RCP - Final Examination
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
Why would someone be instructed to exhale on a chest x-ray?
to see a possibly small pneumothorax
X-ray penetration is inversely related to …
density of the structure
What is semi-fowlers?
a position where the person is lays with their back on a bed
What are the two types of atelectasis?
obstructive and compressive ***. mixed up (ignore this one)
where obstructive is caused by something pushing on the lung (e.g., pneumothorax)
where compressive is caused by plugging or clogging of the bronchioles (e.g., mucus)
What happens in interstitial lung disease?
the lung tissue becomes fibrotic and therefore the lungs compliance decreases
A tension pneumothorax prevents the heart from …?
filling
What is the difference between a pulmonary edema and pleural effusion?
pulmonary - fluid in the lungs (usually caused by CHF)
pleural - outside the lungs
How much fluid is approximately in the intrathoracic cavity?
30 mL
A needle is used to drain [blank] from the pleural cavity?
air; usually at the 2nd intercostal space at the mid-clavicular line
A thoracentesis is performed to remove [blank] from the pleural cavity?
fluid; can be a one-time thing (thoracentesis) or chest tube for a long period of time
this is performed at the 4th or 5th intercostal space in the midaxillary line
A chest tube placed either high or low in the pleural cavity, why?
high - to drain air
low - to drain fluid
What are some indications for chest tube insertion?
-drain hemothorax (blood to collect in pleural cavity) or pleural effusion
-drain pneumothorax greater then 25%
-flail chest
All of the [blank] must be below the dermis upon chest tube insertion?
fenestrations
Why should chest tube tubing be looped horizontally?
to prevent gravity dependant areas from forming and limit pressures from building up in the thorax
Review OSCE Cards:
On a Pleur-Evac system: no bubbling indicates?
everything is drained or their is a blockage
On a Pleur-Evac system: bubbling at times gently indicates?
normal use
Bronchoscopy is mainly used, why?
to obtain samples from the airways and to see them
What are some diagnostic indications for Bronchoscopy?
-chest x-ray provides possible neoplasia (a mass)
-pneumonia
-hemoptysis (blood in the lungs)
-interstitial lung disease
What are some therapeutic indications of Bronchoscopy?
-atelectasis (to remove mucus plugs and secretions)
-remove foreign bodies
-tamponade of a bleeding source
-difficult intubations
What are some contraindications for Bronchoscopy?
-recent myocardial infarction (or heart conditions)
-unstable severe asthma
-severe hypoemia or hypercapnia
-bleeding disorders
-renal failure
What are some results that should be available BEFORE the procedure?
-chest x-ray
-blood work (test for WBC- clotting)
What is the main use for a rigid Bronchoscope?
to manage central airways (e.g., that have an obstruction)
What are some things to check BEFORE use of flexible Bronchoscope?
