pin test head and neck anatomy
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
169 Terms
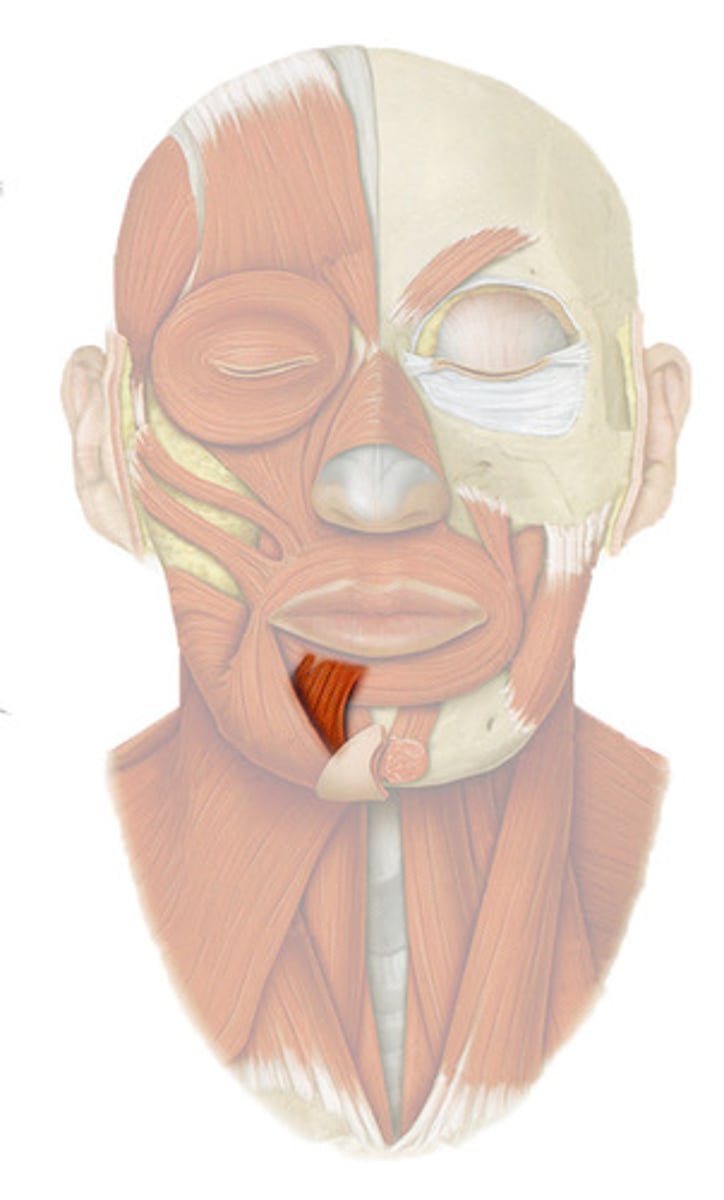
depressor labii inferioris, draws lip down
structure and function
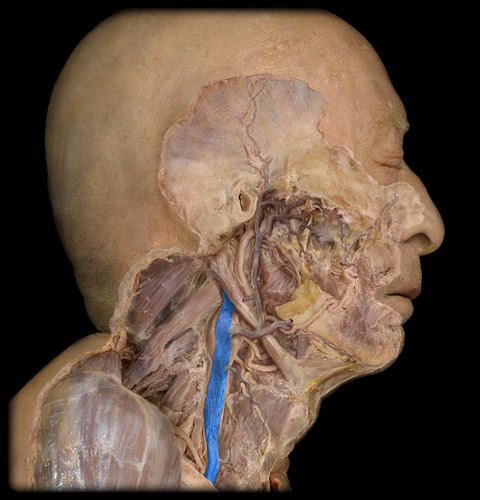
internal jugular vein
cribiform plate of ethmoid bone
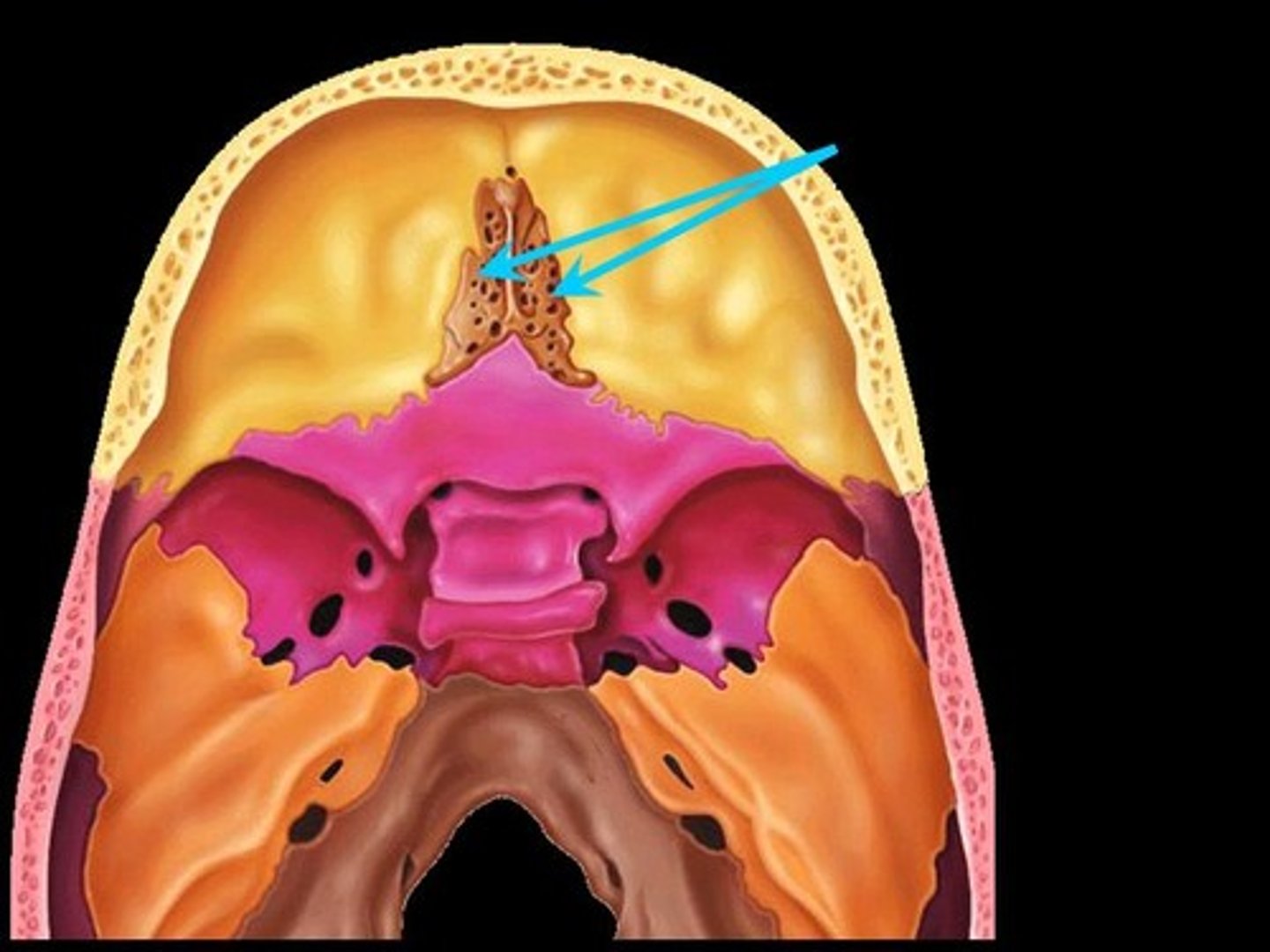
lesser wing of sphenoid bone
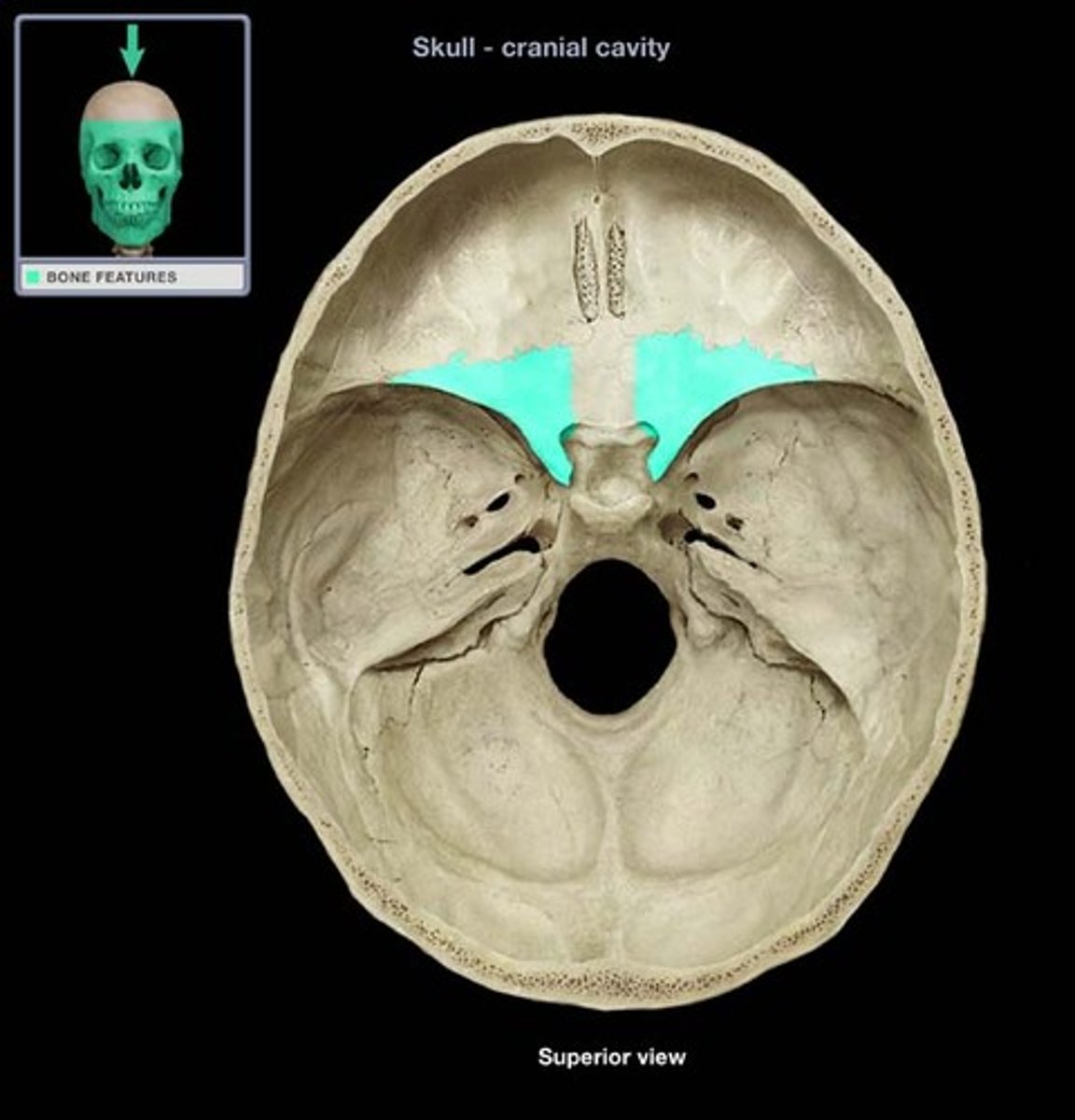
crista galli of ethmoid bone
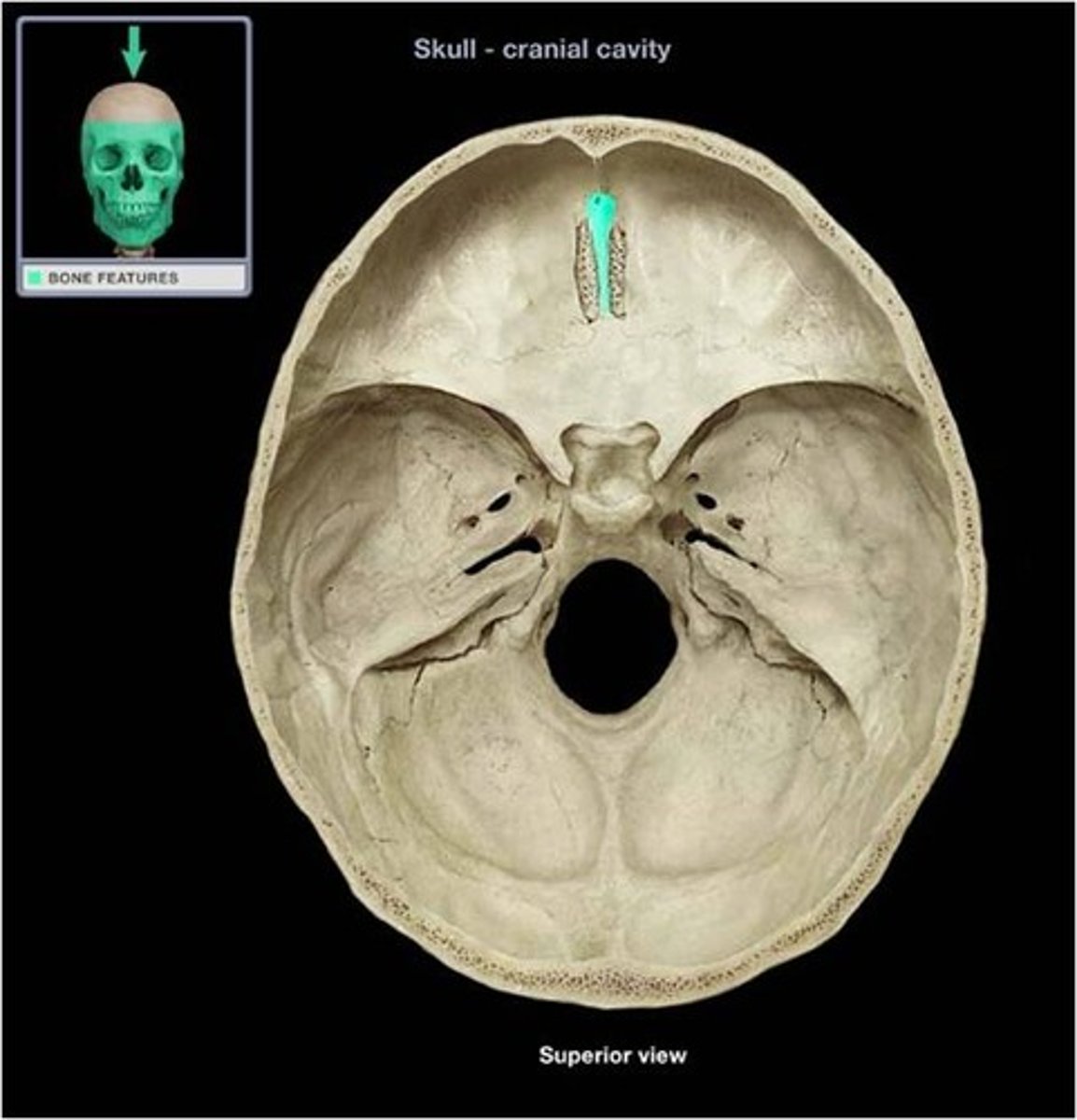
body of sphenoid bone
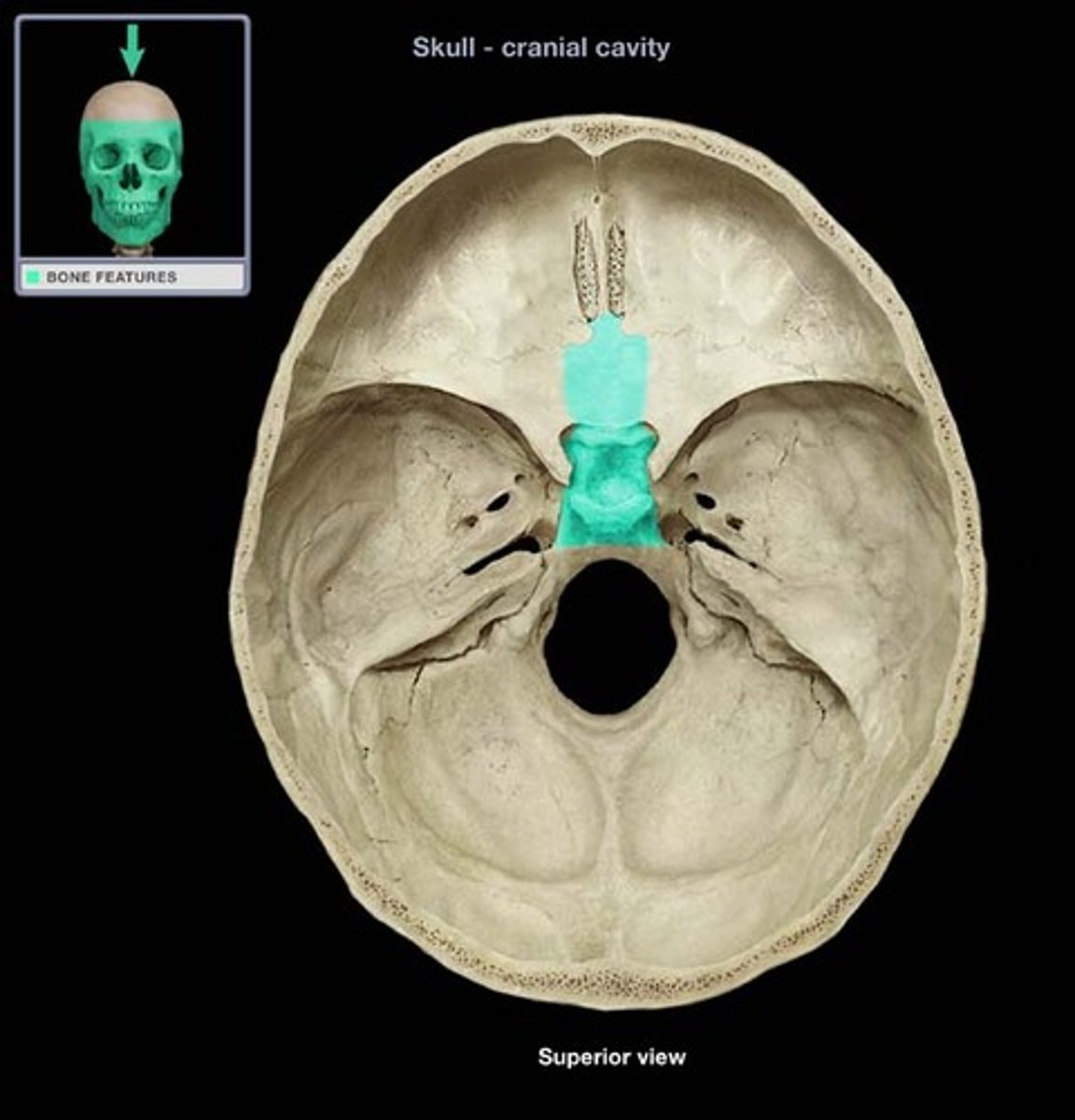
