Physical Science - Unit 7: Electricity
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
electroscope
device that detects the presence of a charge and involves two pieces of metal foil
static electricity
net accumulation of electrical charges on an object
measured in volts
potential difference/voltage
conductors
allow electrons to move through them freely
insulators
do not allow electrons to move through them freely
electric field
area that surrounds an electron and can exert force
transformer
A device that increases or decreases the voltage of alternating current
resistance
tendancy of a material to oppose the flow of electrons
DC
direct current, flows in only one direction through a wire, ex dry cell battery
AC
alternating current, reverses its direction in a regular pattern, ex wall outlet
dry cell battery
electron pump that has a potential difference between the positive and negative ends
type of cell found in your car
wet cell
circuit
closed path through which electrons can flow
current
measured in amps, flow of electrons through a wire or any conductor
electrical power
rate at which electrical energy is converted into another form of energy
electricity travels
out the positive and into the negative
What is Ohms law?
V=IR
Explain how a wall socket works using the terms electrical potential and voltage
There is an electrical difference between the two holes in the socket. The voltage moves from one hole, into the cord, and then into the hole with the lower voltage.
What is the average voltage in an American house?
120 volts
What is the average voltage in a European house?
240 volts
Like charges _____ and opposite charges ______
repel, attract
DC
direct current, flows in only one direction, ex dry cell
AC
alternating current, reverses direction, wall outlet
Name 5 mechanical sources of energy for a generator
fossil fuels, hydroelectric, wind, solar, nuclear, geothermal
If I am using power in an equation and it is in watts, do I need to change it to kilowatts?
no
If I am finding power in an equation and it is in watts, do I need to change it to kilowatts?
yes
What is a common, low resistance materical used in buildings and houses?
copper wire
What is the difference between a series and a parallel circuit?
Series is one current path, parallel has multiple
parallel circuit diagram
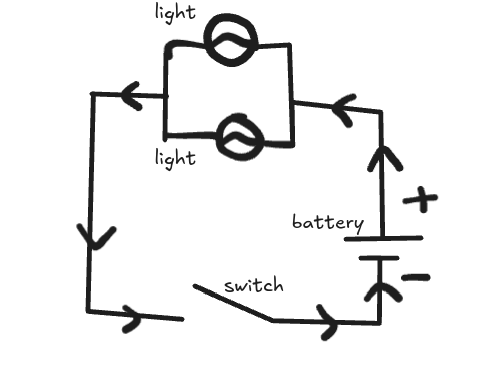
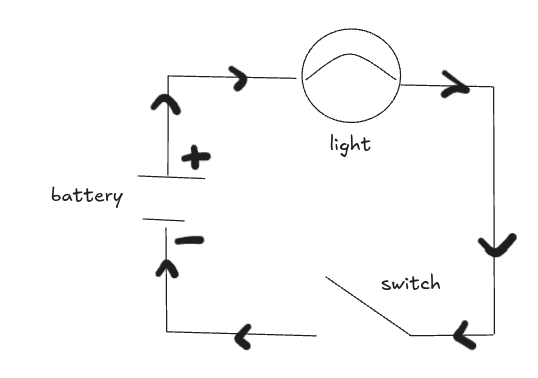
series circuit diagram
label battery, switch and light, current, positive and negative sides
how does an electric generator work?
A piece of wire is spun between two magnets by a mechanical source