Unit 4 - Histology
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Roles of blood vessels
transport blood (hormones, oxygen, nutrients), circulation of white blood cells, removal of waste
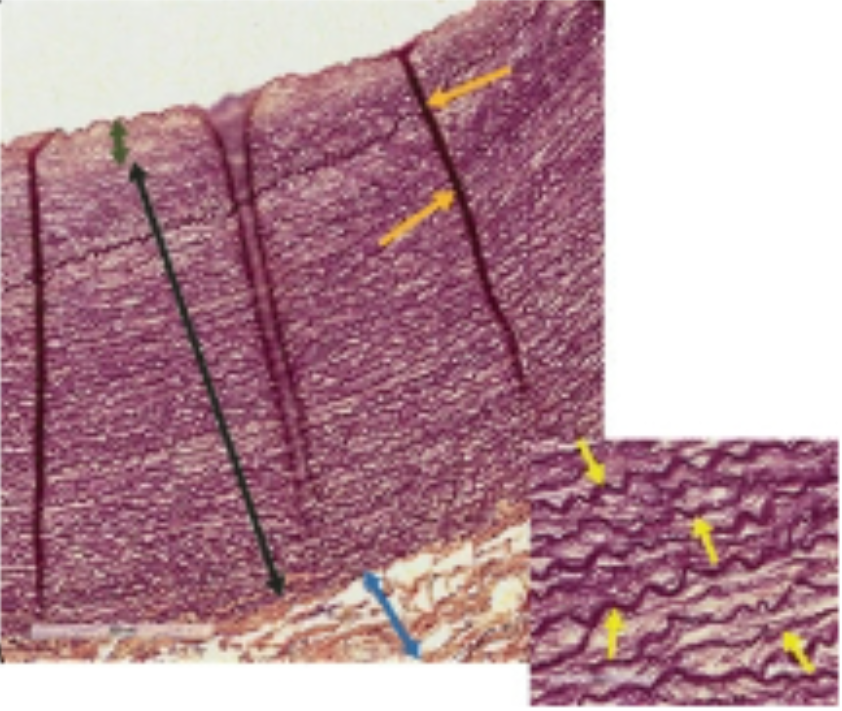
tunica intima
internal layer of blood vessels consisting of endothelium and connective tissue
tunica media
middle layer of blood vessels consisting of smooth muscle cells
tunica externa (adventitia)
outer layer of blood vessels consisting of connective tissue
tunica intima
what is this
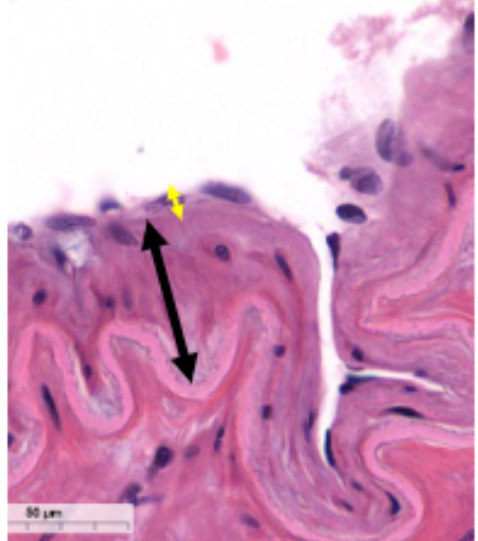
tunica media
what is this (black arrow)
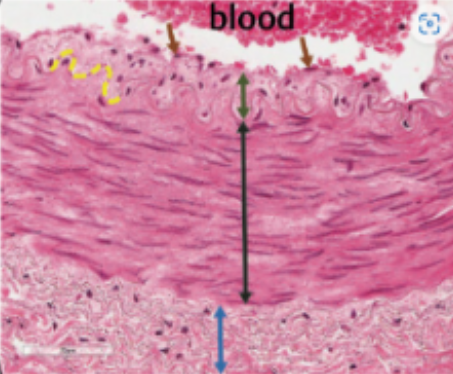
tunica externa
what is this (blue arrow)
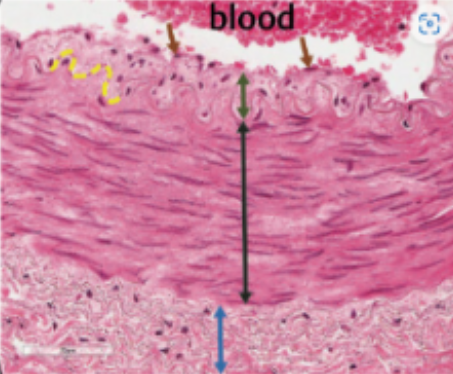
elastic lamina
elastic sheets that may be present in blood vessels, situated between the three layers; role of support and barrier
capillaries
transport blood between arteries and veins, and distribute nutrients to organs
elastic arteries
receive blood from heart; consist of lots of elastic fibers; expand and recoil to allow for uniform blood flow
elastic arteries
what is this (wrinkles)
pericytes
supportive cells of capillaries
pericyte
what is this
continuous capillary
endothelial cells with tight junctions and basement membrane; only allows for passage of small, select molecules (nervous system, skin, and lungs)
fenestrated capillary
endothelial cells with fenestrations within the membrane allowing for more molecules to pass (kidneys, intestine)
sinusoid capillary
fenestrations without membranes between endothelial cells to allow proteins and blood cells to pass through (liver, bone marrow, spleen)
capillary bed
interwoven network of capillaries that supplies an organ
baroreceptors
monitor blood pressure in arteries
chemoreceptors
monitor changes in blood composition of O2, CO2, pH in arteries
blood components
erythrocytes, leukocytes, plasma
plasma components
water, ions, metabolites, albumin, clotting factors
myeloid cells
precursor cell for blood cells, found in bone marrow
erythrocytes (red blood cells)
no nucleus and very little organelles; filled with hemoglobin. shape maximizes gas exchange and provides flexibility to pass through capillaries. life span of 120 days
hemoglobin
iron-containing protein that carries oxygen
platelets (thrombocytes)
