Ch 12 inventory management
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
types of inventory
raw materials
components
work-in-process
finished products
distribution
maintenance, repair, operating inventory
types of inventory ; raw materials
purchased items or extracted materials that are transformed into components or products
types of inventory : components
parts or subassemblies used in the final product
types of inventory : work-in-process
unfinished products that are in process
types of inventory : finished products
products that are ready to be sold to customers
types of inventory : distribution
finished products in the distribution system
types of inventory : maintenance, repair and operating inventory
supplies that are used in the production process without being part of the final product
inventory purposes :
anticipation inventory / seasonal inventory
fluctuation inventory or safety stocj
lot-size inventory or cycle stock
transportation or pipeline invetory
speculkative or hedge inventory
inventory purposes : anticipation / seasonal inventory
built in anticipation of future demand, to maintain level production (eg promotional programs, seasonal fluctuations, vacations)
inventory purposes : fluctuation / safety stock
carried as a buffer against unexpected demand variation, to assure customer service levels
inventory purposes : lot-size inventory/ cycle stock
results from the actual quantity ordered or produced, to lower unit costs (eg quantity discounts, production minimum)
inventory purposes : transportation or pipeline inventory
results from the movement between locations (eg between manufacturer and distribution facilities)
inventory purposes : speculative or hedge inventory
protects against future events, to allow continuous supply (eg strikes, price increases, product scarcity)
inventory management objectives :
provide desired customer service level
ensure cost-efficient operations
minimize inventory related investments
inventory management objectives : provide desired customer service level
percentage of orders shipped on schedule
percentage of line items shipped on schedule
percentage of dollar volume shipped on schedule
idle time due to material and component shortages
inventory management objectives : ensure cost-efficient operations
carry work-in-process inventory between workstations, to avoid idle time
maintain a level workforce despite seasonal demand, to avoid costs of overtime, hiring, firing, training, subcontracting
schedule long production runs, to decrease setup cost
order large volumes, to receive quantity discounts
inventory management objectives : minimize inventory related investments
calculate the inventory turnover = annual cost of goods sold / average invenrtory value
and the weeks of supply = average inventory on hand / average weekly usage
inventory related costs :
item costs
holding costs
ordering costs
shortage costs
inventory related costs : item costs
direct costs associated with the purchase (eg purchase price, transportation, insurance, taxes, handling,
inventory related costs : holding costs
variable expenses related to the value of inventory (eg capital (interest rate/ rate of return), storage, risk)
inventory related costs : ordering costs
fixed costs incurred for each order placed
(eg administration, handling, setup)
inventory related costs : shortage costs
incurred when demand exceeds supply
eg back order handling, loss of customer goodwill, lost saled
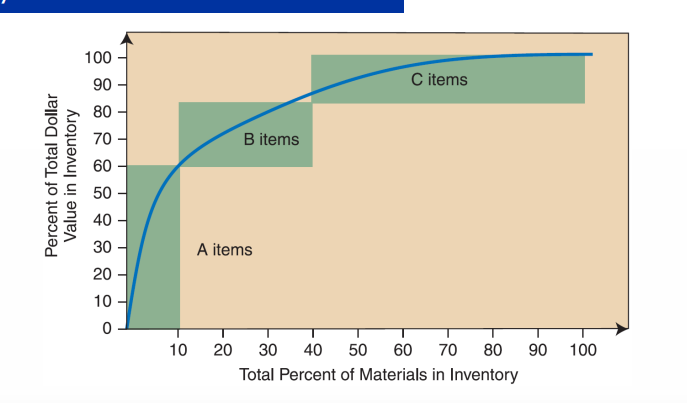
how to determine the appropriate review frequency for inventory items ? → pareto’s law (20/80)
items are segmented based on annual dollar volume
A items : high dollar volume → continuous review (EOQ model) → typically 20% of the items, representing 60-80% of inventory value)
B-items ; medium dollar volume → periodic review (TI model) → typically 30% of the items, representing 25-35% of inventory value
C-items : low dollar volume → less frequent review or two-bin system → typically 50% of the items, representing 5-15% of inventory value
inventory record accuracy errors reasons for occuring
errors occur because of unauthorized withdrawals of material (customer, employees), unsecured stockrooms, inaccurate paperwork, human errors
inventory record accuracy errors meaning
any displacement between what your computer system says you have and what is physically on the shelf
two methods to counter inventory record accuracy errors
periodic counting an opportunity to correct errors
cycle counting for prespecified items
→ automated inventory tracking system
common ordering approaches
lot-for-lot
