Kinesiology - Shoulder Complex
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
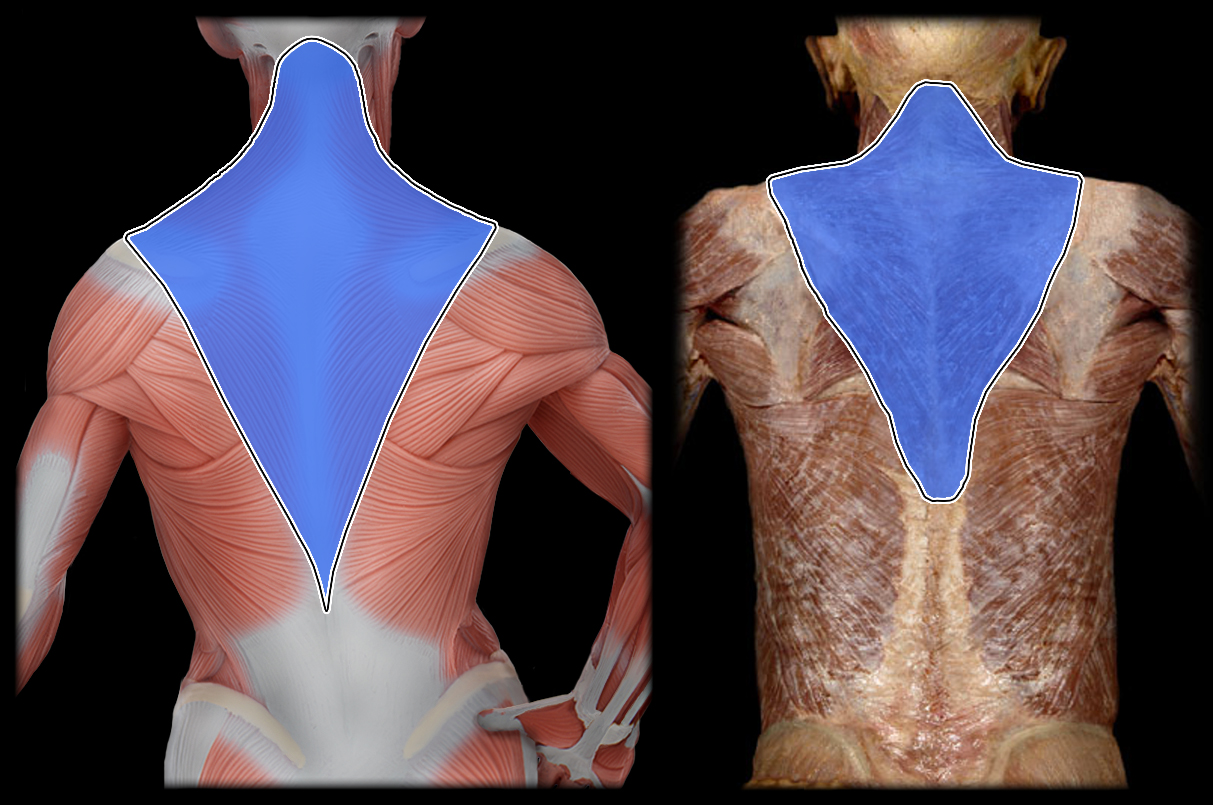
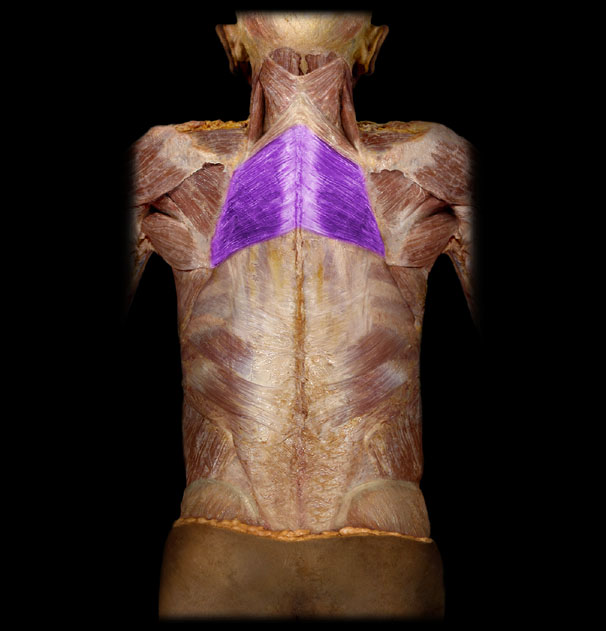
Action of Trapezius 1
elevate scapula, extend head and cervical spine
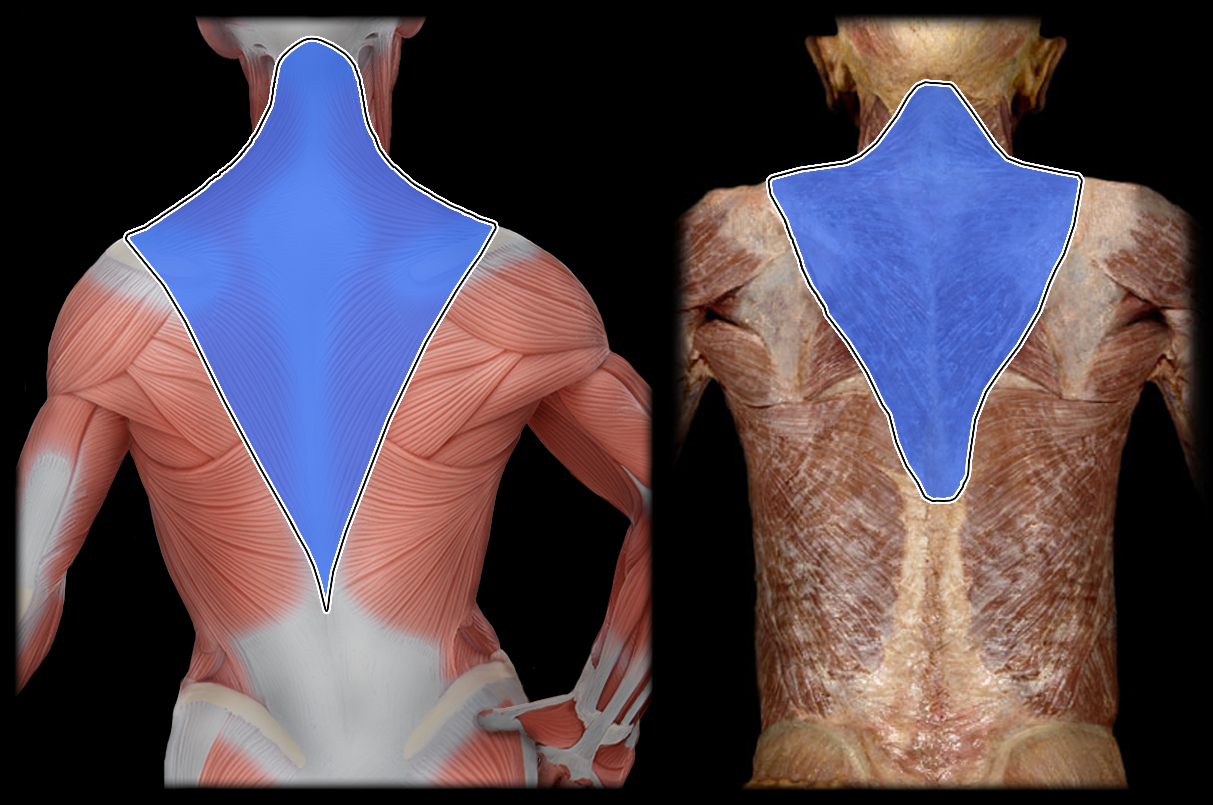
Action of Trapezius 2
upward rotation, retraction, elevation
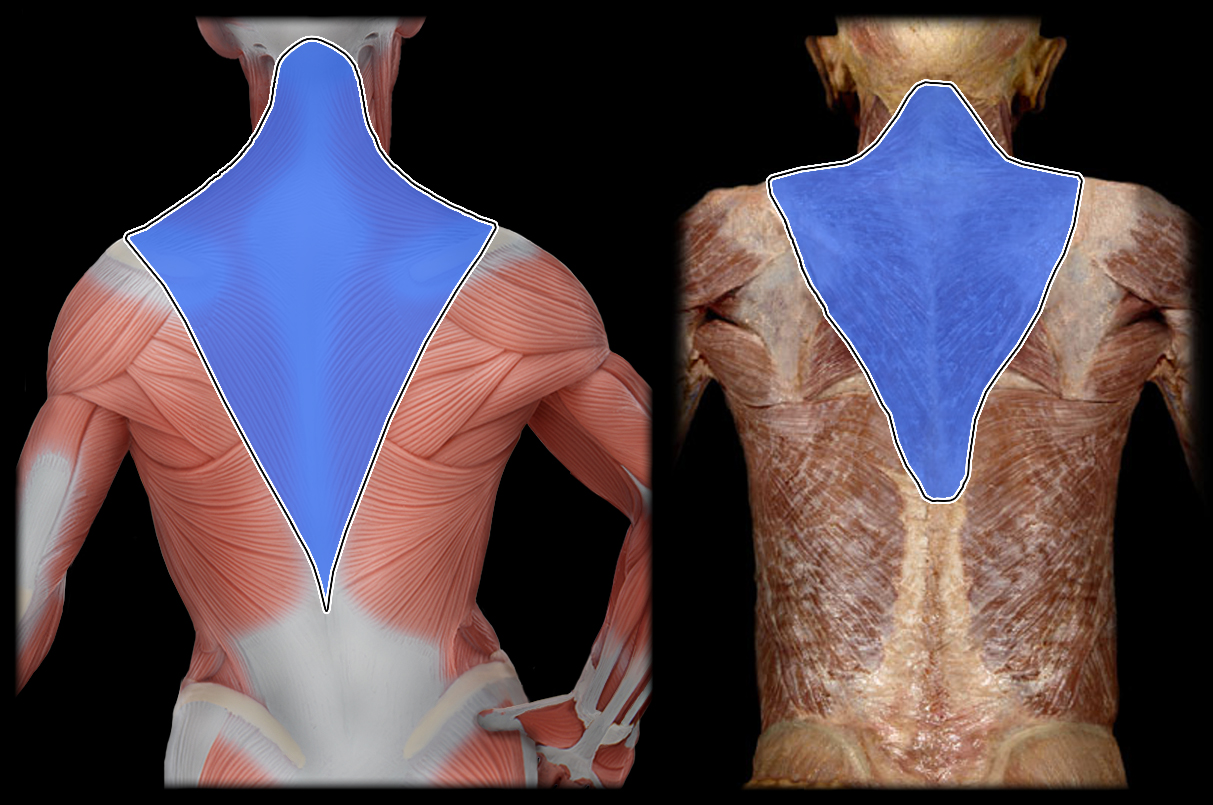
Action of Trapezius 3
retraction, upward and downward rotation
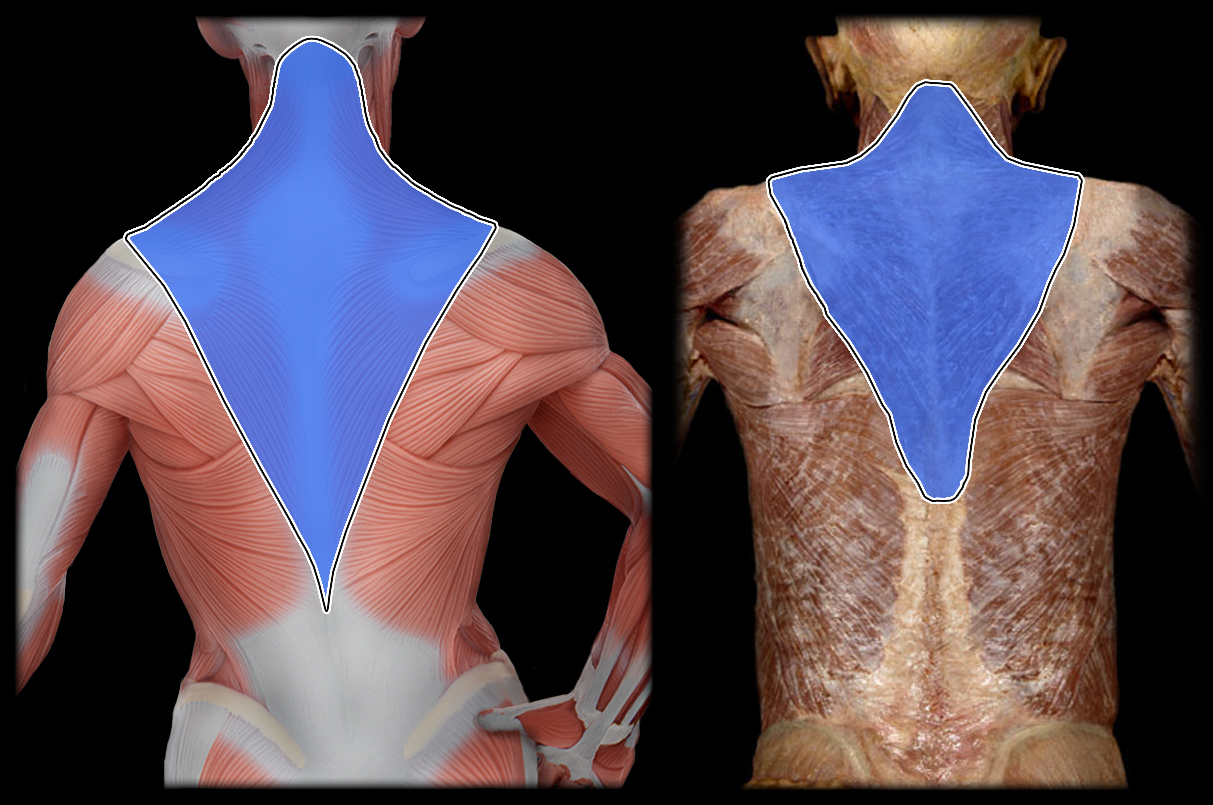
Action of Trapezius 4
depression, retraction, upward rotation
Action of the Rhomboids
retract scapula, elevate scapula, downward rotate scapula
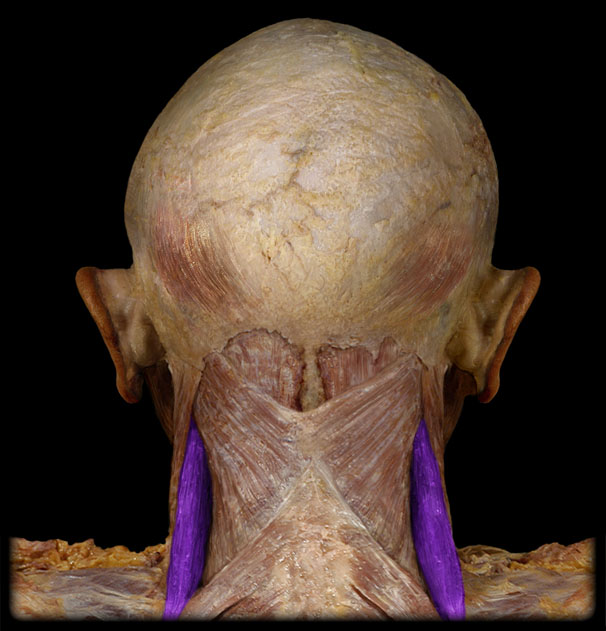
Action of the Levater Scapulae
elevates scapula
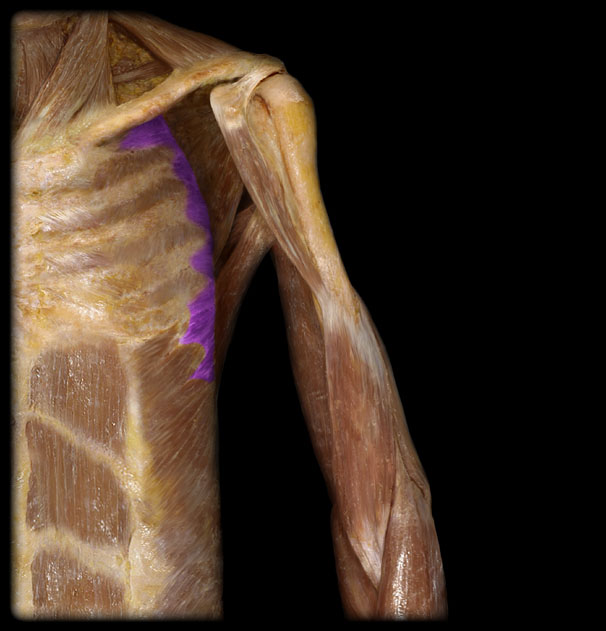
Origin of the Serratus Anterior
1st-8th rib
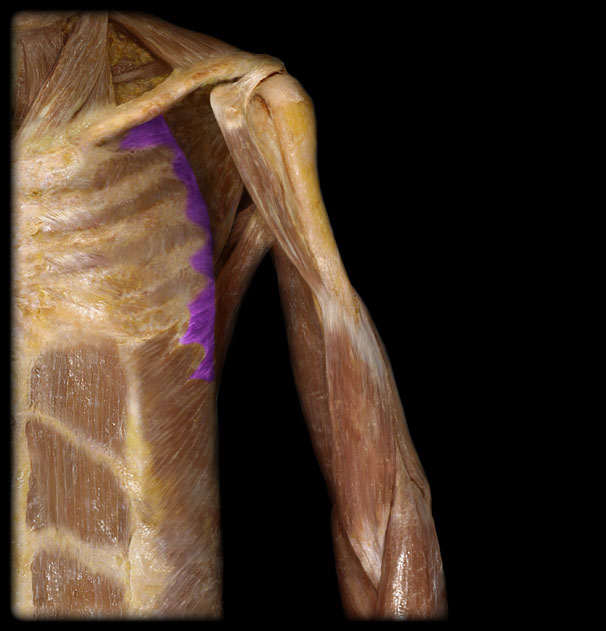
Insertion of the Serratus Anterior
superior angle, medial border, inferior angle of scapula
