Geography- Earth, volcanoes, plate tectonics
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Earth layers
inner core
outer core
mantle
crust
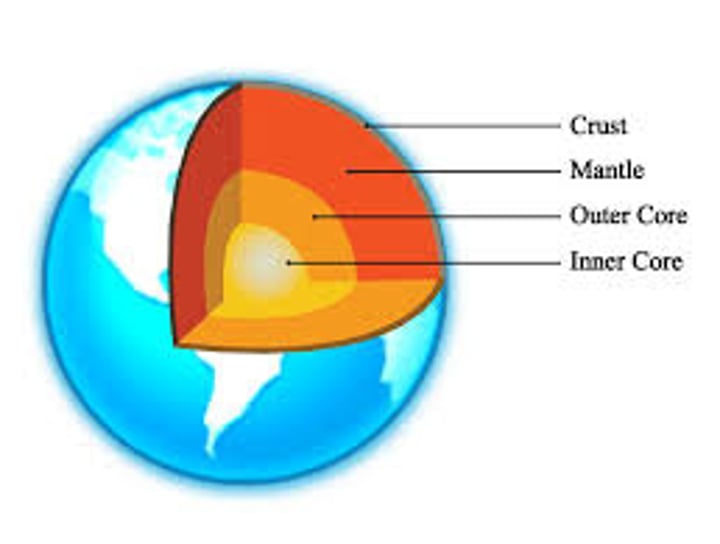
characteristics of the inner core
is in the centre and is the hottest part of the Earth. It is solid and made up of iron and nickel with high temperatures
characteristics of the outer core
layer surrounding the inner core. It is a liquid layer, also made up of iron and nickel. It is still extremely hot, with temperatures similar to the inner core.
characteristics of the mantle( asthenosphere)
the widest section of the Earth.The mantle is made up of semi-molten rock called magma. In the upper parts of the mantle the rock is hard, but lower down the rock is soft and beginning to melt.
characteristics of the crust( lithosphere)
thinnest layer of the earth. it is the solid rock layer upon which we live.
two different types of crust
continental crust- which carries land,
oceanic crust- which carries water.
plate tectonics
the movement of the plates, and the activity inside the Earth
theory of plate tectonics
Earth's solid outer crust, the lithosphere, is separated into plates that move over the upper mantle
process of theory of plate tectonics
The heat rising and falling inside the mantle creates convection currents generated by radioactive decay in the core. The convection currents move the plates.
PLATE Distribution
The Earth's crust is broken up into pieces called plates.
Where are earthquakes most likely to occur?
near or on plate boundaries
PLATE BOUNDARY
the place where two plates meet
3 types of plate boundaries
constructive plate boundary
destructive plate boundary
conservative plate boundary
CONSTRUCTIVE BOUNDARY (Divergent Boundary )
plates are moving apart. As the plates move apart magma rises from the mantle. The magma erupts to the surface of the Earth. This is accompanied by earthquakes. When the magma reaches the surface, it cools and solidifies to form a new crust of igneous rock.
- they tend to be found under the sea
- no fold mountains
DESTRUCTIVE BOUNDARY (Convergent boundary)
plates are moving towards each other. This usually involves a continental plate and an oceanic plate.The oceanic plate is denser than the continental plate so, as they move together, the oceanic plate is forced underneath the continental plate.Also known as subduction zone. As the oceanic plate is forced below the continental plate it melts to form magma and earthquakes are triggered. The magma collects to form a magma chamber. This magma then rises up through cracks in the continental crust.As pressure builds up, a volcanic eruption may occur.
- fold mountains
folding
As the plates push together, the continental crust is squashed together and forced upwards
fold mountains
created through the process of folding. can also be formed where two continental plates push towards each other. This is how mountain ranges such as the Himalayas is formed.Fold mountains occur near destructive plate boundaries
The formation of fold mountains
•Where an area of sea separates two plates, sediments settle on the sea floor. These sediments gradually become compressed into sedimentary rock.
• When the two plates move towards each other again, the layers of sedimentary rock on the sea floor become crumpled and folded.
•Eventually the sedimentary rock appears above sea level as a range of fold mountains.
SUBDUCTION ZONES
Seduction happens when tectonic plates shift, and one plate is pushed under another.This movement of the ocean floor produces a mineral transmutation. which leads to the melting and solidification of magma and the formation of volcanoes.
- happen at destructive plate boundary
CONSERVATIVE BOUNDARY (transform boundary)
plates move past each other ,side by side moving at different speeds. As the plates move, friction occurs and plates become stuck. Pressure builds up because the plates are still trying to move. When the pressure is released, it sends out huge amounts of energy, causing an earthquake. The earthquakes at a conservative plate boundary can be very destructive as they occur close to the Earth's surface.
cause earthquakes
- they have no volcanoes
- no fold mountains
The Ring of Fire
path along the Pacific Ocean characterized by active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes.
earthquake
the shaking and vibration of the Earth's crust due to movement of the Earth's plates
how do earthquakes occur
occur when tension is released from inside the crust. Plates do not always move smoothly alongside each other and sometimes get stuck. When this happens pressure builds up
focus
The point inside the crust where the pressure is released
epicentre
point on the Earth's surface above the focus. it is where the most severe damage caused by an earthquake happens
How is earthquake energy released?
in seismic waves
How seismic waves travel
These waves spread out from the focus. The waves are felt most strongly at the epicentre, becoming less strong as they travel further away.
