Glycolysis (reactions, structures, enzymes, etc.)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
DRAW: Glucose
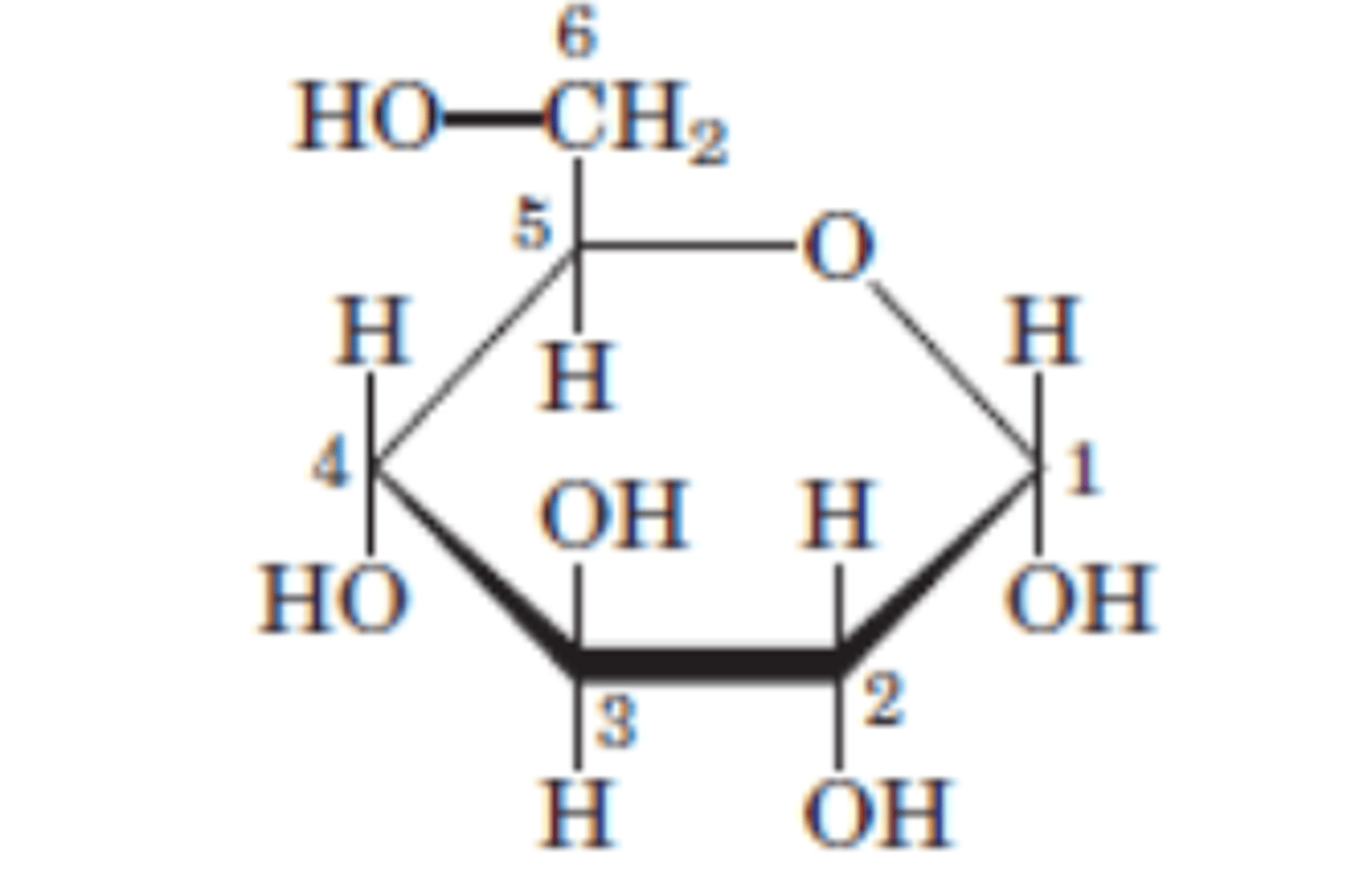
Reaction 1/10
Glucose → Glucose 6-phosphate
(1/2 Energy consuming, NOT reversible)
What is the name of the related enzyme?
What are the names of the cofactors involved in the reaction?
What type of reaction is this?
What happens during this reaction?
Enzyme: Hexokinase
Cofactors: Mg2+, ATP, ADP
Type of reaction: Phosphorylation
Addition of a ℗ onto Glucose from ATP (creating ADP).