greater wing of sphenoid
squamous suture
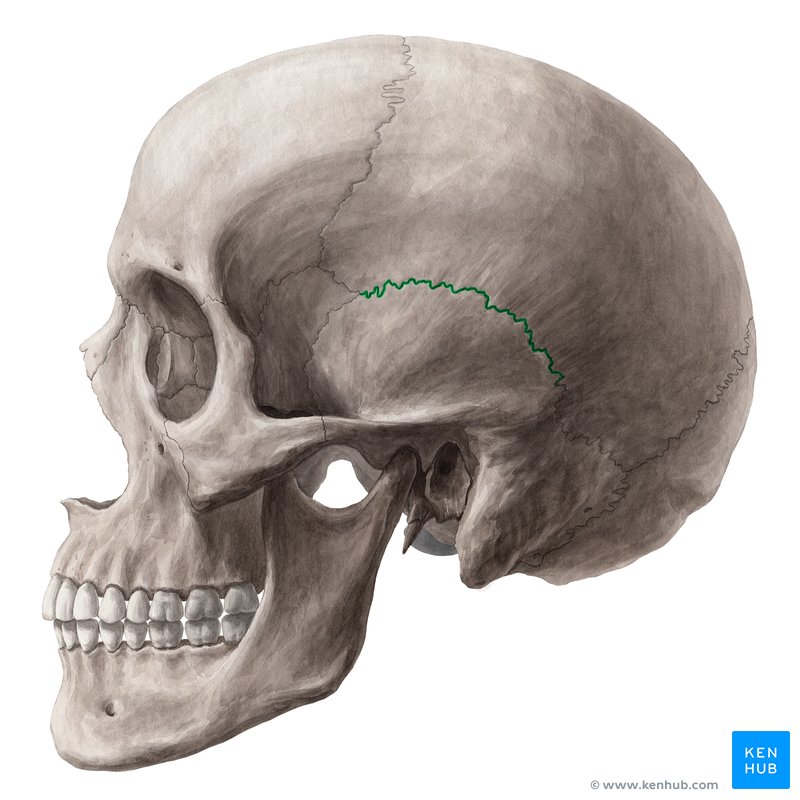
Petrous ridge
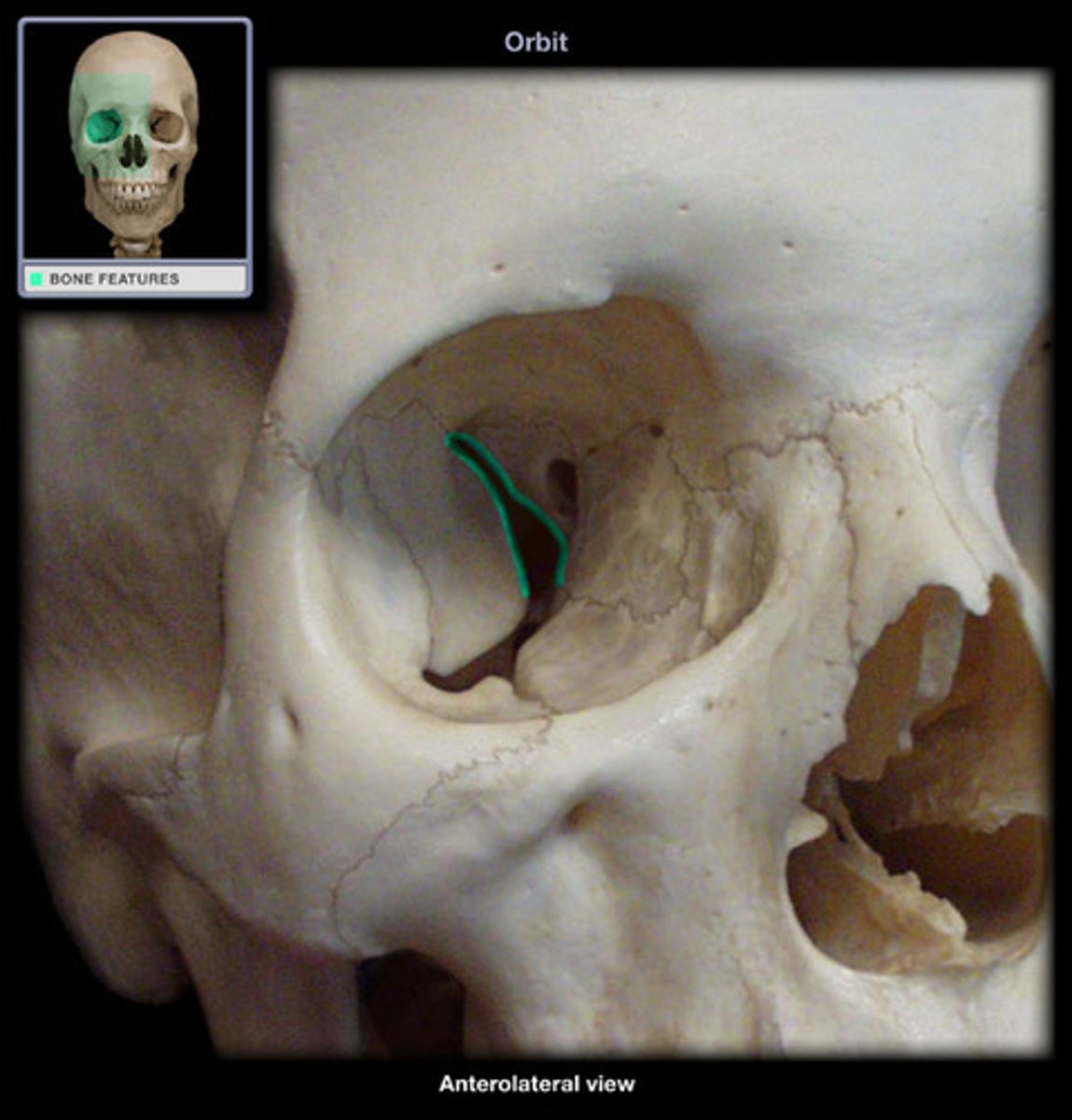
optic canal and optic nerve
what is the name of this structure and what goes through it
supra orbital fissure and CN III, CN VI, CN VI, CN V1
what is the name of this structure and what goes through it
foramen rotundum and CN V2 (maxillary branch)
what is the name of this structure and what goes through it
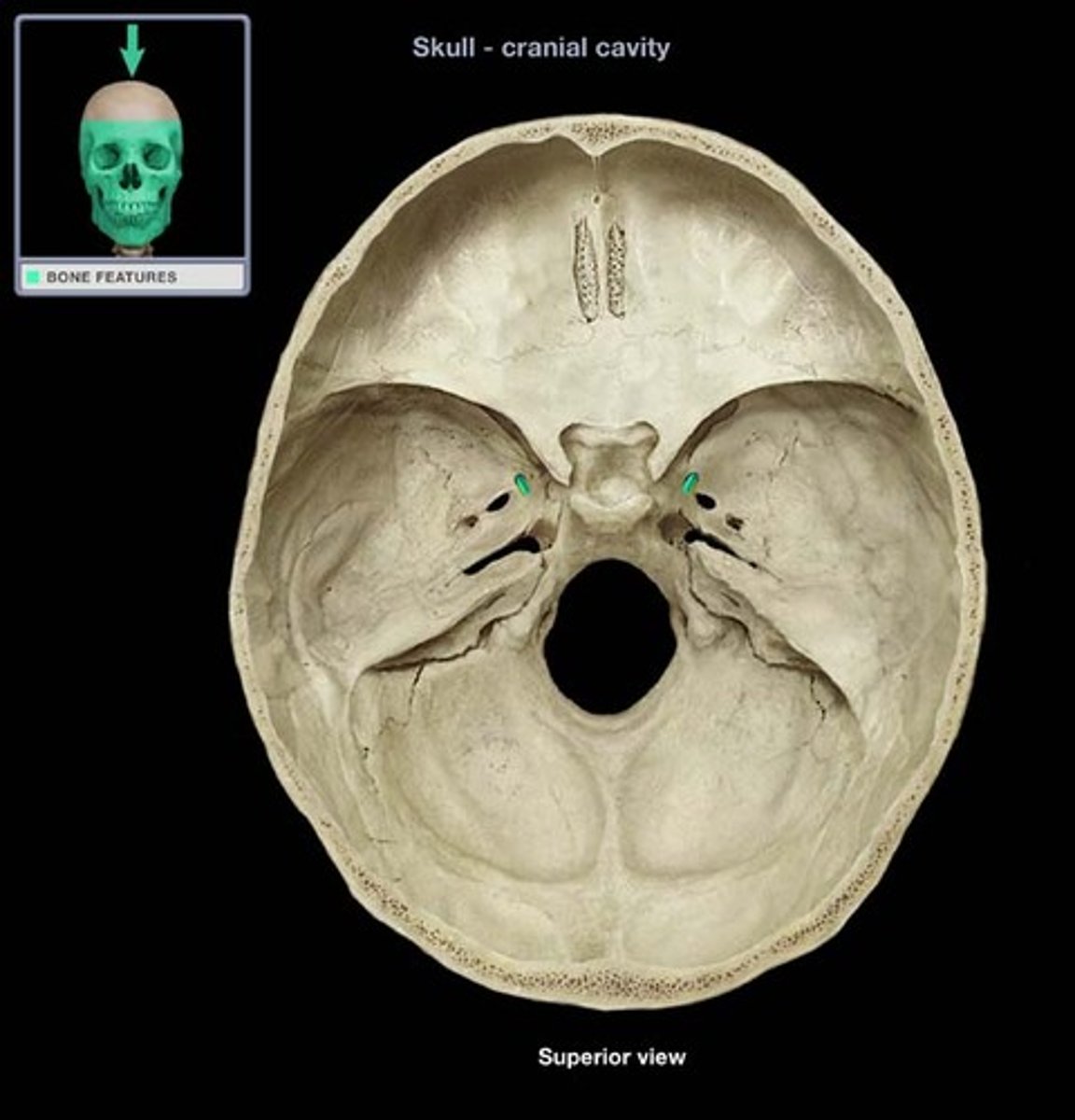
foramen ovale and CN V3 (mandibular branch of opthalmic)
