Chapter 16
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dienes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What does a diene being conjugated mean?
It means that the pi-bonds are separated by a dingle sigma bond and resonance can occur.
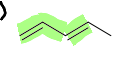
What does cumulate mean in a diene?
It means that there is an sp hybridized carbon between two alkenes, resulting in a unique arrangement that restricts rotation and affects the reactivity of the compound causing localized electrons.
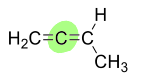
What does isolated mean in a diene?
The two double bonds are separated by two or more single bonds, sp3, preventing any resonance interaction between them.
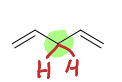
Are pi bonds delocalized in conjugated, cumulated or isolated dienes?
Conjugated

What does the delocalization of electron cause?
Increased stability.
Why does a continuous system of p orbital restrict rotation?
To maintain conjugation
There are favored rotation conformers because all of the other conformers are not conjugated meaning they are higher energy but less stable. What are the favored conformers?
s-cis and s-trans

Between s-cis and s-trans, which confirmation is more stable?
s-trans
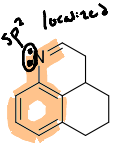
How do you identify a conjugated system?
Look for delocalized lone pairs and sp2 hybridized carbons
What is an allelene?
A compound featuring two double bonds adjacent to each other, resulting in a linear arrangement of atoms.
To prepare a diene what is used and why?
A stericaily hindered base for an E2 elimination because the Hoffman product, the less substituted product, is favored.
In dienes, as s-character increases…
sigma bonds become shorter, and more stable/strong
What are the steps to rank compounds in increasing stability?
First, check the conjugation of each structure
Second, check the s-cis and s-trans conformations
Third, check the substitution of the alkenes
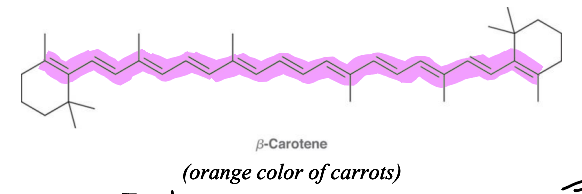
Conjugated compounds absorb UV/visible light, why?
The energy to excite an electron from π to π* (HOMO to LUMO) is in the UV-Vis region.
What is chromophore?
A group of atoms that absorb Uv-Vis light in the compound. The larger the conjugation the more likely the compound is to show color.
As conjugation increases the energy … and the λmax …
decreases; increases
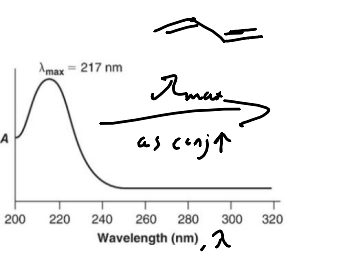
What is the visible region of llight?
400 - 700 nm
What color is observed when a molecule absorbs a wavelength of light?
The opposite color. (Think Color Wheel)
What is the [1,2] addition of dienes?
A reaction where two substituents are added to adjacent carbon atoms of a diene
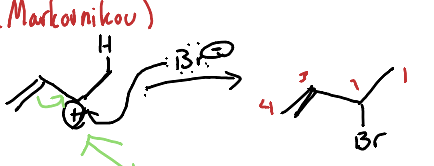
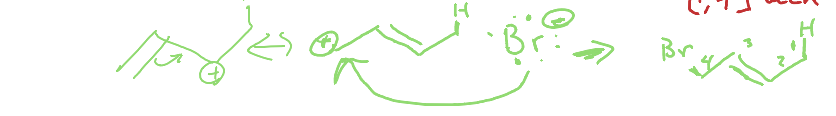
What is the [1,4] addition of dienes?
A reaction where two substituents are added to the first and fourth carbon atoms of a diene, usually proceeding after resonance has occured.
What is the Kinetic product of a diene and when is it favored?
The [1,2] addition product at lower temperatures
What is the Thermodynamic product of a diene and when is it favored?
The [1,4] addition product at higher temperatures.
What are the reagents that follow the electrophilic addition mechanism that follows the [1,2], [1,4] Kinetic vs. thermodynamic product rule?
HX, X2, H2O addition
What are the three types of pericyclic reactions that are being stiudied?
Sigmatropic Rearrangement
Cycloaddition
Electrocyclic reaction
What is the COPE rearrangement?
A [3,3] sigmatropic reaction in which all 6 atoms in the cyclic transition state are carbon atoms. Equilibrium favors more stable alkene (usually more substituted).
![<p>A [3,3] sigmatropic reaction in which all 6 atoms in the cyclic transition state are carbon atoms. Equilibrium favors more stable alkene (usually more substituted).</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cd65c961-547d-428c-adb2-7bbcadb2f14a.png)
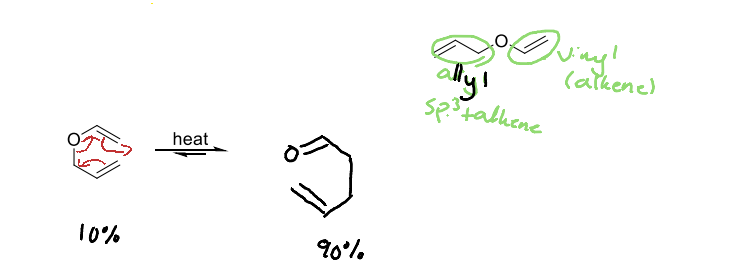
What is the claisen rearrangement?
An oxygen analog of Cope rearrangement. Observed with allyic vinyl ethers and allylic aryl ethers. Equilibrium favors more stable C=O bond.
What is dies-alder cycloaddition?
A [4+2] cycloaddition reaction between a diene and a dienophile, resulting in a six-membered ring formation. It is widely used in organic synthesis due to its ability to create complex structures efficiently. This is a concerted mechanism that can be done with heat or a lewis acid.
![<p>A [4+2] cycloaddition reaction between a diene and a dienophile, resulting in a six-membered ring formation. It is widely used in organic synthesis due to its ability to create complex structures efficiently. This is a concerted mechanism that can be done with heat or a lewis acid. </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/30e739e6-fd30-435e-b6ad-a9754a5bc07d.png)
What is the temperature threshold to have a retro-Diels Alder or a reverse reaction to occur
>200ºC
What are the criteria for a Diels Alder reaction to occur?
The diene must be in the s-cis conformation, and the dienophile should possess electron-withdrawing groups to enhance reactivity.
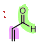
What is the name of the following dienophile?
Acrolein
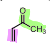
What is the name of the following dienophile?
Methyl Vinyl ketone
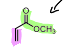
What is the name of the following dienophile?
Methyl Acrylate
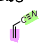
What is the name of the following dienophile?
Acrylonitrile
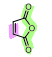
What is the name of the following dienophile?
Maleic anhydride
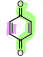
What is the name of the following dienophile?
Benzoquinone

