MI 237 Final
1/300
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
301 Terms
Enterprise Imaging
Allows healthcare members to log on to one account and have access to any image, not just radiology; merged into the EMR
Health Level Seven Standard (HL7)
Manages non-imaging data and provides protocols for exchange, management and integration of clinical and administrative electronic health data
What are advantages of data health monitoring?
Shift from reactive to proactive monitoring reducing the number of issues
Improve the performance of your database and application
Analyze logs and use this knowledge to improve performance
What are cybersecurity issues?
Computer virus
Ransomware
Theft and publication of patient data
What law/right does theft and publication of patient data violate?
HIPAA
Wide Area Network (WAN)
Extends to other businesses or locations that may be at great distances; allows different LANs to communicate
What assigns the accession number to the patient?
Radiology Information System (RIS)
What assigns the MRN to the patient?
Hospital/Health Information System (HIS)
What are benefits of EMR/EHR?
Streamlines clinicians workflow
Support other care-related activities
Strengthen the relationship between patients and clinicians
What are the 3 types of network protocols?
Communication
Management
Security
Every computer within a network has a unique _______________ (ex. 172.811.3.1)
IP address
Network Interface Card (NIC)
Hardware component used to connect a computer with another computer onto a network
PACS (MIMPS)
Makes radiographs, CT scans, MRI scans, US and Nuc Med images for a particular patient available within the network
What are the components of PACS (MIMPS)?
Image acquisition
Display workstations
Archive servers
What is the first point of entry into PACS (MIMPS)?
Image Acquisition
Navigation Functions
Customizable worklists dependent on technologists’ selections during a procedure (ex. verbal reports, image check)
Study Navigation
Allows images to be viewed individually or in a cine run
Magnify
Image manipulation & enhancement used to make things bigger
Archive Servers
Fastest growing component of PACS (MIMPS)
What does archive servers consist of?
Image manager
Image storage
Image Manager
Contains master database of everything in the archive; controls the receipt, retrieval and distribution of the images it stores
What does VNA stand for?
Vendor Neutral Archives
What is the main function of PACS (MIMPS)?
Act as a database
What dept. works with DICOM?
Dept. of Defense
DICOM
Different modalities can now share data with one another or a central server
What is included in the DICOM header?
Date/time of procedure
# of images taken
Body part & position
Technique used
Image format & receptor size
Parameters used to digitally process the image
All information in the DICOM header is stored as ____________.
Metadata
What is the benefit of the DICOM access work order (worklist)?
Reduces human error
Reduces time
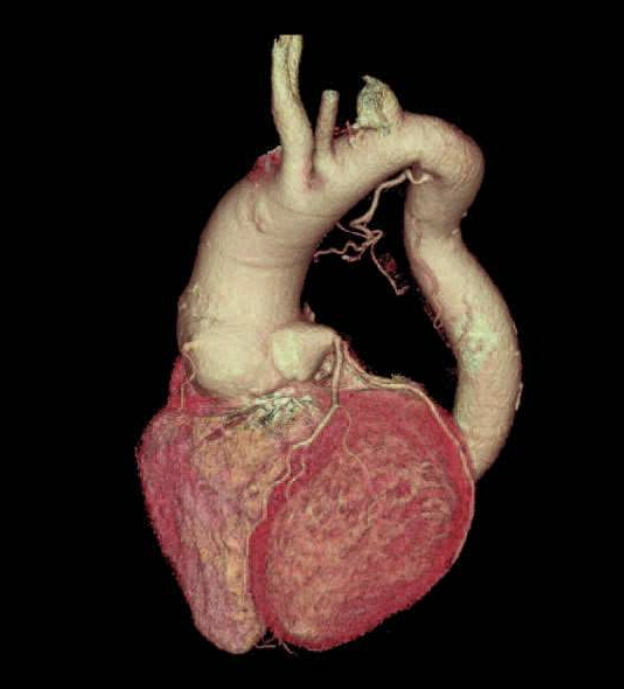
Volume Rendering Technique (VRT)
Shaded Surface Display (SSD)
Creates a 3D, moveable image based on the pixel intensity of choice
What modality uses CAD?