DRAW: Glucose 6-phosphate
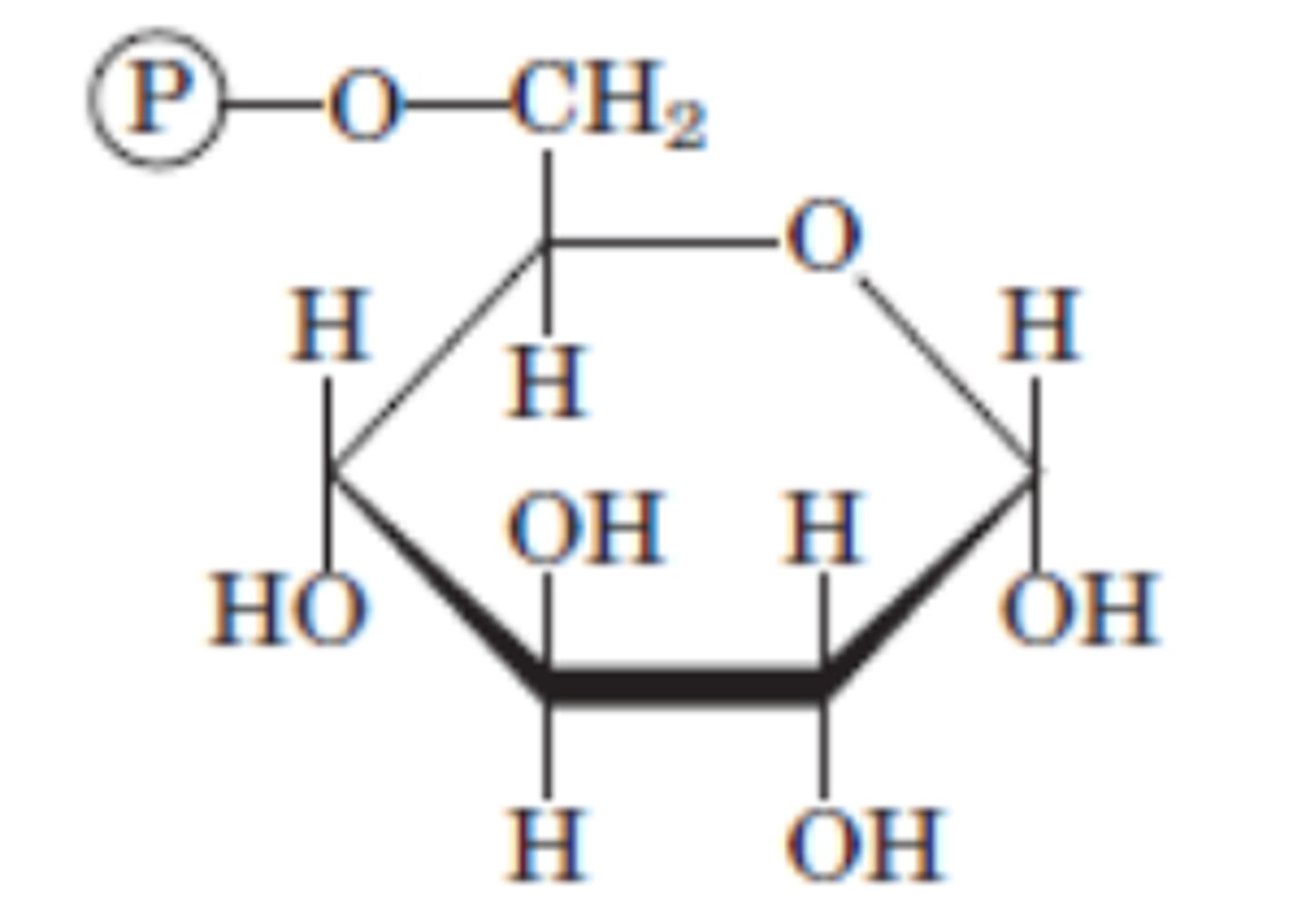
Reaction 2/10
Glucose 6-phosphate → Fructose 6-phosphate
What is the name of the related enzyme?
What is the name of the cofactor involved in the reaction?
What type of reaction is this?
What happens during this reaction?
Enzyme: Phosphohexose isomerase
Cofactor: Mg2+
Type of reaction: Isomerisation
Rearrangement of covalent bonds.
DRAW: Fructose 6-phosphate
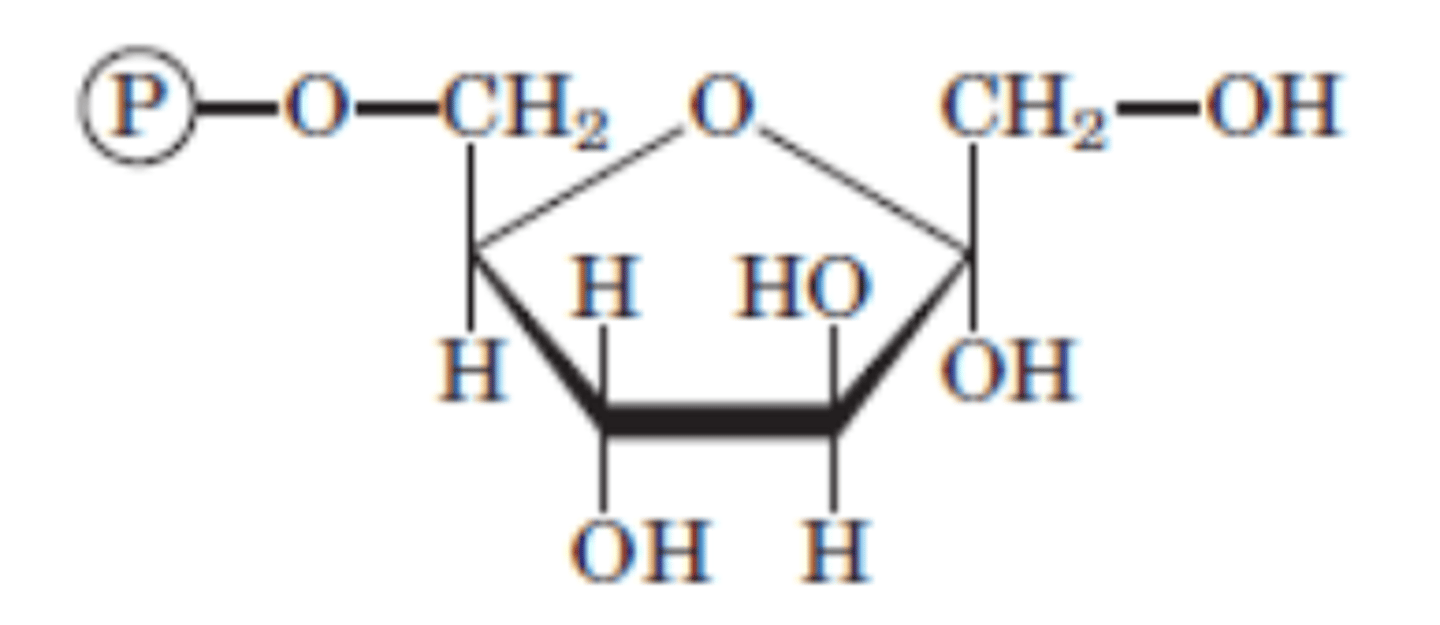
Reaction 3/10
Fructose 6-phosphate → Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
(2/2 Energy consuming, NOT reversible)
What is the name of the related enzyme?
