Unit 6: Energy Resources and Consumption 35-37
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Fossil fuels
-Derived from biological material fossilized millions of years ago --> Dead biomass from anaerobic environments build up, is buried by sediment, and forms these fossil fuels.
-Coal, oil, and natural gas
Nonrenewable energy
-A source of energy that is a finite supply capable of being exhausted.
-Fossil fuels, Nuclear
calorie
-Amount of energy needed to raise temperature 1 gram of water 1 degree C
-1 calorie = 4.184 J
-Common uses: energy expenditure and transfer in ecosystems; human food consumption
Calorie (capital C)
-Calories in food
-1 Calorie = 1000 calories = 1 kilocalorie(kcal) = 4184 J
-Common uses: food labels; human food consumption
British Thermal Unit (BTU)
-Amount of energy it takes to heat 1lb of water 1 degree F
-1 Btu = 1,055 J
-Common uses: Energy transfer in air conditioners and home water heaters
Kilowatt-hour (kWh)
-Amount of energy expended by using 1 kilowatt of electricity for 1 hour
-1 kWh = 3,600,000 J = 3.6 MJ
-Common uses: Energy use by electrical appliances; often given in kWh per yr
Renewable energy sources
-Sources of energy able to be replaced through ongoing natural processes
-Divided into potentially renewable and nondepletable
Potentially renewable energy
-Resources that can be regenerated indefinitely if properly managed
-Wood, biofuel
Nondepletable
-Resources that cannot be used up, no matter the quantity and rate of use
-Wind, solar, hydroelectric, geothermal
Energy use trend
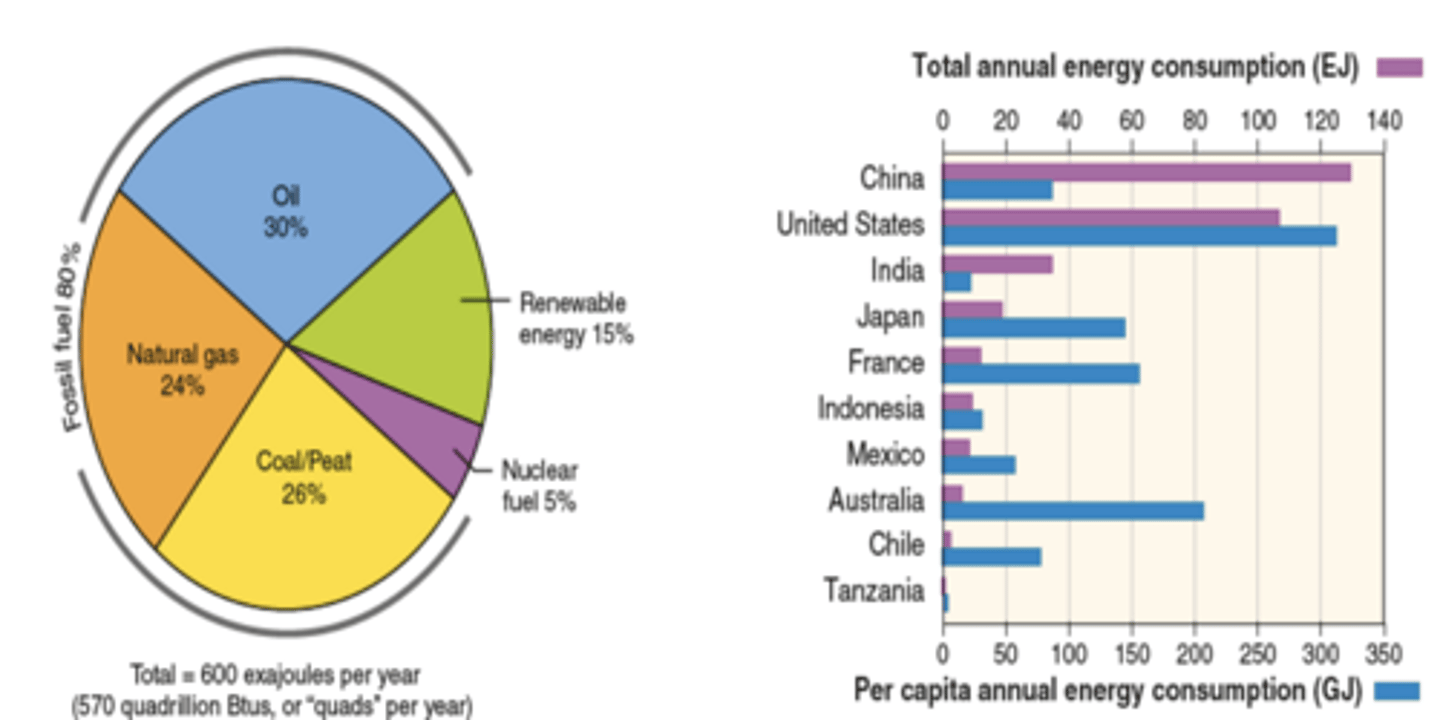
-Globally, 80% of energy is produced by oil, coal, and natural gas.