what is the name of this structure and what goes through it
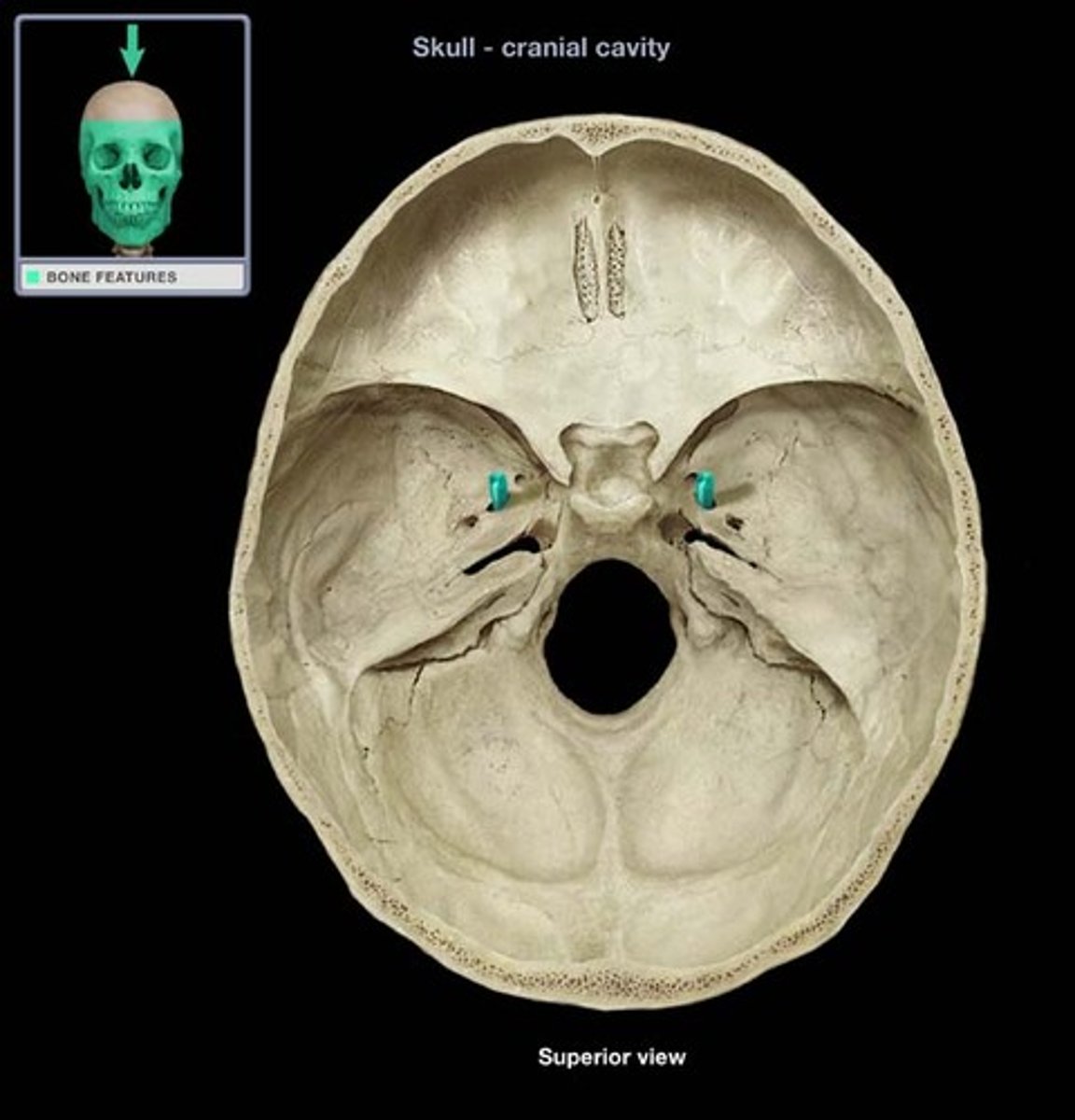
foramen spinosum and middle meningeal artery
what is the name of this structure and what goes through it
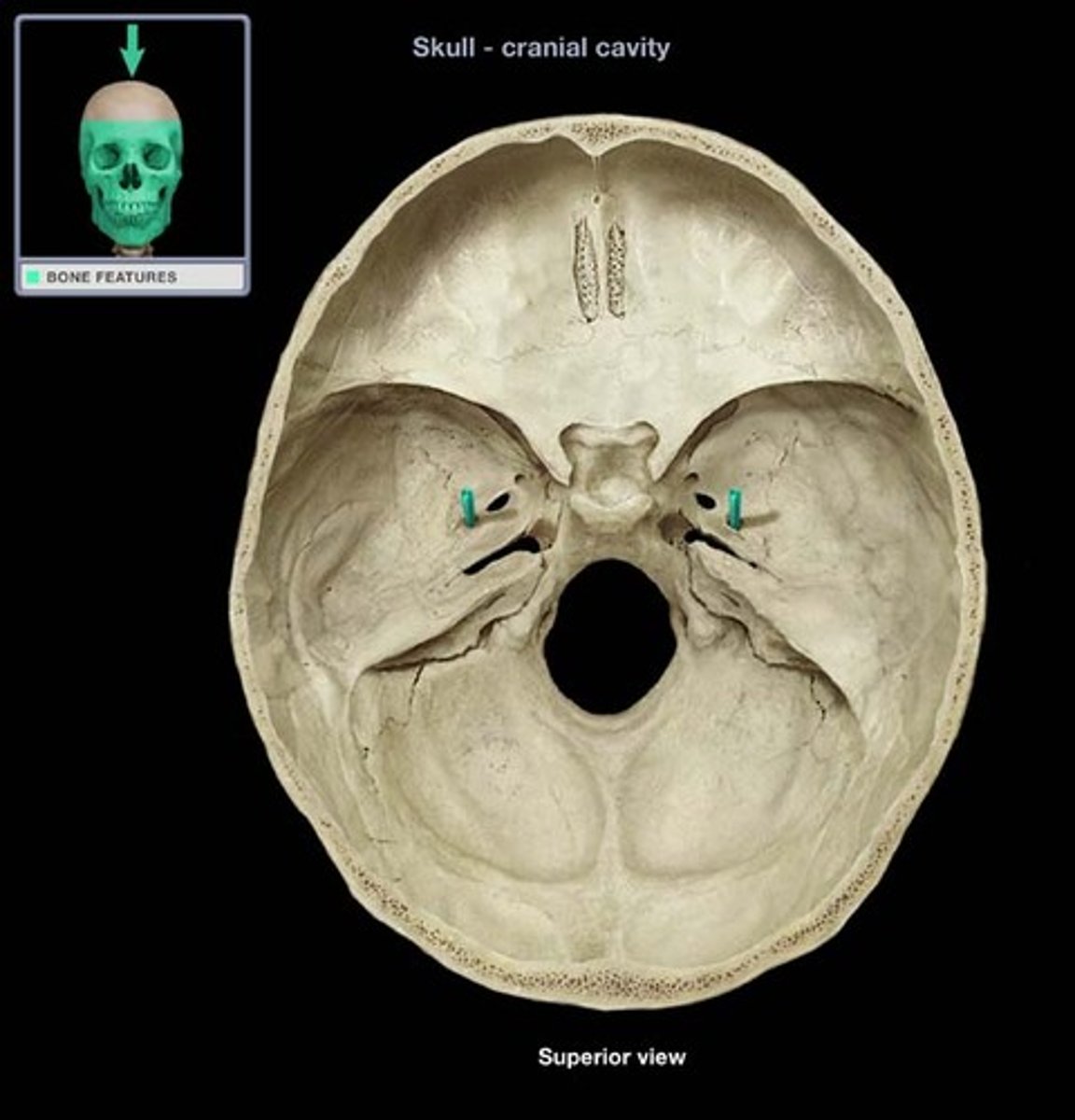
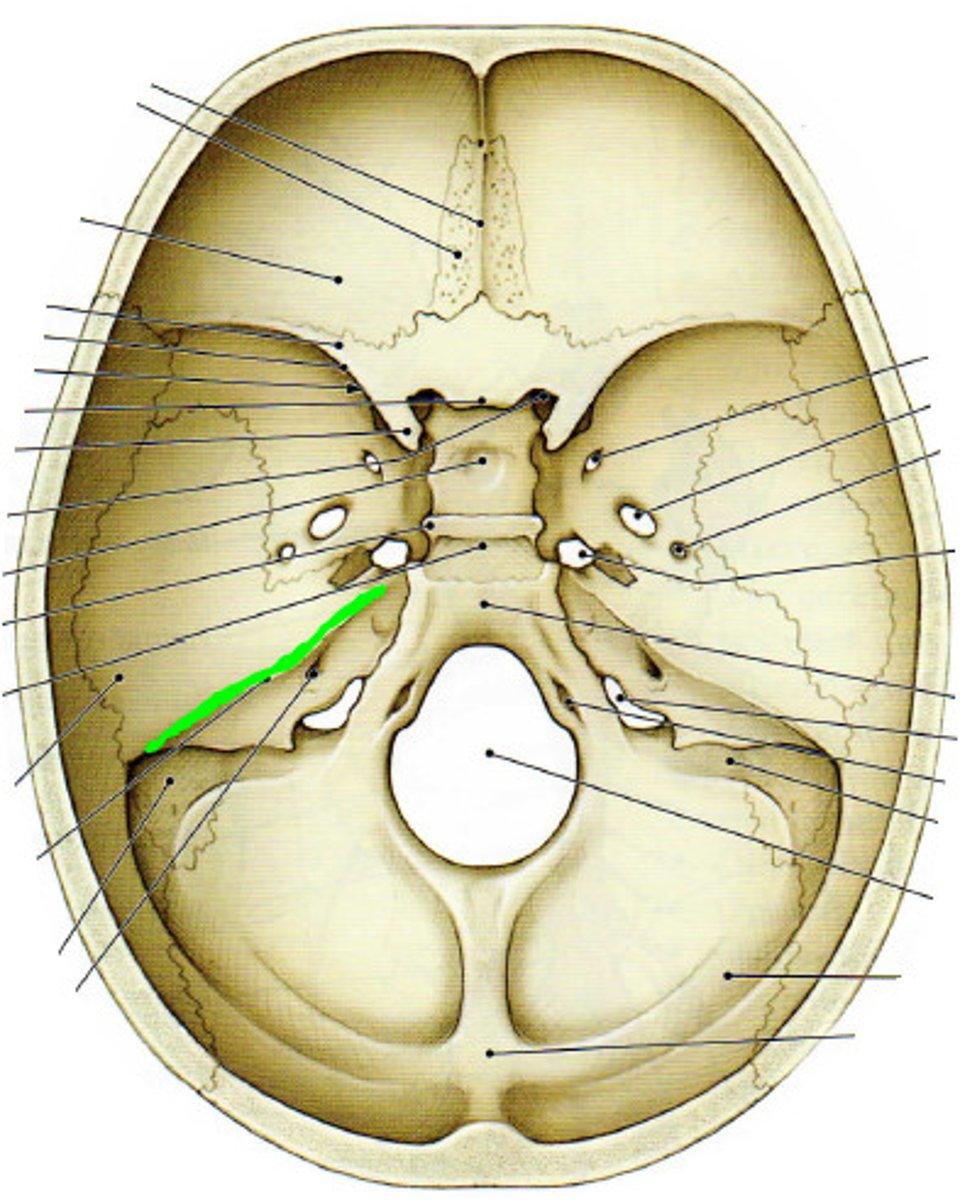
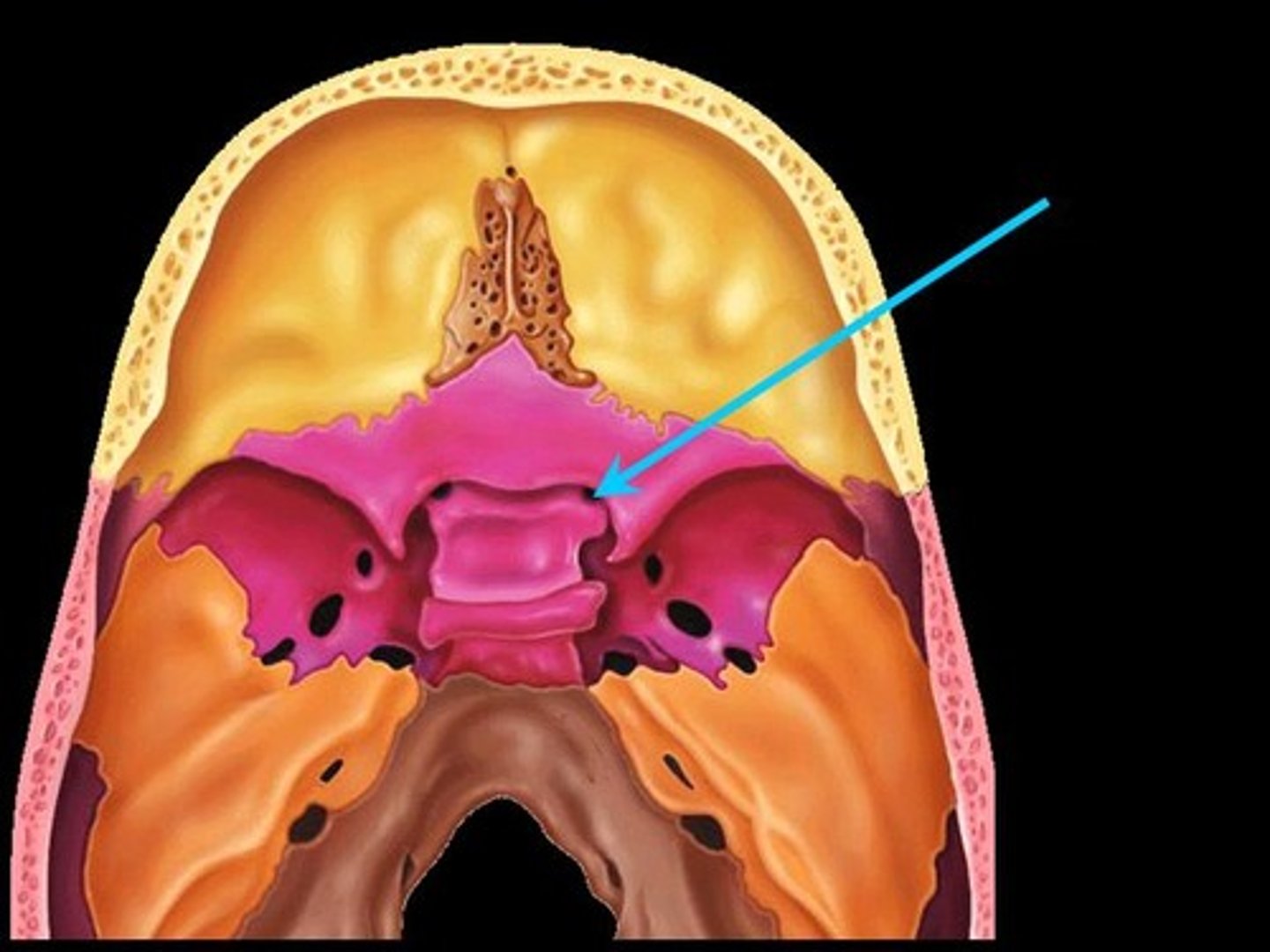
foramen lacerum
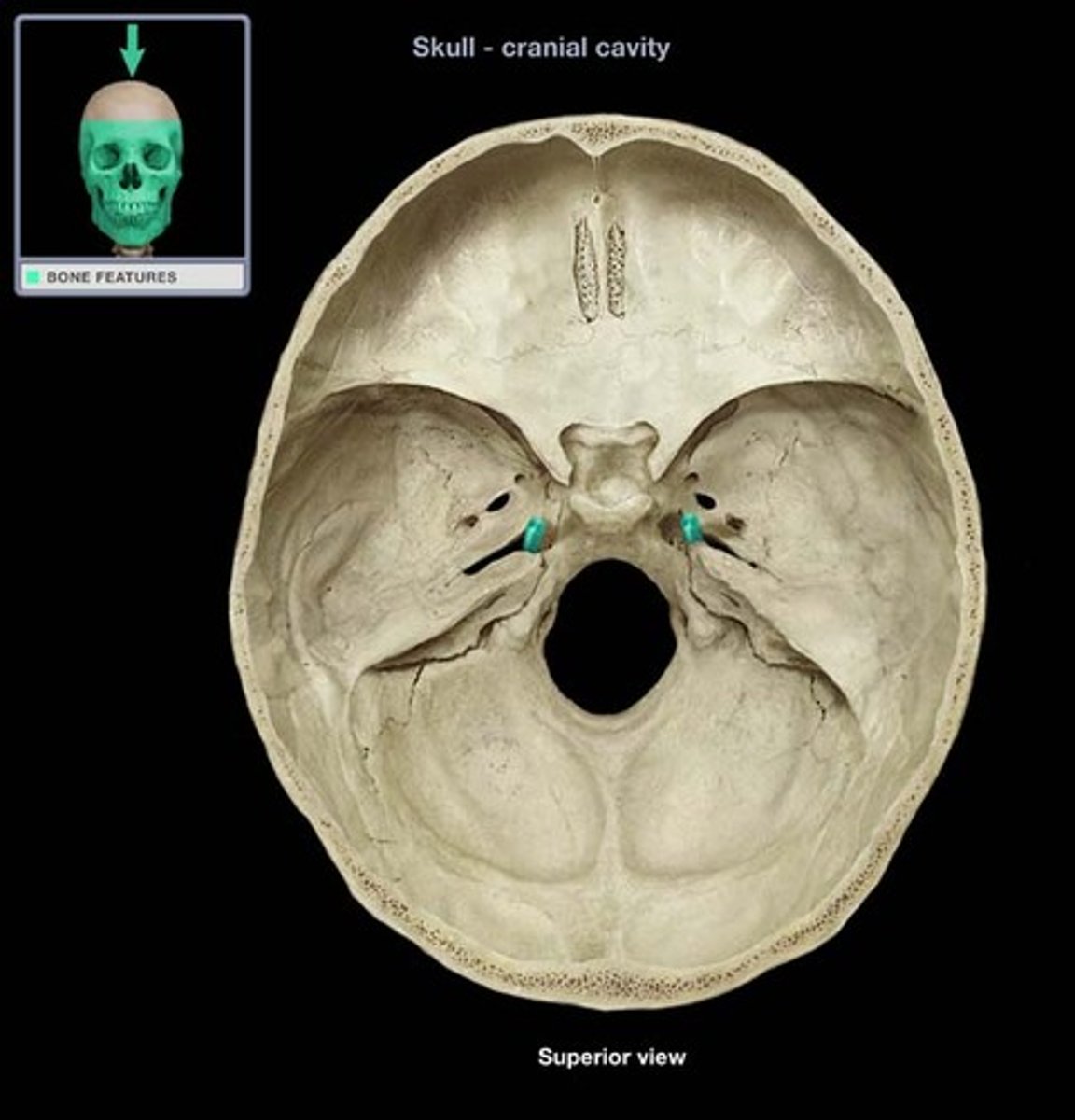
sella turcica
hypophysial fossa
depression in the center of the sella turcica
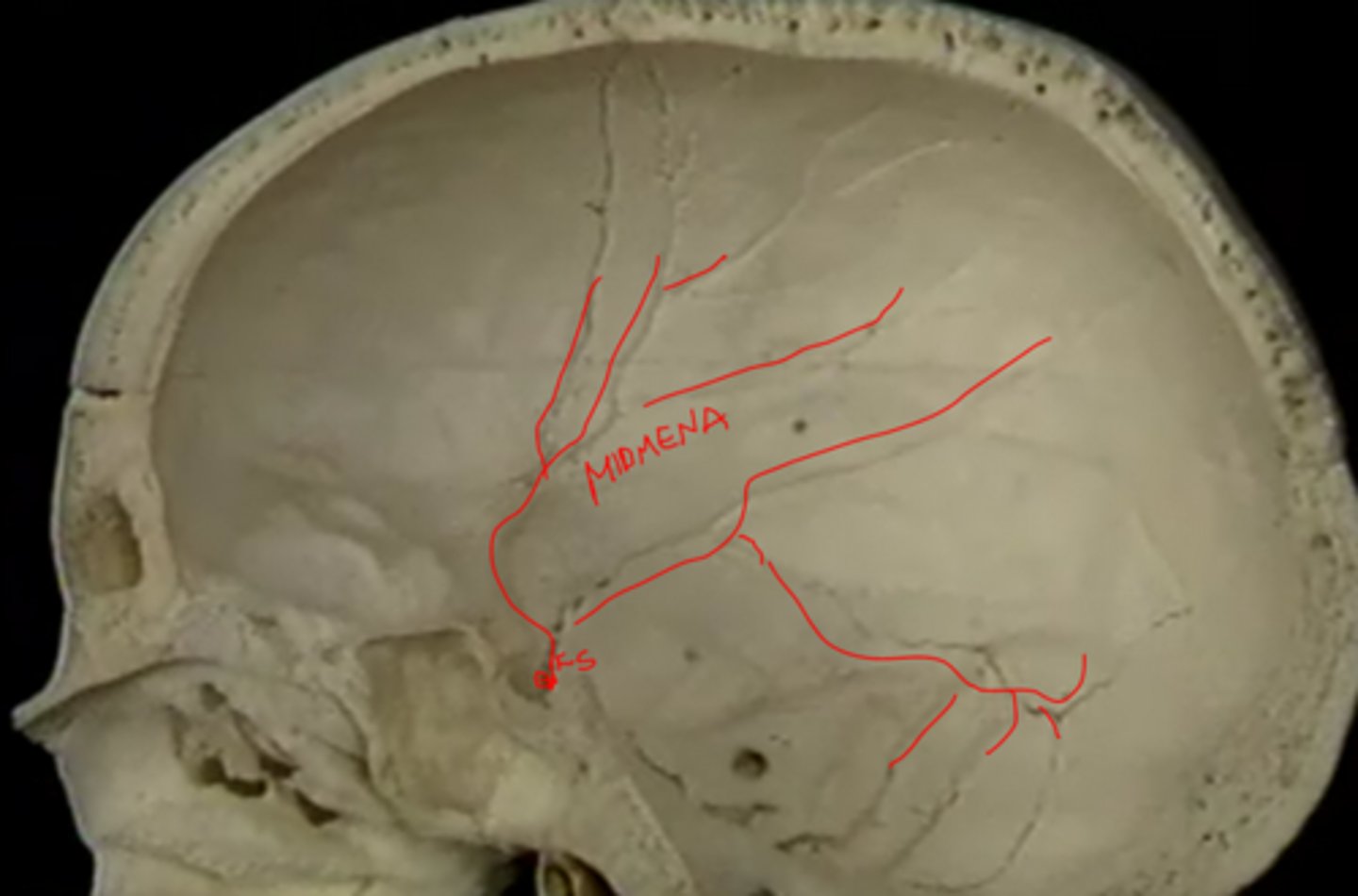