-flexibility of distal port
-suction port patency
-light source works
-broken bundles
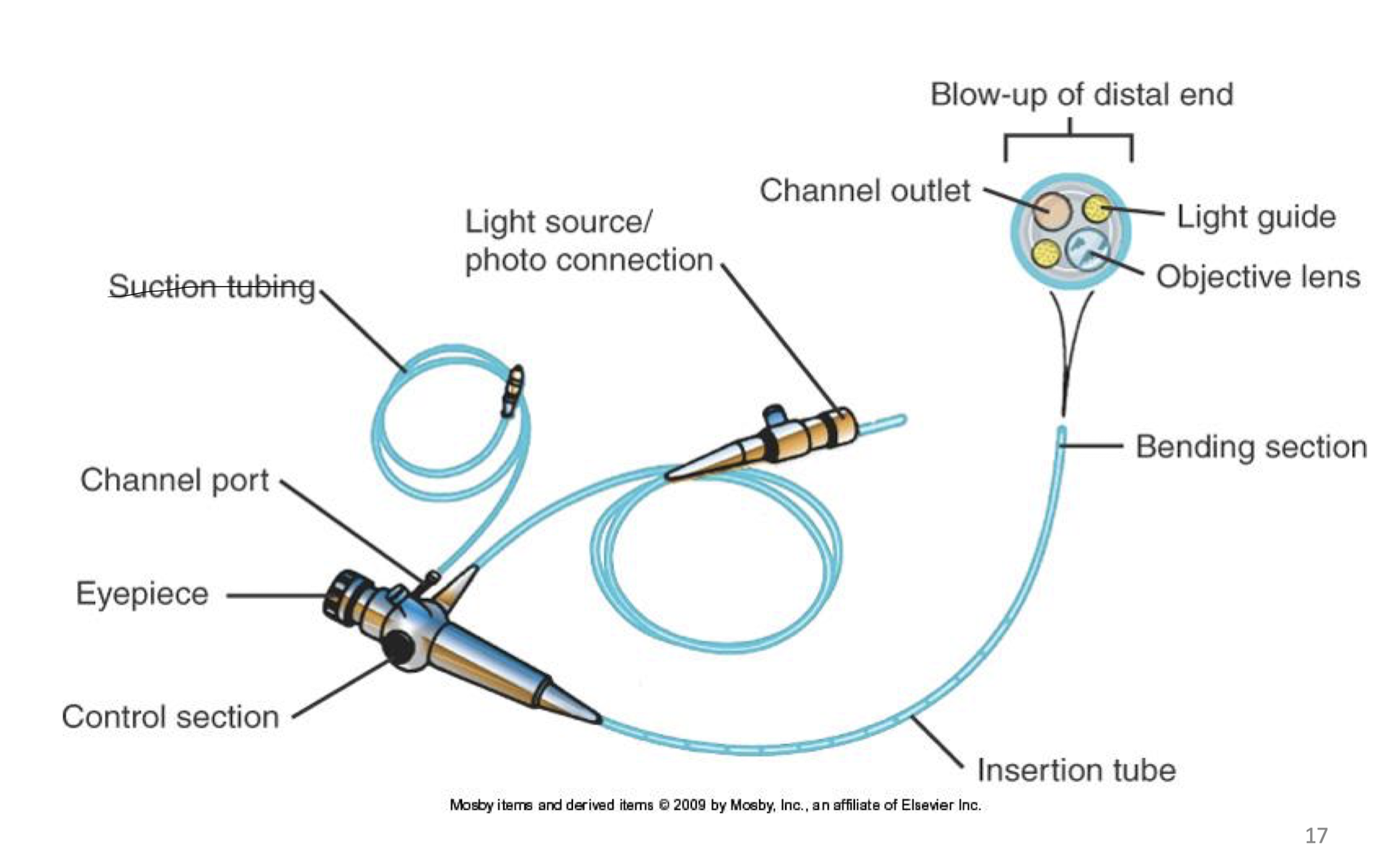
Be familiar with:
List some of the ways to administer anesthetic agents to patients to limit their upper and lower airway perception:
-10 mL 2% viscous lidocaine
-5 mL Neb. 4% lidocaine
-1 to 2% lidocaine directly instilled into lower airways
-nares w/ 2% lidocaine jelly
What are some concerns with lidocaine use?
-limit of use: total dose of 5.0 to 7.0 mg/kg adults
=cause methemoglobininemia (limits blood (Hb) to transport O2)
-added caution with elderly
-those with liver and/or cardiac diseases
What is Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)?
is a procedure during Bronchoscopy to obtain specimens from the alveolar level using saline
Briefly run through the BAL procedure:
-patient in supine position (therefore easier BAL return)
-instill 50 mL of saline (while performing Bronchoscopy) into lower airways
-saline should be around the 4th or 5th generation
-than suction back (15 to 20 mL)
-collected in sputum traps that send to the lab
What are the NORMAL findings in a BAL?
-95% macrophages
-3% lymphocytes
-1 to 2% neutrophils. eosinophils, and basophils
-few epithelial cells
What is Bronchial Washing?
a procedure to obtain for cytologic (cell) examination to test for cancer or infections
=usually done in large airways
What is Bronchial Brushing?