What are the names of the cofactors involved in the reaction?
What type of reaction is this?
What happens during this reaction?
Enzyme: Phosphofructokinase-1
Cofactors: Mg2+, ATP, ADP
Type of reaction: Phosphorylation
Removal of ℗ from an ATP molecule (converting it to ADP) and attaching it to the current Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
DRAW: Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
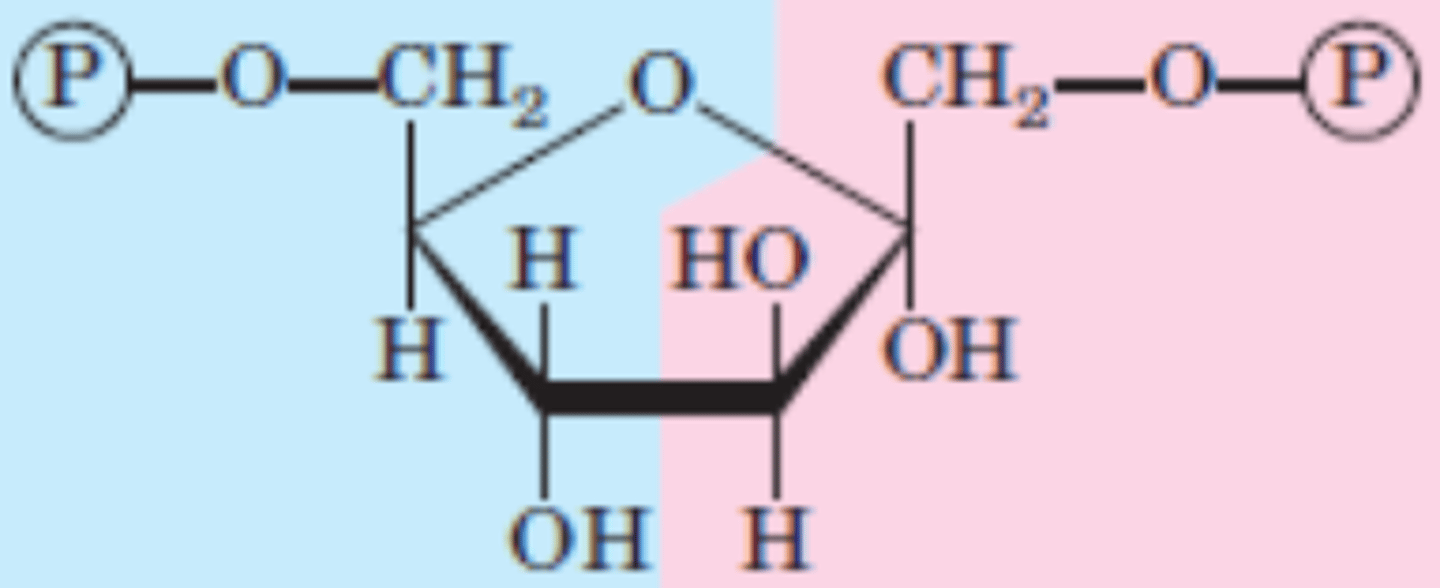
Reaction 4/10
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate → Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
What is the name of the related enzyme?
What type of reaction is this?
What happens during this reaction?
Enzyme: Aldolase (Lyase)
Type of reaction: Cleavage
Cleavage of one 6-Carbon sugar phosphate to two 3-Carbon sugar phosphates.
DRAW: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
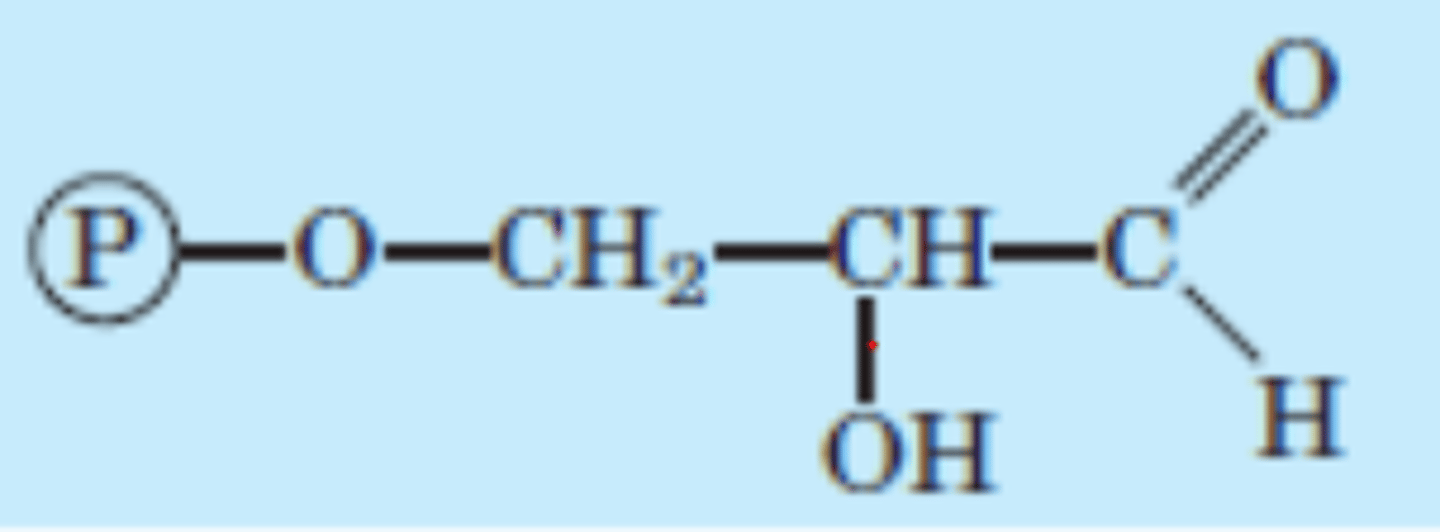
DRAW: Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
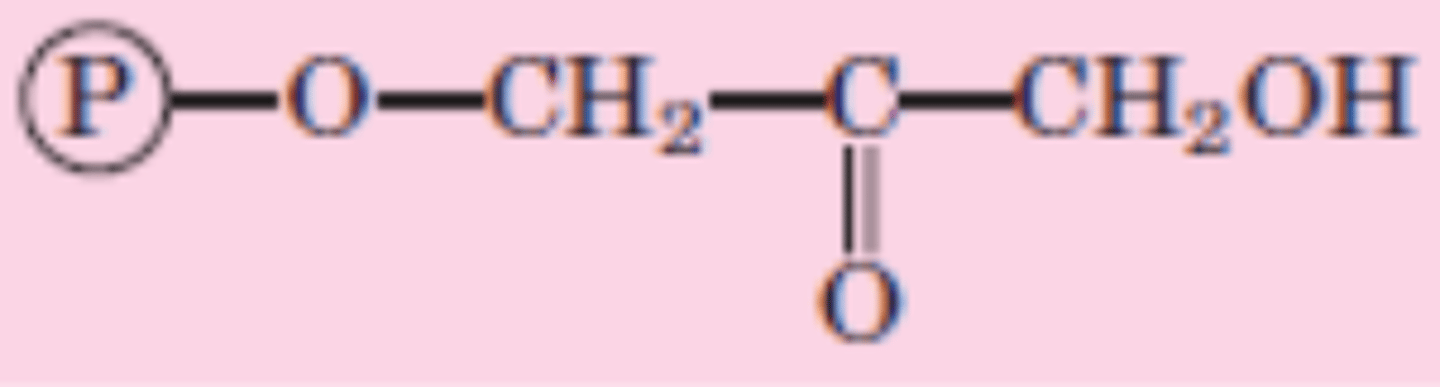
Reaction 5/10
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate → Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