What is the name of the following dienophile?
nitro group
In the process of a Diels-Alder cycloadduct reaction is an exo or endo product favored when both are possible?
The endo product is favored, otherwise known as the endo rule, due to secondary orbital interactions that stabilize the transition state.
What is an endo cycloadduct?
a product of a Diels-Alder reaction where the substituents on the newly formed ring are oriented towards the diene in the transition state, typically resulting in greater stability due to secondary orbital interactions.
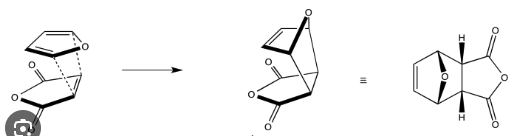
What is an exo cycloadduct?
A product of a Diels-Alder reaction where the substituents on the newly formed ring are oriented away from the diene in the transition state, typically resulting in less stability compared to the endo product.
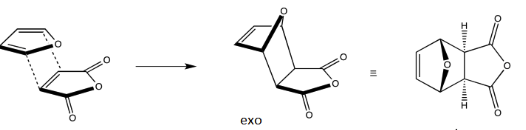
What is the regioselectivity of a Diels-Alder Reaction?
Regioselesctivity favors “ortho” and “para” substitution over “meta”
In a diels alder reaction, if the diene comes from the top, where do the inside groups go and where do outside groups go?
Inside → wedge, Outside → dash
To determine the interaction between the diene and dienophile in a diels alder reaction what must you do if the diene is not in a ring shape?
The molecule must be s-cis
True or False;
Beta Carbon nearly always has a partial charge in an asymetric diels-alder.
True
What is the first step in a diels-alder reaction?
Identify the skeleton structure of the product.
What is the second step in a diels-alder reaction?
Draw the six membered ring
What is the third step in a diels-alder reaction?
Perform the arrow push
What is the fourth step in a diels-alder reaction?
Add the final structures and verify the stereochemistry.