(adjunct of washing)
a procedure where a lesion is brushed back and forth to obtain cell samples
What is Endobronchial Biopsy?
a technique where forceps are used to obtain tissue sample from visible endobronchial lesion
What is Transbronchial Biopsy?
a technique of obtaining a specimen of the lung parenchyma using flexible forceps (e.g., alligator forceps)
=known to cause pneumothorax or bleeding
What is an Endobronchial Ultrasound?
a procedure (TBNA) where a needle is inserted through the bronchial wall to obtain mediastinum or peripheral lung sample using endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS)
=EBUS has improved accuracy of TBNA
What is Thermal Ablation of an Endobronchial Lesion?
-essentially a laser that coagulates, carbonizes, or vaporizes lesions that protrude the airway lumen or obstruct central airways
=risky procedure; hypoxemia, pneumothorax, etc.
What is Cryotherapy?
a method used to destroy tissue by freezing it
=mainly used for central airway obstructions
What is Brachytherapy?
a method used to deliver short-distance radiation
=used for inoperable lung cancer
What is a Endobronchial stent placement?
is where airway stents are used to reduce airway obstruction from a malignant or benign mass that compress the airway from the outside
What are the two most commonly used stents for Endobronchial stent placement?
-metallic; self-expanding stent (can be covered or uncovered)
-silicone; straight Y-shaped
What are some complications of flexible bronchoscopy?
-adverse effects of medications used
-hypoxemia
-hypercapnia
-bronchospasm
-hypotension
-laryngospasm
-bradycardia
-pneumothorax
-hemoptysis
-increased airway resistance
-cross contaimination
Always check the scope for the integrity of the [blank] [blank] covering the scope:
outer sheath; done by attaching an apparatus that will inflate the sheath and check the scope under water
What are some things that need to be done before Bronchoscopy can be done?
-patient fasted for 6 hours
-patient in Fowler’s position
-5 mL Neb. of 4% lidocaine
-IV to start conscious sedation (using fentanyl and versed - common drugs)
-nostril is numbed with Xylocaine
-patient have nasal cannula
A patient can be discharged after a Bronchoscopy when …?
-alert and orientated gag reflex
-sensation in throat is normal
-vital signs are stable
Rigid Bronchoscopes give better access to [blank] [blank] and are best to remove aspirated large [blank] [blank]
large airways - foreign bodies
Flexible scopes are more comfortable, requiring only [blank] [blank] for spontaneously breathing patients
light sedation
What is the most common use for a flexible Bronchoscope?
to diagnose the cause of an abnormality seen on a chest x-ray
Make a [blank] incision through the skin and subcutaneous tissues between the [blank] and [blank] ribs parallel to the rib margins for chest tube insertion
3 to 4 cm; 4th and 5th ribs
What are some contraindications to chest tube insertion?
-infection over the insertion site
-uncontrolled bleeding
What suction pressure is ideal for chest tube drainage systems?
-20 to -30 mmHg
The chest tube should be clamped [blank] hours before removal to assess patient toleration
12
[blank] and [blank] should never be done on chest tubes
stripping or milking
A leak on a chest tube may increase from [blank] ventilation and with increase in [blank] used to inflate the lungs
spontaneous; pressure
[blank] can cause continuous bubbling in a chest tube drainage system
PEEP
Chest tube drainage system: intermitten bubbling (gently)
normal
Chest tube drainage system: continuous bubbling
leak and/or PEEP
Chest tube drainage system: rise and fall of float
normal; up - inspiration
down - exhalation
*vice versa for PPV
Chest tube drainage system: no bubbling
done drainage or blockage
Chest tube drainage system; spontaneous exhalation
small leak, so therefore bubbling
What would you use to confirm NG or OG tube placement?