*(So we end up having 2 units in total of this type of molecule along with the previous one from Reaction 4/10.)
What is the name of the related enzyme?
What type of reaction is this?
What happens during this reaction?
Enzyme: Triose phosphate isomerase
Type of reaction: Isomerisation
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate gets rearranged by the above isomerase to form a second Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate molecule.
DRAW: (2x) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
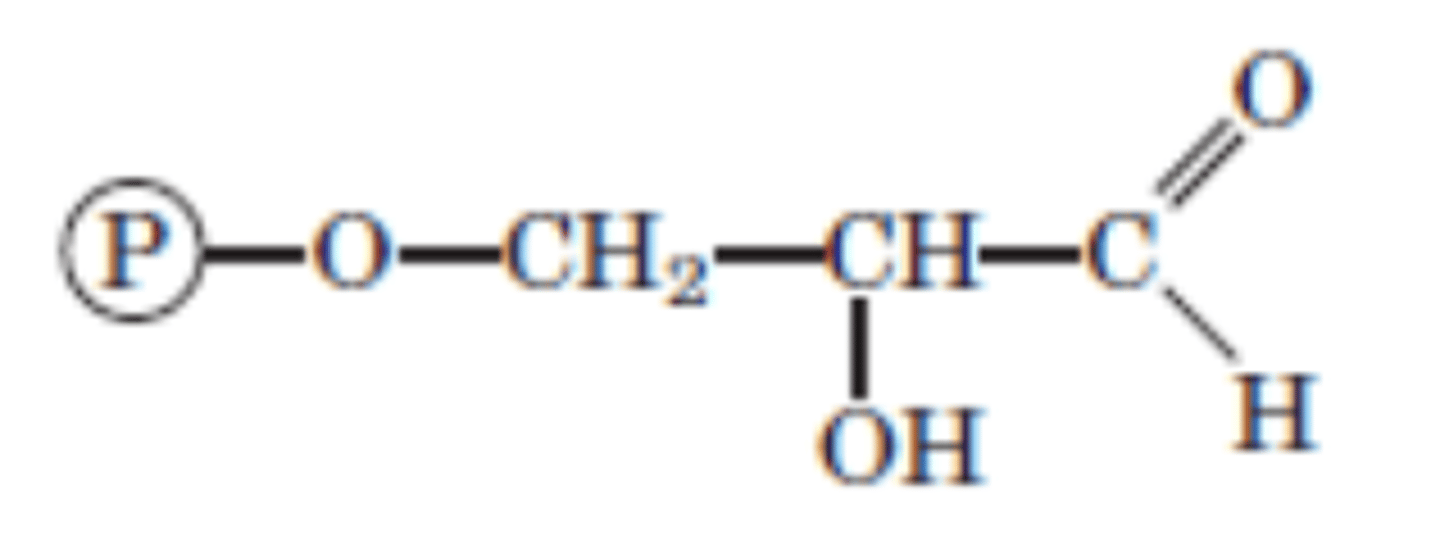
Reaction 6/10
(2x) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + (2x) ℗ → (2x) 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate
What is the name of the related enzyme?
What are the names of the cofactors involved in the reaction?
What type of reactions are these? (2)
What happens during this reaction?
Enzyme: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Cofactors: NAD+, NADH
Type of reactions: Dehydrogenation (oxidation) and phosphorylation
Both Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate molecules get oxidized and they produce 2 NADH in total (from 2 NAD+).