Mammography
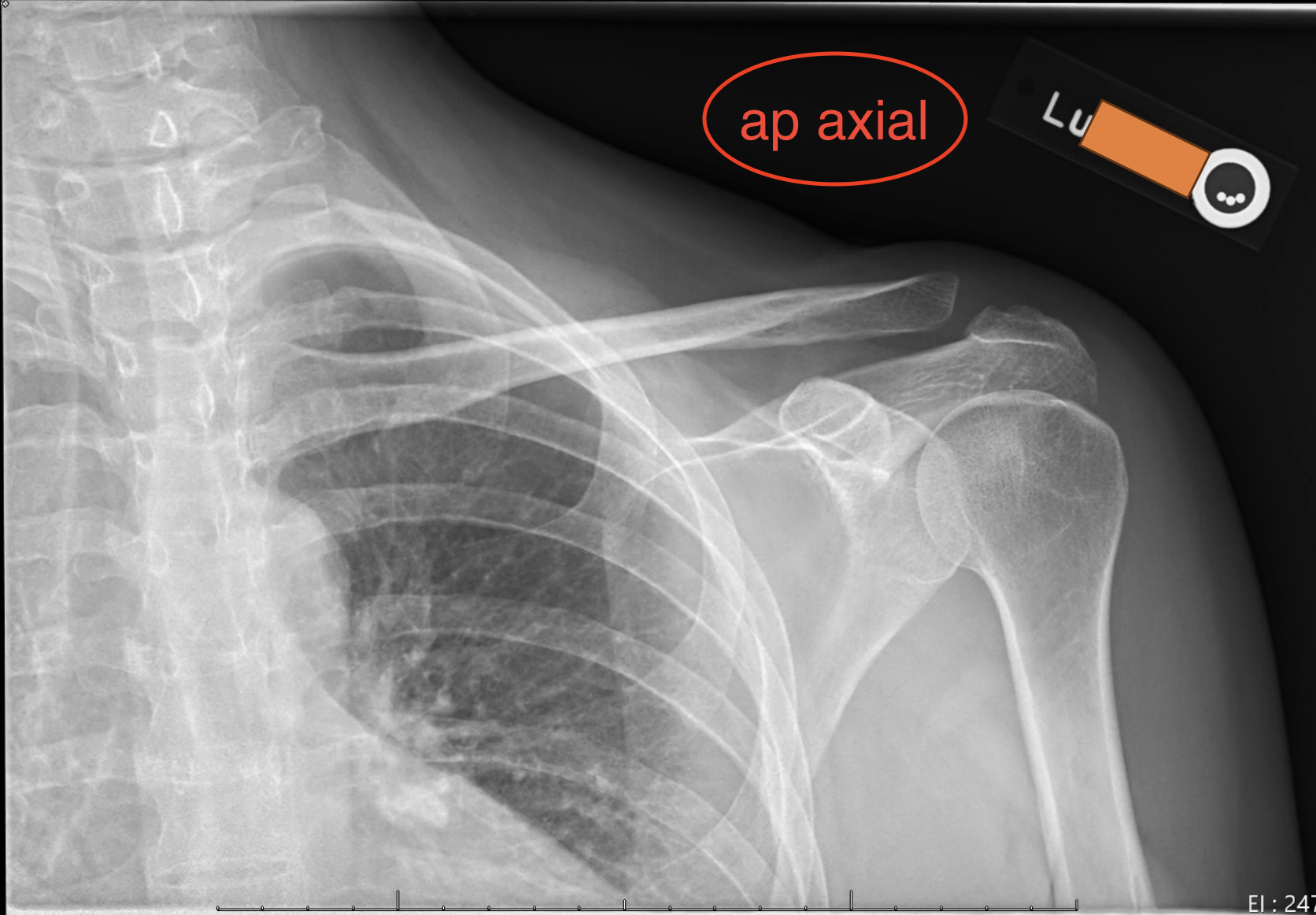
What is the circled part?
Image markup
Network Attached Storage (NAS)
Users on a local area network (LAN) access the shared storage via an ethernet cord
Storage Area Network (SAN)
A dedicated, independent high-speed network that interconnects and delivers shared pools of storage devices to multiple servers
Direct Attached Storage (DAS)
Dedicated server or storage device that is not connected to a network (ex. laptop, phone)
Which RAID level is the most common used for a PACS (MIMPS) archive?
5
Striping
RAID distributes data across multiple disks to increase storage capacity and improve speeds
What makes up Service Object Pair (SOP)?
Service Class User (SCU)
Service Class Provicer (SCP)
What digital image compression is a smaller file and can result in a loss of detail?
Lossy
What function of hard copy images has the most storage?
Blu-ray
What is the weakest link of image display?