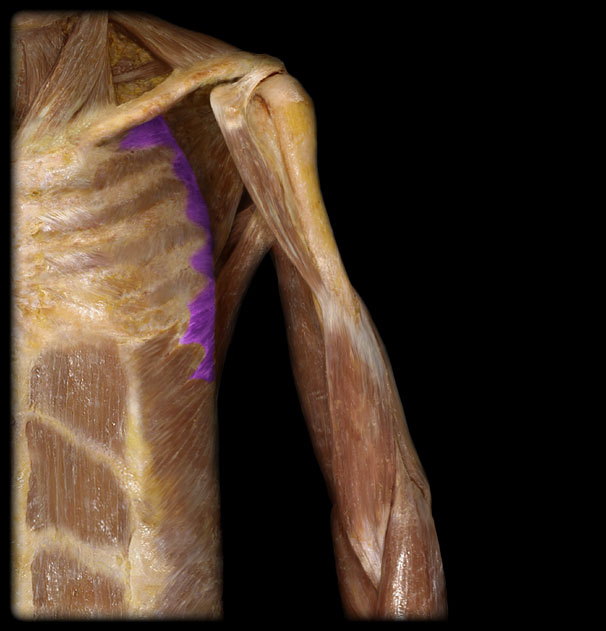
Action of the Serratus Anterior
protraction of scapula
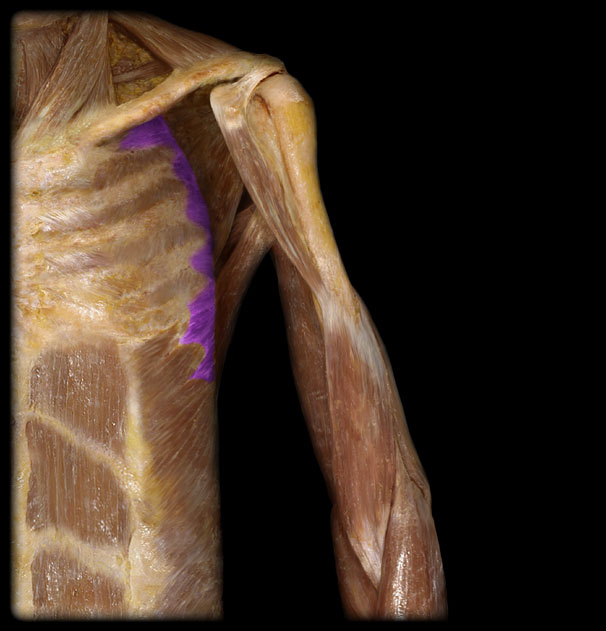
Inervation of the Serratus Anterior
long thoracic (c5-c7)
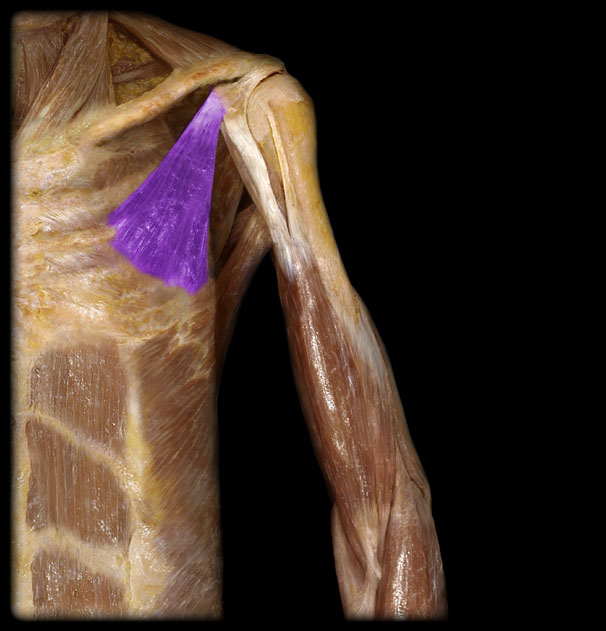
Origin of the Pectoralis Minor
3rd-5th ribs
Insertion of the Pectoralis Minor
coracoid process
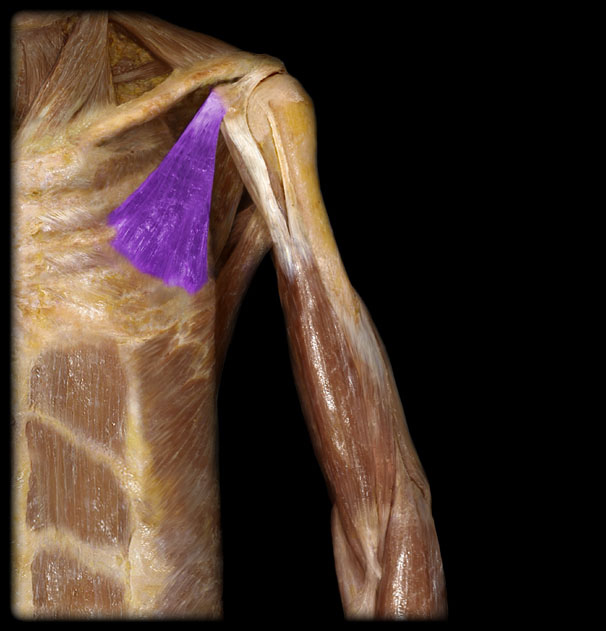
Action of the Pectoralis Minor
stabilization, depression, downward rotation, forward tipping of the scapula, accessory to inspiration
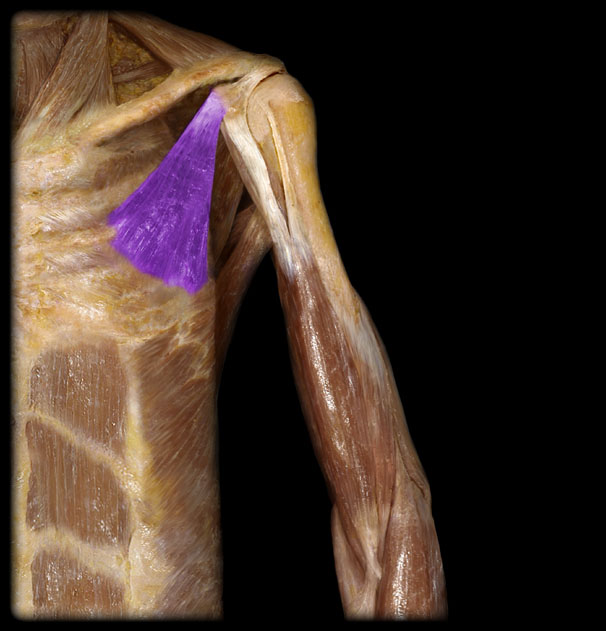
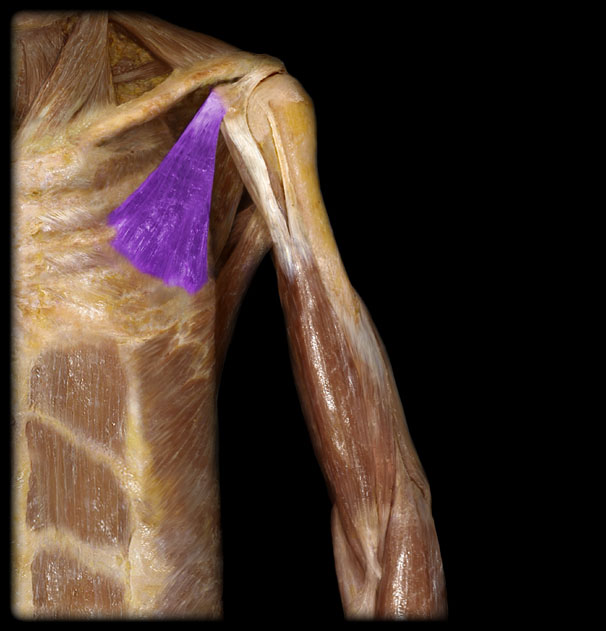
Innervation of the Pectoralis Minor
medial pectoral nerve
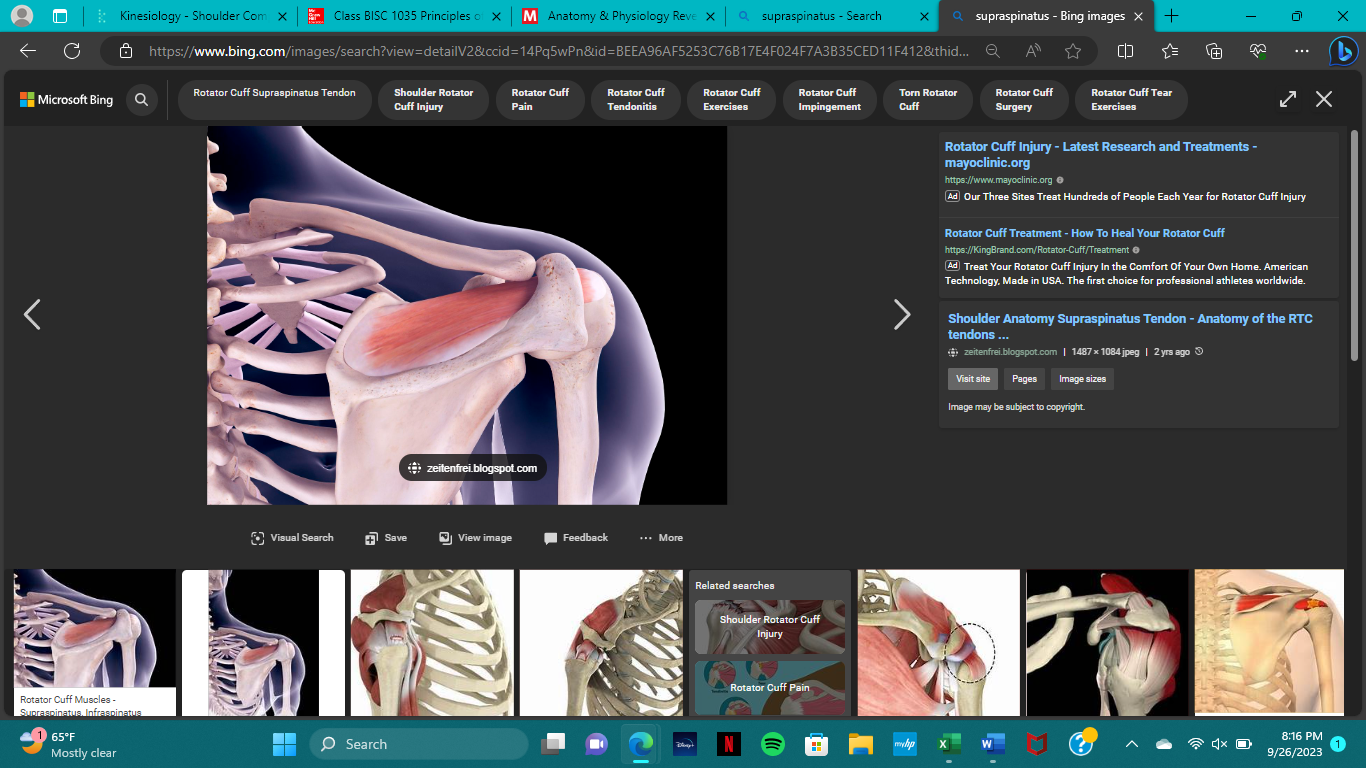
origin of the supraspinatus
supraspinatus fossa of the scapula
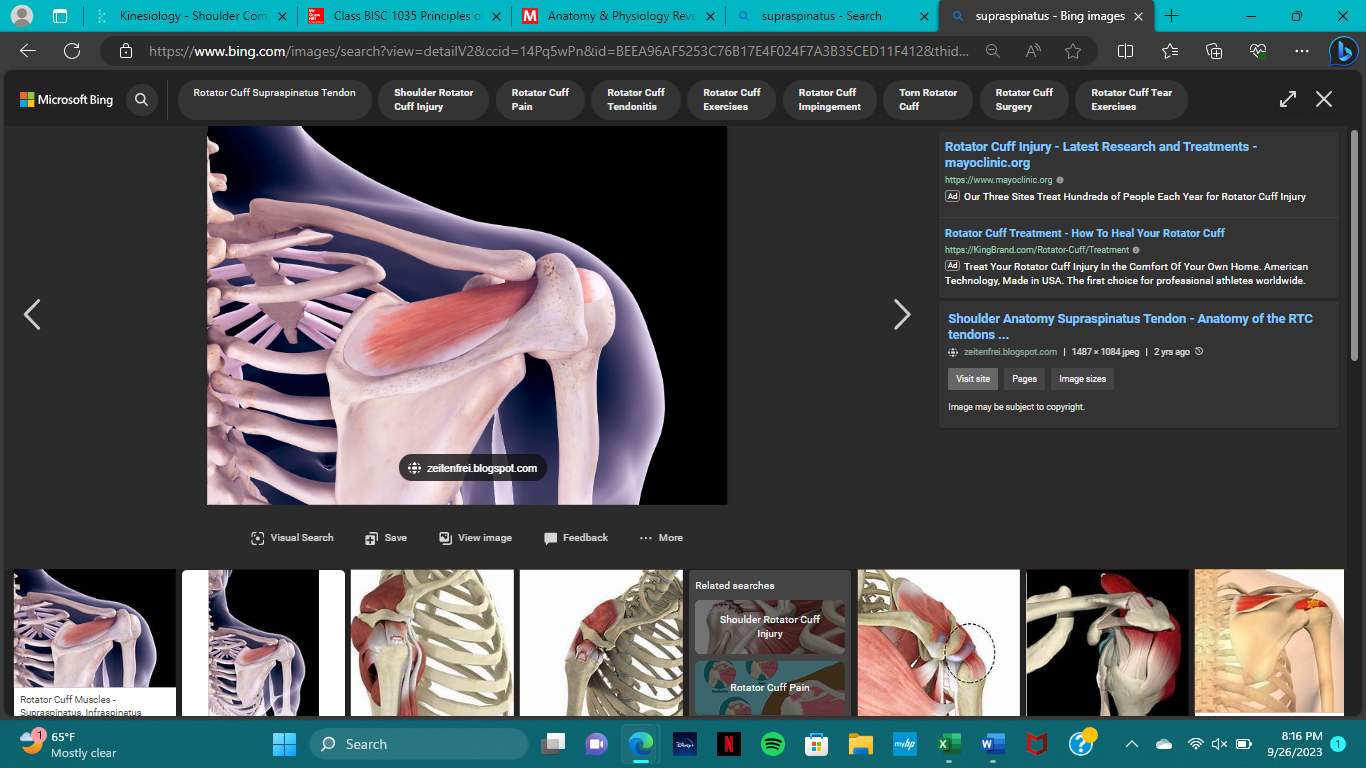
insertion of the supraspinatus
greater tubercle of the humerus
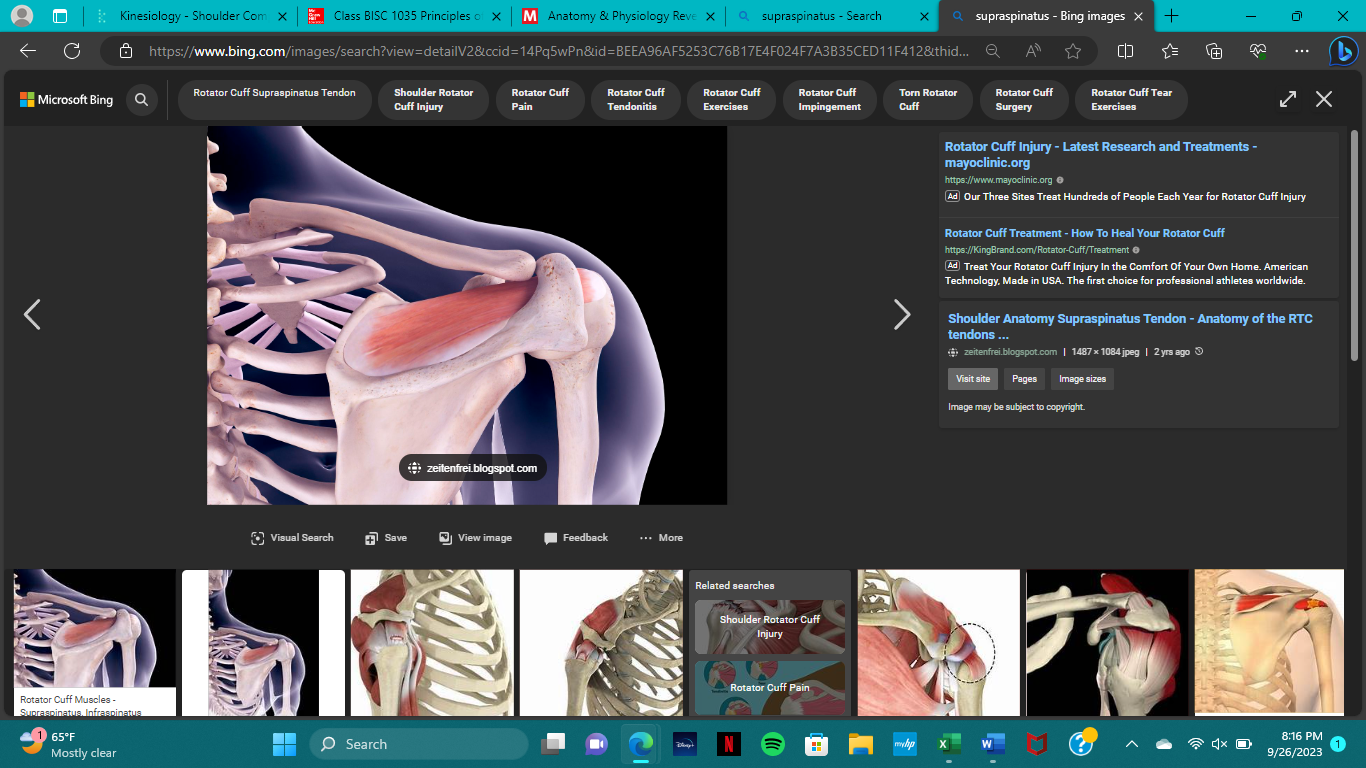
action of the supraspinatus
abduction, external rotation