Both Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate molecules get an additional ℗ (these are not coming from ATP but they are inorganic phosphate molecules).
DRAW: (2x) 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate
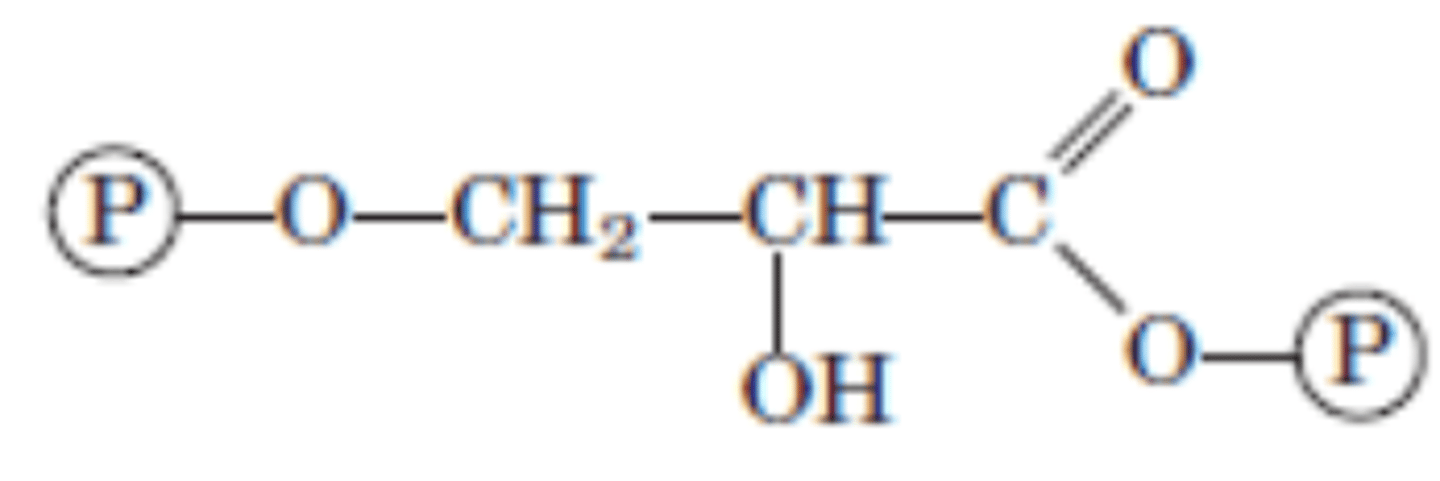
Reaction 7/10
(2x) 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate → (2x) 3-Phosphoglycerate
(1/2 Energy creation, reversible)
What is the name of the related enzyme?
What are the names of the cofactors involved in the reaction?
What type of reaction is this?
What happens during this reaction?
Enzyme: Phosphoglycerate kinase
Cofactor: Mg2+, ADP, ATP
Type of reaction: Substrate-level phosphorylation
From both 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate, the above kinase transfers a ℗ to ADP, thus forming 2 ATP molecules in total (from 2 ADP).
DRAW: (2x) 3-Phosphoglycerate
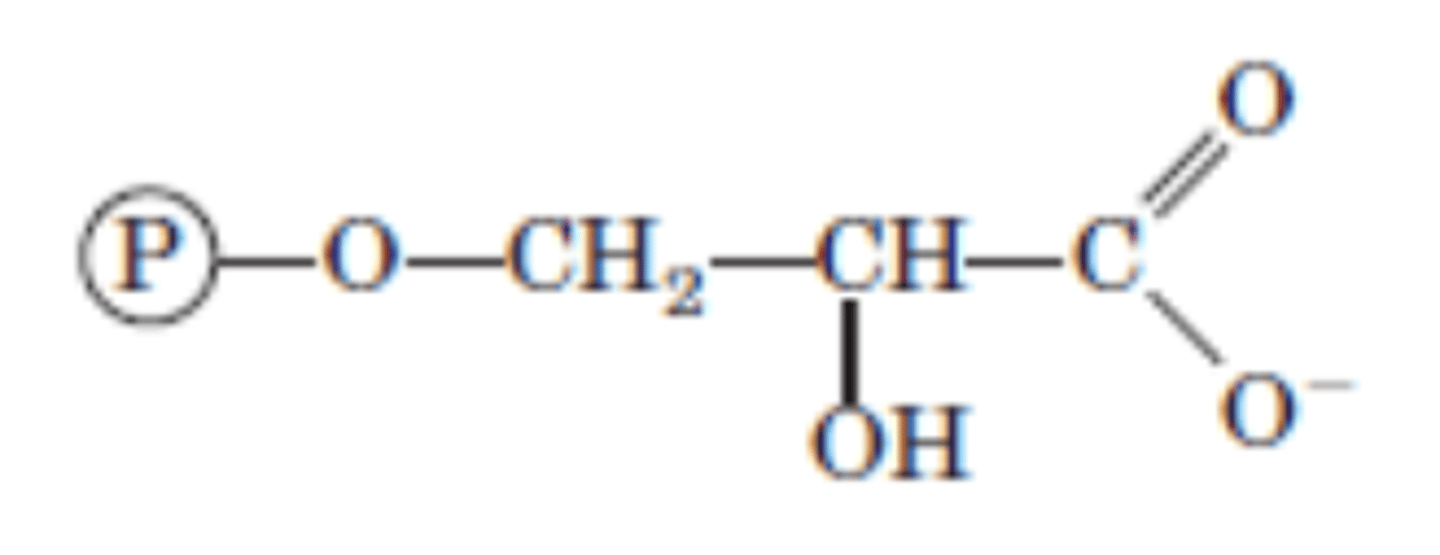
Reaction 8/10
(2x) 3-Phosphoglycerate → (2x) 2-Phosphoglycerate
What is the name of the related enzyme?