-The developed nations of the world use more than 40% of the world's energy, even though they only comprise of 20% of the population.
Renewable Energy Resources in the US
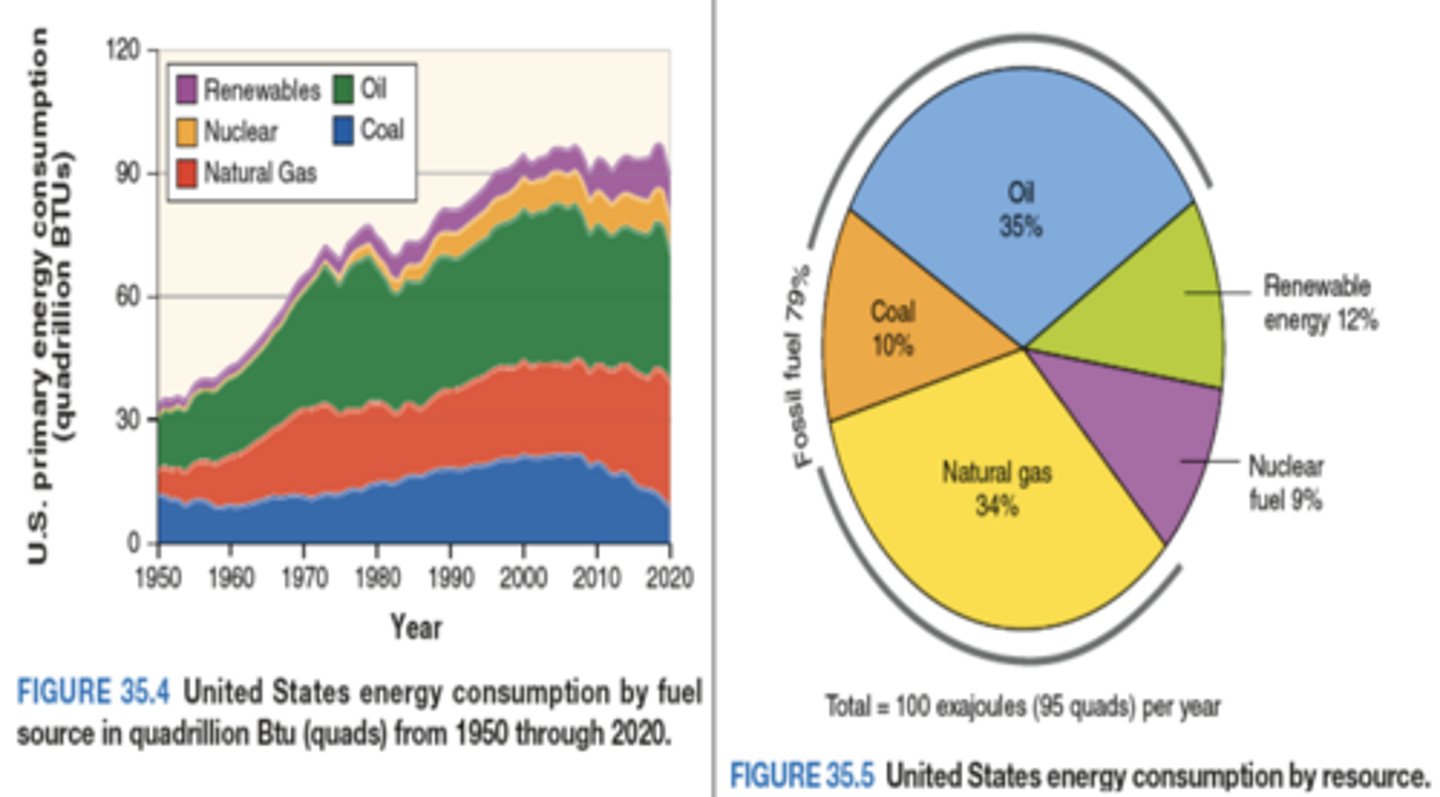
-In the United States, Energy has transitioned from: Wood → coal → oil → natural gas
-None of the resources have ever stopped being used entirely, but have diminished in the amount of energy provided as compared to other resources.