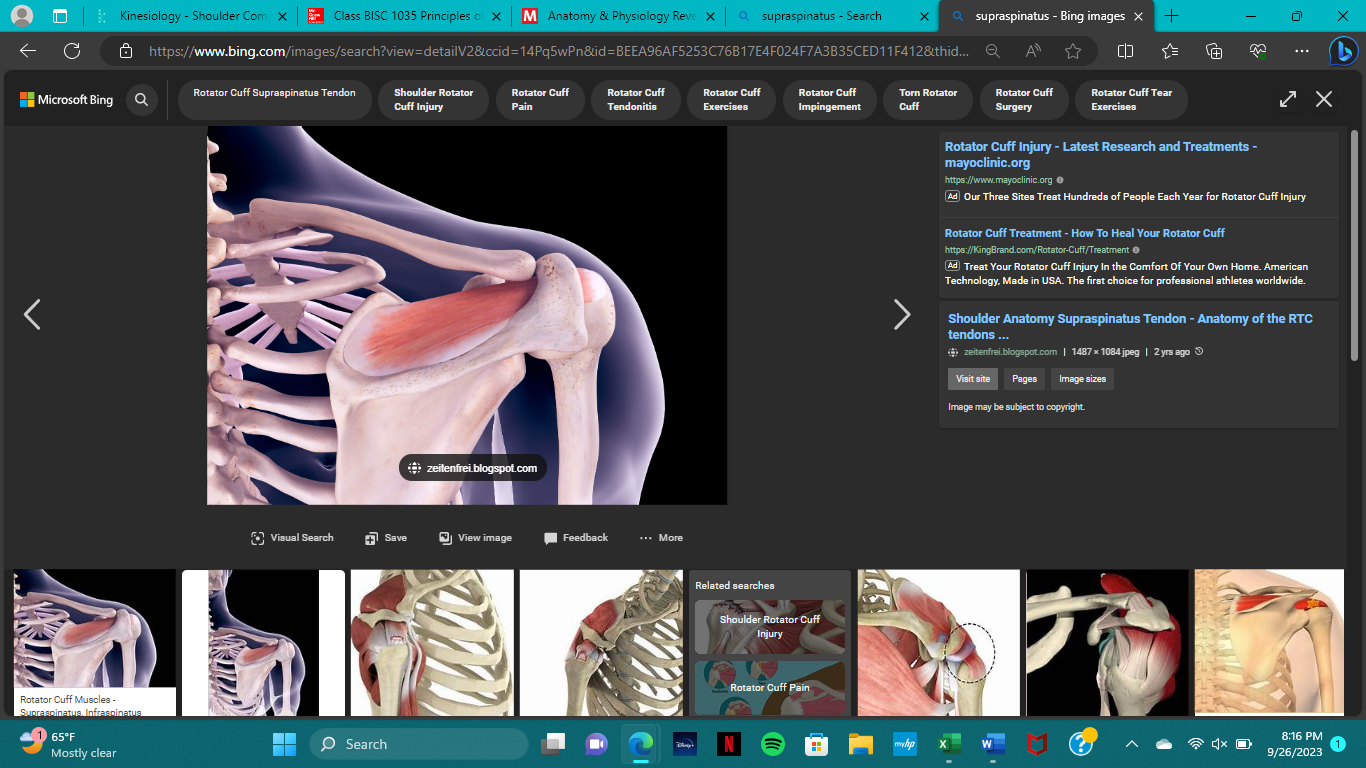
innervation of the supraspinatus
suprascapular
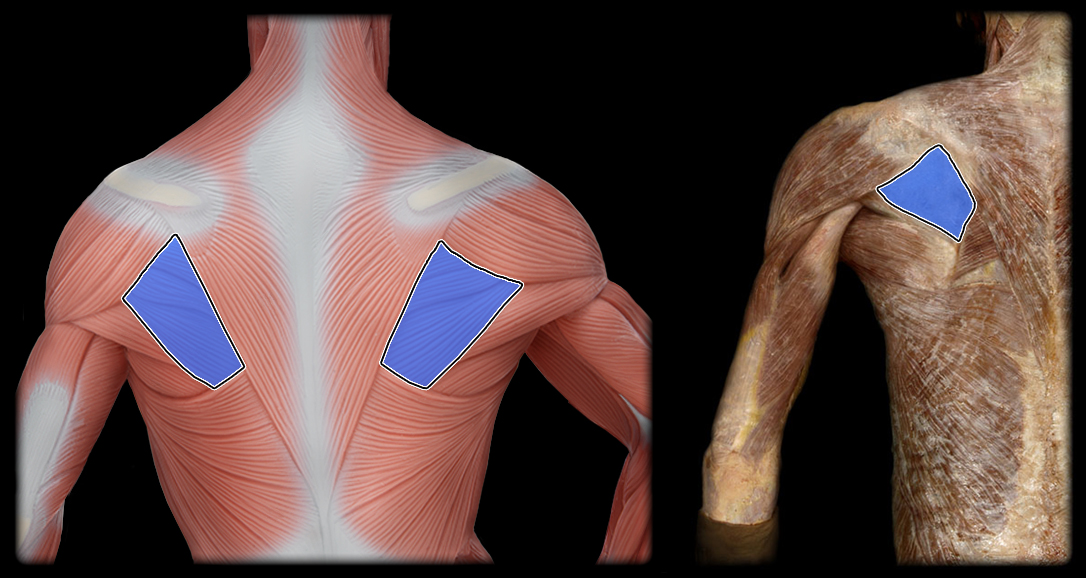
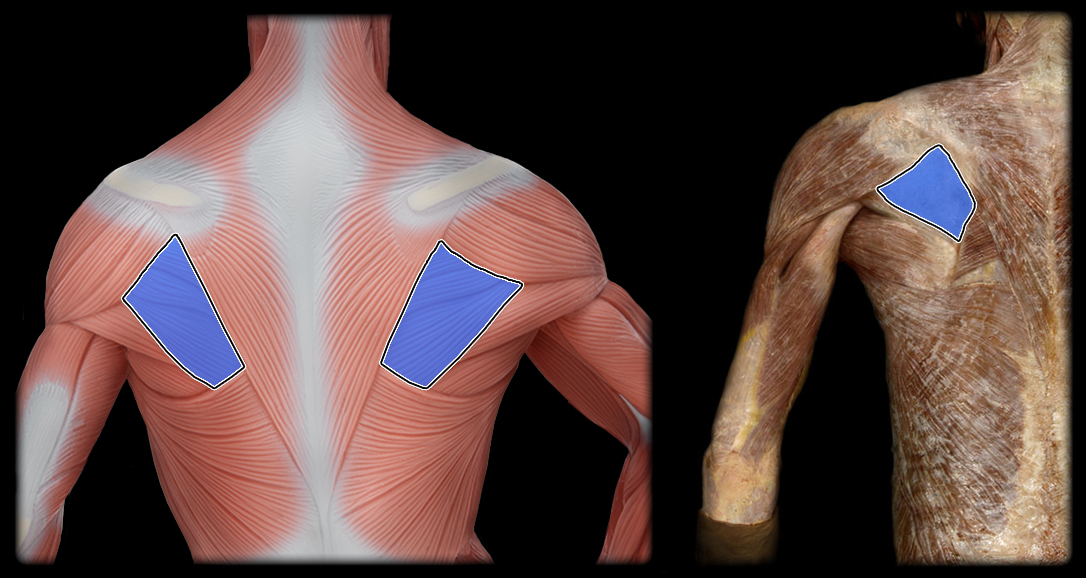
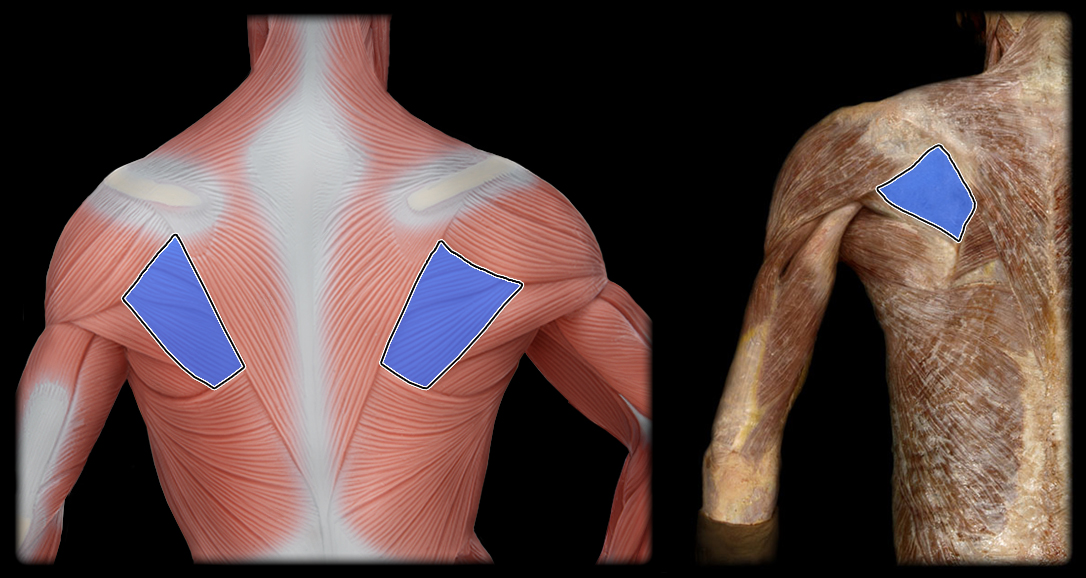
origin of infraspinatus
infraspinatus fossa of scapula
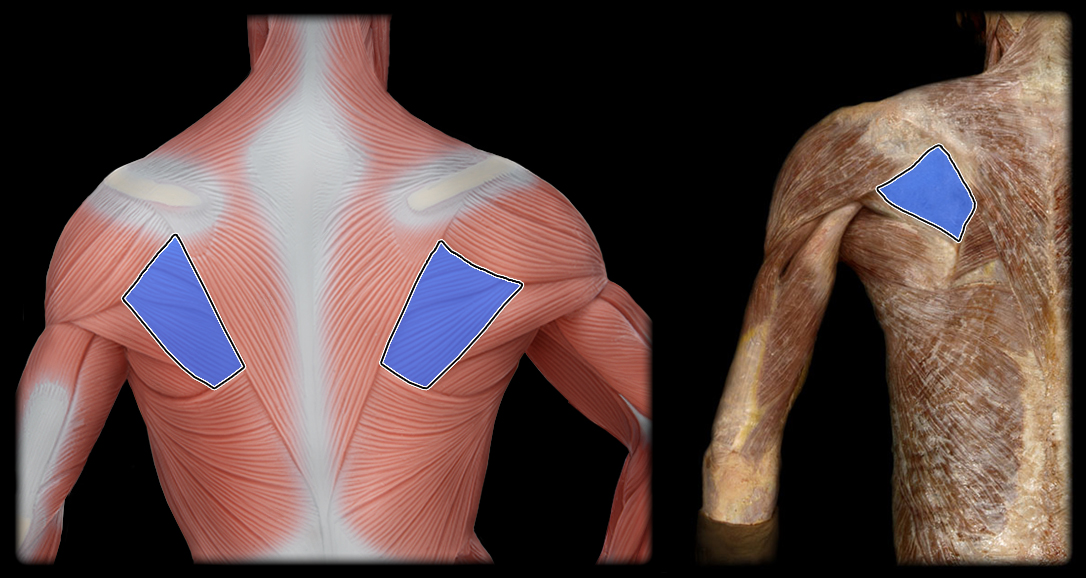
insertion of the infraspinatus
greater tubercle of humerus
action of infraspinatus
external rotation, horizontal abduction
innervation of infraspinatus
subscapular nerve
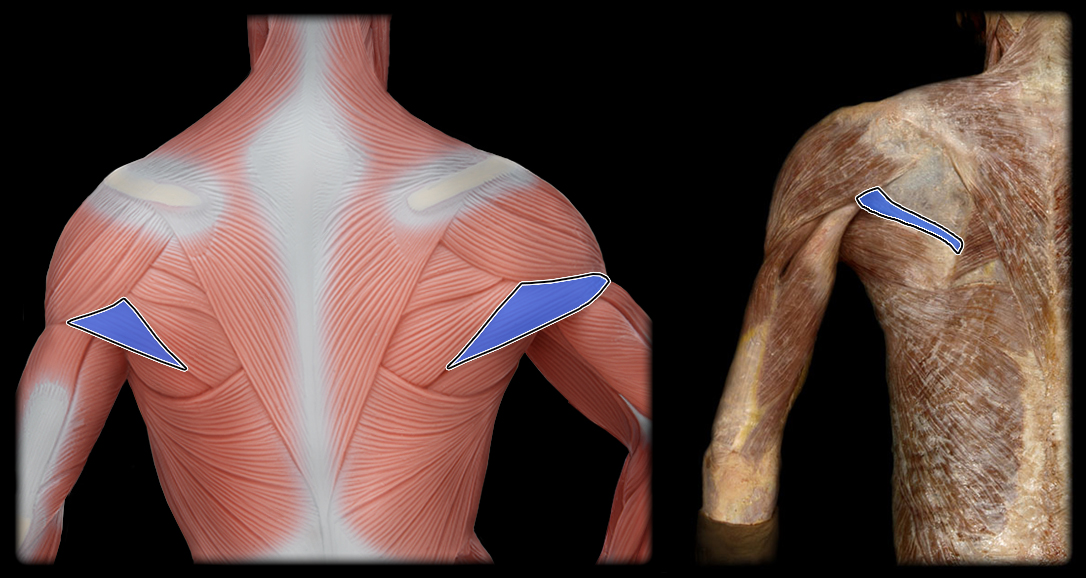
origin of teres minor
posterior lateral border of scapula
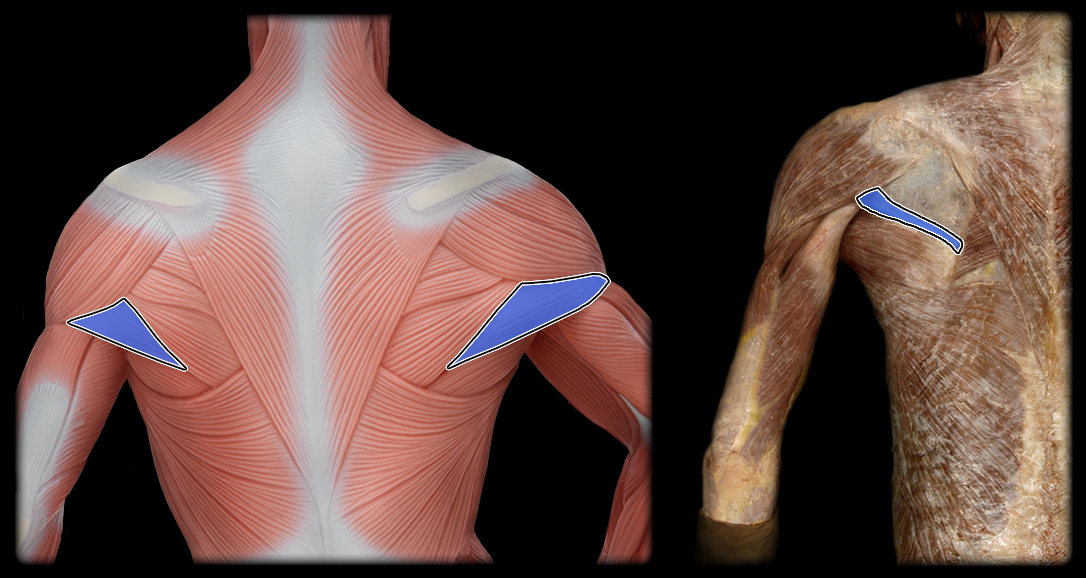
insertion of teres minor
greater tubercle of the humerus
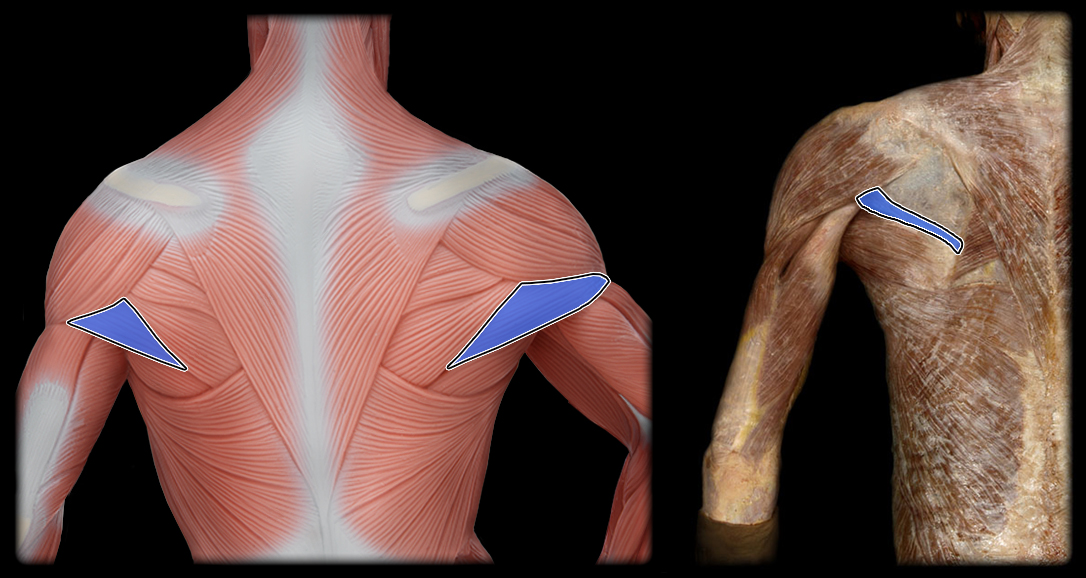
action of teres minor
external rotation, horizontal abduction
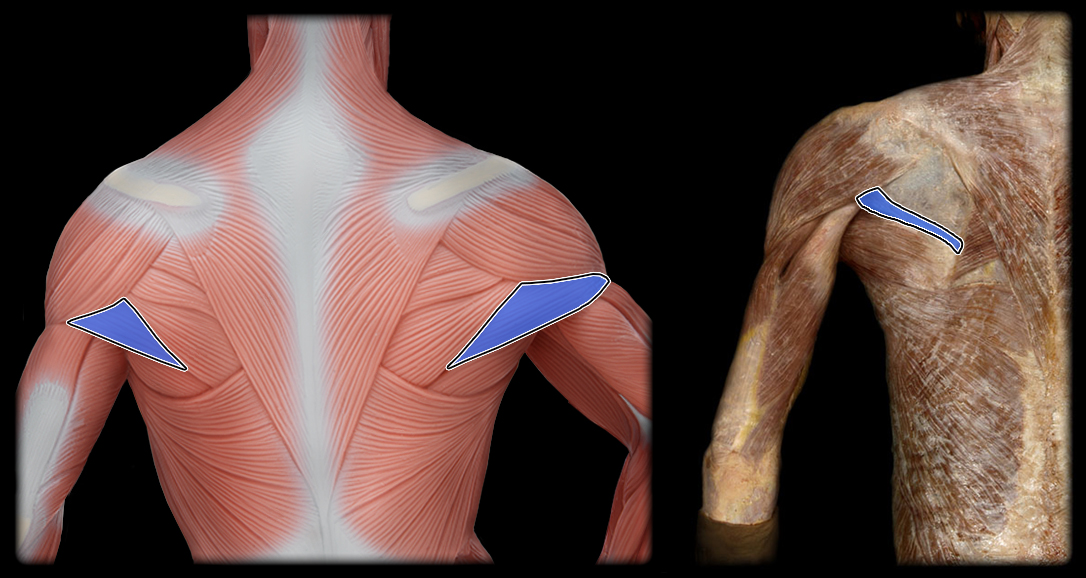
innervation of teres minor
axillary nerve
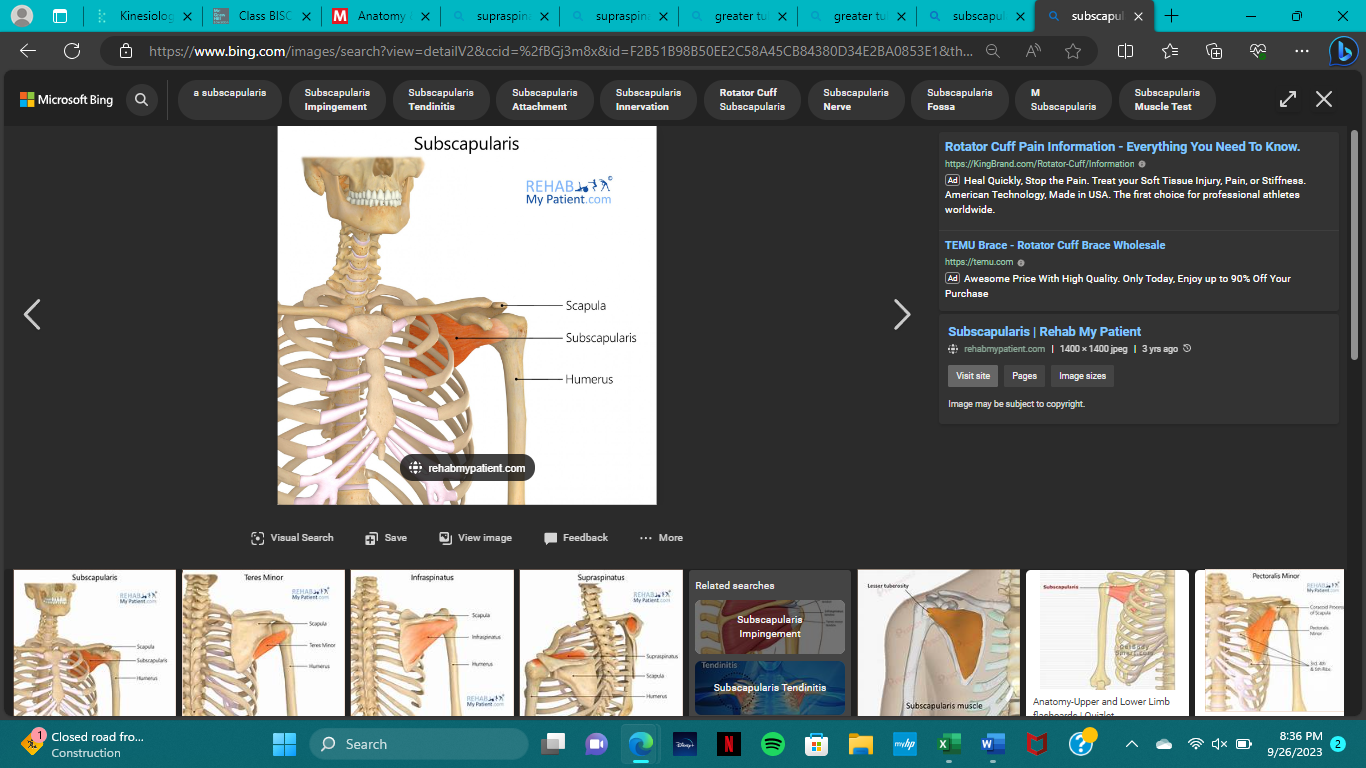
origin of subscapularis
subscapular fossa of scapula (ant.)