1 - auscultation upon air pushed through the tube
2 - chest x-ray (ordered right after no matter what)
3 - withdrawal fluid and test for pH (should be less than 5.5)
What are the two reliable methods of confirming tube placement in the lungs?
-EtCO2 (should be yellow)
-breath sounds and chest rise
The inferior tip of the ETT should be [blank] to [blank] above the carina
3 to 5 cm
What is the most reliable method we use to determine the correct insertion and depth AFTER intubation?
chest x-ray
Secretions decrease and increase what …?
decrease compliance and v/q
increase airway resistance
When is nasotracheal suction used?
when patients cannot clear their own secretions (e.g., cannot cough - elderly)
*not a first option used
What are some risks of nasotracheal suction?
-edema (bleeding)
-irritate vocal cords
What position should a patient be in for nasotracheal suction?
sniffing postion
What are some contraindications (not be done) to nasotracheal suction?
-epiglotitis
-laryngospasm
-nasal bleeding
-occluded nares
-worsening the overall patient status
What are some hazards to nasotracheal suction?
-atelectasis
-bronchospasm (constriction)
-decrease heart rate
-increase or decrease BP
-gagging and vomiting
-incresed ICP
-laryngospasm
-hypoxemia
-hypoxia
-infection spread (not closed system)
Suction time should be <= [blank]
15 seconds
What causes an edema?
by suctioning the walls of the airway over and over again
[note: this increases airway resistance and decreases the v/q ratio]
What evidence can prove nasotracheal suction should be performed?
-ABG deterioration
-coarse breath sounds
-increased WOB
-x-ray changes
-visible secretions seen
-vent changes: increase ppeak, decrease vt, change in flow expiration graph
What are the suction pressures for an adult, child, and infant?
adult - 100 to 120. mmHg
children - 50 to 100. mmHg
infants - 40 to 60 mmHg
What are the clinical goals to suctioning?
-improve ABGs and O2 sat’s
-improve breath sounds
-re-establish vent. parameters: decrease ppeak, decrease r, increase vt, and increase dynamic compliance
=overall remove secretions
Prior to suctioning a patient should be [blank]-[blank] with [blank] O2 for [blank] seconds
hyper-oxygenated; 100%; max. 30 seconds
[note: patient MAY be hyperinflated or hyperventilated]
After suction you should [blank] your patient …
re-oxygenate for 60 seconds or less
What is the equation to size an ETT?
ETT size x 2 = number, therefore downsize
8 × 2 = 16 therefore use 14
(Fr size: 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18 …)
What is the ½ rule?
the external diameter of the suction catheter should not be more than ½ of the internal diameter of the ETT
When should suction closed systems be changed?
every 24 to 48 hours
What are some uses of Esophageal or Gastric Tubes?
-remove fluid and gas from gastrointestinal tract
-obtain specimens of gastric contents
-allow drainage and/or lavage in drug overdoses or posionings
-for short term med. admin. and feeding
a NG and/or OG tube will not be inserted if …?
-patient has suspected basal skull fracture
-danger or perforation with patients who have recent throat, esophageal or gastric surgery
-facial deformaties
-has severe coagulopathies (blood cannot clot)
Insertion of NG or OG tube
-patient should NOT be in sniffing position
-if you meet resistance rotate the tube
What should be done after NG or OB tube in inserted?
x-ray should be ordered
What method is questionable to confirmed NG and OG insertion?
the air auscultation method
-could be in esophagus, stomach or duodenum
What are some complications of NG and OG insertion?
-trauma to nares, esophagus, and/or stomach
-gastric drainage could lead to metabolic alkalosis
-placement in trachea
[blank] [blank] is used to prevent the tube from adhering to the gut wall
intermittent suction
Airway care management is important because usually unconscious patients their [blank] falls back into the [blank] and blocks [blank]
tongue, pharynx, and airflow
What are oropharyngeal airways useful for?
