Biology Paper 1 aqa gcse
1/255
Earn XP
Description and Tags
doesn't cover all information, only stuff idk.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
256 Terms
What is surface area of alveoli?
About 75 meters squared for humans.
What features of alveoli make it good for gas exchange?
thin walls, big surface area, moist lining for dissolving gases, good blood supply.
What the projections in small intestines called?
Villi (singular form villus)
What the typical sub-cellular structures in animal cell?
Nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosome, cell membrane
What is the nucleus?
contains genetic material, controls activites of cell
What is the mitochondria?
where most aerobic respiration takes place, releases energy in order for cell to work properly
What is the cytoplasm?
gel like substance, where most chemical reactions are. contains enzymes which controls these reactions.
What is the cell membrane?
supports cell, controls what goes in/out of cell.
The typical sub-cellular structures in plant cell
Cell wall, permanent vacuole, chloroplast
What is the cell wall?
rigid, made from cellulose. strengthens and supports cell.
What is the permanent vacuole?
contains cell sap made from weak solution of salt and sugar.
What is the chloroplast?
where photosynthesis occurs, makes glucose for plant, contains green substance called chlorophyll, which absorb light energy for photosynthesis.
Features of villi?
Increase surface area, single layer of surface cells, good blood supply.
Where are the villi located?
small intestine
What is in the villi?
Network of capillaries under layer of cells, circular muscles are the dots in muscle under capillaries, longitudinal muscle under circular muscle.
Typical structure of bacterial cell.
Plasmids - circular loops of DNA
Cytoplasm, Cell wall, Genetic material not enclosed in nucleus.
Gas exchange in leaf?
CO2 diffuses into air spaces within leaf, then to cells where photosynthesis happens(upper leaf).
Walls of cells inside leaf form exchange surface.
Where does water vapour diffuse out of in the leaf?
Water vapour mostly diffuses out of stomata, and some out of whole leaf(surface).
How is gas exchange made more quicker in leaves?
Flattened shape of leaf adds area to exchange surface. Air spaces inside leaf add area to surface.
What happens if plant loses water from leaf faster than replaced in roots?
stomata closes by guard cells
What happens to the leaf without guard cells?
would soon wilt
When drawing cells after looking through microscope, how much of page should it fill, and what should you do in the process?
drawings should cover at least half page, with labels, title, no shading/colouring, unbroken and clear lines, also write down magnification, you observed with.
What is differentiation?
process where cells become specialised for its function, by developing different sub-cellular structures, and turn into different types of cells.
When does differentiation occur in organisms?
Most of the time when organisms develop.
Differentiation in animal cells?
Lose the ability to differentiate at early stage after differentiation.
Differentiation in plant cells?
don't lose ability to differentiate.
Differentiation for animals, that don't lose ability to differentiate.
called mature animals, differentiation only use for repairing/replacing faulty cells.
The main function of sperm cell?
carry the male DNA to female DNA
Typical sperm cell structure?
Streamlined head, tail, acrosome, mitchondria in middle part of the body.
What is the acrosome?
top of head, enzyme filled(penetrate outer egg), nucleus inside head, contain one set of genetic material.
Function of nerve cell?
carry electrical impulses around body
Typical structure of nerve cell?
Long shape to connect with other nerve cells to carry impulses, cell body, sheath, axon
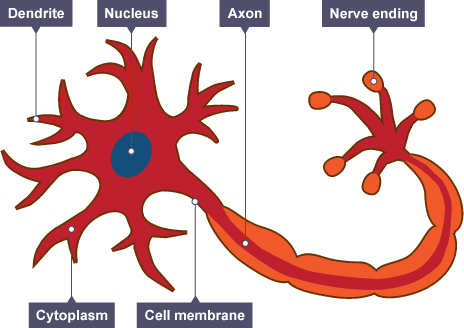
What is a dendrite?
little arms at end of nerve cell
What is a cell body?
contains nucleus(nerve cell)
What is the sheath?
little parts that make up axon.