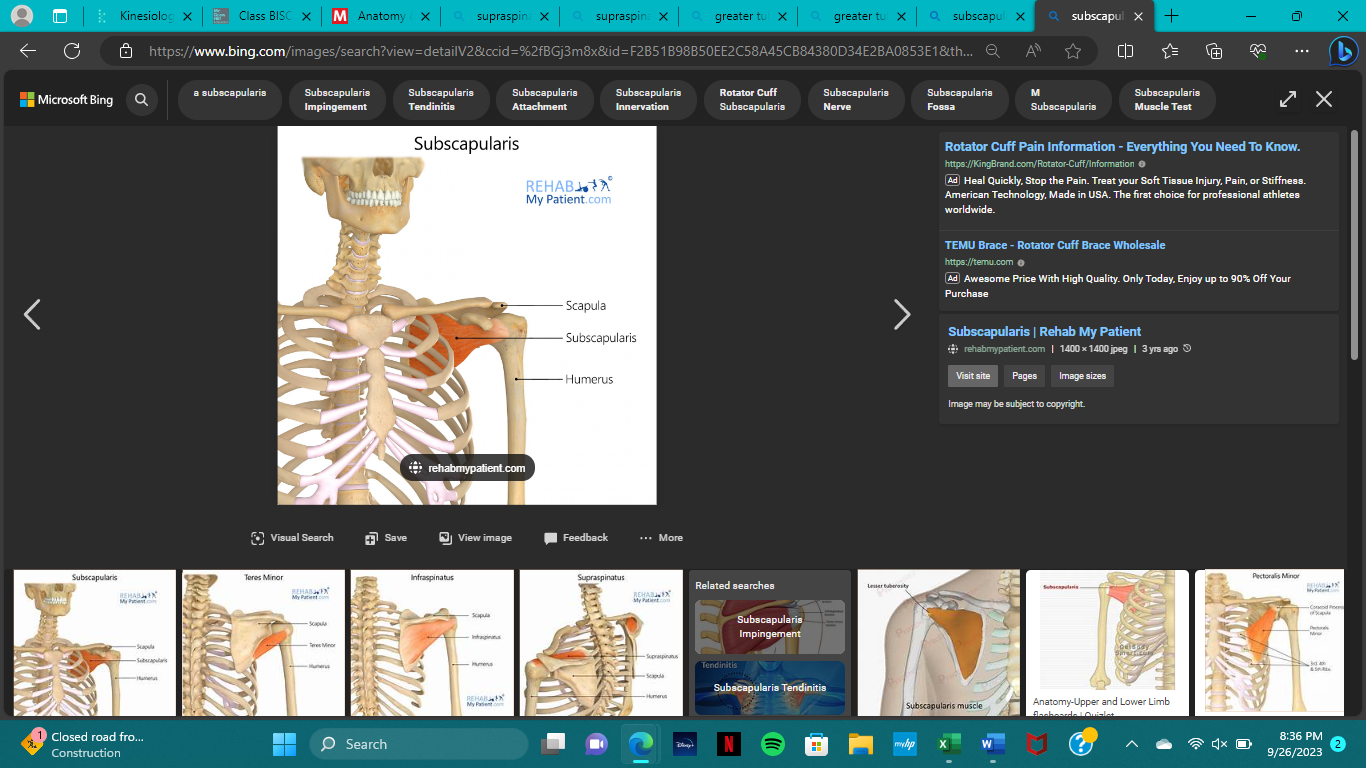
insertion of subscapularis
lesser tubercle of humerus
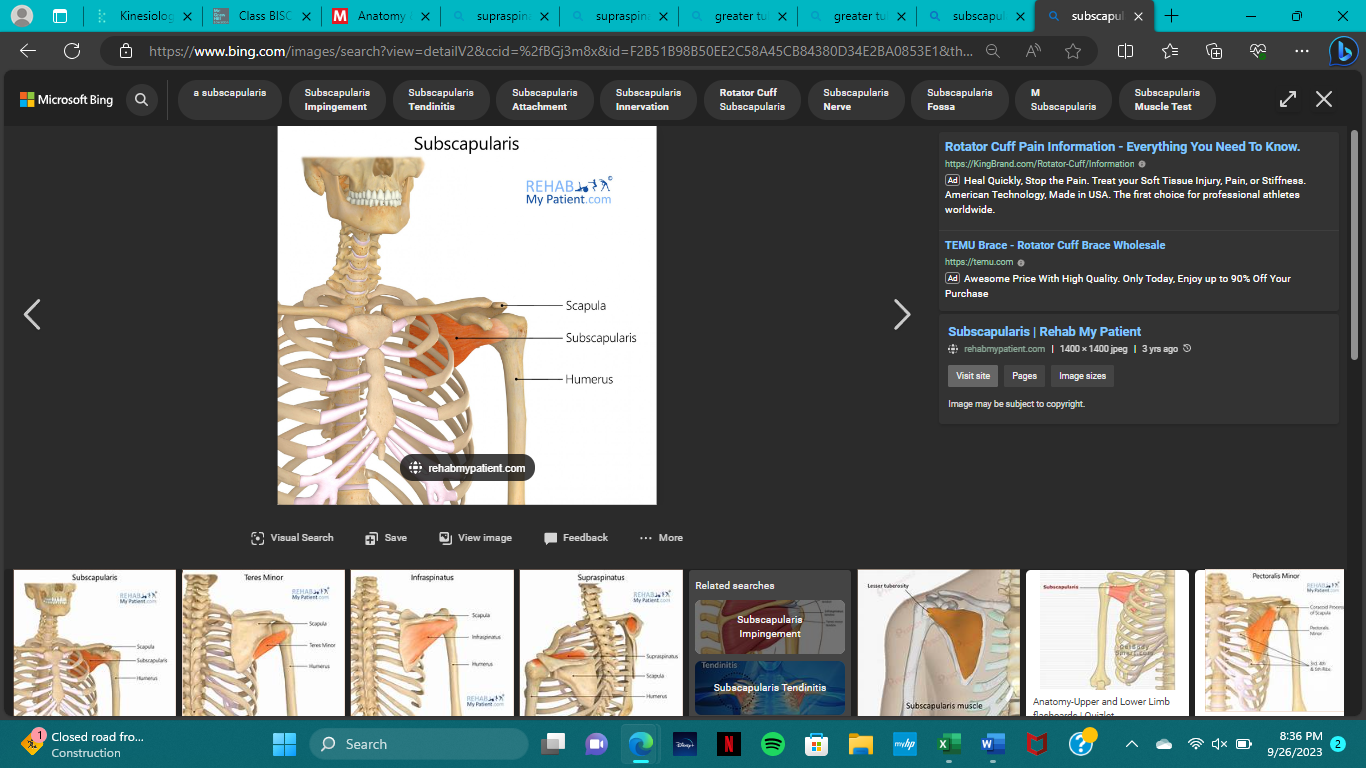
action of subscapularis
medial rotation
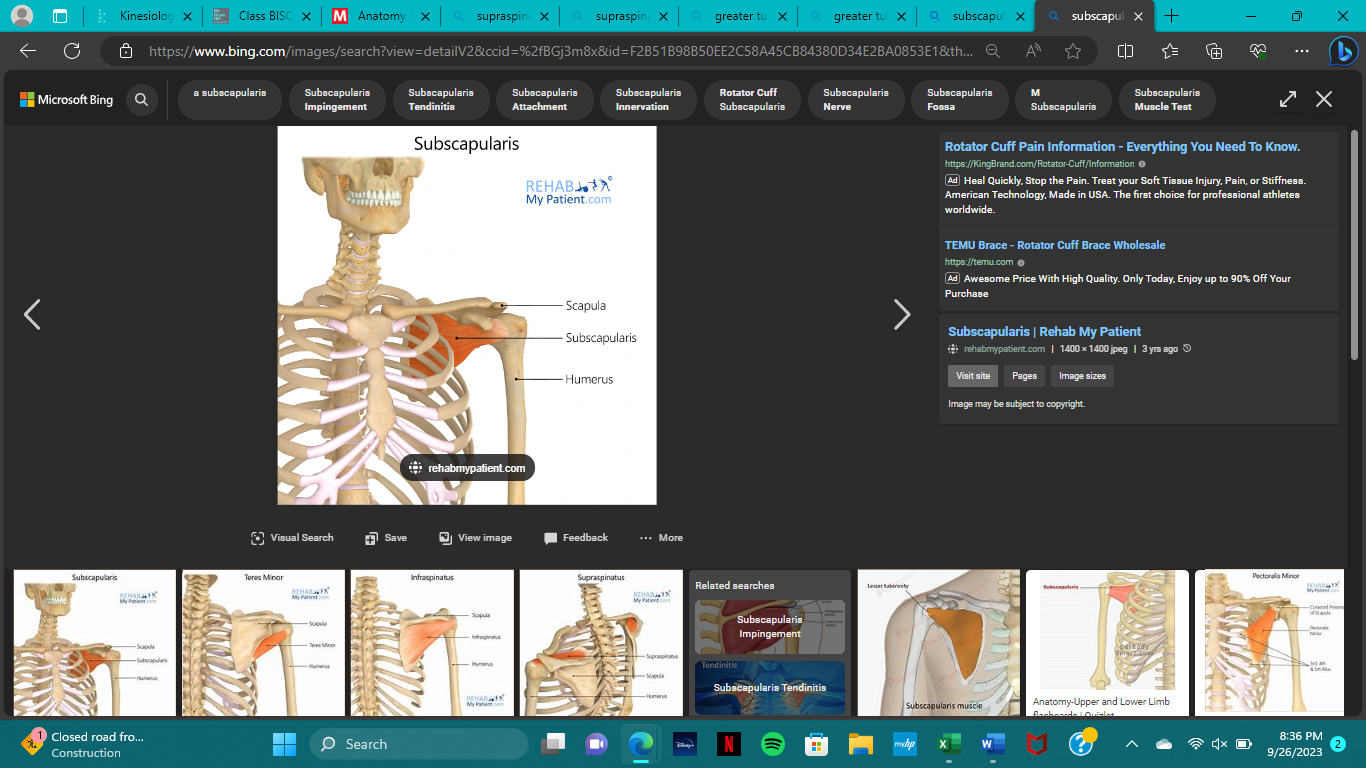
innervation of subscapularis
subscapular nerve
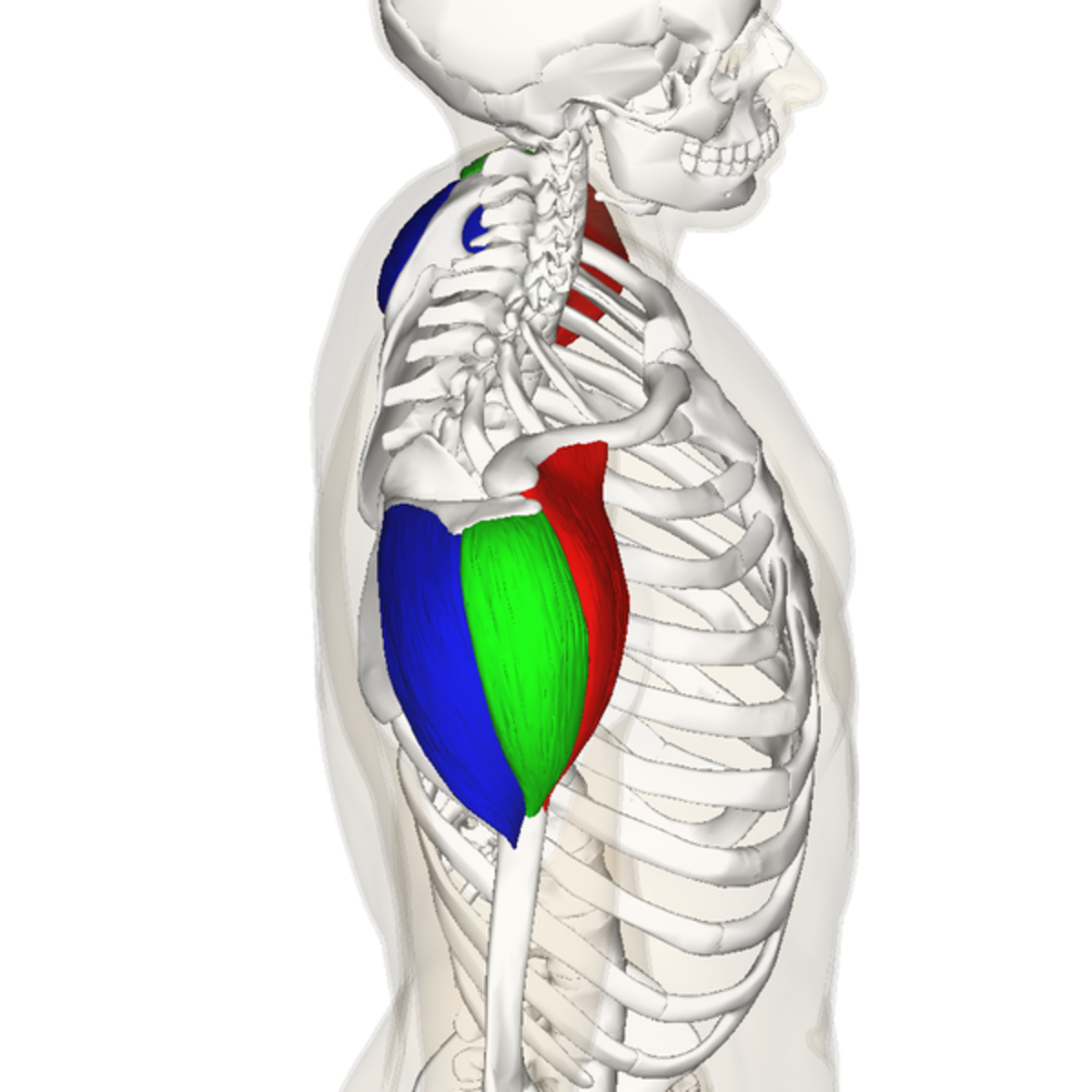
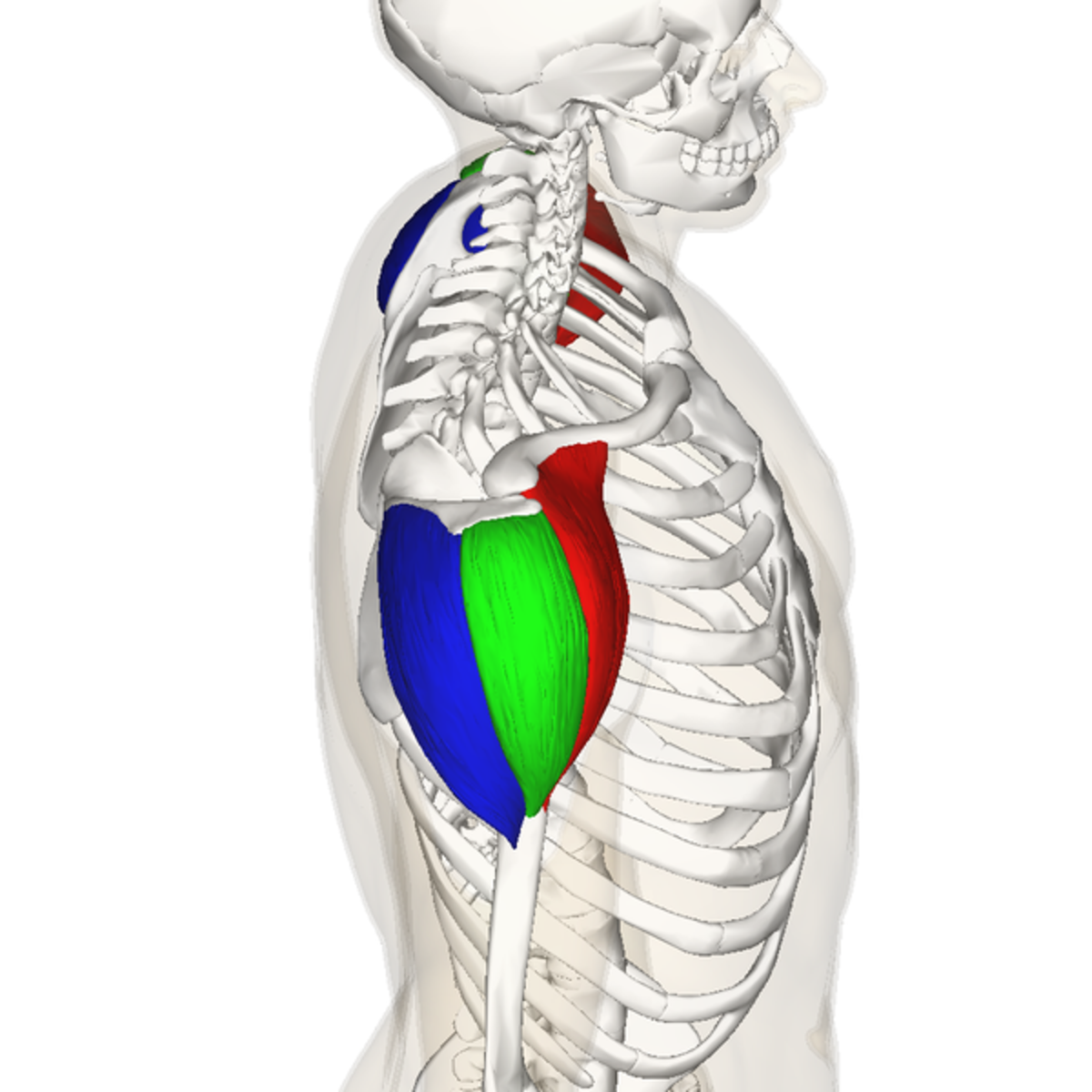
origin of anterior deltoid
outer 1/3 clavicle, top acromion scapular spine
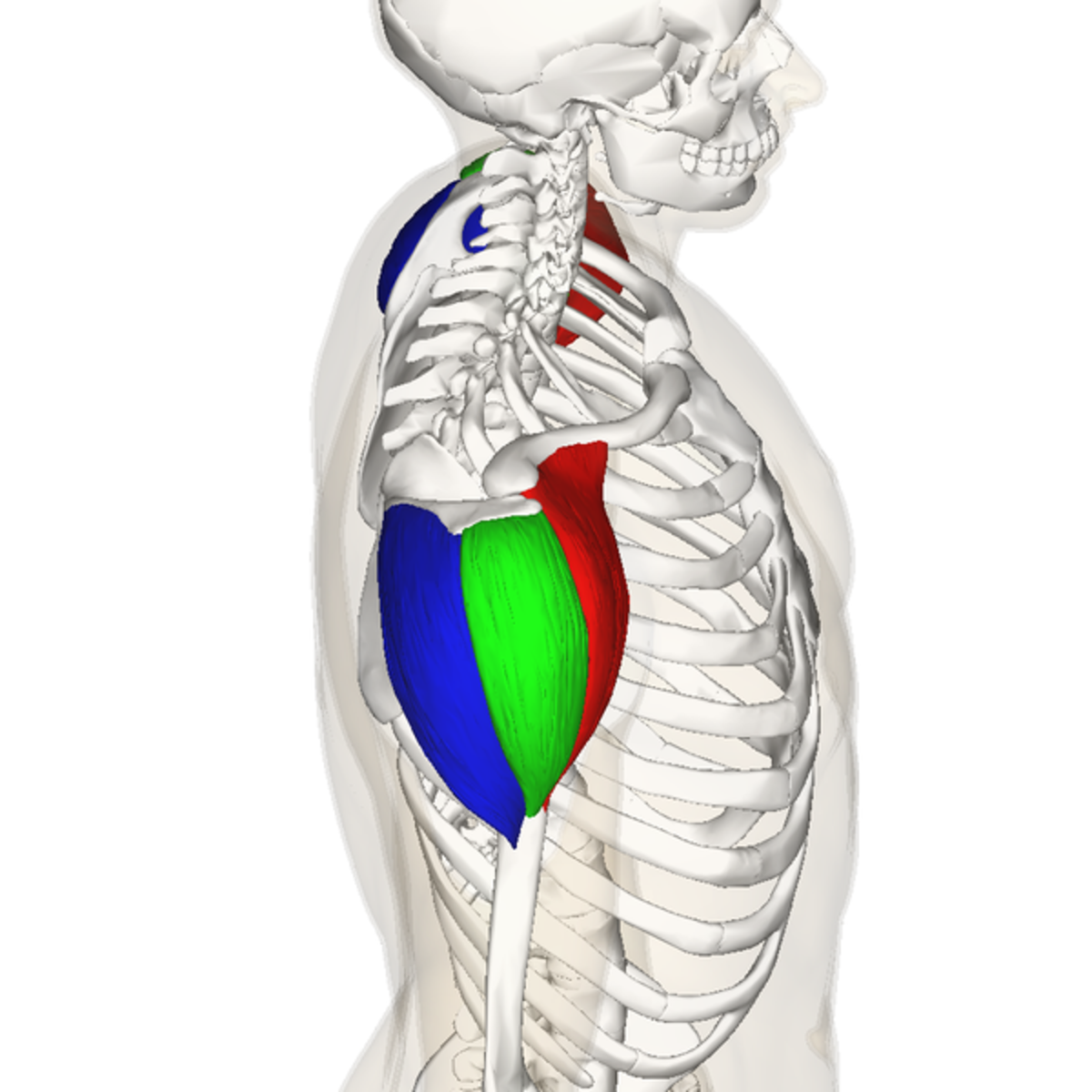
insertion of anterior deltoid
deltoid tuberosity of the humerus
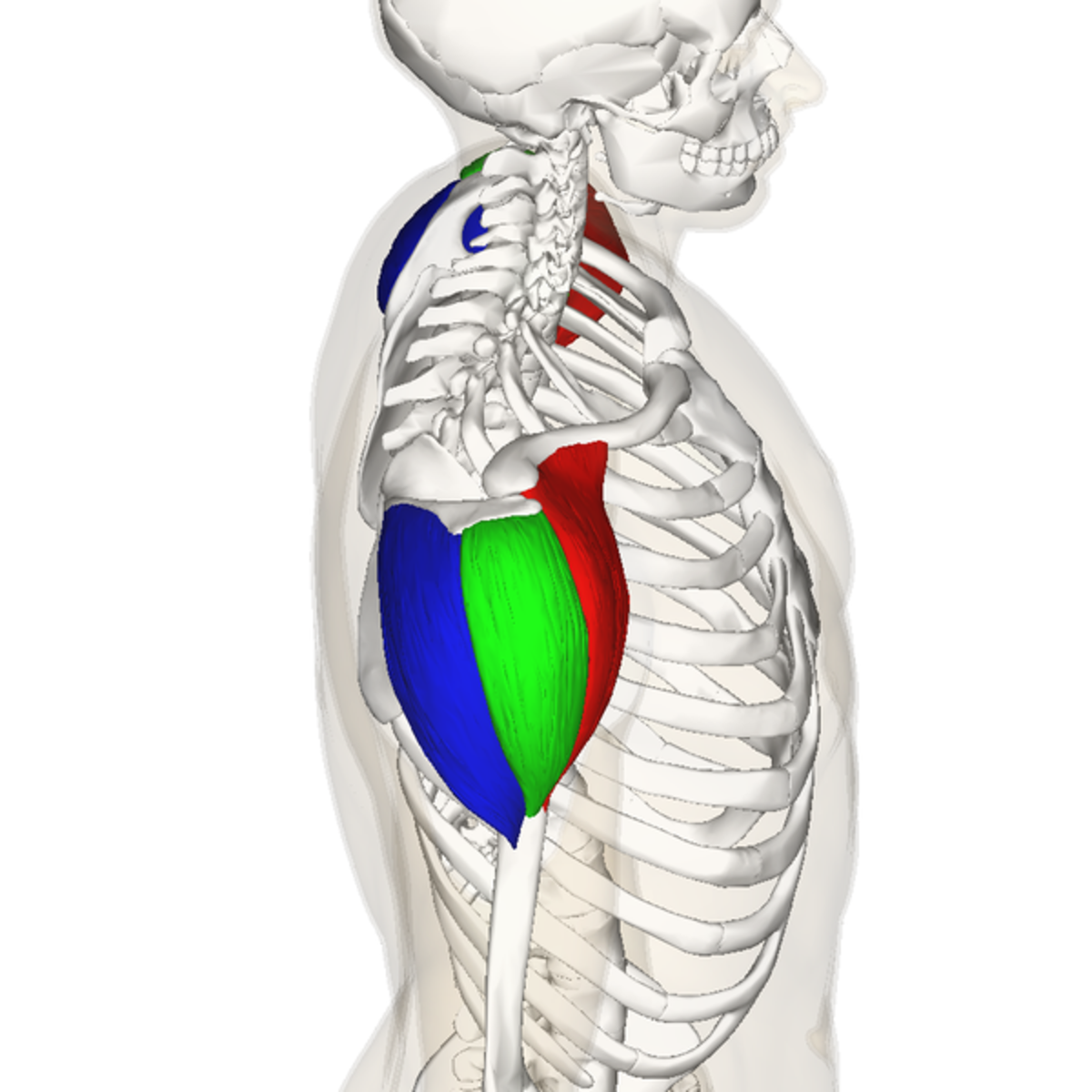
action of anterior deltoid
flexion, horizontal adduction, medial rotation
