VCE Psych Unit 3 AOS 1
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Central Nervous System
(CNS) brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous system
Body Nerves that connect to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Connects the central nervous system to the body's organs and limbs.
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary bodily functions (not consciously controlled), such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestive processes - (PNS)
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary bodily functions (consciously controlled), such as controlling skeletal muscles - (PNS)
Stimulus
Things that initiate nerve impulses (ex. hot room)
Motor Functions
Complex muscle-and-nerve acts that produce movement (walking, writing, typing running etc.)
"Electrochemical"
A nerve impulse is partially electric (change in polarity/charge) and partially chemical (neurotransmitters)
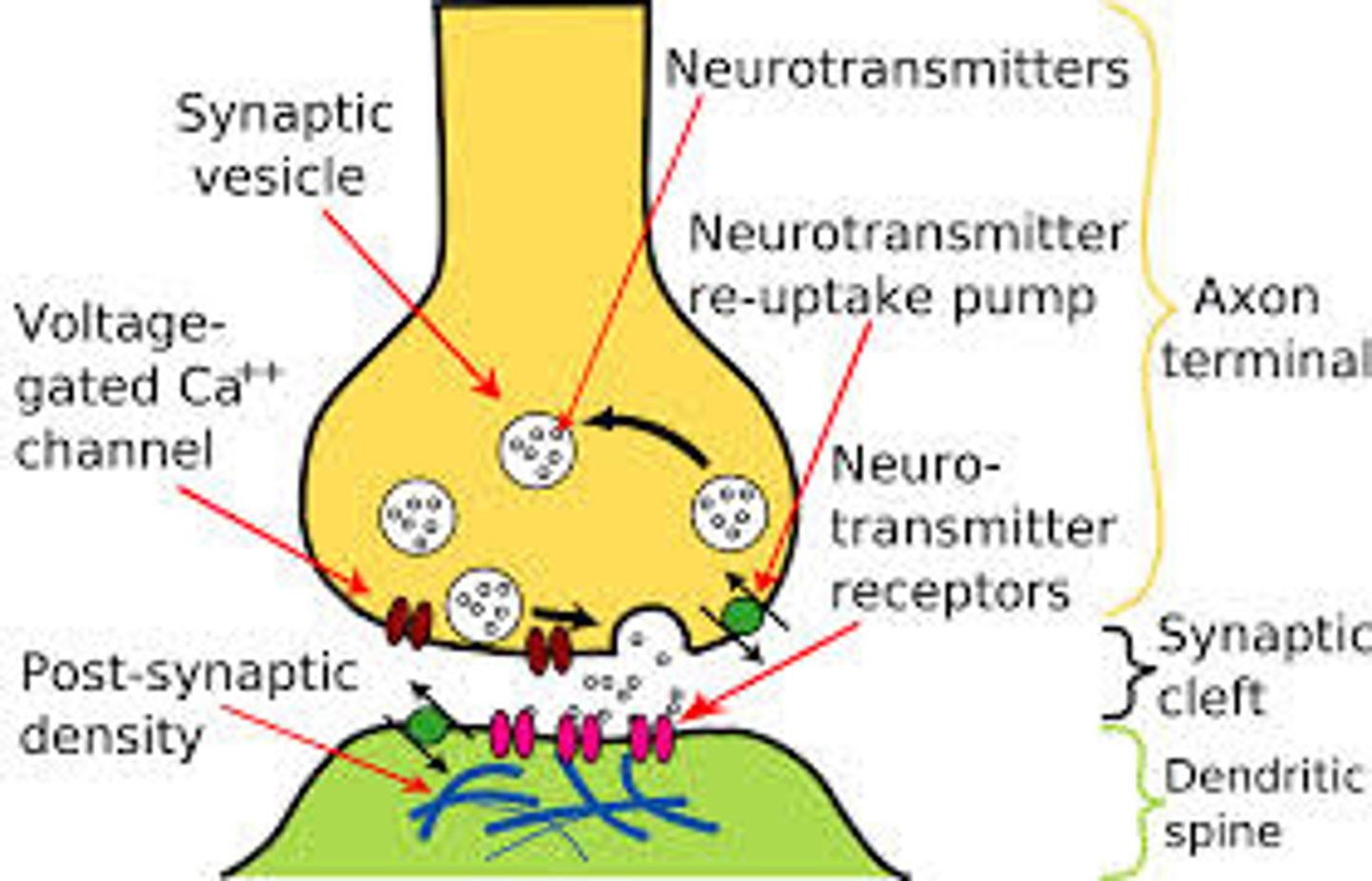
Synapse
Where the nerve impulse is sent (connection of 2 neurons) .
