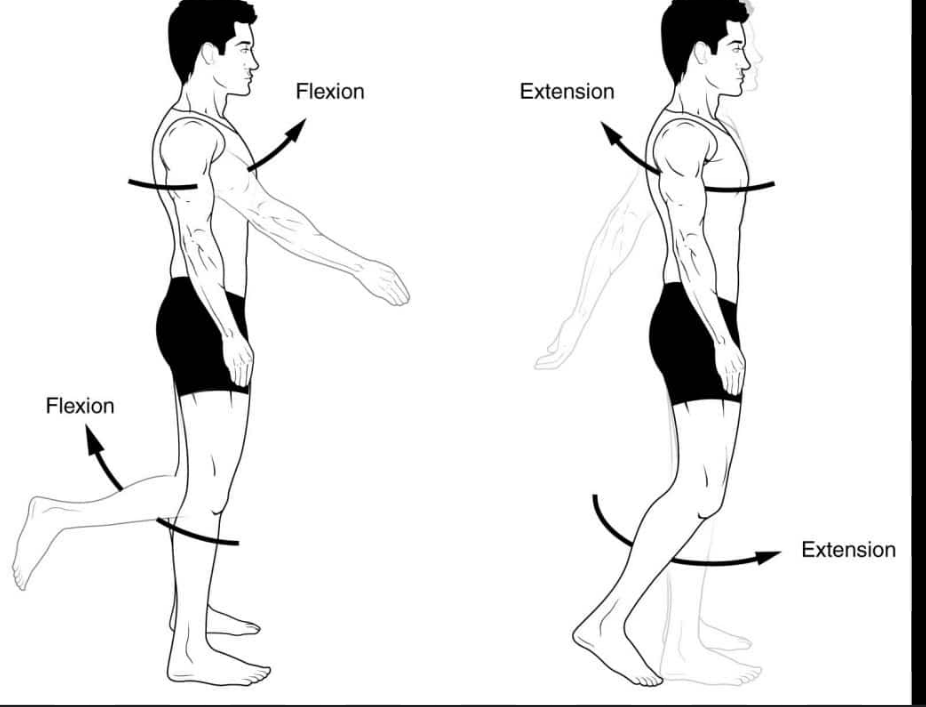
define flexion
moving one bone in relation to another so the joints angle decreases
AKA limb is retracted/folded, digit is bent, back is arched dorsally
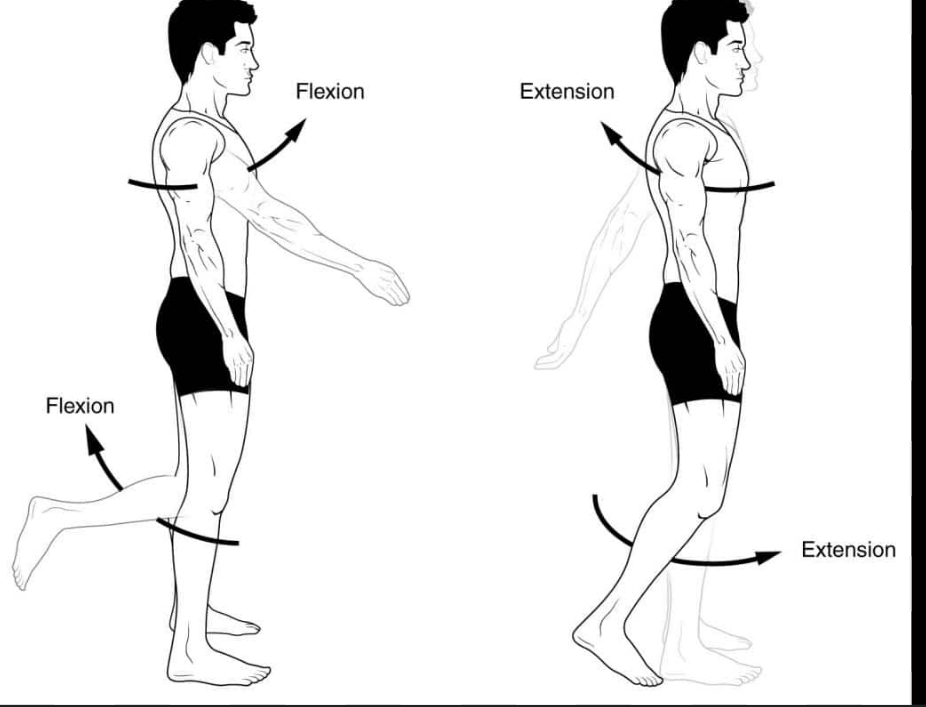
define extension
moving one bone in relation to another so the joints angle increases
AKA limb reaches out/extends, digit/back straightens
overextension if stretched over 180 degrees
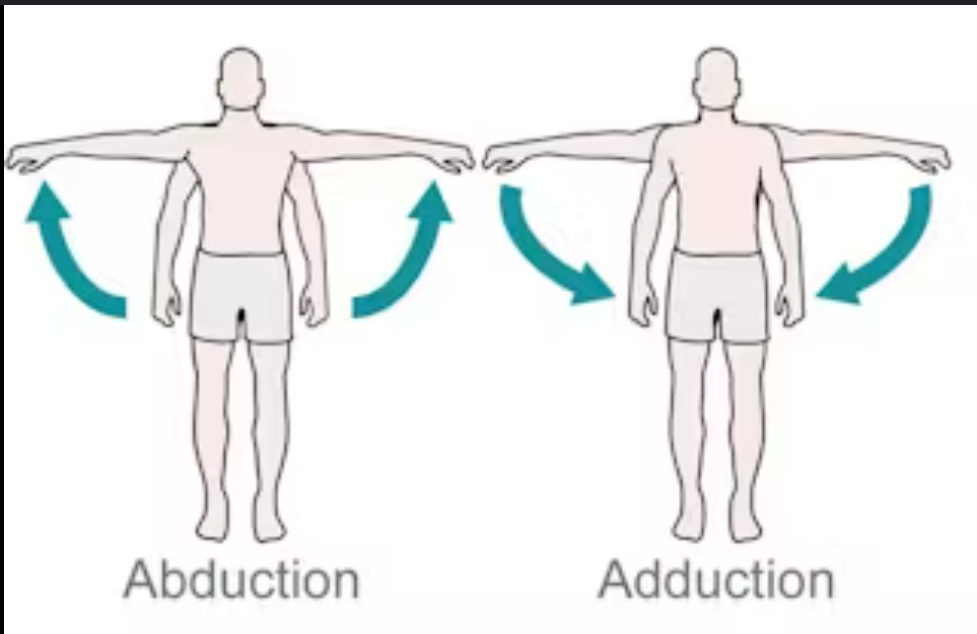
define abduction
moving a part away from median plane
opposite adduction
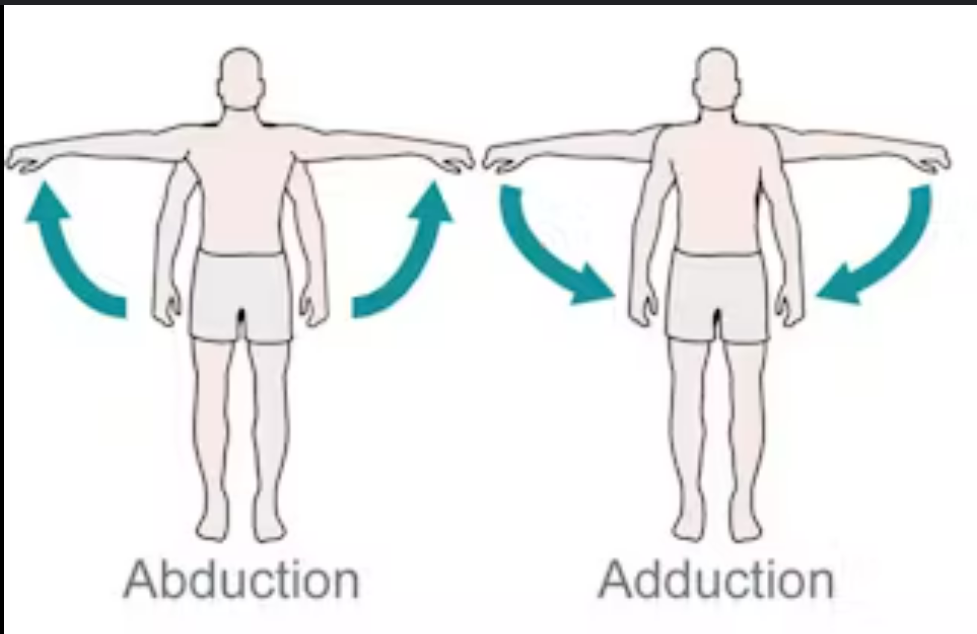
define adduction
moving a part toward median plane
opposite abduction
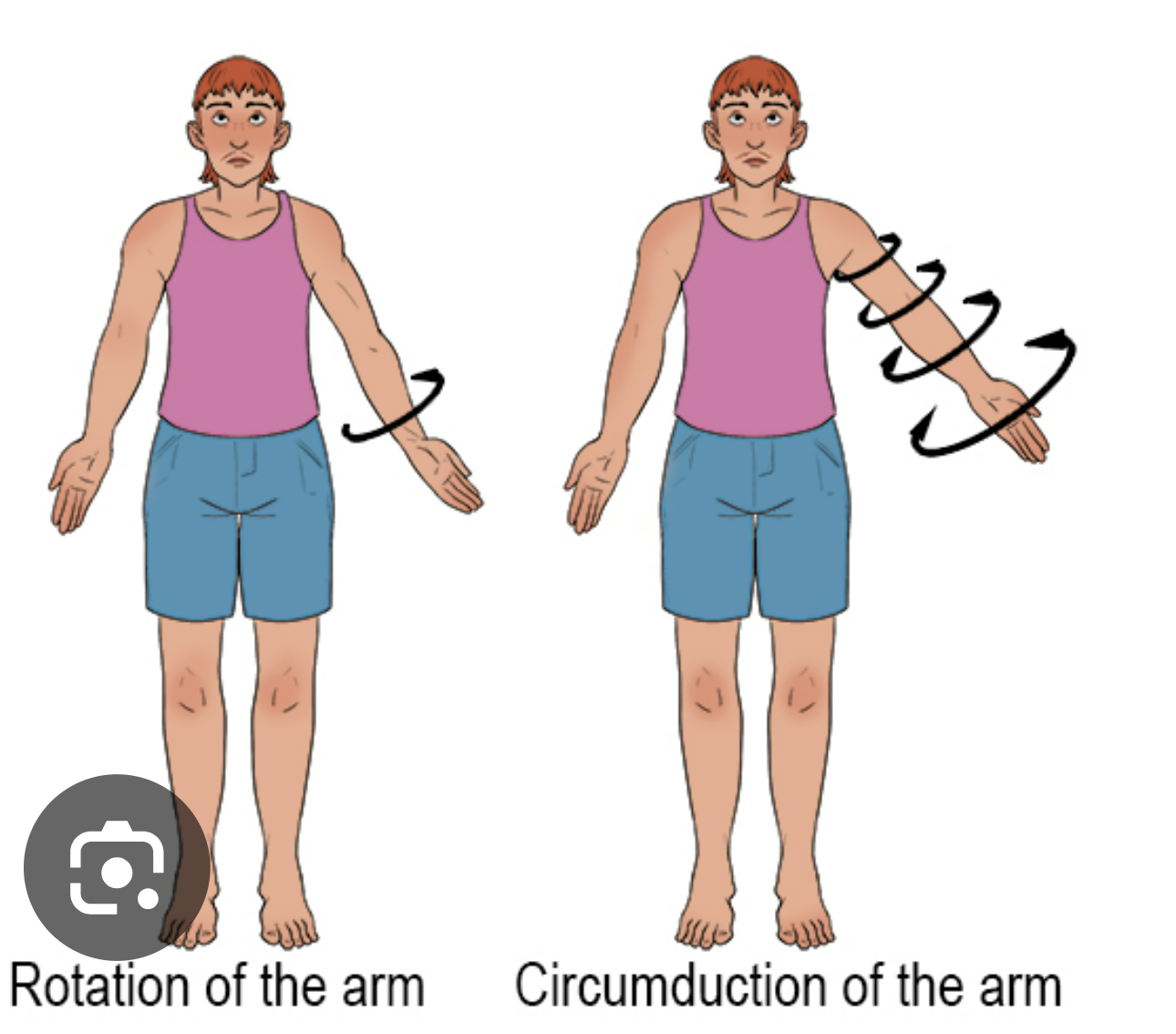
define circumduction
moving a part in the shape of a circle
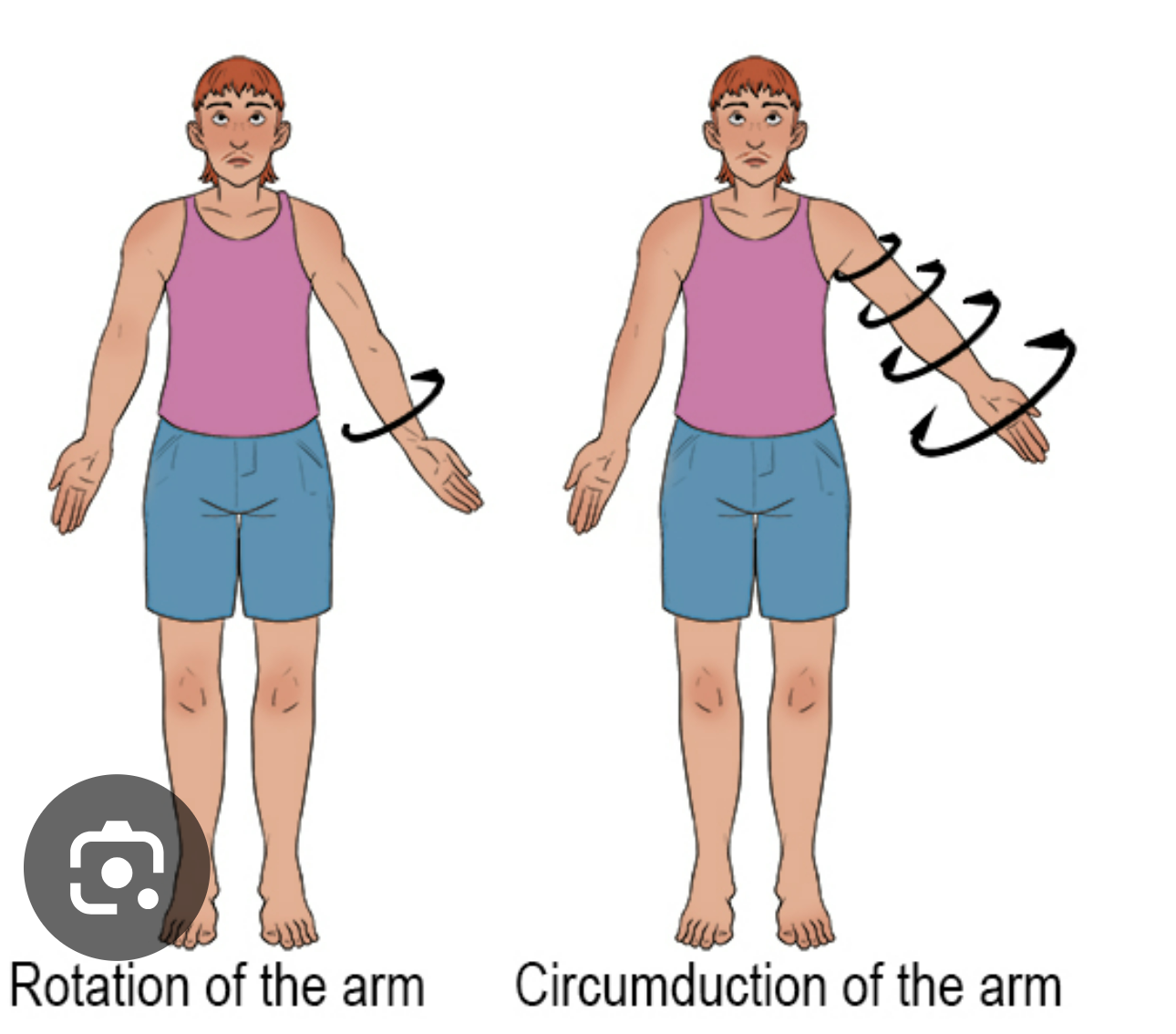
define rotation
moving a part around its long axis (e.g. screwing a screwdriver)
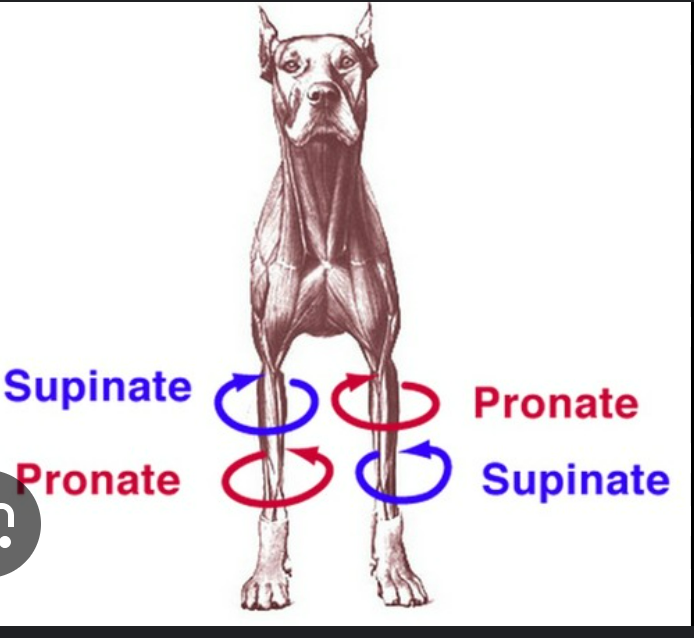
define supination
rotating the leg so the palmar/plantar surface of the paw faces medially (top of paw faces outward)
opposite pronation
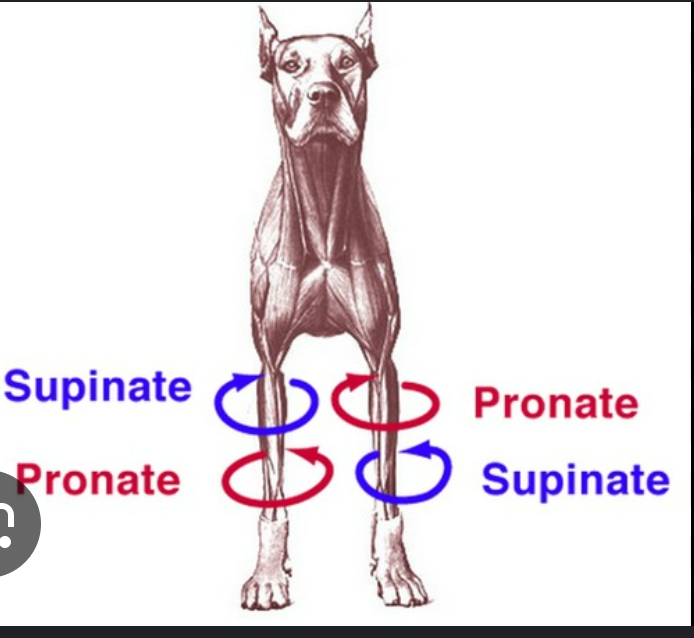
define pronation
rotating the leg away from the supine position so palmar/plantar surface faces the substrate (top of paw faces inward)
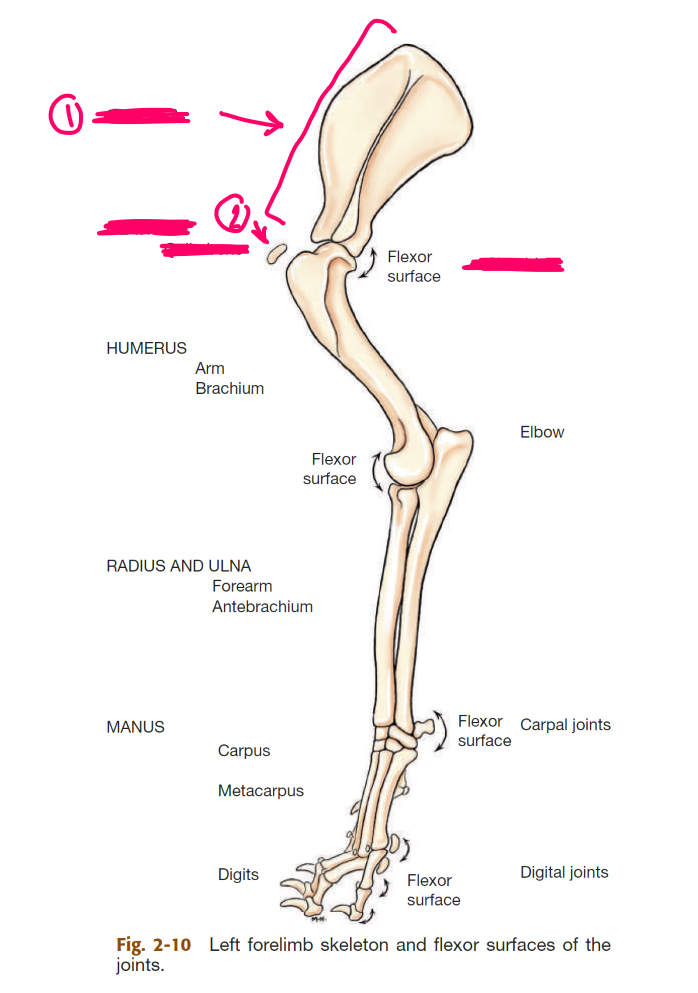
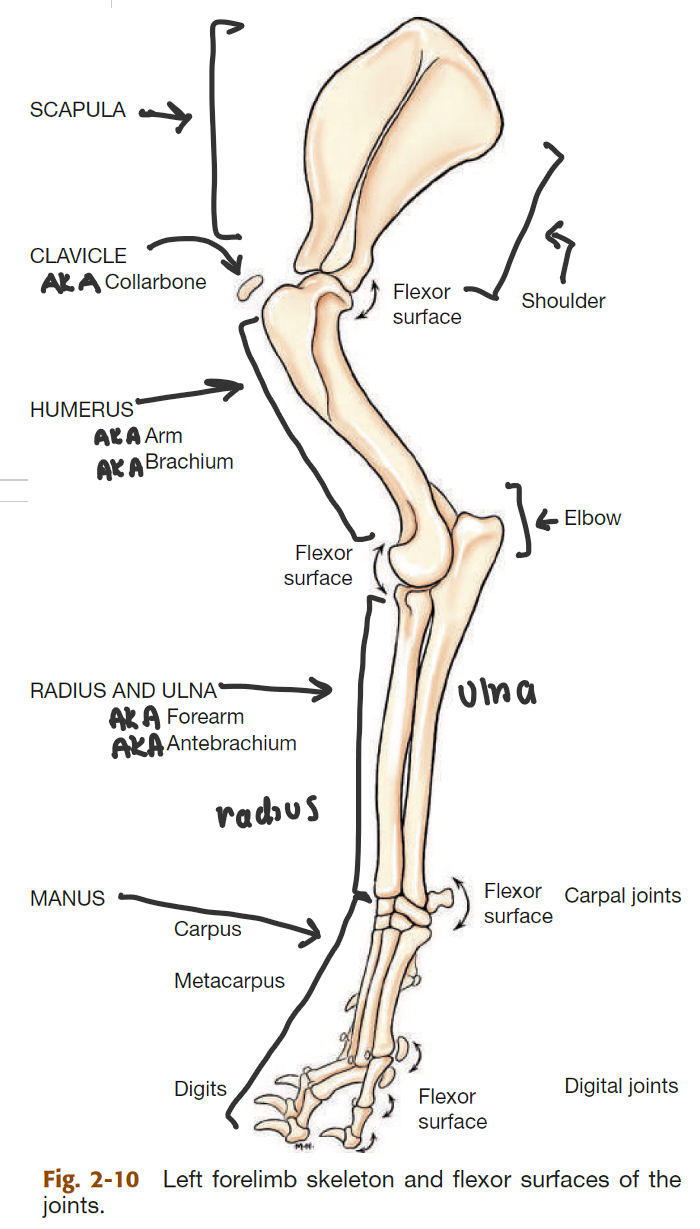
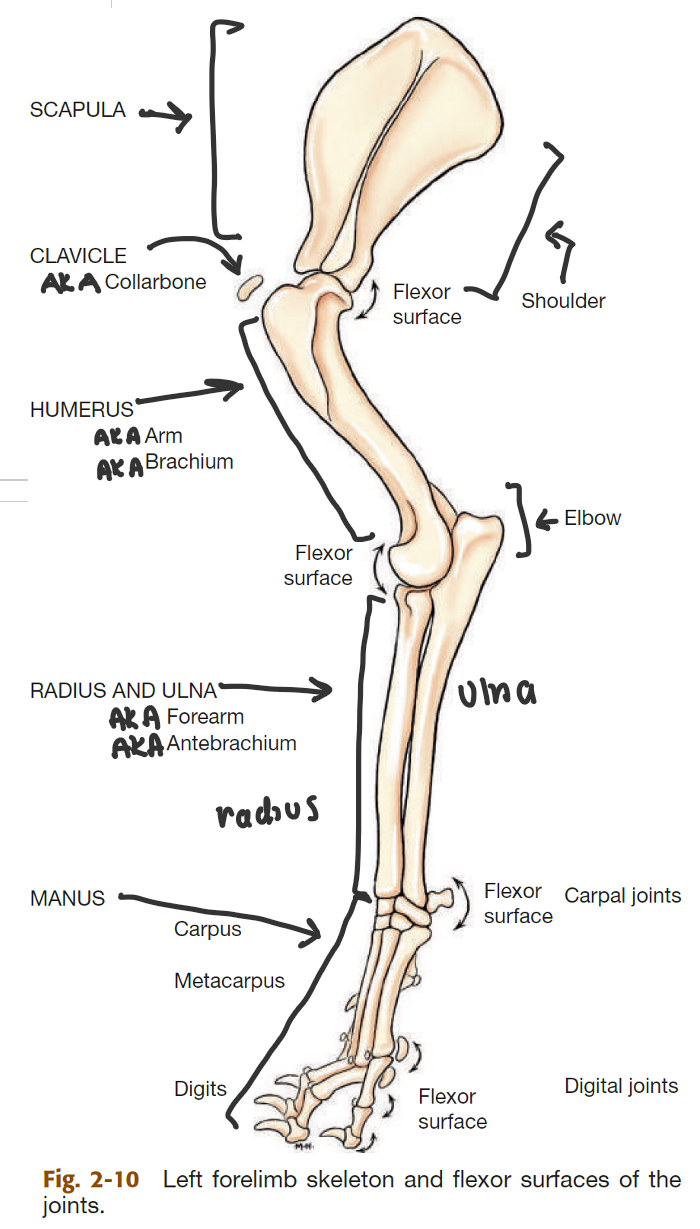
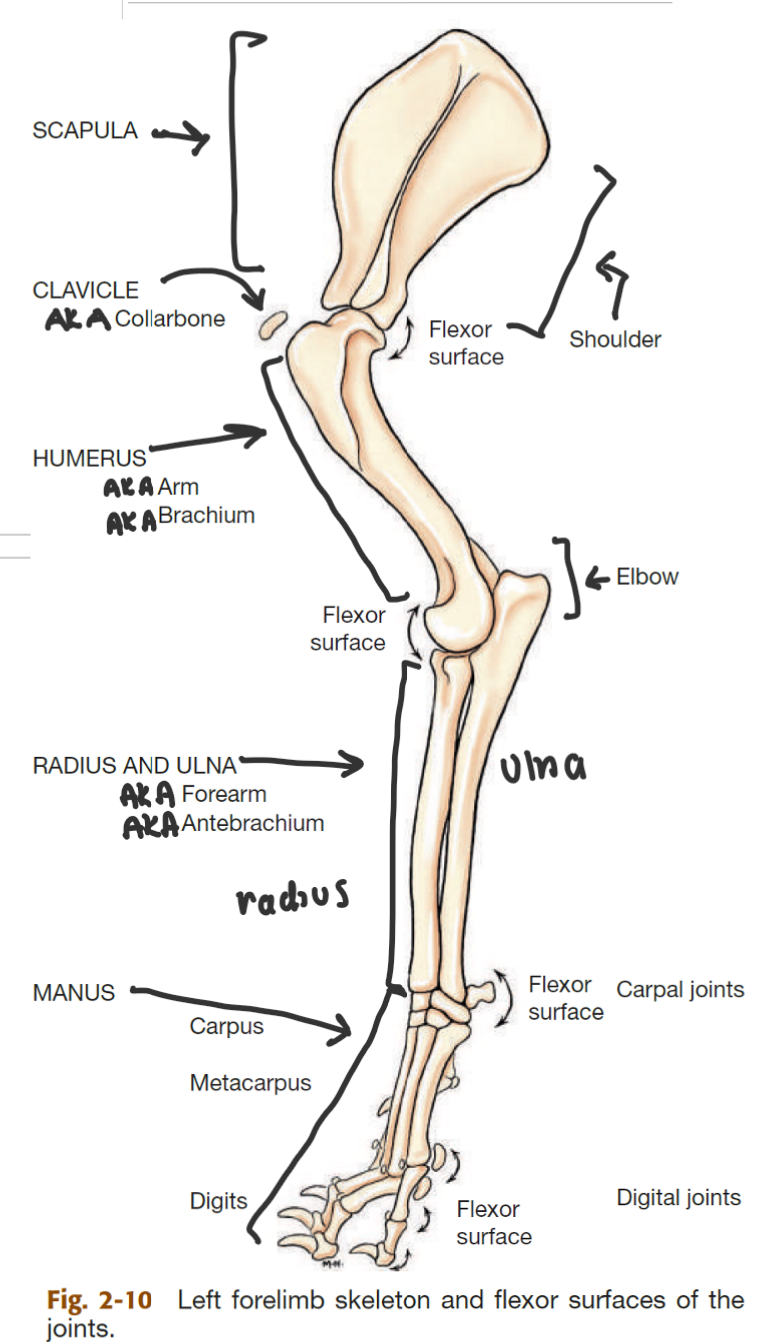
label the bones of the thoracic girdle
scapula (big triangle)
clavicle (small, detached, AKA collarbone)
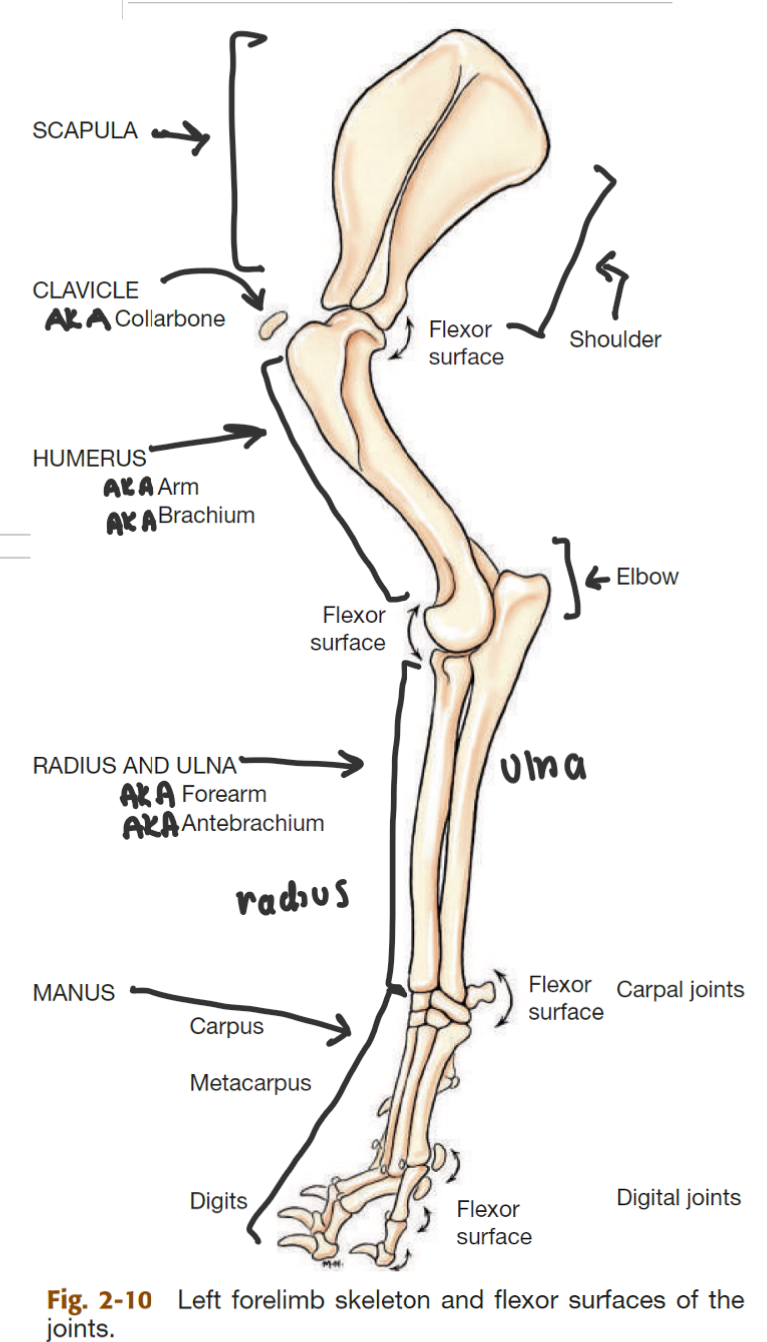
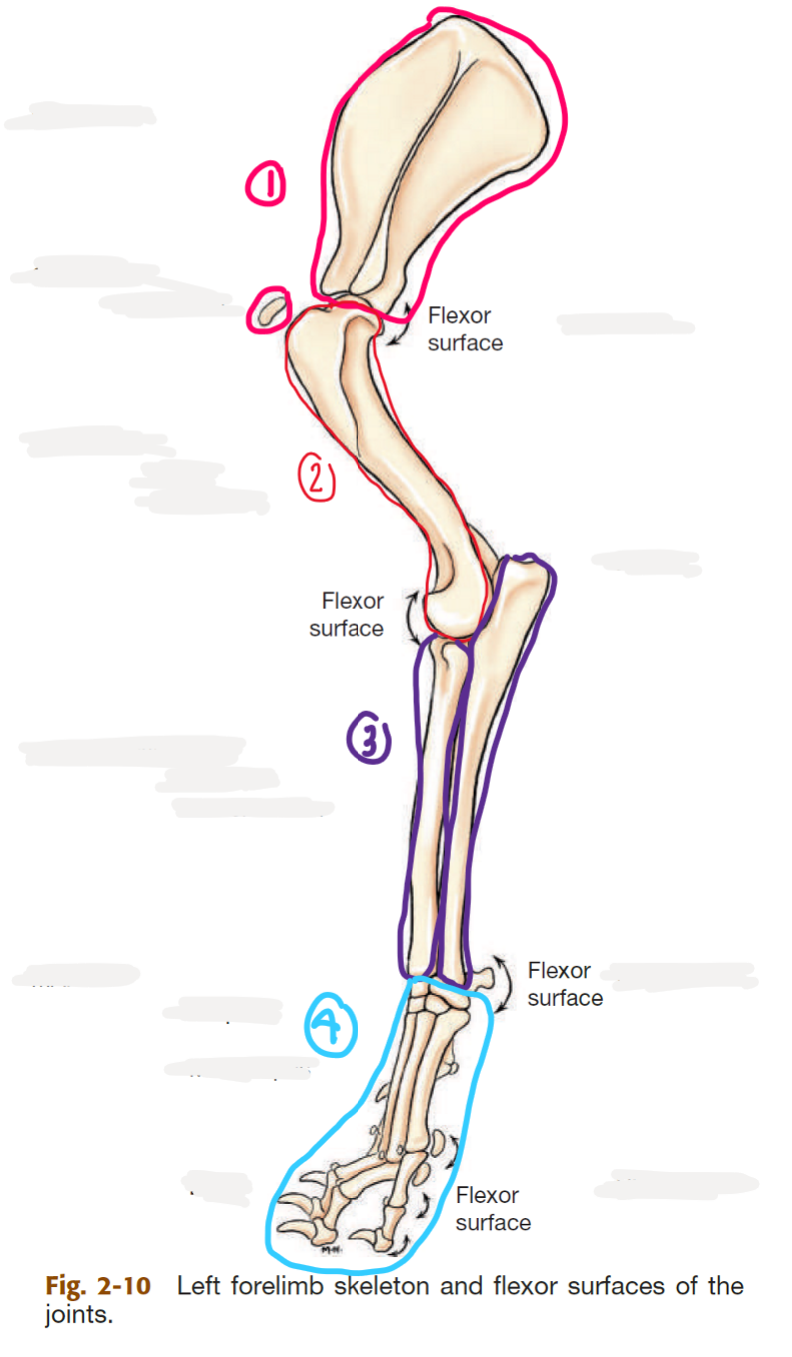
label the segments of the thoracic limb (AKA forelimb)
whats the name of the bone in 2
thoracic girdle (AKA shoulder)
brachium (AKA arm)
antebrahcium (AKA forearm)
manus (AKA forepaw)
humerus
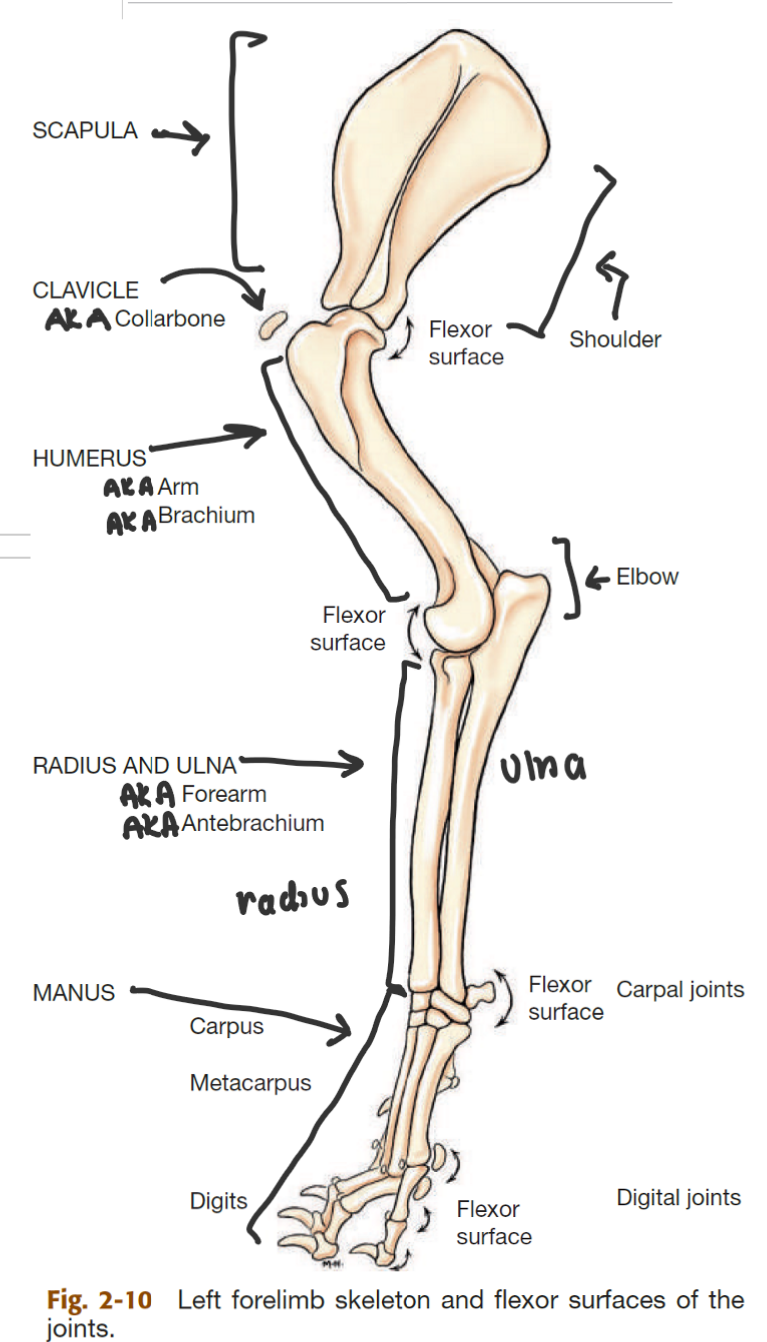
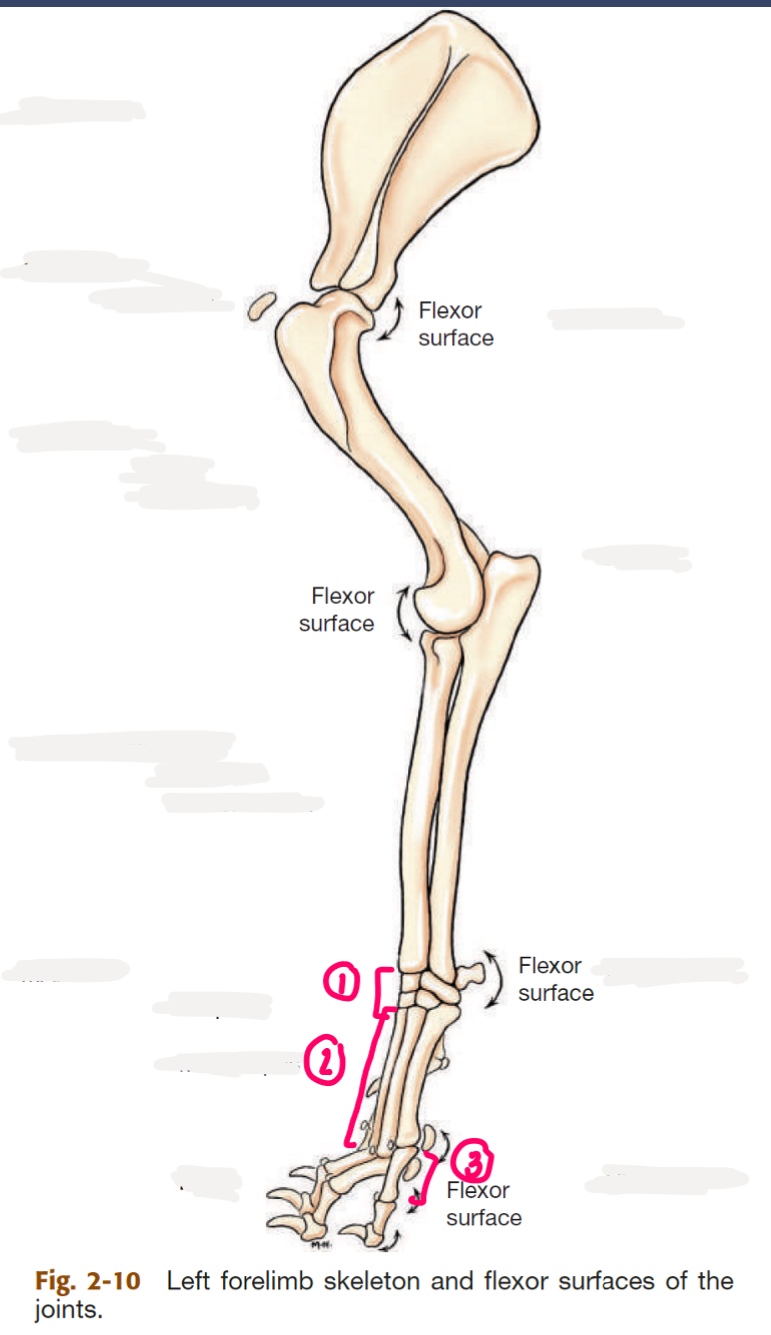
label the bones of the manus
2 → SPELLING
carpal bones
metacarpal bones
phalanges
whats the dogs vertebral formula
C7 T13 L7 S3 Cd20
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, caudal
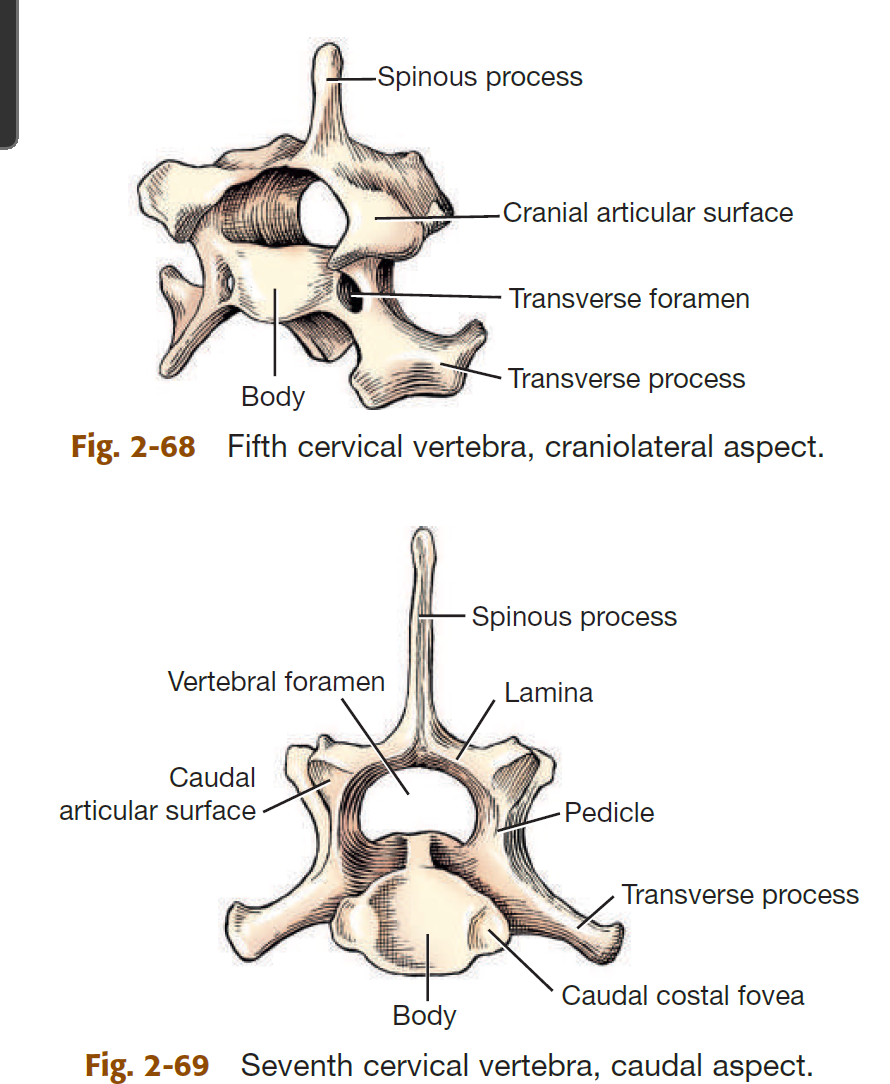
name the 3 parts of a vertebra
body
vertebral arch (formed by pedicles & laminae)
tranverse, spinous, & articular processes
whats the common name of the 1st & 2nd cervical vertebrae
atlas
axis
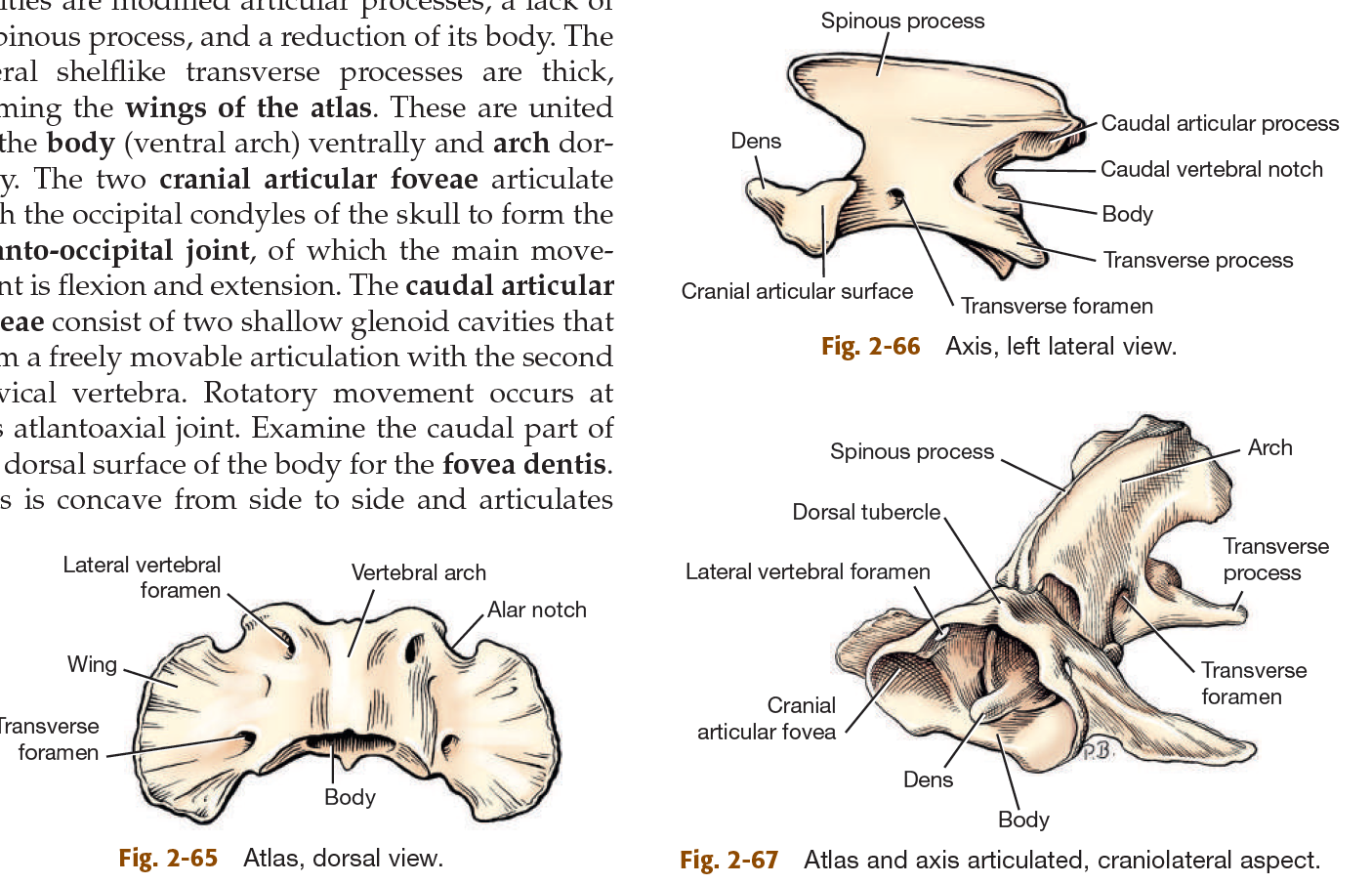
ventral view of dogs neck:
label 1 & 2 & 3
sternocephalicus muscle (compound muscle, runs from sternum to head, shaped like V, on both sides)
sternohyoideus muscle (runs right in middle of ^)
sternothyroideus m: lateral to 2
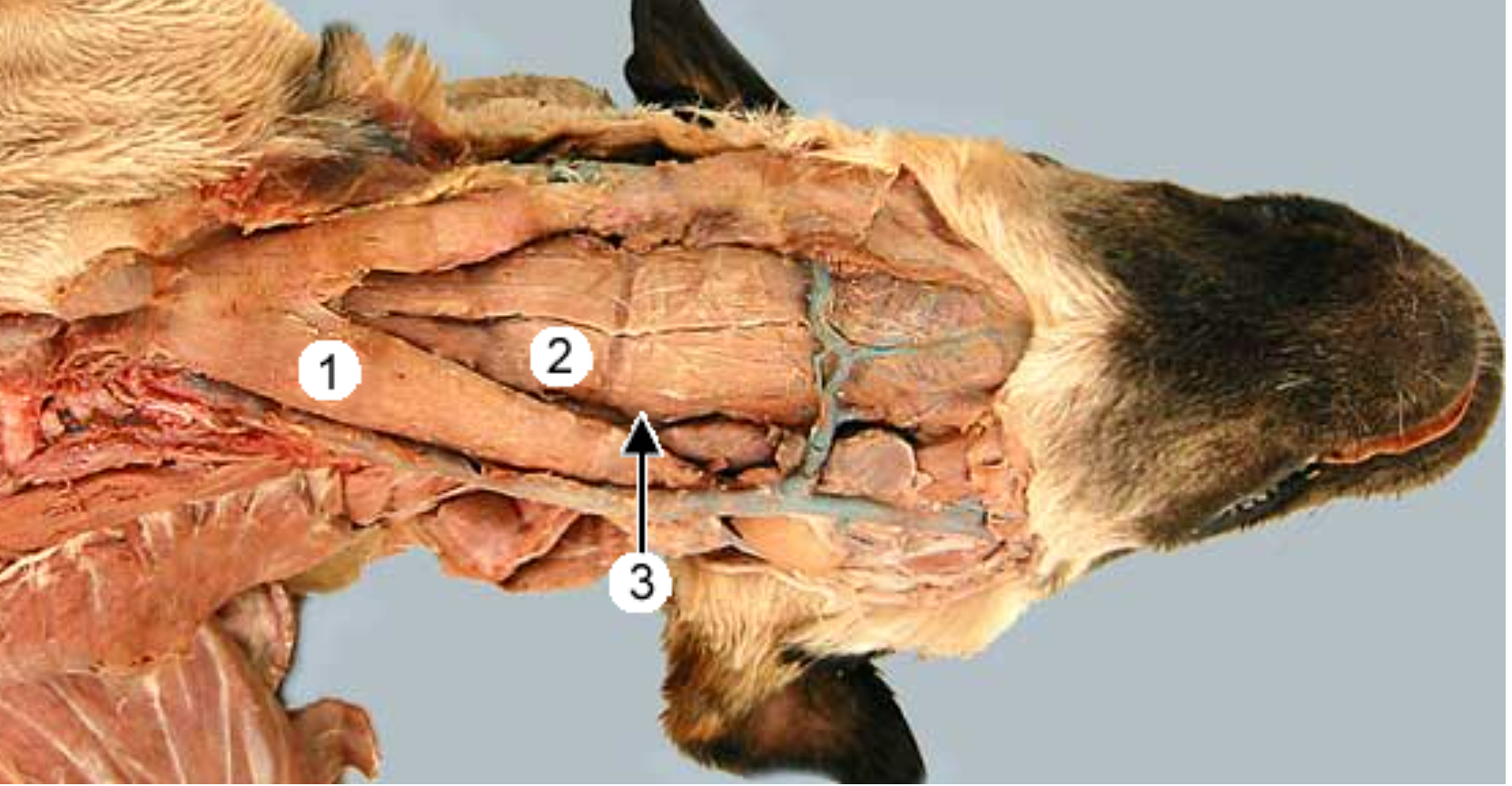
lateral (side) view of the ventral dog neck:
label 1, 2, 3, 5
common carotid artery (pink, part of carotid sheath)
vagosympathetic trunk (white, part of carotid sheath)
esophagus (to the left of the trachea if you’re looking at dog in the face)
trachea (hard, white, has cartilage rings)
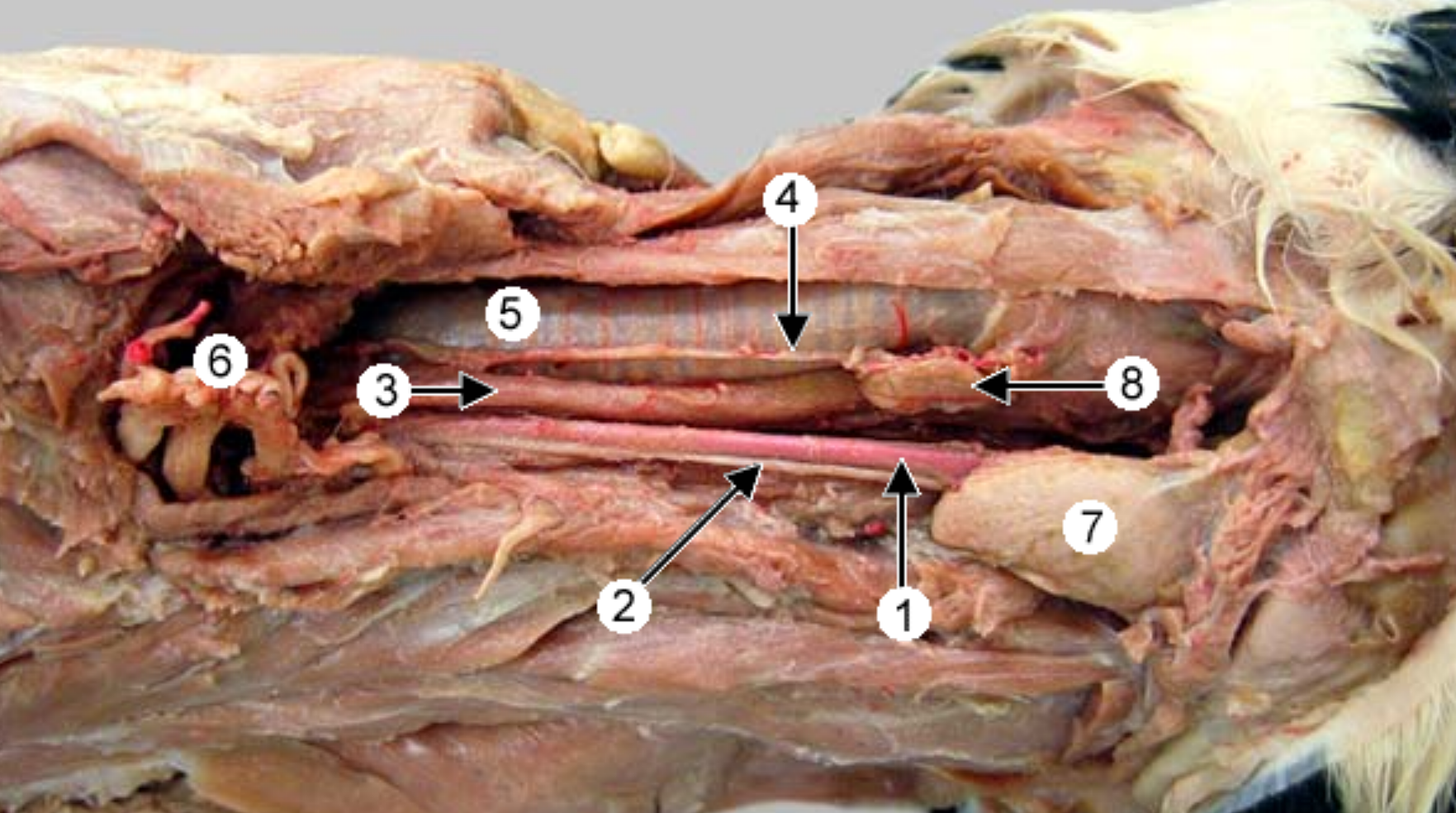
lateral view of dogs neck:
label 1, 2, 4, 10
what is 1,2,4 called together
clavicular intersection (white line that sepearates 2 parts of the brachiocephalicus muscle)
cleidocephalicus muscle (part of brachiocephalicus that runs from head to 1)
cleidobrachialis muscle (part of brachiocephalicus that runs from 1 to humerus)
external jugular vein (this is what we poke during blood draws, located between sternocephalicus & brachiocephalicus)
brachiocephalicus (compund muscle, runs from head to arm)
“cleido” = clavicle
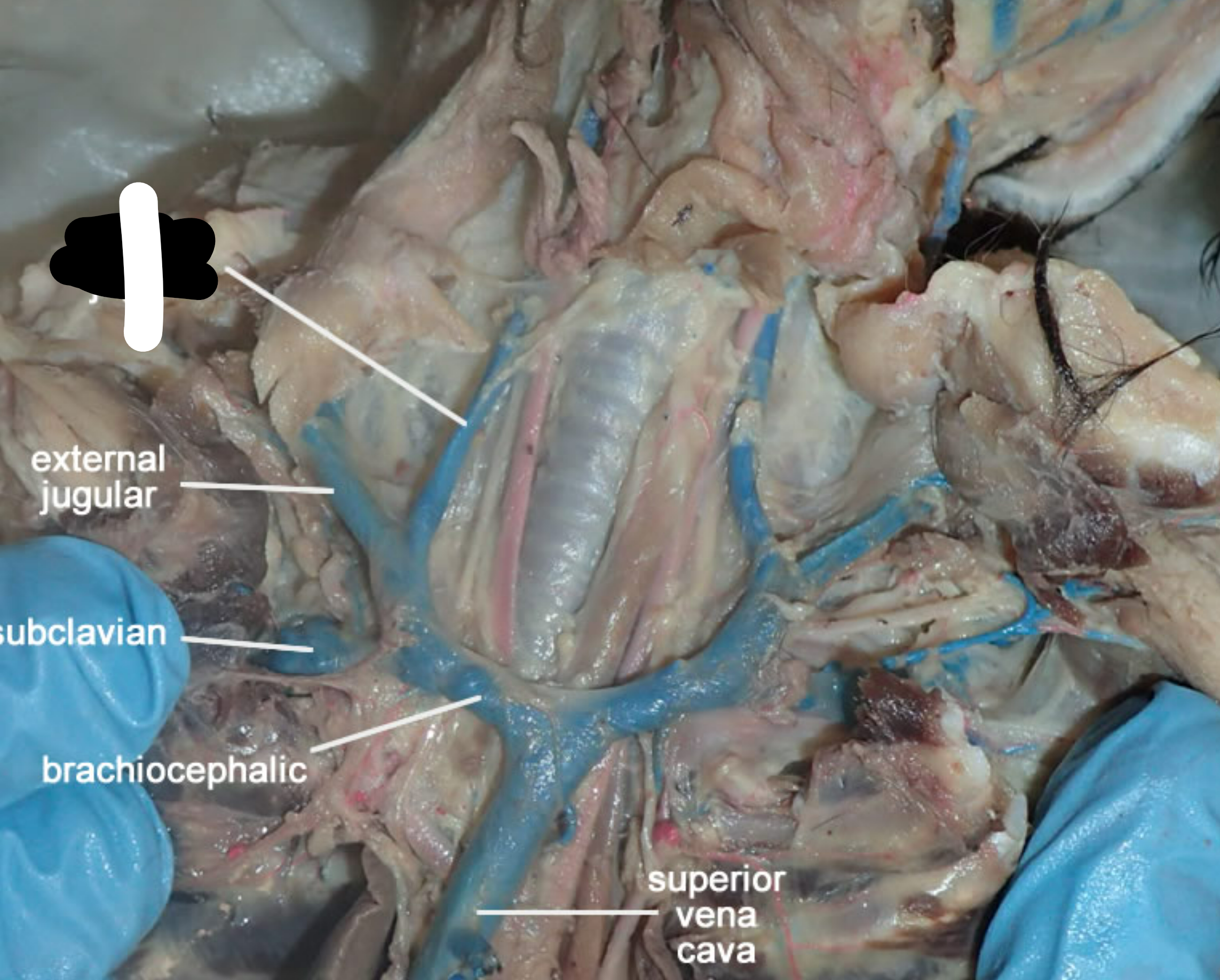
ventral view of the neck:
label 1
internal jugular vein (part of carotid sheath along w/ common carotid artery & vagosympathetic trunk, usually blue)
whats a compound muscle
a muscle made of multiple individual muslces that are anatomically joined together
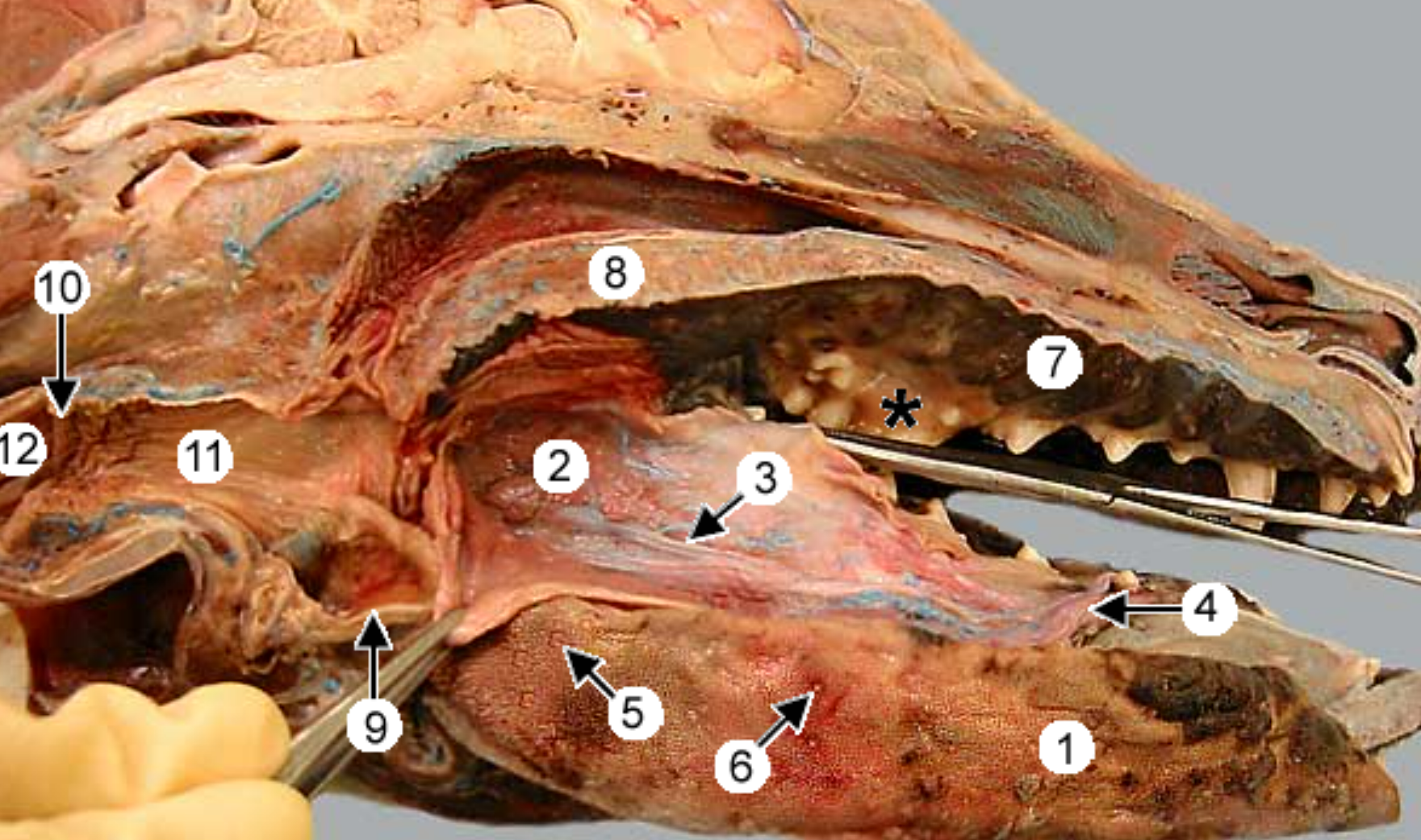
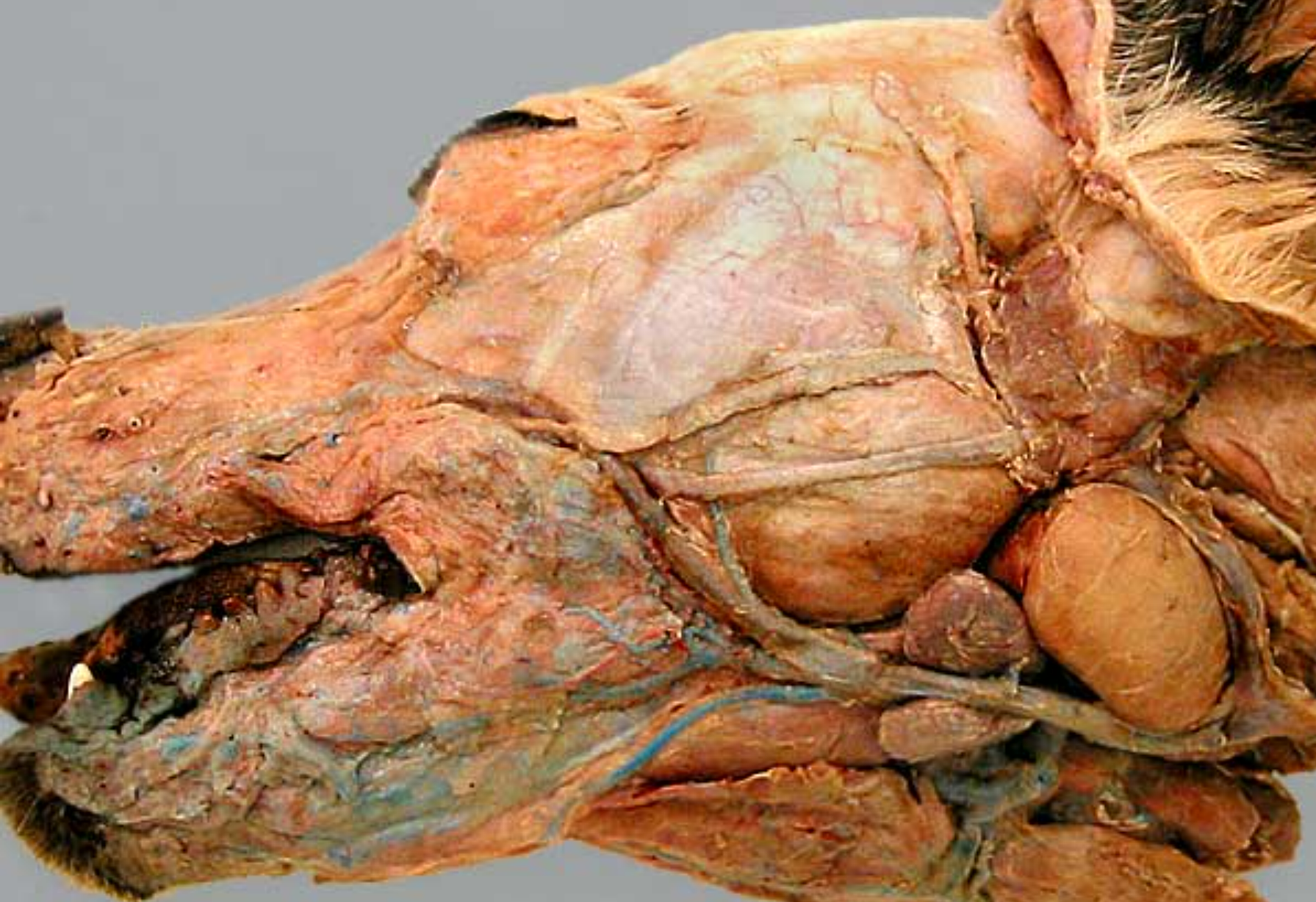