-Energy can vary regionally and seasonally:
-^Coal remains the primary fuel source in southeastern and some western states
-^northern and some western states use a mix of nuclear fuels, dams, and natural gas
-Natural gas is the fastest-growing resource used today.
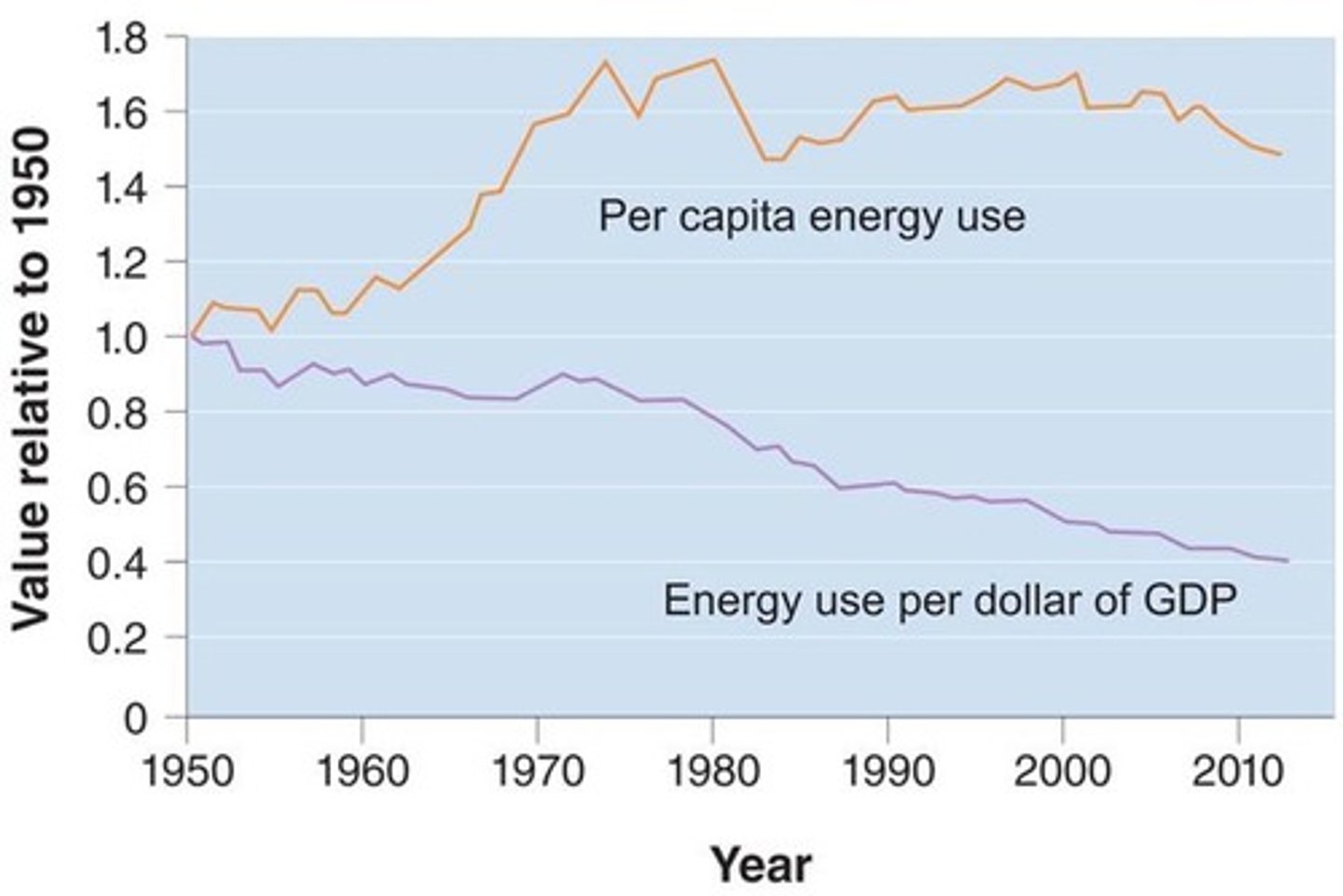
Energy intensity
-The energy use per unit of gross domestic product
Fossil fuel combustion
-The products of the chemical reaction of oxygen and fossil fuels --> energy, water and carbon dioxide
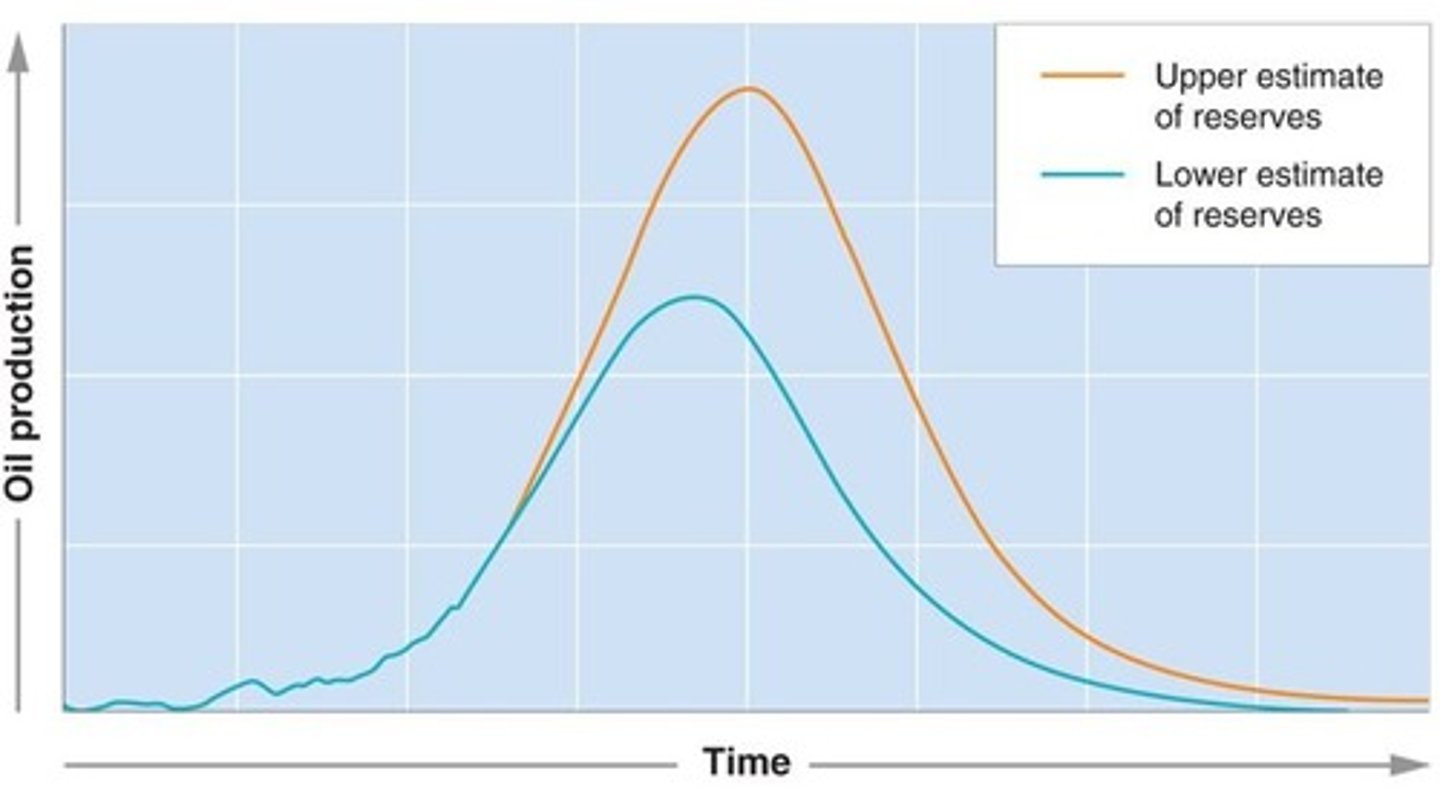
The Hubbert curve
-A graph that represents when world oil production will reach as maximum, leading to peak oil, where more than half of reserves will be used
Energy conservation
-Finding ways to use less energy
Energy efficiency