What is the name of the cofactor involved in the reaction?
What type of reaction is this?
What happens during this reaction?
Enzyme: Phosphoglycerate mutase
Cofactor: Mg2+
Type of reaction: Isomerisation
(2x) Transfer of ℗ from the 3rd Carbon atom to the 2nd Carbon atom.
DRAW: (2x) 2-Phosphoglycerate
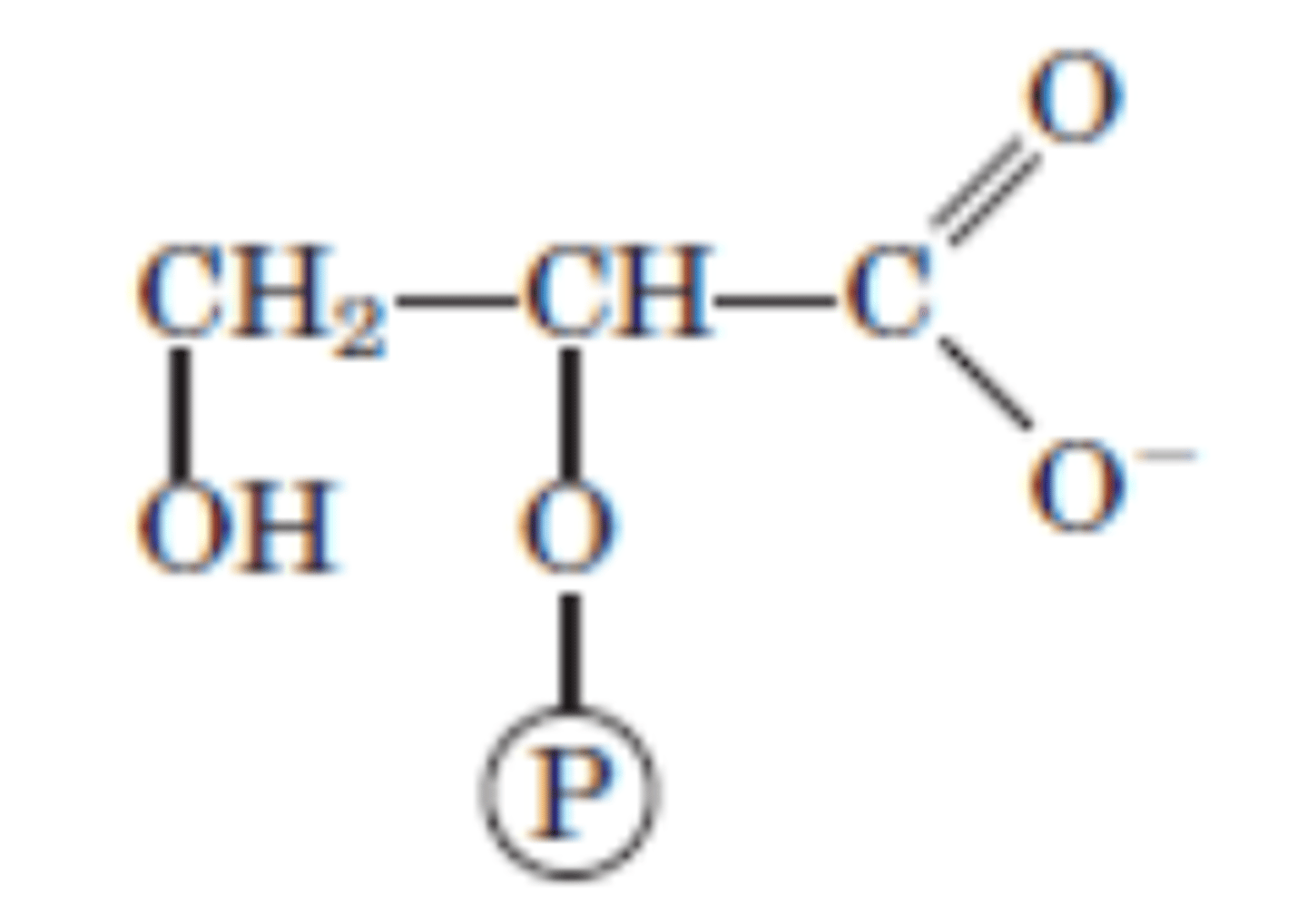
Reaction 9/10
(2x) 2-Phosphoglycerate → (2x) Phosphoenolpyruvate
What is the name of the related enzyme?
What type of reaction is this?
What happens during this reaction?
Enzyme: Enolase
Type of reaction: Dehydration
(2x) Removal of a water molecule.