label the parts of the oral cavity (canine head split in half): 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12
(1) is the tongue & it’s pulled to the side (tweezers pulling it back)
tongue
-
-
sublingual caruncle: small tissue on floor of mouth, on either side of lingual frenulum, this is where subman & subling ducts empty into mouth
vallate papillae: at junctionf of body & root of tongue, in V shape, largest papilla, big circles
fungiform papillae: smooth & round, look like fungus (“fung”)
hard palate: near front of mouth, rugae under it
soft palate: caudal to ^
epiglottis: flap that covers trachea during swallowing
-
pharynx
esophagus
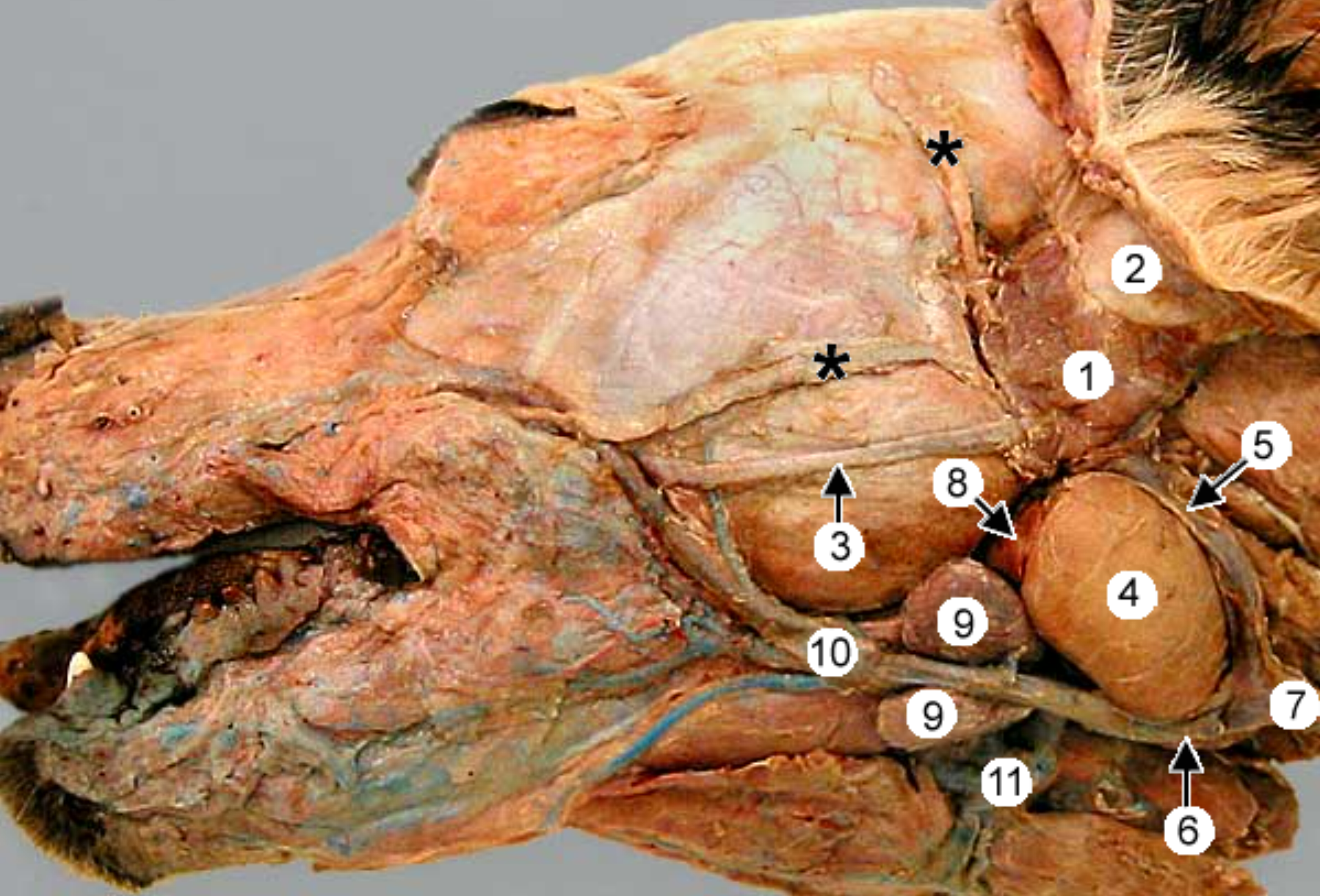
label the salivary glands: 1, 4 (anine head split in half)
parotid salivary gland: at base of ear, V shape
-
-
mandibular salivary gland: golf ball shape
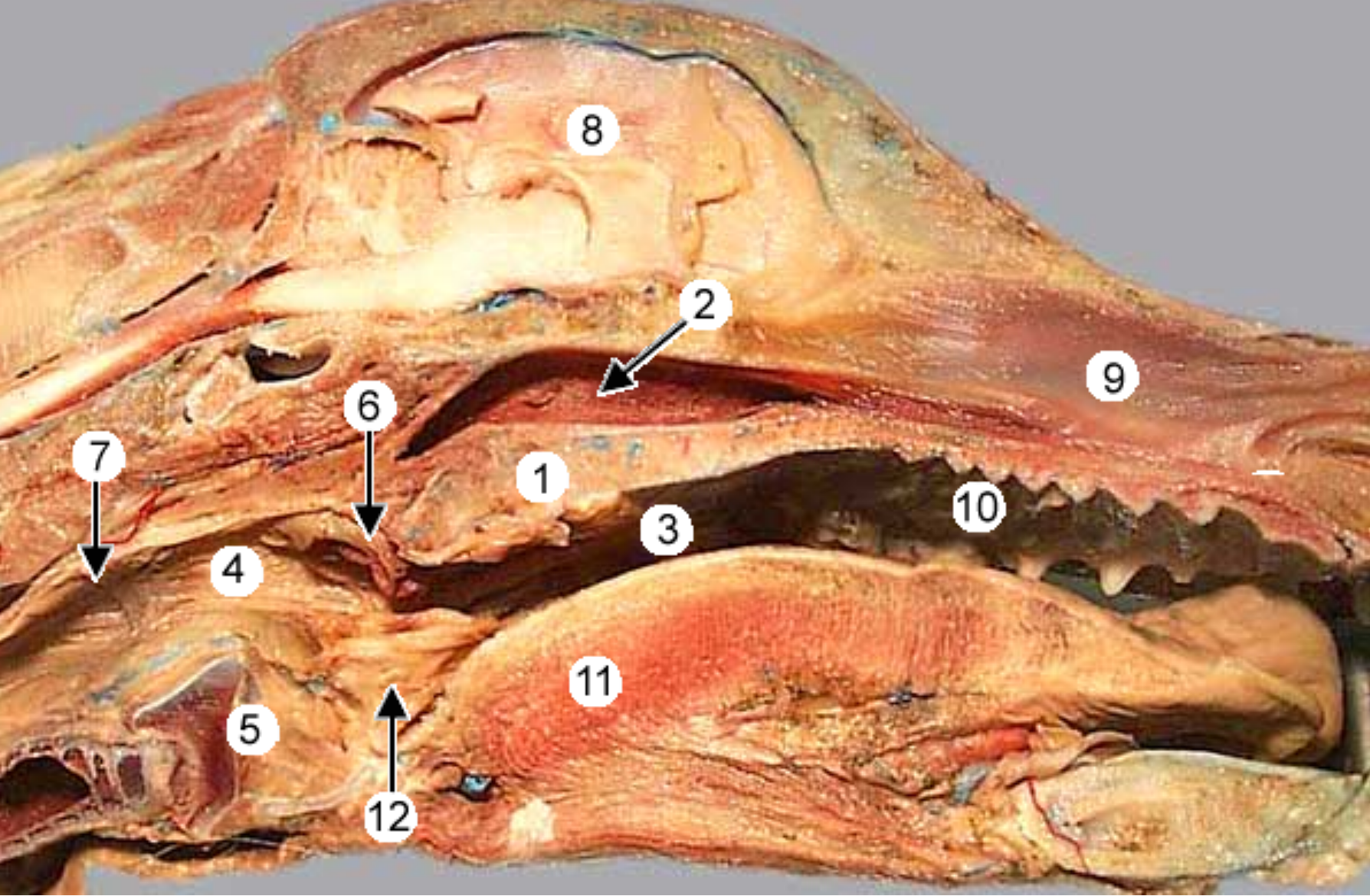
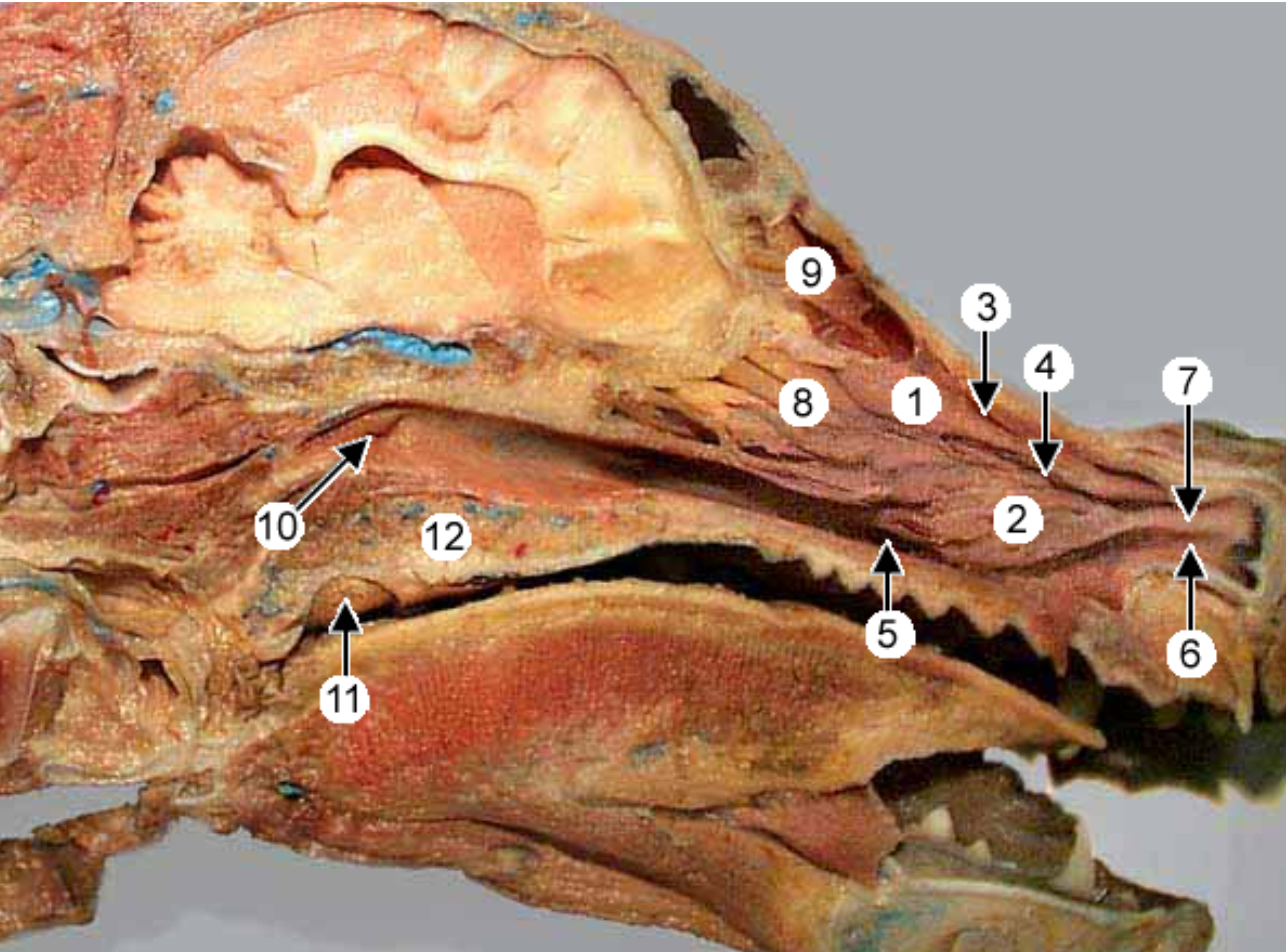
label the parts of the oral cavity (canine head split in half, mouth opening on right): all except 8
soft palate: caudal to hard palate
nasopharynx: open space above soft palate
oropharynx: open space at back of mouth, extends from soft palate to base of epiglottis (includes tonsils)
laryngopharynx: caudal to soft palate, on top of larynx
larynx
palatopharyngeal arch: fold of tissue that marks caudal end of soft palate, clolses off nasopharynx during swallowing
pharyngoesophageal limen: marks boundary between pharynx & esophagus, at caudal end of laryngopharynx
-
nasal septum: bone/cartilage wall that divides nose into 2 nostrils
hard palate: near front of mouth, rugae under it
root of tongue: the caudal third of the tongue (back part)
epiglottis: flap that covers trachea during swallowing
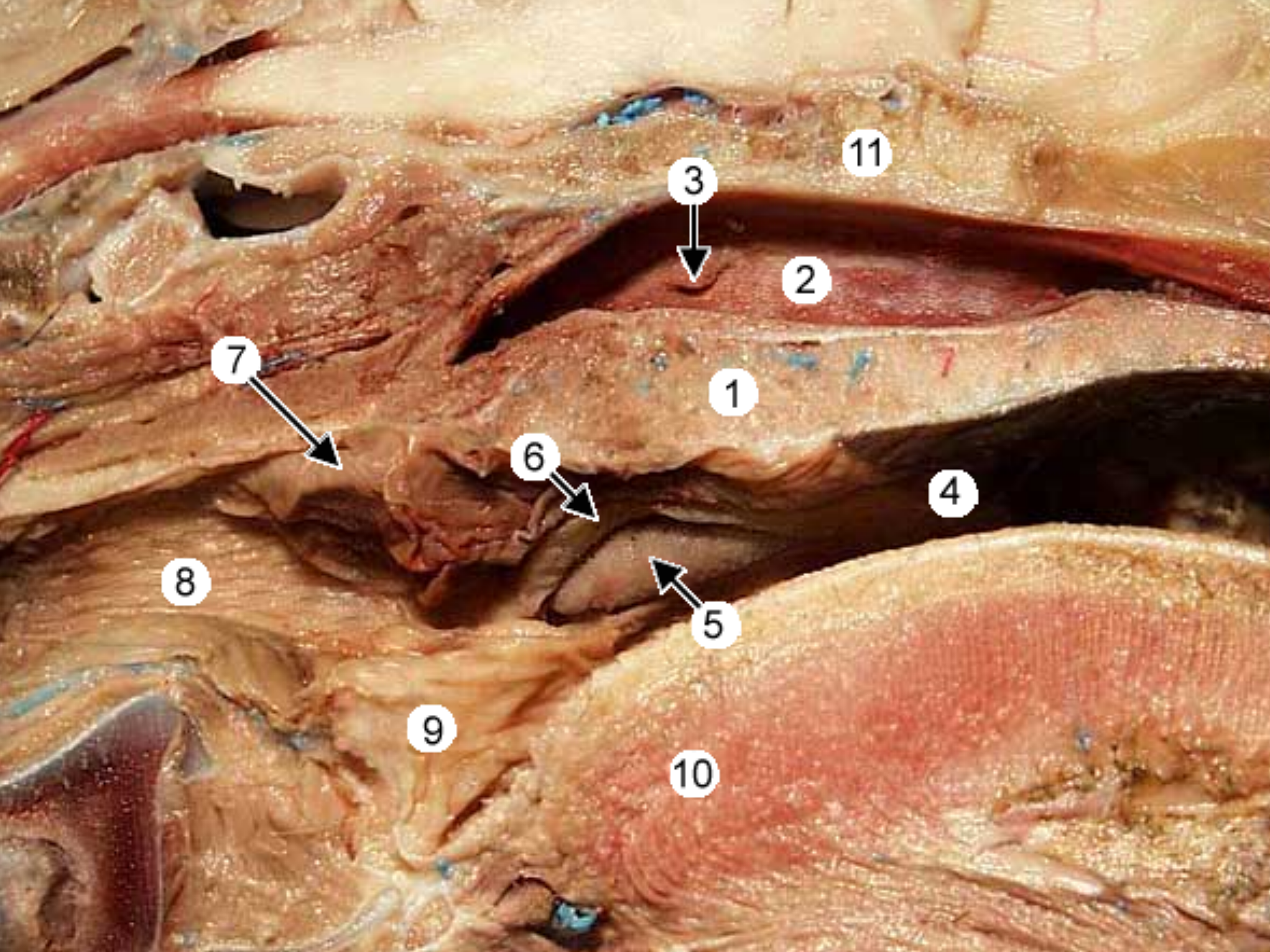
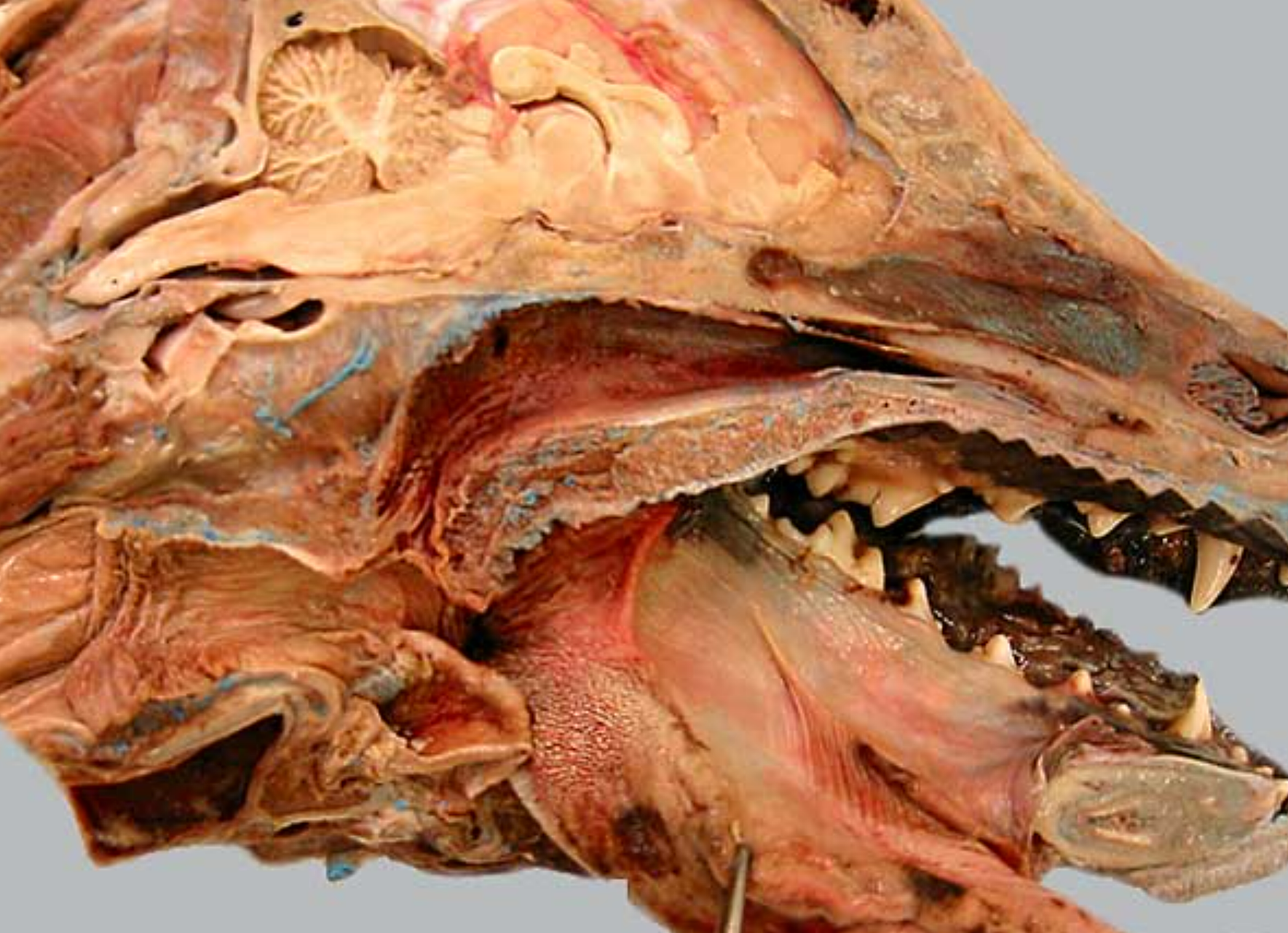
label this close up view of the back of the dog’s mouth 2-9
for reference: 10 is the root of the tongue, 4 is the oropharynx, 1 is the soft palate
-
nasopharynx: open space above soft palate
pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube: slitlike opening in nasopharynx
-
palatine tonsil: in back of throat inside oropharynx
semilunar fold: tissue that covers the ^
palatopharyngeal arch: fold of tissue that marks caudal end of soft palate, clolses off nasopharynx during swallowing
laryngopharynx: caudal to soft palate, on top of larynx
epiglottis: flap that covers trachea during swallowing
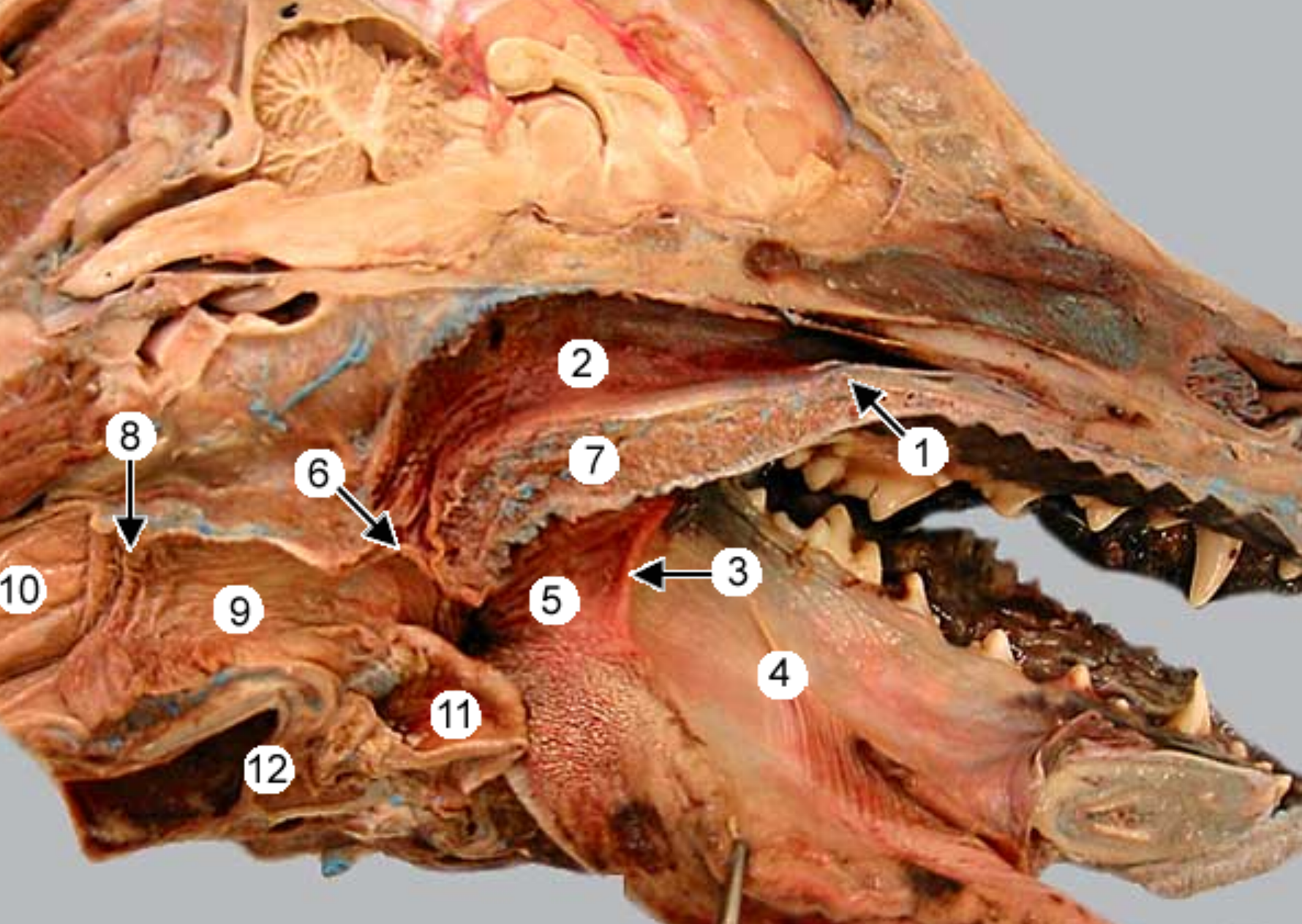
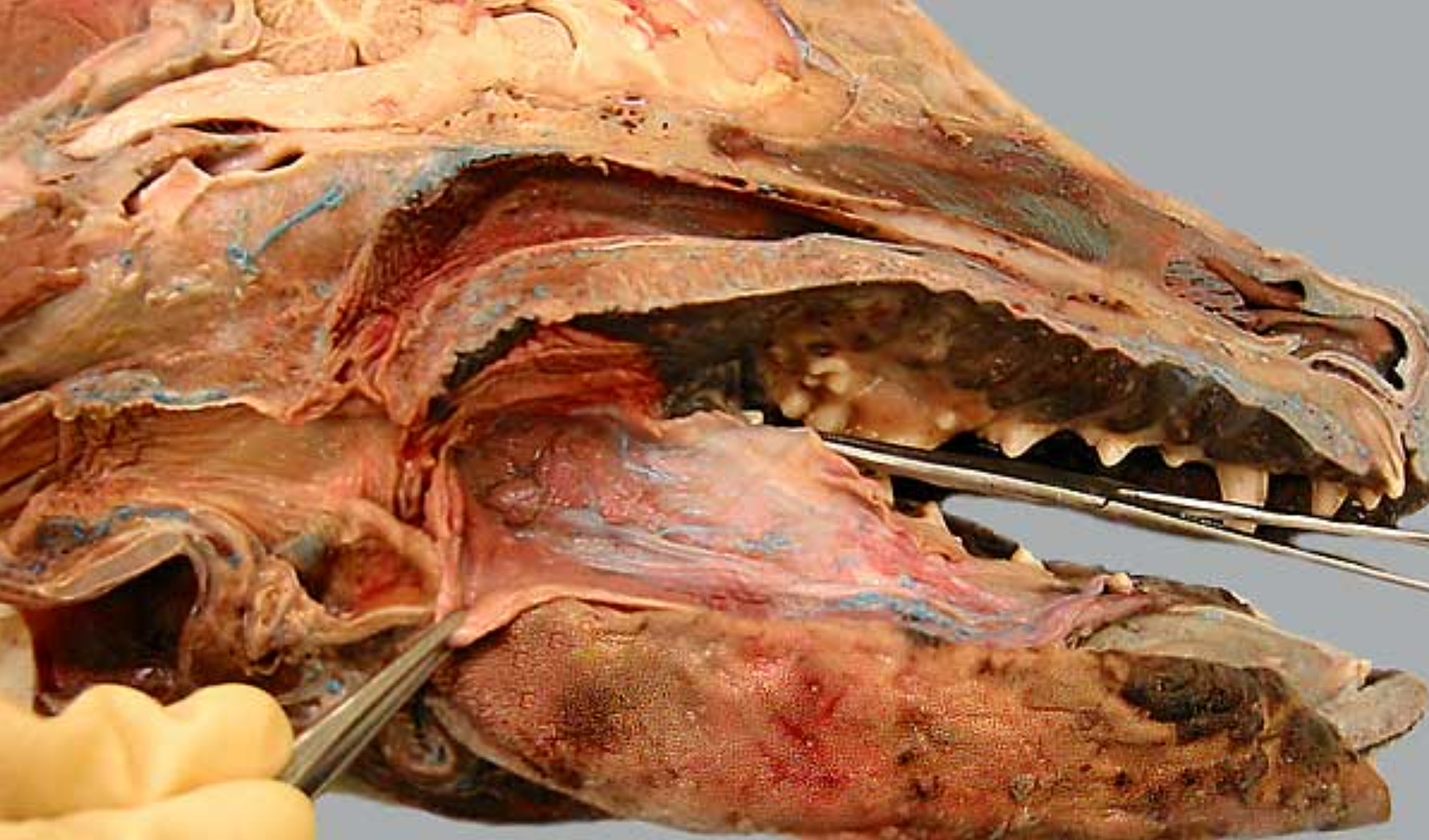
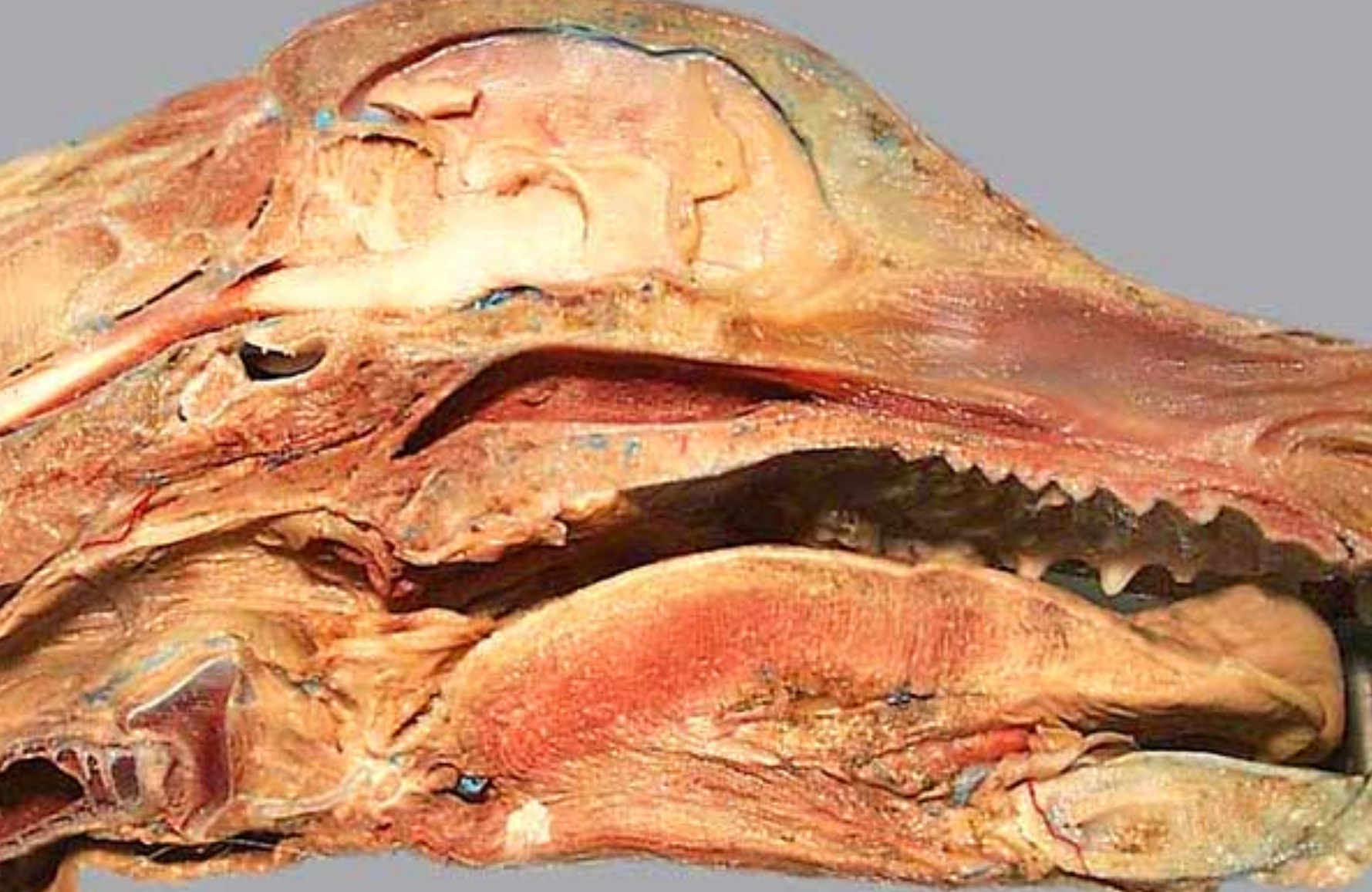
label the parts of the oral cavity (canine head split in half): all except 4 & 5, 12
the tongue & it’s pulled to the side (tweezers pulling it back)
hard palate: near front of mouth, rugae under it
nasopharynx: open space above soft palate
palatoglossal arch: tissue that connects side of tongue to soft palate, marks boundary between the mouth & oropharynx (throat, 5)
-
-
palatopharyngeal arch: fold of tissue that marks caudal end of soft palate, clolses off nasopharynx during swallowing
soft palate: caudal to hard palate
pharyngoesophageal limen: marks boundary between pharynx & esophagus, at caudal end of laryngopharynx
laryngopharynx: caudal to soft palate, on top of larynx
esophagus
epiglottis
label the parts of the oral cavity (canine head split in half, nasal septum removed): all excpet 6 & 7
concha are curved bones in nasal passages, helps warm air
meatuses are the small open spaces formed between the conchae
dorsal nasal concha: most dorsal concha
ventral nasal concha: largest conch
dorsal nasal meatus: between (1) and top of nasal cavity
middle nasal meatus: between (1) and (2)
ventral nasal meatus: between (2) and bottom of nasal cavity
-
-
ethmoidal labyrinth: behind the nasal cavity
frontal sinus: air filled cavities within frontal bone
pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube: slitlike opening in nasopharynx