groove for middle meningeal artery
clivus
foramen magnum and vertebral artery
what is the name of this structure and artery that runs through it
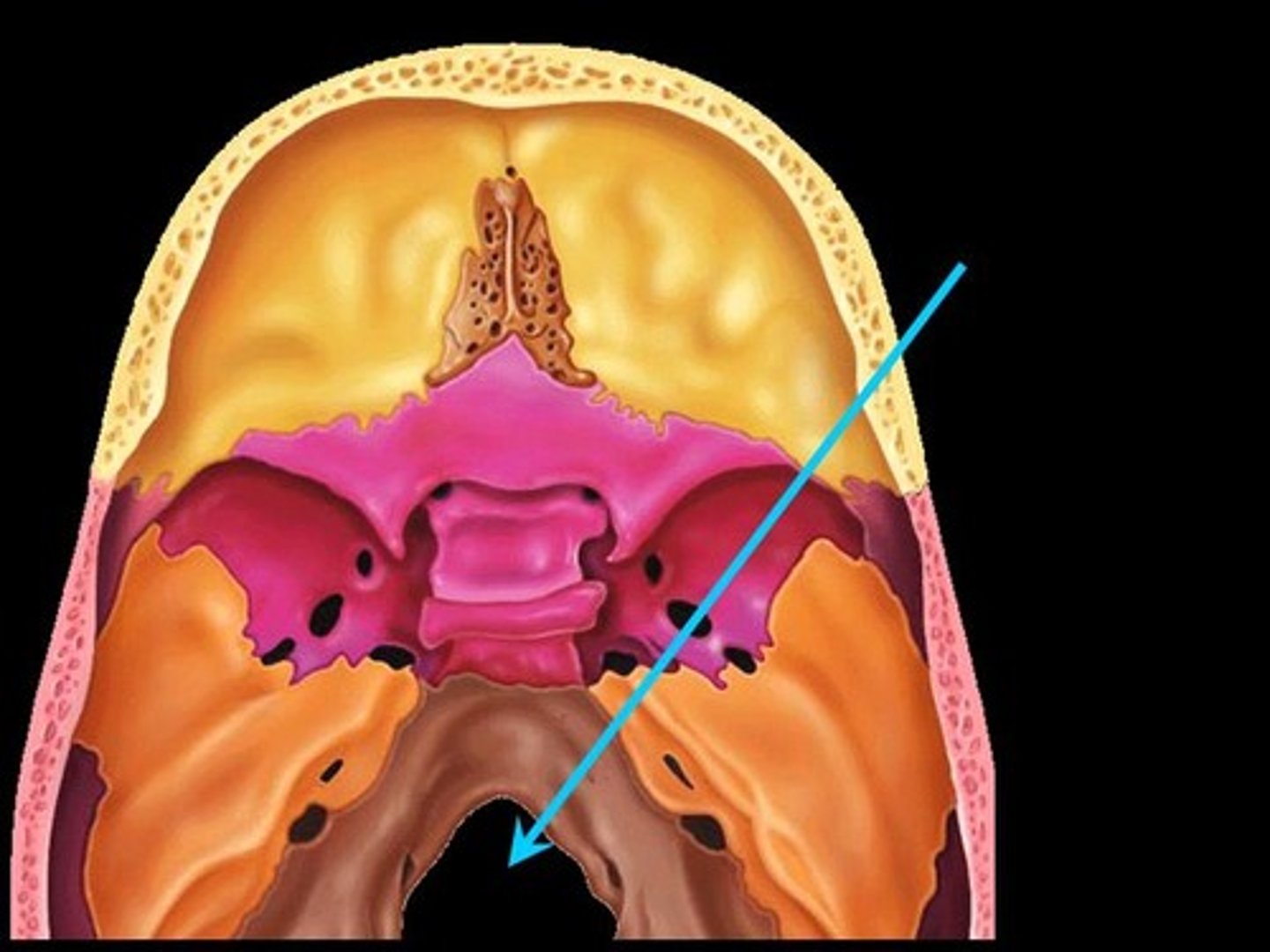
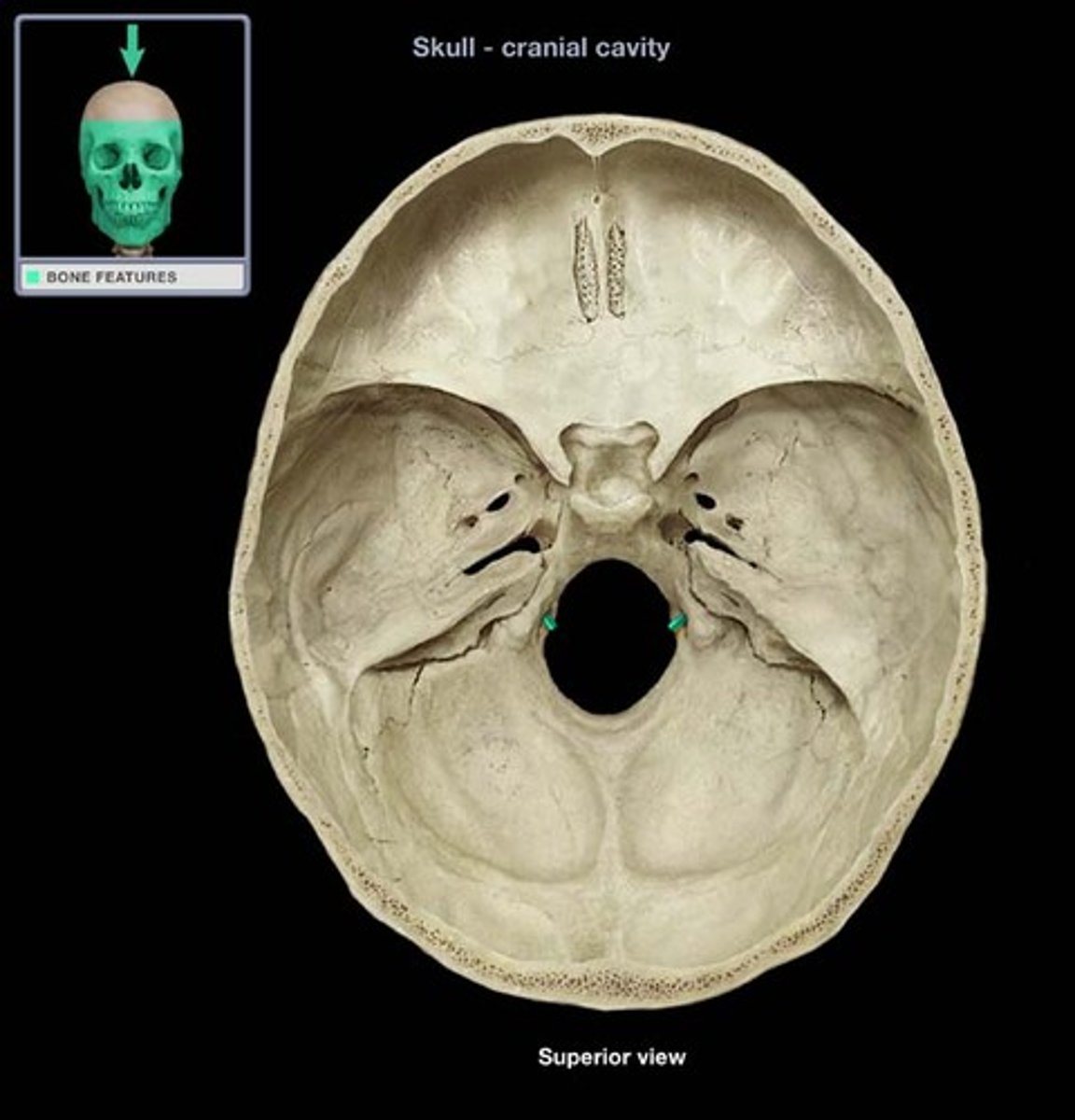
hypoglossal canal
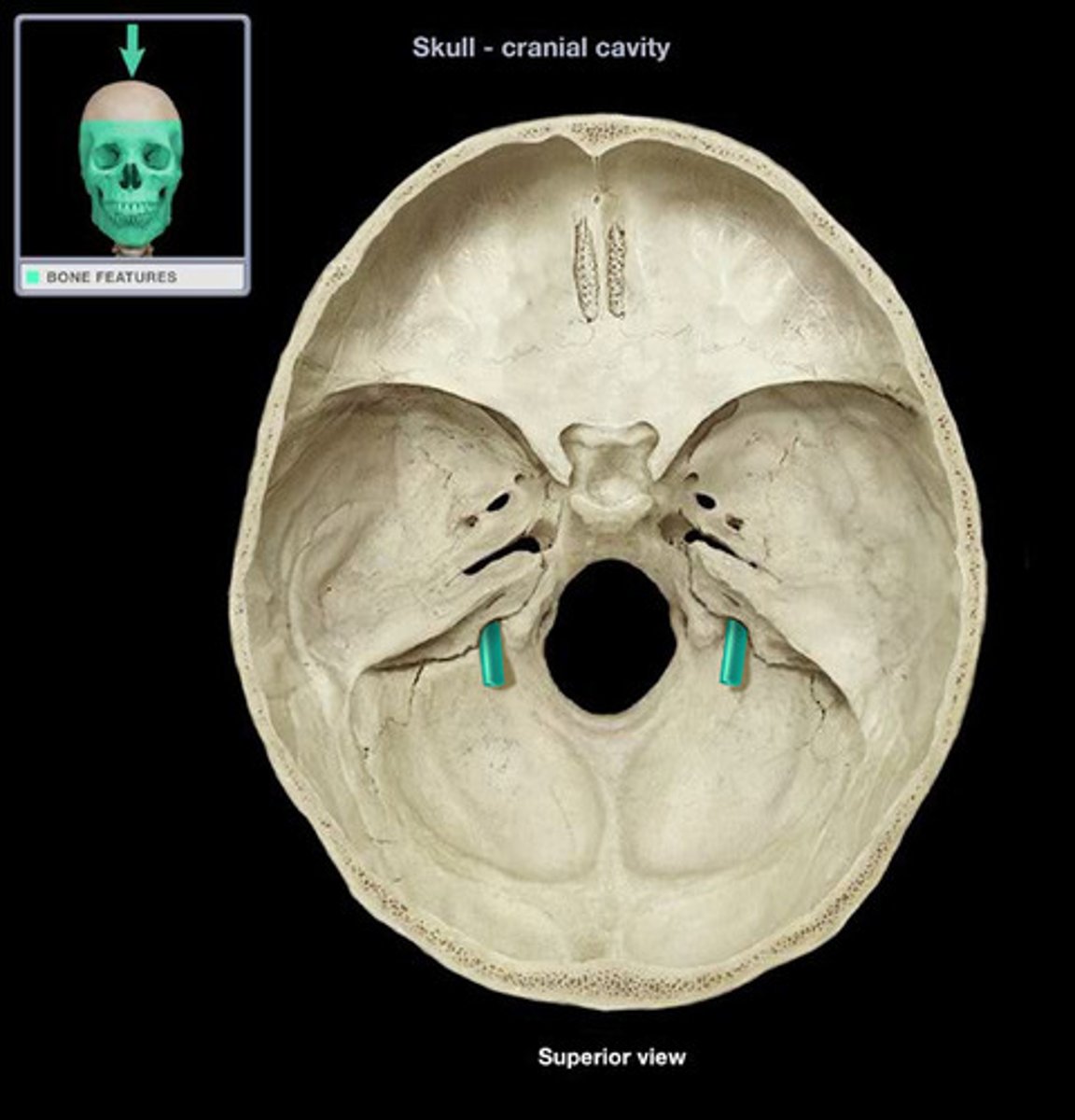
jugular foramen
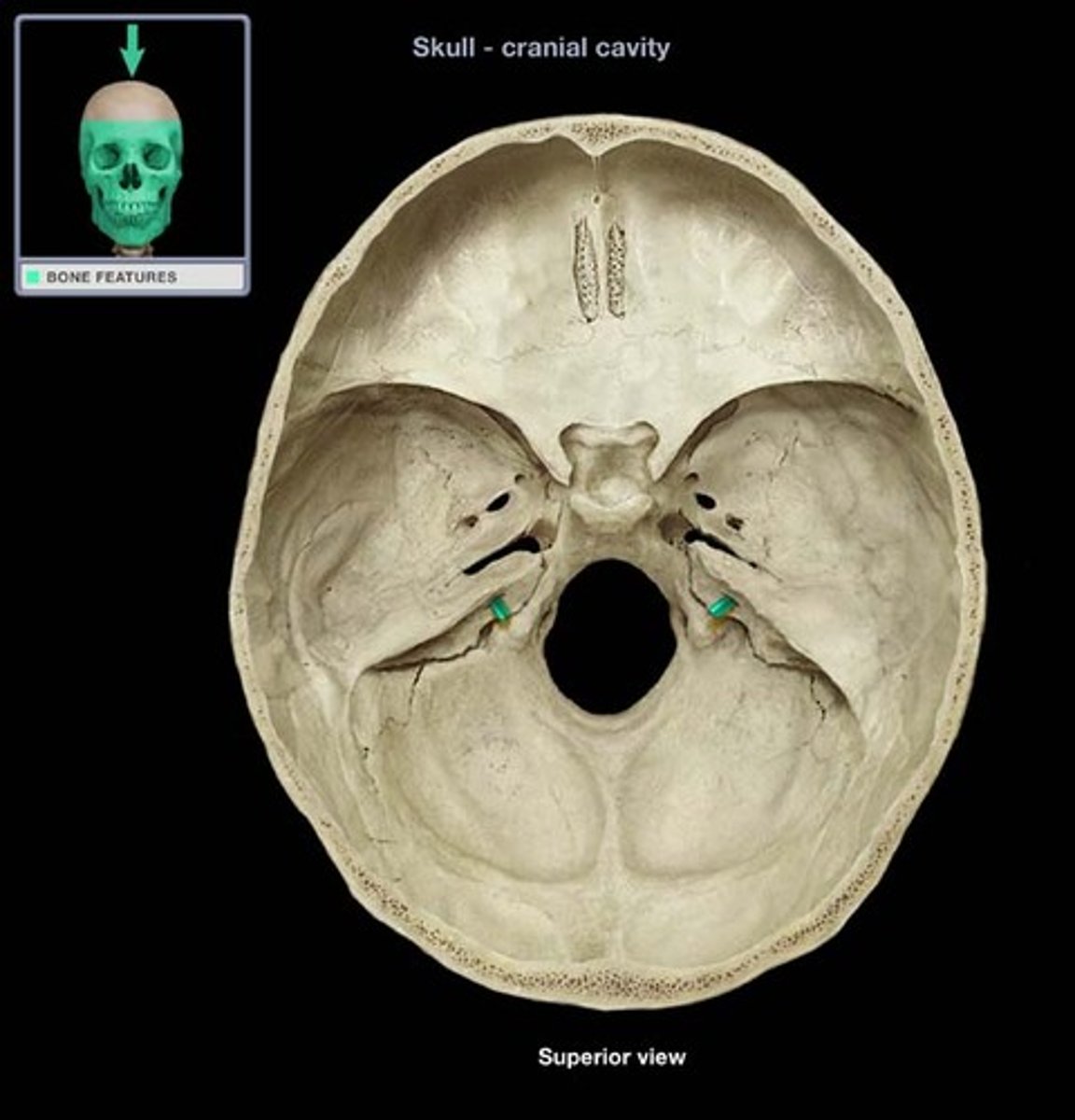
internal acoustic meatus, CN VII and CN VIII (facial nerve and vestibulocochlear nerve)
what is the structure and what goes through it
superior petrosal sinus
what structure lies in this groove