small, non-nucleated cells that promote blood clotting and wound repair to prevent blood loss. contain granules and have a life span of 10 days
alpha granules
contain a clotting agent and growth factors
delta (dense) granules
contain serotonin and calcium
pseudopodia
extended by activated platelets; enable adherence to neighboring platelets and other cells, and increases plasma membrane surface area
antiplatelet
decrease platelet aggregation
anticoagulant
decrease fibrin production
leukocytes (white blood cells)
cells of the immune system; destroy pathogens by phagocytosis; contain granules that contain digestive enzymes and cytokines (hormones)
antigen
molecule that stimulates the immune system (pathogen, part of a pathogen, dead cell…)
antibody
receptor on a leukocyte from adaptive immunity that binds to an antigen
granulocytes
abundant granules in their cytoplasm, often involved in innate response
agranulocytes
fewer or no granules in their cytoplasm, mostly involved in adaptive response
neutrophils
short lived cells that are part of the non-specific immune response. first type of leukocytes to arrive at sites of infection during the inflammatory response. they are involved in bacterial infection and immune disease
neutrophils
what is this (yellow arrow)
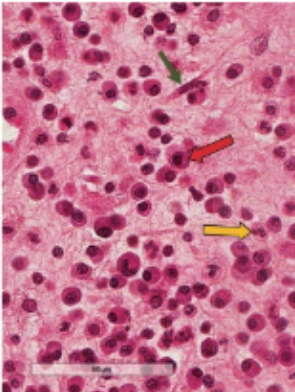
eosinophils
small percentage of leukocytes that live days to weeks in tissues and are part of the nonspecific response; involved in allergic reactions and destructions of large parasites
eosinophils
what is this
basophils
less than 1% of leukocytes with a short life span, involved in the non specific immune response; involved in allergic reactions
basophils
what is this
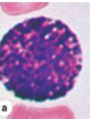
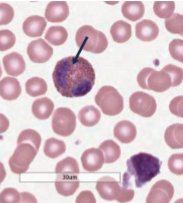
monocytes (agranolocytes)
largest white blood cells that live multiple days in blood until they enter tissues and become active; phagocytosis and antigen presentation; may develop into macrophages or dendritic cells, which activate the adaptive immune response
monocyte
what is this
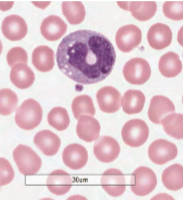
macrophage
respond to viral, microbial, and fungal contamination as well as cancer cell propagation; contain secretory granules used for phagocytosis
lymphocytes
30 percent of immune cells, involved in adaptive immunity; vary in life span from a few days to many years