Main function of muscle cell?
contract quickly
Typical structure of muscle.
Long cell to contract easily, nucleus bumps on top of muscle cells, mitochondria inside surface of muscle to release energy for contraction.
Protein fibres in muscle cells which cause contraction in muscle cell. And can contract themselves.
Main function of root hair cell?
absorb mineral ions to it's already sufficient enough cell of mineral ions, and to also absorb water
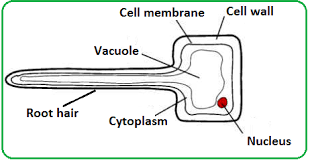
Typical structure of root hair cell?
Cells in surface of plant roots which grow into long hairs, indicated by picture of root hair cell.
This gives them huge surface area for absorption.
Lots of mitochondria to release energy in order to pull concentrated solution in soil to root hair cell.
Stem cell features?
divide into more stem cells differentiate into different types of cells, depending on what instructions they're given.
Where are embryonic stem cells found?
early human embryo, umbilical cord of newborn baby, some organs and tissues
Where are stem cells found?
Found in early human embryo, umbilical cord of newborn baby, some organs and tissues
What are stem cells called found in the early human embryo?
embryonic stem cells.
What type of age group also have stem cells?
Adults
Adult stem cell features?
Found in certain places such as bone marrow, some organs or tissues only differentiate into certain cells such as blood cells.
What can both types of stem cells be used for?
grown in lab to produce clones, genetically identical to each other, and to differentiate into specialised cells for medicine or research.
Adult stem cells of healthy person can be used to replace faulty blood cells
What can embryonic stem cells be used for?
Insulin producing cells for diabetes, nerve cells for people paralysed by spinal injuries.
What other type of cloning for stem cells is there?
Therapeutic cloning
Typical features of therapeutic cloning?
Embryo made to have same genetic information as patient, so stem cells produced won't be rejected by patients body because both the patient and stem cell have same gene.
Risks of therapeutic cloning?
Stem cells grown in lab may be contaminated with virus, can be passed to patients making them sick.
Risks/problems people have with stem cells?
viral infection, people with religious/ethical objections
Reasons people are against stem cell research?
Researching using human embryos is possible cost of one's life.
Curing patients who are suffering is more important than rights of embryos.
embryos in research often unwanted from fertility clinics, which if weren't used for research would be destroyed.
feel scientists should focus more on other sources of stem cells, so people won't have to be help with embryos.
Where are stem cells found in plants?
Meristems in roots and shoots.
What does the nucleus contain in form of?
Genetic material in form of chromosomes, which are coiled lengths of DNA molecules (at the start when cells not divide(mitosis), DNA molecules are in long strands).
Features of a chromosome?
Carry large number of genes, which each have code to make different proteins, that control development of different characteristics.
How many copies of each chromosome does a body cell normally have?
2
Where does mitosis happen?
multicellular organisms.
do all cells go through mitosis at the same time?
no, the body controls which cells to divide and when.
Where does water go in osmosis?
Through partially permeable membrane
Where can active transport also happen?
In humans such as taking glucose from gut, and from kidney tubules.
How is urea taken out of body?
Urea, which is waste product from breakdown of proteins, diffused from cells into blood plasma for removal from body by kidneys.
Exchanging gas in single celled organisms?
efficient, because gas directly diffuses into/out of them.
They have larger surface area/volume ratio.
Which is why enough gas can be exchanged to supply volume of organism
How does gas pass through fish(gas exchange)?
Water containing oxygen enters fish through mouth, then gills.
As this happens oxygen from water diffuses into blood in gills and carbon dioxide diffuses from blood into water.
How is gas exchange made faster in fish?
Gills are exchange surface in fish
Each gill made of thin plates called gill filament, adds surface area.
Gill filament covered in tiny structure called lamellae, adds surface area.
Lamellae have blood capillaries, thin surface layer of cells for quick exchange.
Blood flows through lamellae in one direction, and water flows over in the other.