Action Potential changes the charge of the synapse (causes electricity) and Neurotransmitters are sent.
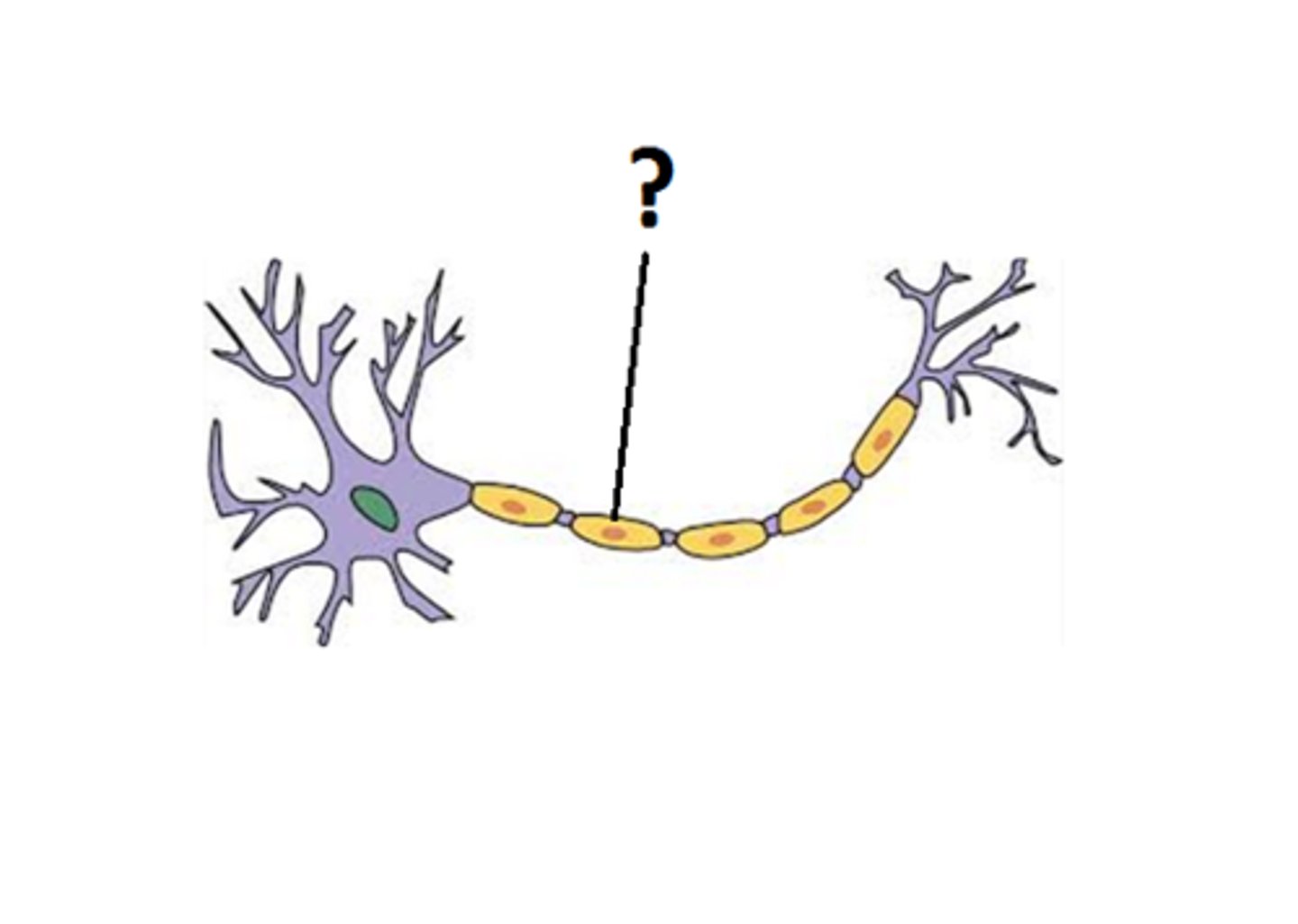
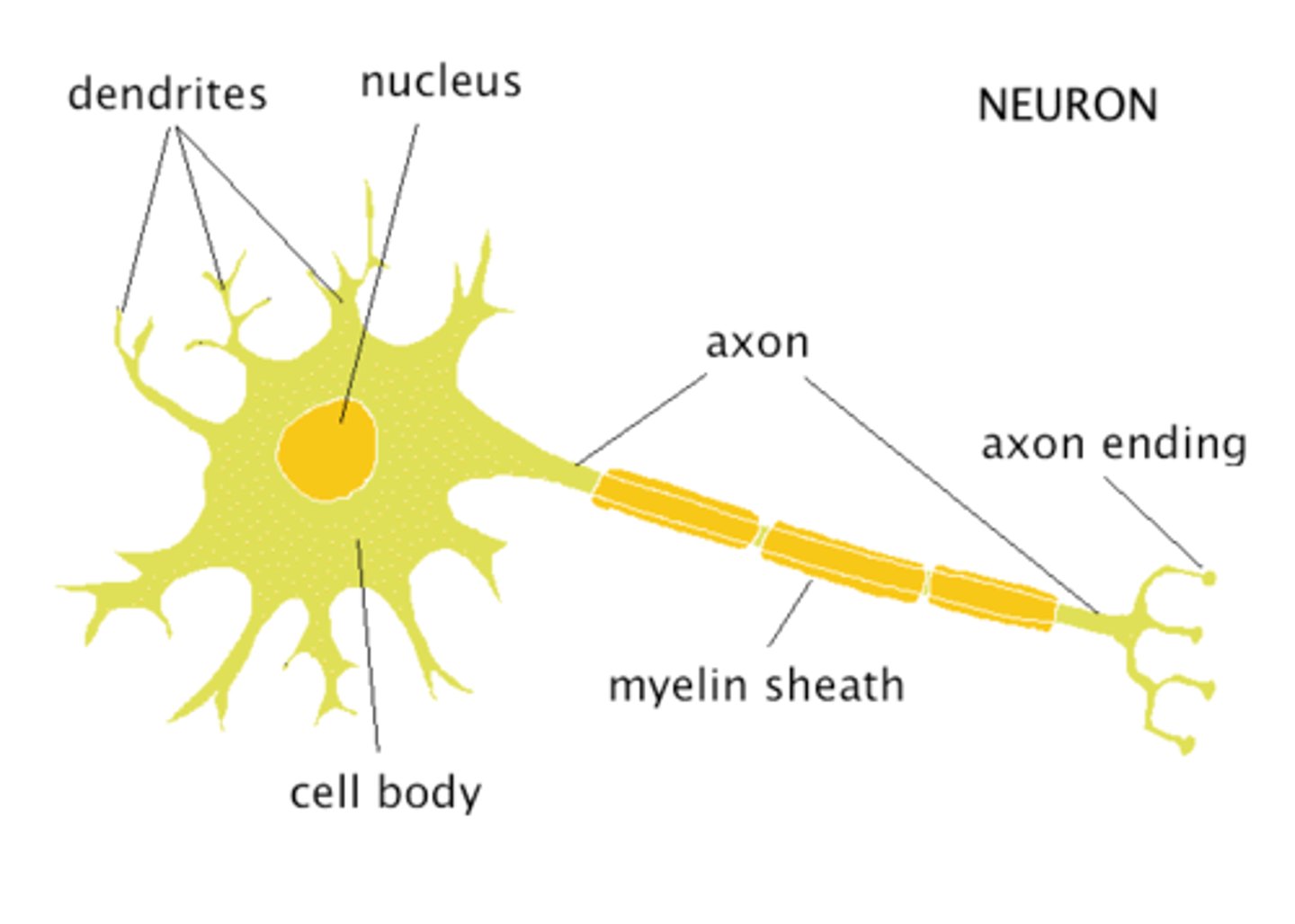
Myelin Sheath
Offers protection to the neuron, Speeds up nerve impulses.
Axon
The long threadlike part of a nerve cell that carry the nerve impulse
Dendrites
Branch like extensions on a neuron that GET signals and connect to the synapse
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another 'target' neuron
Sensory Neuron
Nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, smell, sound etc.)