DRAW: (2x) Phosphoenolpyruvate
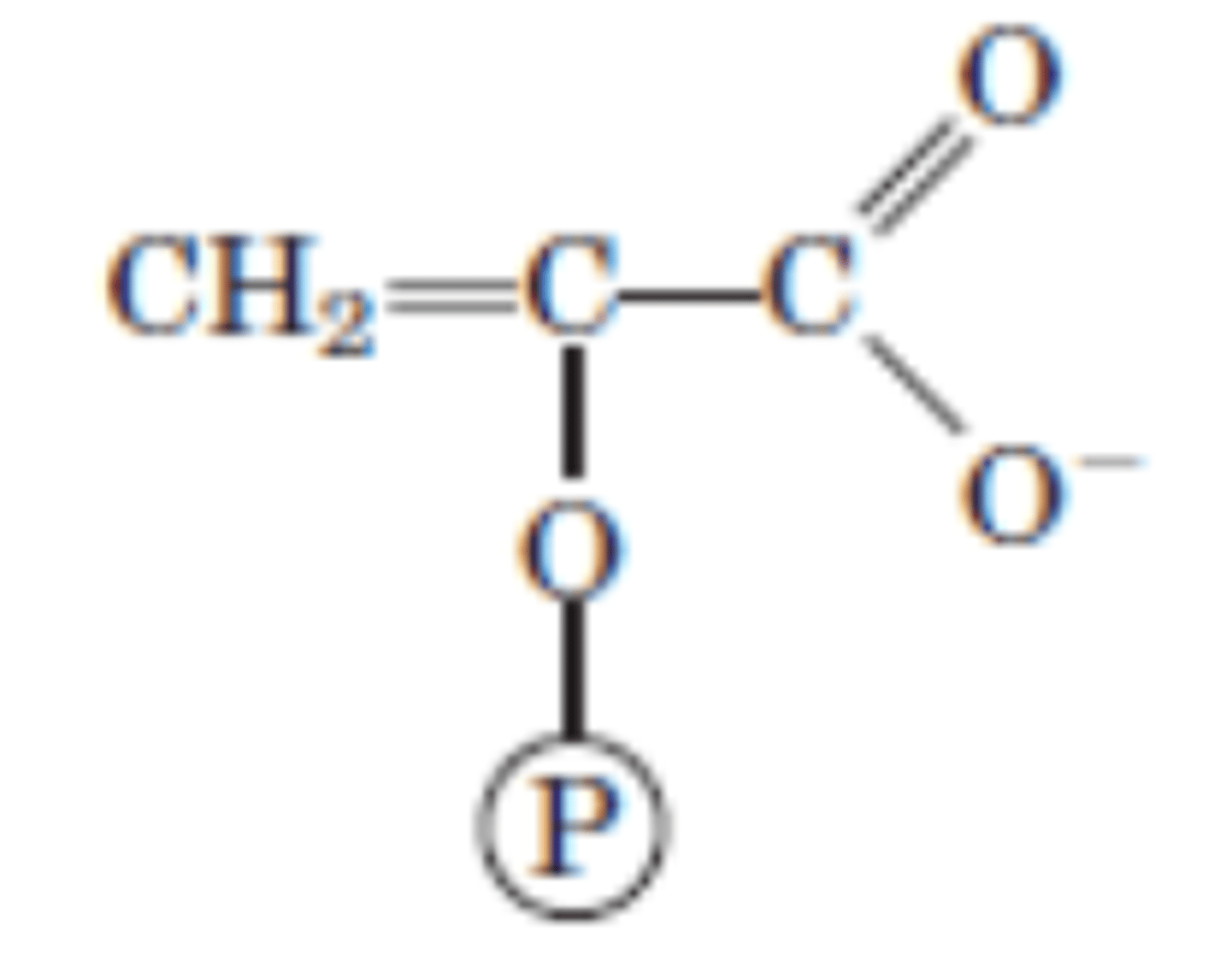
Reaction 10/10
(2x) Phosphoenolpyruvate → (2x) Pyruvate
(2/2 Energy creation, NOT reversible)
What is the name of the related enzyme?
What are the names of the cofactors involved in the reaction?
What type of reaction is this?
What happens during this reaction?
Enzyme: Pyruvate kinase
Cofactor: Mg2+, K+, ADP, ATP
Type of reaction: Substrate-level phosphorylation
Removal of ℗ from both molecules and donate them to 2x ADP, thus creating 2 ATP molecules in total.