innervation of the anterior deltoid
axillary nerve
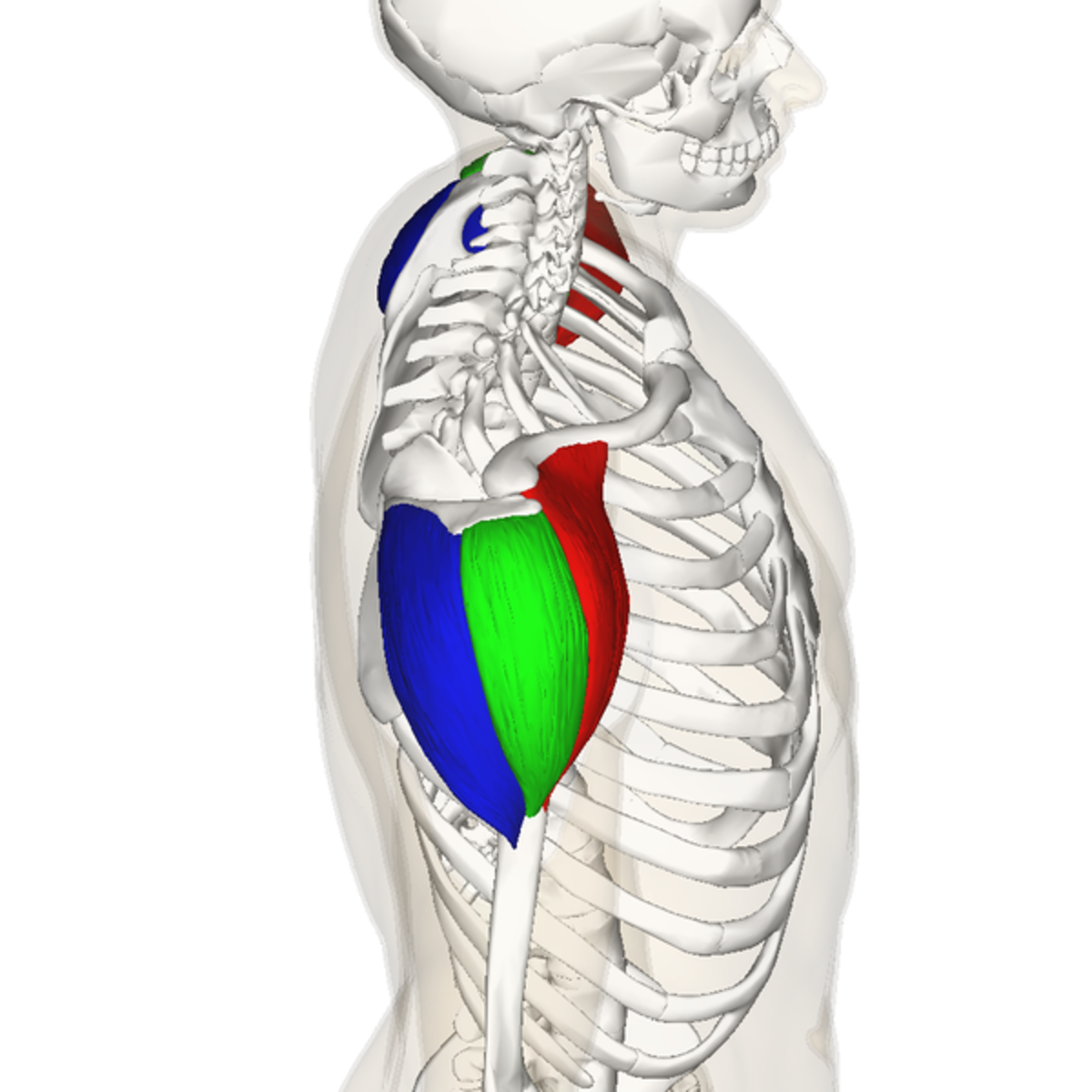
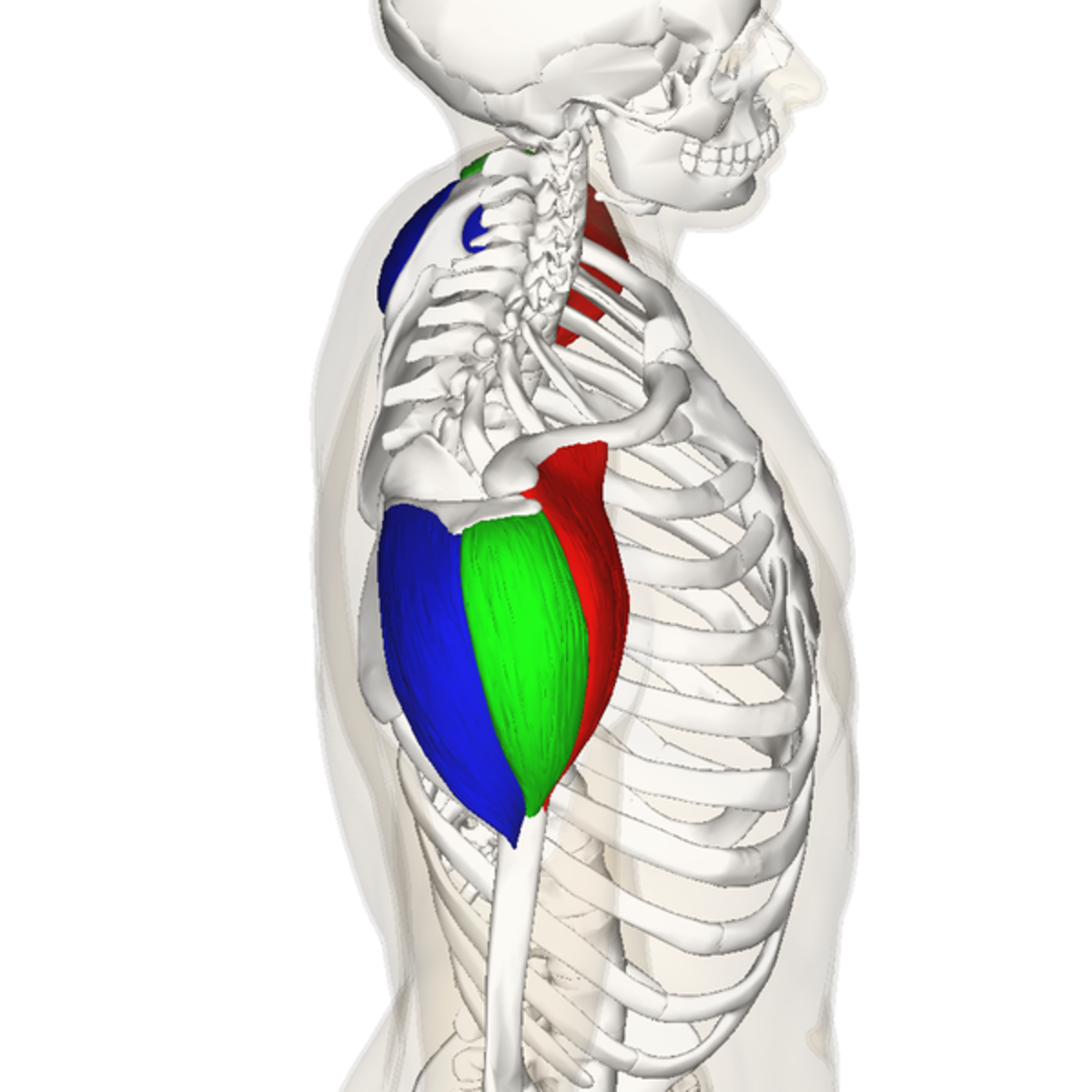
origin of middle deltoid
outer 1/3 clavicle, top of acromion scapular spine
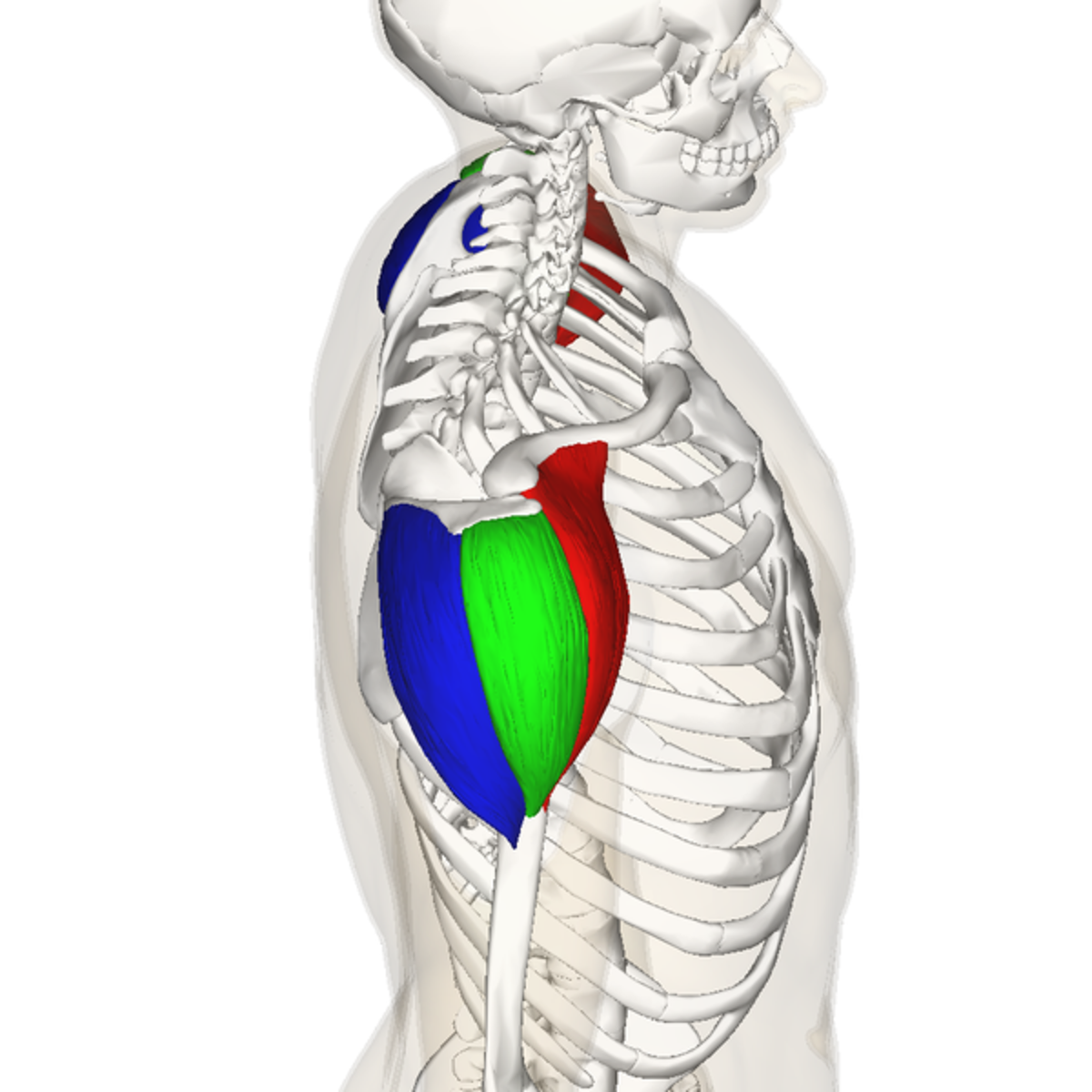
insertion of middle deltoid
deltoid tuberosity of the humerus
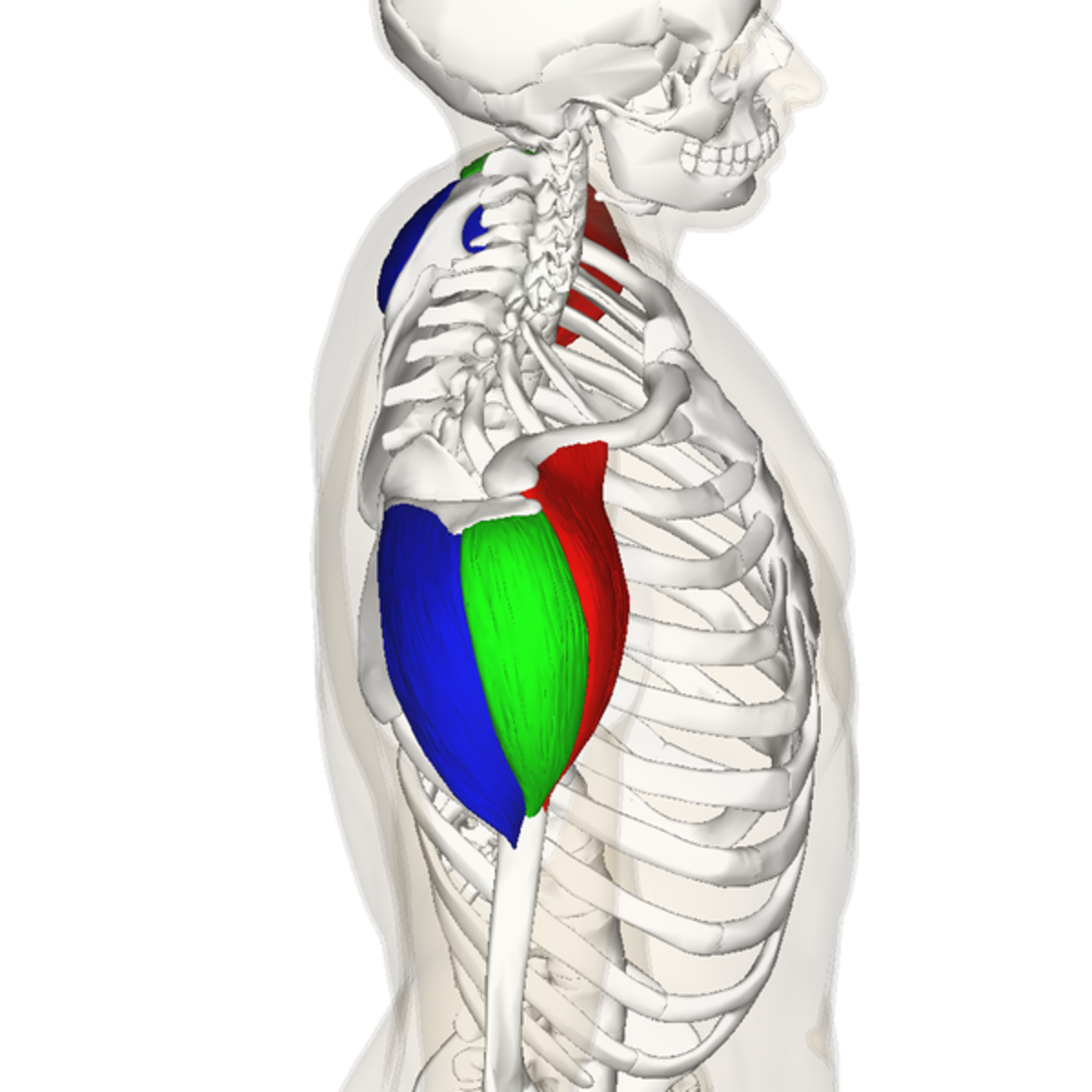
action of middle deltoid
abduction, horizontal abduction
innervation of middle deltoid
axillary nerve
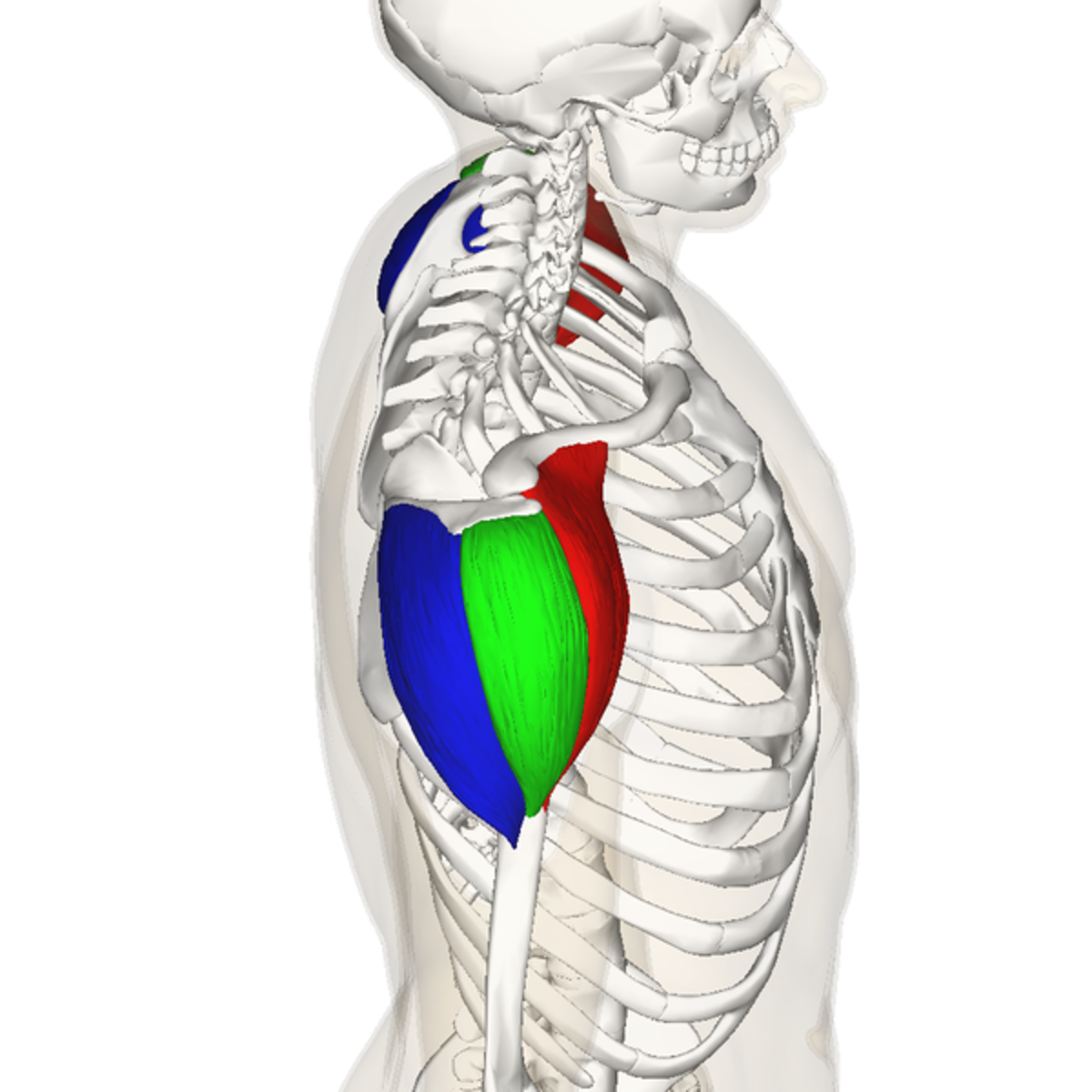
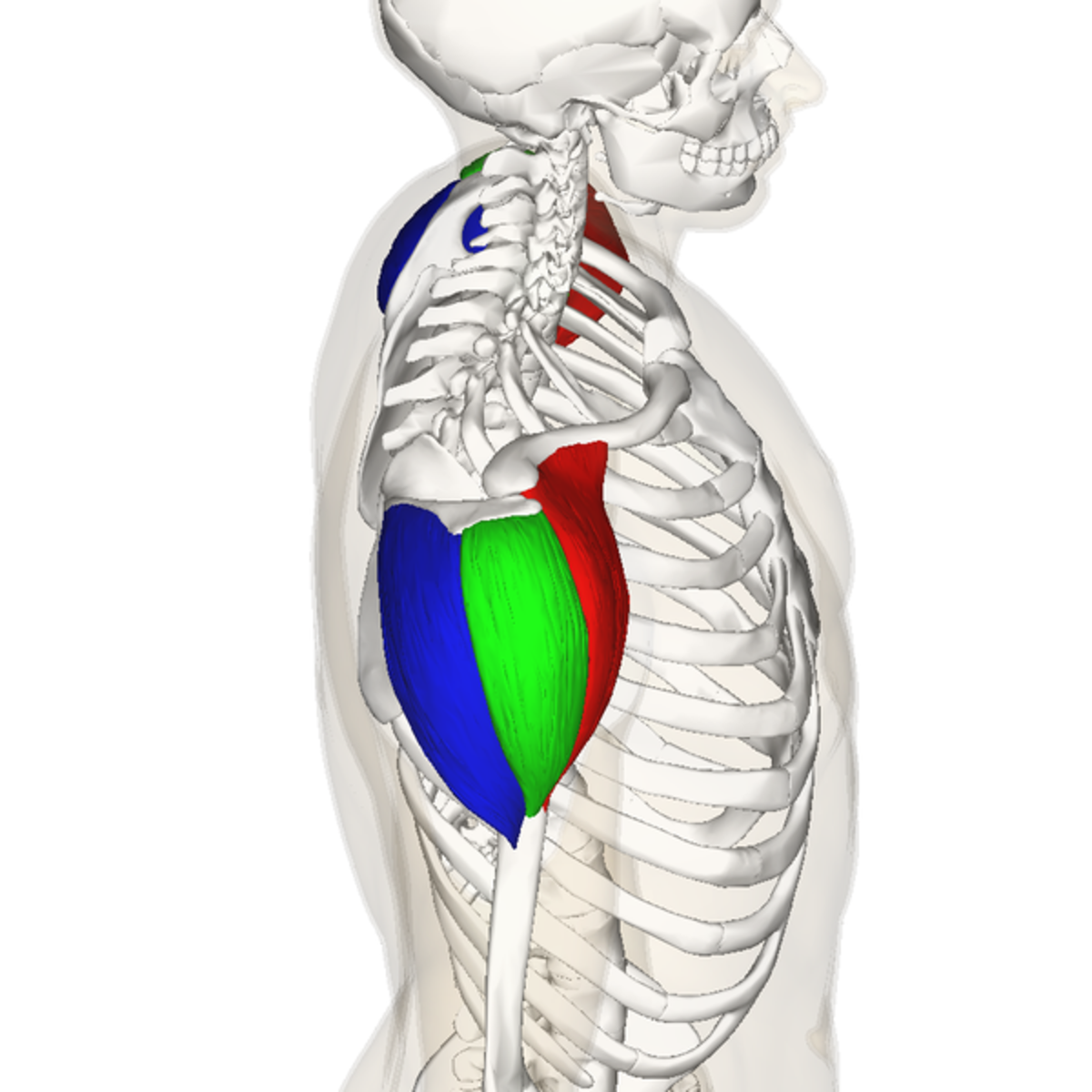
origin of posterior deltoid
outer 1/3 clavicle, top of acromion scapular spine
insertion of posterior deltoid