palatine tonsil: in back of throat inside oropharynx
soft palate
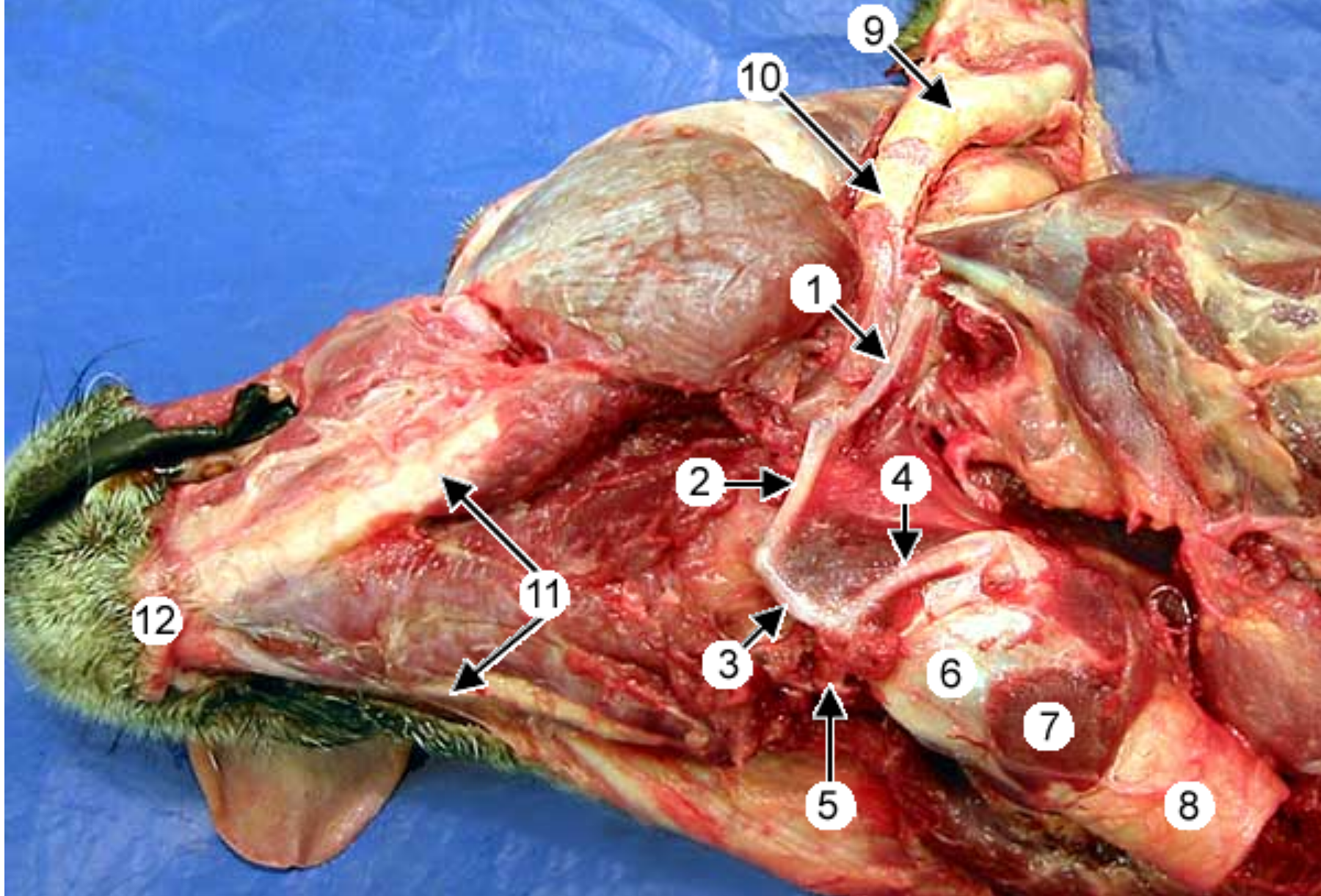
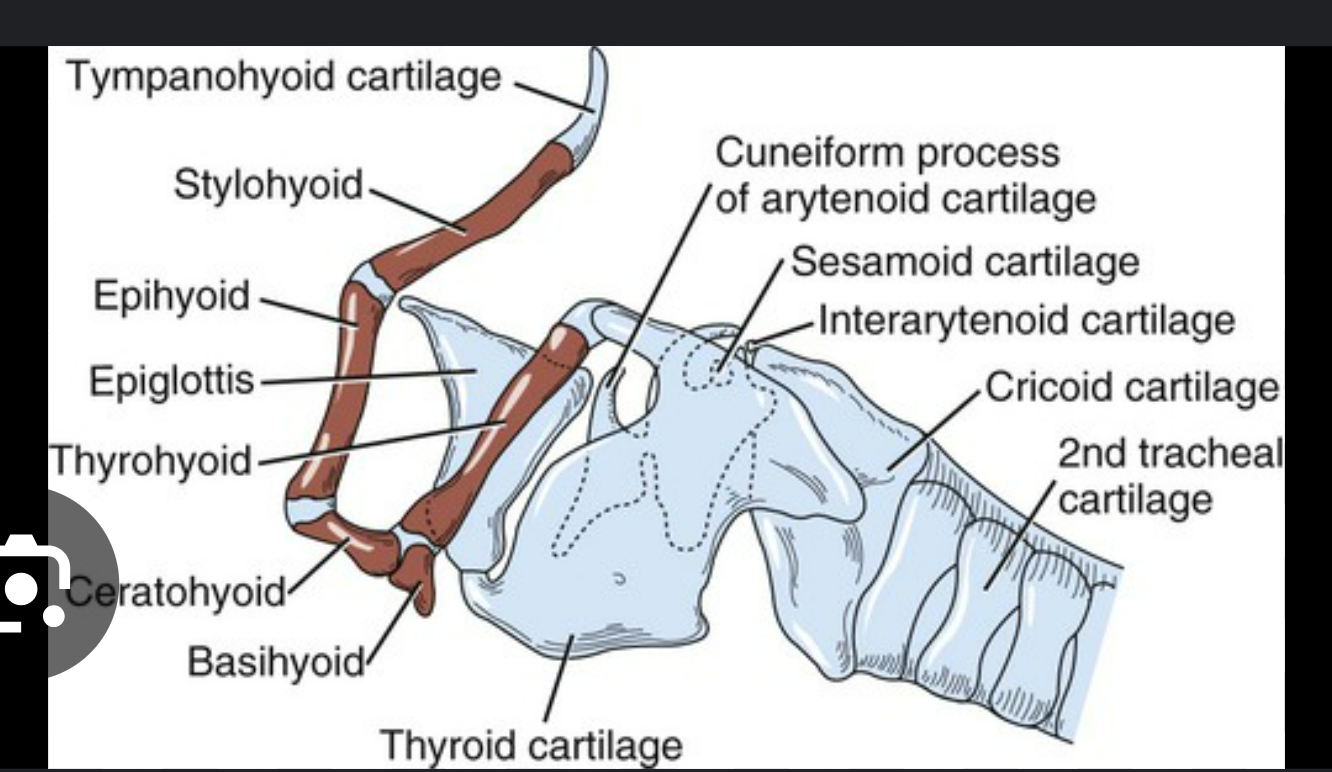
label the parts of the hyoid apparatus (this is bones and muscles that acts as an attachment platform for the tongue and larynx) (ventrolateral view of canine head): all except 7-10
*there’s 2 of each of these hyoid bones, except only 1 basihyoid connects both sides
stylohyoid: top bone, at tip
epihyoid: below ^
ceratohyoid: below ^
thyrohyoid: on top of basi and extends out caudally
basihyoid: at the base
thyroid cartilage of the larynx: large cartilage that forms wall of larynx
-
- (trachea)
-
-
mandible: 2 of these, left & right, form the jawbone
Some Elephants Can Be Tall
think of it like a big necklace that supports the tongue & larynx: top are big stud earrings (stylohyoids), small beads under to start the necklace (epihyoid), larger beads (ceratohyoid), basihyoid is the center pendant, thyrohyoid is a tassle hanging from the pendant
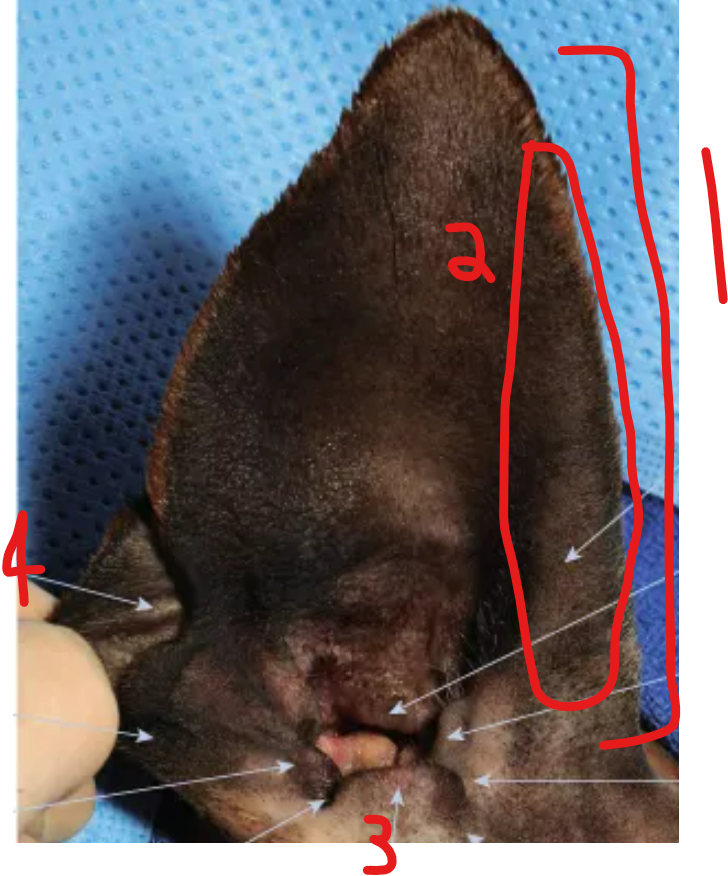
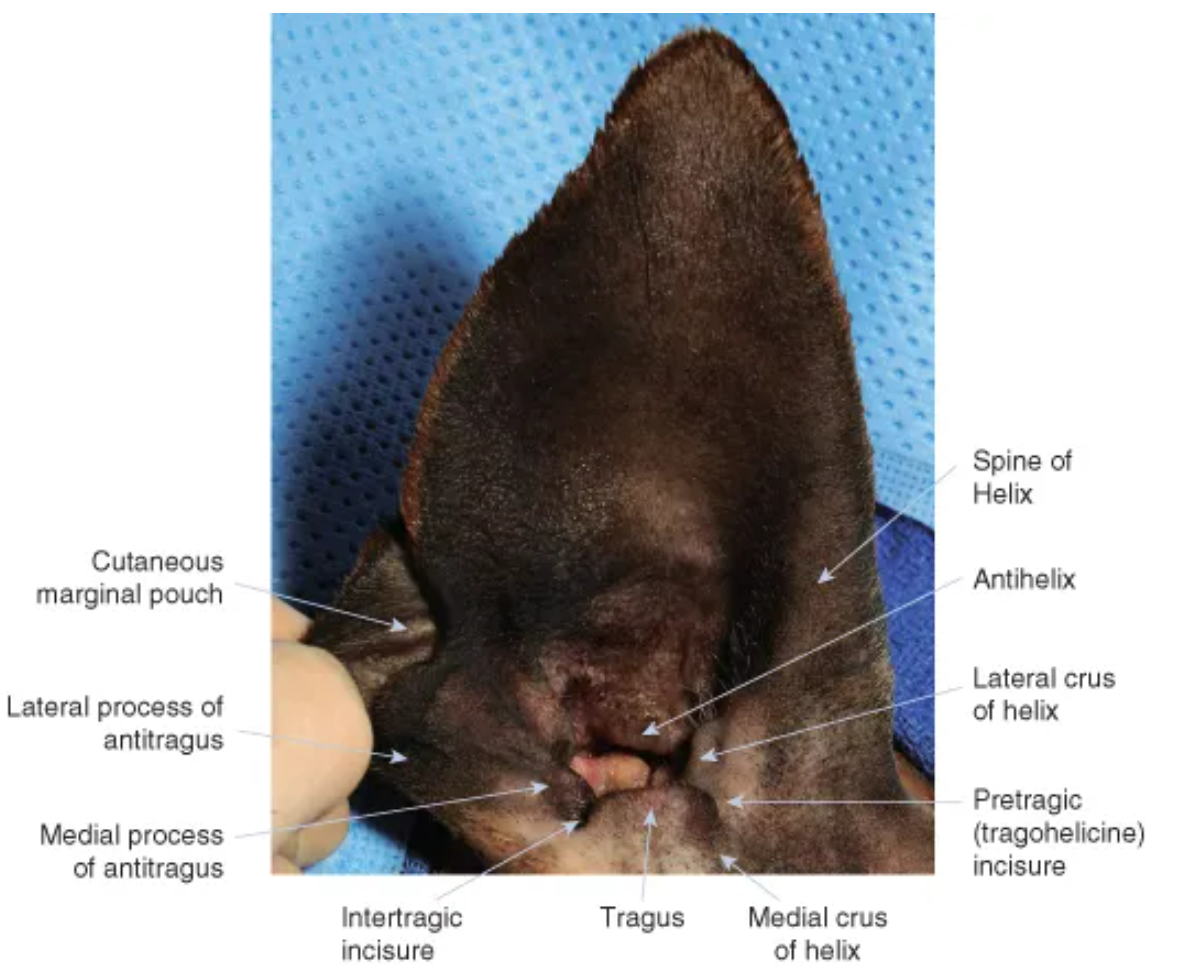
label the parts of the canine ear
auricle/pinna: the outer visible part of the ear
helix: outer curved rim of the ear
tragus: pointed cartilage structure of entrance of ear canal, forms boundary of opening
cutaneous maringal pouch: fold of skin on lower, back ear
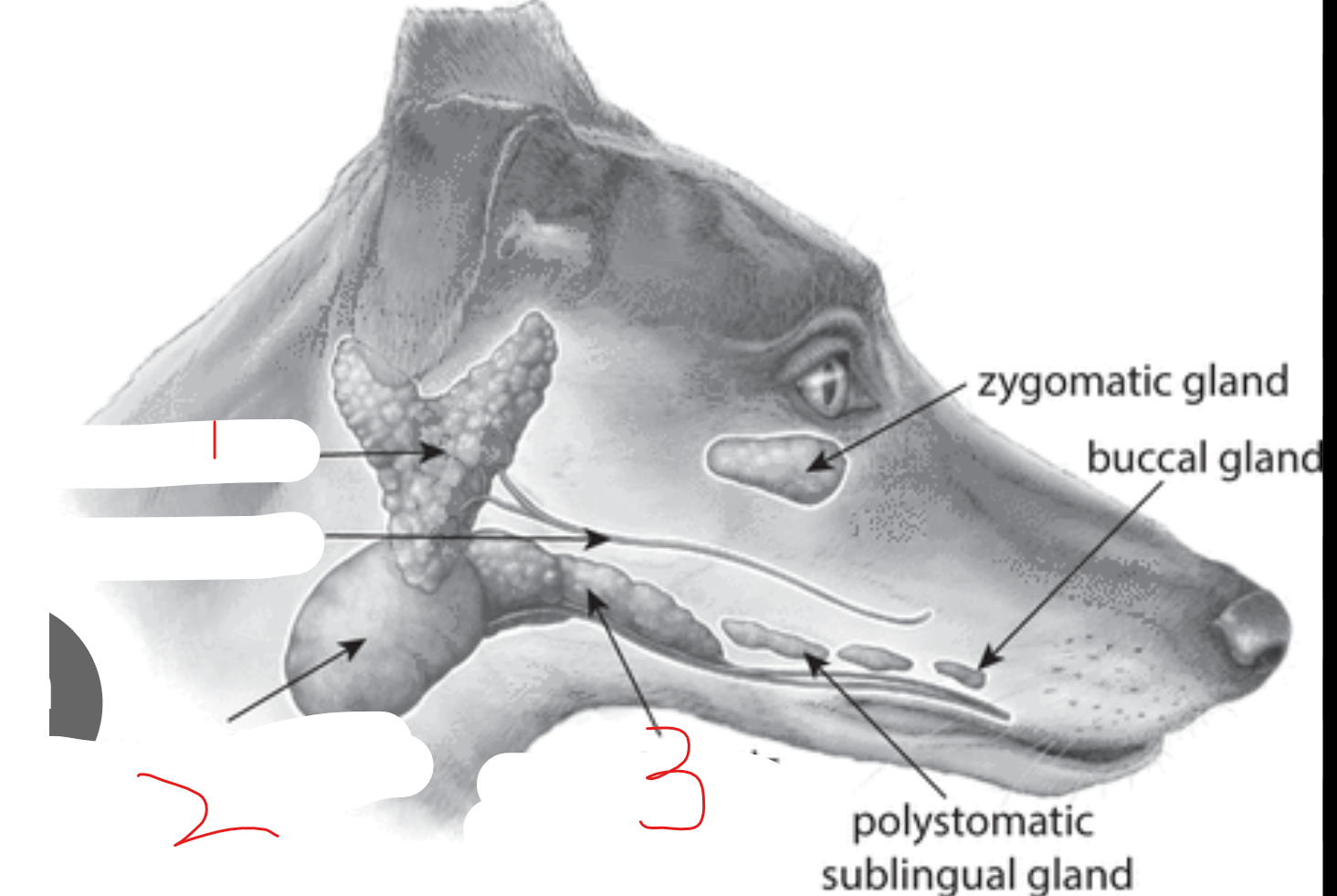
label the salivary glands
parotid gland: at base of ear, V shape
mandibular gland: gold ball shape
monostomatic sublingual gland: rostral to ^, near floor of mouth
label the cartilages of the larynx
epiglottis: flap of cartilage that covers trachea during swallowing
thyroid cartilage: forms front & sides of larynx, in front of cricoid
cricoid cartilage: below ^, forms complete circle around larynx
arytenoid cartilage: small, triangular, sit on top of ^
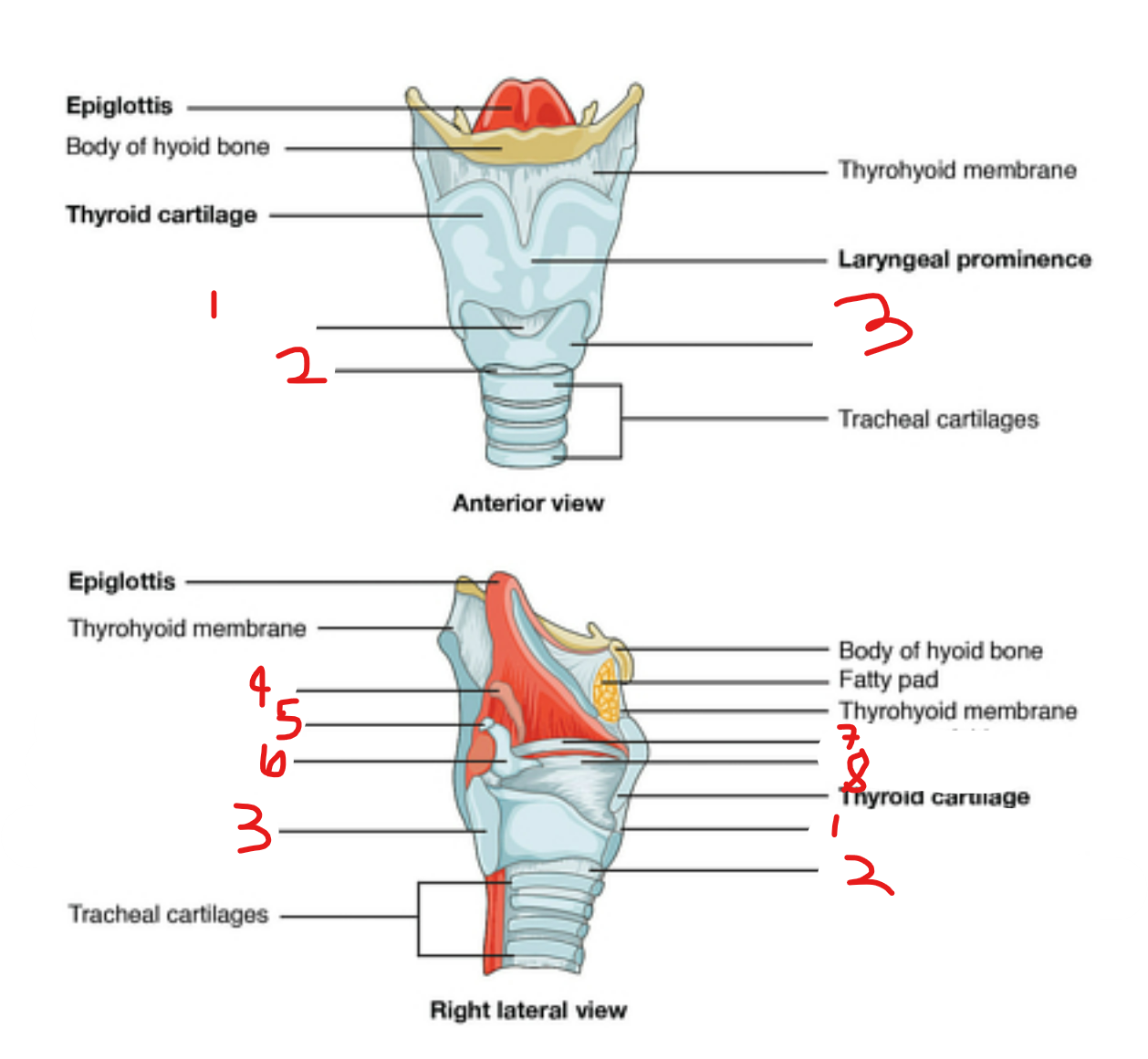
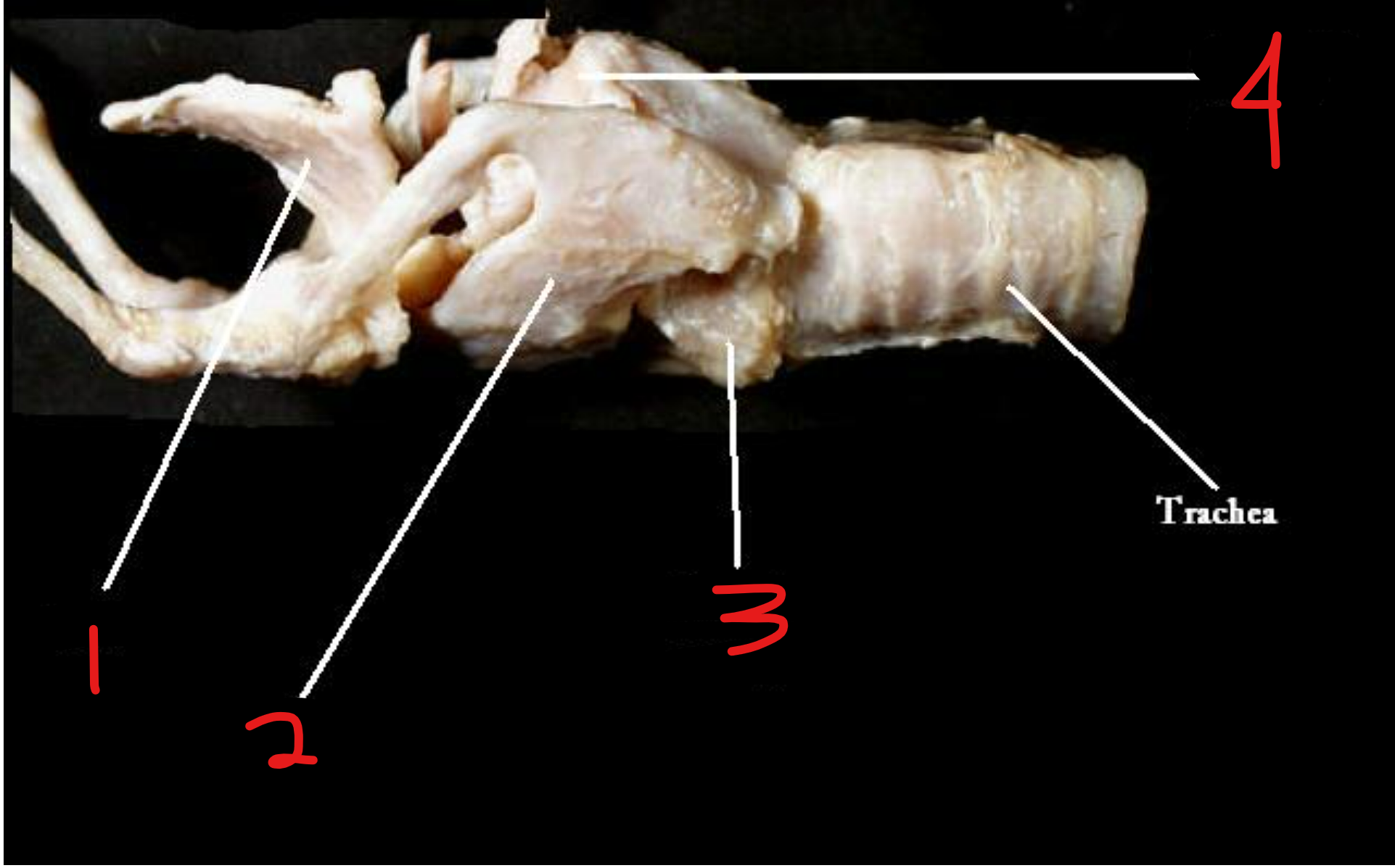
label the larynx
cricothyroid ligament: fibrous tissue that connects cricoid cartilage to thyroid cartilage in larynx
cricotracheal ligament: fibrous tissue that joins cricoid cartilage to first ring of trachea
cricoid cartilage: below thyroid cartilage, forms complete circle around larynx
cuneiform cartilage: most rostral part of artenoid cartilage, lies within aryepiglottic fold
corniculate cartilage: small horn shaped cartilage piece on top of arytenoid cartilage
arytenoid cartilage
vestibular fold: protective upper set of vocal folds to protect them, on top of (8)
vocal fold: extends from artyenoid to thyroid cartilage
cornucopia = horn, corniculate cart is a horn on the arytenoid
cuneus = wedge shape
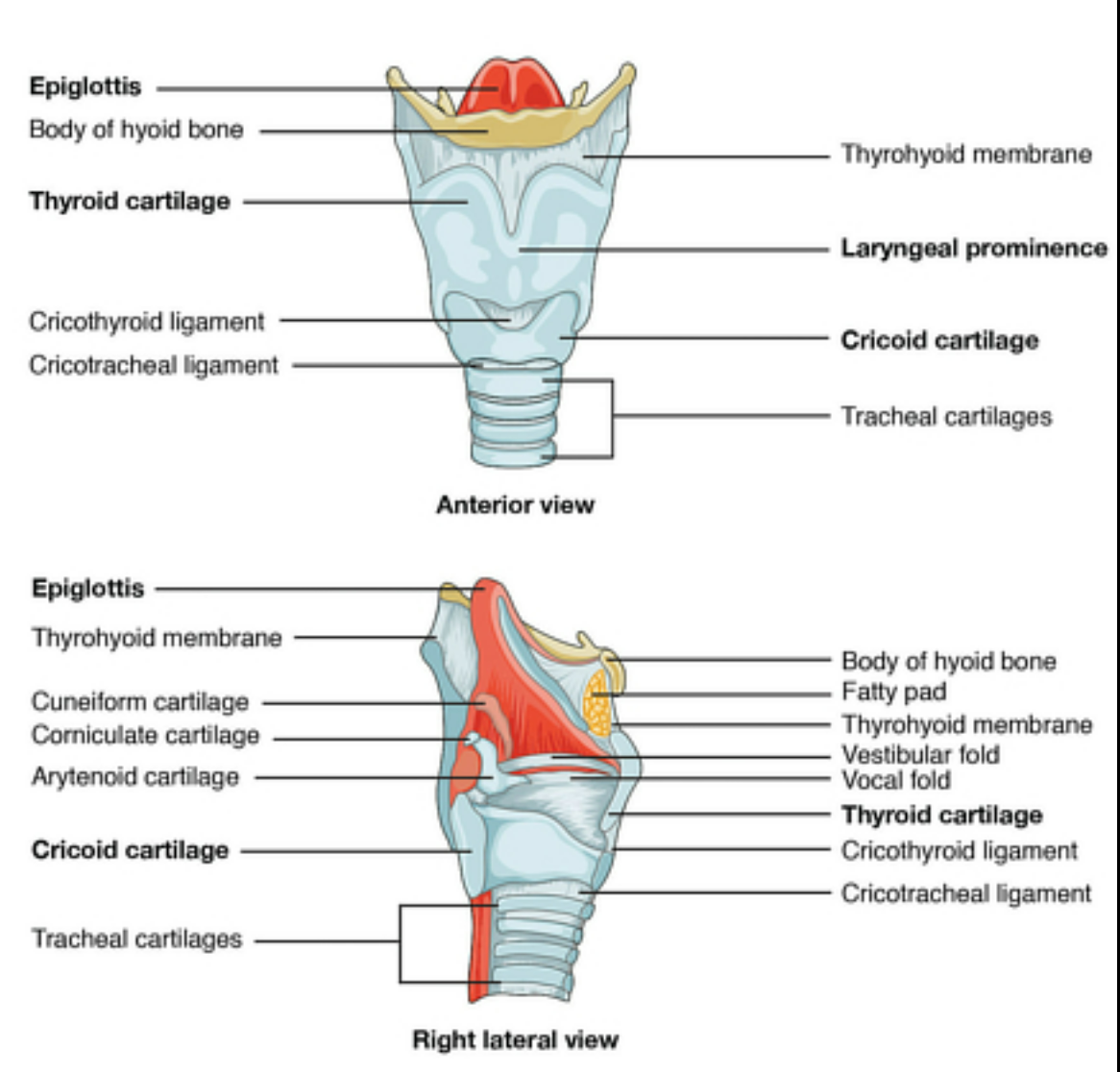
whats this part of the larynx
aryepiglottic fold (2 folds on each side of larynx)
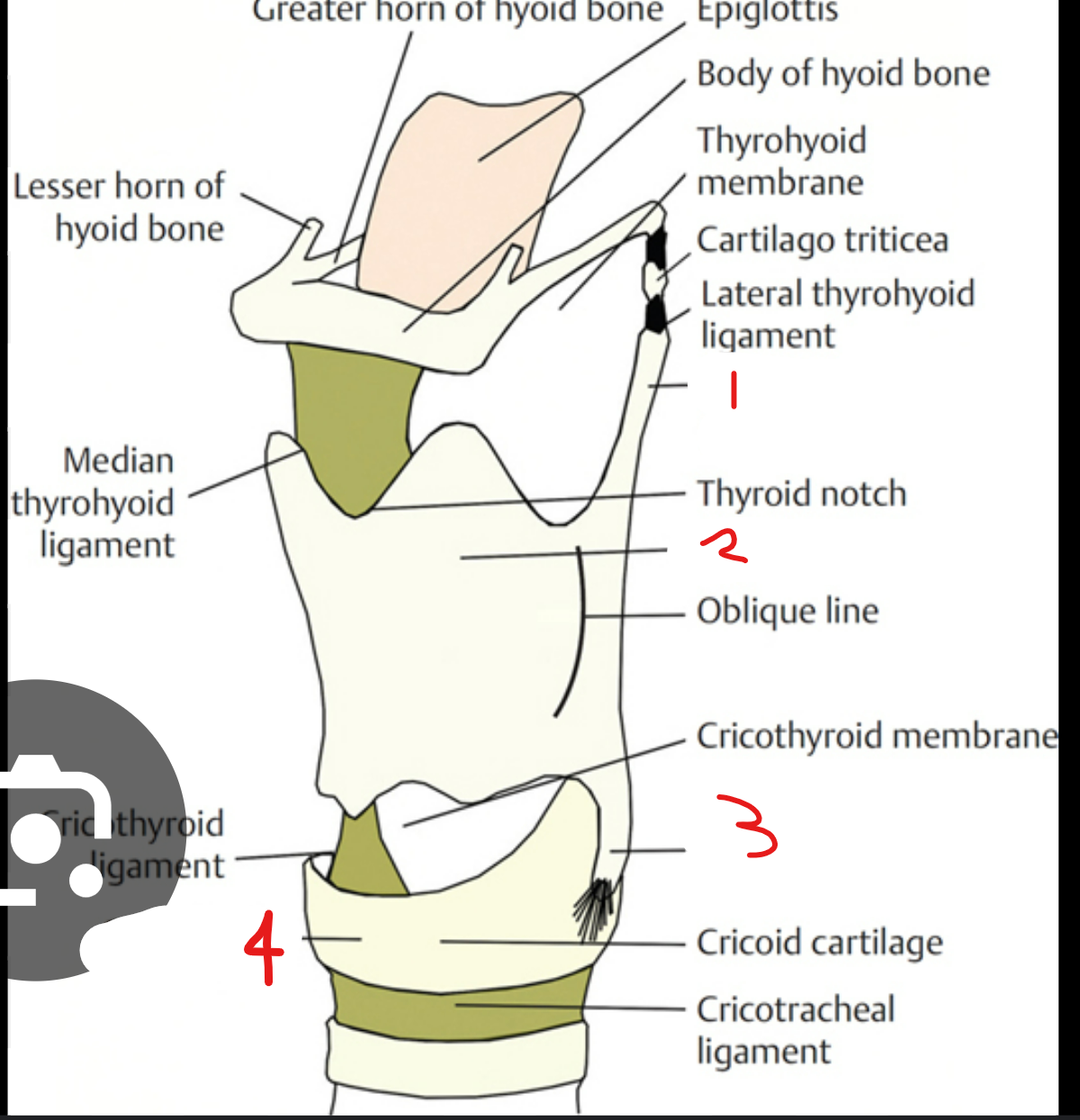
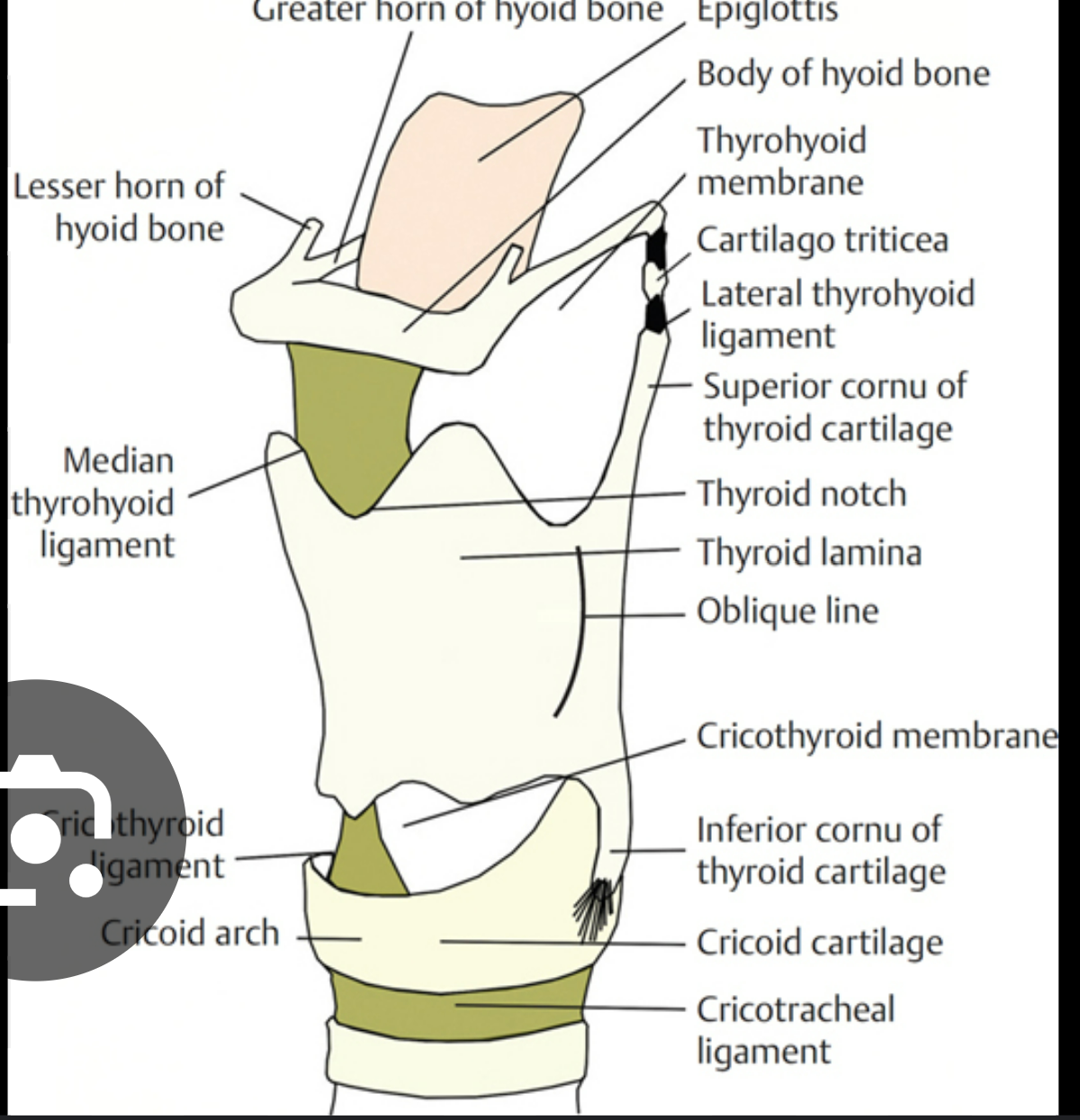
label these parts of the thyroid and cricoid cartilage in the larynx
rostral cornu of thyroid cartilage: long, narrow projection going rostral from thyroid cartilage
thyroid lamina: flattened, shield shaped plate that forms thyroid cartilage (there’s 2 of these)
caudal cornu of thyroid cartilage: same as (1) but going caudal
cricoid arch: curved part at back of cricoid cartilage
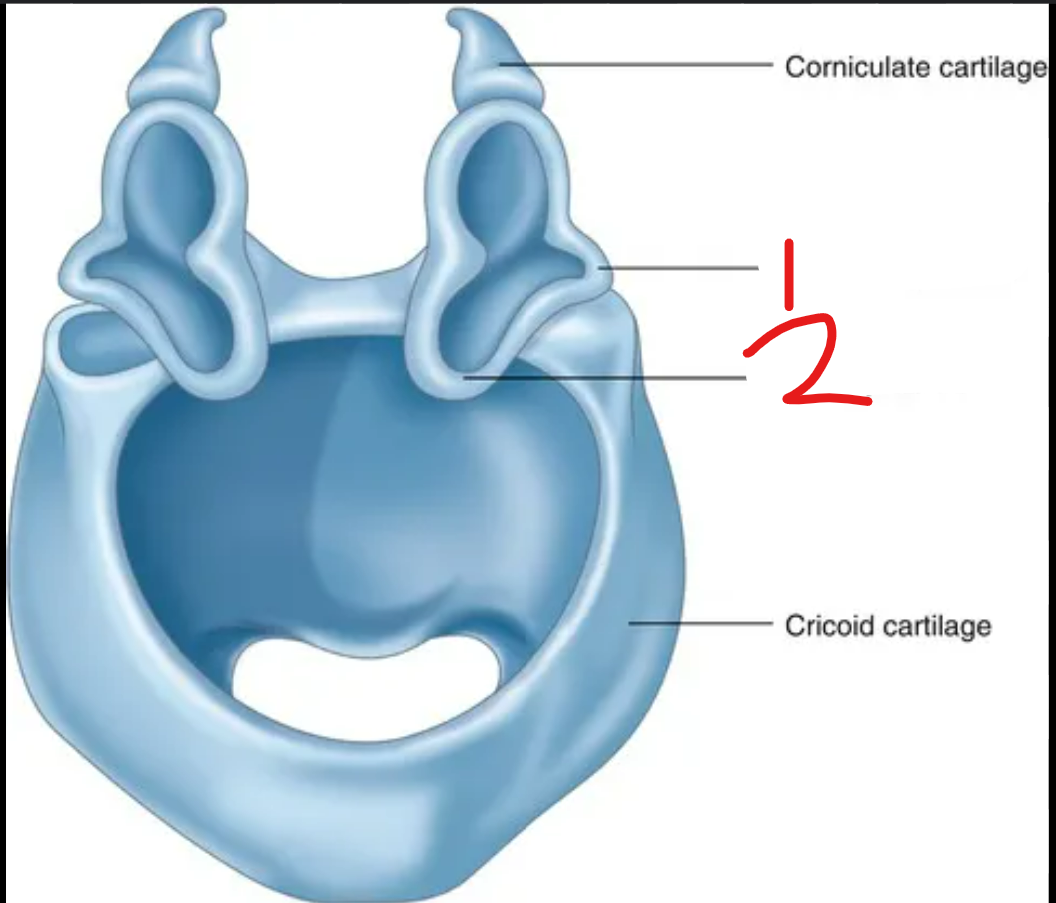
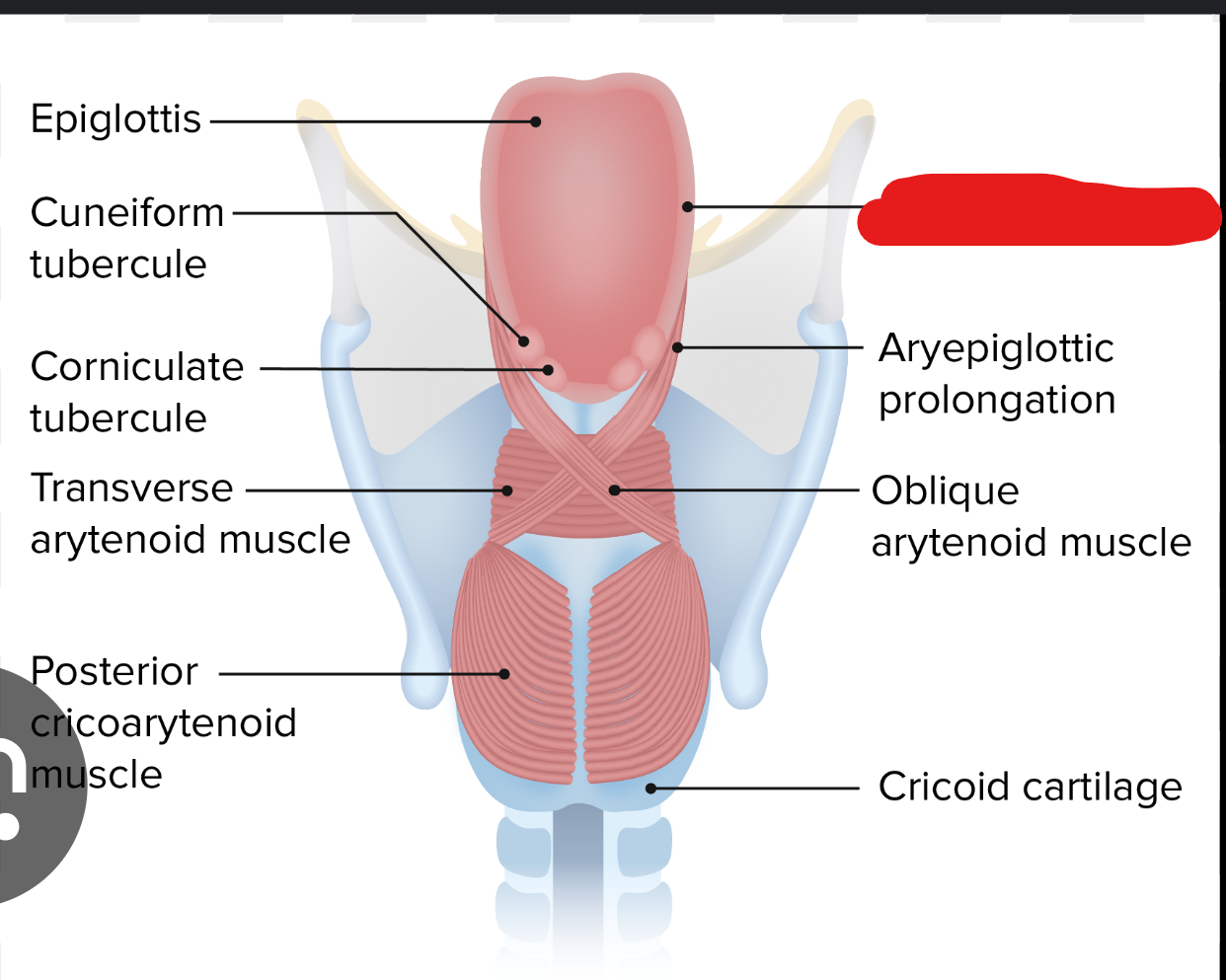
label the parts of the arytenoid cartilage in the larynx
muscular process: muscles attach here, projects laterally
vocal process: vocal folds attach here, projects caudally
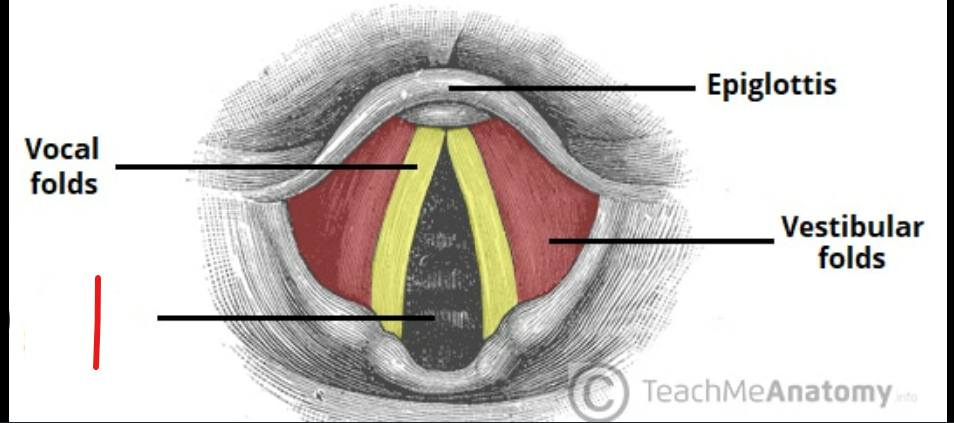
label this
whats the glottis
rima glottidis: the opening/space between the 2 vocal cords
glottis: in larynx, vocal cords + rima glott = glottis
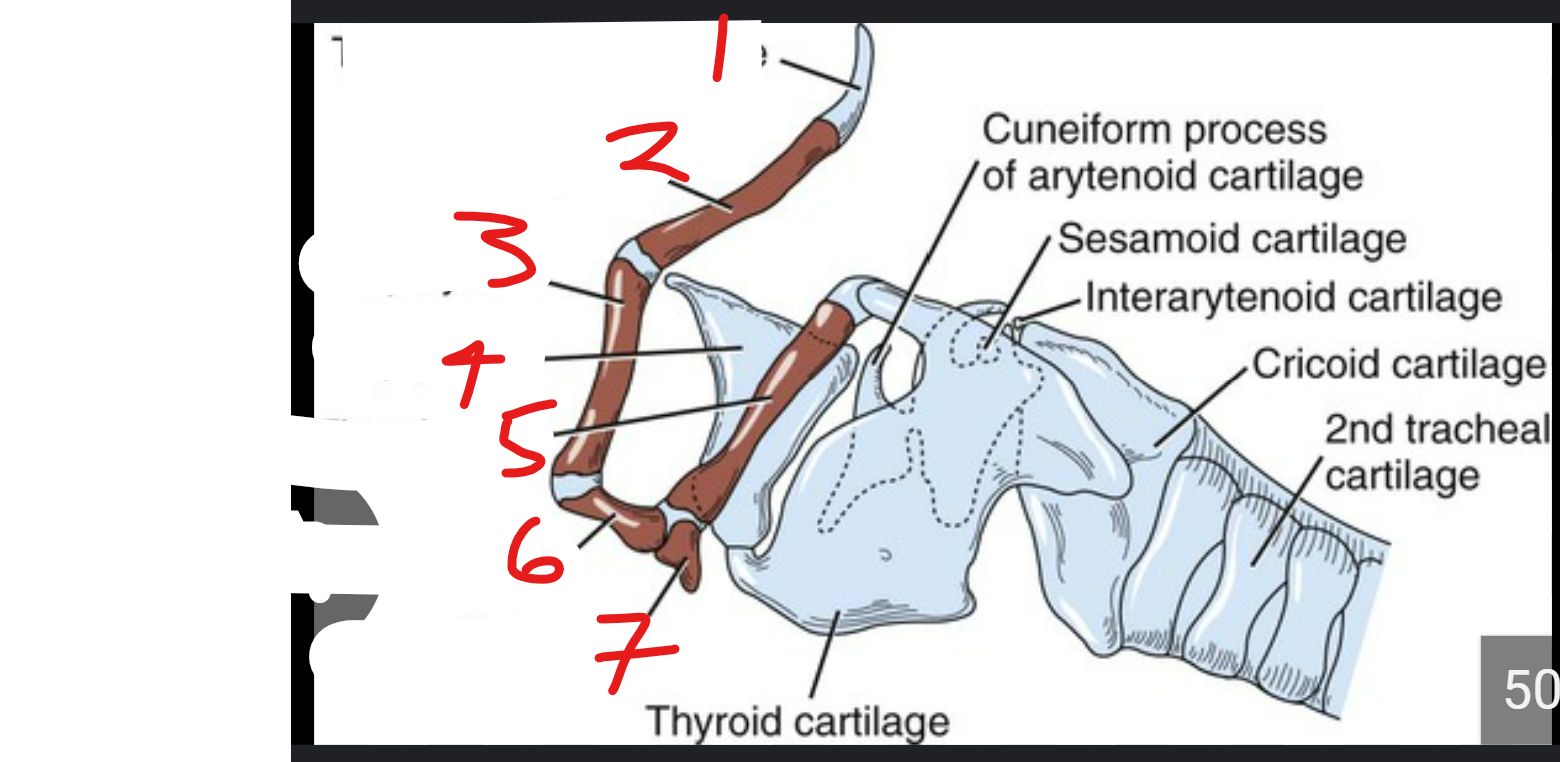
label the parts of the hyoid apparatus
*there’s 2 of each of these hyoid bones, except only 1 basihyoid connects both sides