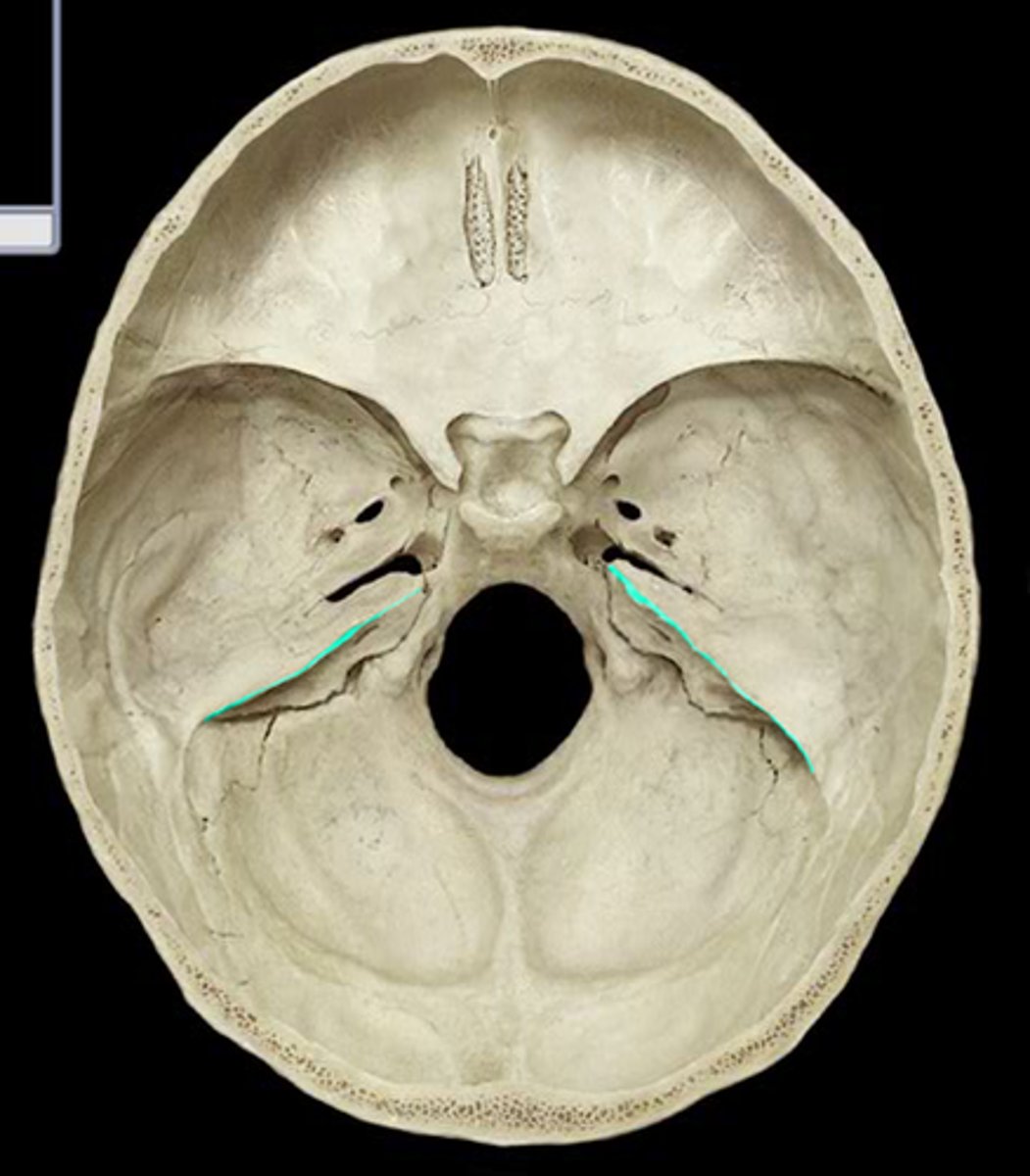
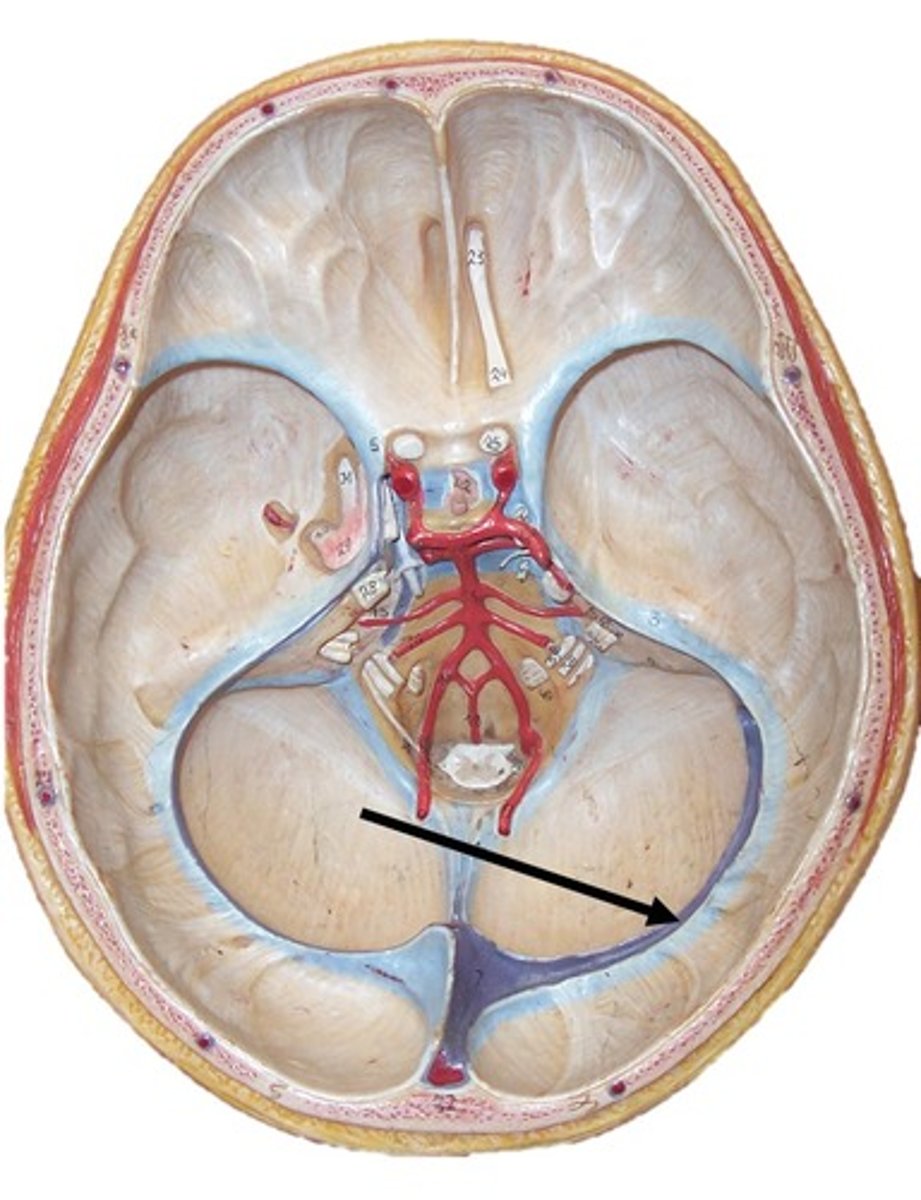
transverse sinus
what structuree lies in this groove
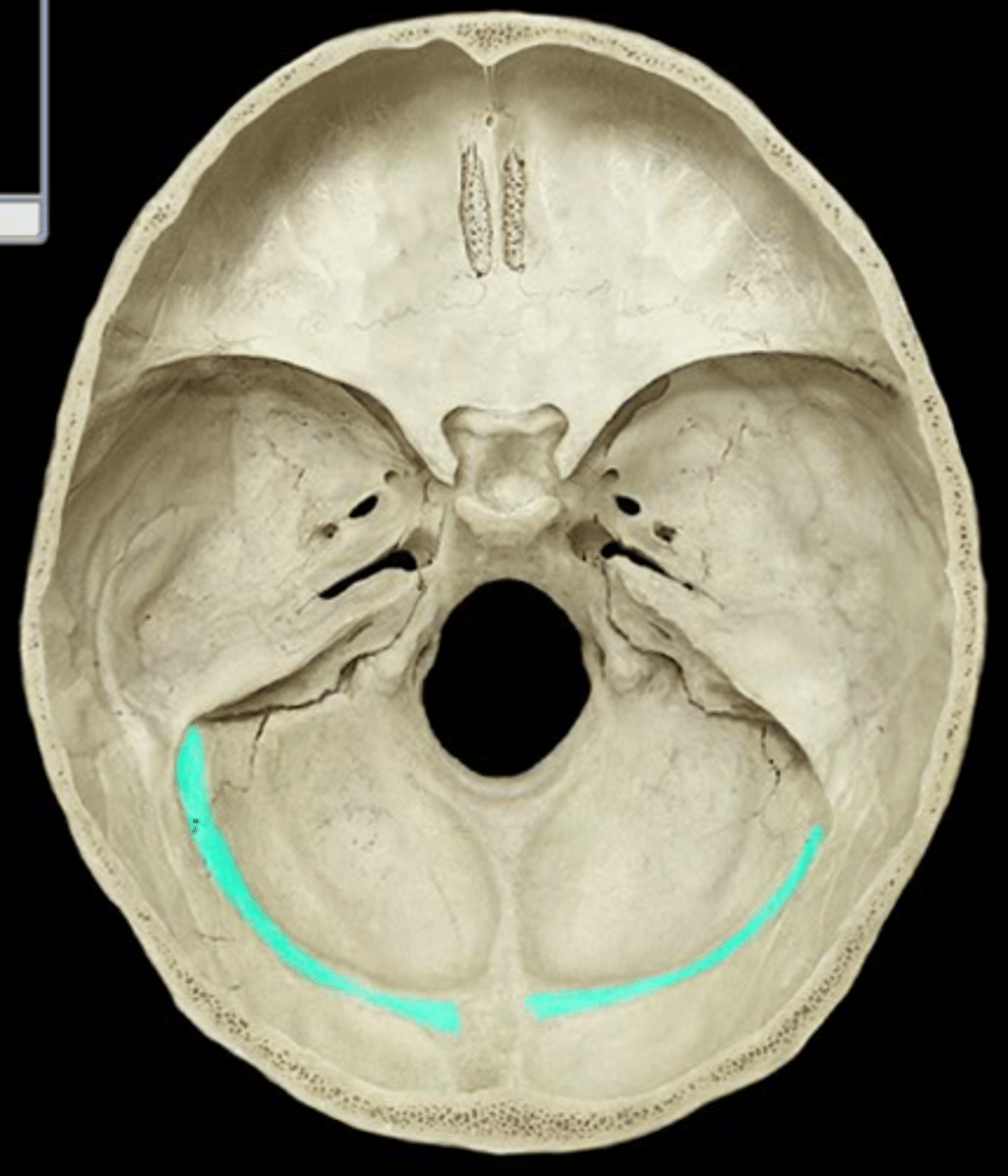
sigmoid sinus
what structure lies in this groove
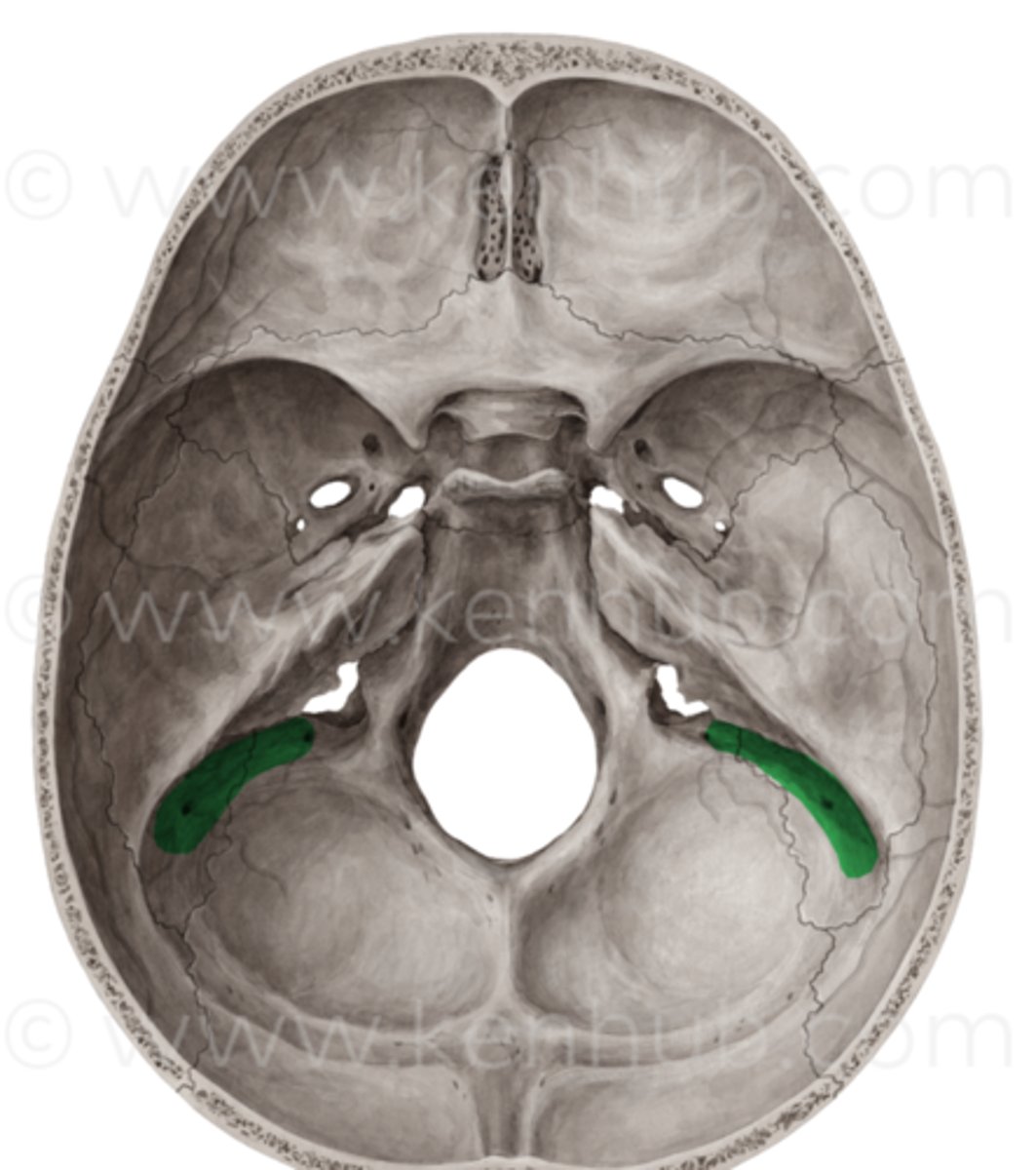
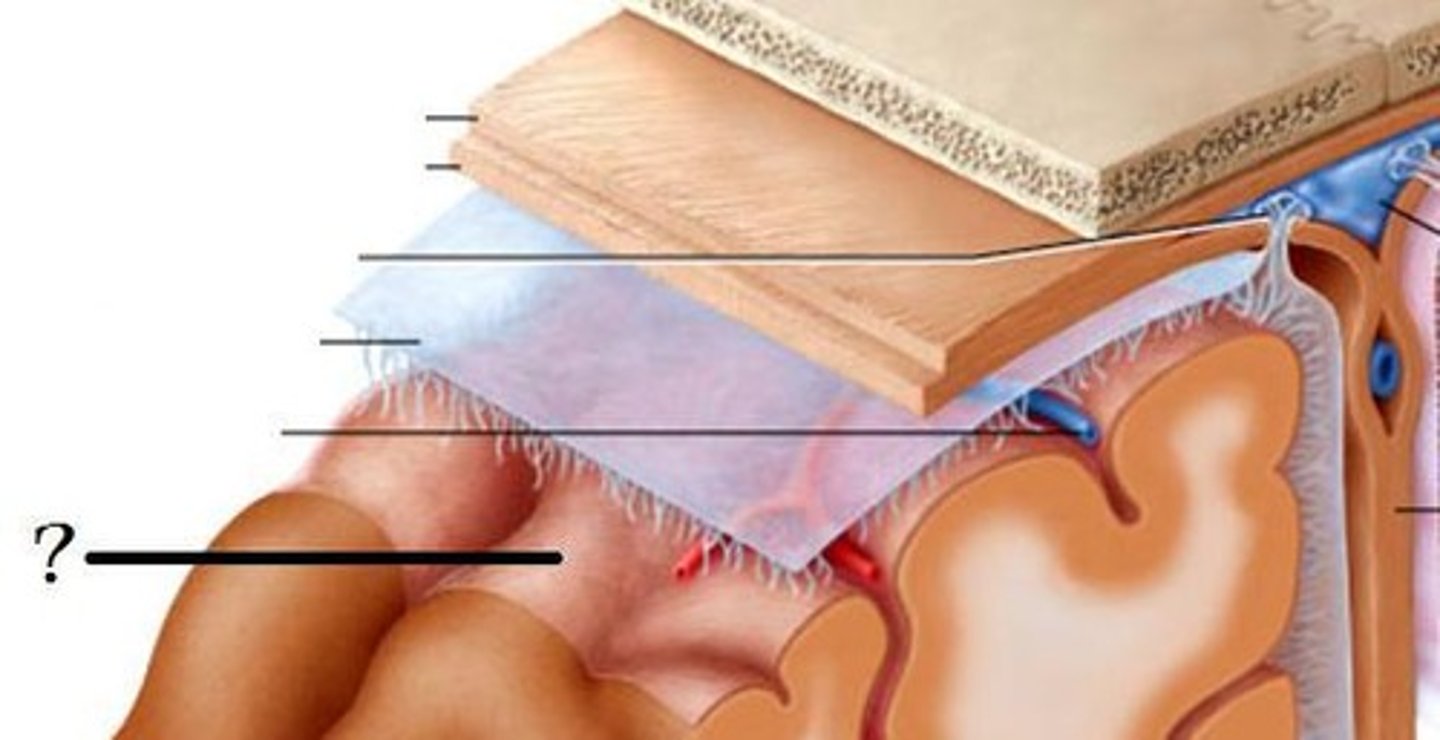
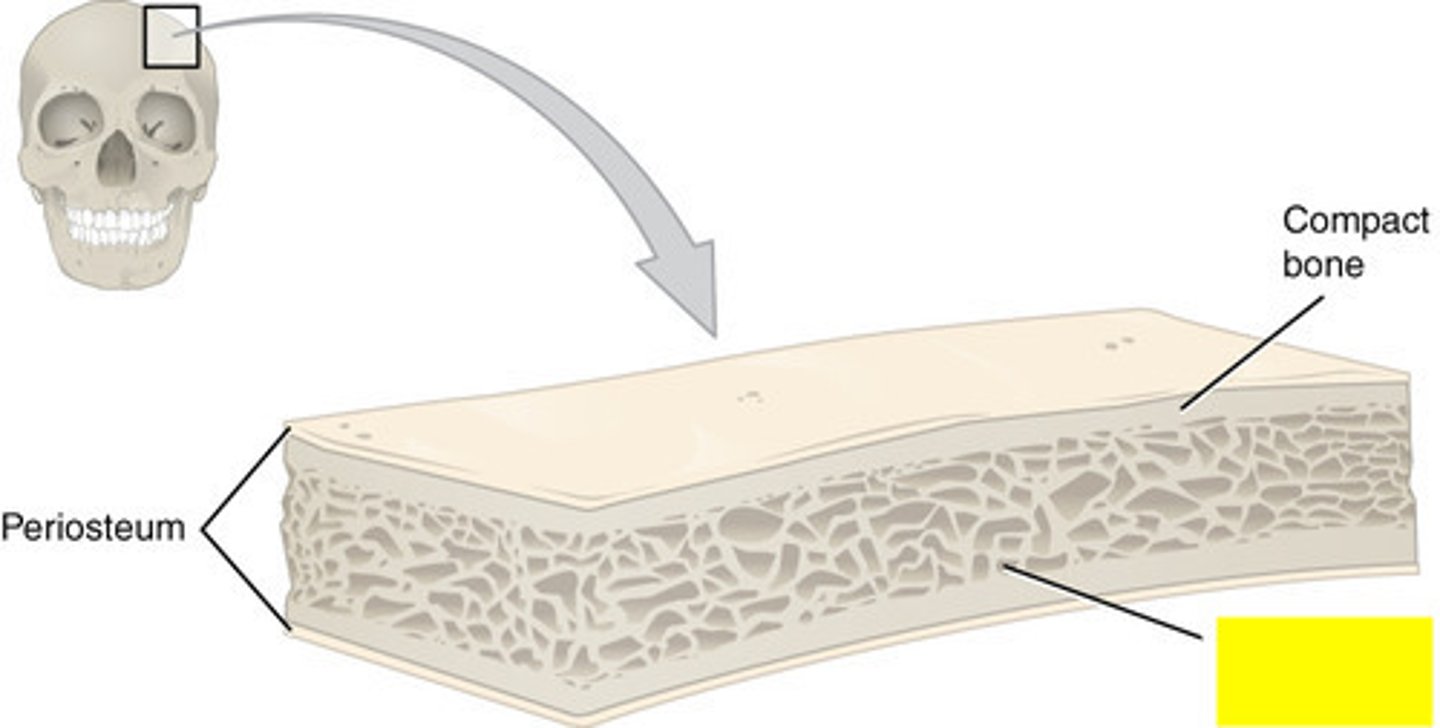
skin, dense connective tissue, aponeurosis, loose connective tissue, periosteum
Layers of the scalp
supraorbital nerve
Affects the skin of the forehead, scalp, eyebrow, and upper eyelid.