deltoid tuberosity of the humerus
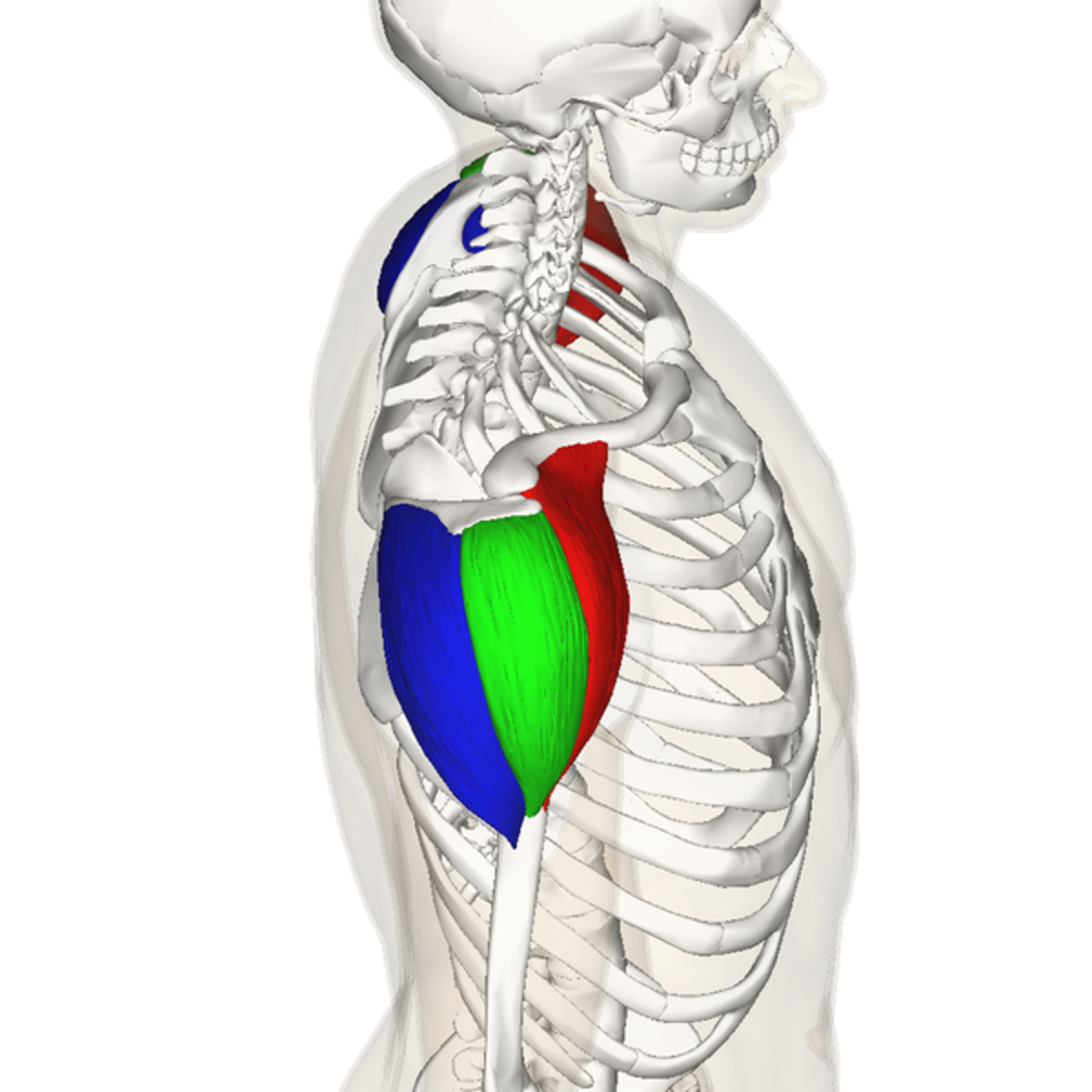
action of posterior deltoid
extension, horizontal abduction, external rotation
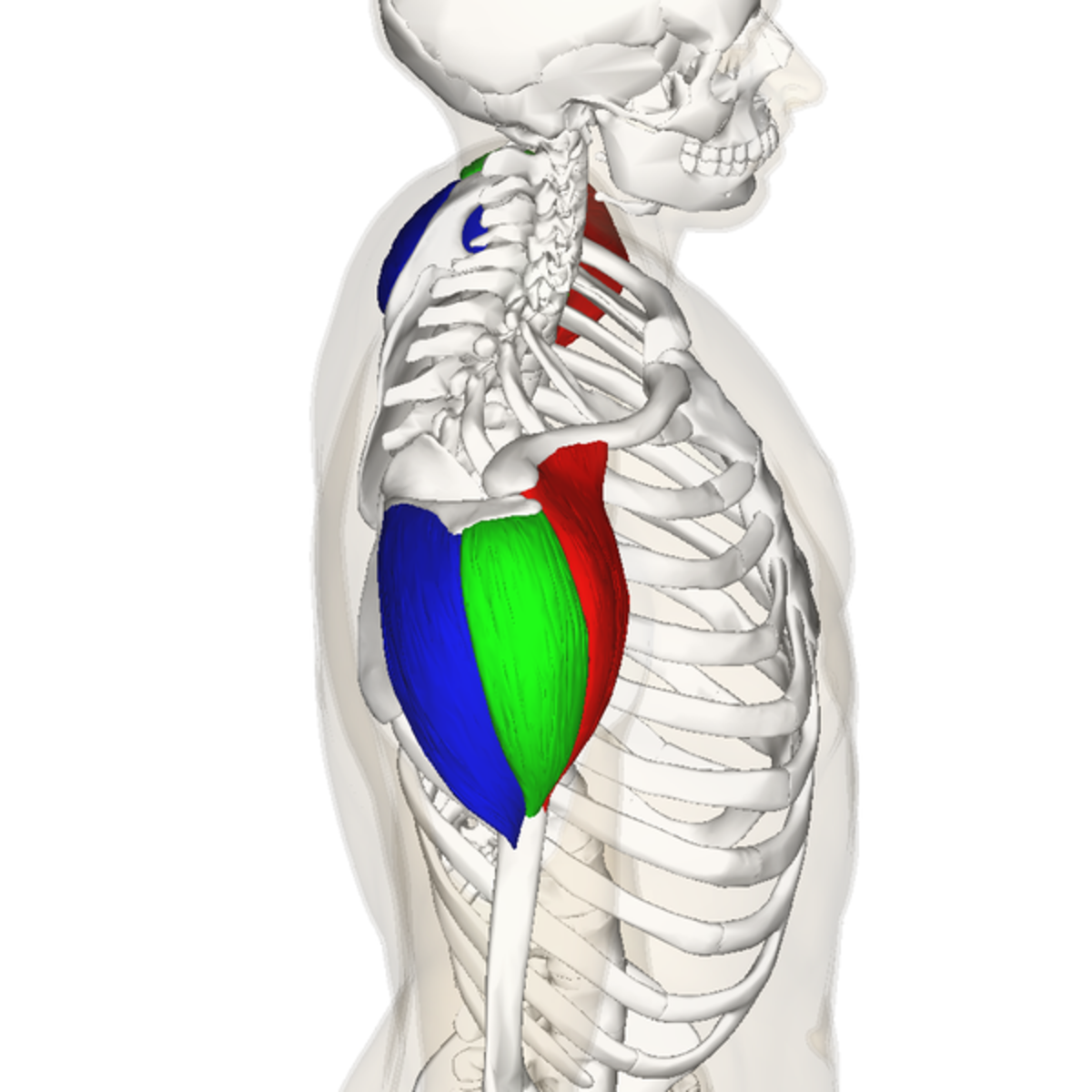
innervation of posterior deltoid
axillary nerve
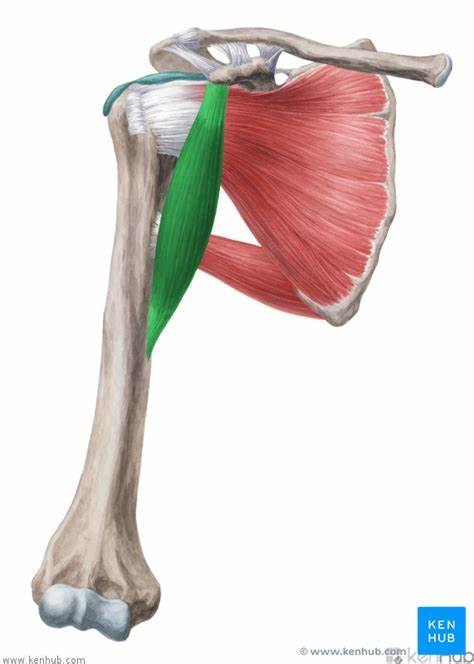
origin of coracobrachialis
coracoid process of the scapula
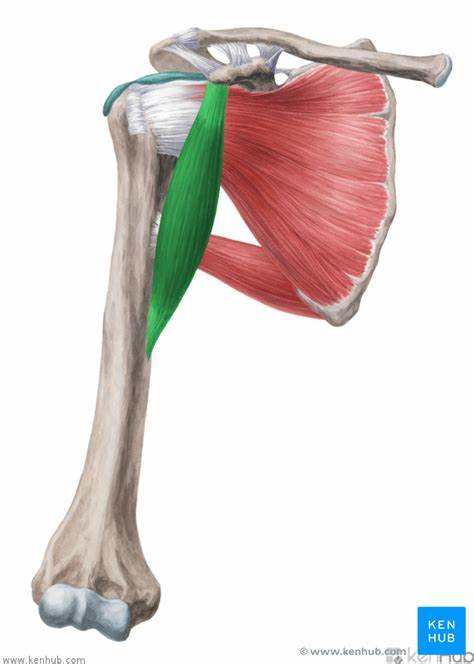
insertion of coracobrachialis
medial anterior humerus
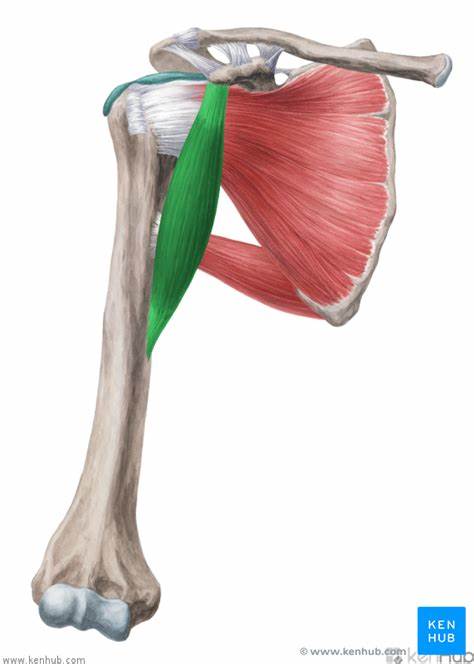
action of the coracobrachialis
flexion, adduction, horizontal adduction
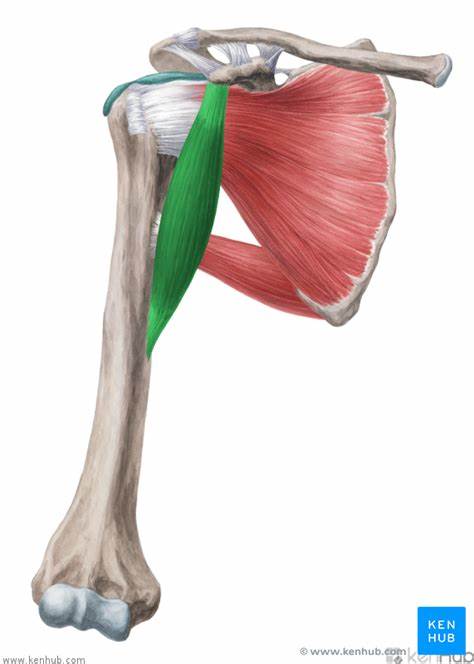
innervation of the coracobrachialis