-Finding ways to get the most out of energy used.
Source of energy is dependent on
-The intended use
-Transportation → gasoline or diesel fuel from oil
-Home energy → wood, natural gas, or coal
-Energy is lost in transferring it into another form; recall the first and second laws of thermodynamics --> energy can only be transformed, entropy inc.
energy return on energy investment (EROEI)
-Calculates energy efficiency or the amount of energy we get out for every unit of energy that goes in
-Energy obtained from the fuel/ Energy invested to obtain the fuel
Biofuels
-Biomass that gets processed and refined into liquid fuels like biodiesel and ethanol.
-Biofuels and other biomass make up 40% of renewable energy and 5% of all energy consumed in the US today.
The sun
-The ultimate source of most energy sources
Atmospheric carbon concentrations
-Both fossil fuels and biomass raise atmospheric carbon concentrations.
-Carbon recently found in atmospheric biomass is modern carbon.
-Carbon that was contained in fossil fuels for millions of years and has recently been released is fossil carbon.
Carbon neutral
-Most biomass and biofuels --> they don't change carbon dioxide concentrations.
Common fuel types include:
-Wood --> provides heating and cooking to 2-3 billion people in the world (currently, forests are cut too fast to allow trees to maintain carbon neutrality.)
-Coal/Peat
-Natural Gas
-Crude Oil
-Tar Sands
Coal
-A solid fuel that comes from remains of trees, ferns, and other plant materials preserved 280-360 million years ago.
