Chapters 11, 12 Chemistry 102 - EXAM 1
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
intramolecular forces
covalent and ionic bonds that cause substances to form molecules and formula units; primarily impacts the chemical properties of substances
intermolecular forces
interactions that influence different properties of molecules such as phase, viscosity, surface tension, and more.
ion-dipole forces
an attractive force that results from the electrostatic attraction between an ion and a neutral molecule with a dipole (polar covalent).
smaller ions and/or higher charges will have stronger forms of these interactions
dipole-dipole forces
an attractive force that results from the electrostatic attraction between the positive dipole of one molecule and the negative dipole of another.
this type of IMF typically with polarity
london dispersion forces (LDFs)
type of IMF where the random motions of electrons in an atom or nonpolar molecule can cause the formation of an instantaneous dipole that induces dipoles in surrounding molecules
has a weak and short range
increases in strength with higher molecular weights and more linear molecules
Hydrogen bonding
a special type of dipole-dipole interaction that exists between the lone pair of the most electronegative atoms (O,N,F) and an H atom
much stronger than most dipole-dipole interactions and increases IMF to significant points beyond what is expected on the basis of mass
viscosity
resistance of liquid to flow
surface tension
resistance of liquid to spread out an increase its surface area
vapor pressure
partial pressure of a gas in equilibrium w/ a liquid at a constant temperature
normal boiling point
temperature at which boiling occurs at exactly one atmosphere
normal melting point
temperature at which melting occurs at exactly one atmosphere
critical point
combination of temperature and pressure beyond which a gas cannot be liquified
supercritical fluid
a state of matter beyond the critical point that is neither liquid nor gas
solid
state of matter wherein the forces between the atoms, ions or molecules are sufficiently strong to hold the particles in fixed positions, where they vibrate but have little to no translational or rotational motion
amorphous solid
state of matter where atoms, molecules or ions are distributed randomly in solid
crystalline solid
state of matter where ions, atoms or molecules are organized in a structured/repeating pattern
molecular solid
solid composed of individual molecules with IMFs holding the particles in the solid state
soft, does not conduct electricity
metallic solid
solids composed solely of metal atoms
hard or soft and conducts electricity
ionic solid
solid composed of ions attracted to one another via electrostatic attraction
hard and brittle; conducts electricity in solution
covalent network solid
solid consisting of atoms covalently bonded to one another in a 3-dimensional array
hard and typically does not conduct electricity (in most cases)
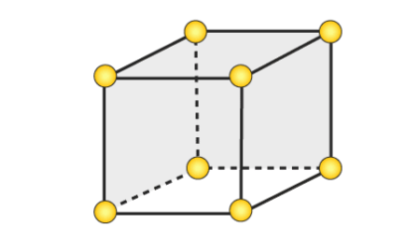
simple cubic unit cell
unit cell where atoms are arranged in a 3-dimensional cube with an atom in each corner
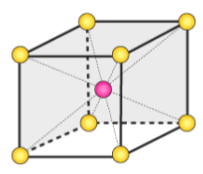
body centered unit cell
unit cell where atoms are arranged in a 3-dimensional cube with an atom in each corner, as well as one in the center
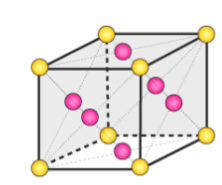
face centered unit cell
unit cell where atoms are arranged in a 3-dimensional cube with an atom in each corner, as well as one in the center of each face of the cube