b lymphocytes
humoral response; mature in bone marrow, respond to extracellular pathogen; may mature further into plasma cells
t lymphocytes
cell mediated immunity; mature in thymus, respond to intracellular pathogens
NK cells
mature in all lymphoid tissues, non-specific
hematopoiesis
production of all blood cells
hematopoietic stem cell
precursor of all blood cells
erythropoiesis
production of red blood cells
leukopoiesis
production of white blood cells
thrombopoiesis
production of platelets
bone marrow
the site of synthesis of all formed elements of the blood
red bone marrow
produces all blood cells; also contains some adipose cells and connective tissue
yellow bone marrow
stores adipose tissue, but can produce red blood cells in emergencies
sinusoids
allow newly formed blood cells to pass through them and enter the circulation
thymus
primary lymphoid organ developed from epithelial cells; site of T cell maturation
capsule
connective tissue that surrounds the thymus
trabeculae
extensions of the capsule that partition the thymus into lobules
cortex
darked outer portion of each lobule, contains immature T cells
medulla
central area of lobules containing mature T cells
epithelial reticular cells
present in the medulla; protect and favorize maturation; over time, come together and condense to form larger Hassall’s corpuscles
Role of kidneys
filter the blood to remove excess water, ions, molecules, and cellular waste through formation of urine; also secretion
renin
enzyme important for regulation of blood pressure
erythropoietin
glycoprotein that stimulates erythrocyte production
role of urinary system
transport, store, and remove urine from the body
renal cortex
outer region of the kidney
medulla
central region of the kidney containing renal pyramids
minor calyx
pyramids drain into this structure
major calyx
when two or more minor calyces join
renal pelvis
joining of major calyces; forms the ureter
renal capsule
thin connective tissue that covers the kidney
renal lobes
multiple lobes that make up the kidneys; each lobe contains a renal pyramid and associated cortex
nephron
functional unit of the kidney; produces urine in a renal lobe and drains into the minor calyx of that lobe
cortical nephrons
almost entirely in the cortex with a short loop of Henle; general urine production and solute reabsorption