-It is typically used for electricity generation and industrial processes, and can be found in many forms:
-^Peat, lignite, bituminous coal, anthracite
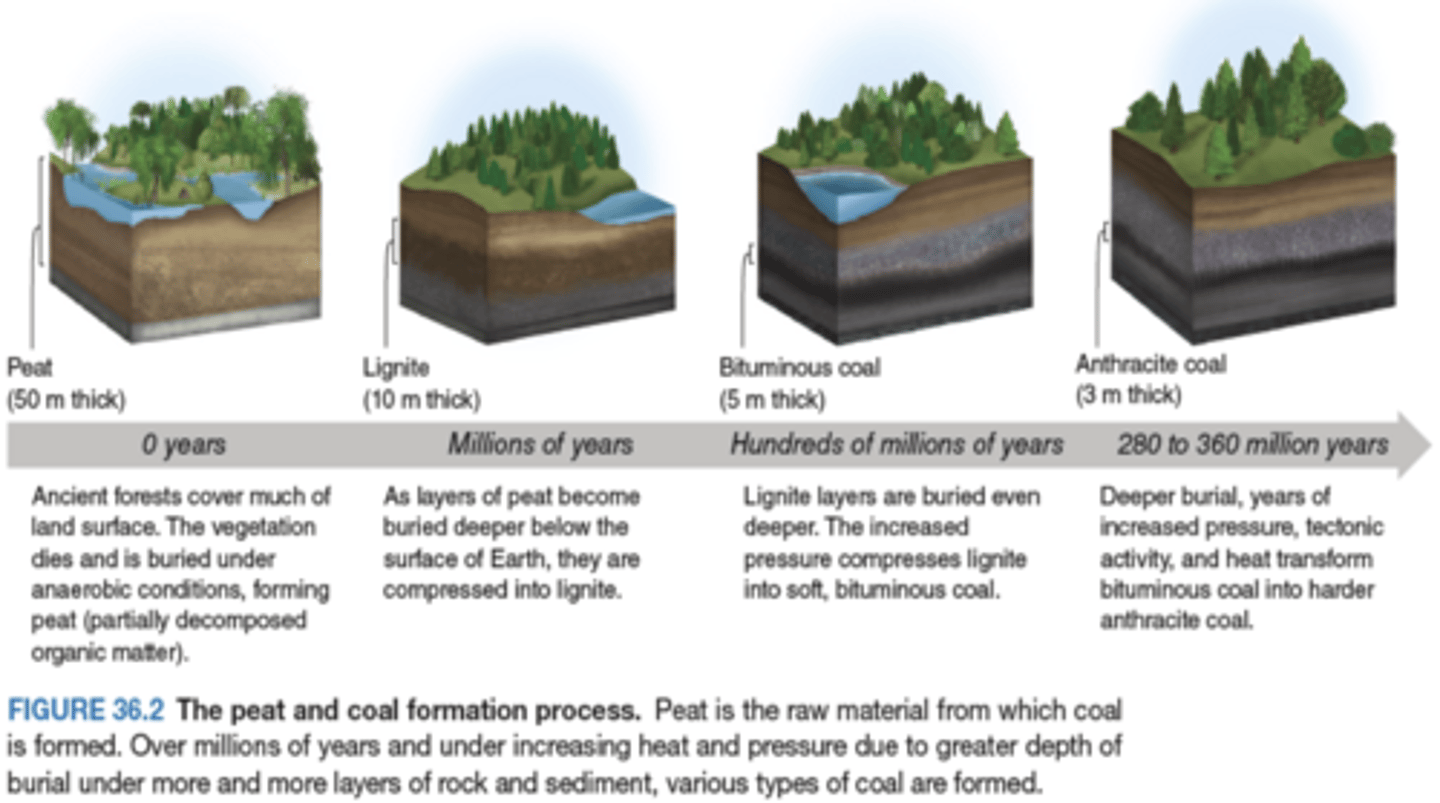
Peat
-Partly-decomposed organic material, like mosses
Lignite
-Soft sedimentary rock with traces of plant structure (60-70% carbon), also called brown coal
Bituminous coal
-Black or dark brown coal has bitumen, known as asphalt
Anthracite (hard coal)
-Contains greater than 90% carbon, highest in energy per volume
Natural gas
-Considered a cleaner source of combustion due to its smaller amount of particulates, sulfur dioxide, and carbon dioxide than coal or oil.
-Most of the gas is methane (CH4) and the remaining is ethane, propane, and butane.
-It can be compressed and liquified for transport.
-Natural gas comprises 24% of total energy consumption globally.
-Produces the most electricity in the US
Crude oil
-A mixture of hydrocarbons such as oil, gasoline, kerosene, as well as water and sulfur, that exists in a liquid state underground and when brought to the surface.
-Oil is used in vehicles and can be refined into a variety of compounds.
-Through a process of boiling, you can get a variety of compounds:
-^Tar
-^Asphalt
-^Gasoline
-^Diesel
-^Kerosene
Tar sands/oil sands
-Slow-flowing, viscous deposits of bitumen or asphalt, mixed with sand, water, and clay.
