Biomed Lab I FINAL
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Prokaryotes
organisms made up of cells without a nucleus or any membrane-encased organelles
ex: bacteria
Plasmid
small, circular extrachromosomal DNA found in bacteria
Genome
the complete set of genetic information of an organism
Chromosomes
long strands of DNA molecules that store an organism’s genome
Genes
short segments of DNA containing protein-coding information
located in chromosomal DNA
DNA
aka deoxyribonucleic acid
long chains composed of repeating subunits called nucleotides
Adenine, Tyrosine, Cytosine, Guanine
antiparallel strands
DNA 5’ … 3’
RNA 3’ … 5’
pGLO Plasmid
recombinant pGLO plasmid that contains several genes and DNA sequences that enable replication of the plasmid DNA, differentiate and re pGLO transformed bacteria
GFP
a jellyfish gene that codes green fluorescent protein; responsible for green fluorescent phenotype
pBAD Promoter
a specific DNA sequence upstream from the GFP gene, which binds to araC-arabinose and promotes RNA polymerase binding and transcription of GFP
bla
a gene that encodes the enzyme beta-lactamase
beta-lactamase breaks down the antibiotic ampicillin
responsible for antibiotic resistant phenotype
ori
the origin of pGLO plasmid DNA replication
araC gene
a gene that encodes the regulatory protein that binds to the pBAD promoter
only when arabinose binds to the araC protein is the production of GFP switched on
araC Protein
regulatory protein encoded by the araC gene
binds to the pBAD promoter
Arabinose
a sugar that binds to the pBAD promoter and displaces the acaC protein from pBAD promoter so RNA polymerase can bind and initiate transcription
only when arabinose binds to araC protein is the production of GFP switched on
Ampicillin
an antibiotic that kills bacteria by destroying beta-lactamase
Recombinant DNA Technology
a method used to modify the gentic properties of an organism
useful in preparing proteins that are used in research and therapy
Steps of Recombinant DNA Technology
1) Synthesis of a recombinant plasmid
genes are cut & recombined to create a plasmid
plasmid must contain gene of interest, DNA for replication sequence, antibiotic resistance (may also have regulating & transcription gene
2) Transformation of the organism
plasmid is inserted into bacteria cell
3) Selection of the transformed organism
transformed cell is grown in antibiotic-containing media to allow plasmid to grow
4) Synthesizing the gene product (protein of interest)
cells are grown in media that contain molecules required for producing protein
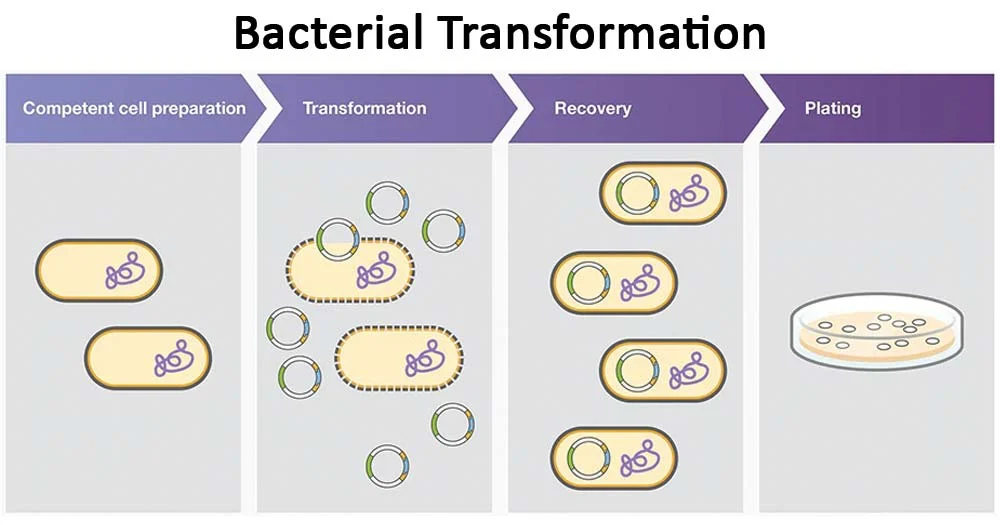
Competent Cells
cells are capable of taking in foreign DNA
positive charge is used to treat cells to allow DNA to enter cell through cell membrane
Bacterial Transformation
method used to introduce plasmid DNA in bacteria
bacteria is made competent to take up foreign negatively charged DNA
QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit
Buffer P1
Buffer P2
Buffer N3
Buffer PE
Distilled Water
Buffer P1
Resuspension Buffer
removal of ions weakens cell membrane for lyse
solution looks cloudy
Buffer P2
Alkaline Lysis Buffer
ruptures cells and denatures DNA into single strands
solution looks clear to show lysis of cells & solubilation of cellular components
Buffer N3
Neutralization Buffer
neutralization allows DNA to renature
solution appears milky
Buffer PE
Wash Buffer
ethanol helps wash chaotropic salts & other contaminants (buffer removed by centrifuge)
Distilled Water
water recovers “hydration shells” around plasmid DNA & dislodges plasmid DNA from silica gel membrane
Mutation
a change in nucleotide sequence of short region of genome, resulting in changes that may lead to disease
Silent Mutation
mutations that do not show a change in translated amino acid, hence no change in phenotype
Polymorphism
naturally occurring genetic differences among organisms in the same species that does not lead to disease
Beer-Lambert’s Law in Relation to Nucleic Acid Quantification
A = εbc
A = absorbance (AU)
ε = absorptivity coefficient for extinction coefficient ((ug/mL)-1cm-1)
b = light path (cm)
c = concentration (ug/mL)
Average Extinction Coefficient for DNA
0.020 (ug/mL)-1cm-1
Average Extinction Coefficient for RNA
0.025 (ug/mL)-1cm-1
Nucleic Acid Purity for 260/280 Ratio
1.8-2 Pure DNA
<1.8 Presence of proteins, alcohol, acidic pH, other contaminants
>2 RNA contamination, basic pH
Nucleic Acid Purity for 260/230 Ratio
2.0-2.2 Pure DNA
<2 EDTA, carbohydrates & phenol
Palindromic Sequence
a segment in DNA or RNA that is the same sequence when read from 5’ to 3’ on one strand and 5’ to 3’ on the complementary strand
Restriction Enzymes
EcoRI
Hind III
Codon
a three-nucleotide sequence of DNA that codes for a particular amino acid