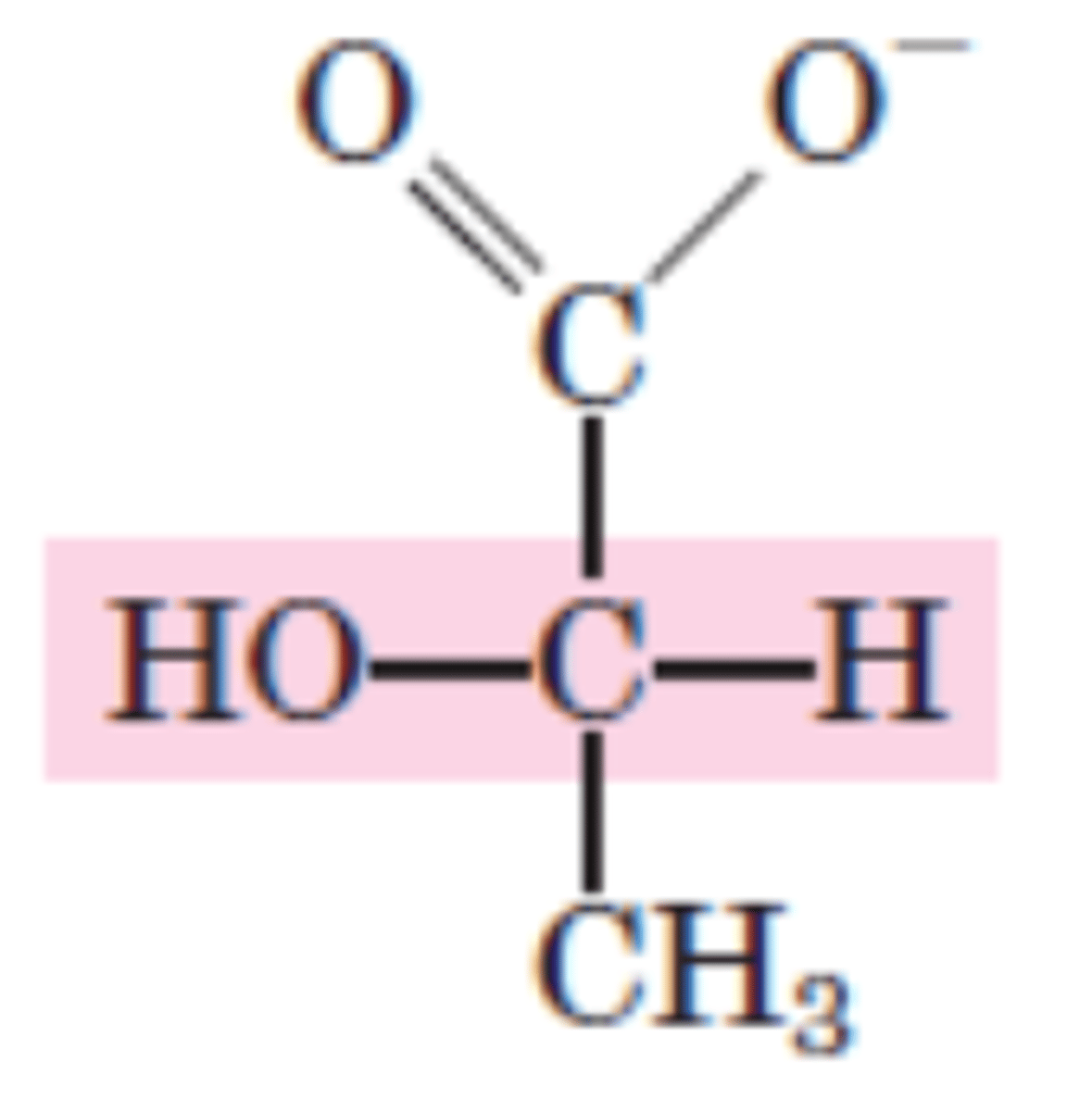
DRAW: (2x) Pyruvate
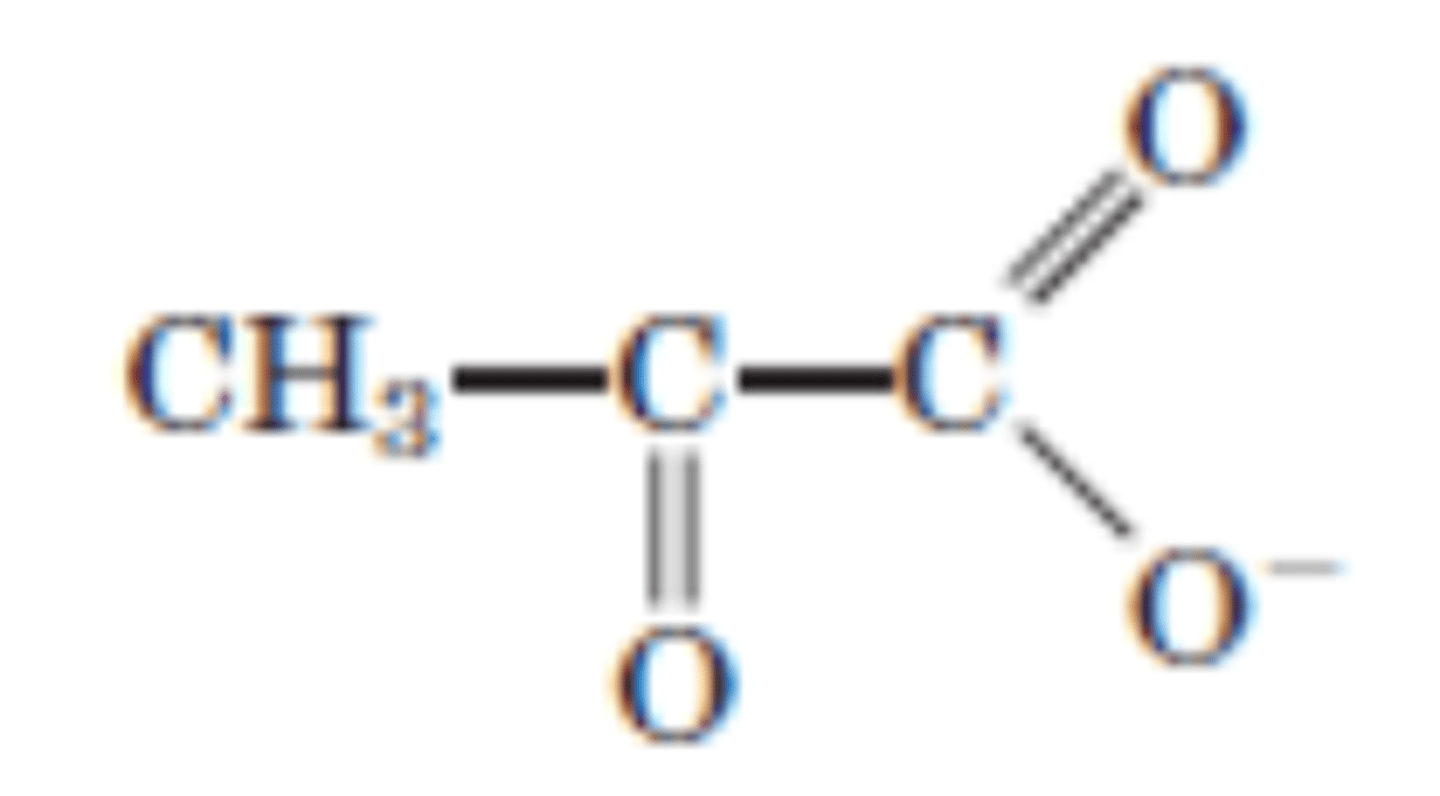
Additional step in anaerobic condition
(2x) Pyruvate → (2x) L-lactate
What is the name of the related enzyme?
What happens during this reaction?
Enzyme: Lactate dehydrogenase
When animal tissues cannot be supplied with sufficient oxygen to support aerobic oxidation of the pyruvate and NADH produced in glycolysis, NAD+ is regenerated from NADH by the reduction of pyruvate to lactate by Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH).
DRAW: L-lactate