supraorbital foramen and supraorbital artery
what is the name of this stucture and the artery that passees through it
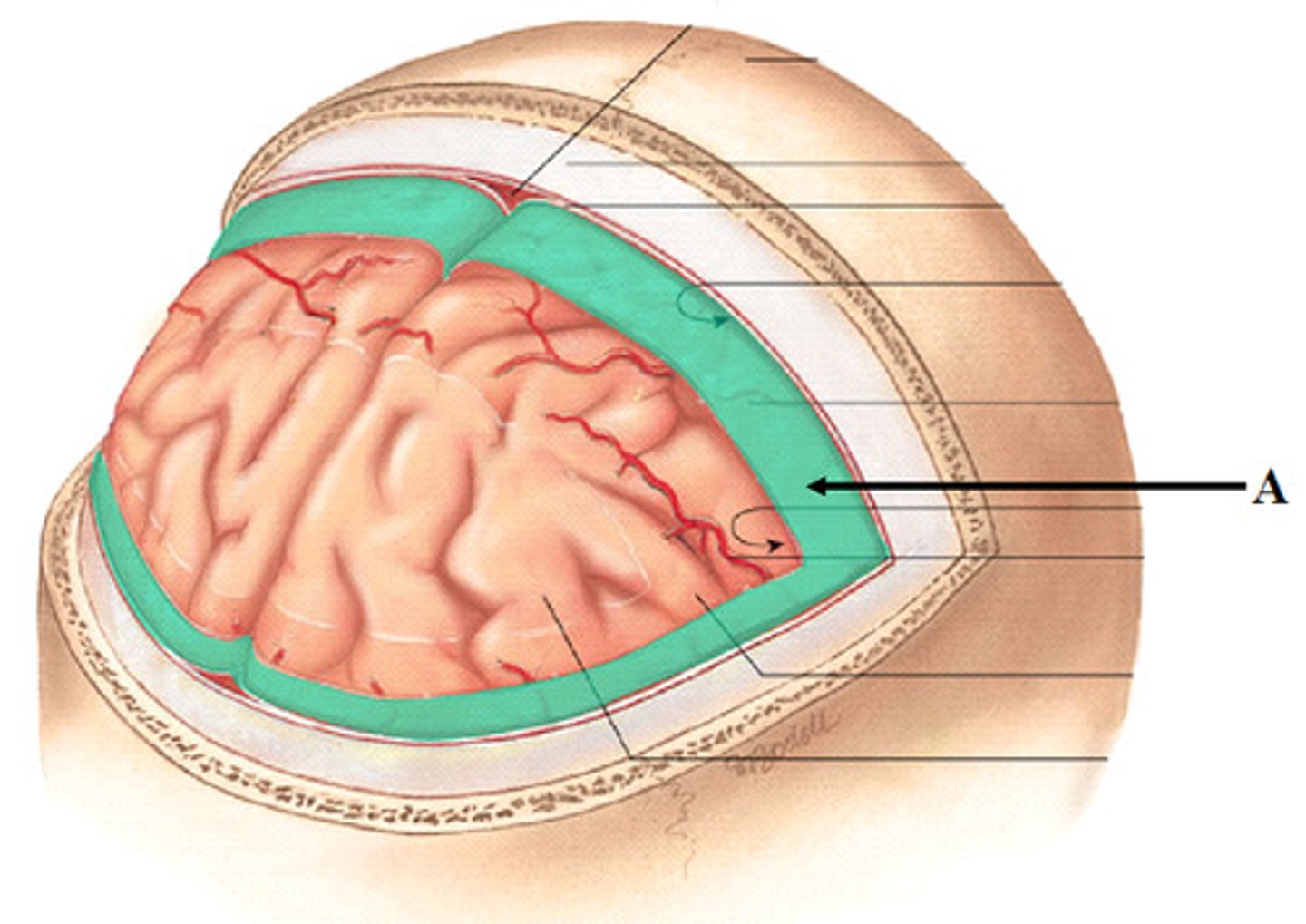
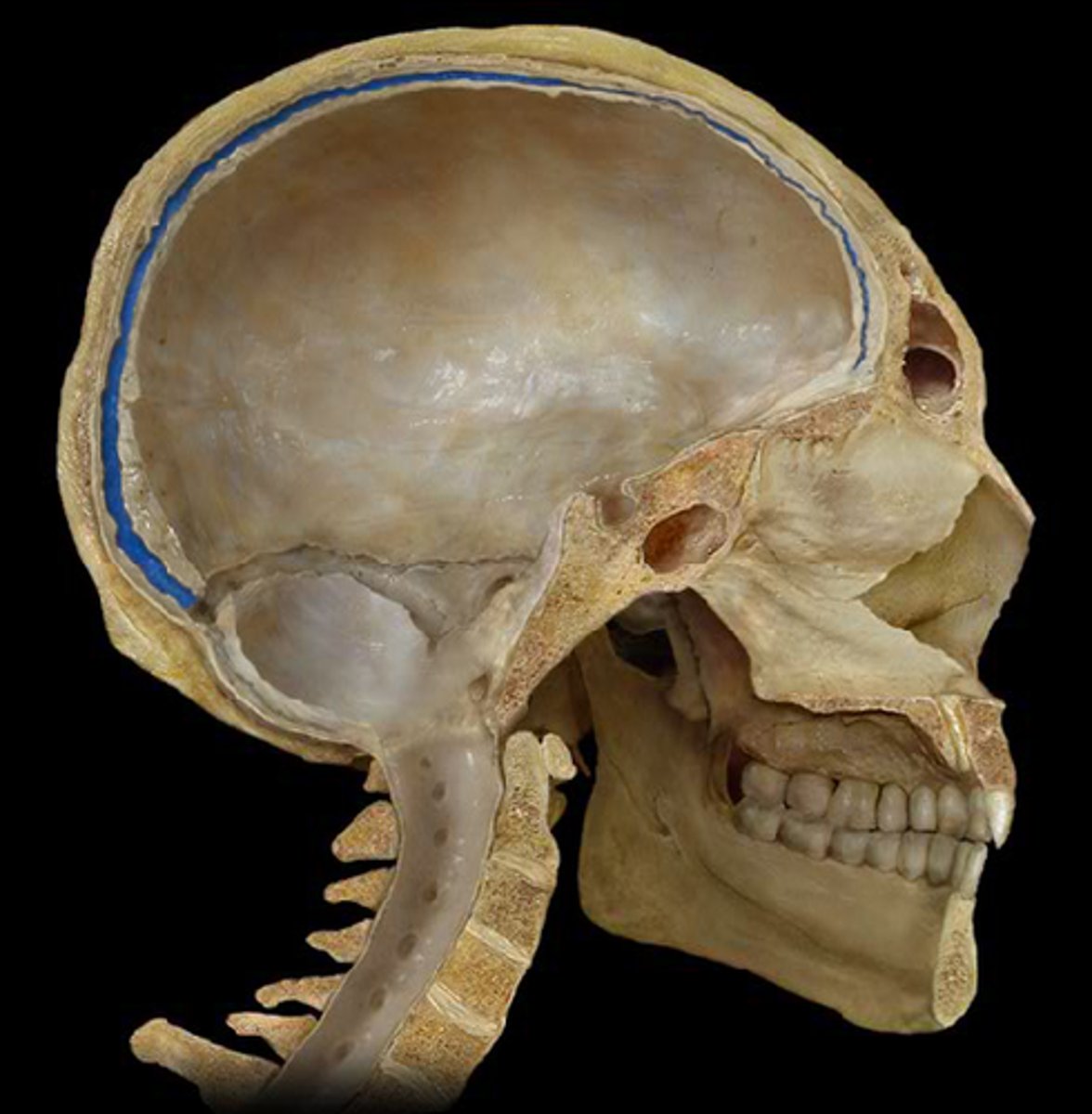
dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
arachnoid mater
weblike middle layer of the three meninges
pia mater
Innermost layer of the meninges
epidural space
space between the dura mater and the wall of the vertebral canal
subdural space
space between dura mater and arachnoid mater
subarachnoid space