-Due to oil near the surface, it no longer flows, and is mixed with sand and soil.
-It is extracted at the consequence of serious negative environmental impacts throughout the mining process (fracking)
Use of energy: transportation
-35% of energy use in the US is for the transportation of people and goods.
-Public transportation is the most efficient method of transportation.
-Single driver cars and larger vehicles like SUVs and trucks are least efficient.
-Electric cars and plug-in hybrid cars make use of electricity as an energy source.
Energy carrier
-A source like electricity that can move and deliver energy in a convenient, usable form to end users.
-Energy conversion is only about 36% efficient, and fossil fuels can release many pollutants in this process.
-All thermal powerplants work the same basic way: converting potential energy into electricity.
Combined cycle
-Some natural gas-fired power plants use both a steam turbine and separate turbine powered by exhaust gases to generate more efficient electricity
Capacity of a powerplant
The maximum electrical output it can handle.
Capacity factor
The fraction of time a plant operating in a year is known
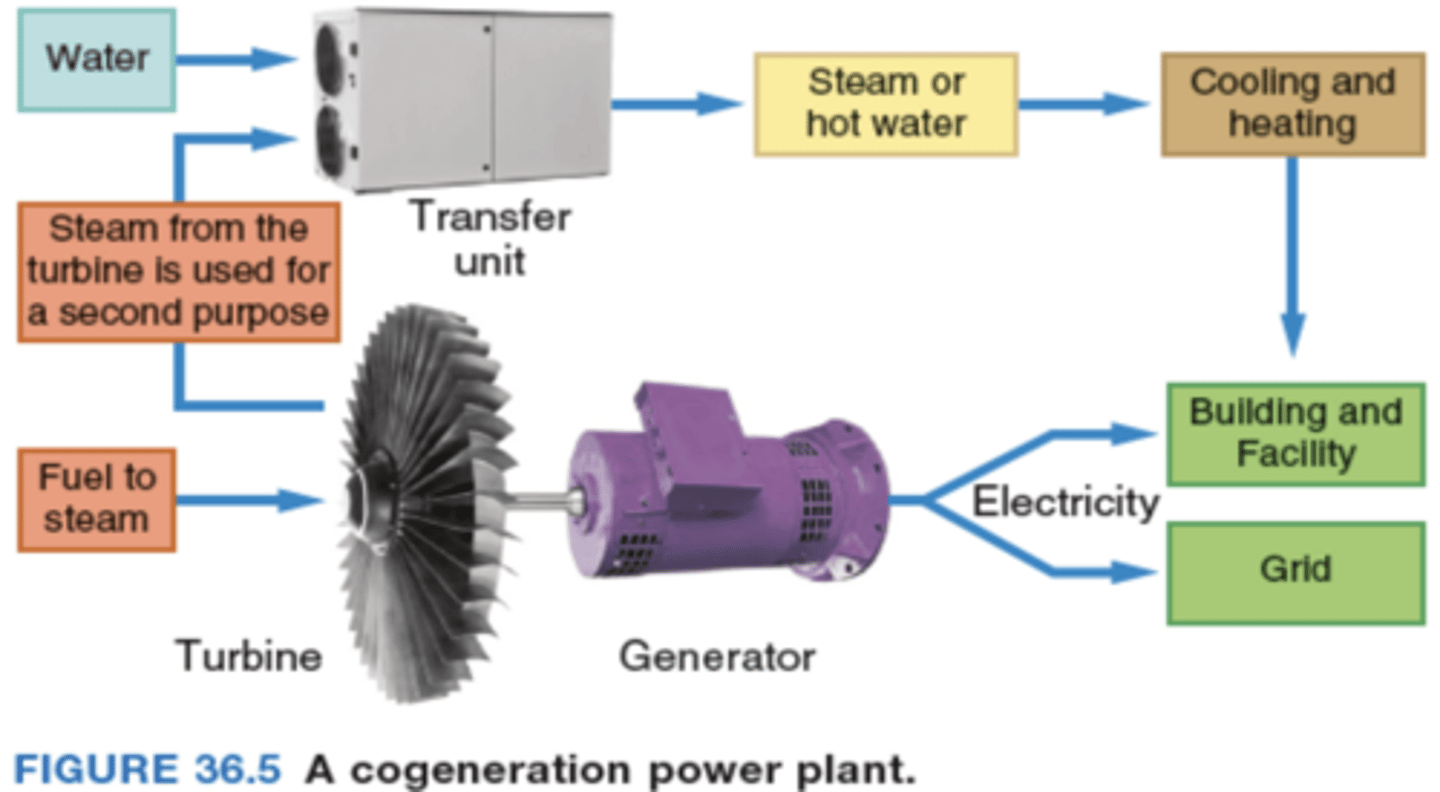
Cogeneration/combined heat and power
-One way to increase efficiency of a fuel source
-Generate electricity use "waste" heat to power a building or industrial process.