tympanohyoid (at very tip)
stylohyoid: below ^
epihyoid: below ^
epiglottis
thyrohyoid: on top of basi & extends out caudally
ceratohyoid: below ^
basihyoid: at the base
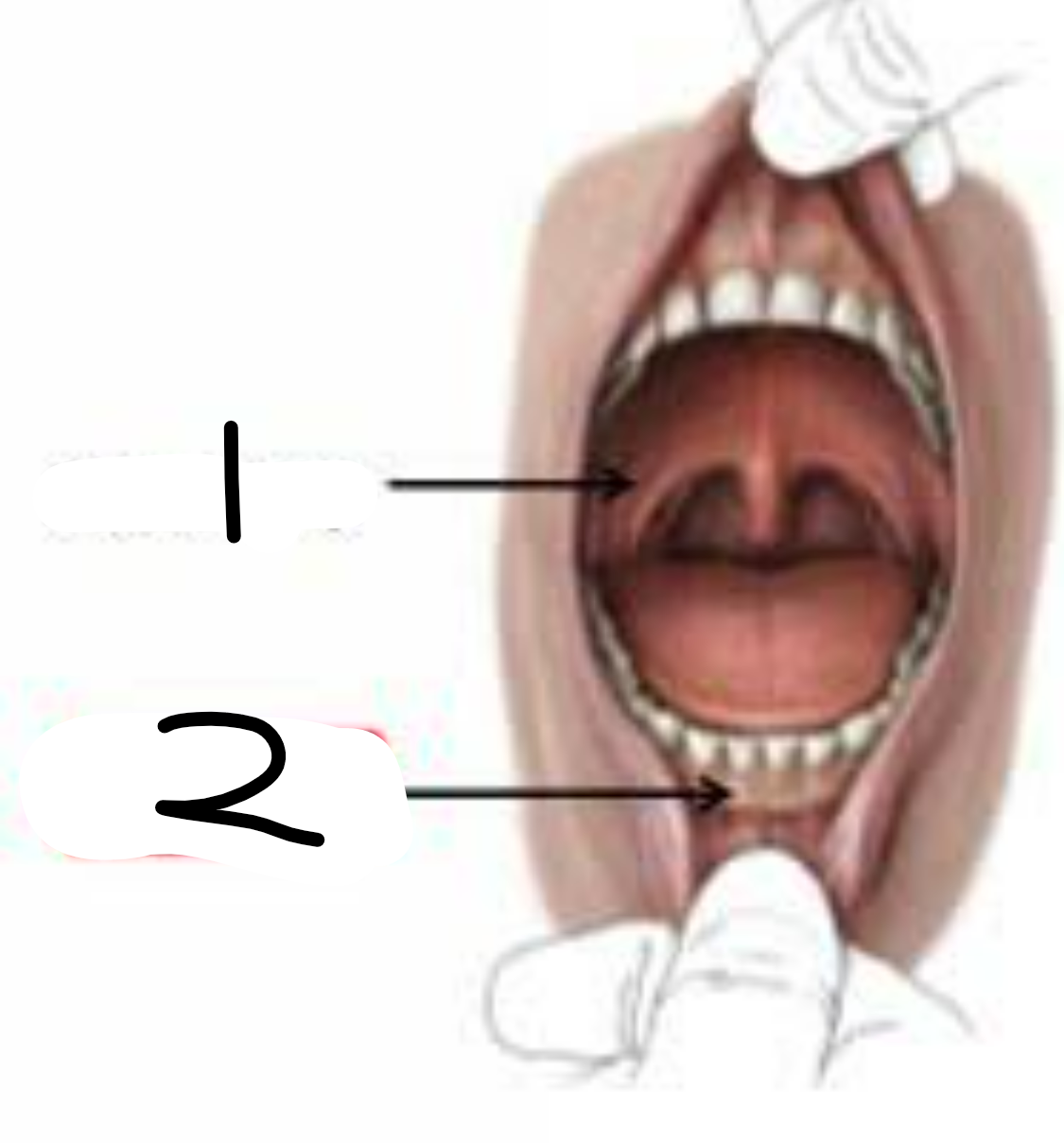
the mouth (in dogs too) is divided into 2 parts… label them
oral cavity proper: just the inner part of the mouth
vestibule: space between lips and cheeks, on outside of teeth but inside gums
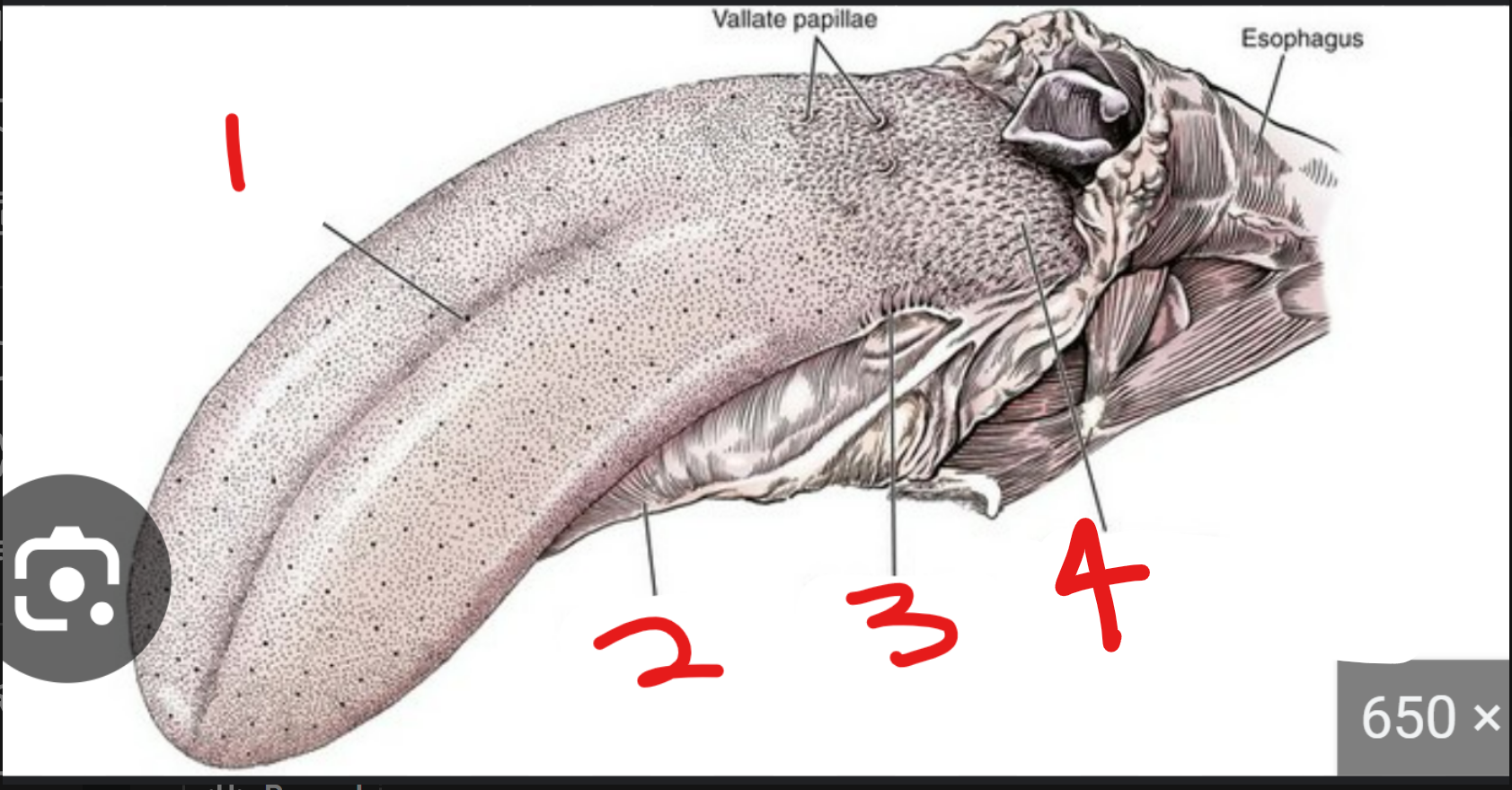
label the parts of the tongue (3 and 4 are a type of papillae)
where are filiform papillae
1 → SPELLING
median sulcus: groove on tongue that divides it into left and right
lingual frenulum: thin tissue that connects tongue to floor of mmouth
foliate papilla: pap on sides of tongue
conical papillae: on very back of tongue, large and rough
all throughout, smooth and round, but super small so can’t really see
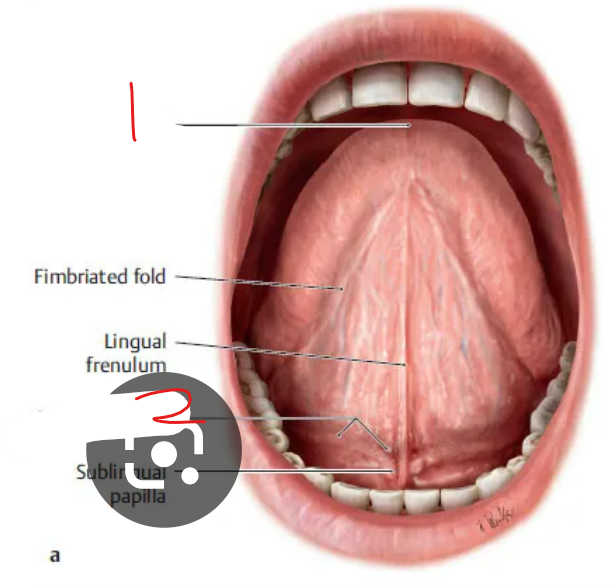
label the parts of the tongue
whats the body and lyssa
what are the intrinsic lingual muscle
apex: free end/tip of tongue
sublingual fold: U shaped structure on floor of mouth nex to lingual frenulum
body is the main part of tongue, between root & apex
lyssa is a rod shaped structure under the apex
this is the meat of the tongue
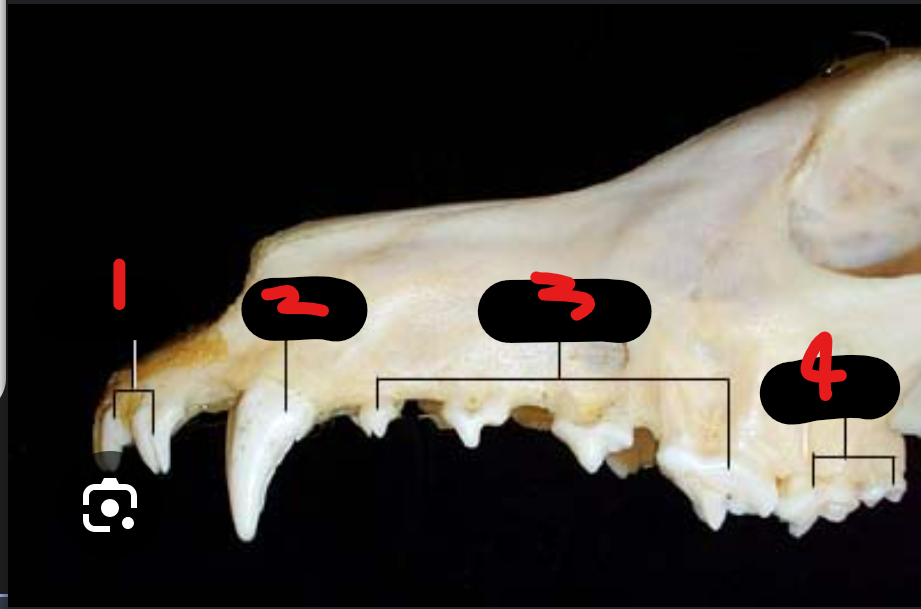
label the teeth
whats the alveolus
incisors
canine
premolars
molars
this is the bony socket where the root of the tooth sits
to help remember, can think of canine tooth formula (pic, top is # teeth on top of mouth & vice versa)
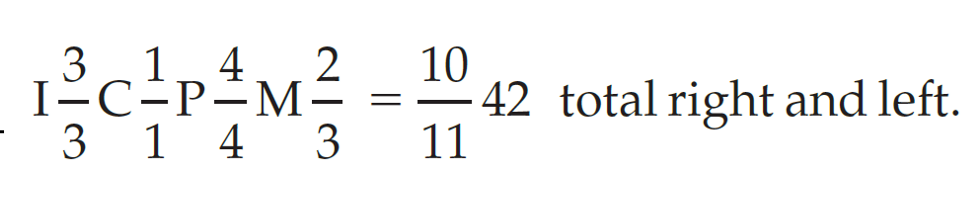
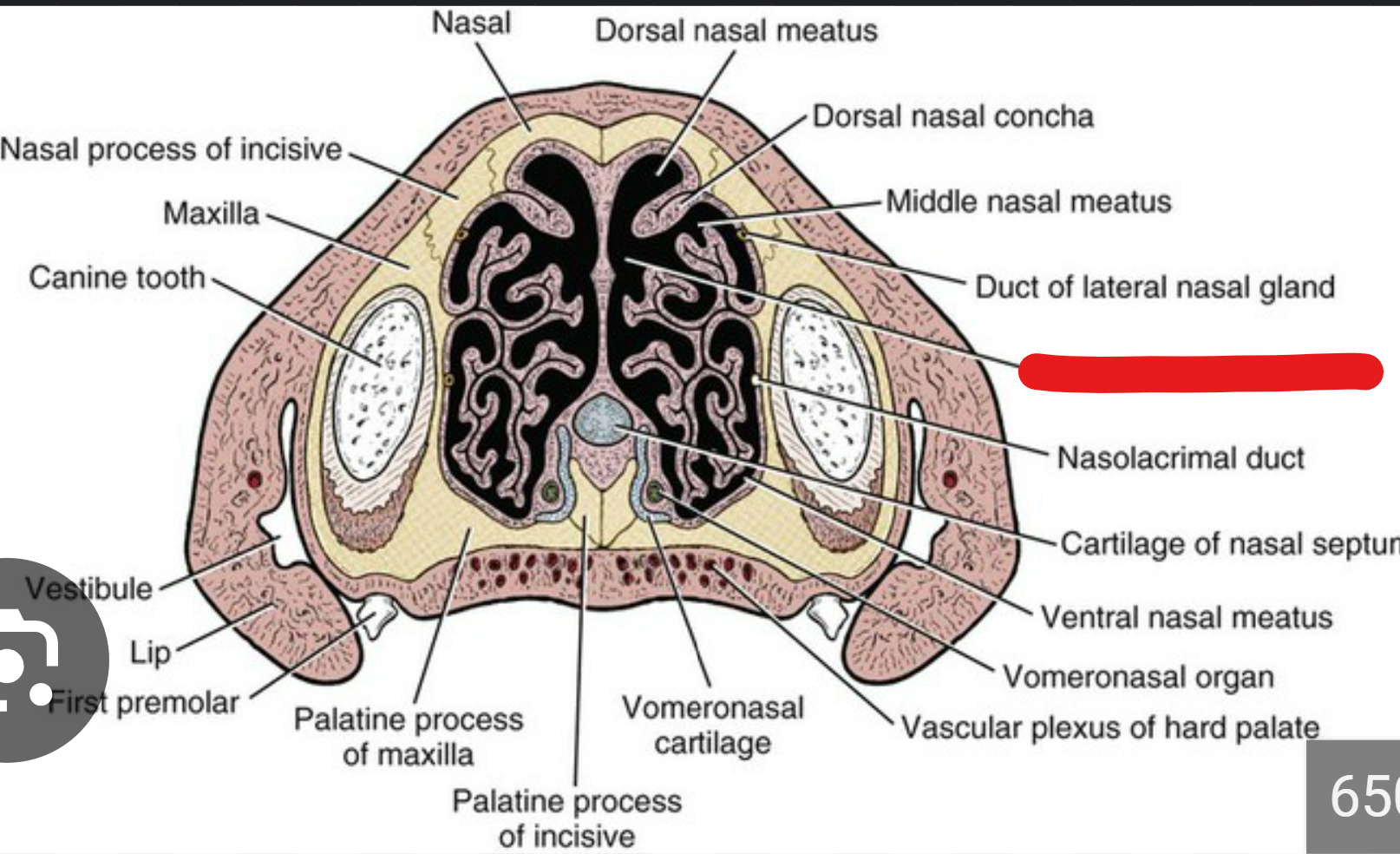
this is the cross section of a dogs nose.
label the red part
whats the nasal aperture and choanae
common nasal meatus
nas ap is the opening of the nose (inside the nostrils)
chon is the opening at the back of the nose that opens into the nasopharynx
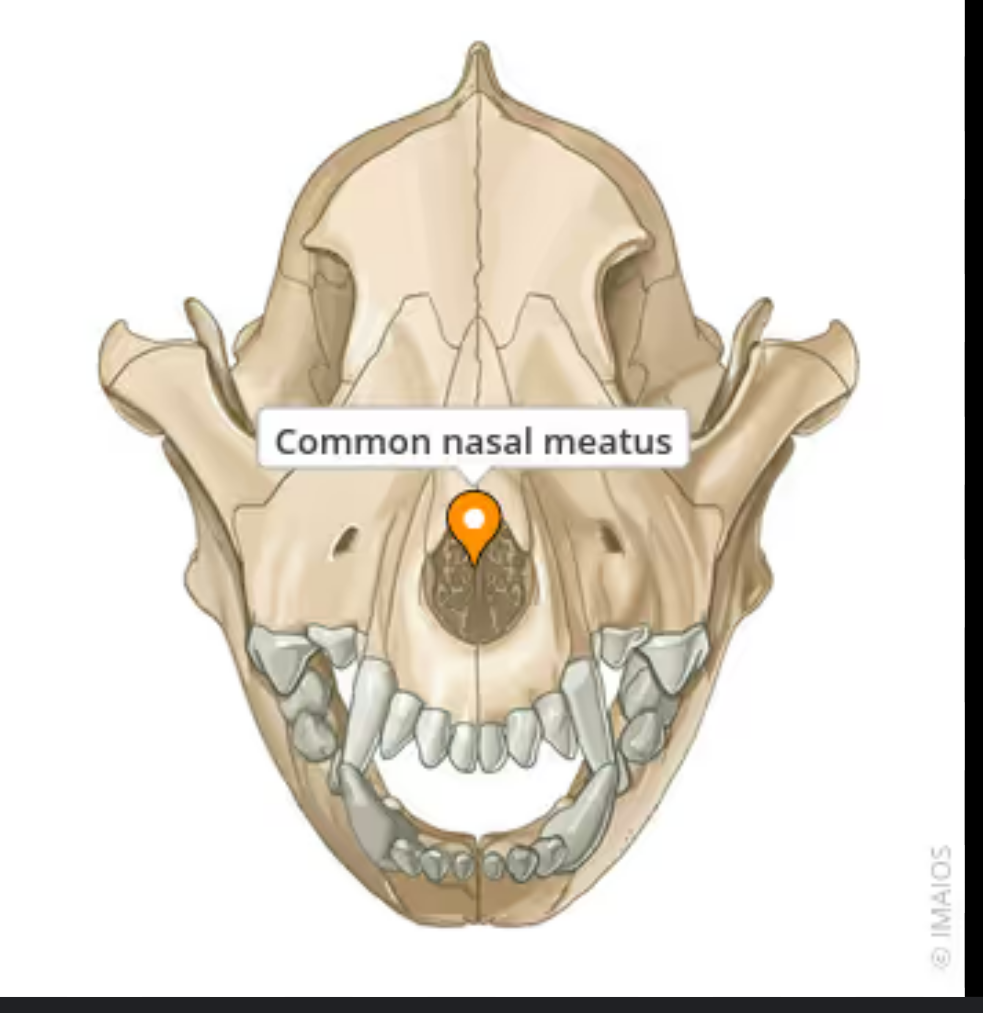
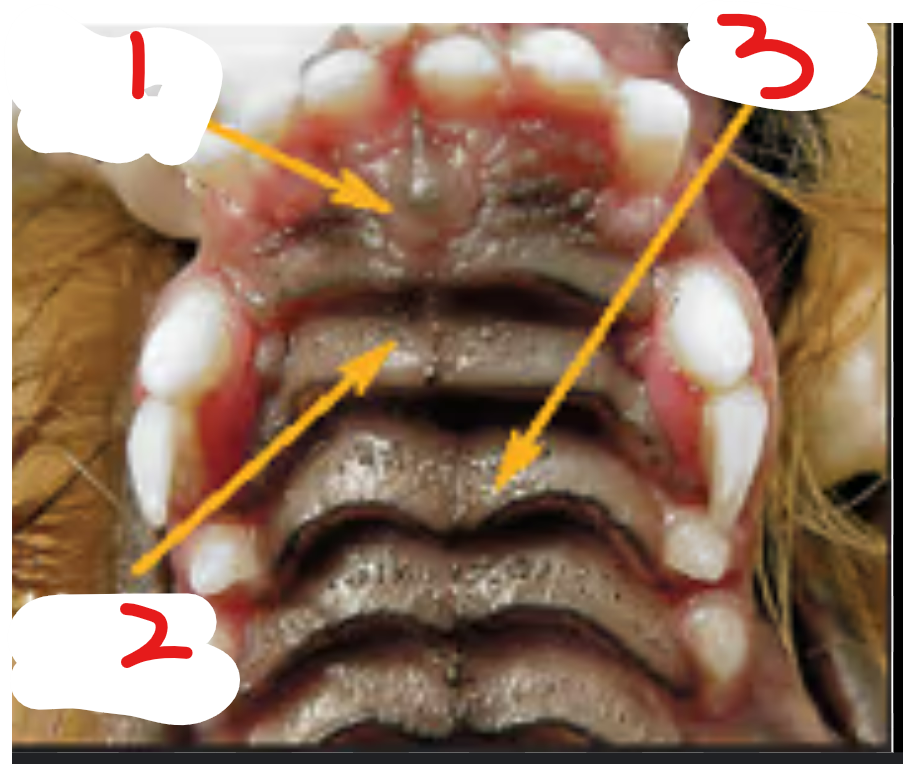
this is the top of a dogs mouth.
label it
incisive papilla: raised bump at front of hard palate
raphe: line going down the middle of the hard palate
rugae: transverse ridges on hard palate
label 1, 2, 3
external jugular vein: splits into maxillary & linguofacial, caudal to mandibular saliv gland
maxillary vein
linguofacial vein
label 3 & 4
ventral buccal nerve
dorsal buccal nerve
these are branches of the facial nerve, go acorss masseter muscle & innervate muscles of cheek/lips/nose
splits into dorsal & ventral around parotid duct
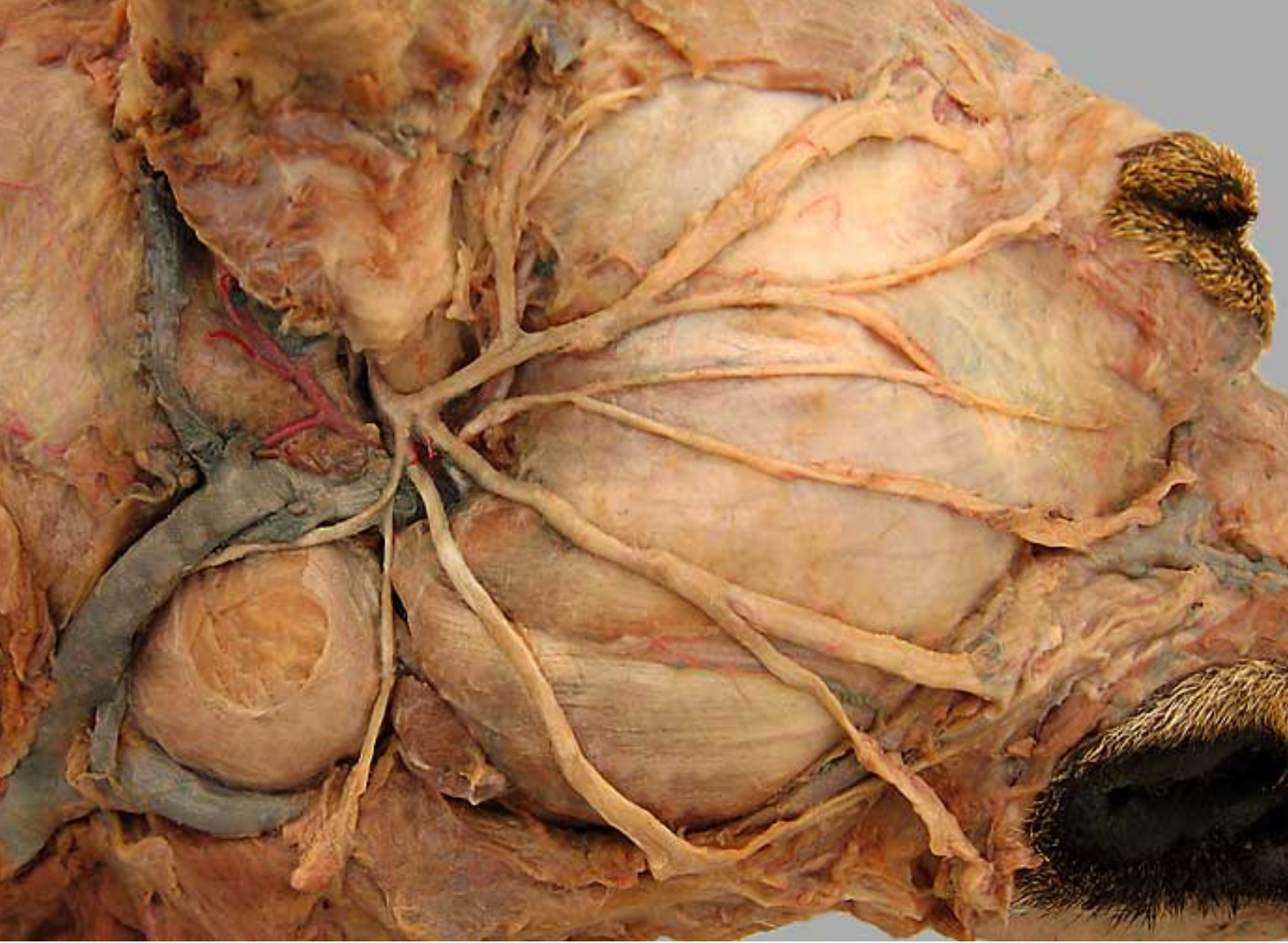
this is an up close image of a canine’s face/eye.
labe 2 & 3
inferior alveolar nerve: in the mandible, supplies sensory nerves to teeth
lingual nerve: larger & more rostral than ^, runs under the tongue, runs on mylohyoid m.

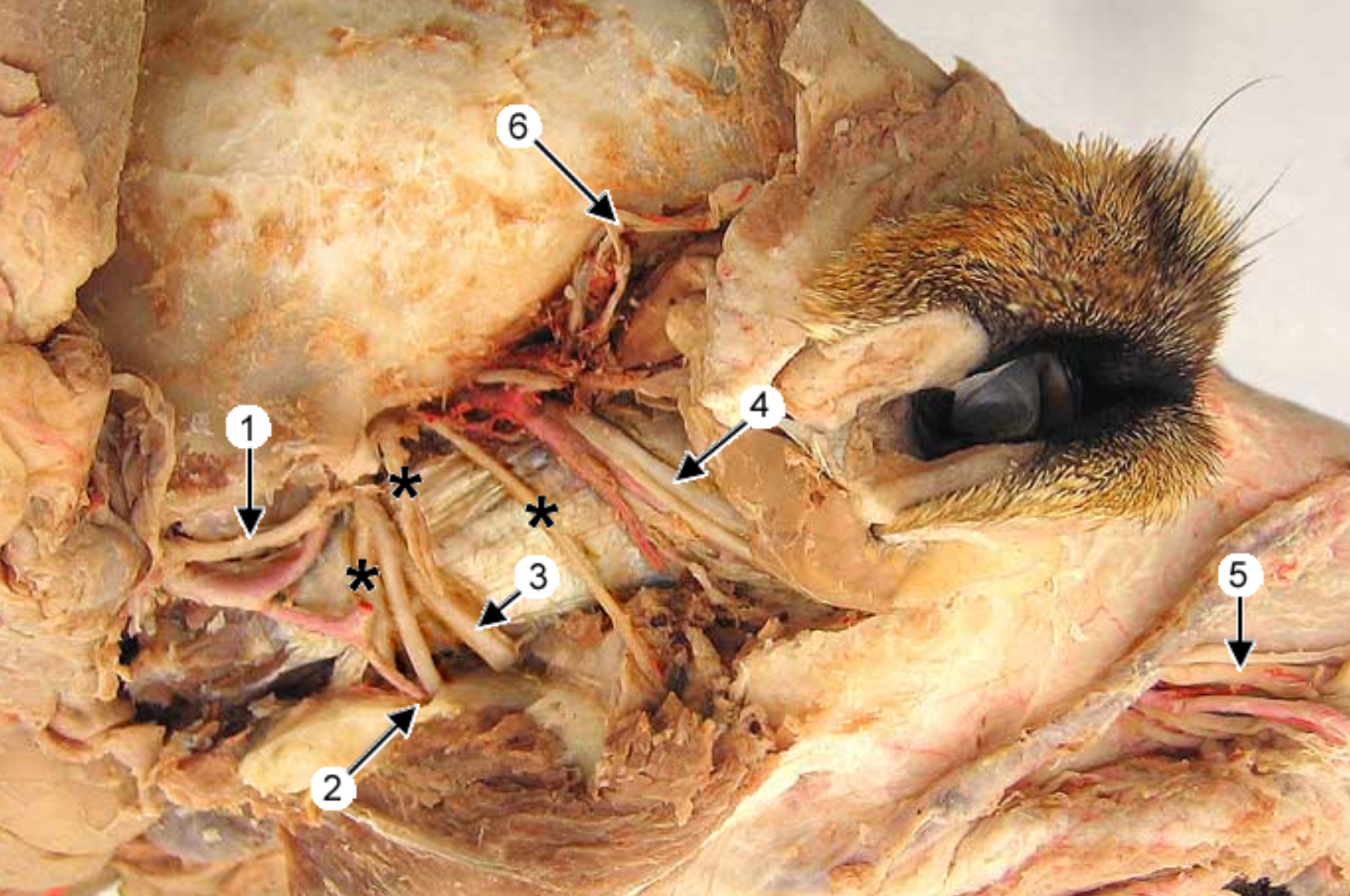
this is an up close image of the head and the tongue is pulled to the side (teeth on left side).
label 1-9, except 3
what nerve is right before 1 (behind the muscle 7)
lingual nerve: from mandibular divison of trigeminal n., runs under tongue and on mylohyoid m.
mylohyoideus muscle: thin sheet than spans intermandibular space, caudally inserts on basihyoid
-
hypoglossal nerve: ventrorostral to carotid sheath, medial to mandib saliv gland, innervates tongue muscles
lingual artery: ventral branch of ECA, supplies tonsil & tongue
styloglossus muscle: arises from stylohyroid bones, located in the tongue, retrats & elevates tongue
pterygoid muscle: arises from pterygopalatine fossa, on medial side of mandible
digastricus muscle: extends from base of skull to lower mandible, involved in mastication
mandibular salivary gland: golf ball shape
mandibular branch of cranial nerve V (this splits into MIL → …, inferior alveolar nerve, lingual nerve)

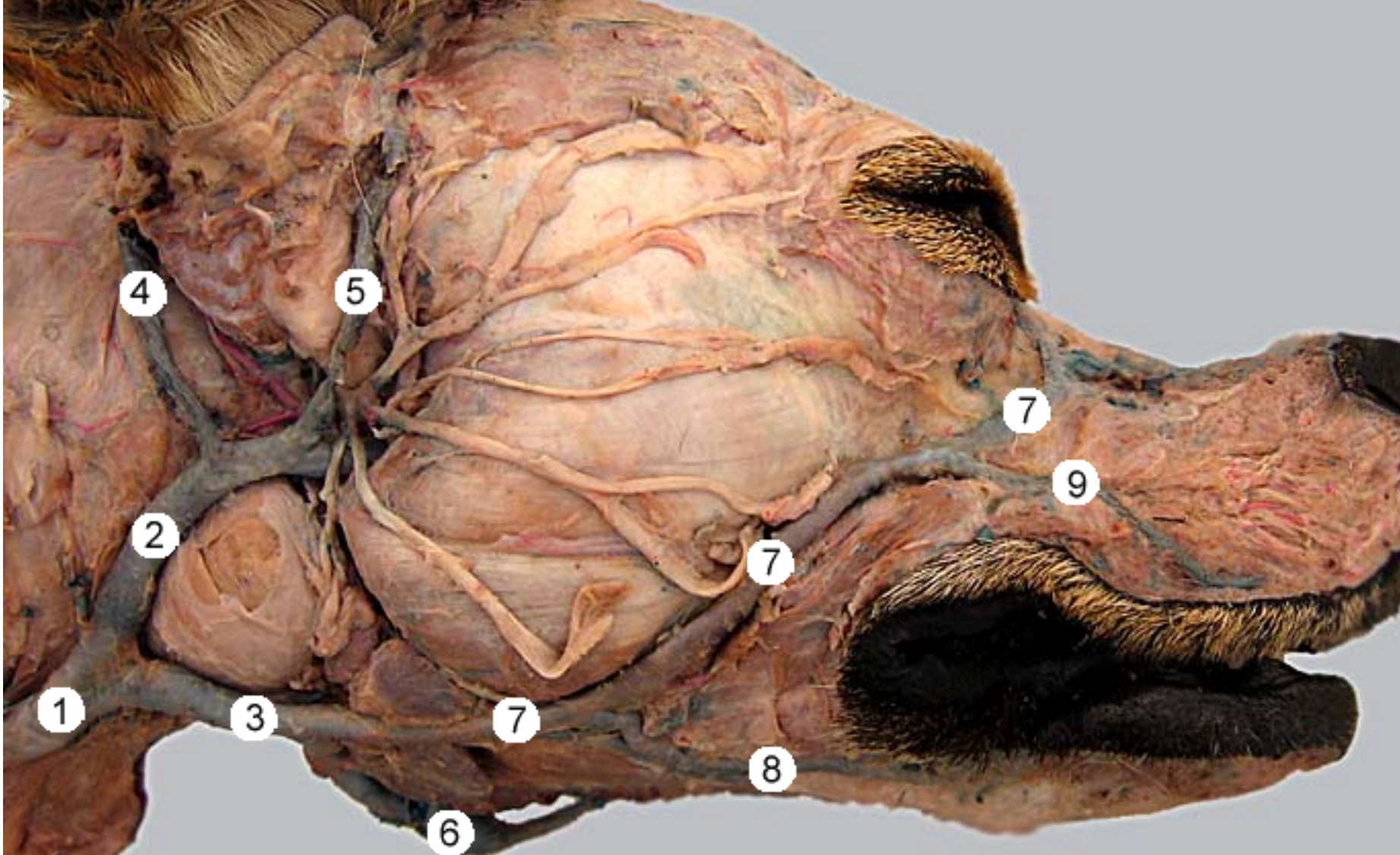
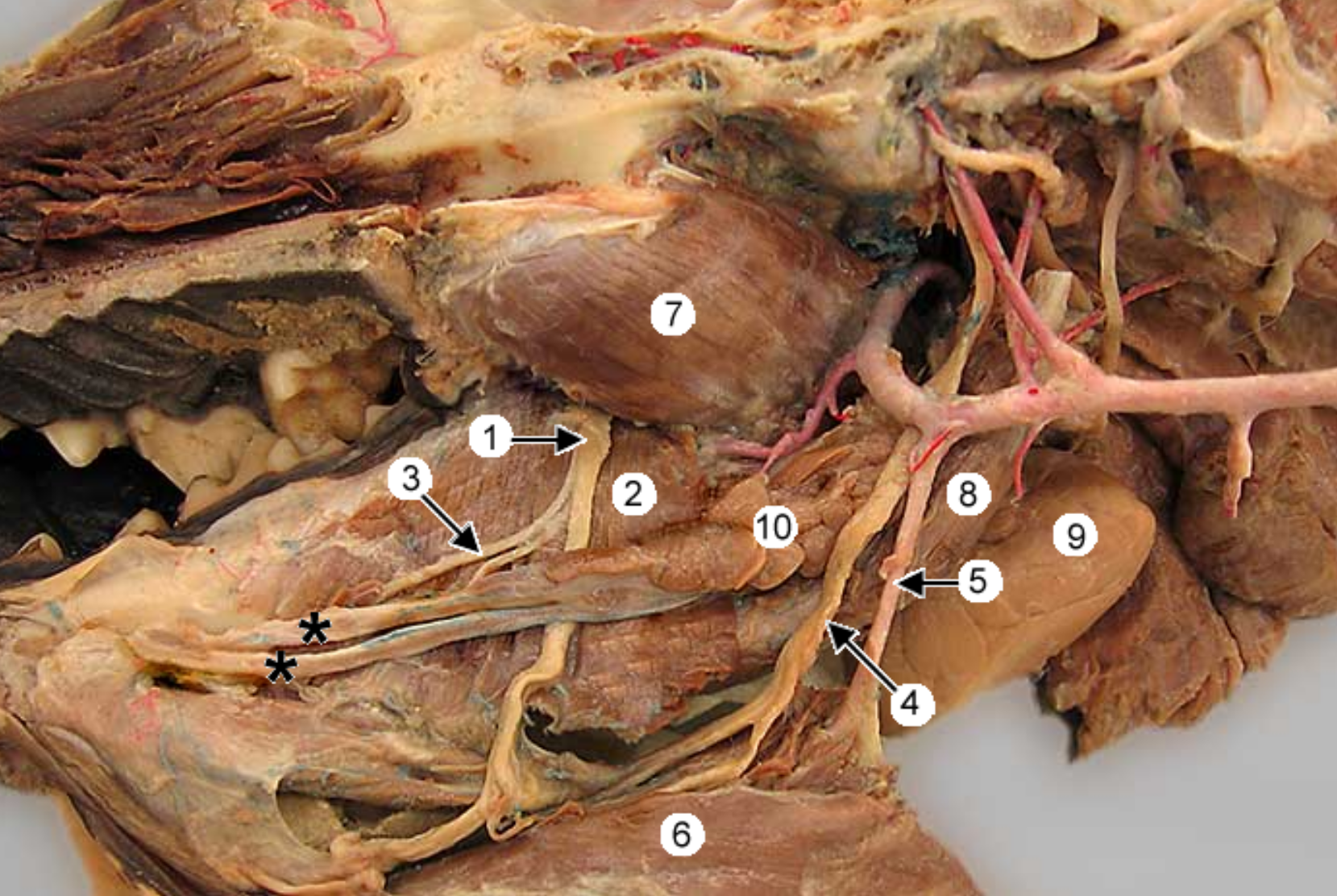
this is an up close imahge of the head, eye is to the right.