different codons can translate to the same amino acid, leading to silent mutations
Restriction Digest as a Tool to Detect Mutagenesis
when there is a silent mutation within a restriction enzyme’s restriction site, the mutated sequence will not be cut by the enzyme
DNA Shapes
Supercoiled DNA
Linear DNA
Nicked DNA
UV vs Nanodrop Spectrophotometer
UV uses larger sample sizes
Nanodrop uses smaller sample sizes
Protein Structure
Proteins are made up of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
AA Sequence of GFP
serine-tyrosine-glycine
Gene Expression
entire process from transcription through protein synthesis
Gene Regulation
process that allows mRNA and protein synthesis only when and where the encoded protein is required
Promoter
DNA sequence upstream to the coding region of a gene to which the RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription
Regulatory Molecules
activates or inhibits gene transcription
Gel Electrophoresis
procedure used to separate biomolecules using a gel matrix based on size using electric currents
larger molecules migrate more slowly than small
Gel Matrix
contains pores of uniform size through which molecules can pass through
the smaller the pores, the higher the concentration of the gel
SDS PAGE
made up of polyacrylamide gel used to separate proteins by molecule size
Laemmli Buffer dissociates proteins into individual polypeptide subunits
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) denatures protein complexes (and added to running buffer to mask charges)
Dithiothreitol (DTT) cleaves disulfide bonds
Protein Marker
mixture of proteins of known molecular weight that is loaded on the gel to estimate the size of proteins in an unknown sample
Total Protein Estimation
quantified (assayed) using Coomassi blue dye
arginine and nonpolar AA residues interact with the dye causing a shift in dye absorption max, from 465 to 595nm to give blue color
intensity of blue is proportional to protein concentration
Bovine Serum Albumin
commonly used for generating a standard curve
DNA Marker Example
Lambda DNA digested with Hind III enzyme
Amino Acid Functional Groups
Carboxyl group (COOH)
Amino group (NH2)
Isoelectric Point
the pH at which a protein carries no charge
below, proteins carry net positive charge
above, protein carry net negative charge
Chromatography
procedure used to separate individual compounds present in a mixture based on the different physical and chemical properties and determine relative concentration of the compound in mixture
Stationary Phase
thin layer on solid support where compounds are separated based on their relative affinity to the stationary and mobile phase
if compound has greater affinity for mobile phase, compound will move with mobile phase
each compound in sample moves at different speeds through stationary phase
Normal Phase Chromatography
relatively more polar stationary phase and usually made of silica gel
hydrophobic compounds will move quickly
silica gel is acidic and offers poor separation of basic samples, causing deterioration
Reversed Phase Chromatography
relatively more nonpolar in stationary phase due to matrix particles (silica gel) being coated with hydrophobic chains (C18 chains)
Mobile Phase
can be liquid or gas that moved through the stationary phase via capillary action or with the use of pressure
Gel Electrophoresis vs Chromatography
Gel separates based on molecule size
Chromatography separates based on polarity
Size Exclusion Chromatography
SEC separates molecules based on size by filtration through gel (consisting of spherical beads with pores of specific size)
smaller molecules will get trapped in the pores
larger molecules will flow to the bottom more quickly
Thin Layer Chromatography
technique where sample is spotted onto a stationary phase with the bottom edge is placed in a mobile phase
mobile phase moves up the stationary phase via capillary action
compound with greater affinity for mobile phase moves up along with the mobile phase
Retardation Factor
value used to compare movement of individual compounds in sample mixture
Rf = distance traveled by compound / distance traveled by mobile phase
Ninhydrin
color reagent used to convert AA to colored compound (usually purple)
High Performance (or Pressure) Liquid Chromatography
technique that uses a solid stationary phase packed in a column, mobile phase (aka eluent) is pushed through column under constant pressure using pressure pumps
reverse phase most common in analysis of drugs & body fluids
Chromatograph
recording of absorbance changes
when compound is eluted, there is an increase in absorbance, peak is recorded
Retention Time
time required for eluting the compound through the column