Fossil Fuel and Ore Locations
-Fossil fuels are not found everywhere; only in certain locations.
-Coal forms only through organic matter becoming buried quickly.
-Places that were tropical areas (wetlands, river deltas, etc.) millions of years ago are the locations where coal is found today:
-^United States
-^Russia
-^China
-^Australia
-^India
Crude oil/petroleum
-Formed from ocean-dwelling phytoplankton (microscopic algae).
-Oil is found in porous rock covered by nonporous rocks.
-Natural gas is typically found above petroleum.
-Oil consumption is at 4 billion gallons per day, of which the US uses 21%.
-Top producers of petroleum are:
-^United States
-^Saudi Arabia
-^Russia
-^Canada
-^China
Advantages of coal
-Energy dense
-Plentiful
-Provides heat to industrial processes and electricity generation
-Mining is low cost
-Easy to move
Disadvantages of coal
-Tailings have enviromental consequences
-Subsurface mining is expensive and dangerous
-Impurities of coal can be harmful: sulfur, Hg, Pb, As
-Pollutants like sulfur dioxide and particulates are released through burning
-Carbon in coal is converted into carbon dioxide, contributing to climate change
Advantages of oil
-Liquid form is easy to transport and use
-Energy-dense
-Cleaner-burning than coal
-Ideal fuel for mobile combustion engines
-Produces only 85% as much carbon dioxide as goal
Disadvantages of oil
-Also contains sulfur and other trace metals
-Oil may leak into ground or ocean when extracted
-Tankers and pipeline may break or spill
-Habitats can be destoryed to mine for oil or to create pipelines to transport it
-Oil flaring --> burning off excess natural gas --> can lead to air pollution
-Still emits carbon dioxide
Advantages of natural gas
-Extensive gas pipeline system already in place
-Fewer impurities than coal and oil
-Almost 0 amounts of sulfur dioxide and particulates released
-Only released abt 60% as much carbon dioxide as coal
-Can be liquified to provide fuel for homes and businesses
Disadvantages of natural gas
-Unburned natural gas (methane) can be released and is 25x more potent than carbon dioxide
-Extraction leads to large extraction fields, destroying habitat
-Hydraulic fracturing can contaminate the water table
-water used in the fracking process is contaminated instead of being used for homes and businesses
-Fracking releases volatile organic compounds VOCs which evaporate quickly at atmospheric temps
Coal burning fire powerplant steps
1. Coal is delivered to a boiler and burned
2. Energy is transferred to water by heat
3. Water becomes steam
4. The steam turns a turbine
5. The turbine is attached and turns a generator to produce electricity
6. The electricity generated is transported along a network of transmission lines known as the electrical grid
7. Steam is condensed back into water and sent to a cooling tower or cooling pond
Calculating energy efficiency
Coal to electricity x transport of electricity x light bulb efficiency = overall efficiency
Energy quality
-The ease with which an energy source can be used to do work.
-Higher quality of energy sources don't require too much energy to move it from one place to another.
-Gasoline is a high-quality energy source due to its concentrated energy and current infrastructure to transport it.
-Wood is lower quality due to low concentration of energy and the challenge it takes to transport it.