a space in the meninges beneath the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
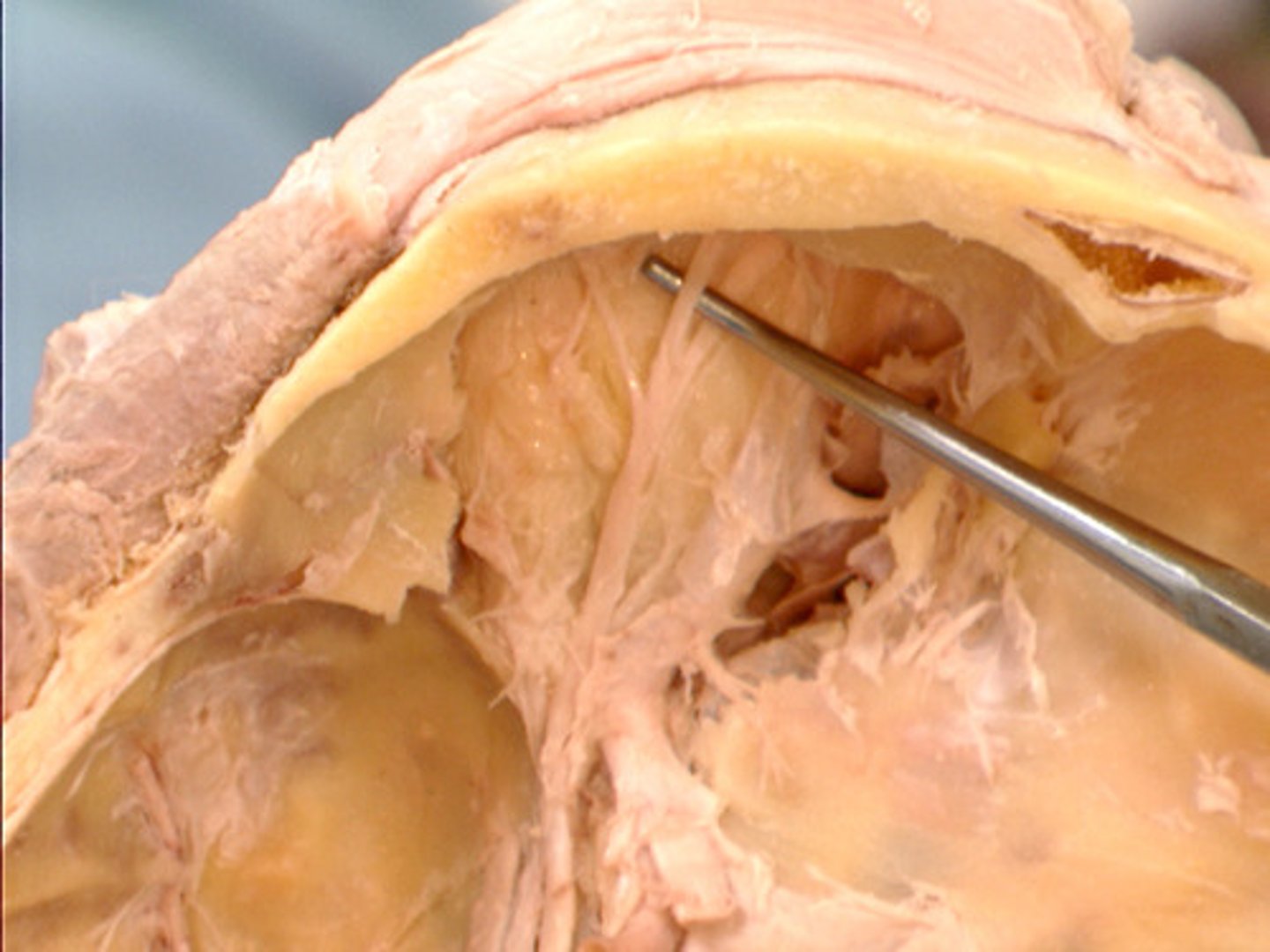
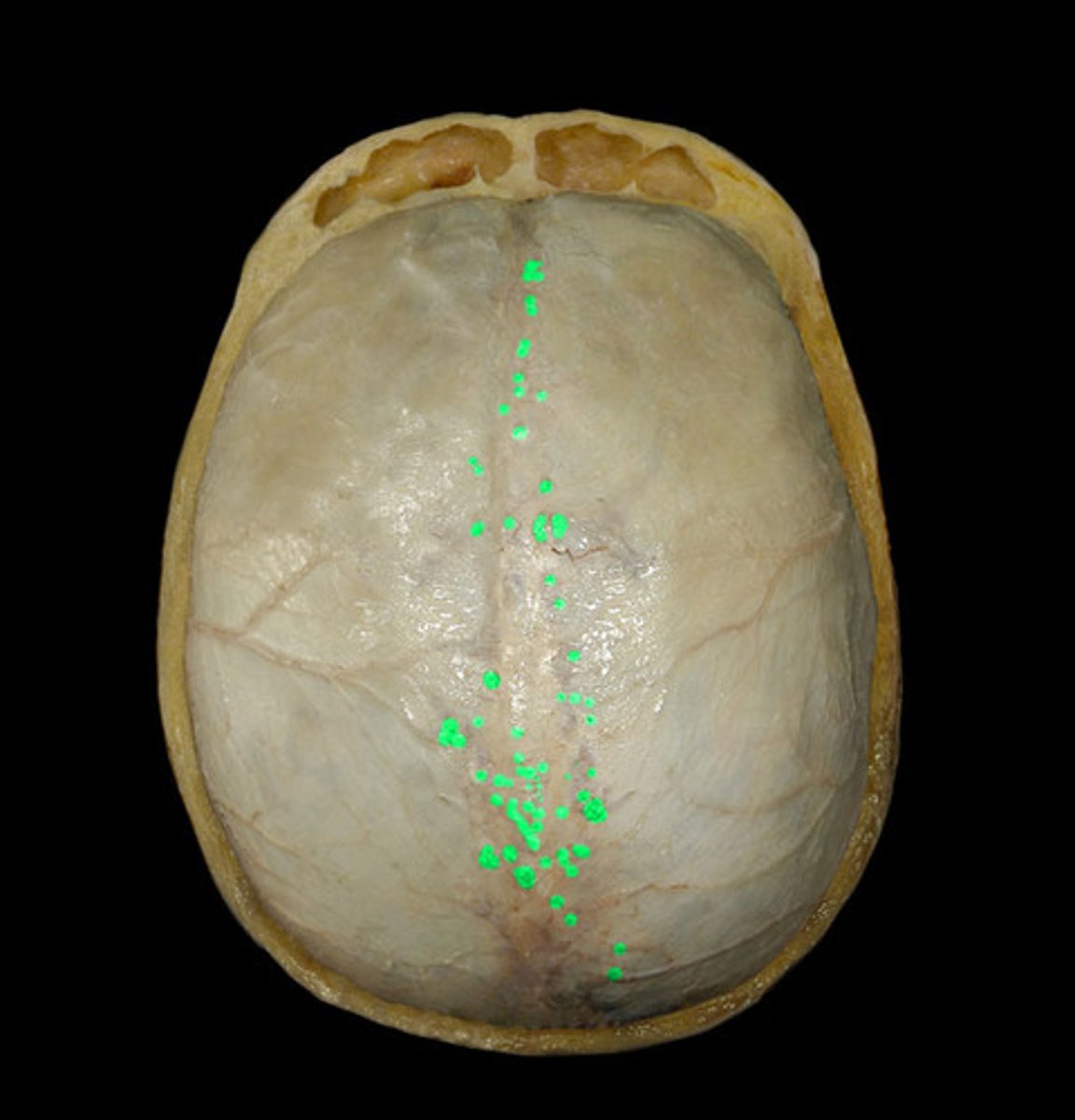
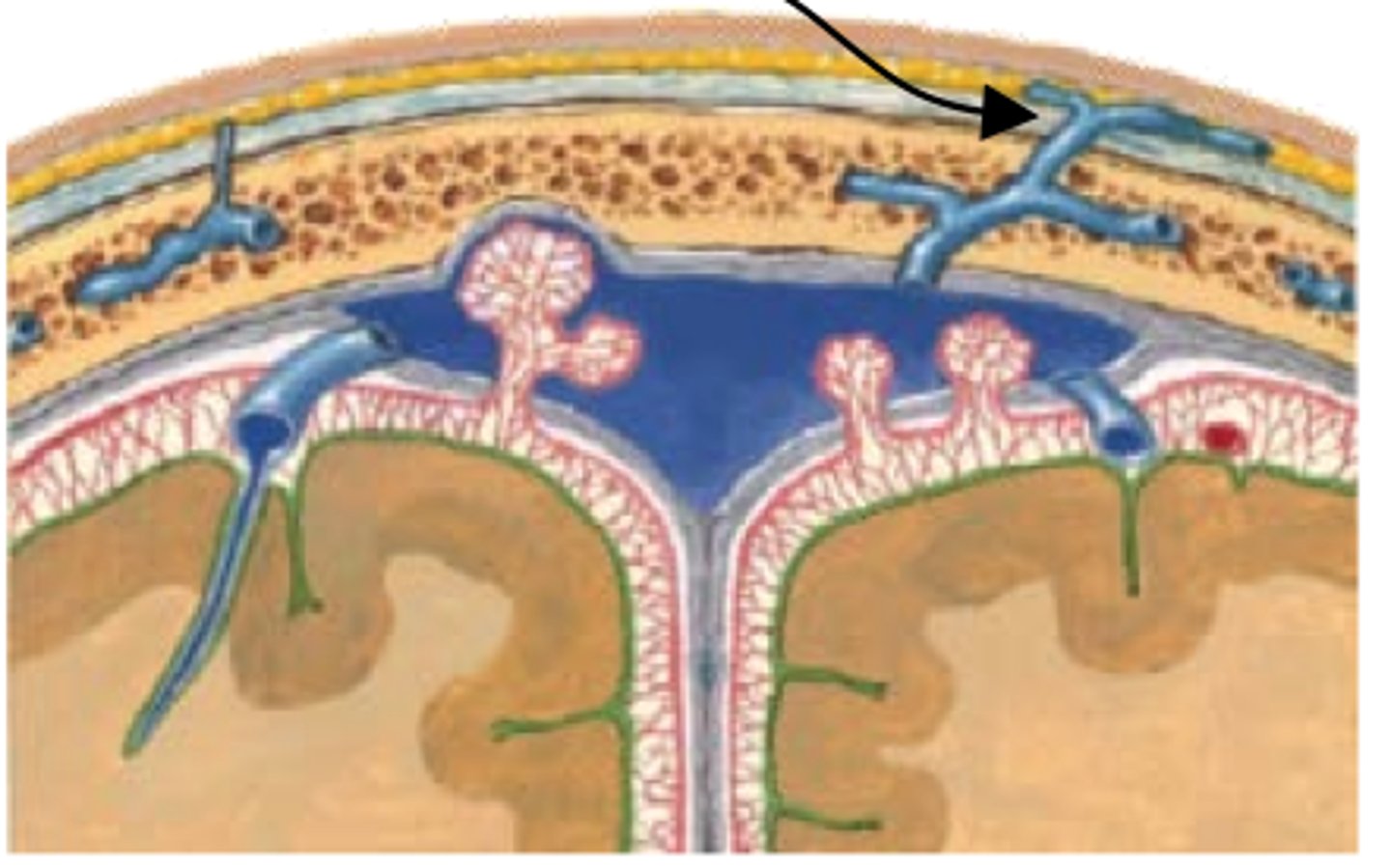
arachnoid granulations
what creates these small dents in the skull
superior saggital sinus
inferior saggital sinus
straight venous sinus
transverse venous sinus
sigmoid sinus
superior petrosal venous sinus
CN III,IV,VI,V1 and internal carotid artery
what runs through the cavernous sinus
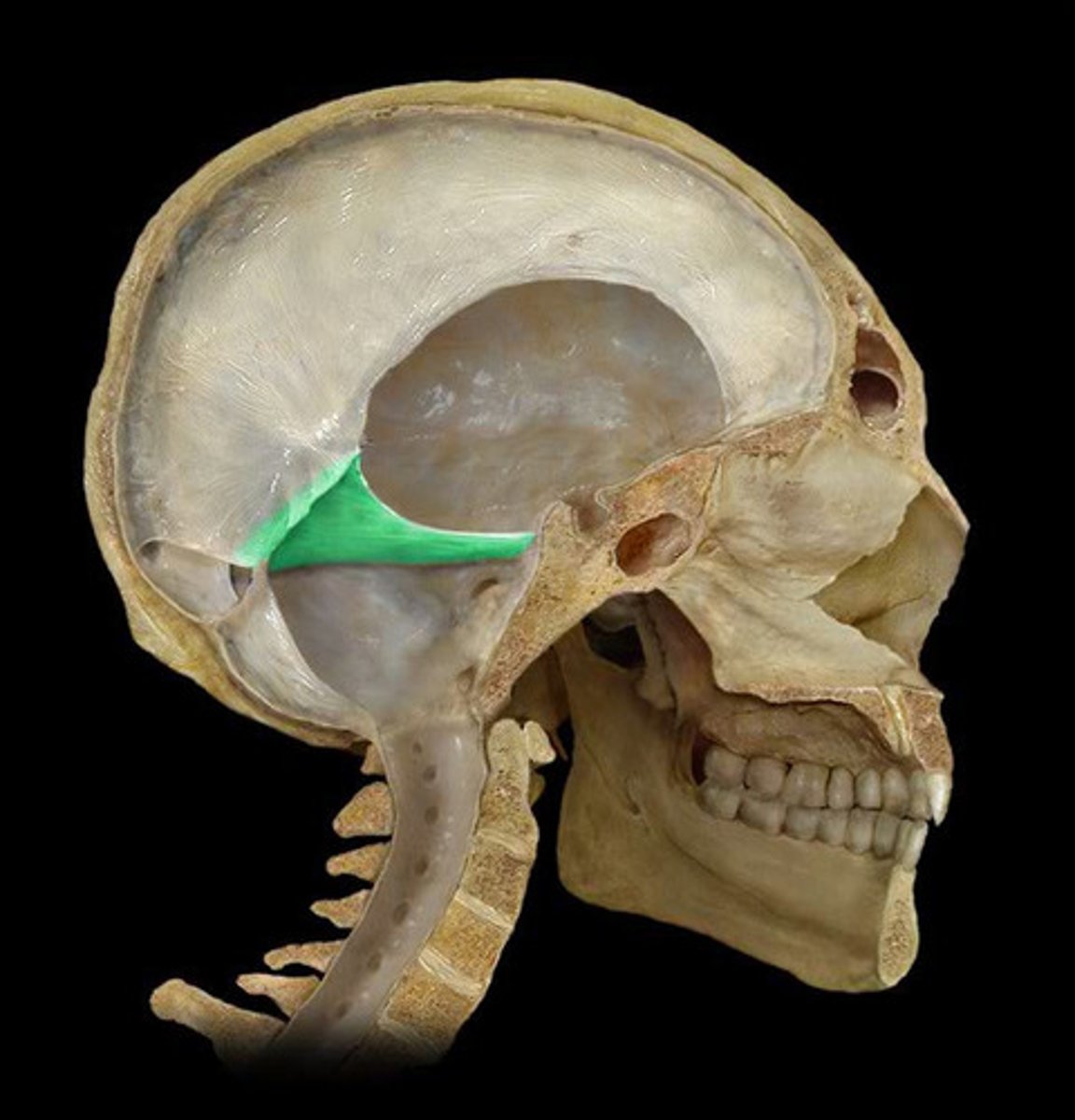
falx cerebri