label 1-11, except 5,6,8
common carotid artery: in carotid sheath, splits into internal & external
internal carotid artery: smaller branch
external carotid artery: larger branch
maxillary artery: larger terminal branch of ECA, supplies blood to head
-
-
occipital artery: branch of ECA, right next to ICA, supplies meninges & skull
-
lingual artery: ventral branch of ECA, supplies tonsil & tongue
facial artery: branches off ECA after ^, supplies nose & lips
superficial temporal artery: small terminal branch of ECA, rostral to caudal auricular, supplies parotid gland & temporal muscles & eyelids
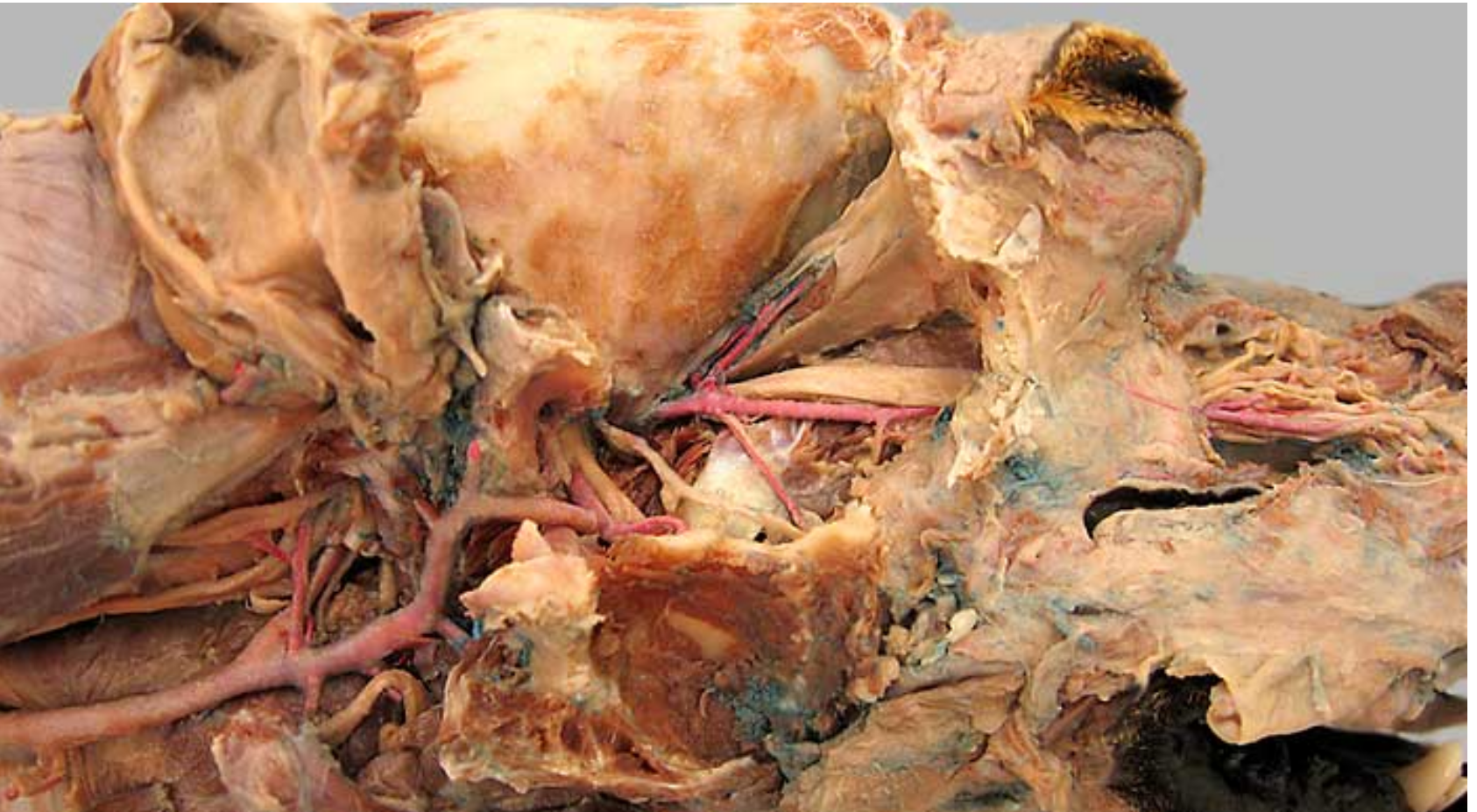
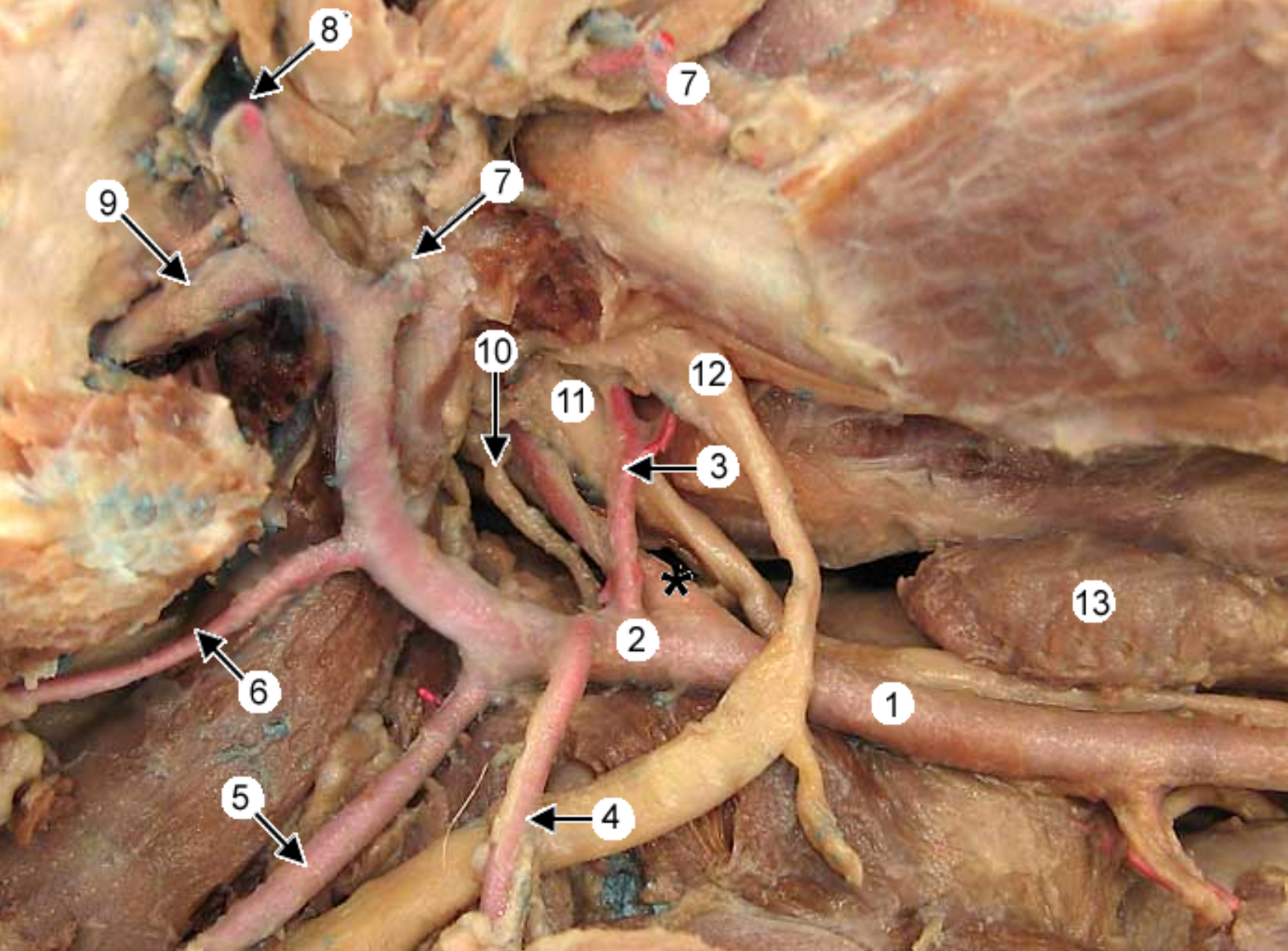
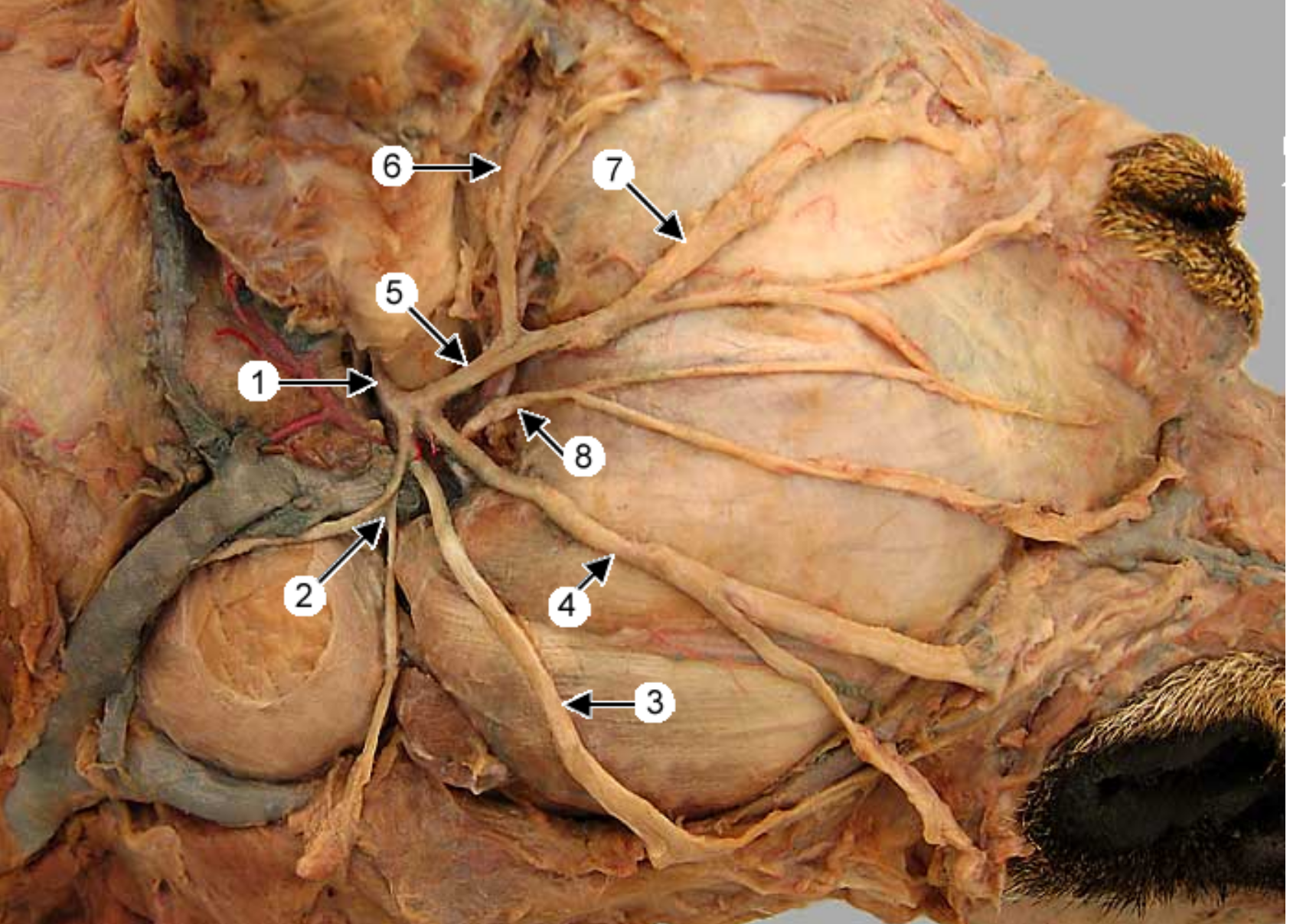
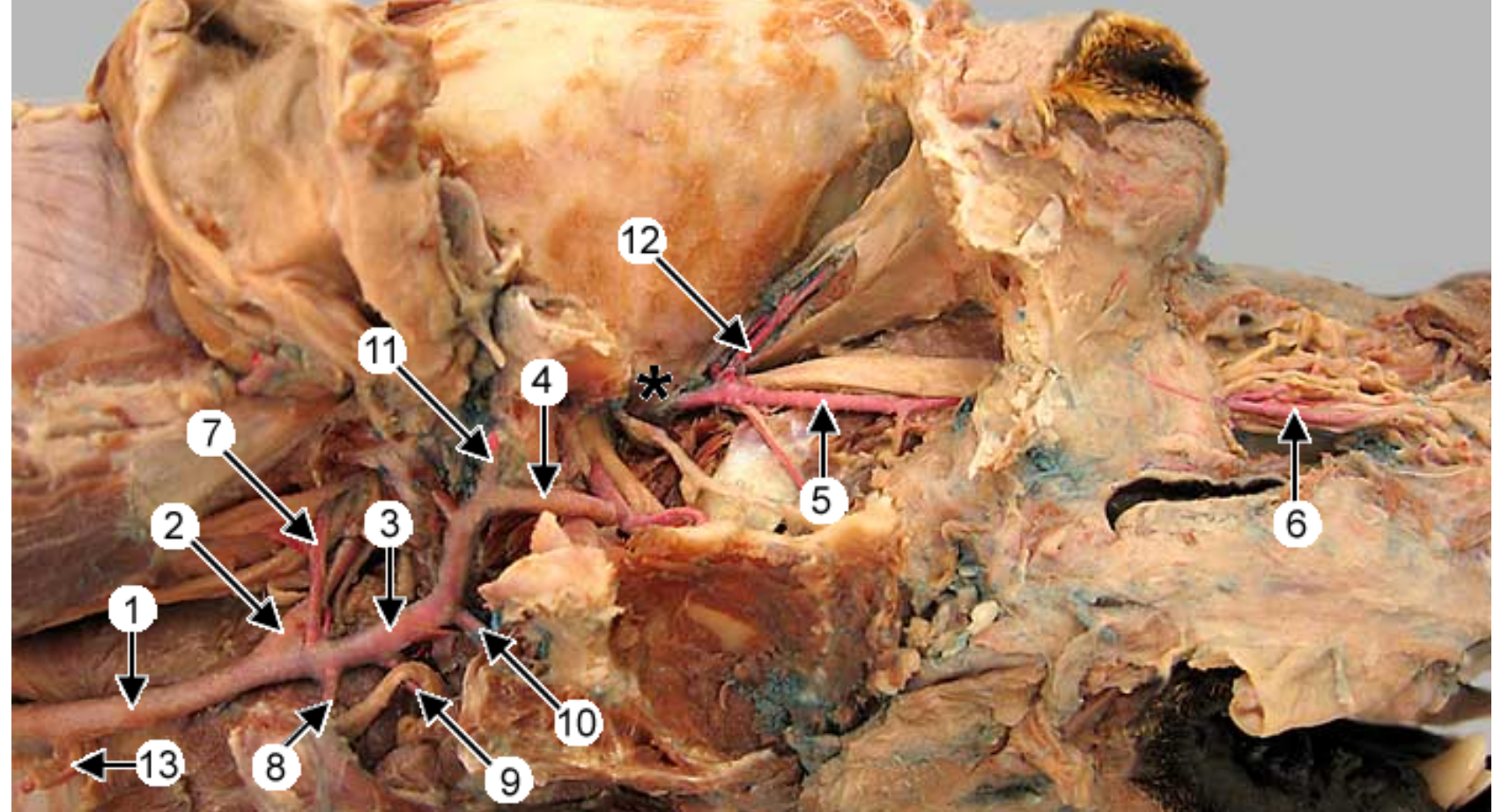
this is an up close image of the common carotid artery (1), the head is to the left
2 is the external carotid artery & * is the internal.
label all arteries except 4, 10, 11
label the other structures 12, 13
13 → SPELLING
occipital artery: branch of ECA, right next to ICA, supplies meninges & skull
-
lingual artery: ventral branch of ECA, supplies tonsil & tongue
facial artery: branches off ECA after ^, supplies nose & lips
caudal auricular artery: branch of ECA at the base of the ear
superificial temporal artery: small terminal branch of ECA, rostral to caudal auricular, supplies parotid gland & temporal muscles & eyelids
maxillary artery: larger terminal branch of ECA, supplies blood to head
-
-
hypoglossal nerve: white not pink, ventrorostral to carotid sheath, medial to mandib saliv gland, innervates tongue muscles
medial retropharyngeal lymph node: dorsal to CCA, more cranial than thyroid gland
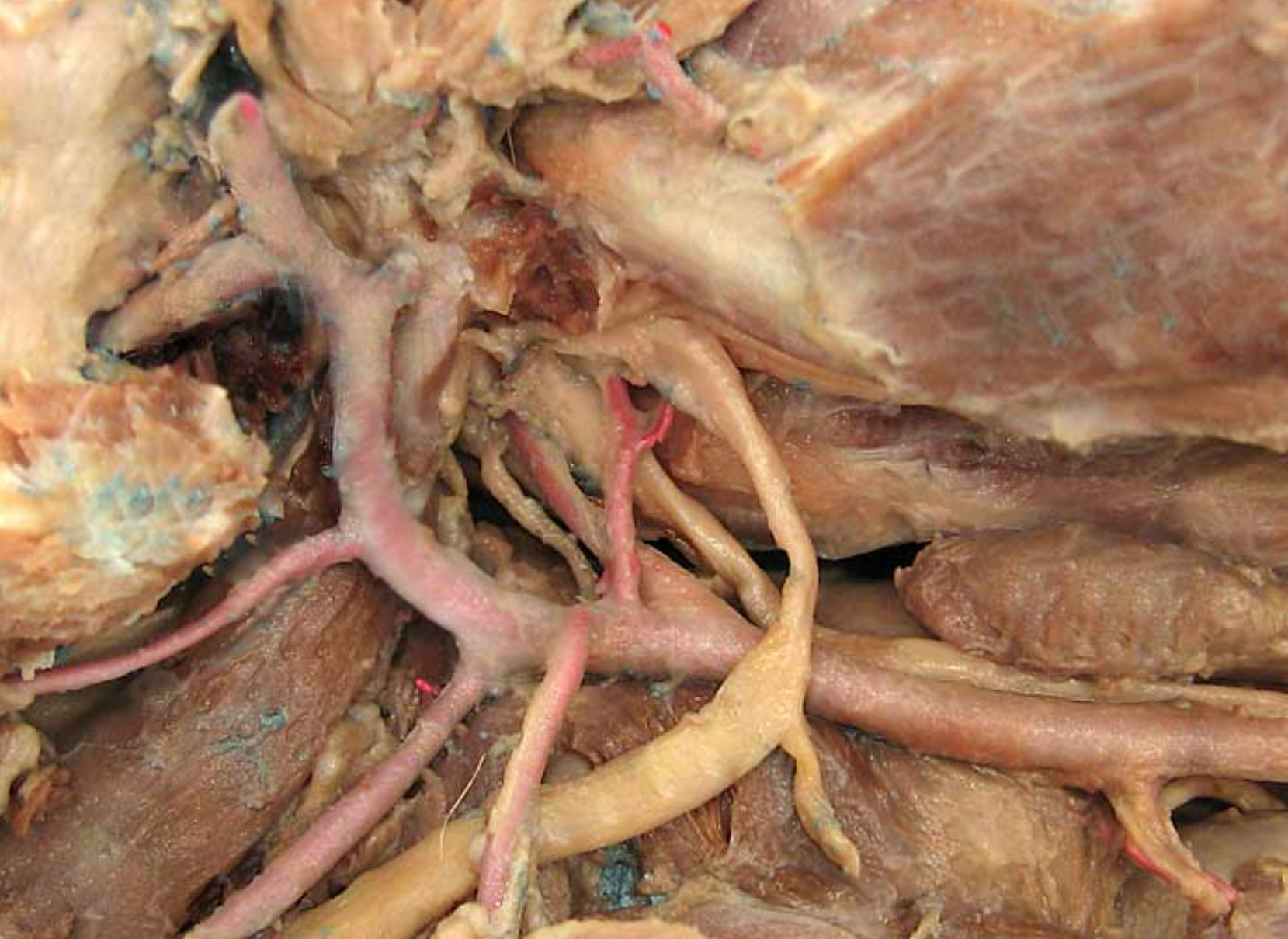
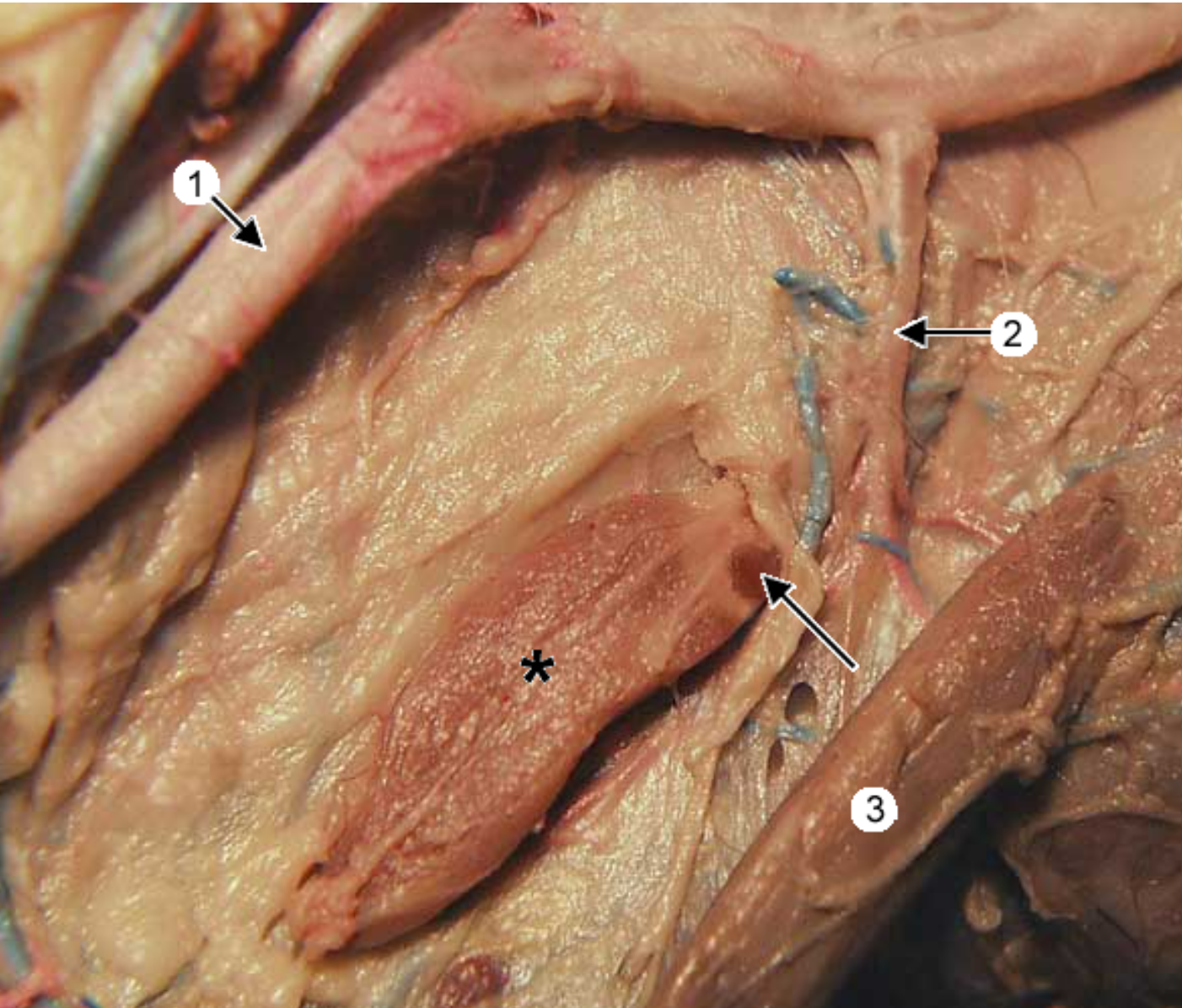
this is an up close view of the common carotid artery (1). 3 is the sternothyroideus muscle. the head is to the right.
whats *
the thyroid gland (only right lobe is shown, more caudal to larynx)
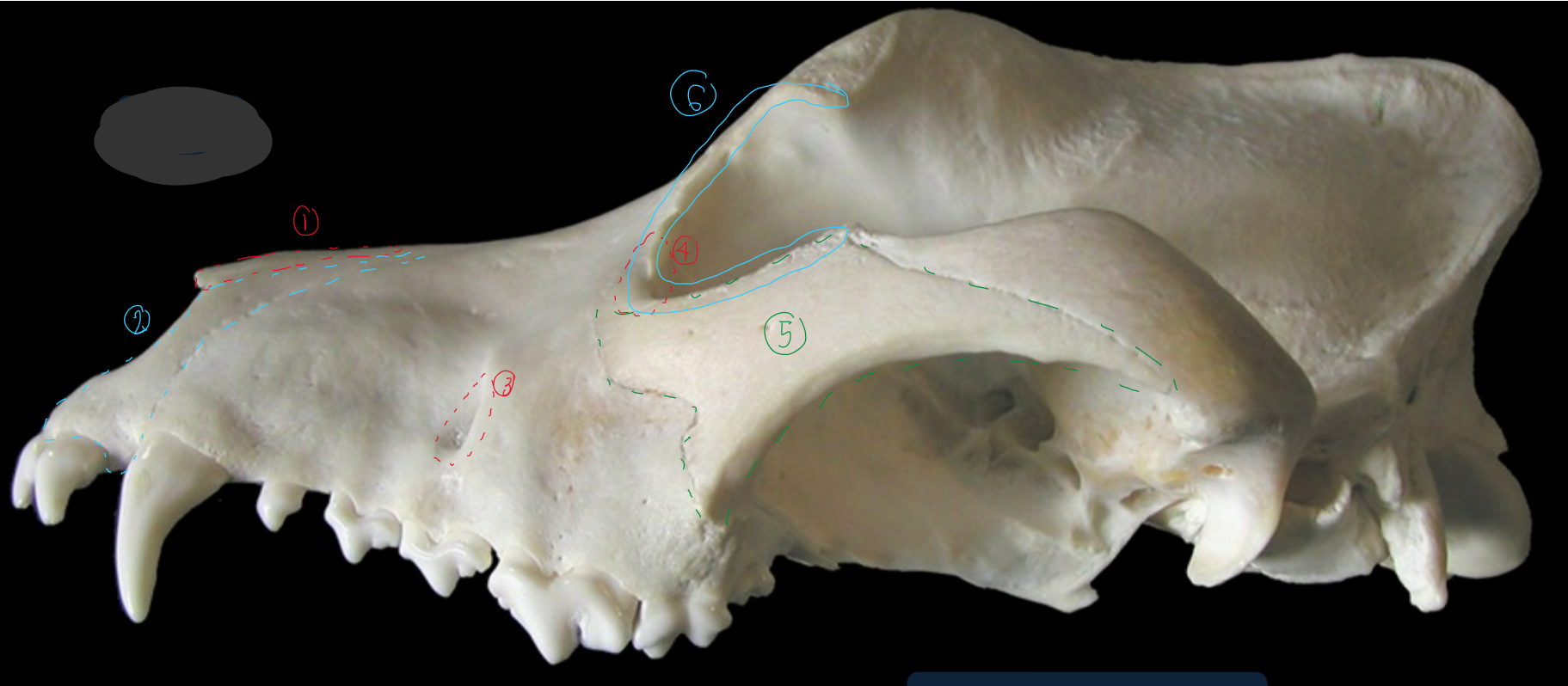
label the bones from the lateral side of the canine skull
nasal bone
incisive bone: supports incisiors in alveoli, forms rostral end of nasal cavity w/ hard palate
infraorbital foramen: opening of infraorbital canal (has nerves & BV to supply upper lips & nostrils)
lacrimal bone: by median corner of the eye. this is where nasolacrimal duct starts
zygomatic bone/temporal process of zygomatic bone(?): lateral to zygomatic saliv gland
orbit: eye socket, globe sits in it
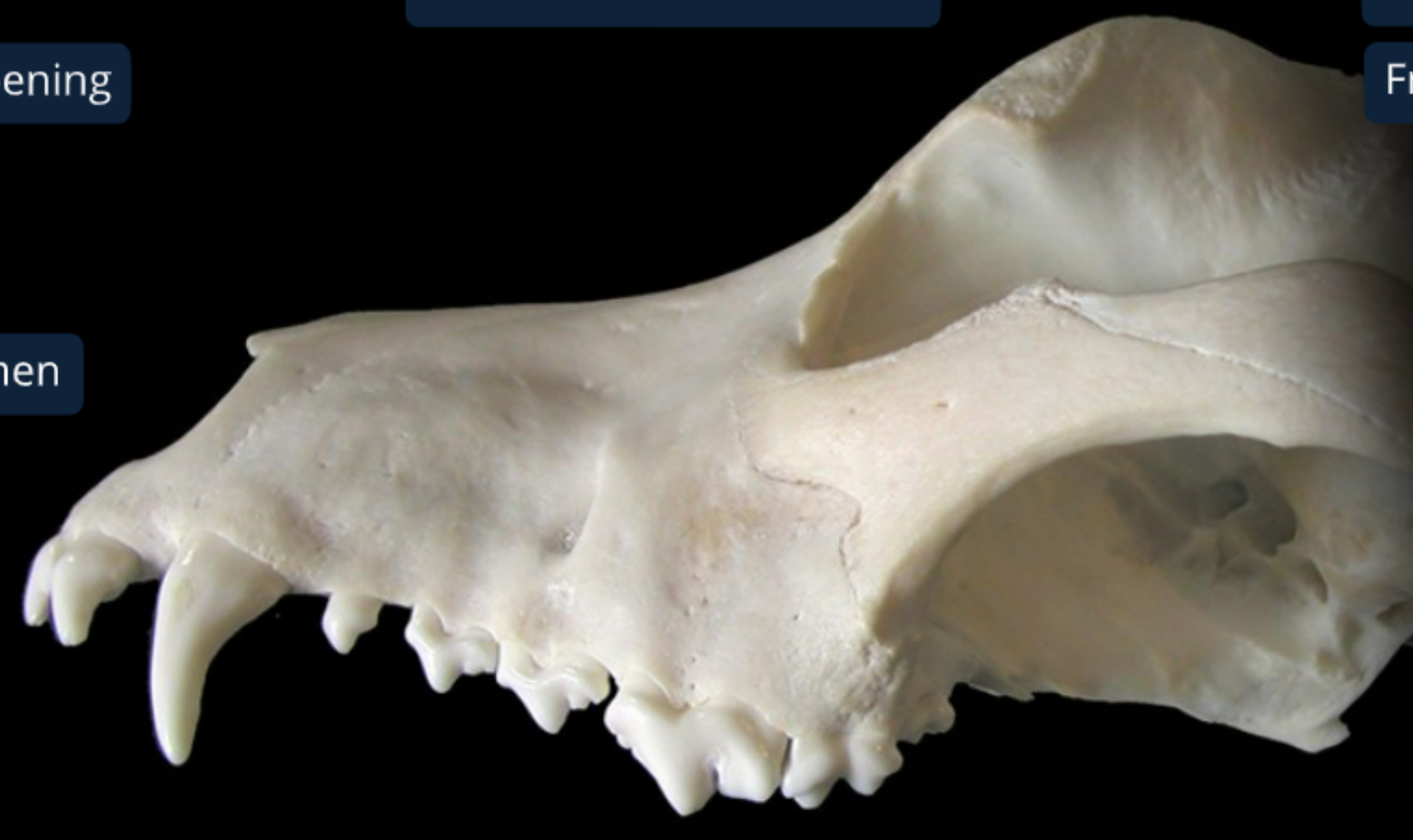

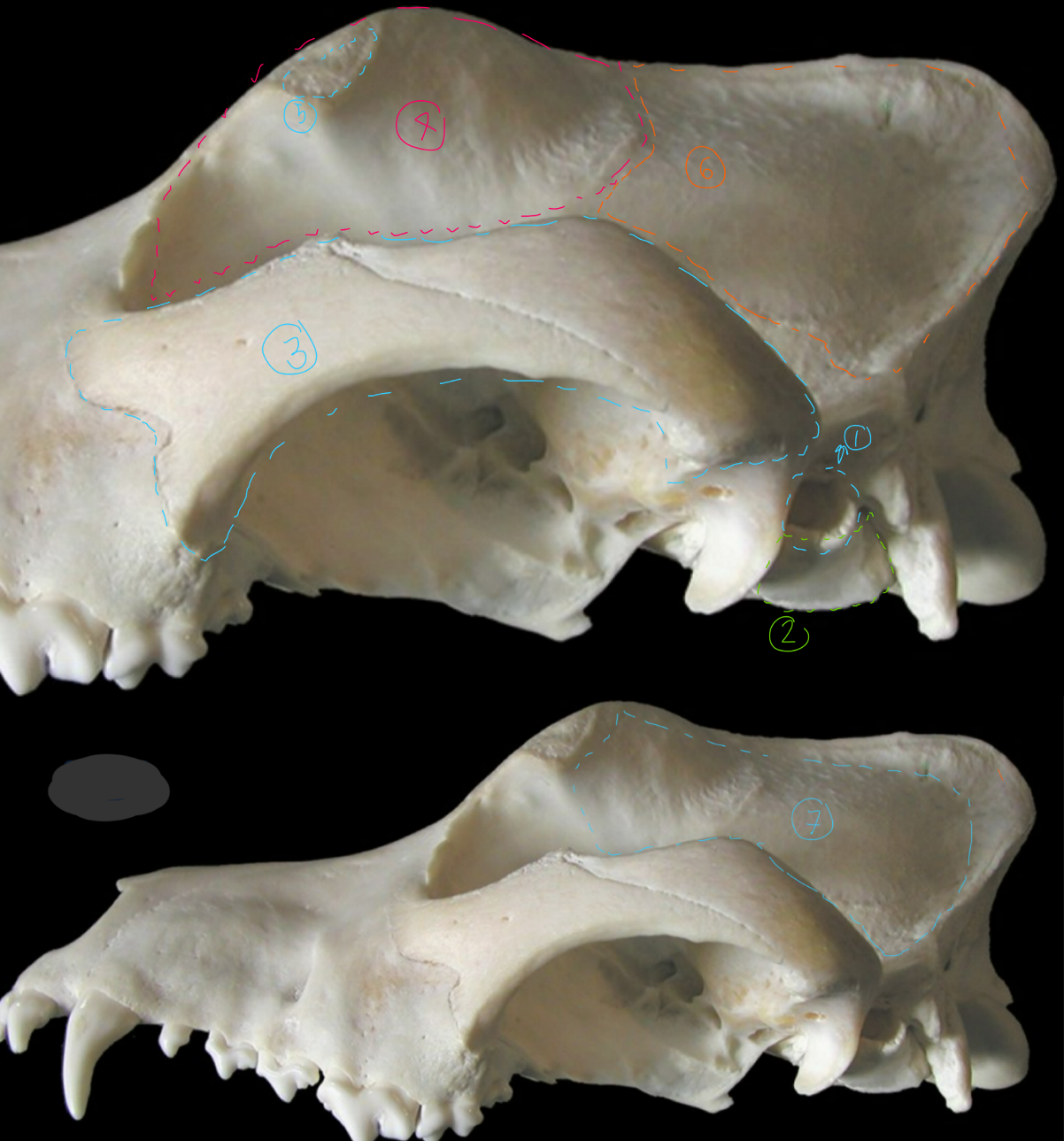
label the bones from the lateral side of the canine skull
external acoustic meatus: allows air to flow from external ear to tympanic membrane
tympanic bulla: thin walled air filled part of middle ear
zygomatic arch
frontal bone: forms forehead
zygomatic process of frontal bone: attaches palpable ligament to complete the orbit
parietal bone: forms shape of the head
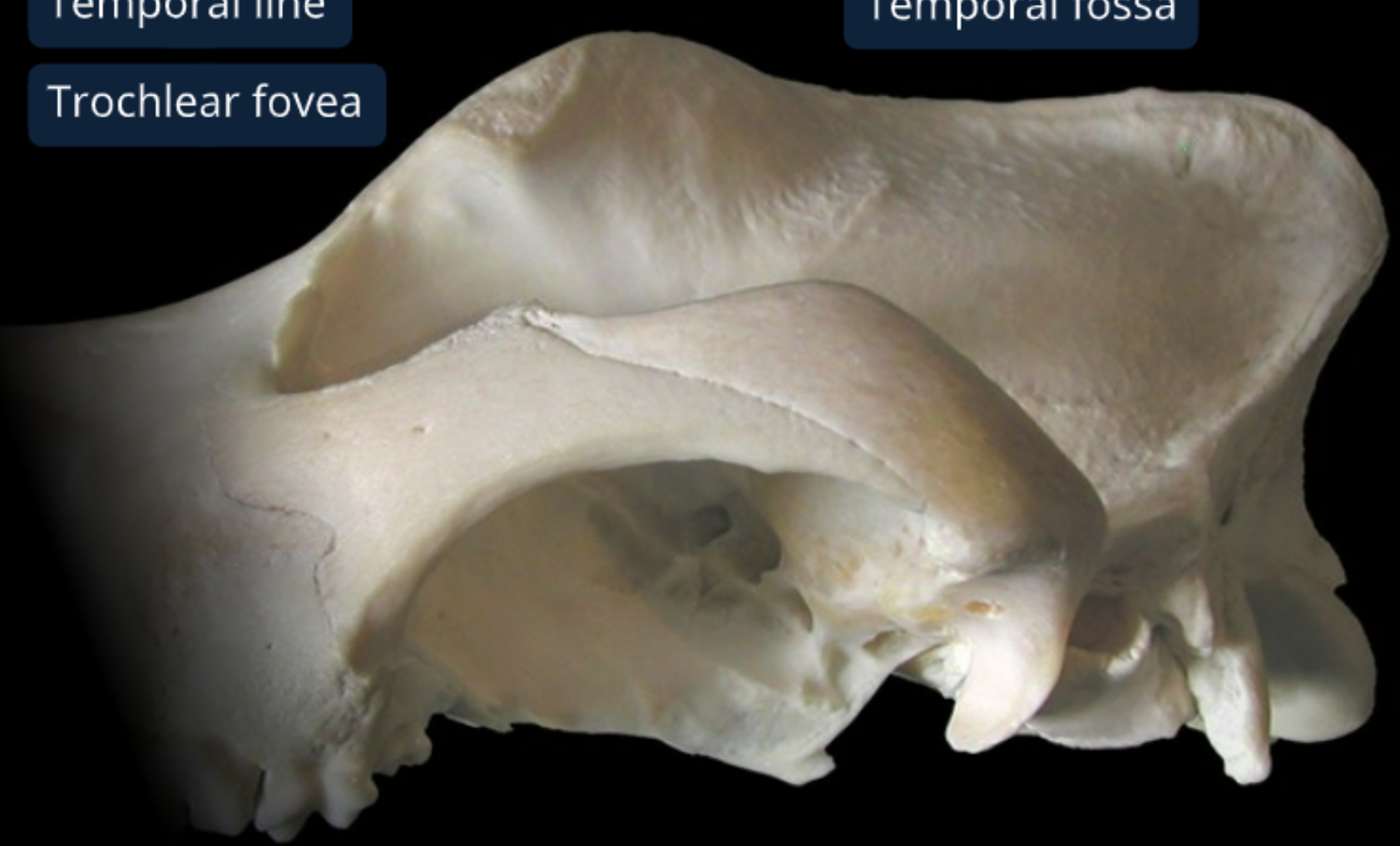
temporal fossa: convex surface where temporalis m. originates
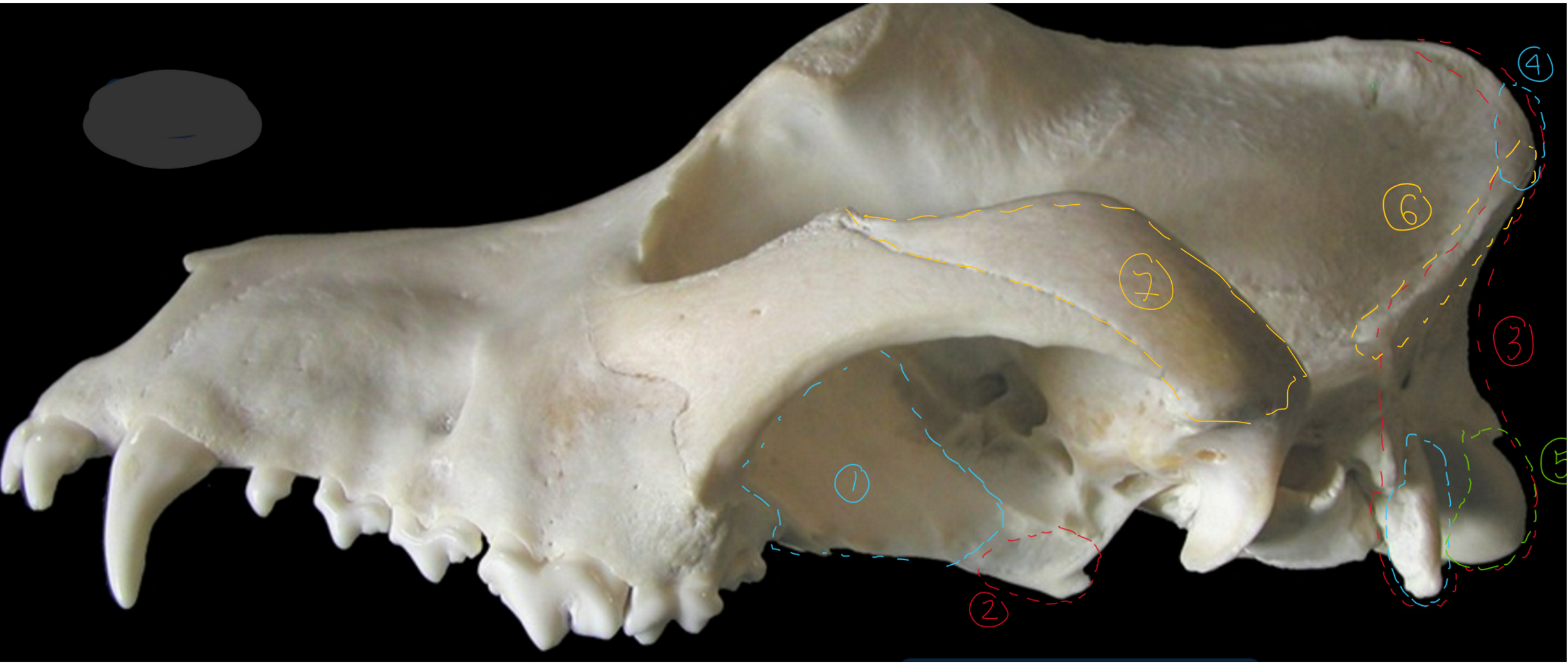
label the bones from the lateral side of the canine skull
palatine bone: forms caudal end of hard palate & rostral part of nasopharynx
pterygoid bone: wing shaped, caudal end of nasopharynx
occipital bone: most caudal part of head so looks like vertebra, touches pons/medulla oblongata/cerebellum
external occipital protuberance: this is where digastricus m. originates to open the jaw
occipital condyle: allows for head flexion/extension
nuchal crest: divides caudal & lateral surface of cranium
zygomatic process of temporal bone
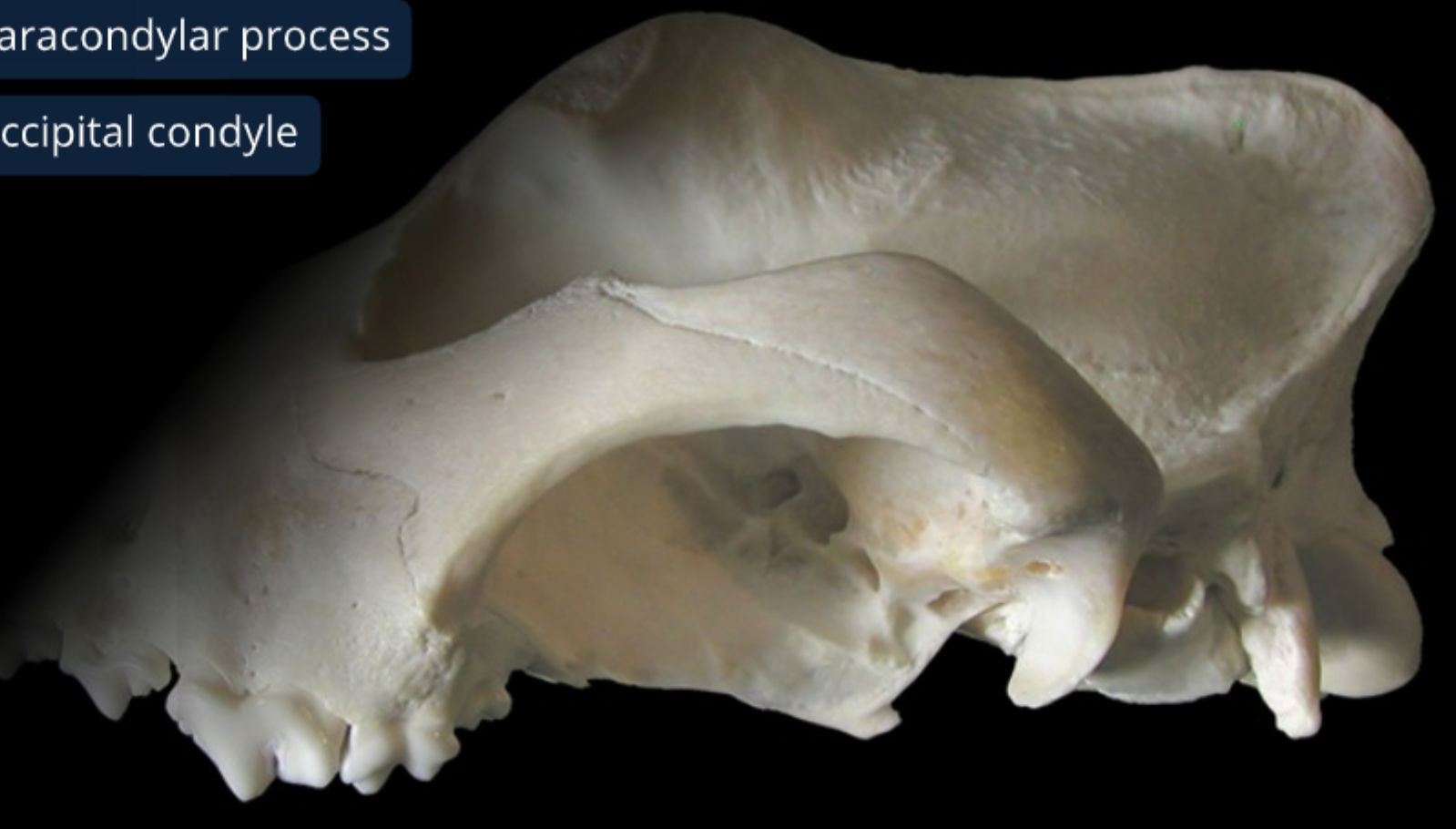
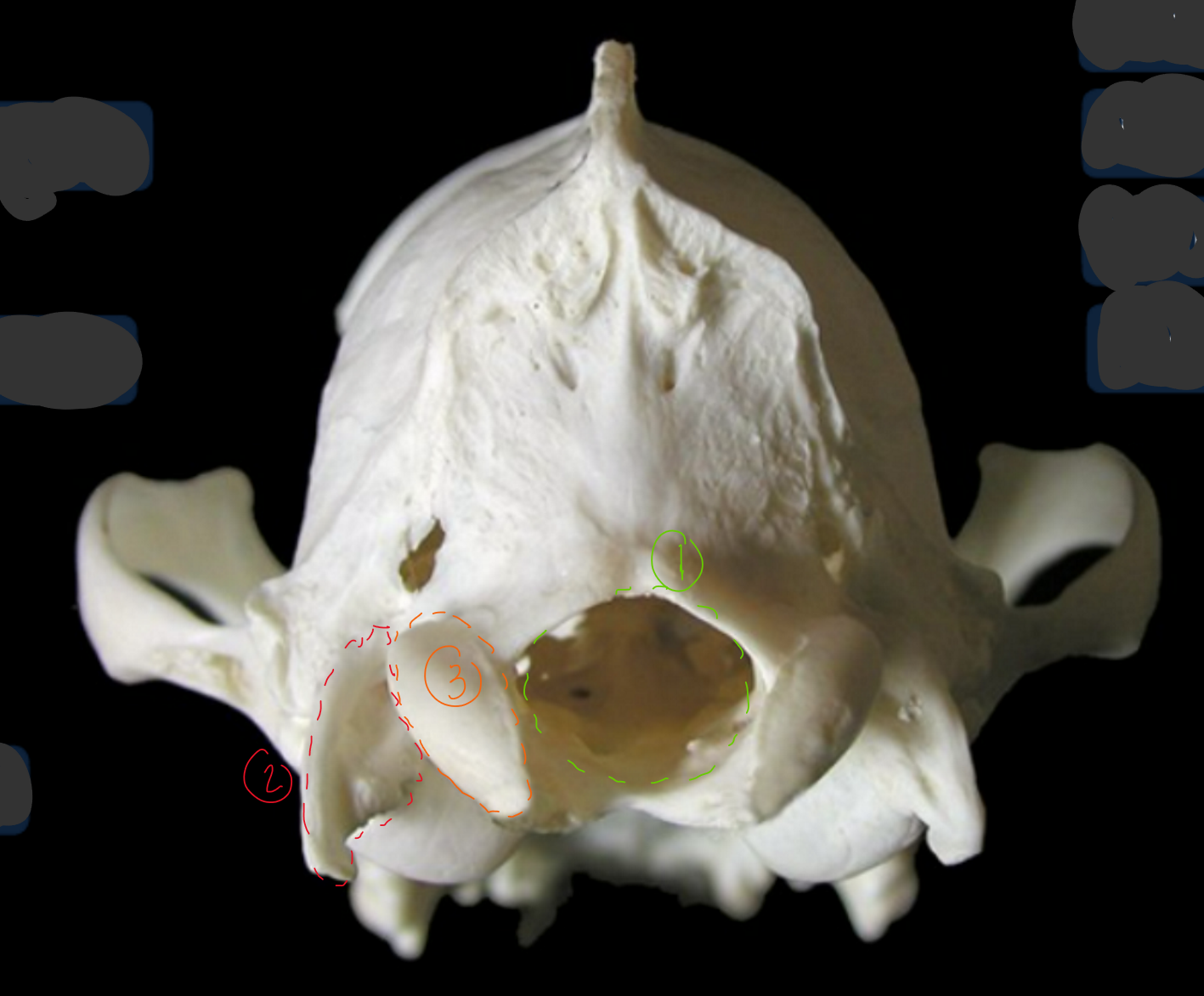
label the bones from the caudal (back) view of the canine skull
foramen magnum: has caudal end of medulla oblongata
paracondylar process: origin of digastricus m.
