PRACTICAL RESEARCH
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
explains phenomena by gathering numerical data and analyzing it using mathematical methods
VARIABLES
is a factor that a researcher measures, controls, and manipulates
NUMERIC VARIABLES
These variables describe a measurable numerical quantity and answer "how many" or "how much".
CONTINOUS VARIABLES
Can have any value between a set of real numbers
DISCRETE VARIABLES
Have any whole value within a given limit
CATEGORICAL VARIABLES
These describe the quality of a data unit and answer "what type" or "which category".
ORDINAL VARIABLES
Variables that can be ranked
NOMINAL VARIABLES
Variables that cannot be ranked
DISCHOTOMOUS VARIABLES
Variables that has 2 categories
POLYCHOTOMOUS
Variables that has multiple categories
EXPERIMENTAL VARIABLES
Variables that can be manipulated by the researchers
INDEPENDENT VARIABLES
Variables that are manipulated to affect the outcome
DEPENDENT VARIABLES
Those affected by the changes made in the independent variables
INTERVENING VARIABLES
Variables that are there already and may effect the dependent variables
NON-EXPERIMENTAL VARIABLES
Observed in the natural setting without manipulation
PREDICTOR VARIABLES
Changes other variables
Criterion Variables
Affected by the changes in predictor
UNIVARIATE STUDY
Studies only 1 variable
BIVARIATE STUDY
Studies 2 variables
POLYVARIATE STUDY
Studies 2 or more variables
EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
Concerned with cause-and-effect relationships where the independent variable is manipulated
TRUE EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
Has full manipulation of the variables like setting and participants
QUASI-EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
Has no control over the subjects and they are randomly chosen
PRE-EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
Has little control
NON-EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
Involves survey studies and self reports
DESCRIPTIVE
Gather information to define a population a situation or phenomenon through observation
CORRELATIONAL
Explores and measures the relationship between 2 things
EX POST FACTO
investigates cause and effect relationships
research title
The first thing a reader sees; it names the research and gives a glimpse of its content. It should summarize the main idea, include major variables, the researcher's main task, and mention participants and setting. It should be 10 to 15 words and avoid jargon
RESEARCH PROBLEMS
Found in areas with discomfort, a gap between theory and practice, daily experiences, procedures needing better equipment, a trend, untested solutions, or unexplained phenomena.
EXTERNAL CRITERIA
outside factors affecting the research such as numbers of studies and researches available
INTERNAL CRITERIA
Inside factors affecting the research such as motivation and hard work, personally someone’s inner qualities
STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
Contains a clear problem statement and questions to be answered, with two parts: the general problem and the investigative problems
GENERAL PROBLEM
A long-term objective derived from the research problem and title.
INVESTIGATIVE PROBLEMS
Specific questions in interrogative form that, when answered, solve the research problem.
NON-RESEARCHABLE QUESTIONS
Questions that can be answered with yes or no.
RESEARCHABLE QUESTIONS
Questions that requires significant gathering of data and answers wh questions.
FACTOR-ISOLATING
Isolating and categorizing factors
FACTOR-RELATING
Determining relationship factors
SITUATION-RELATING
hypothesis testing.
SITUATION-PRODUCING
Establishes goals and develops plans.
Background of the study
Explains why the study is being done or why did they pick that topic
TOPIC
Starts broad and uses a "narrative hook" (like statistical data, a clear need for research, or the study's purpose) to grab the reader's interest.
RESEARCH PROBLEM
Narrows the broad topic down to a specific issue the researcher wants to investigate
EVIDENCE
Uses reasons from other literature or personal experience to validate the problem's existence
DEFICIENCIES
Highlights weaknesses in related literature to show why the research is needed to fill a gap.
AUDIENCE
Reiterates the study's purpose and how it will benefit different readers.
EDUCATION
Research can be used to assess the effectiveness of the methods, programs, and the satisfaction of all stakeholders in the educational sector
BUSINESS
Research can improve the overall marketing strategy, help make informed decisions, and solicit consumers’ opinions for productivity
MEDICAL AND ALLIED HEALTH SERVICES
Healthcare procedures, routines, and other systems must be based on the result of scientific investigation
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Collected information leads to a more responsible and accountable operation of different components of technology
Pretest-posttest controlled group design
Subjects are randomly assigned to groups
A pretest is given to both groups
The experimental group receives the treatment while the control group does not
A posttest is given to both groups
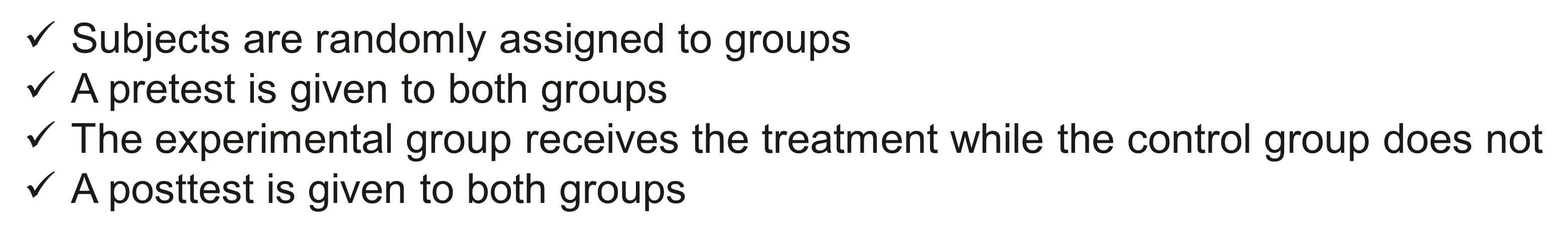
Posttest-only controlled group design
Subjects are randomly assigned to groups
The experimental group receives the treatment while the control group does not
A posttest is given to both groups
QUASI-EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
A design in which either there is no control group or the subjects are not randomly assigned to groups
NON-EQUIVALENT CONTROLLED GROUP DESIGN
Subjects are not randomly assigned
A pretest is given to both groups
The experimental group receives the treatment while the control group does not
A posttest is given to both groups
TIME SERIES DESIGN
Subjects are not assigned to any control group
The subjects are observe periodically (pretest and posttest)
PRE-EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
A design that is very weak because the researcher has little control over the research
ONE-SHOT CASE STUDY
A single group is exposed to an experimental treatment and observed after the treatment
ONE-GROUP PRETEST-POSTTEST DESIGN
It provides a comparative description of a group of subjects before and after the experimental treatment
NOVELTY
the topic must not have been used by many researchers