musculotaneous nerve
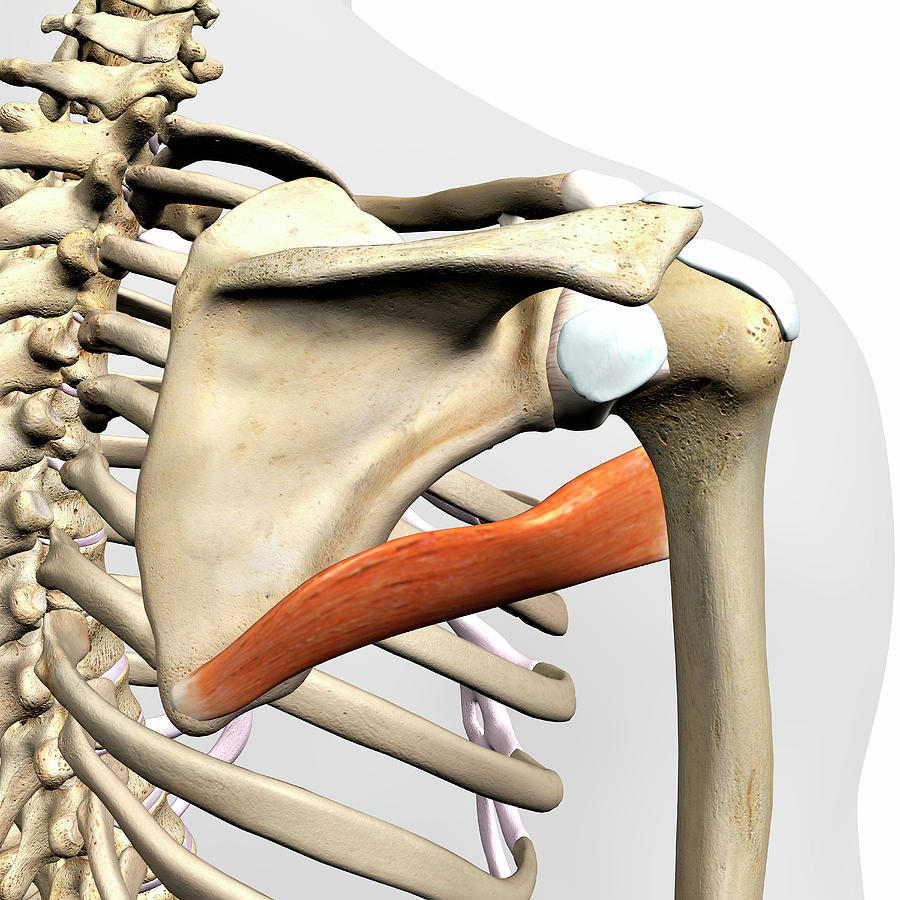
origin of Teres major
lower 1/3 of posterior lateral border (scapula)
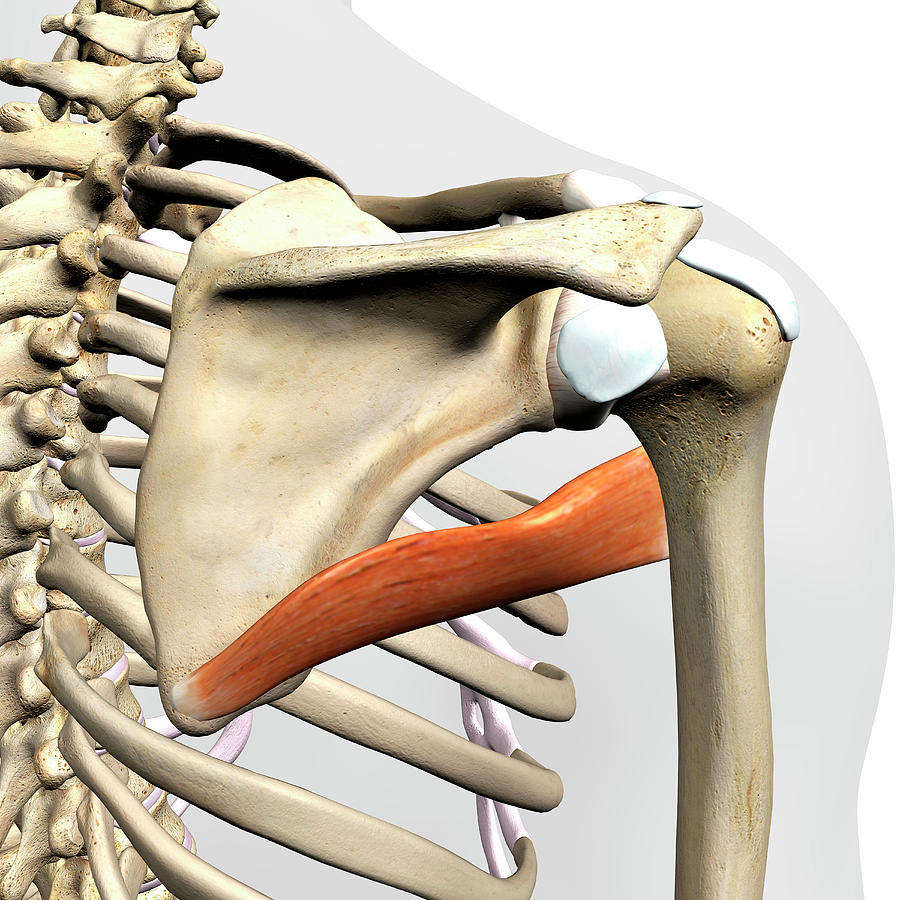
insertion of Teres major
anterior humerus
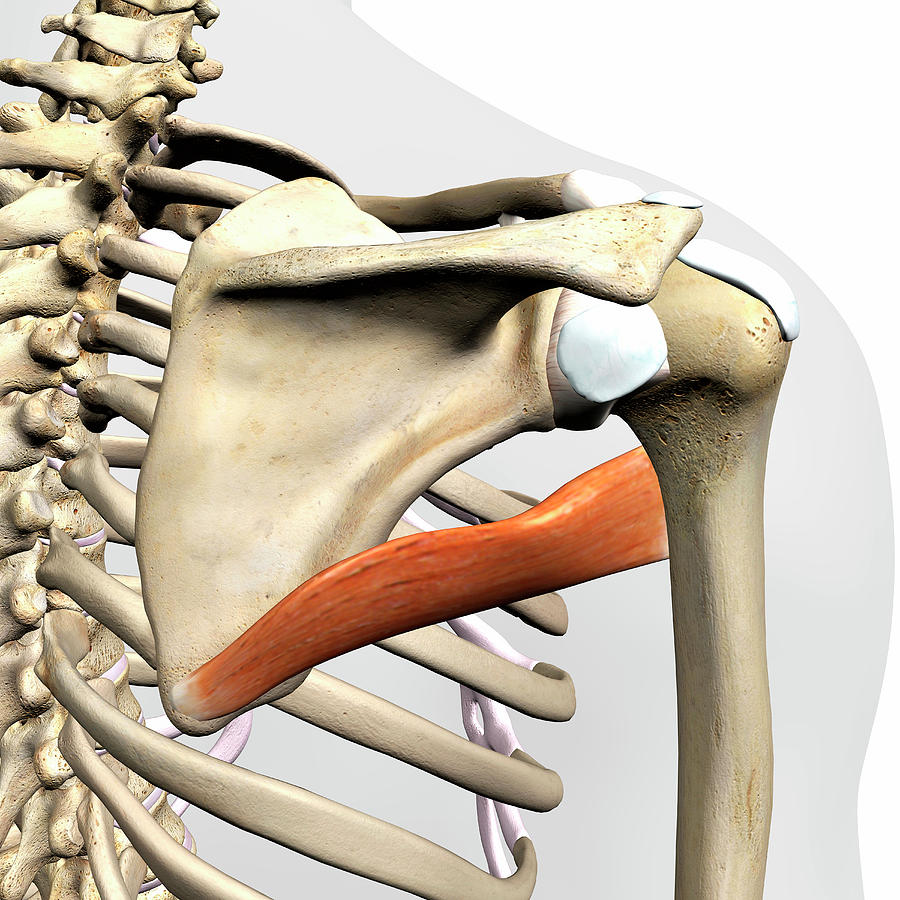
action of teres major
extension, adduction, medial rotation
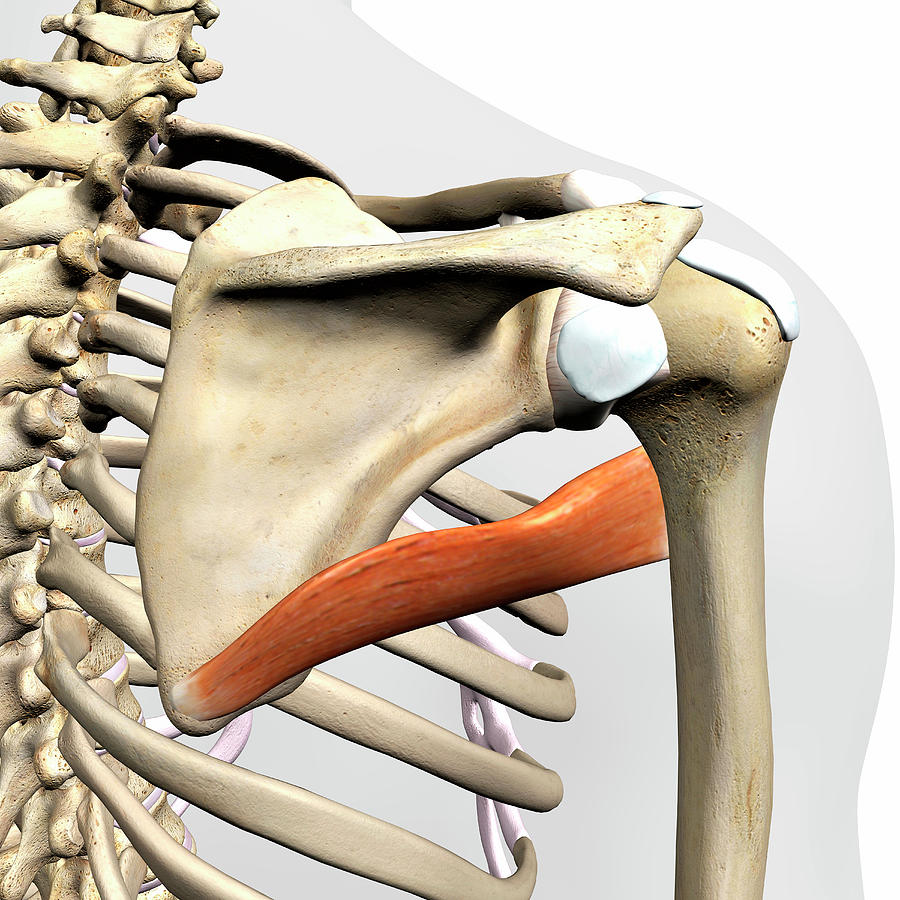
innervation of teres major
subscapular nerve
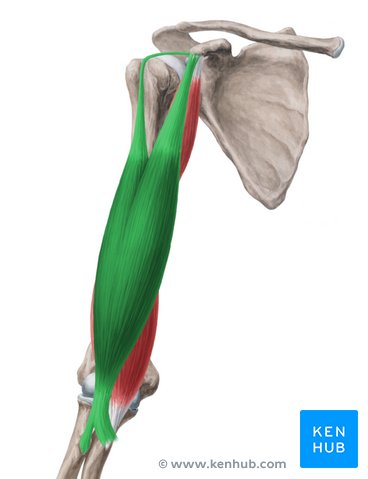
Origin of the Biceps brachii long head
supraglenoid tubercle
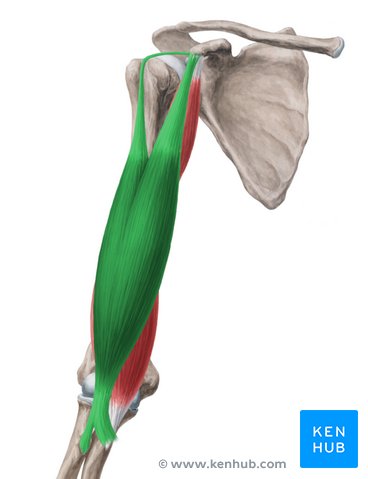
origin of biceps brachii short head
coracoid process
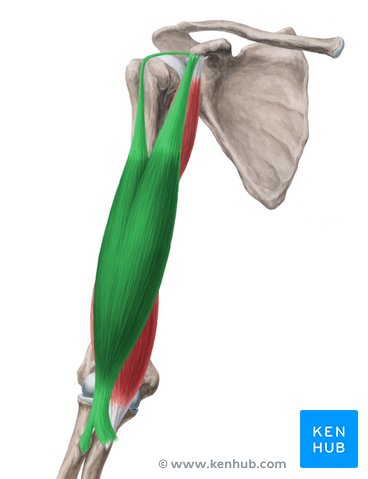