occipital condyle: allows head to flex & extend
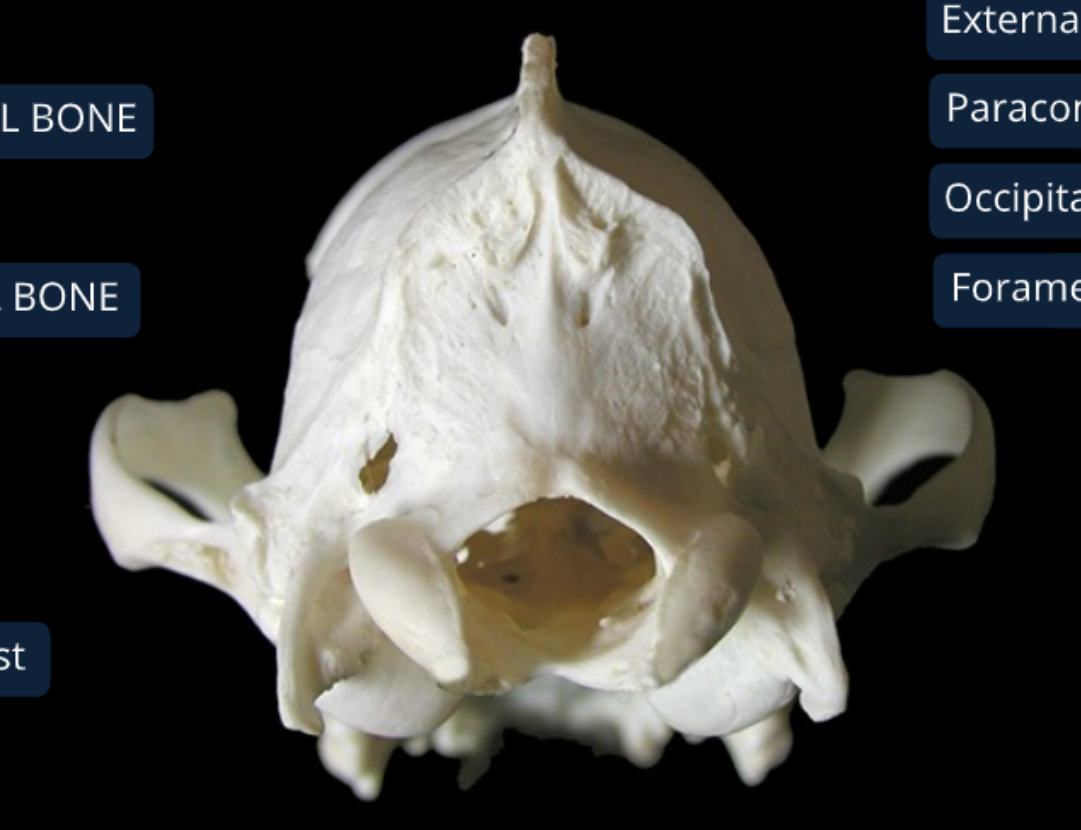
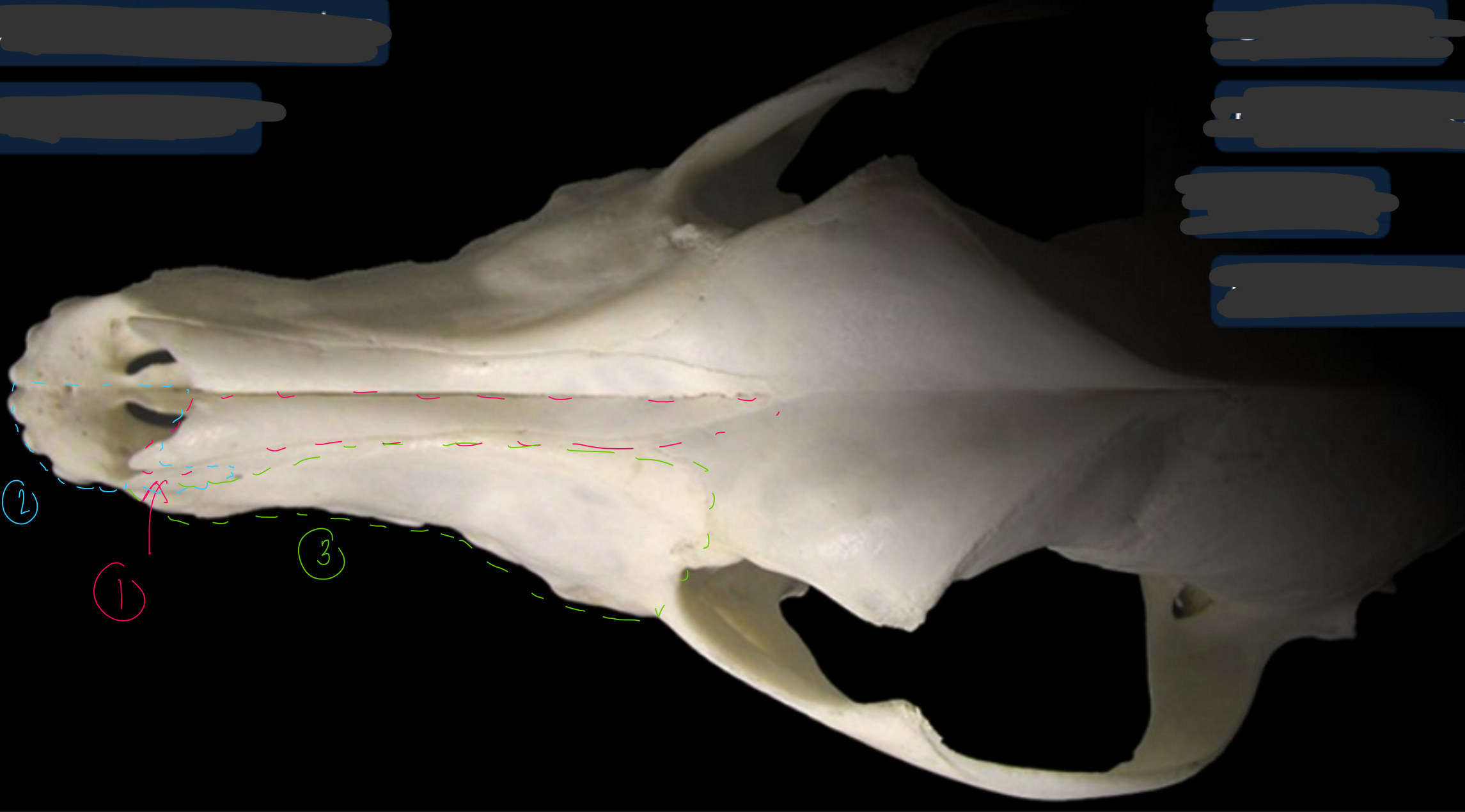
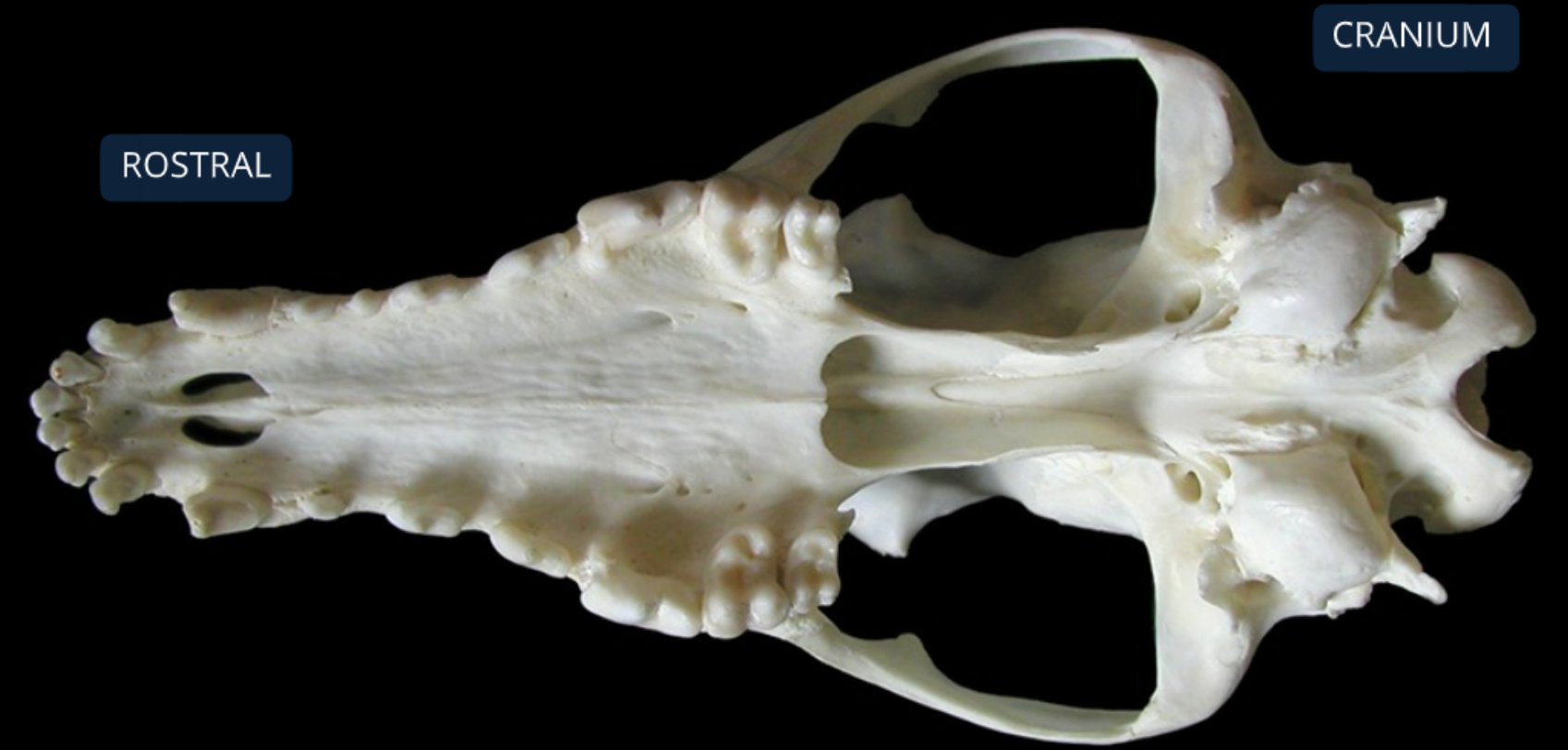
label the bones from the dorsal (top) view of the canine skull
nasal bone
incisive bone: supports incisor teeth
maxilla bone: supports canine, premolar, and molar teeth, forms bony division between nasal & oral cavities
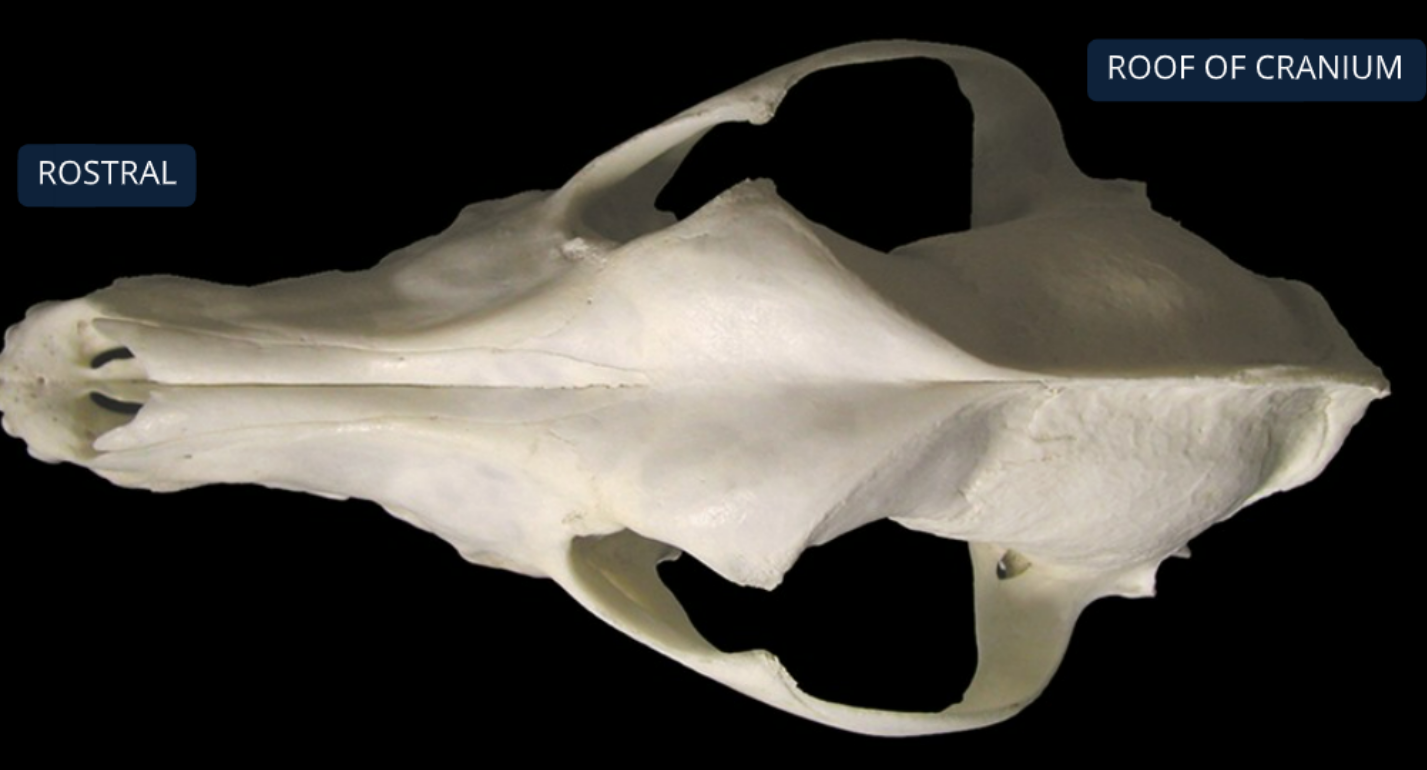
label the bones from the ventral (bottom) view of the canine skull
maxilla: supports canine, premolar, molar teeth
vomer: ossified ventral part of nasal septum
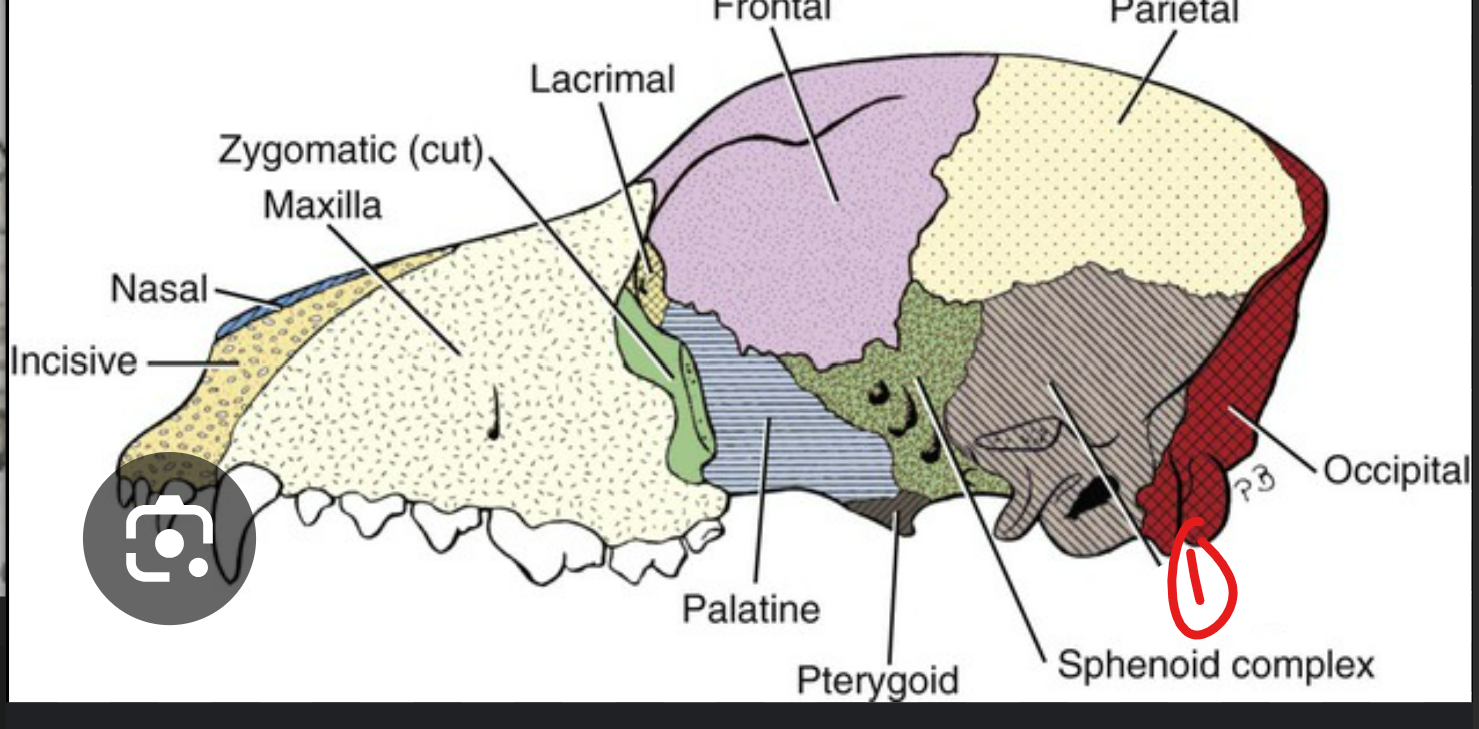
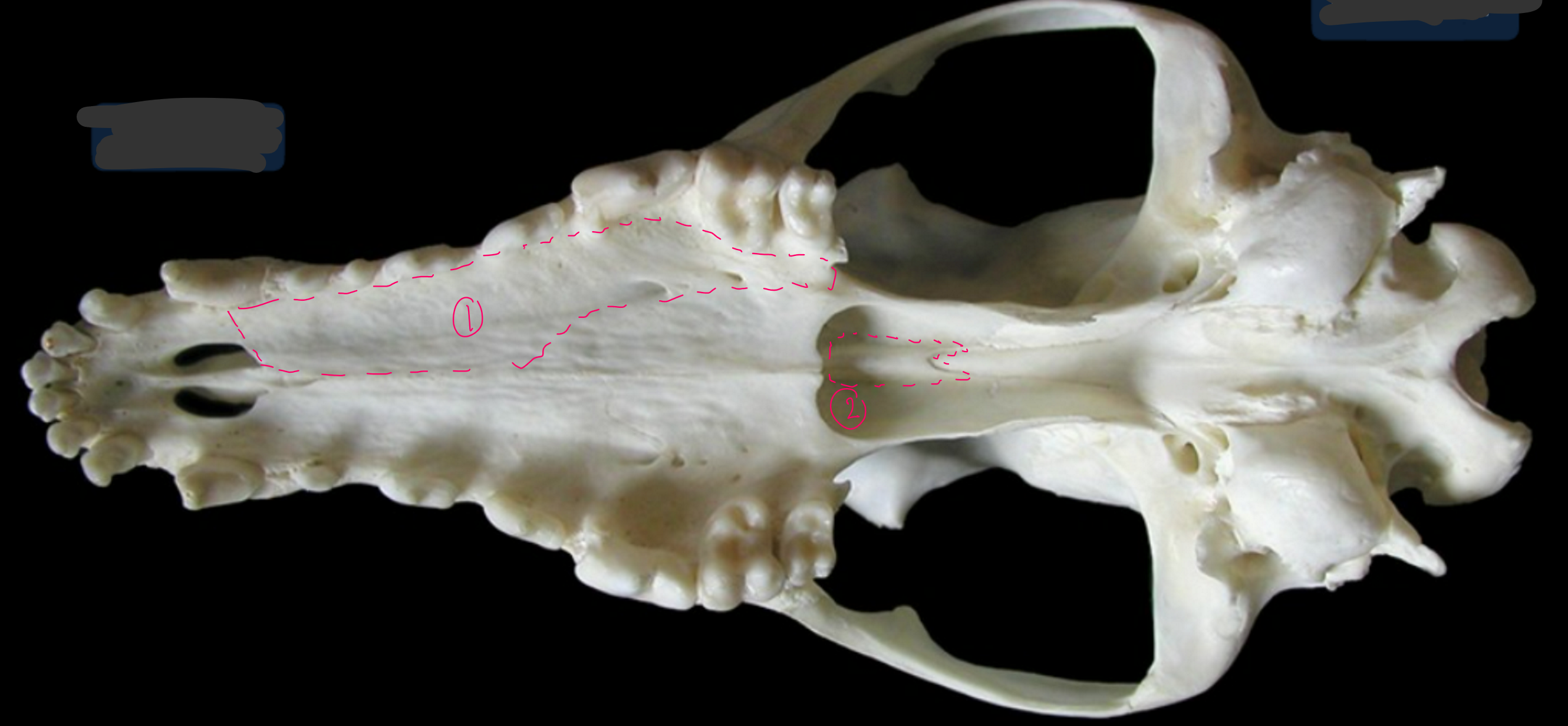
label the bone in grey
temporal bone
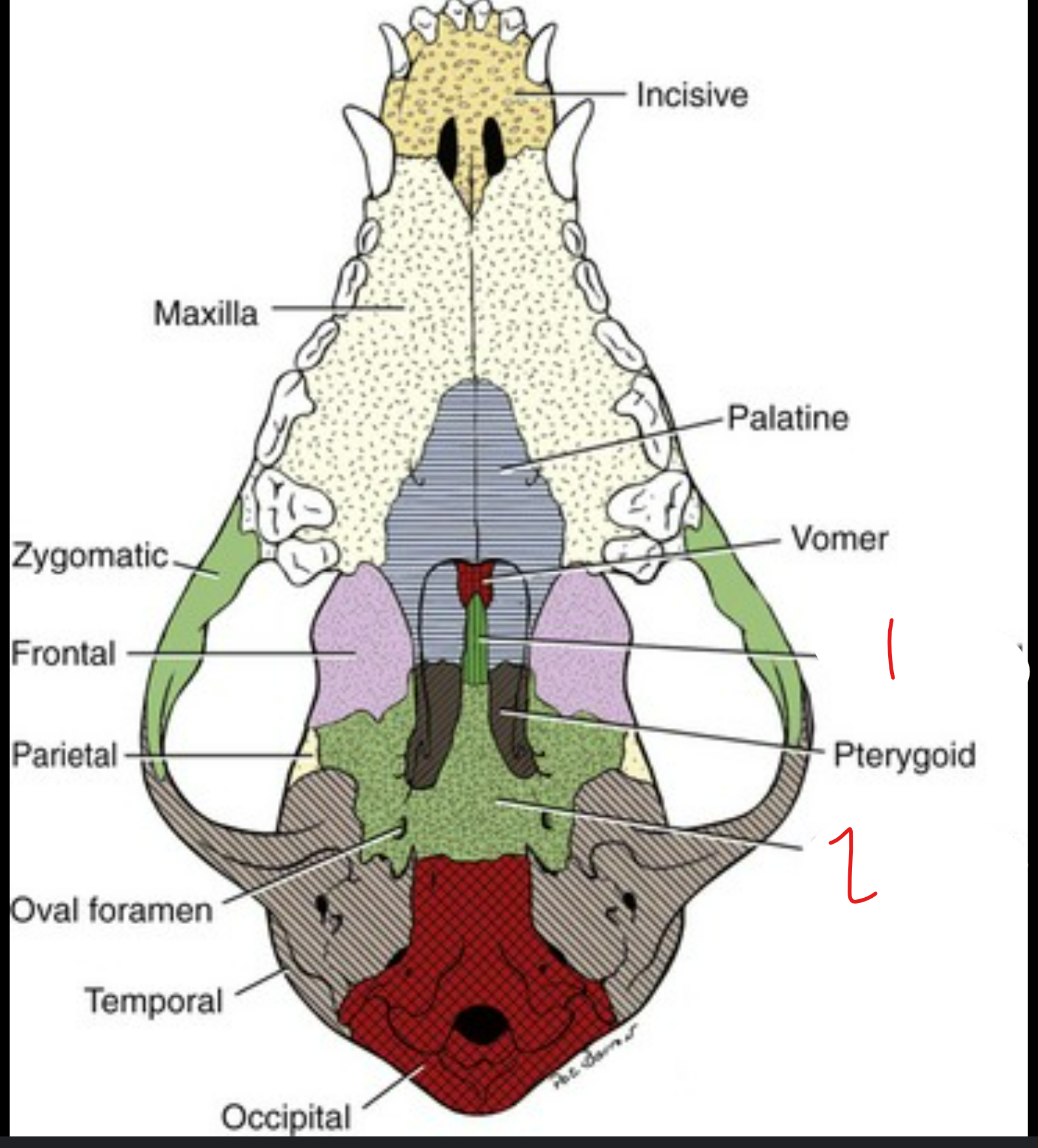
label the ventral view (underside) of the canine skull
presphenoid
basisphenoid
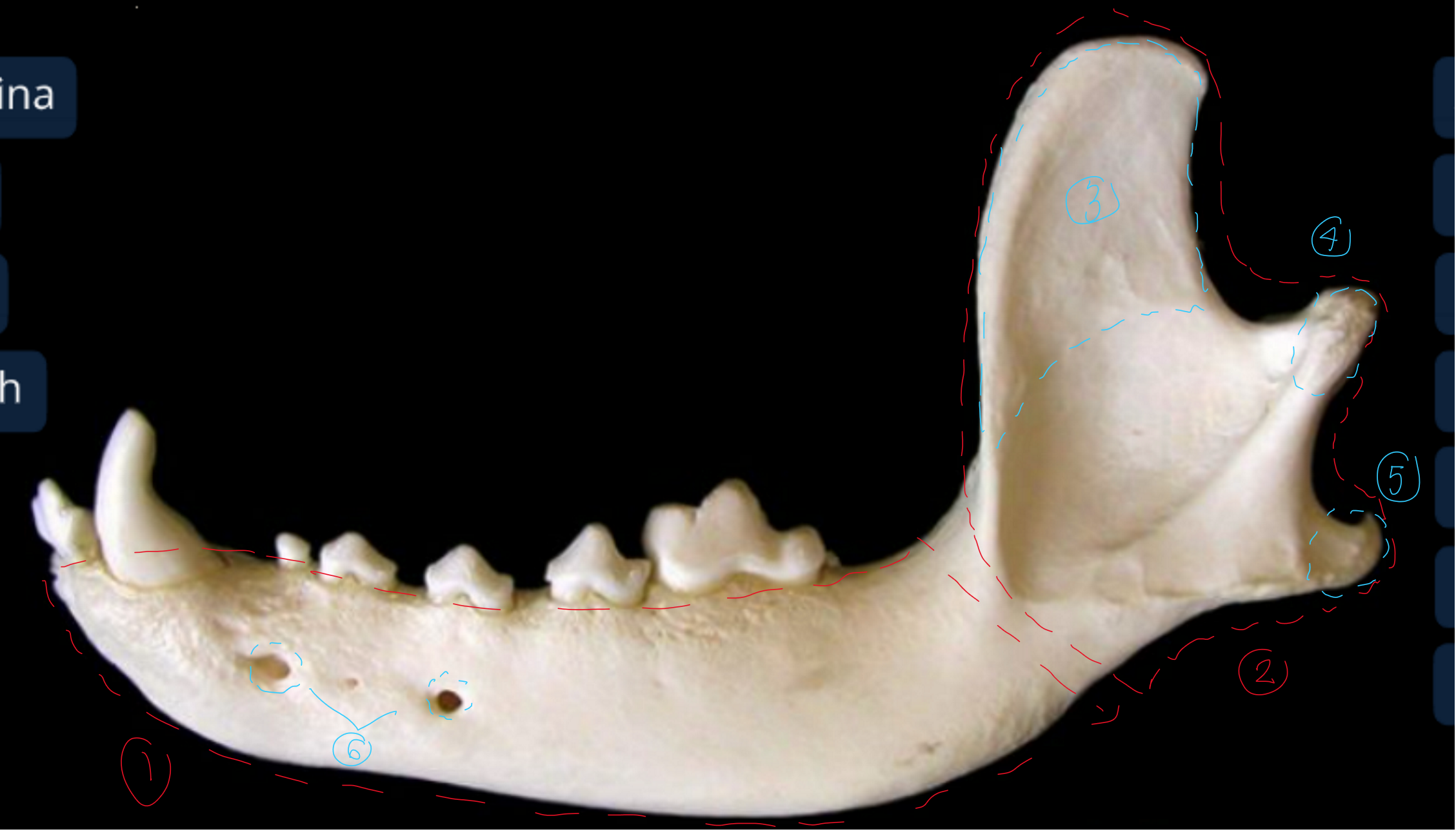
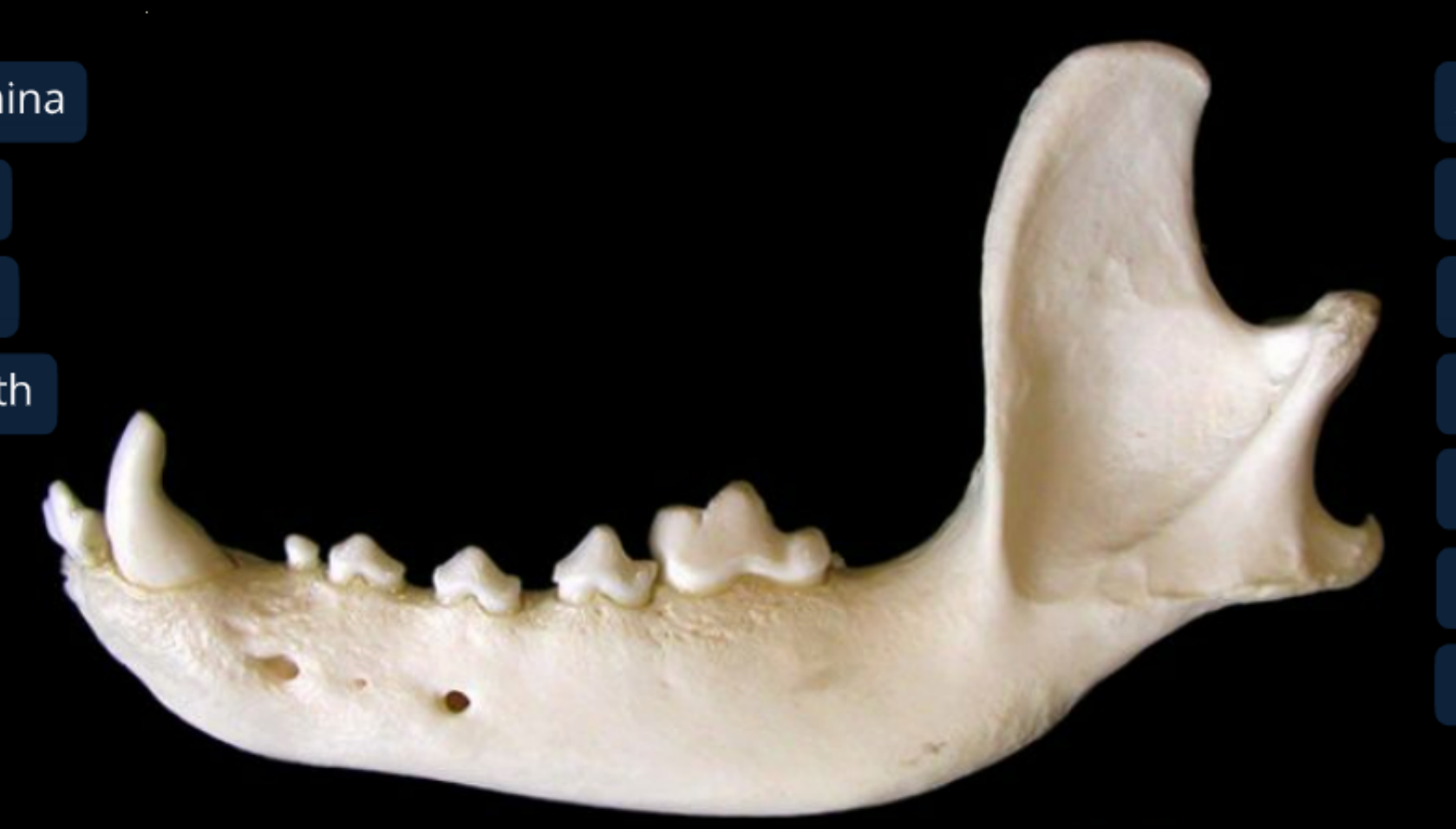
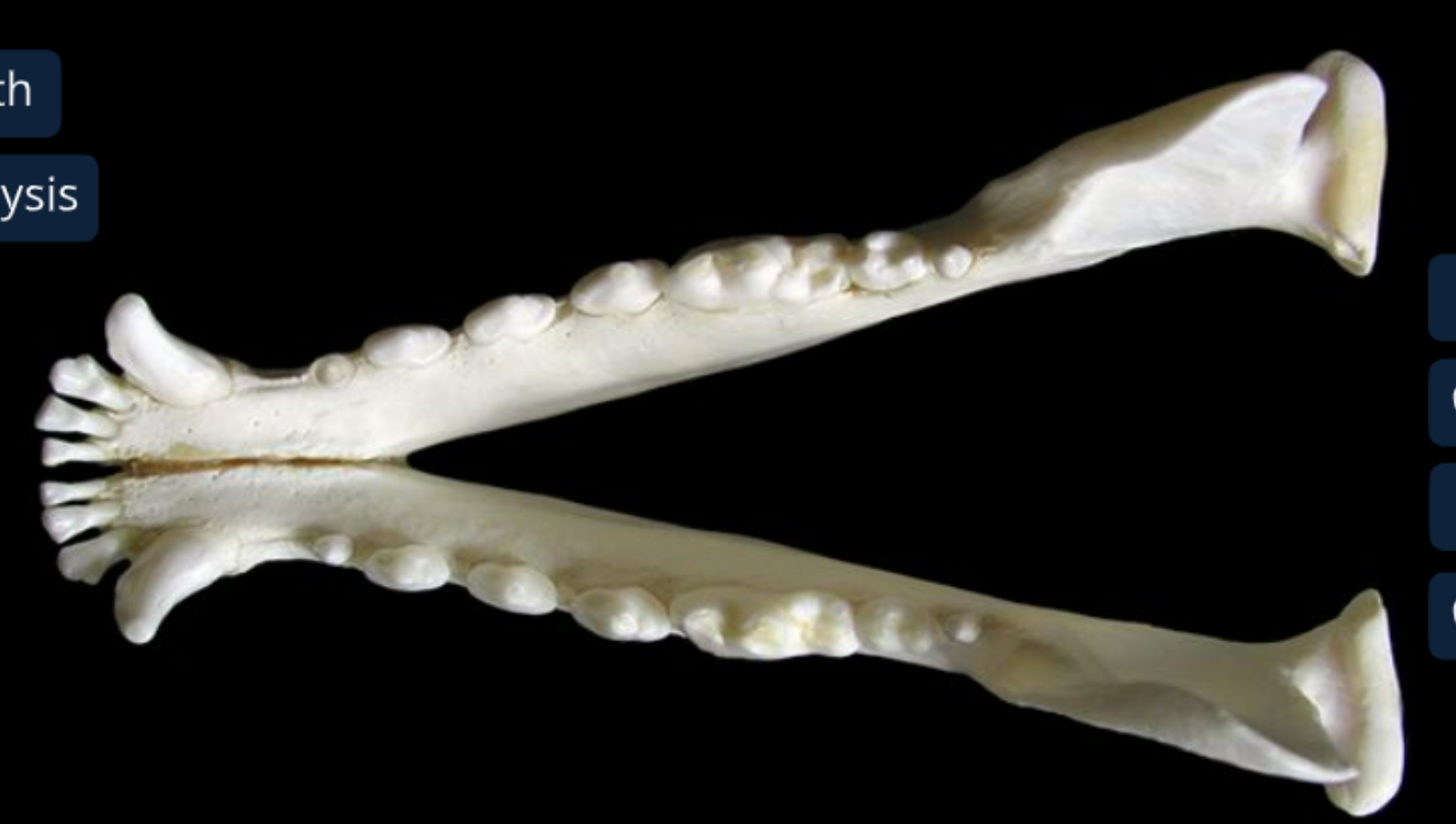
label the lateral view of the canine mandible
body of the mandible: includes alveoli of teeth
ramus of the mandible: attaches to skull & mastication muscles
coronoid process of the ramus: dorsal and medial to zygomatic arch of the skull, temporalis m. inserts here
condyloid process of the ramus
angular process of the ramus: pterygoideus m. inserts here
mental foramina: has nerves and BV to lower lip
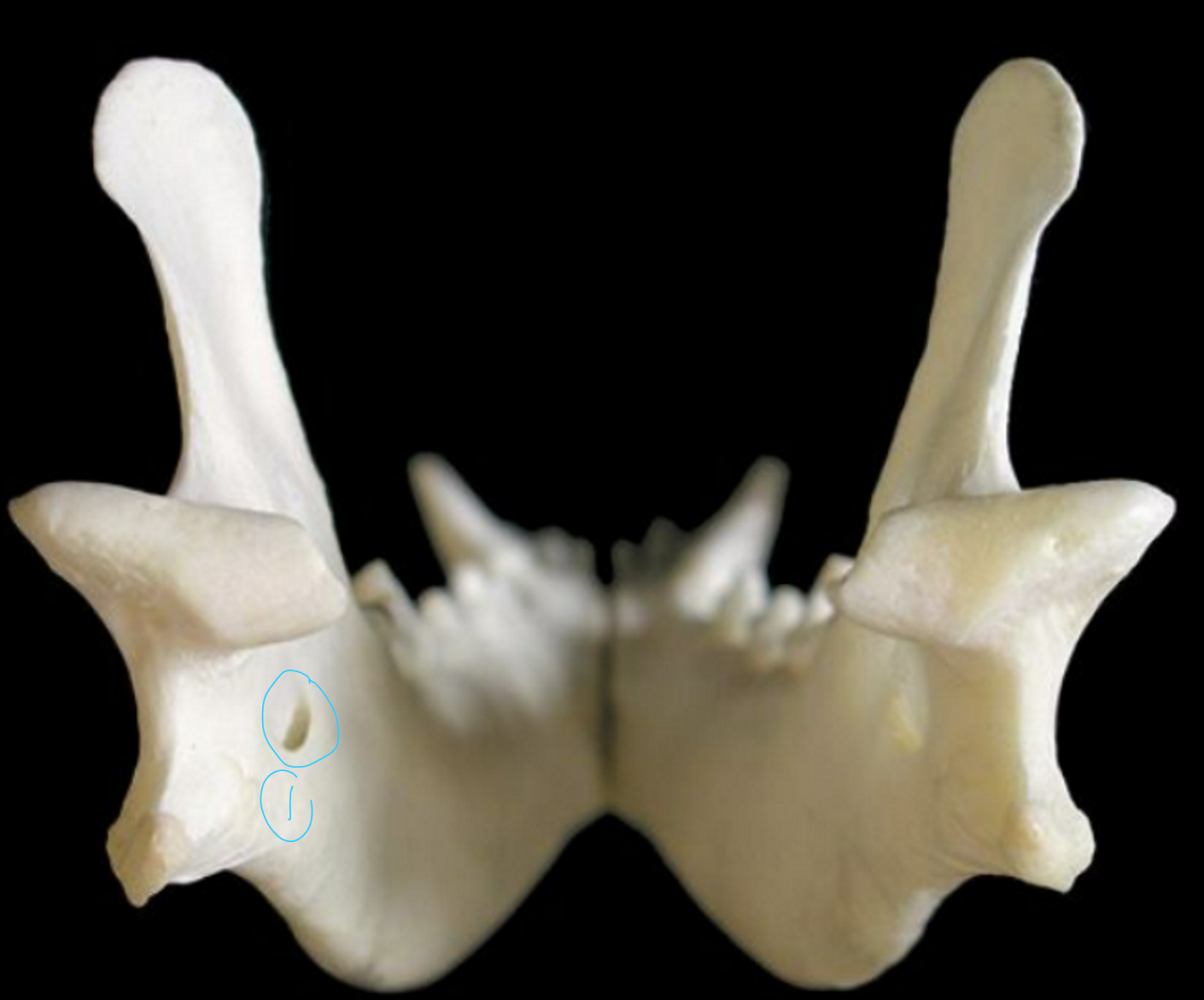
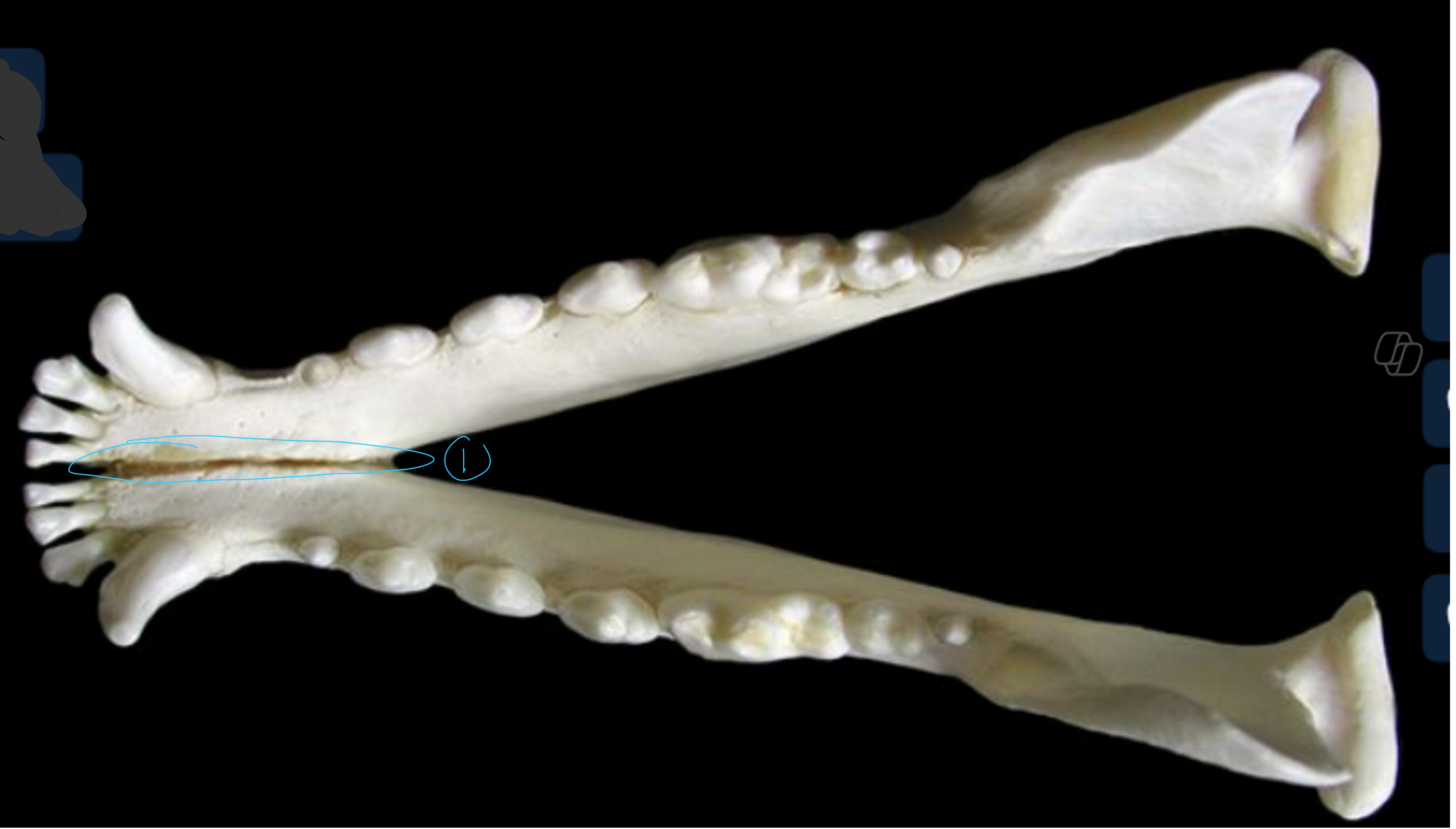
label the caudal (back) view of the canine mandible
mandibular foramen: this is where mandibular alveolar BV and nerves enter to supply teeth & lower lip
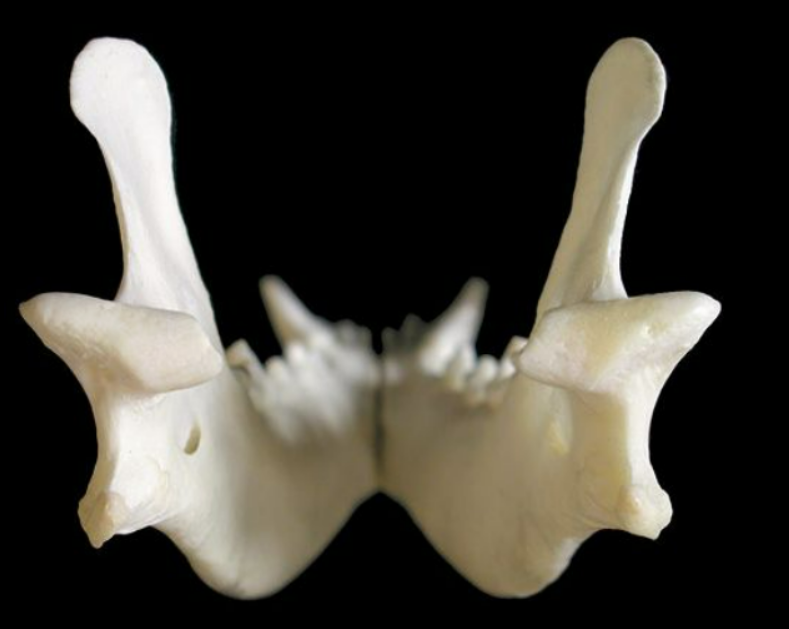
label the dorsal/top view of the canine mandible
SPELLING
intermandibular symphysis: cartilage joint between 2 mandibles

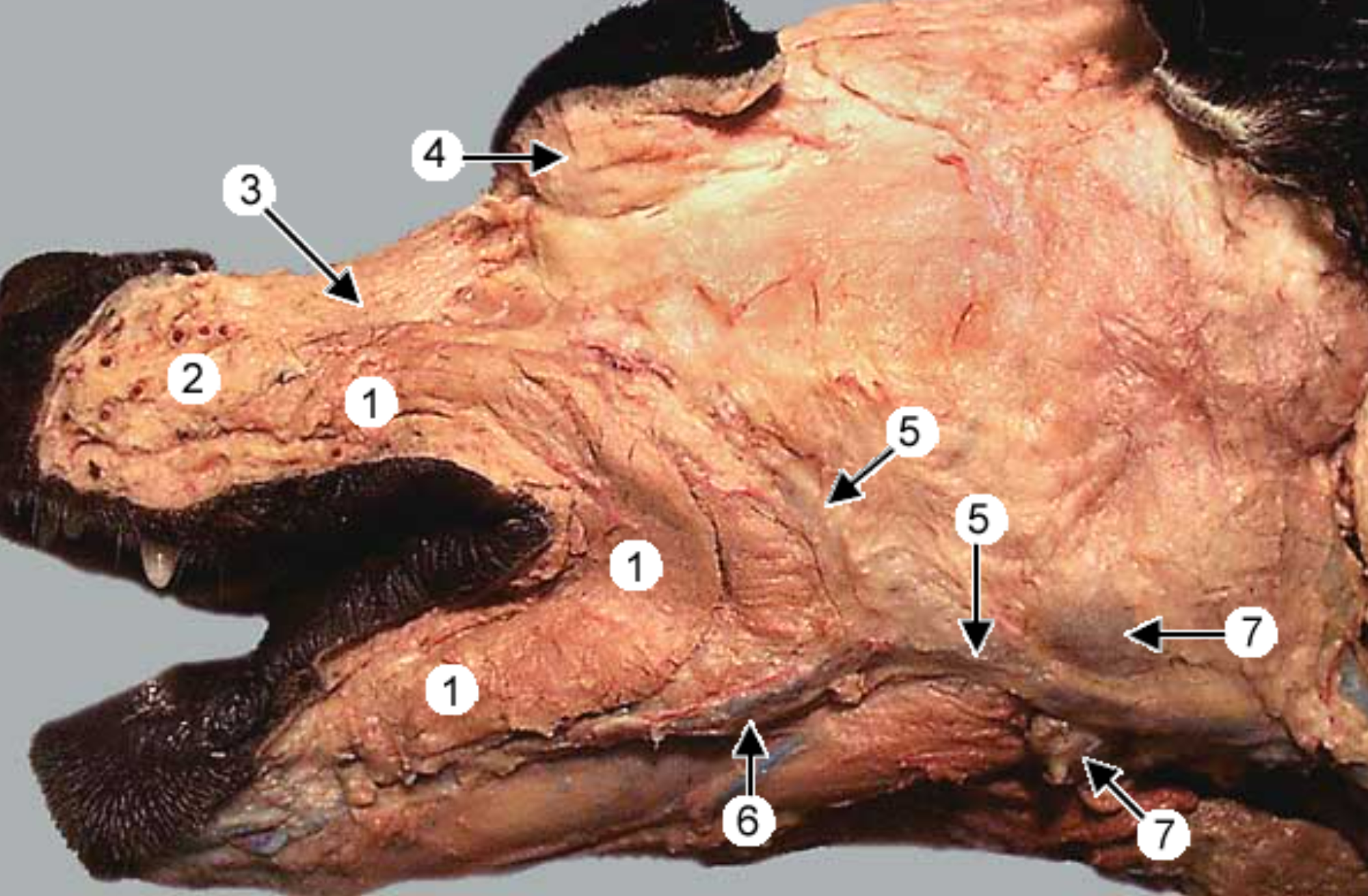
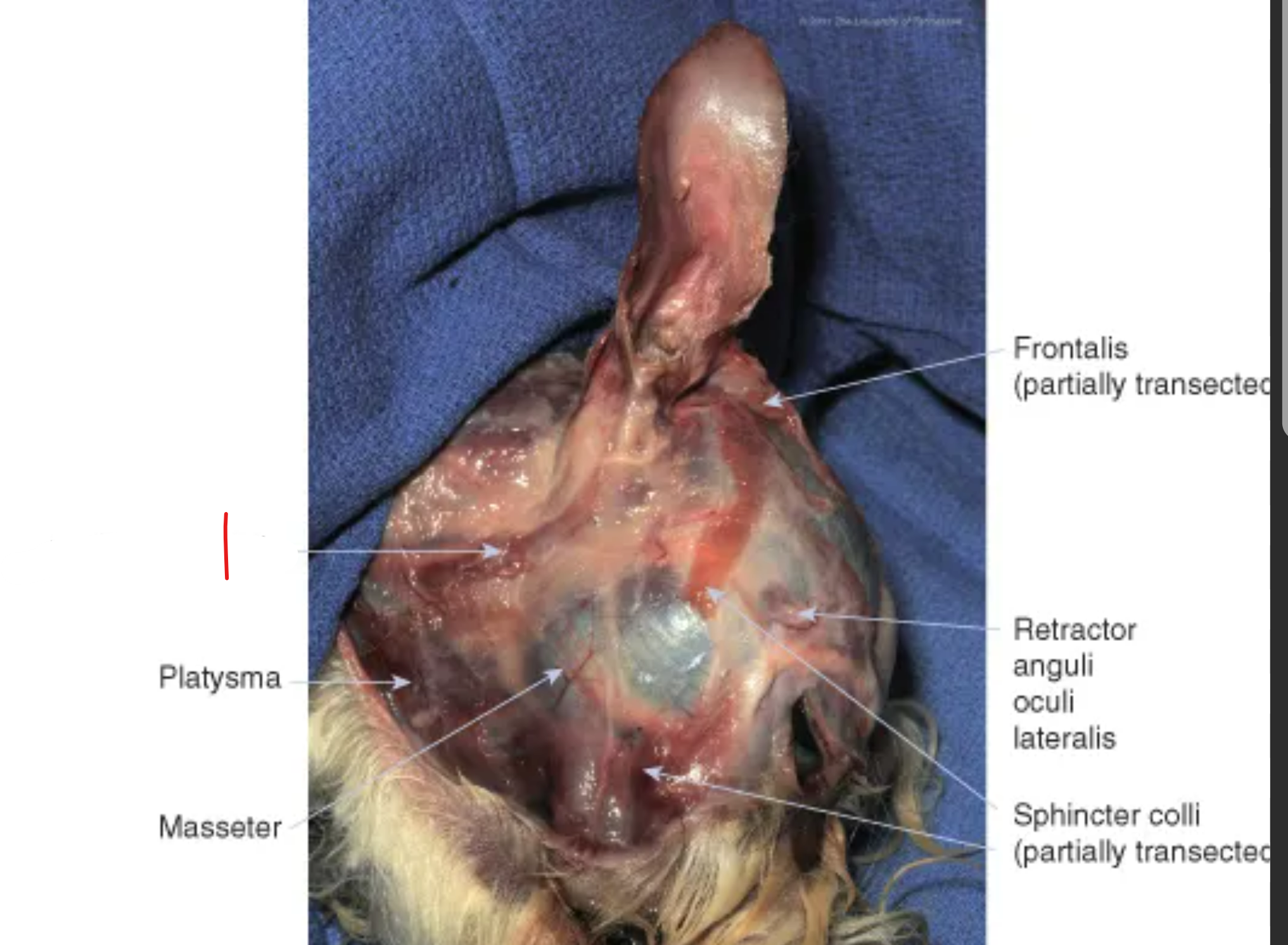
label the muscles 1, 3, 4 (orbicularis oris is gone)
buccinator muscle: within walls of lips & cheek
-
levator nasolabialis muscle: retracts nose & upper lip
orbicularis oculi muscle
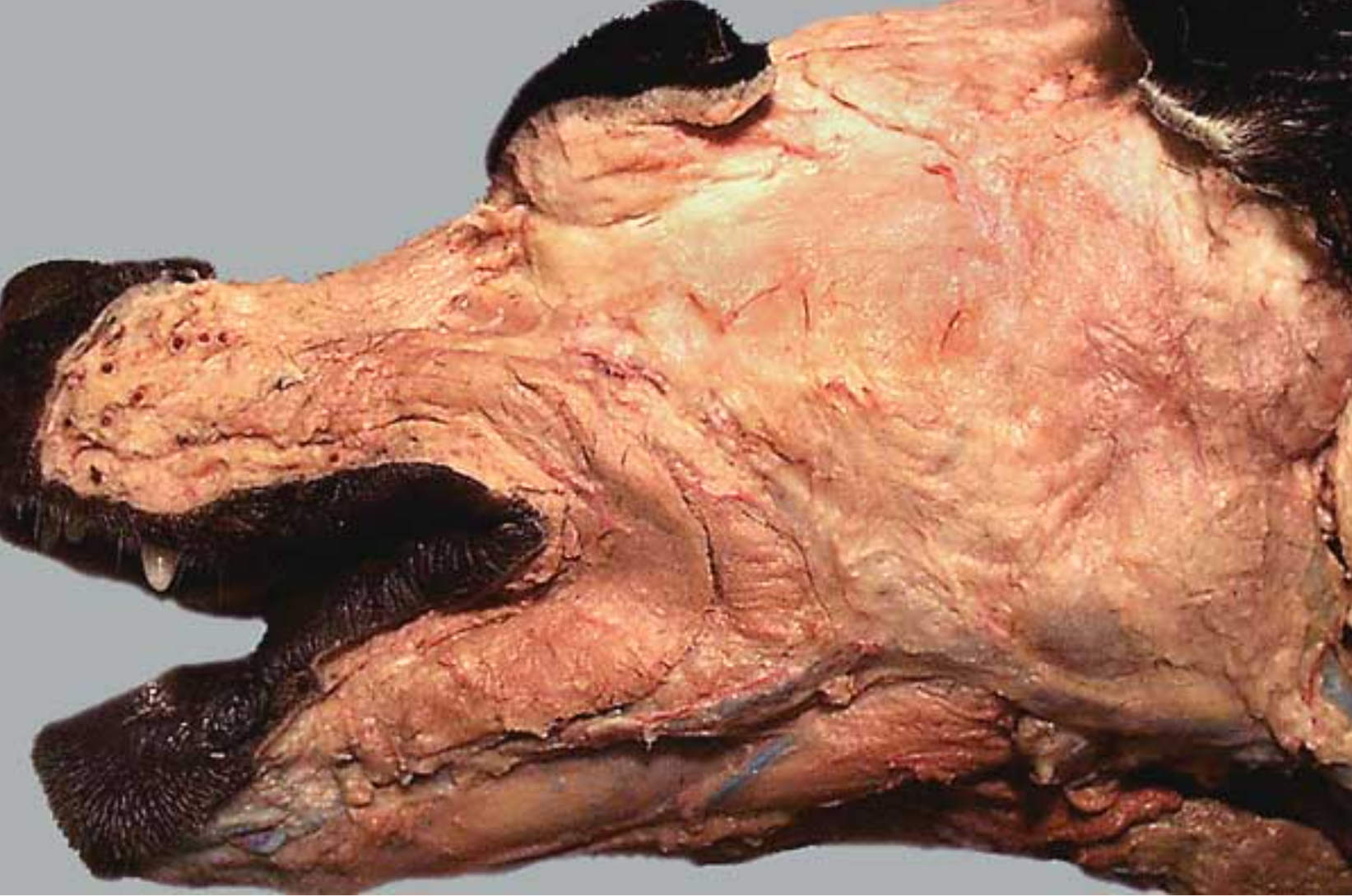
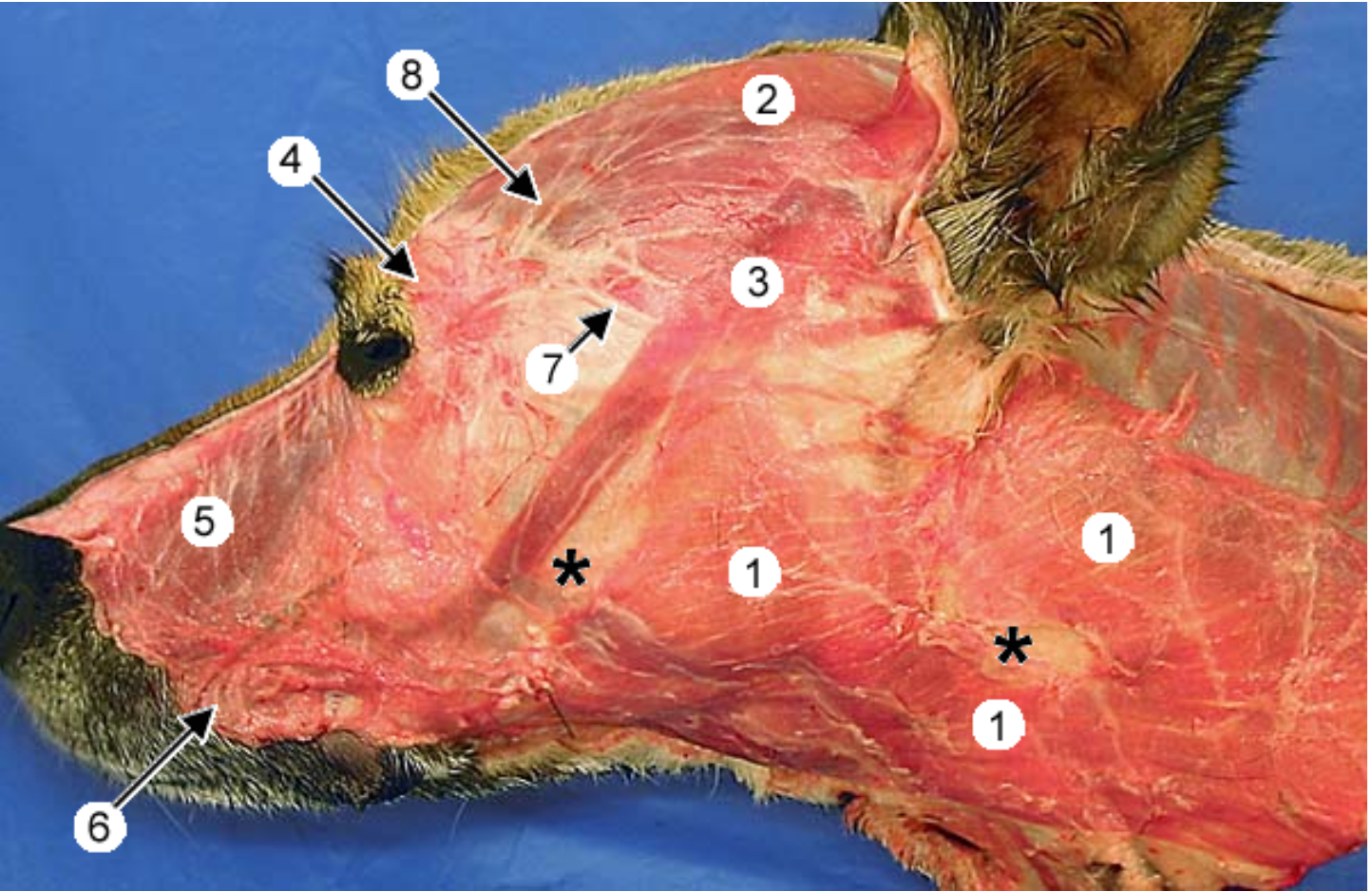
label the muscles 1, 4, 5, 6
platysma m.: runs from neck to commissure of lips
-
-
orbicularis oculi m
levator nasolabialis m: retracts nose & upper lip
orbicularis oris m: within the lips
what muscle is labeled
parotidoauricularis
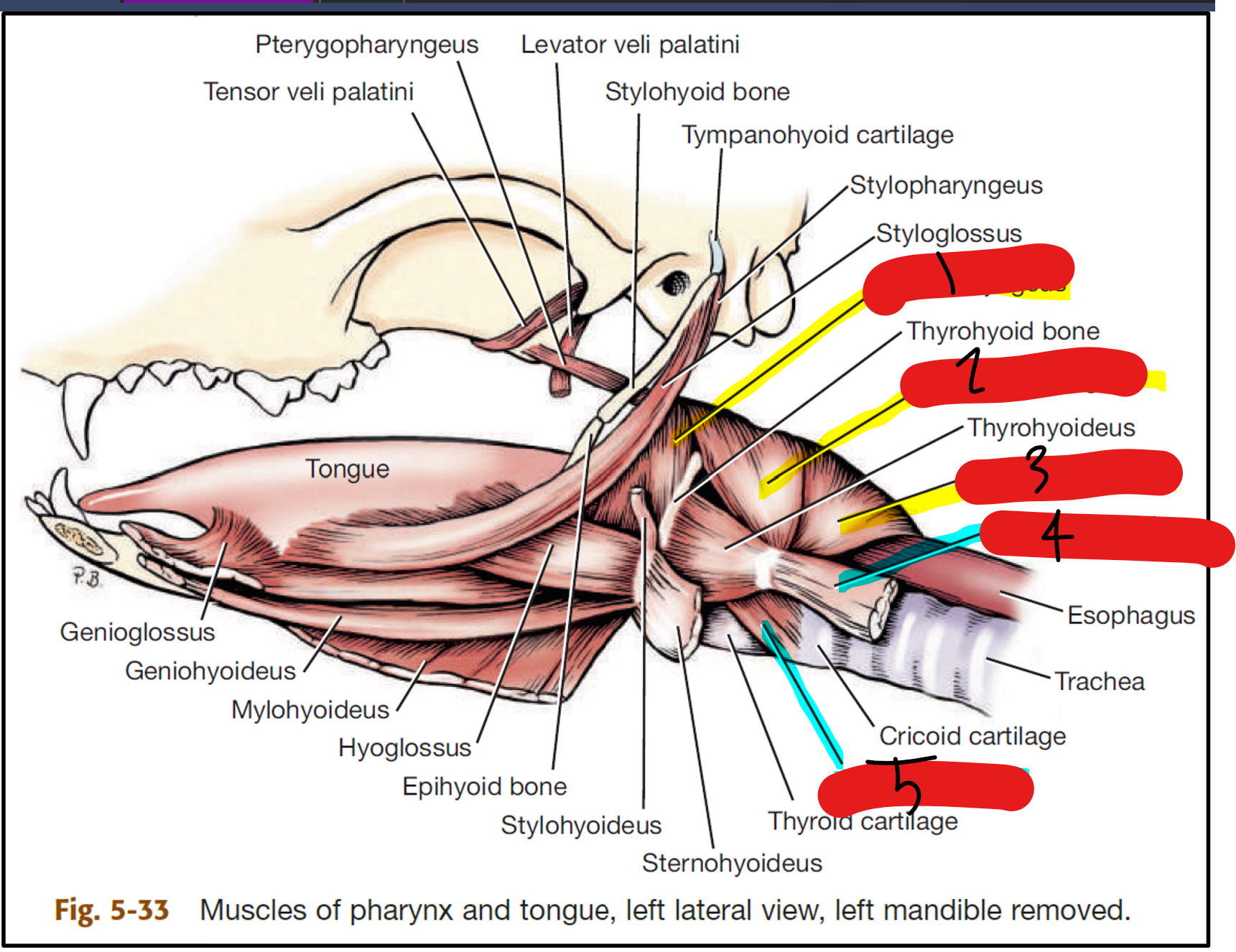
label the muscles of the pharynx/larynx
hyopharyngeus
thyropharyngeus
cricopharyngeus: aids in swallowing, helps push food down
sternothyroideus
cricothyroideus (bow tie shape)
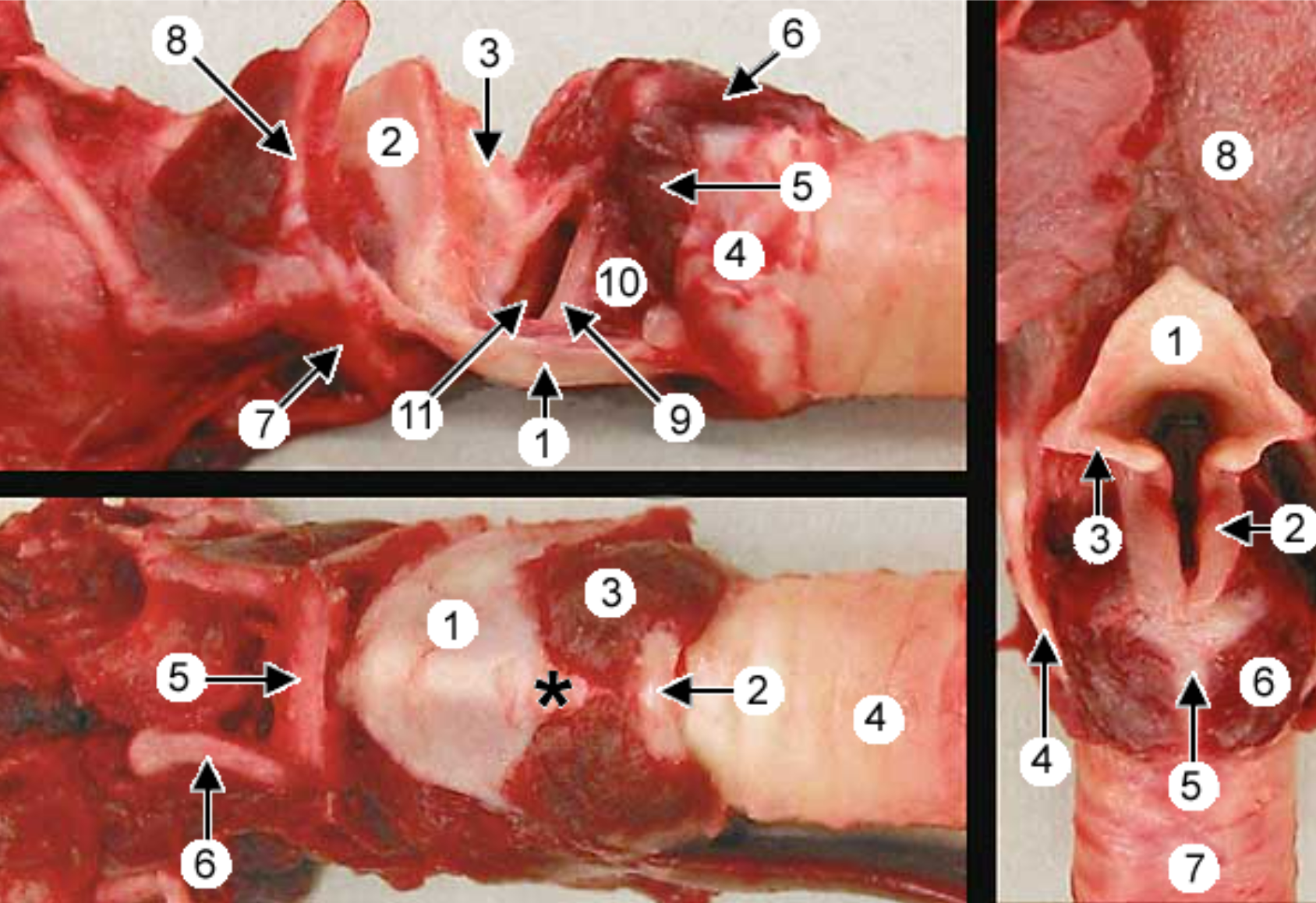
label the larynx: 3 (bottom left pic), 6 (top left and right pic)
cricothyroideus muscle
cricoarytenoideus dorsalis
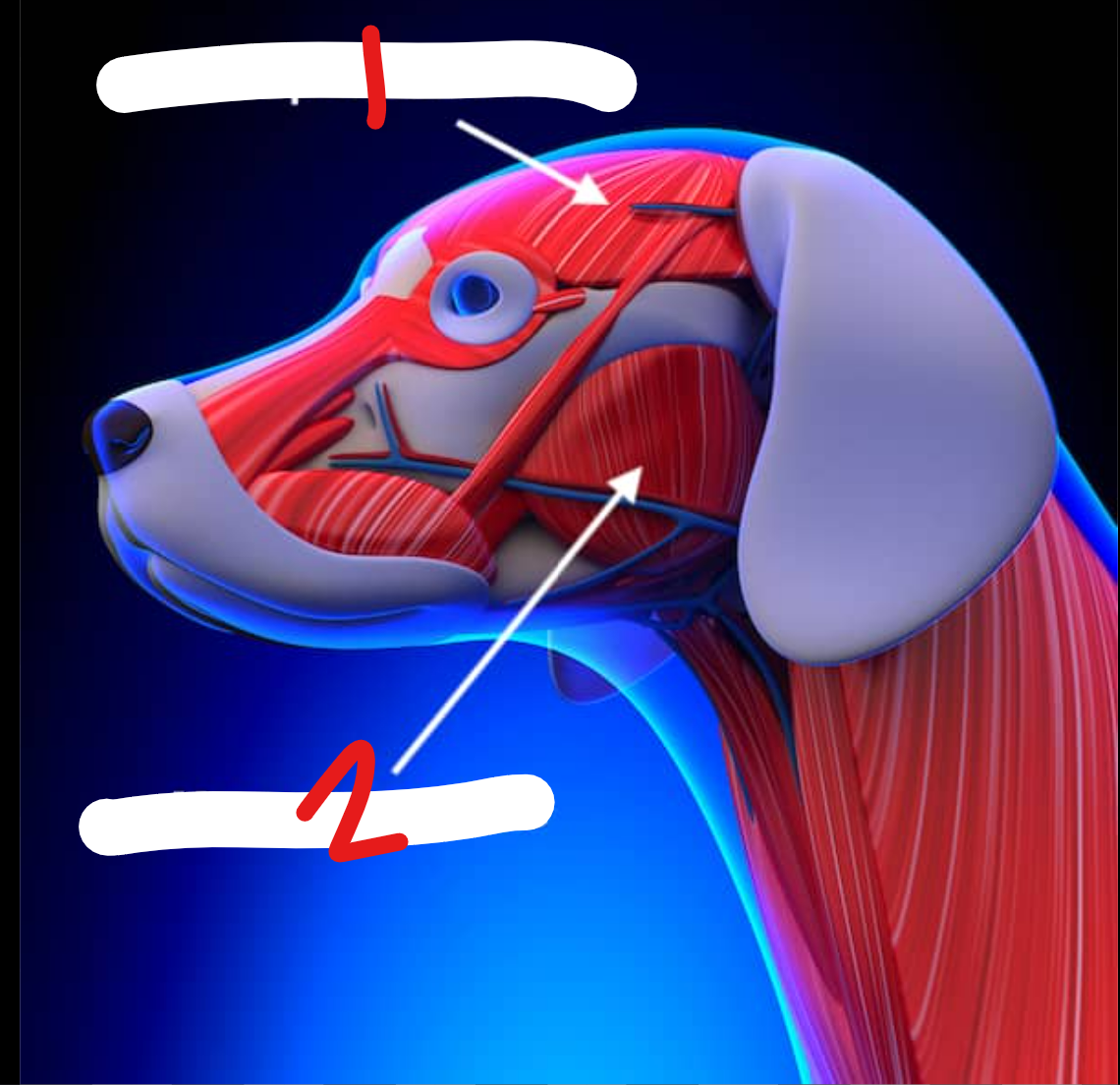