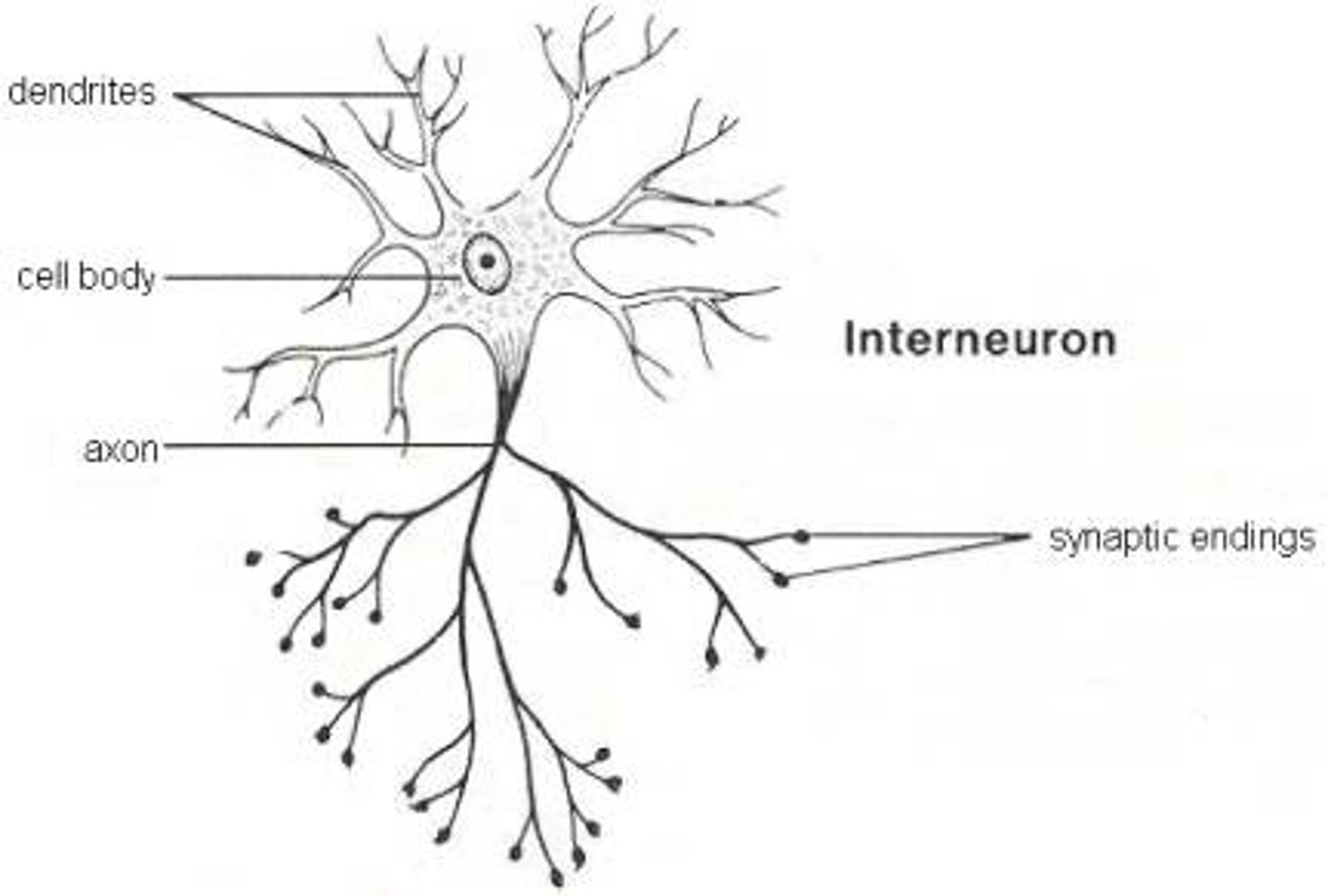
Interneuron
Nerve cells that connect motor neurons and sensory neurons. Only found in the CNS.
Motor Neuron
Nerve cells responsible for making an action or movement happen.
Efferent Tracts
A nerve pathway that goes downwards from the brain toward the PNS carrying motor information
Afferent Tracts
A nerve pathway that goes upward from the spinal cord toward the brain carrying sensory information
Excitatory Neurtransmitters
Stimulates a post synaptic neuron to fire. Activates the brain.
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Stops a post synaptic neuron from firing. Calms the brain and helps create balance.
Adrenaline
a hormone that may affect memory consolidation of emotionally arousing experiences; also called epinephrine
Glutamate
an EXCITATORY neurotransmitter that plays crucial roles in the growth and strengthening of synaptic connections during learning and memory formation
GABA
An INHIBITORY neurotransmitter in the brain, which decreases the likelihood of the post-synaptic neuron firing
Eustress
Positive psychological response to a percieved stressor.