Monitors
Aspect Ratio
Used to describe the shape of the monitor
Pixel (dot) Pitch
The distance between the centers of any two adjacent hardware pixels
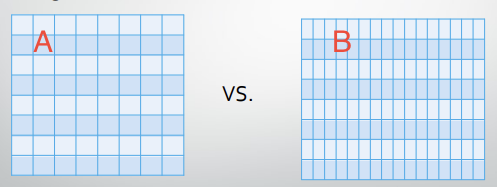
Which has better spatial resolution?
B
Photometer
Used to measure the brightness output of an LCD
Contrast Resolution
Ability of the display to distinguish between multiple densities in a radiographic image

Which has better contrast resolution?
B
Monochrome Monitors
Has only one phosphor of color
What phosphors make up a color monitor?
Red
Green
Blue
If all 3 phosphors in a color monitor were set at 255, what color would be seen on the monitor?
255
In an LCD monitor, a single pixel consists of how many individual bar-like segments?
18
Hardware Pixel
Intersections of flat, transparent wires crossing over each other to form an overall square shape
On a display monitor, a pixel that appears dark against a light background is ________.
Stuck
What monitors do we use in the radiology department?
LCD
What are benefits of a LCD monitor?
Lightweight
No glare/reflection of the screen; ambient light is minimal
A ray of light is electromagnetic radiation that consists of a double wave; these waveforms are ___________ to one another.
Perpendicular
LCD monitors consist of 2 thin sheets of glass each with a light polarizing layer that are __________ to one another.
Perpendicular
Nematic Liquid Crystals
A crystalline arrangment of molecules that are inserted between polarizing glass sheets/lenses in an LCD monitor
If there is an electrical charge being applied to the electrodes of an LCD monitor, it is considered to be in an ______ state.
Off
What is the most common type of backlighting.
LED
LCD or LED are in what matrix?
Active
Each hardware pixel possess its own _______.
TFT
What types of cleaners should not be used on monitors?
Acetone (ethyl alcohol)
Grayscale Standard Display Function (GSDF)
Allow medical images to be transferred according to the DICOM standard to be displayed on any DICOM-compatible display device with a consistent gray scale appearance
Luminance Ratio
Compares maximum luminance to the minimum luminance

Luminance Uniformity
Digital imaging spatial resolution is determined primarily by:
Matrix size
Pixel size

What does this test for?
Resolution
What is the best viewing angle of a monitor?
At the screen directly
Decrease ambient light

Specular Reflection
What post-processing can help to eliminate veil glare?
Apply a black surround mask
Who discovered the fluoroscope?
Thomas Edison
What is the typical fluoro mA range?
0.5-5
What is the material of the input phosphor in the II?
Cesium iodide (Csl)
What does the photocathode in the II do?
Convert light photons to electrons
What is the charge of the electrostatic focusing lenses in the II?
Negative
What does the electrostatic focusing lenses in the II do?
Accelerate the electrons
Ensure electrons travel an equal distance from the photocathode → anode
What is the charge of the anode in the II?
Positive
What does the ouptut phosphor in the II do?
Convert electrons back into light photons
Magnification
Voltage of the electrostatic lenses is increased causing a smaller diameter of input phosphors to be used and the focal point to shift closer to the input phosphor
Magnification causes a reduction in _______________.
Minification gain
Flux Gain
The increase in brightness from input to output as a result of the acceleration of the electrons traveling across the II
Total brightness gain decreases ______ each year due to aging of the tube.
10%
Conversion factor is equal to approximately _______ of the total brightness gain.
1%
Coupling
Takes light from II to next component in imaging chain
Continuous fluoro produces _____ frames a second.
30
Pulse Width
Exposure length of each pulse
T/F: Input phosphor does not absorb all x-ray photons.
True
Pincushioning Distortion
The borders of fluoro image are inherently magnified
Vignetting Distortion
Reduction of brightness at the edges of a fluoro image
Spot Image
Static image recorded at diagnostic mA levels; from radiation before it reaches the II
Any fluoroscopy system can be made digital with the addition of ________.
An ADC
Dynamic FPDs have what kind of DELs?
Larger DELs (smaller AMA)
What is a benefit of digital fluoroscopy?
The flat surface eliminates vignetting and pincushioning distortion
Road Mapping
A cine run is performed during an injection of contrast
In fluoro, the audible timer goes off every _____ minutes.
5
What is the SSD of fixed fluoro units?
15 in (38 cm)
Last Image Hold
Displays the last image on the monitor allowing fluoro to be stopped
What is the best method of technologist protection during fluoro?
Stand to the side of the table
Use the remote operation
What is the lead curtain & bucky slot cover lead equivalent?
0.25 mm