label the muscles on the head
temporalis m: inserts on ramus of mandible (8), involed in mastication
masseter m: runs between body of mandible (5) & zygomatic arch (6), involved in mastication
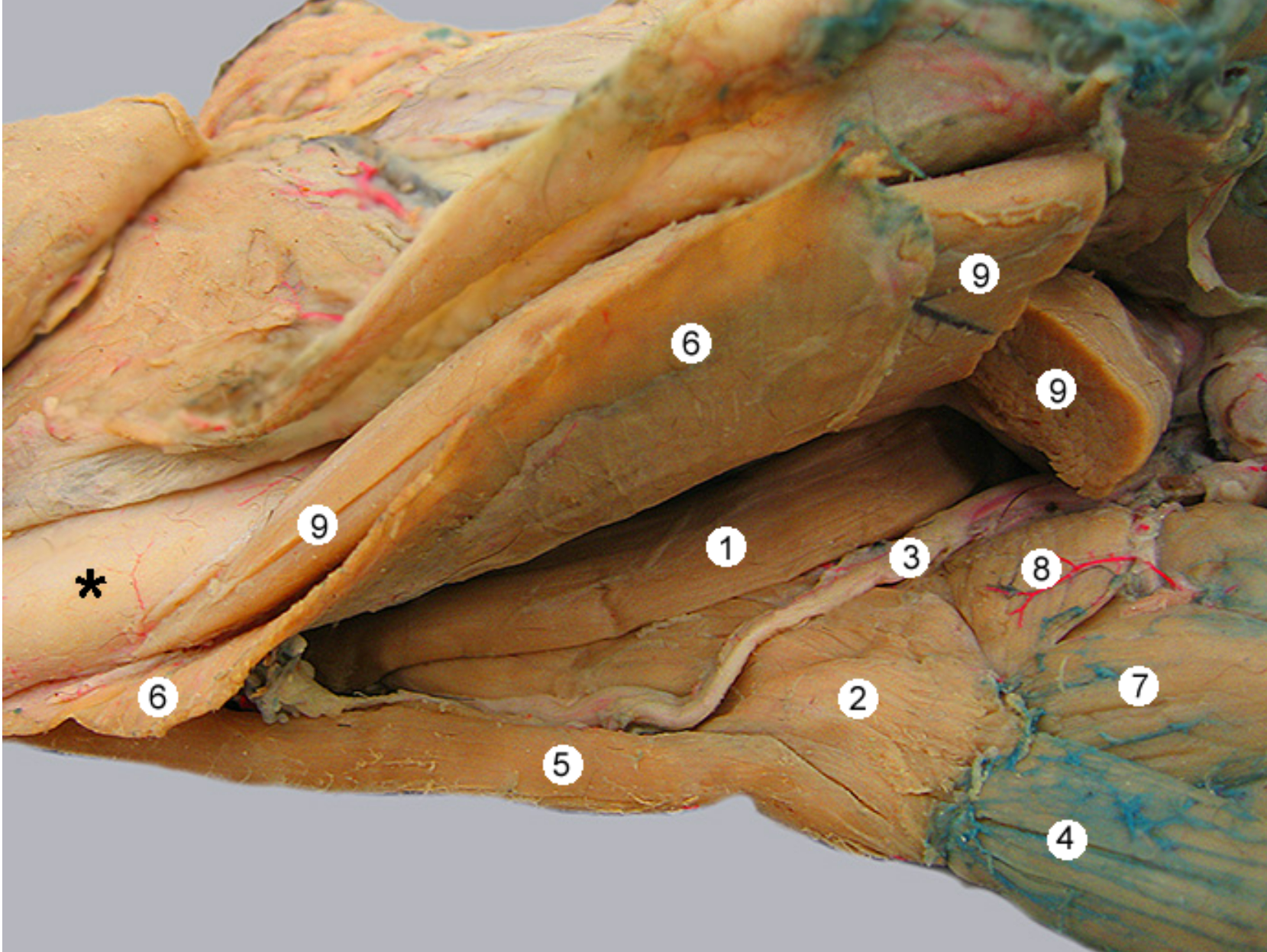
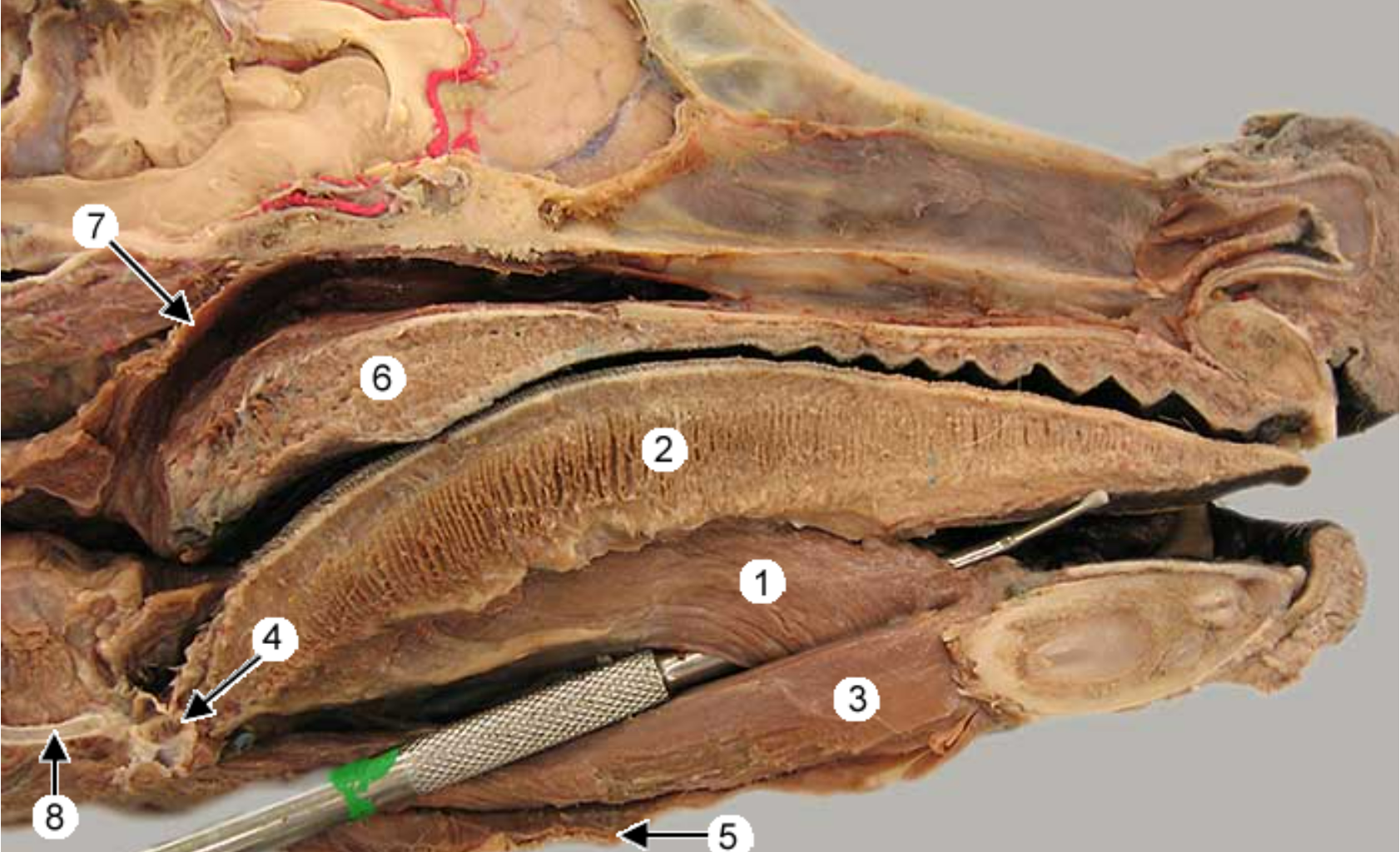
this image shows two tongue muscles from a ventrolateral view.
head is facing to the left
for reference: 9 is the digastricus m, 3 is hypoglossal nerve, 6 is the mylohyoideus, 4 is the sternohyoideus
label 1,2,7
styloglossus m
hyoglossus m: runs from hyoid apparatus to root of tongue
-
-
-
-
thyrohyoideus
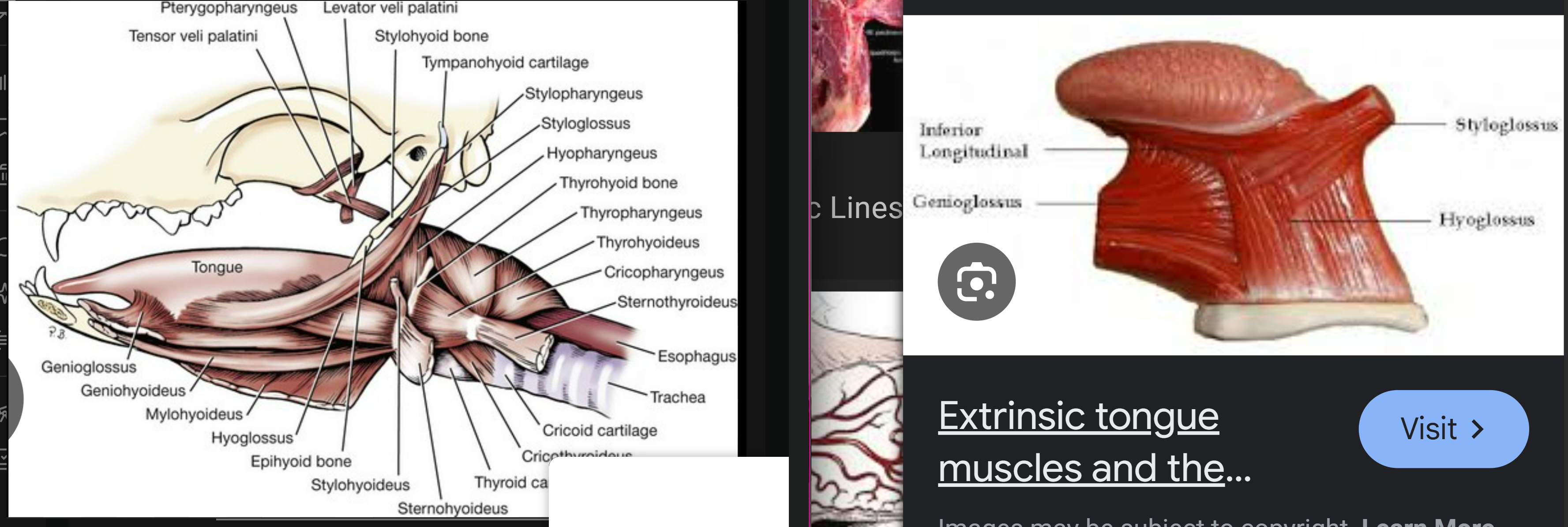
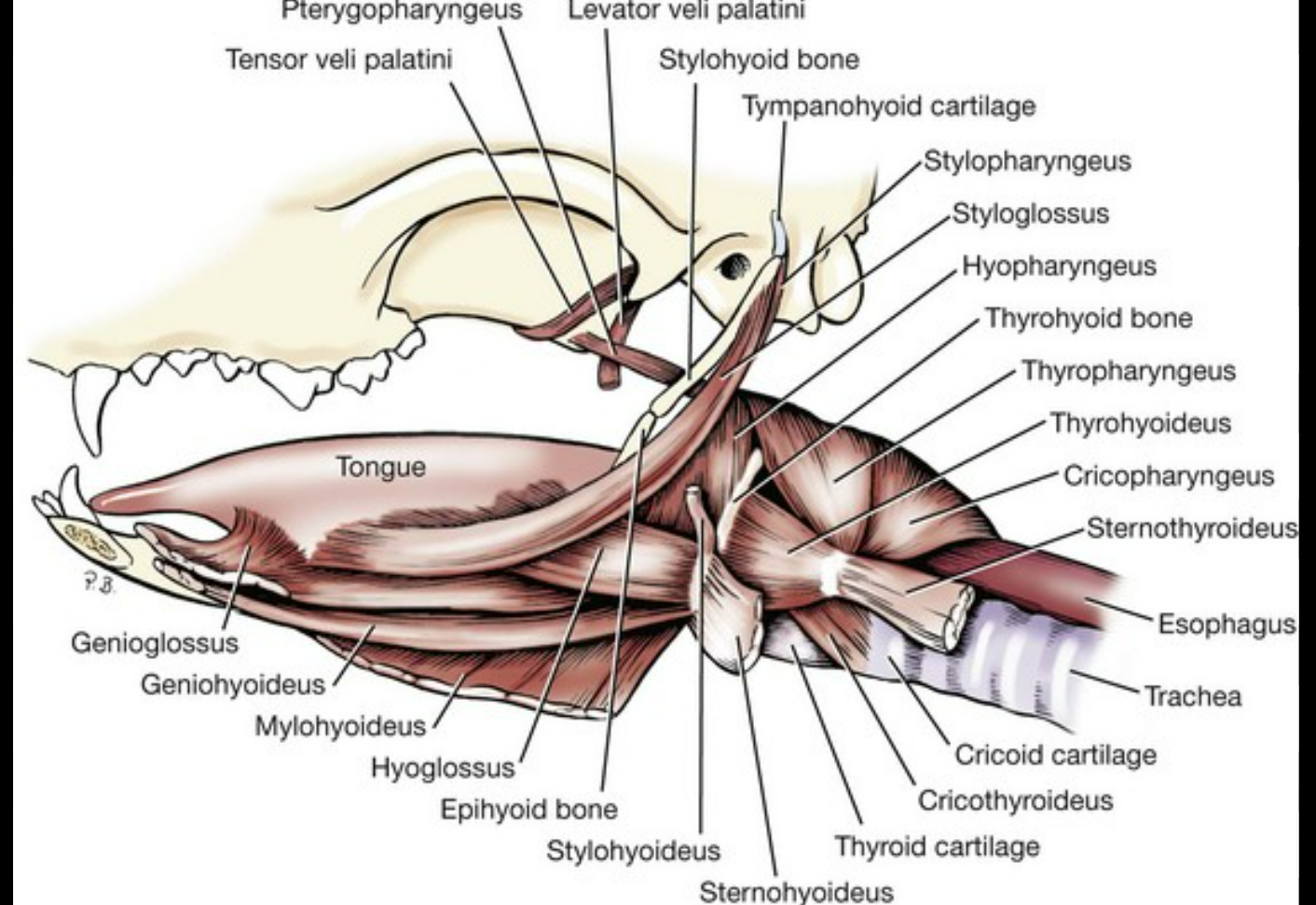
this is a medial view of the canine head (nose to the right).
label the muscles 1, 3, 5
genioglossus m: runs from chin to tongue
-
geniohyoideus m
-
mylohyoideus m.
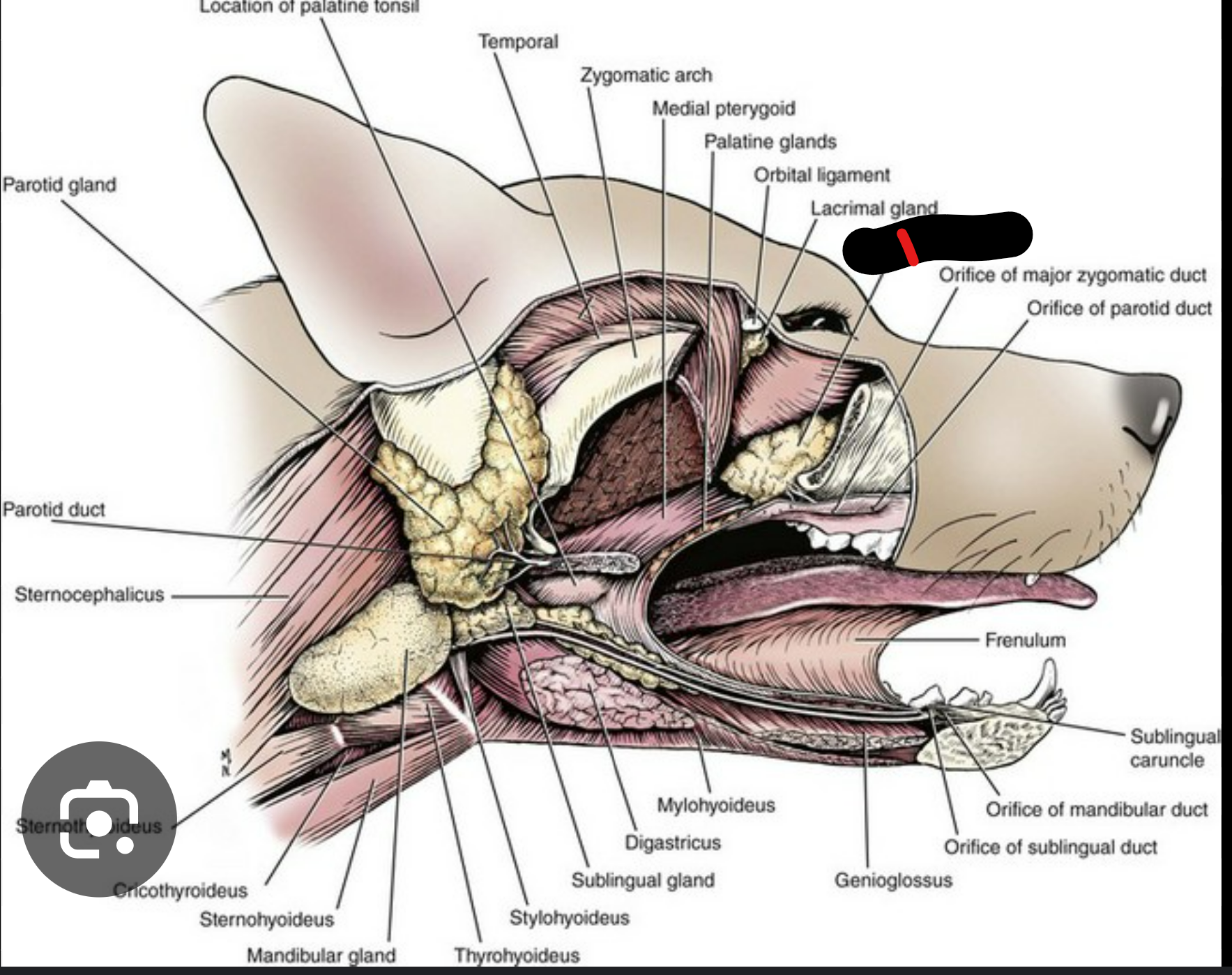
what salivary gland is this
zygomatic salivary gland
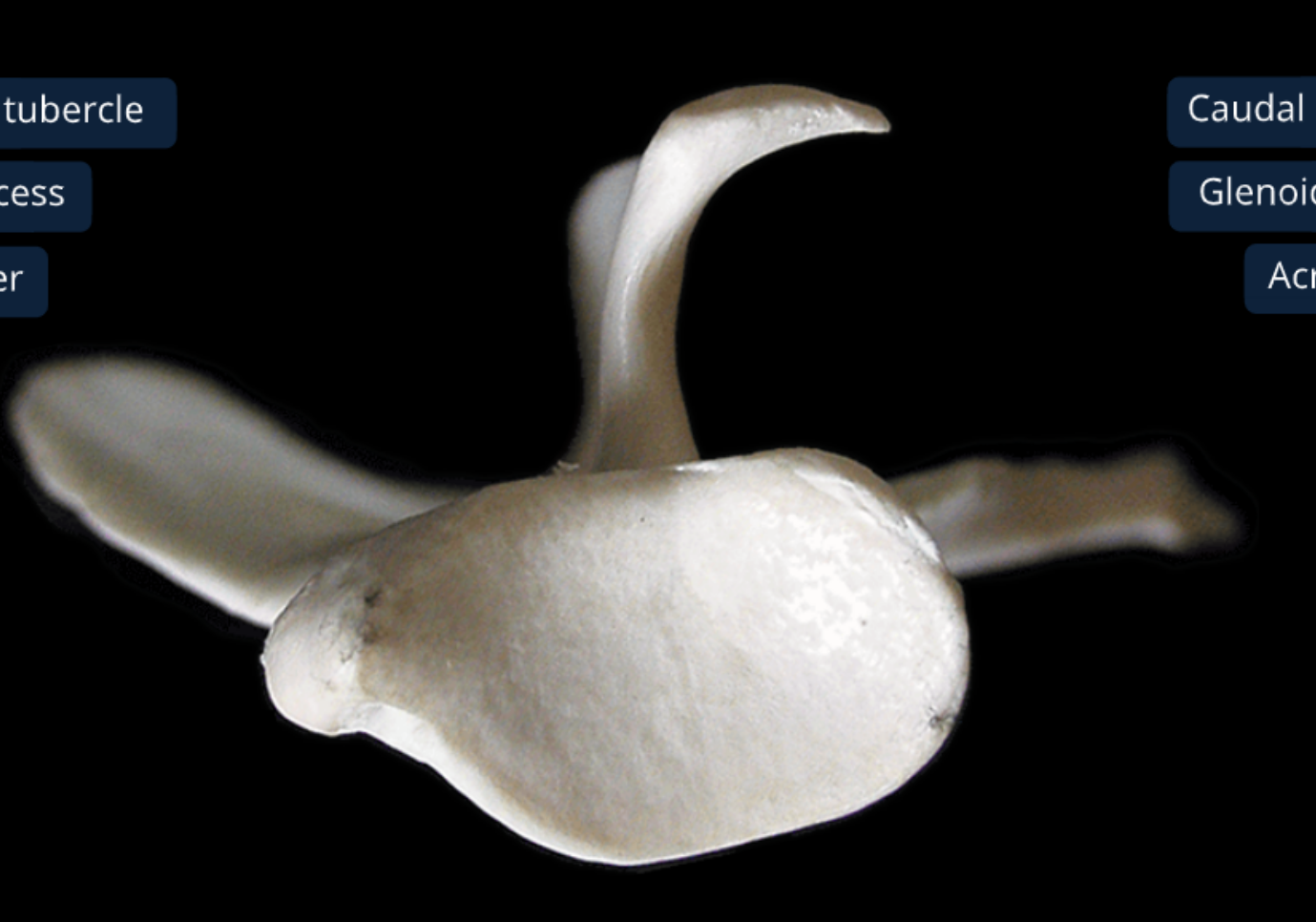
label the lateral side of the scapula (dorsal edge on top, ventral on bottom, cranial edge on left, caudal on right)
supraspinous fossa: supraspinatus m originates here
infraspinous fossa: infraspinatus m originates here
acromion: distal end of spine
spine: divides lateral surf into 2 equally sized fossa
supraglenoid tubercle: cranial prominence at ventral angle
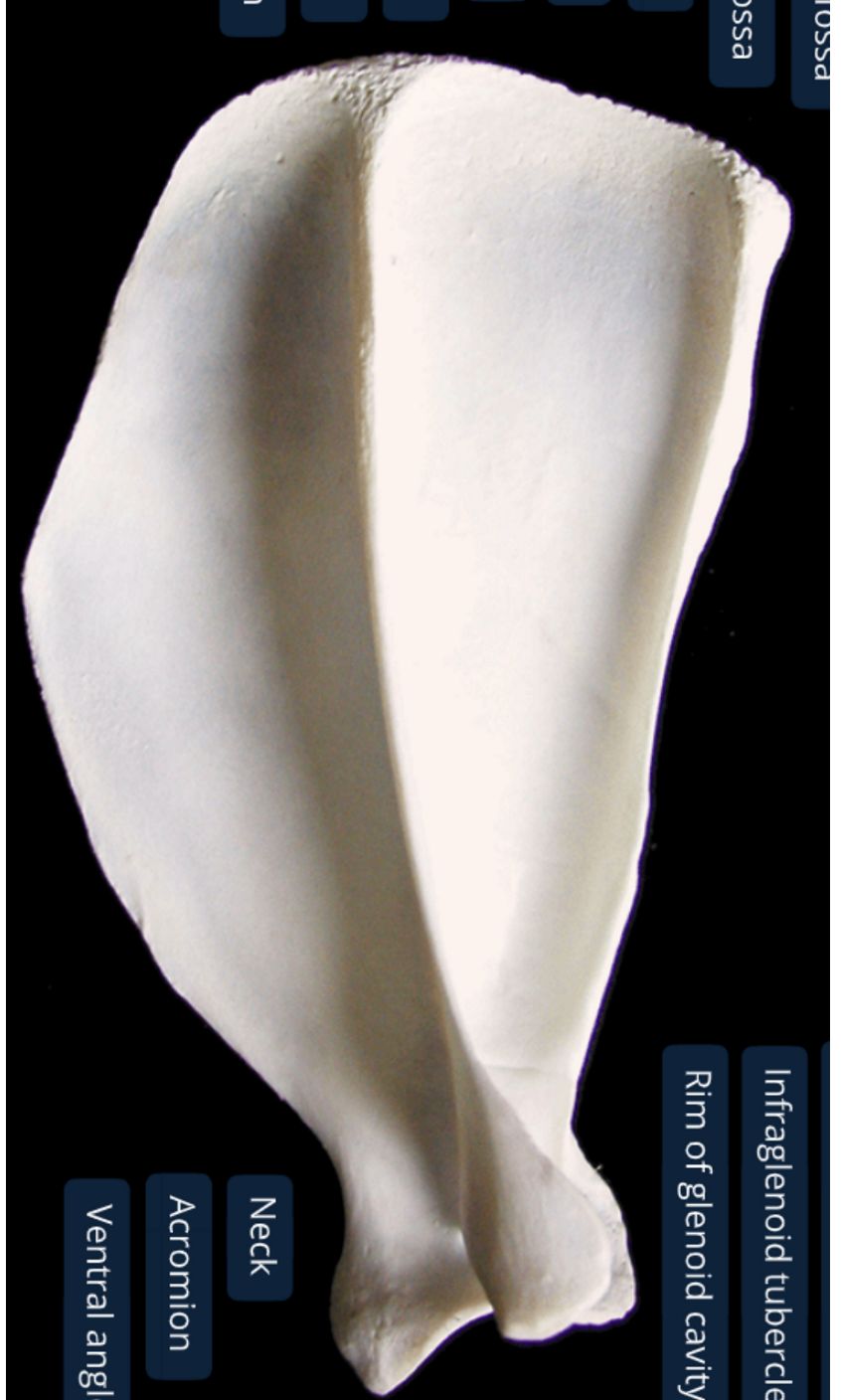

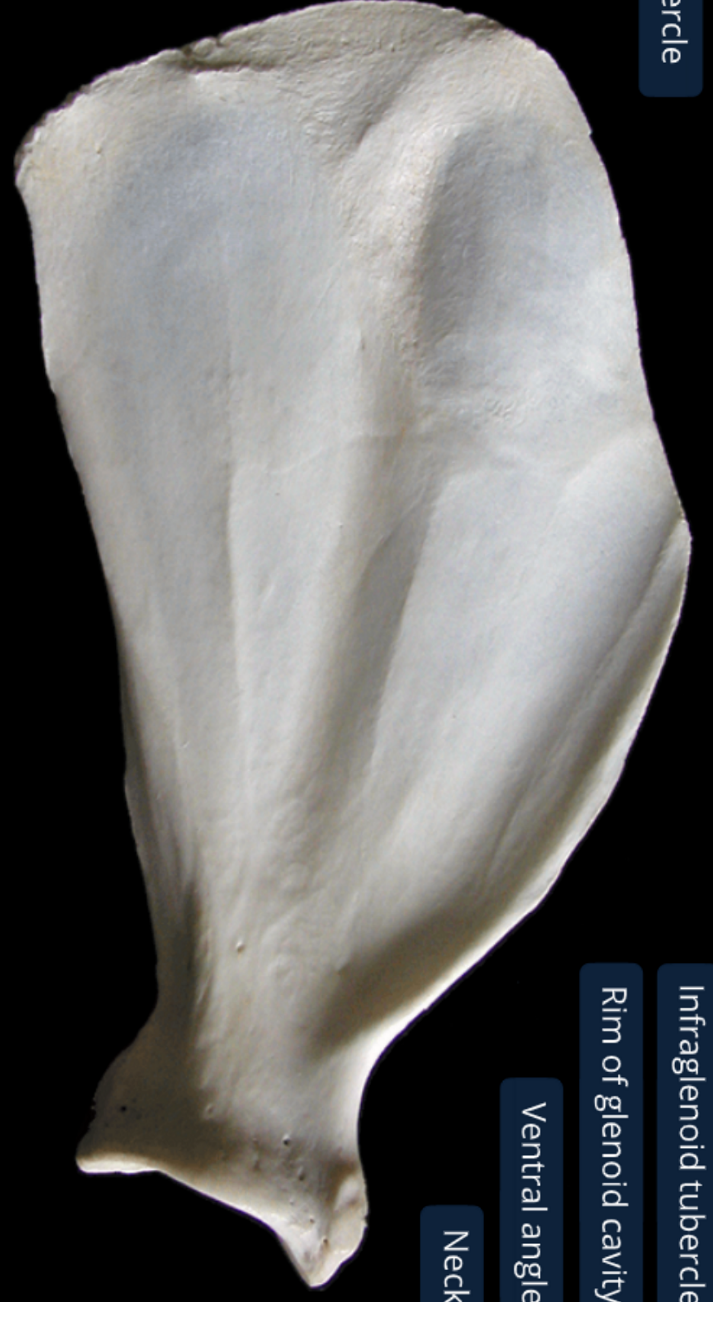
label the medial side of the scapula (dorsal edge on top, ventral on bottom, cranial edge on right, caudal on left)
subscapular fossa: almost flat, has 2 rounded ridges, concave between the ridges
serrated face
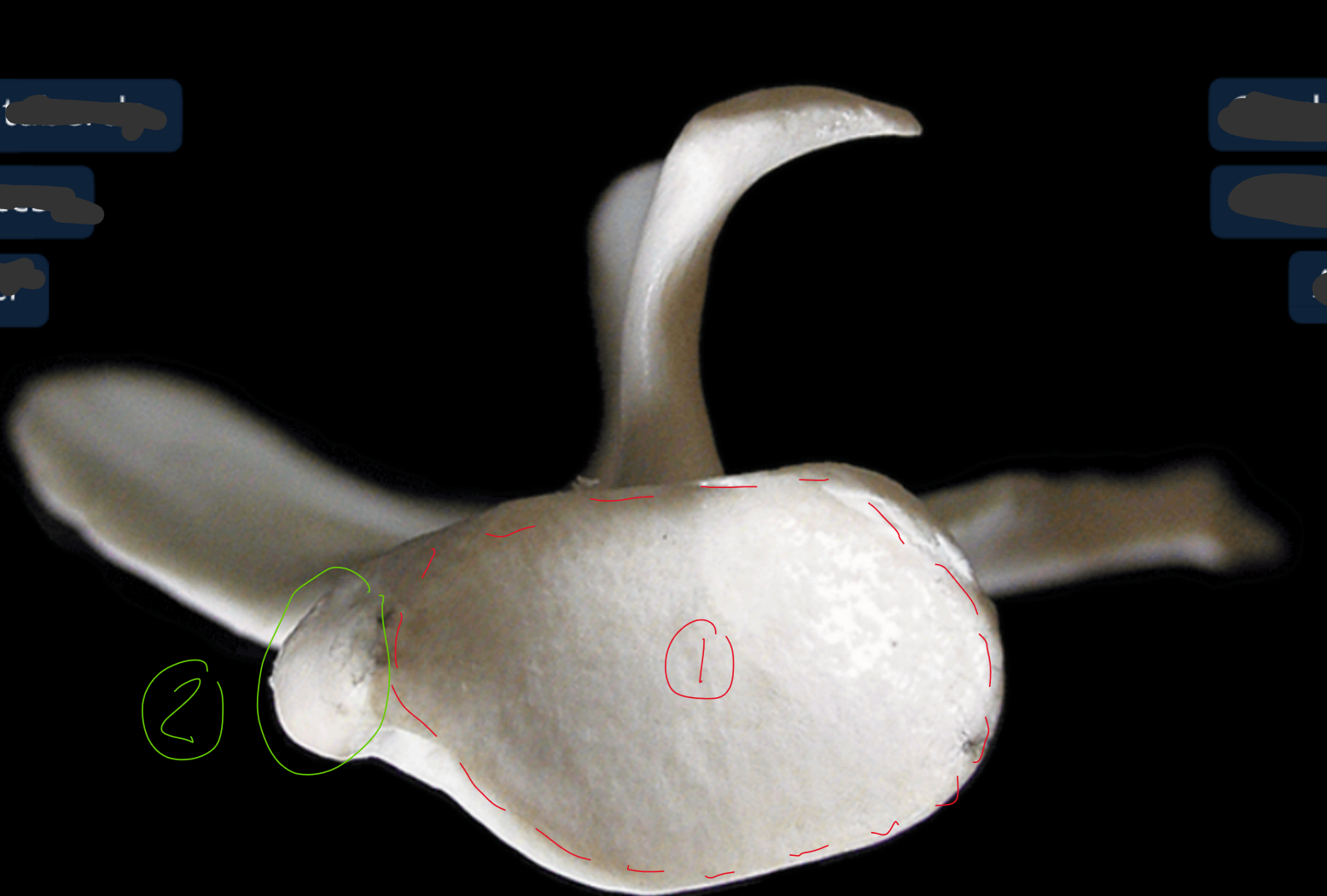


label the ventral end of the scapula (this is looking from bottom to top)
glenoid cavity: shallow joint surf where head of humerus sits
supragleniod tubercle: toward cranial side of scapula

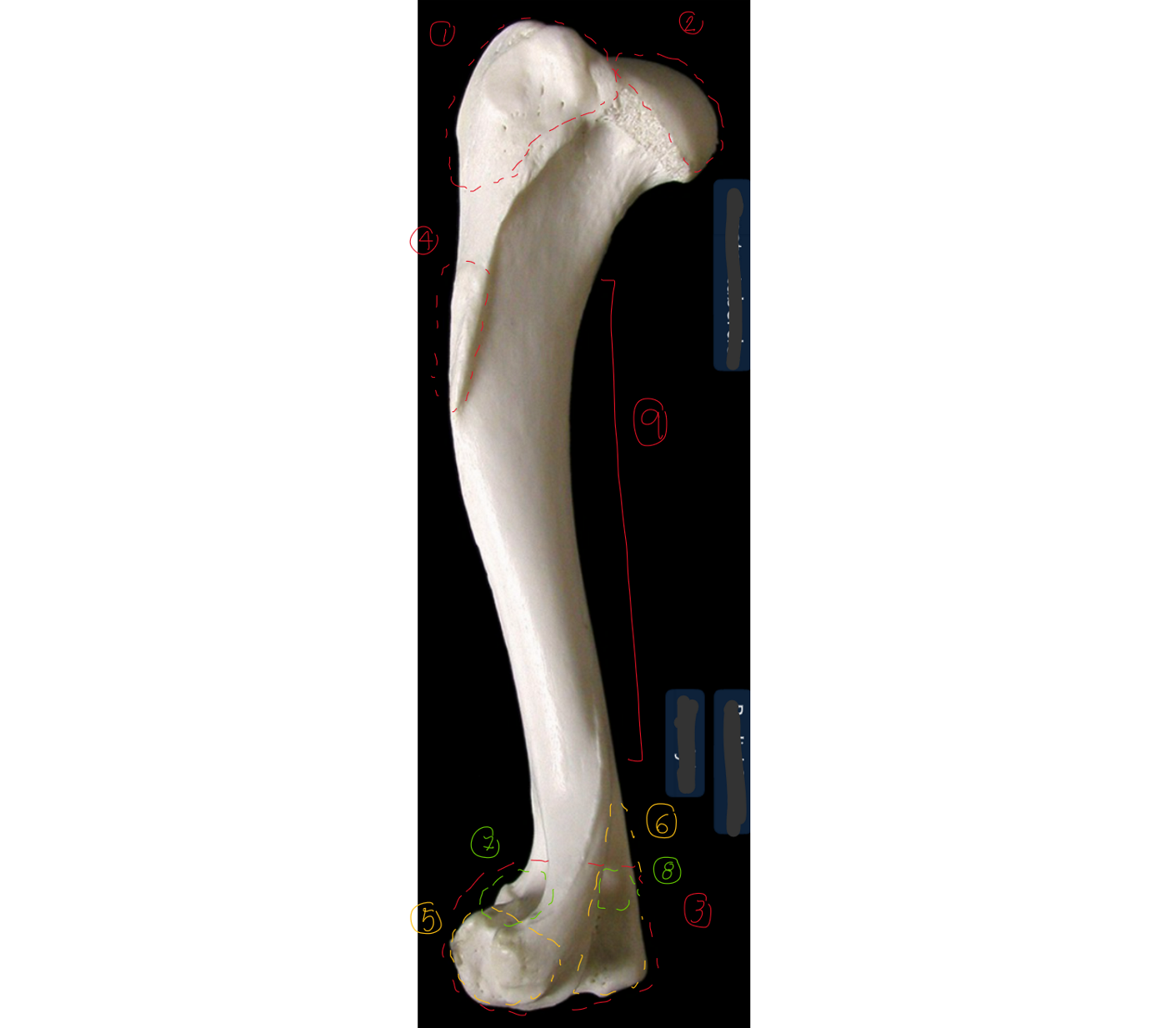
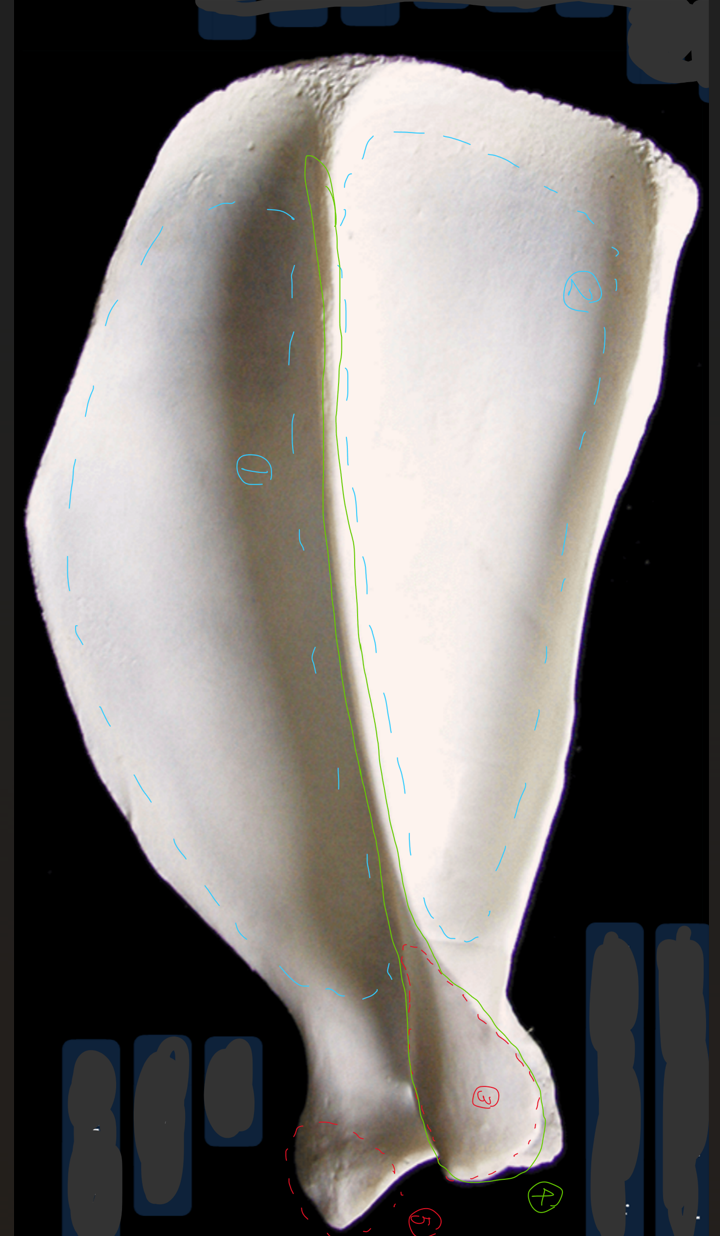
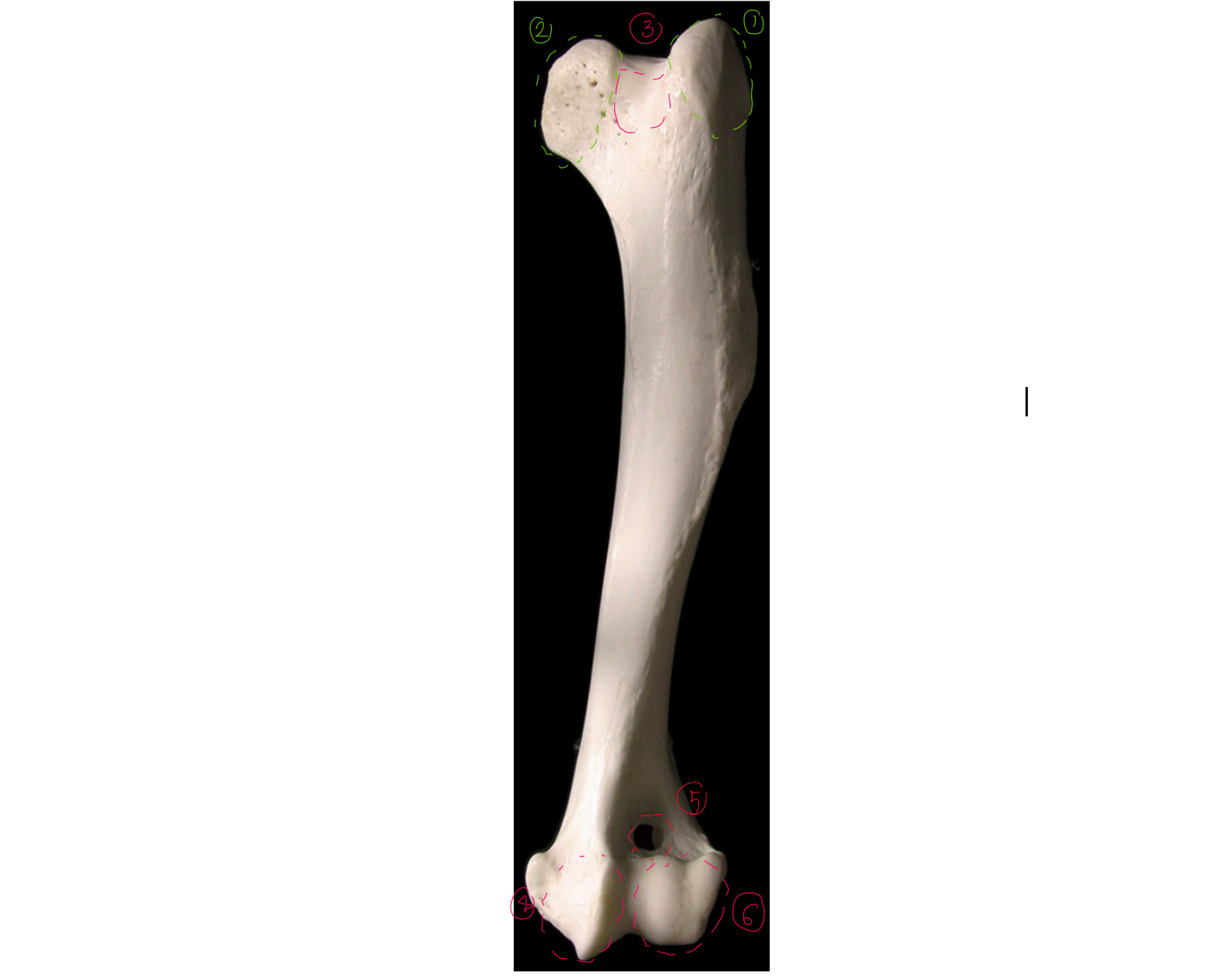
label the lateral side of the left humerus (dorsal/proximal end on top, cranial to the left)
6 → SPELLING
greater tubercle
head: convex articular surf of shoulder joint
condyle: distal end of humerus
deltoid tuberosity: rough part
lateral epicondyle: lateral part of 3, less prominent than 6, elbow ligament attaches here
medial epicondyle: medial part of 3, same ligament ^
radial fossa: depression where head of radius is & elbow is flexed
olecranon fossa: depression where ulne is when elbow extends
body
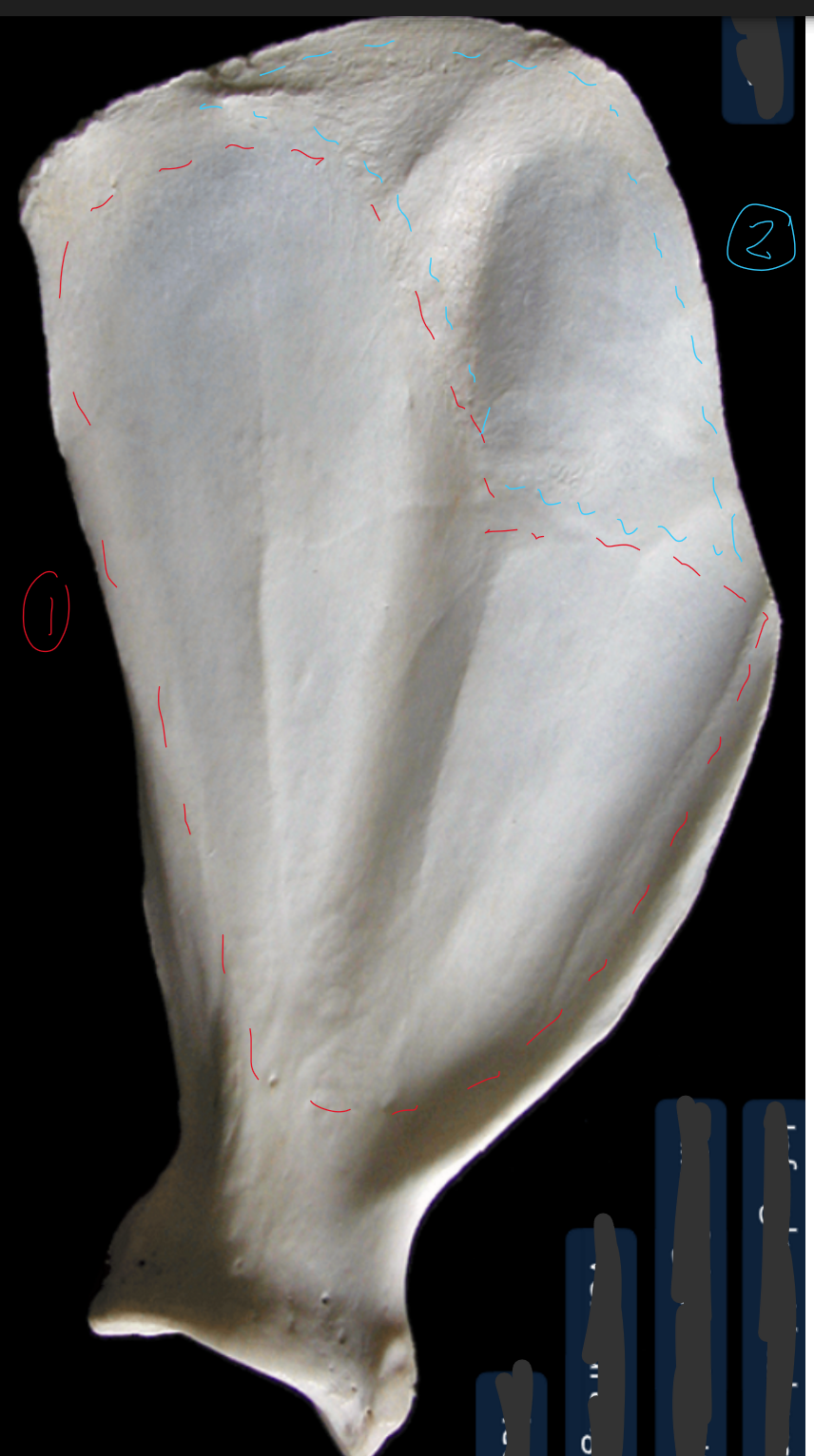
label the cranial view of the left humerus (this is like looking from right in front of the dogs face)
3 → SPELLING
greater tubercle
lesser tubercle: medial to head of humerus (head in between 1 & 2)
intertubercular groove: smooth surf between 1 & 2