juxtamedullary nephrons
renal corpuscle is in the cortex, but loops of Henle are long and extend into deeper portions of the medulla; critical role in urine concentration
secondary capillary beds
pertitubular cappillaries and vasa recta; role in reabsorption and secretion
medullary ray
straight portions of the nephron (limb loops of Henle, collecting ducts)
pars convoluta
coiled parts of the nephron (corpuscle, PCT, DCT)
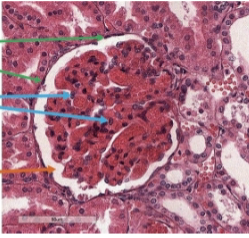
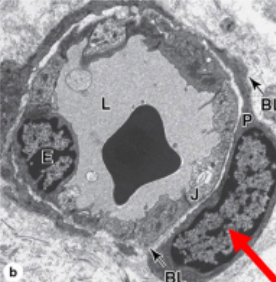
podocytes
epithelial cells that surround the capillaries of the corpuscles
mesangium
connective tissue that connects the capillaries of the glomerus
capsular space
space between the glomerulus and parietal cells
pedicels
extensions of podocytes; allows them to interlock, with filtration slits in between
juxtaglomerular apparatus
made of macula densa and juxtaglomerular cells; regulates blood volume by releasing hormones
erythropoietin
increases the rate of production of red blood cells in response to falling levels of oxygen in the tissues
when renin is released
blood pressure drops or there is not enough sodium in the blood
Renin-angiotensin process
renin converts angiotensin into angiotensin I. becomes active when converted to ang. II by ACE from the lungs; ang II increases blood pressure to stimulate release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex; aldosterone stimulates Na+ reabsorption
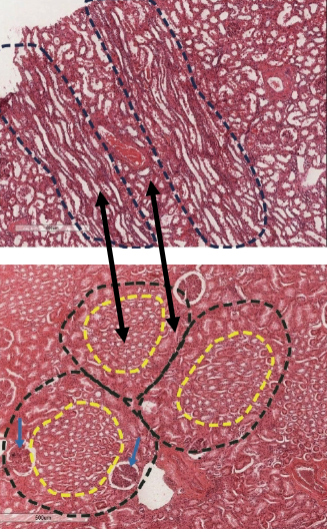
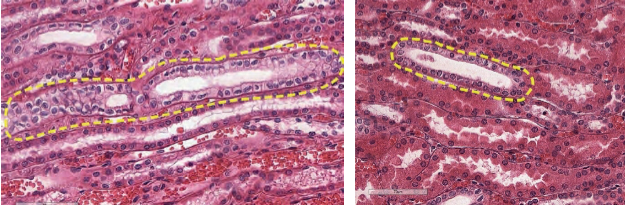
medullary rays
what is this (yellow outline)
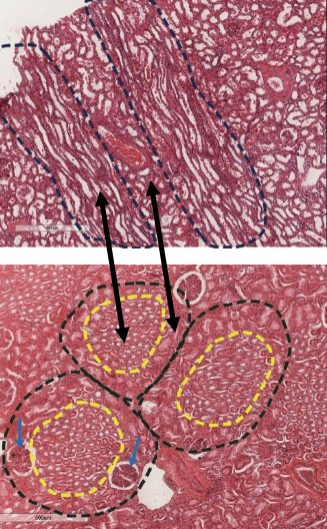
pars convoluta
what is this (in between outlines)
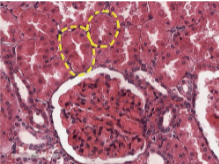
proximal convoluted tubules
what is this
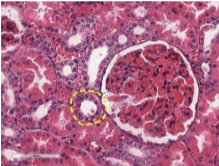
distal convoluted tubules
what is this
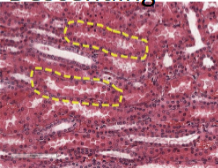
descending loop of henle
what is this
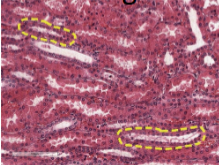
ascending loop of henle
what is this
collecting ducts
what is this
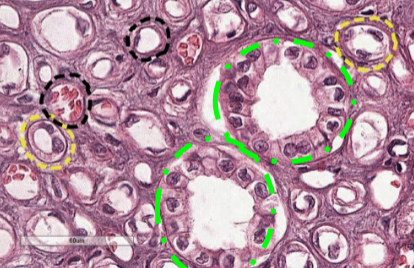
collecting duct
what is this (green)
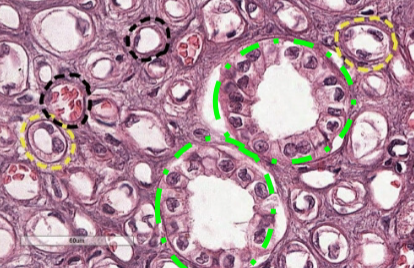
thin loop of henle tubule
what is this (yellow)
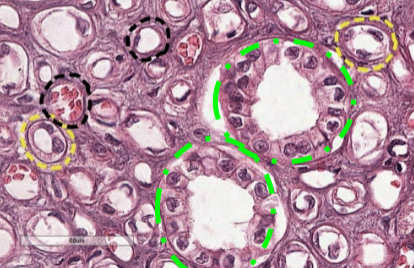
vasa recta
what is this (black)
corpuscle
what is this
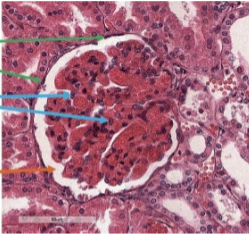
podocytes
what is this (blue)