insertion of bicep brachii
radial tuberosity
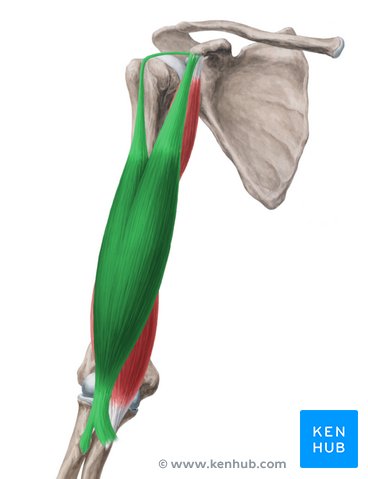
action of biceps brachii
abduction (long), flexion, adduction, medial rotation, horizontal adduction (short)
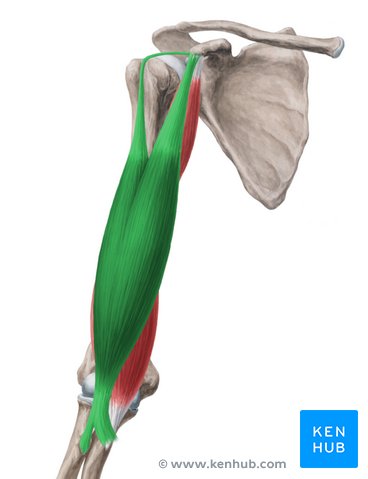
innervation of biceps brachii
musculocuntaneous
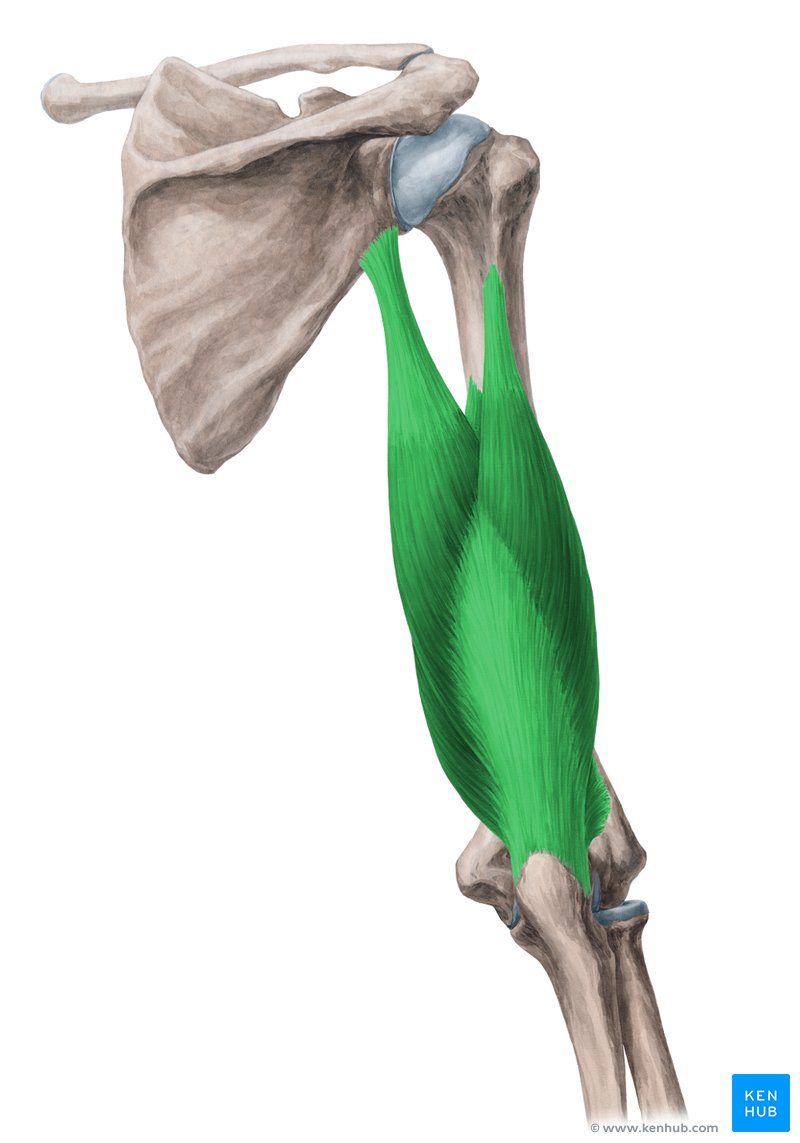
origin of triceps brachii
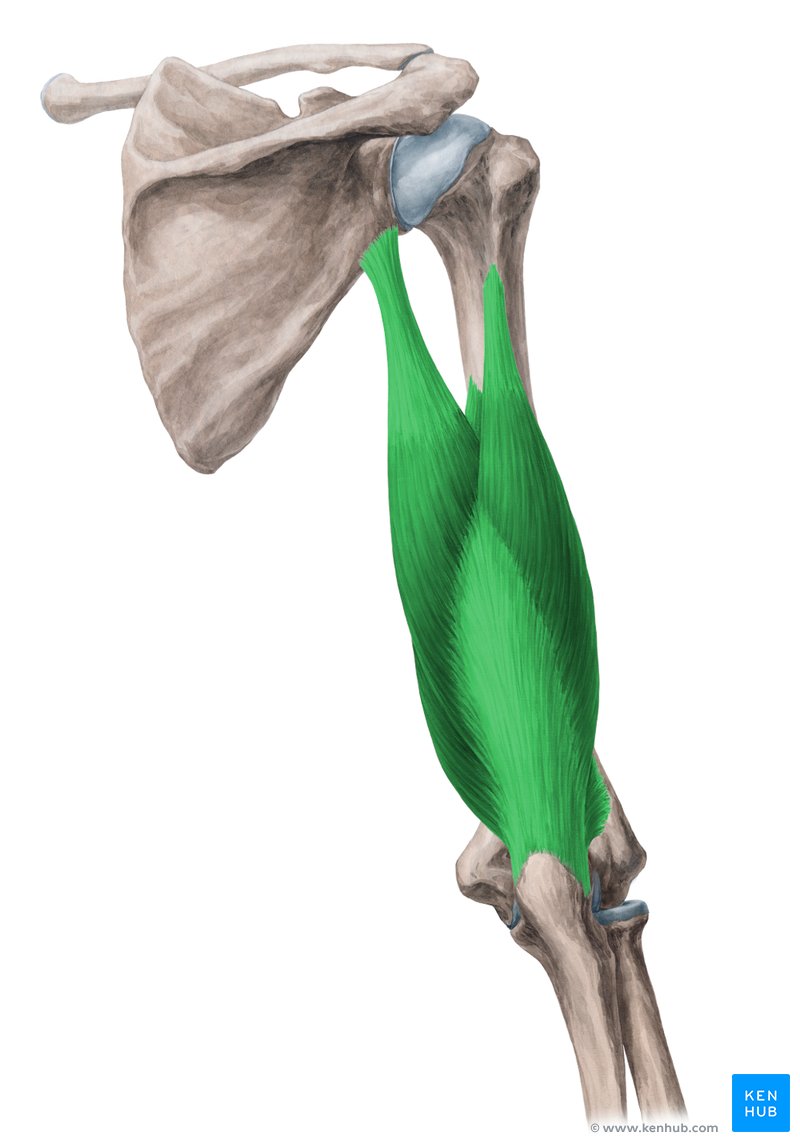
insertion of triceps brachii
post. olecranon process of the ulna
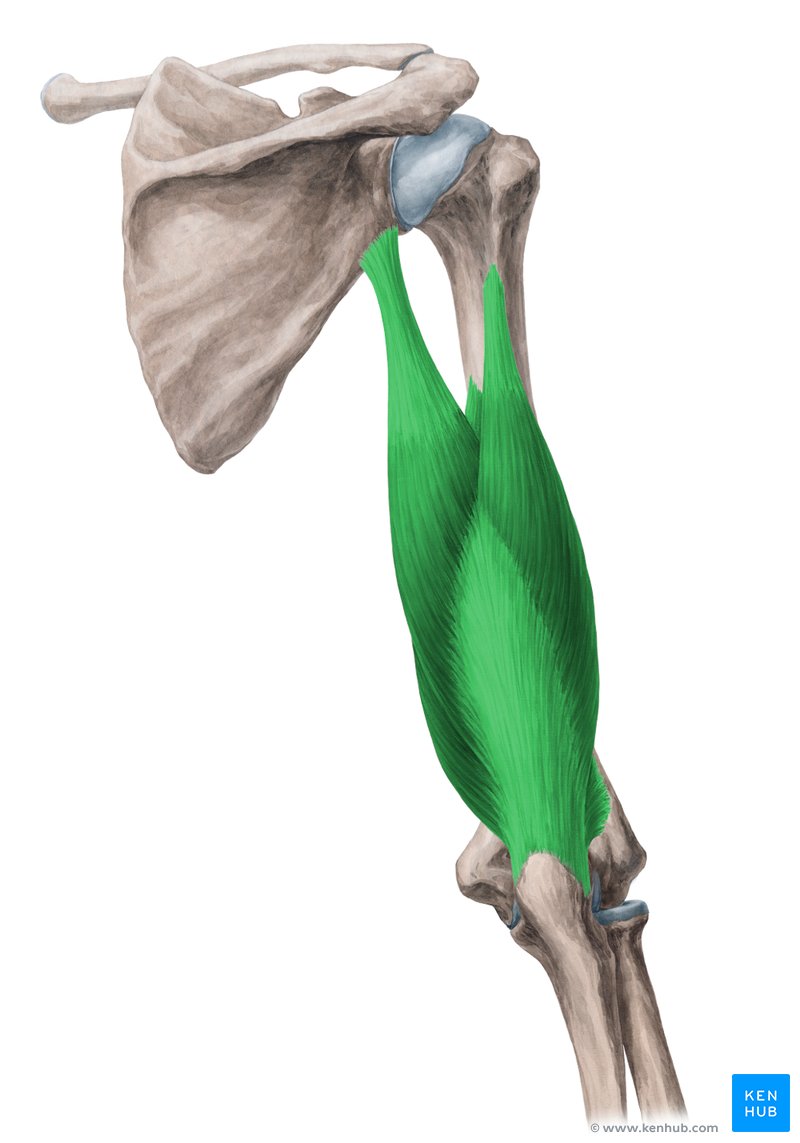
action of triceps brachii
extension, adduction
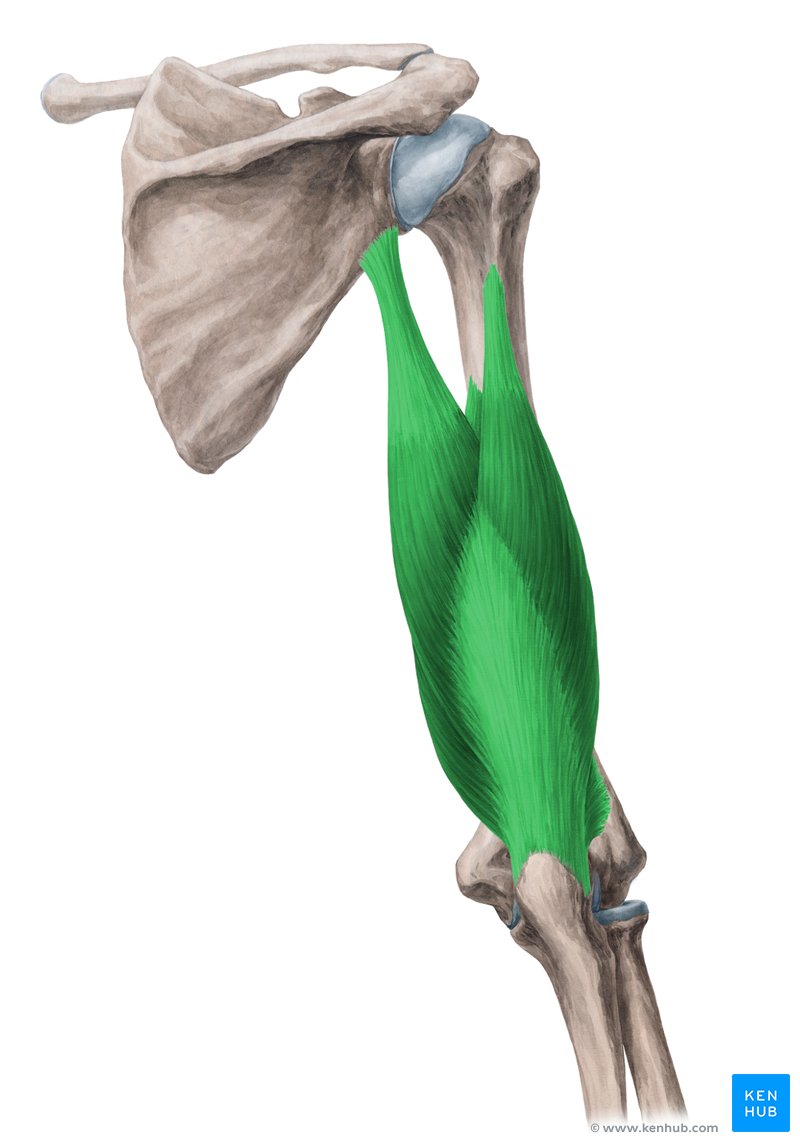
innervation of triceps brachii
radial nerve