Maintains large concentration gradient between water and blood.
Where is the concentration of oxygen higher in water or blood (fish)?
water
What are Enzymes?
A biological catalyst, increases speed of reaction without being changed/used up.
What are enzymes used in digestion?
made from cells, then released to gut.
What are enzymes used in the digestive system?
made from specialised cells in gland/gut lining.
What are enzymes made from?
Made from large proteins(chains of amino acids folded to form unique shapes).
What is the optimum pH that all enzymes work best at?
7, but not always.
What is pepsin?
enzyme used to break proteins in stomach. Peak pH=2
What is it called when a subtrate tries to fit in active site?
induced fit.
Effect of pH activity experiment Amylase?
Boil water to 35 degrees (keep temp constant).
Put drops of iodine solution into spotting tiles.
1cm cubed of amylase, buffer solution of pH 5 into boiling tube for 5 mins.
Use diff pipette to add 5cm cubed starch solution into boiling tube and mix, then start stop clock, as well as adding the solution to the tiles every 30 secs, and time how long it takes for amylase to break down starch.
What is lipase?
break down lipid into glycerol/fatty acid
made:pancreas, small intestine
What is amylase?
carbohydrase. Break down starch into sugars:maltose, glucose, dextrins
made: salivary gland, pancreas, small intestine
What is protease?
called pepsin in stomach. break down protein into:amino acid, peptide
made:stomach, pancreas, small intestine.
What does the body do with broken down stuff?
products of digestion, can make new carbohydrate, proteins, lipids. Glucose made is use for respiration.
Food test preparation?
Break up food to beaker, then add distilled water. Stir to dissolve food, then filter to get rid solid bits.
What should you do before food tests?
Food test preparation.
Except for lipid test.
testing for lipid?
5cm cubed food, 3 drop Sudan III stain solution to test tube, then shake.
Result: Sudan 3 stains lipid
Top layer red/bottom clear=present
Tube sample clear =no present.
testing for protein?
2cm cubed food/biuret solution to test tube, then shake.
Result: blue=present
Purple=no present
testing for starch?
5cm cube food, few drop iodine solution to tube, then gently shake.
Result: blueblack=present
Brownorange=no present
testing for sugars?
5cm cubed food, 10 drop Benedict reagent to tube.
Boil water to 75 degree. Wait 5min Results: (ascending) blue, green, yellow, brickred
sudan III stain solution precaution?
flammable
benedicts reagent precaution?
water bath experiment too hot
Biuret reagent precaution?
chemicals inside are dangerous, if spill on skin, wash off
Iodine solution precaution
irritant to eyes
Lungs
Thorax=top part body, separated from low part by diaphragm.
Lungs=big sponge protect by ribcage surround by pleural membrane.
What is the system called where your heart rate is?
circulatory system
What is an artificial pacemaker?
same as biological pacemaker, but implanted underskin, with wire going to heart, which spread impulse. For patient with irregular heartbeat.
How does the pacemaker control your resting heart rate?
Produce electrical impulse, spreads to surrounding muscle cell, causing them to contract, and make regular heartbeat
What is the resting heart rate controlled by?
group of cells in right atrium, act as a pacemaker
what is the wall of heart made of?
muscle tissue
What is another name for the circulatory system in humans and why?
double circulatory system, because blood travel through heart 2x on each circuit.
Features of white blood cell?
Have nucleus
Disease in the heart?
cardiovascular disease=disease of heart or blood vessel
Stent features?
Effective long time, recovery from surgery quick,
risk:complication in surgery (heart attack, infection, blood clot near stent=thrombosis.
Cholesterol features
Essential for body to function, too much of bad/LDL cholesterol=bad
much LDL in bloodstream=fat in artery
What is a statin?
drug reduce/slowdown growth of LDL in bloodstream
Advantages of statins?
reduce risk(stroke, coronary, heart attack), increase HDL cholestrol in bloodstream. HDL remove LDL from blood. can help other disease.