Distress
Negative psychological response to a percieved stressor.
GAS
General Adaption Syndrome, three stage model explaining physiological response to stress that occurs regardless of stressor.
Lazarus and Folkman's Transactional Model of Stress and Coping
Model created to explain the psychological process of stress - containing TWO stages: Primary Appraisal & Secondary Appraisal
Primary appraisal
Assesses the effect of stressor on the individual. Looks at harm/loss, threat and challenge
Secondary appraisal
Work out how to best deal with the situation. Do they have the resources to cope or not?
GAS (General Adaptation Syndrome) created by Selye
A model created by Hans Selye to explain the biological process of stress - including three main stages:
- Alarm Reaction (shock & counter-shock)
- Resistance
- Exhaustion
Cortisol (in GAS)
Stress hormone, initially aids body in the stress response, goes up when stressor remains present for an extended period of time.
Adrenaline (in GAS)
Helps the body respond to stress initially in the flight-fight-freeze response
Noradrenaline (in GAS)
Works with adrenaline to help the body respond to stress initially
Alarm reaction
Becoming aware of stressor. Has two stages - shock and counter shock.
Shock
Body responds as though injured. Resistance to stress is lower than normal.
Counter-Shock
Fight-flight-freeze response is activated by sympathetic nervous system. Resistance to stress starts to increase ABOVE normal level of resistance
Resistance
Body continues to operate ABOVE average level of resistance to stress
Cortisol + adrenaline still fighting stressor, body is aroused with more energy to deal with situation, if keeps going can get sick
Exhaustion
When resistance phase lasts too long body becomes depleted = serious illness
(due to prolonged cortisol release, which has suppressed immune system function)
Coping flexibility
the ability to effectively modify or adjust one's coping strategies in accordance with the demands of the stressful situation
Approach coping strategies
Involve efforts that confront a stressor and deal with it directly.
Avoidant coping strategies
Efforts that evade a stressor and deal with it indirectly.
Coping Strategy
a specific method, behavioural or psychological, that people use to manage or reduce the stress caused by the stressor
Context specific effectiveness
when there is a match or good fit between the coping strategy used and the stressful situation
Dopamine - roles
voluntary motor movements / reward-based learning / motivation / pleasure response
Serotonin - roles
mood regulation / mood stabilisation / regulating sleep-wake cycle / appetite & digestion / arousal levels
Neurochemicals
chemical substances that transmit neural information within the nervous system (includes BOTH neurotransmitters and neuromodulators)
Neurotransmitter
- chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between two neurons
- has an effect on the post-synaptic neuron
Neuromodulator
chemical molecules that have an effect on MULTIPLE postsynaptic neurons
Long-term depression (LTD)
long-lasting and experience-dependent WEAKENING of synaptic connections between neurons that are NOT regularly co-activated
- enables forgetting/pruning of unused pathways
Long-term potentiation (LTP)
long-lasting and experience-dependent STRENGTHENING of synaptic connections that are regularly co-activated
- enables faster memory retrieval and/or performance of skills
Sprouting
the ability of dendrites or axons to develop new extensions or branches
Rerouting
the ability of a neuron that is connected to a damaged neuron to create an alternative synaptic connection with an undamaged neuron
Pruning
the elimination of synaptic connections that are not adequately activated
Gut microbiota
all of the microorganisms that live in the gut
Gut microbiome
all of the GENES of the microorganisms that live in the gut
Gut-brain axis
- the bidirectional connection between the gut and the brain through the enteric and central nervous systems
- connected via the vagus nerve
Vagus nerve
the longest cranial nerve that connects the gut and the brain, enabling them to communicate
80%-90% of messages along vagus nerve from _____ to _______
- 10-20% of nerve fibres in the vagus nerve are involved in conveying information from the brain to the gut and
- 80-90% are responsible for conveying information from the gut TO the BRAIN
Context-specific effectiveness
when the coping strategy or mechanism used is appropriate for the unique demands of the stressor
Coping flexibility
the ability to ADJUST or CHANGE one's coping strategies depending on the unique and changing demands of a stressor
Internal stressor
a stimulus from WITHIN a person's body that prompts the stress response
- eg. attitude, rumination, source of pain, low self-esteem, nervous system dysfunction (low GABA levels)
External stressor
a stimulus from OUTSIDE of a person's body that prompts the stress response
- eg. test/exam, meeting new people, arguments with friends/family/strangers, working long hours, financial difficulties