Deep focus earthquakes
associated with Subduction zones
- destructive plate boundary
Shallow focus earthquakes
located along conservative plate boundaries where two plates move past each other
seismometer
measures the power of an earthquake. by detecting the vibrations caused by an earthquake and plotting them in a seismograph.
Ritcher scale
measures magnitude or strength of an earthquake
human activities that cause earthquakes
Nuclear testing
Building large dams
Drilling for oil/ natural gas
Coal mining
short term Effects of an earthquake- Social
people die
homes destroyed
communication and transport links disrupted
water pipes and gas pipes may burst
short term Effects of an earthquake- economic
shops and businesses destroyed
damaged communication and transport links
short term Effects of an earthquake- environmental
built landscape destroyed
fires can spread due to gas pipes bursting
landslides and flooding due to tsunamis may occur
long term Effects of an earthquake- Social
diseases may spread
people may have to be re-located
long term Effects of an earthquake- economic
cost of rebuilding is high
income lost
only certain areas heavily affected by the earthquakes may be fixed taking away the money that could have been used for other places
long term Effects of an earthquake- environmental
important human landmarks may be lost
water contamination
Factors affecting the impact of an earthquake
-Distance from the epicentre - the effects of an earthquake are more severe at its centre.
-The higher on the Richter scale- the more severe the earthquake is.
-Level of development - MEDCs are more likely to have the resources and technology for monitoring, prediction and response.
-Population density (rural or urban area)- The more densely populated an area, the more likely there are to be deaths and casualties.
-Communication - accessibility for rescue teams.
The effects of an earthquake in LEDCs
-Communication systems may be underdeveloped- so the population may not be well educated about what to do in the event of a volcanic eruption or an earthquake.
-Construction standards tend to be poor in LEDCs.- Homes and other buildings may suffer serious damage when a disaster occurs.
-Evacuation and other emergency plans can be difficult to put into action due to limited funds and resources.
-There may not be enough money to rebuild homes quickly and safely.
-Many people could be forced to live in emergency housing or refugee camps.
Prediction
involves using seismometers to monitor Earth tremors. Experts know where earthquakes are likely to happen.
However, it is very difficult to predict when they will happen.
Protection
Many areas prone to earthquake hazards now use building codes. Any new building or adjustment to existing buildings must be carried out to strict guidelines to help protect people from future earthquake hazards.
examples of building improvements from earthquakes
-rubber shock absorbers in the foundations to absorb the Earth tremors
-steel frames that can sway during Earth movements
-open areas outside of the buildings where people can assemble during an evacuation
-Lightweight roofs designed to reduce damage and injury
Volcano
an opening in the Earth's crust that allows magma, hot ash and gases to escape
How volcanoes form
-Pressure builds up inside the Earth.
-When this pressure is released, as a result of plate movement, magma explodes to the surface causing a volcanic eruption.
-Magma rises through cracks or weaknesses in the Earth's crust.
-The lava from the eruption cools to form new crust.
-Over time, after several eruptions, the rock builds up and a volcano forms
volcanoes occur at
They occur at destructive and constructive plate boundaries.
- but not at conservative boundaries.
magma chamber
collection of magma inside the Earth, below the volcano
main vent
main outlet for the magma to escape.
Secondary vents
smaller outlets through which magma escapes
crater
created after an eruption blows the top off the volcano.
eruption occurs when
pressure in the magma chamber forces magma up the main vent, towards the crater at the top of the volcano. Some magma will also be forced out of the secondary vent at the side of the volcano
Volcanoes can be described in terms of activity
-Still active and erupt frequently.
-Dormant -temporarily inactive but not fully extinct
- Extinct-never likely to erupt again
Different types of volcano
- Shield volcanoes
- Strato volcanoes / composite volcano
- Cinder Cones
Shield volcanoes
-Shield volcanoes are usually found at constructive boundaries.
-They are low, gently sloping sides.
-They are formed by eruptions of thin, runny lava.
-Eruptions tend to be frequent but relatively gentle.
- largest of all the volcanoes on the earth, which are not steep.
-mostly made up of basalt.
-become explosive if in some way water gets into the vent, otherwise, they are characterized by low-explosivity.
- The lava that is moving upwards does so in a fountain-form and emanates the cone at the vent's top and then develops into a cinder cone.
•Eg: Hawaiian shield volcanoes
pyroclastic flow
-mixture of hot steam, ash, rock and dust.
can roll down the sides of volcanoes at high speed
Strato volcanoes / composite volcano
- are made up of alternating layers of lava and ash
- found at destructive boundaries.
- eruptions from these volcanoes may be a pyroclastic flow rather than a lava flow.
ex: Mayon Volcano in the Philippines, Mount Fuji in Japan, and Mount Rainier in Washington
Cinder Cones
-smallest and most common type of volcano.
-cone shape, but is much smaller than a composite volcano.
- found ag destructive boundary
- have steep sides.
- composed of small fragments of rock,
ex: Mauna Kea, a volcano on the American island of Hawaii, and Mount Etna, a volcano on the Italian island of Sicily,
What are the advantages of Volcanoes?
- attracts tourists bringing income to the area
- lava and ash give valuable nutrients and create fertile soils
- give geothermal energy
What are the disadvantages of Volcanoes?
- lives lost
- pollution
- kills crops
- destroys infrastructure
warning signs of volcanoes
- rise in temperature
- small earthquakes
- release of gas
Monitoring Techniques for volcanoes
- seismometers- to monitor earthquakes
- thermal imaging- to detect heat around volcano