trochlea of condyle: medial part of condyle, cylinder shaped articular surf of condyle, has a groove, part of elbow joint
supratochlear foramen: connection between radial fossa & olecranon fossa
capitulum of condyle: lateral part of condyle
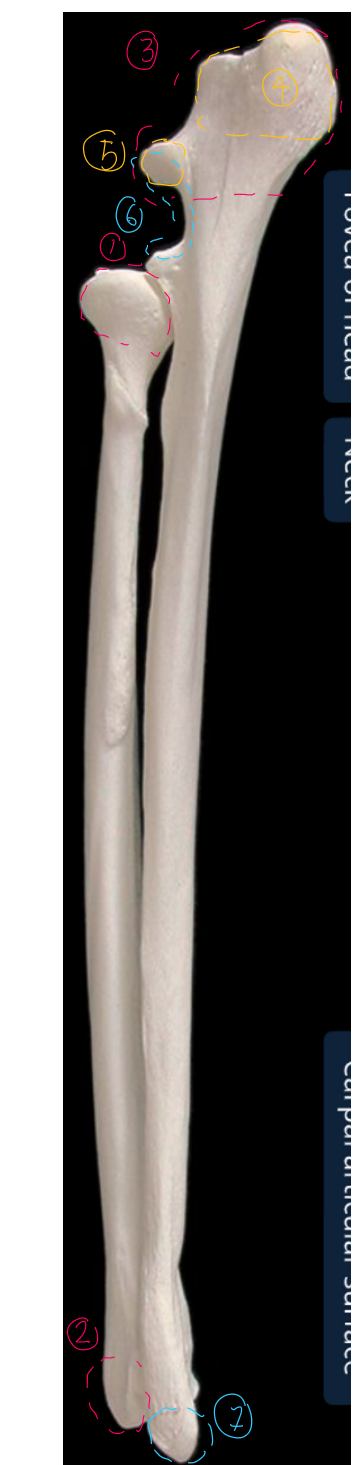
label the lateral side of the ulna & radius (dorsal/proximal end on top, cranial/head to the left)
head of the radius: proximal end of radius
trochlea of radius: distal end of radius
olecranon of the ulna: biggest part of ulna, medial surf is more concave than lateral
olecranon tuberosity of ulna: proximal end is grooved cranially, enlarged & rounded caudally
anconeal process of ulna: distal part of olecranon
trochlear notch of ulna: semilunar shaped articular surf
styloid process
ulna is longer & to right of radius
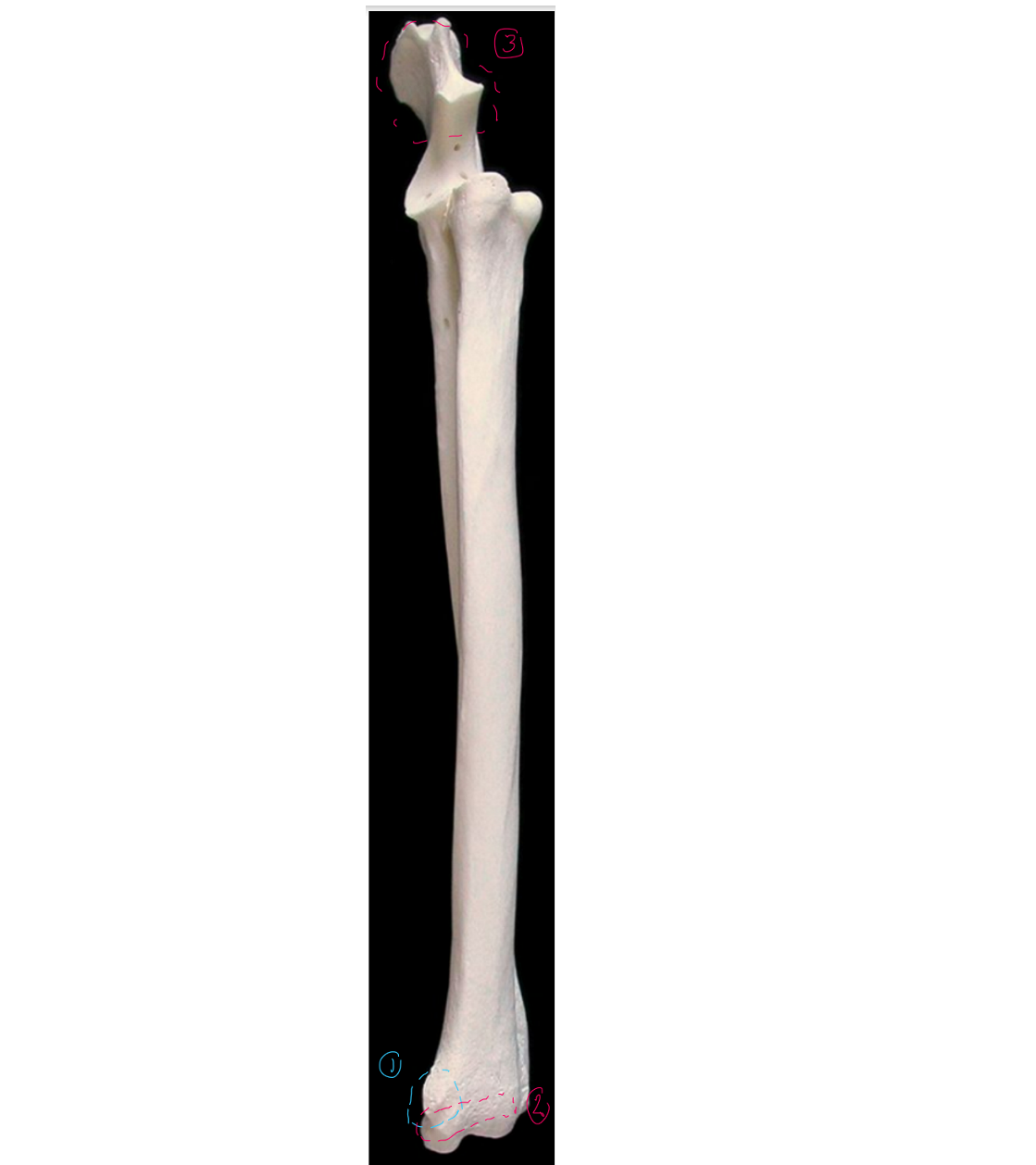
label the medial side of the ulna & radius (dorsal/proximal end on top, cranial/head to the left)
styloid process of the trochlea in the radius
trochlea of the radius: distal end of radius
olecranon of the ulna: biggest part of ulna, medial surf is more concave than lateral
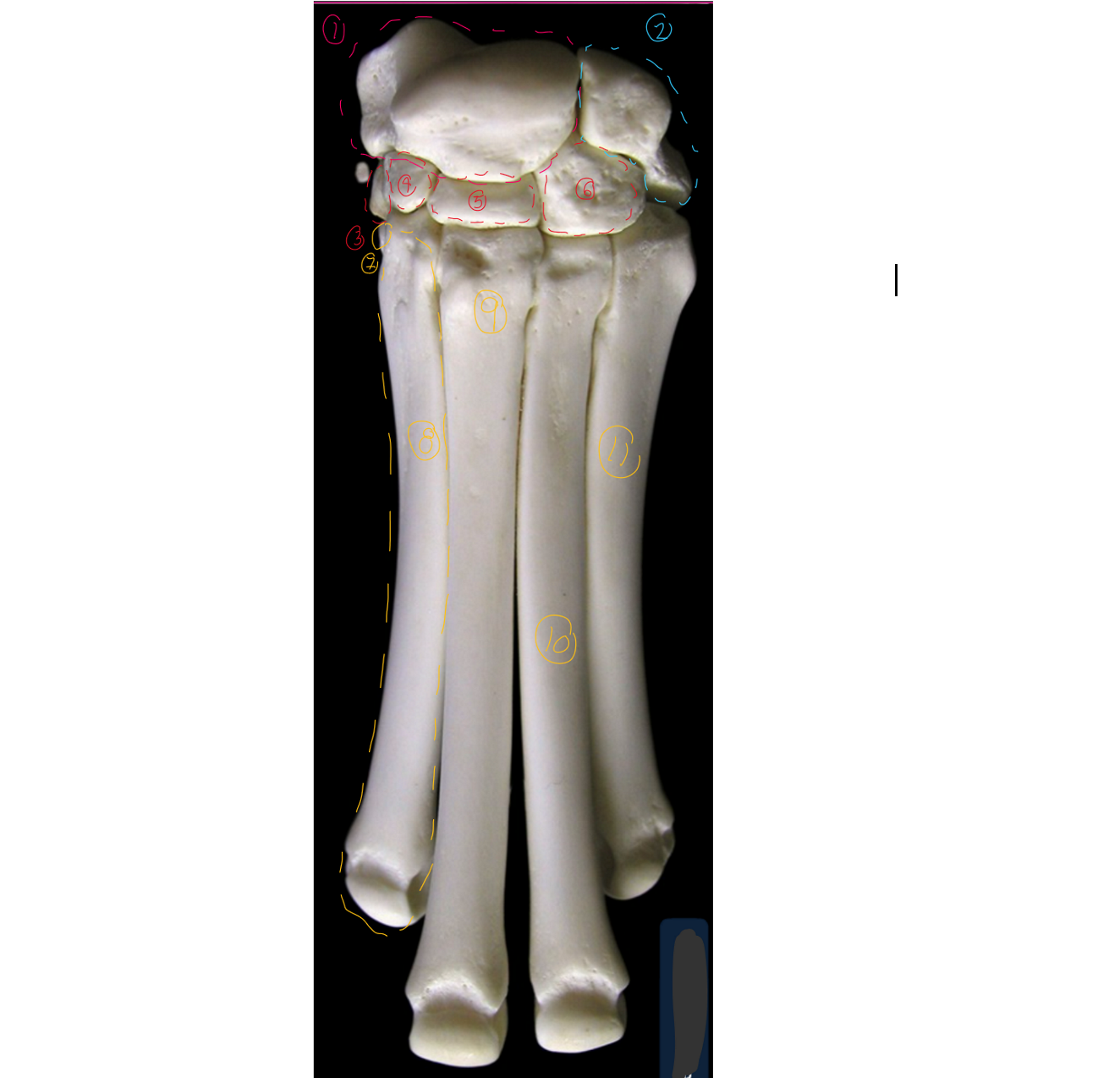
label the cranial view of the carpus/metacarpus (this is like looking right in front of the dog, medial to left, lateral to right)
7-11 → SPELLING
radial/intermedioradial carpal bone
ulnar carpal bone
first carpal: most medial carpal
second carpal
third carpal
fourth crapal: most lateral carpal
first metacarpal bone
second matacarpal
third metacarpal
fourth metacarpal
ffth metacarpal
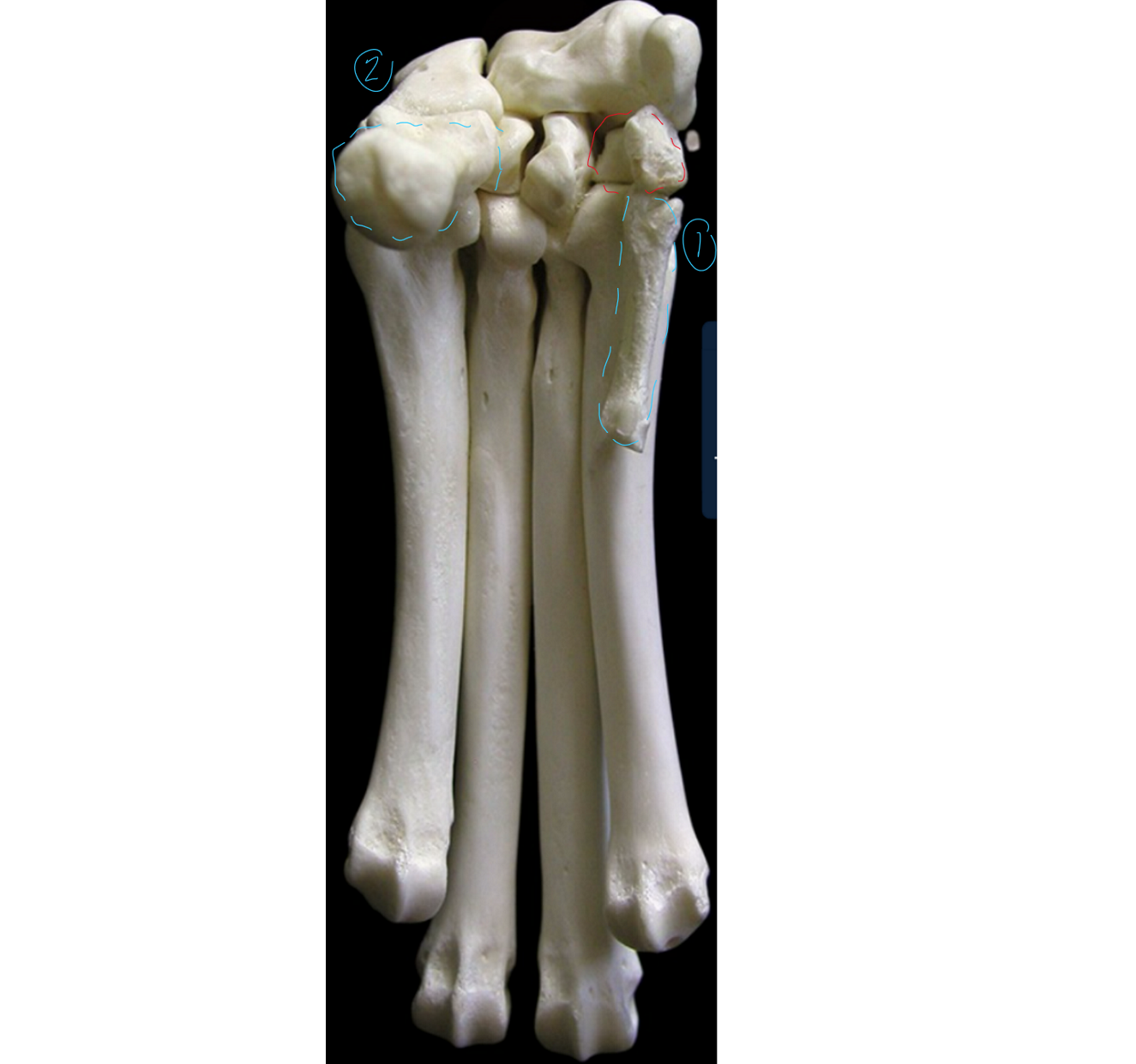
label the palmar/bottom view of the carpus/metacarpus (this is like looking right under the dogs foot, medial to right, lateral to left → first carpal bone in red)
1 → SPELLING
first metacarpal bone
accessory carpal bone
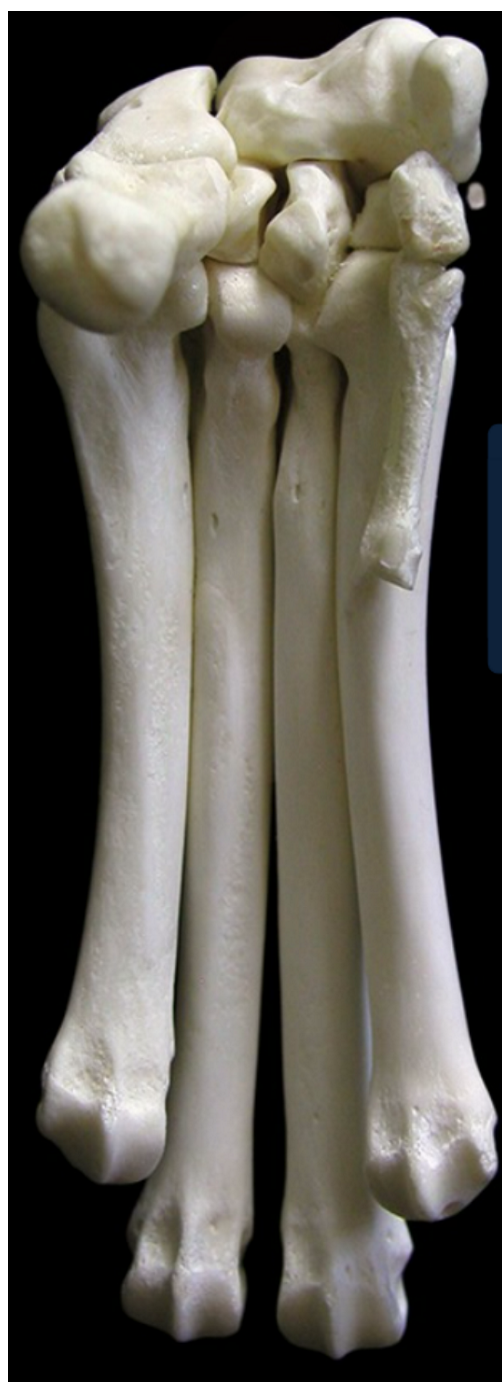

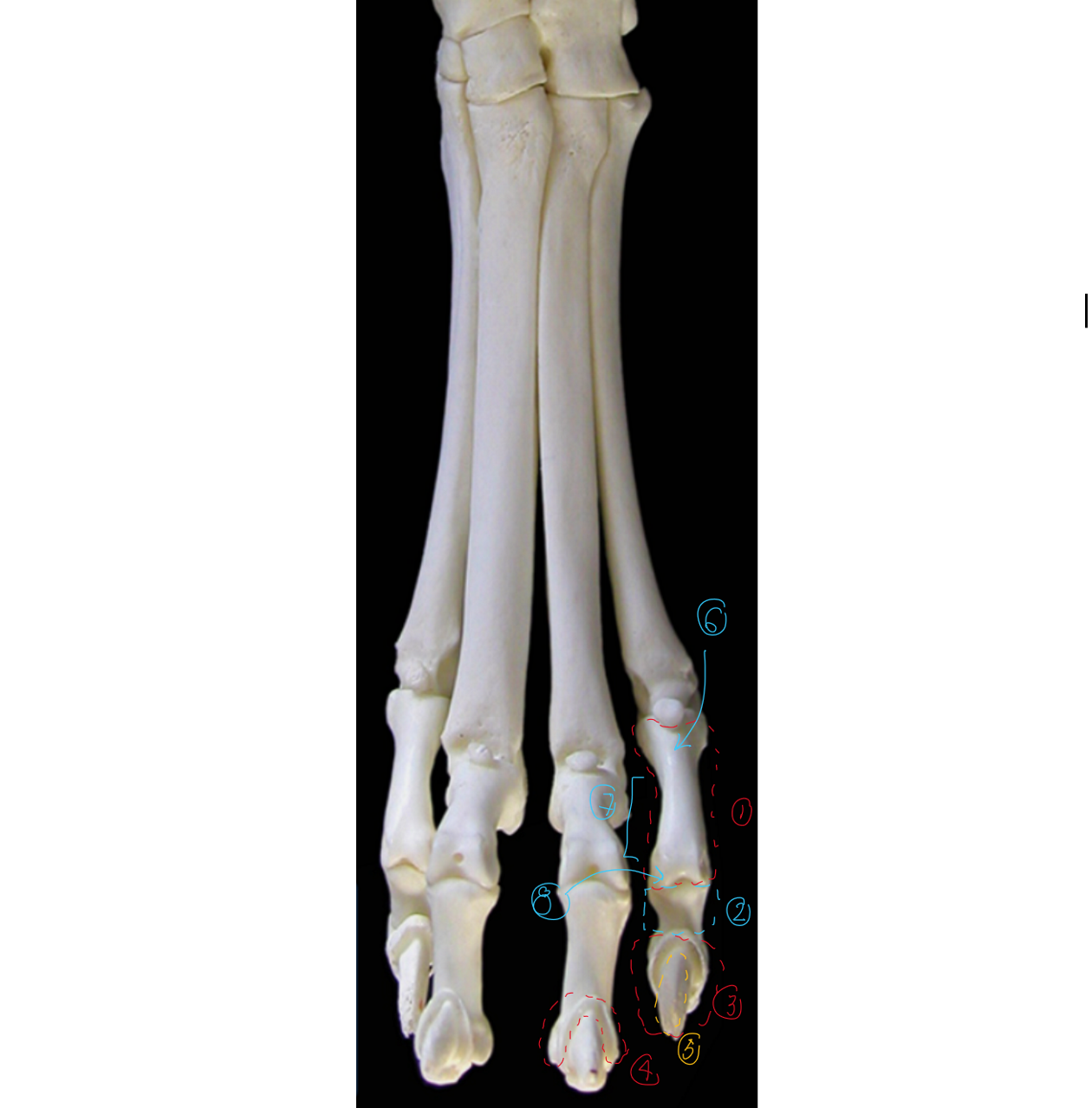
label the cranial view of the phalanges/digits (this is like looking right in front of the dog, medial to left, lateral to right)
proximal phalanx (digit 1 only has proximal & distal)
middle phalanx
distal phalanx
ungual crest: overhangs 5
ungual process
base of phalanges
body of phalanges
head of phalanges
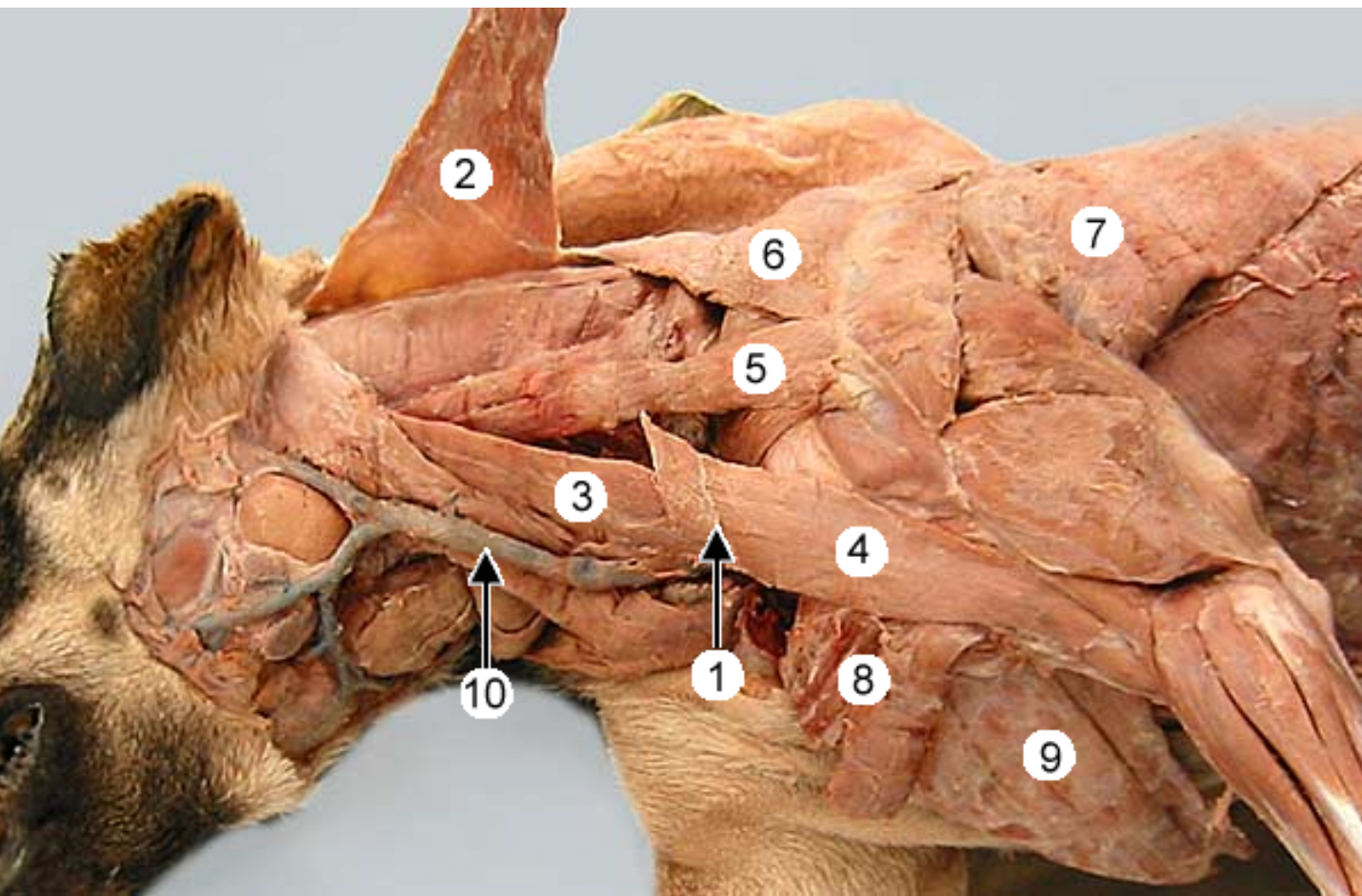
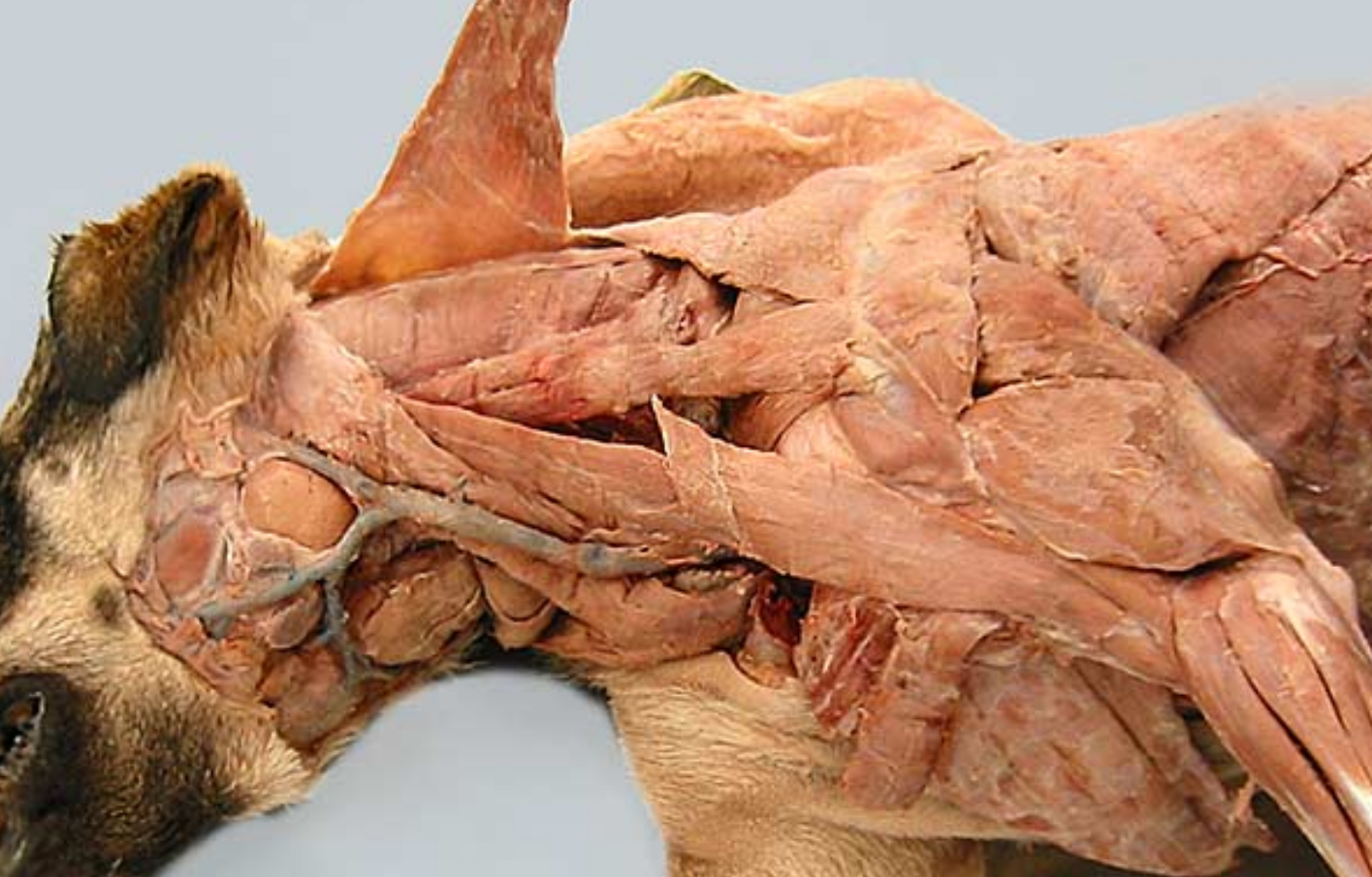
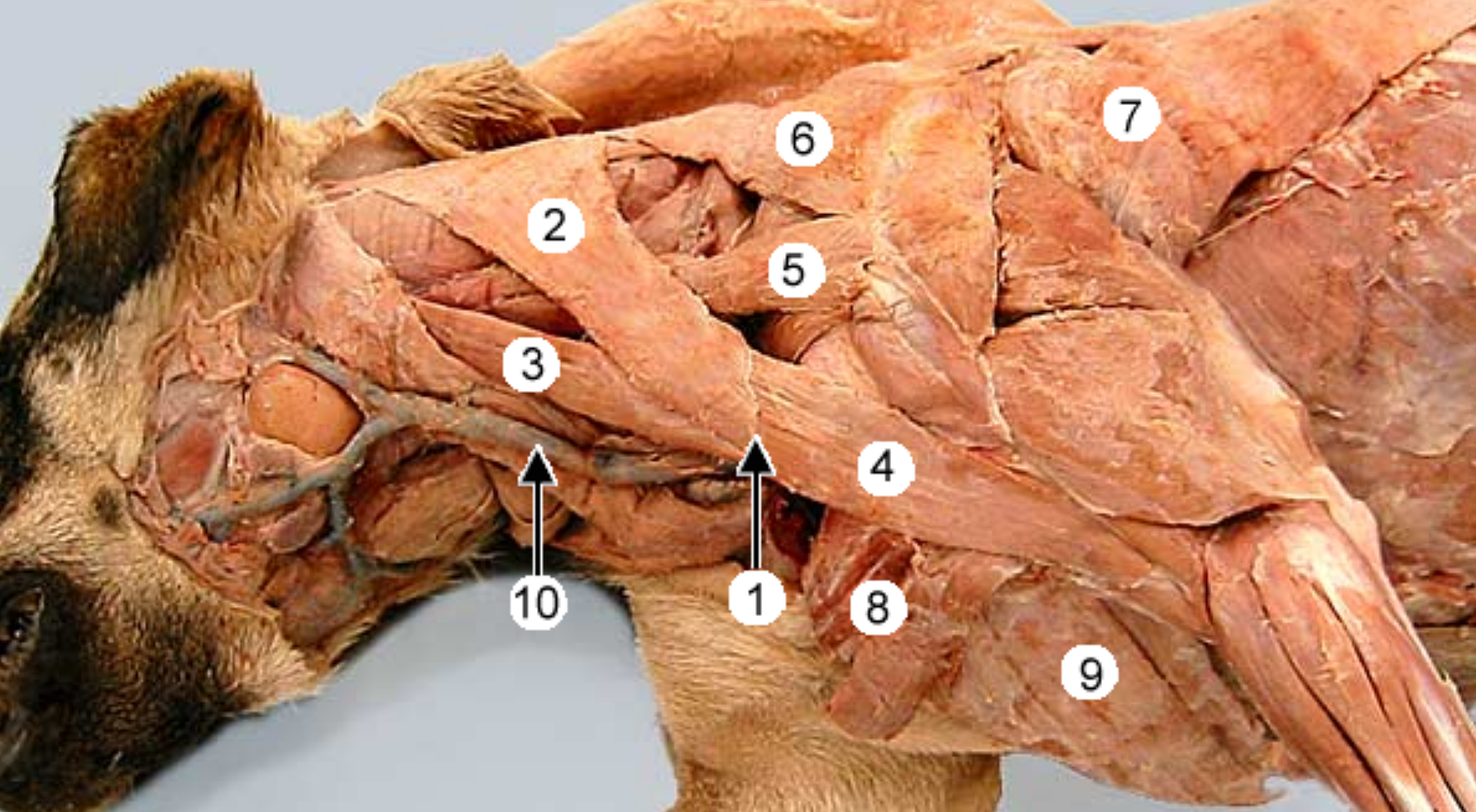
label muscles 2-9 of the dog. (muscle 2 was cut and lifted up, usually connects to 1)
name the compound muscle that makes up:
2,3
2,3,4
-
cleidocervicalis m (cervical part of cleidocephalicus)
cleidomastoideus m (mastoid part of cleidocephalicus)
cleidobrachialis m
omotransversarius m
trapezius m
latissimus dorsi m
superficial pectoral m
deep pectoral m
2+3 = cleidocephalicus
4+2+3 = brachiocephalicus