-useful when the tongue and epiglottis fall back against the posterior pharynx to correct this
[may cause gag reflex and vomit - just remove]
An oropharyngeal airway sizing: too short, too long?
too short - cannot displace tongue
too long - cause further airway obstruction
[note: sizes range from 000 to 5]
Name all the artificial airways:
-oropharyngeal
-nasopharyngeal
-esophageal
-endotracheal
-trachesotomy
How do you measure a nasopharyngeal airway?
from the nares to the meatus of the ears
Which nare typically has the least obstruction
the left
What are some contraindications of a nasopharyngeal airway?
-anti coagulated patients (reduce clotting in blood medication)
-basilar skull fractures
-nasal infections
-infants and children
[note: can be used to inset NG tube in patient with facial injuries]
What are some benefits to a nasopharyngeal airway?
-good for patients who require frequent suctioning
Inserting a nasopharyngeal airway [blank] must be always toward to septum
the bevel at the end
What is the purpose of an esophageal airway?
to prevent gas from going into the GI tract
What are some hazards of esophageal airways?
-esophageal rupture
-tracheal intubation and failure to seal mask
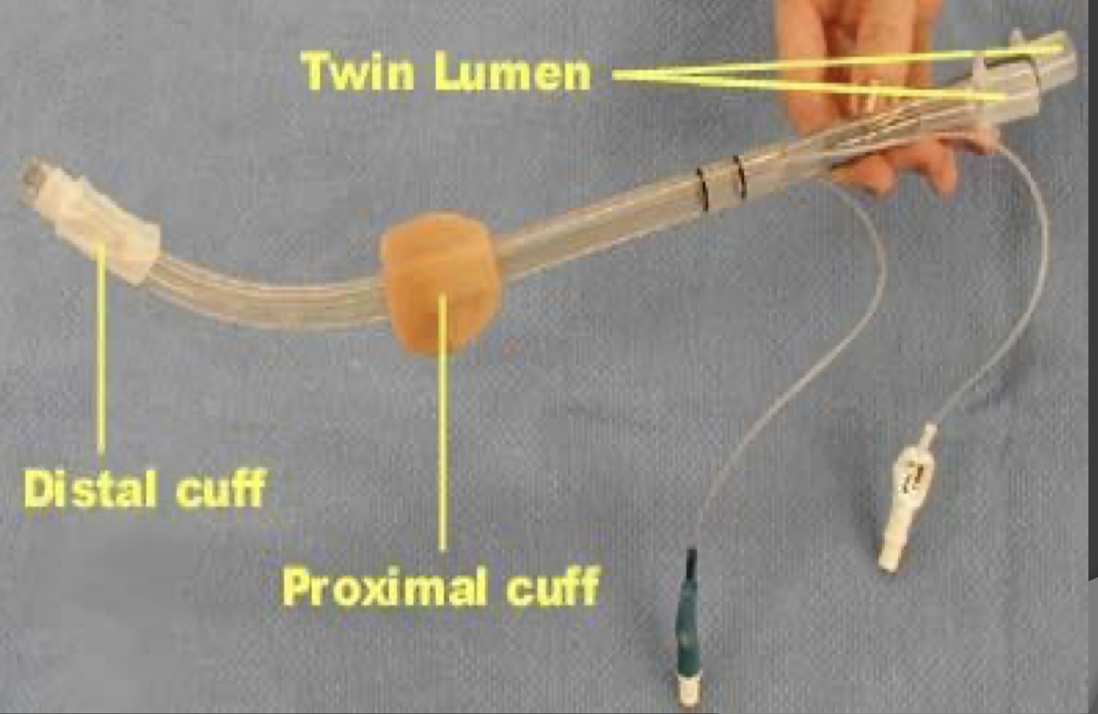
What is this image?
a esophageal airway - used when ETT is not feasible, therefore emergency
Upon insertion of a esophageal airway inflate …
-the blue pilot balloon with 40 mL of air
-the white pilot balloon with 5 mL of air
After inflation of esophageal airway attempt …
-attempt ventilation through the blue opening; if breath sounds, continue,
-if no breath sounds through #1, attempt ventilation through #2