Gravitational fields
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Definition of a gravitational field:
It is the region around a body in which other bodies will feel a force due to the mass of the body
What are gravitational fields due to?
They are due to objects having mass
Definition of gravitational field strength
At any point in a gravitational field, the force acting per unit mass at that point (Nkg-1)
How is mass normally modelled?
the mass of a spherical object as a point mass in its centre
what shows a greater gravitational field on a diagram
more densely packed field lines
equation for gravitational field strength
Gravitational field strength = gravitational force/ mass
g = F/m
units for gravitational field strength
(Nkg-1)
gravitational force equation
F = -GMm/ r² where:
F = gravitational force
G = newtons gravitational constant
M or m = mass of each object
r = separation between (point masses of) the two objects
gravitational acceleration/ field strength equation
a = -GM/ r² (note we also see a as g)
Because:
F = -GMm/ r²
F=ma
ma = -GMm/ r² (cancel m)
a = -GM/ r²
close to the surface of the earth, what can we assume about the gravitational field?
That it’s uniform: represented by parallel lines, uniformly spaced and also always enter surface at 90 degrees.
Newtons law of gravitation
The gravitational force between two point masses is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of their separation
Keplers 1st law
Planets travel around the sun in elliptical orbits
Keplers 2nd law
A line segment joining the sun to a planet will sweep out equal areas in equal times
Keplers 3rd law
The time period of the orbit squared is proportional to the mean radius of the orbit cubed: T² ∝ r³
And for bodies that move in a circular path, what does this become?
T² = (4π² / GM ) x r³
How else can we write the relationship between T² and r³
T² ∝ r³
T² = kr³
T²/ r³ = k (a constant)
T²1/ r³1 = T²2/ r³2
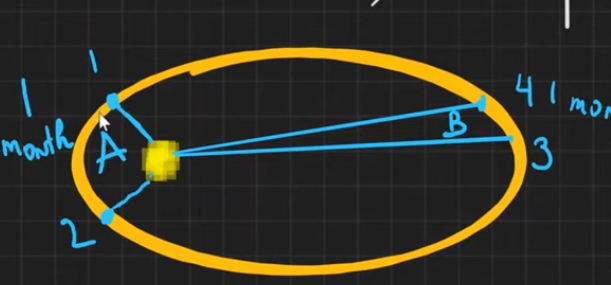
What happens to the planet in orbit around the sun when it is closer to the sun, near A?
The planet speeds up, due to the fact its experiencing a greater gravitational force
Keplers third law proof
To start derivation, remember gravitational force acts towards centre of rotation of planet.
Fg = Fc (gravitational force = centripetal force)
GMm / r² = mv²/ r (Cancel m)
Remember v = 2πr/ T
V² = 4π²/T²
GM / r² = (4π²r²/rT²)
T² = (4π²/GM) r³
What 3 things define a geostationary orbit?
1) They have an orbital period of 24 hours in the same direction as the rotation of the Earth
2) They are in equatorial orbit
Therefore:
3) They remain fixed in the sky to an observer on Earth
How to calculate height of geostationary orbit
Height, we are finding r:
T² = (4π²/GM) r³
Radius of earth = 6400km
Mass of earth = 6 ×1024 kg
r = cube root of T²GM / 4π²
Plugging values in we get r = 4.23 × 107 however this isn’t the distance from the surface of the earth, it’s the distance to the point mass (the centre of the earth). So we must do 4.23 × 107 - 6400 ×10³ = 3.6 ×107m
Definition of gravitational potential energy
The gravitational potential energy of a mass m (for a radial field around a point or spherical mass M) at a distance r from M is defined as:
Energy = -GMm / r ( unit is joules J )
Take note that its not over r²
Definition of gravitational potential
The gravitational potential at a point in a gravitational field is the energy required to move a unit mass from infinity to that point in the field of the body of mass M
Vg = -GM/r
The reason it is negative, as is the grav. potential energy, is because we define the gravitational potential energy as being equal to zero at infinity, so equation must be negative as work must be done on the body when moving it in the opposite direction to an attractive gravitational field, and as Vg at infinity is 0, Vg must be negative before it reaches infinity.
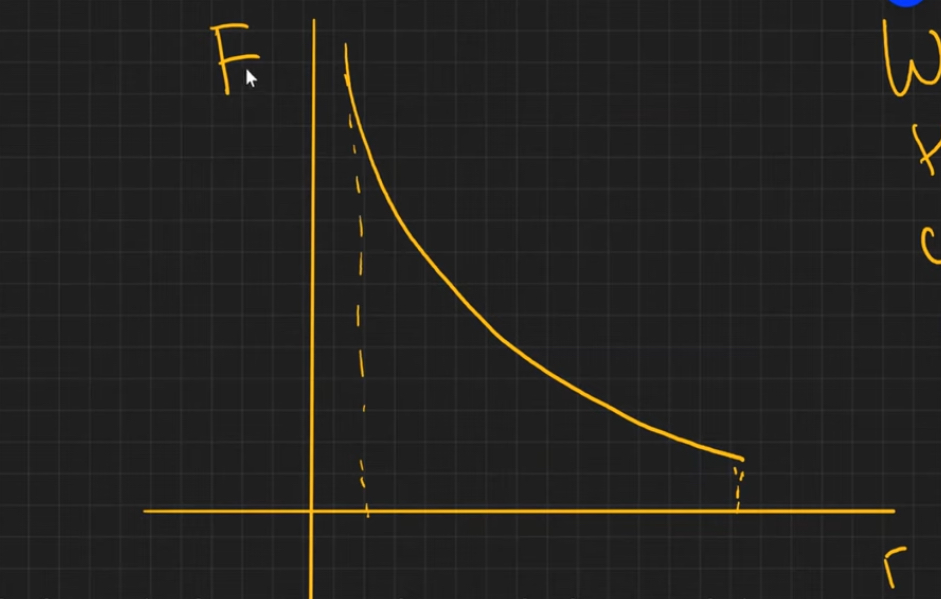
For a force-distance graph for a point or spherical mass, what does the area under the graph equal?
The work done
Escape velocity of the earth
The escape velocity from a point in a gravitational field is the minimum launch velocity required to move an object from that point to infinity
How would we calculate the escape velocity?
Think about energy:
GPE must = KE
GMm/r = ½ mv²
v = (2GM/r)1/2
Now sub in values we know for the earth.