fixed order quantity
min-max system
order n periods
common ordering approaches : lot for lot
order exactly what is needed
common ordering approaches : fixed order quantity
= order a predetermined alount each time an order is placed
common ordering approaches : min-max system
when on hand inventory falls below a predetermined minimum level, order a quantity that will take the inventory back up to its predetermined maximum level
common ordering approaches : order n periods
order enough to satisfy demand for the next n periods
determining order quantities : multiple-period models
fixed order quantity models → continous review
economic order quantity (EOQ)
economic production quantuty (EPQ)
extensions to the EOQ model : quantity discounts, safety stock
fixed time interval models → periodic review
target inventory TI
(single-period model)
objective Economic order quantity (EOQ)
= satisfy demand with minimized sum of order costs and holding costs
→ to be determined : when to order and how many items per order
assumptions :
the total demand is known and constant (no safety stock)
all demand needs to be satisfied on time (no backorders)
the lead time L is known and constant
the fixed ordering cost S is known and constant (independent of quantity)
the holding cost is known and proportional to the average inventory level
no quantity discounts are applicable
the ordered items are delivered at once
economic order quantity (EOQ) order size that minimzes TC
screen
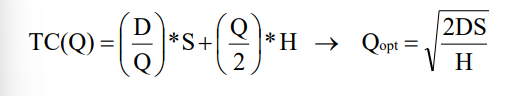
economic order quantity ; EOQ - when to place a new ordder
R = d*L (d = demand / week / day)
economi production quantity EPQ - difference compared to EOQ model
inventory is gradually replenished and can be used as soon as it arrived (eg internally made items)
Higher optimal order quantity
lower inventory level and costs
→ production rate p must be larger than depletion rate d
maximul inventory level Imax must be smaller than EPQ
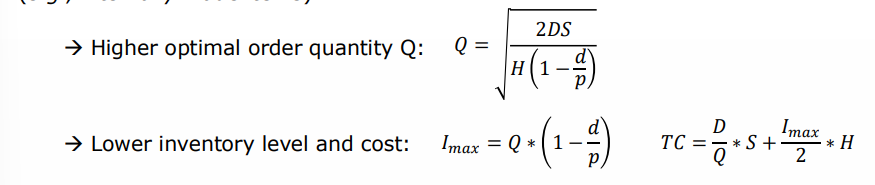
quantity discount model : difference compared to EOQ model
vendors allow quantity discounts when large quantities are ordered → multplie unit proces levels (P) depending on the quantity ordered
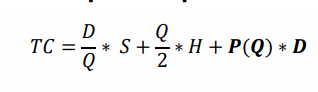
quantity discount model - procedure
1) starting from the lowest item price P, check which value of P is the first for which a feasable EOQ is obtained and compute TC
2) compute te TC for all order quantities Q at price breaks to curves associated with a lower item price P
3) select the option involving the lowest TC
when might companies invest in safetystock
if demand during the lead time is uncertain, to decrease the probability of shortages
determine an adequate level of safety stock (SS) based on the order-cycle service level
the probability that demand during the lead time will not be exceed on-hand inventory
the use of safety stock changes the reorder point
the company places a new order when the remaining stock is 250 (instead of 200), which creates a buffer to avoid stockouts during the lead tume
the amount of safety stock to hold depends on
the variabillity of demand and lead time
and the desired order-cycle service level
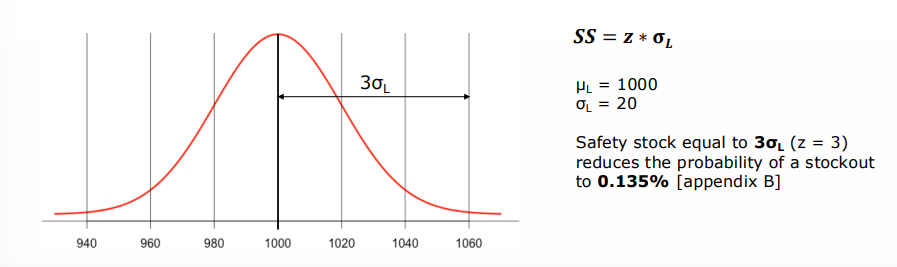
order-cycle service level approach
assumption : demand during the lead tiem is normally distributed with meal mu L and standard deviation sigma L
target inventory model : periodic review system
the inventory on hand is measured at fixed time intervals (eg once a week) → review period RP
the order quantity is variable and determined based on the difference between a target inventory level (TI) and the current inventory level on hand (OH)
periodic review system : advantages
no need to continuously monitor the inventory level
items from the same supplier can be reviewed on the same day to save order costs
periodic review system : disadvantages
replenishment quantities vary and may not qualify for quantity discounts
higher average inventory levels needed to protect against stockouts
target inventory level (periodic review system)
based on the expected demand during a review period and the lead time
compared to continous review models, a larger safety stock is needed to protect the company against uncertainty during the review period as well

single-period inventory level
designed for products with these characteristics
sold at their regular price at a specific occasion or during a short period (eg newspapaers, perishable products)
a discrete demand distribution is known
the salvage value is less than the purchasing cost → a loss is made on products that cannot be sold at their regular price