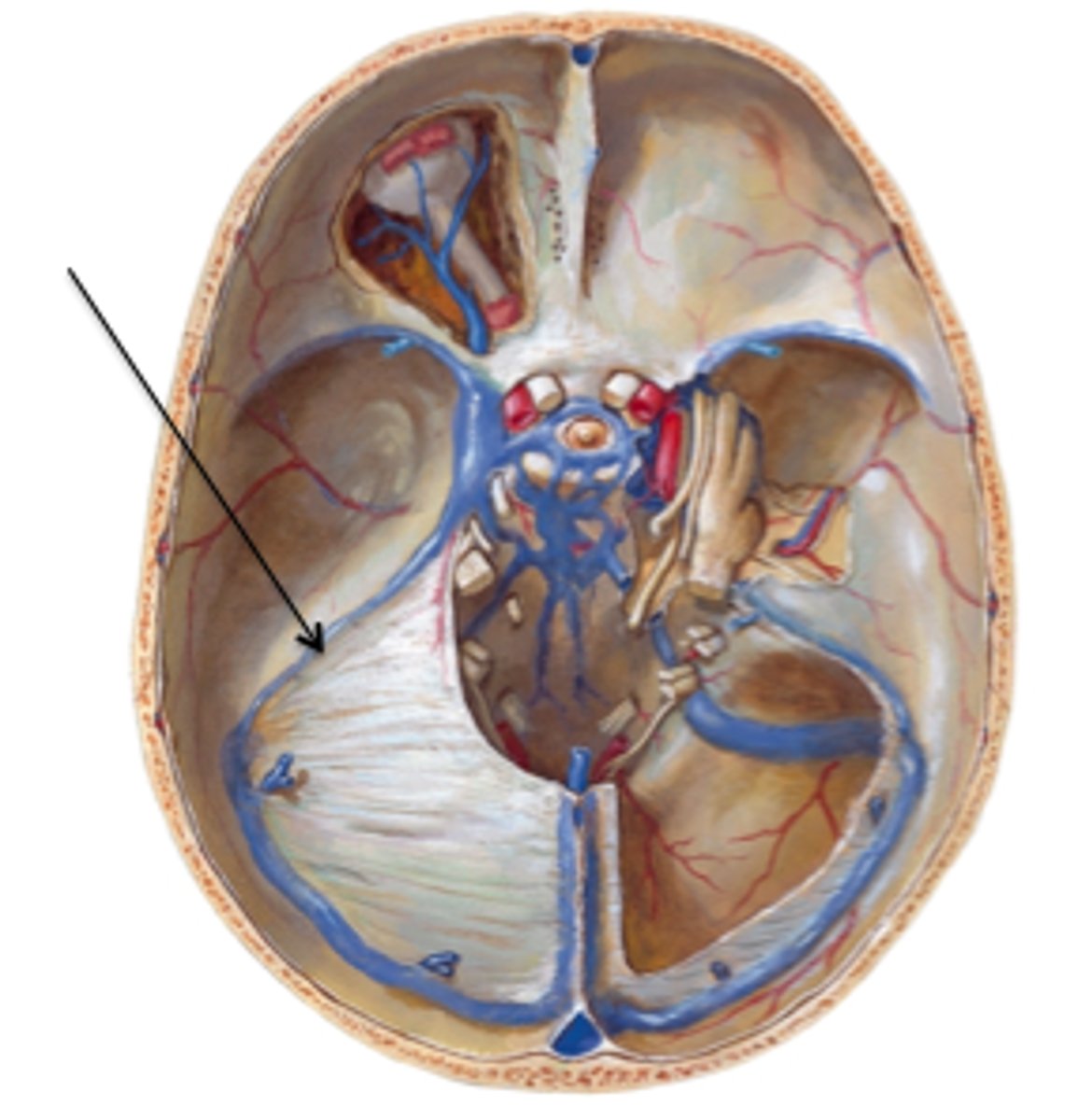
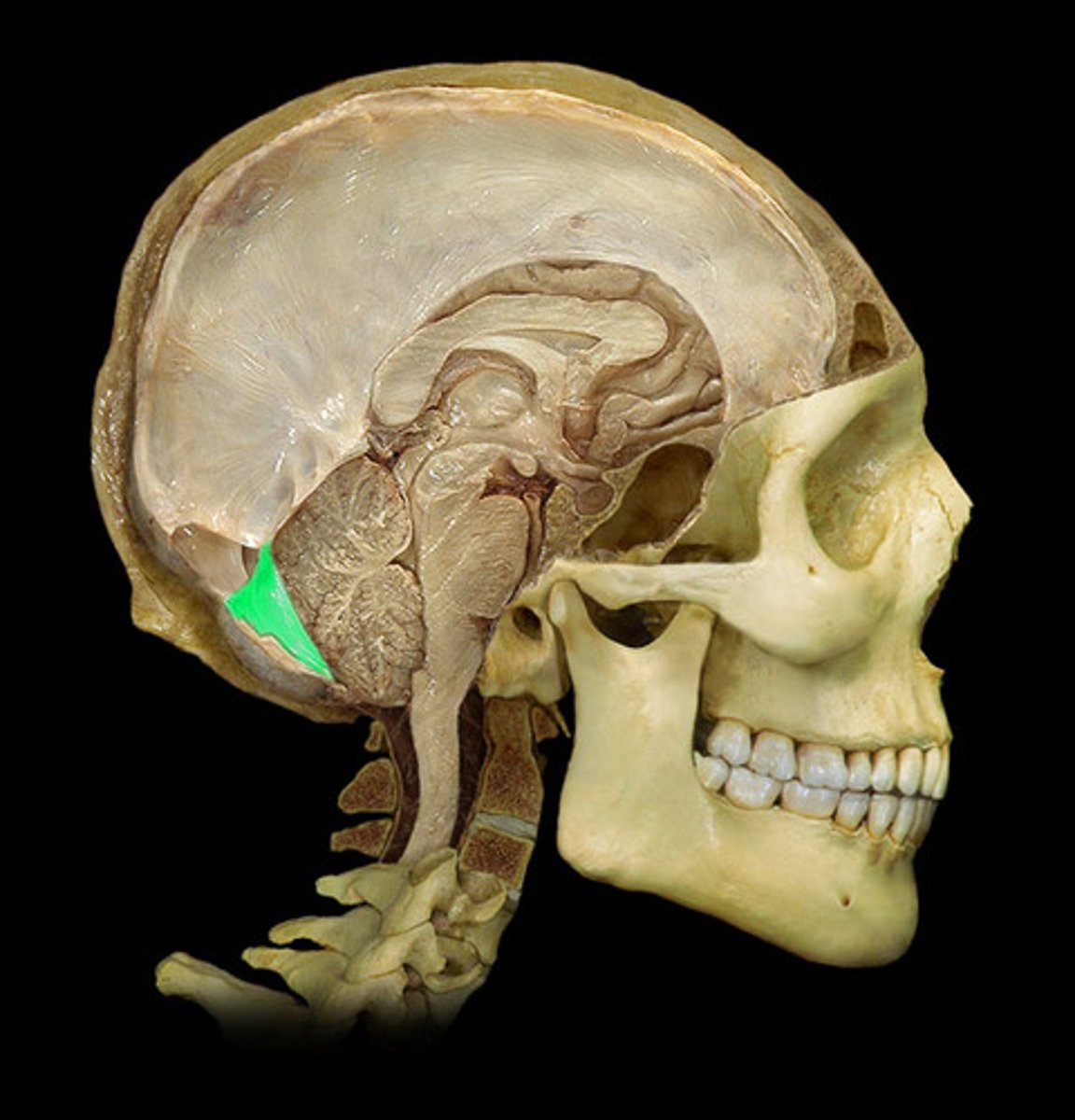
tentorium cerebelli
separates cerebrum from cerebellum
falx cerebelli
tentorial notch
the space in the tentorium through which the brainstem passes
vertebral artery
basilar artery
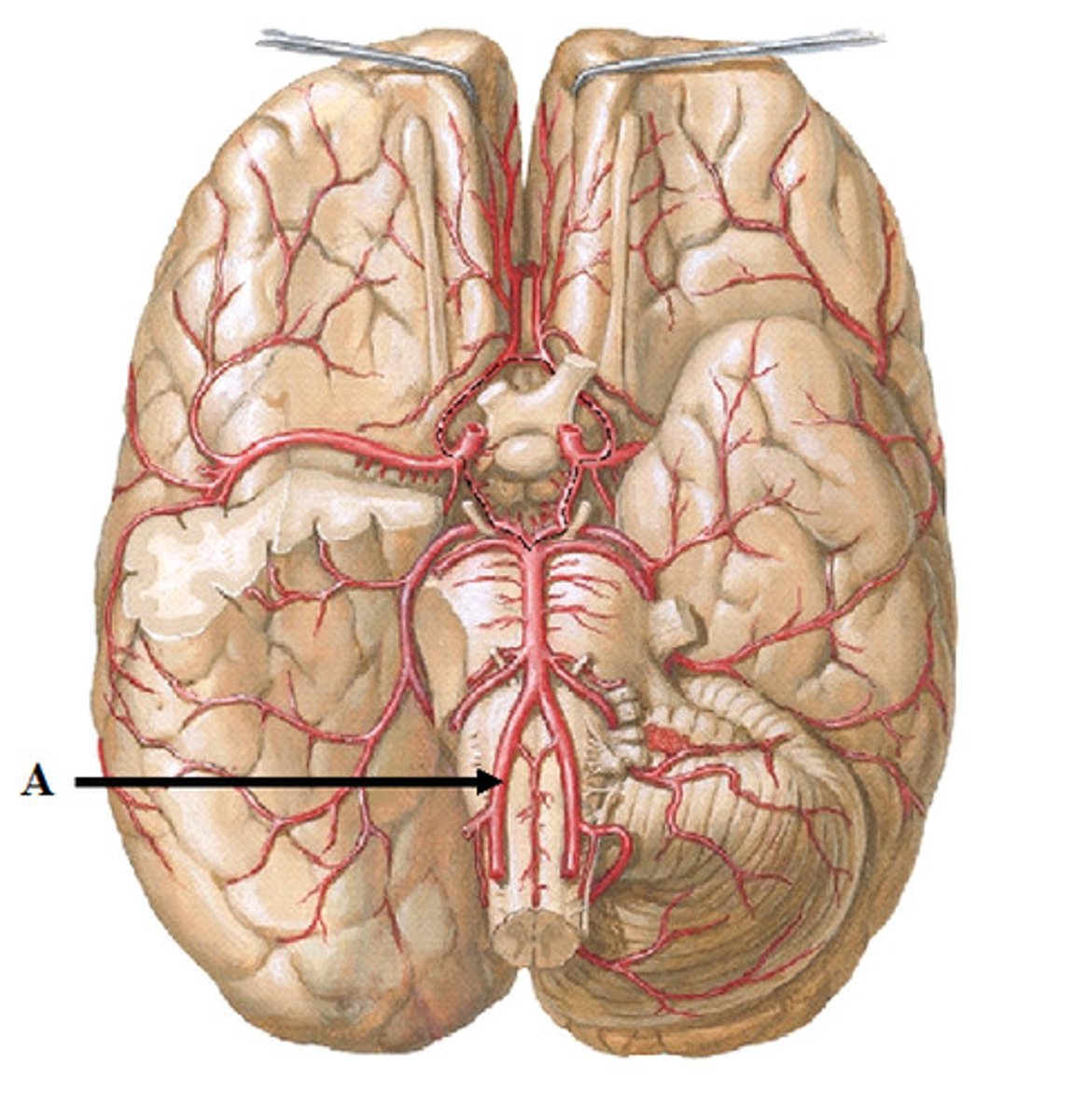
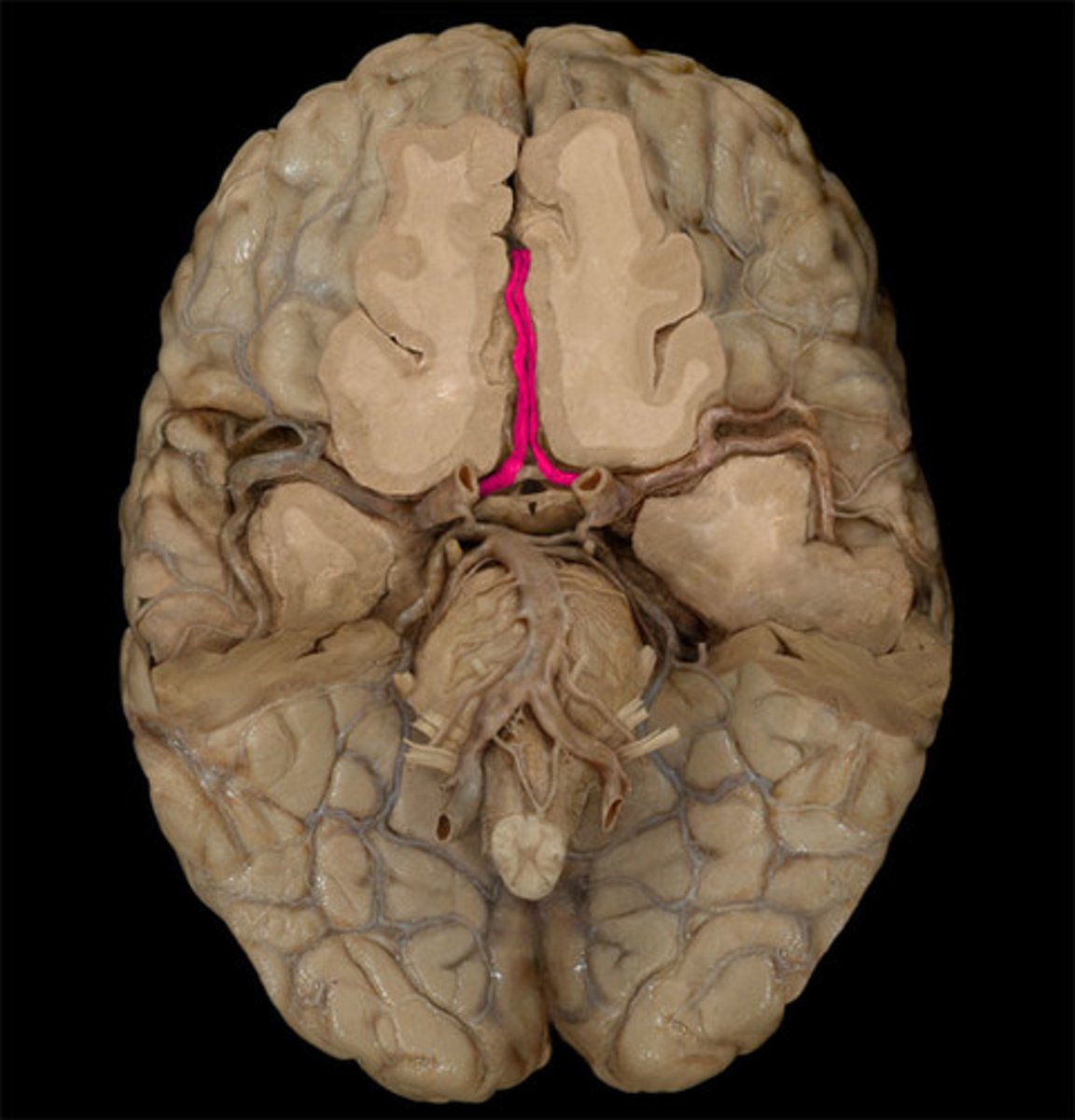
internal carotid artery
branches off the common carotid and runs inward and upward to supply the brain
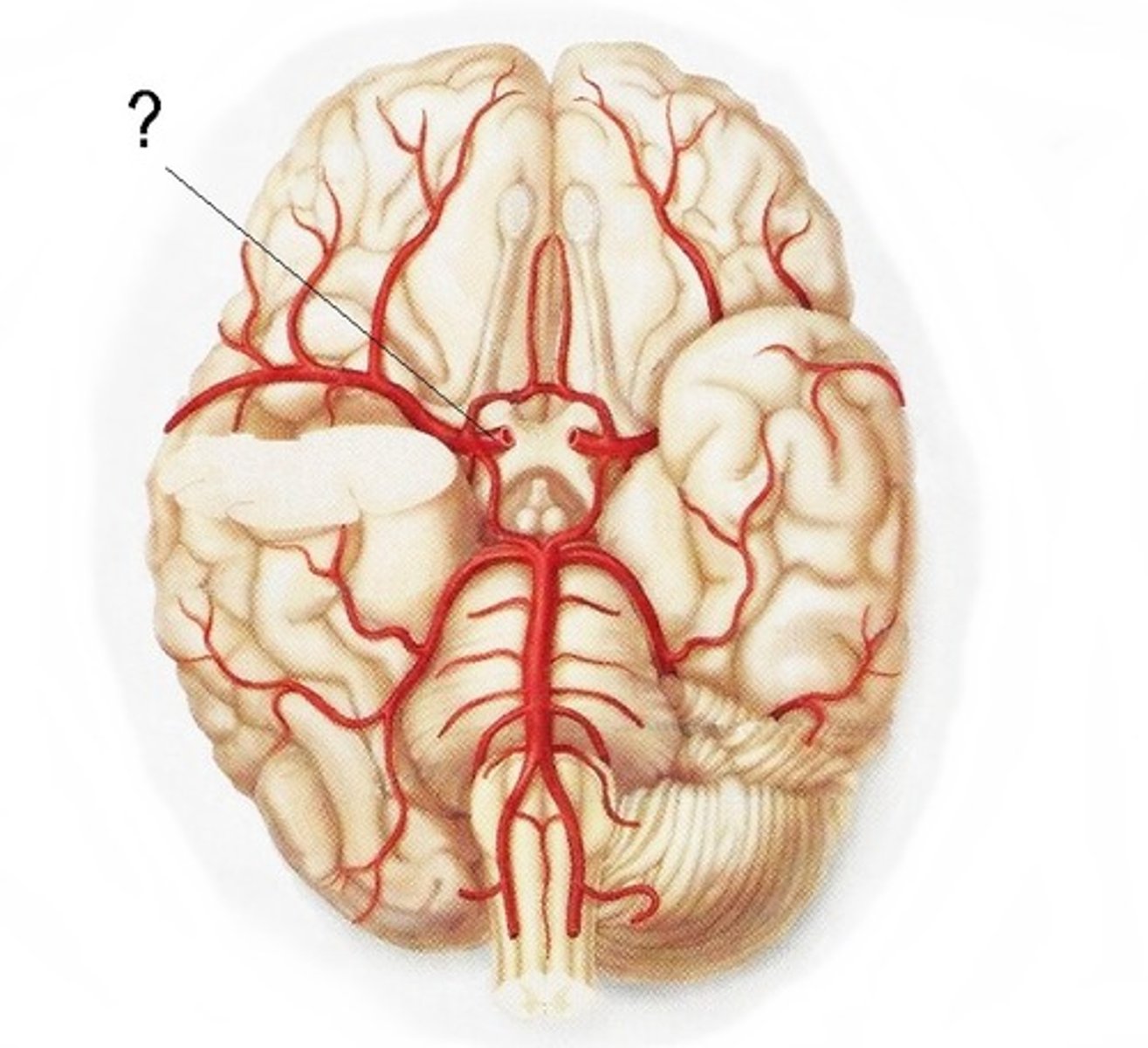
anterior cerebral artery
supplies frontal lobe
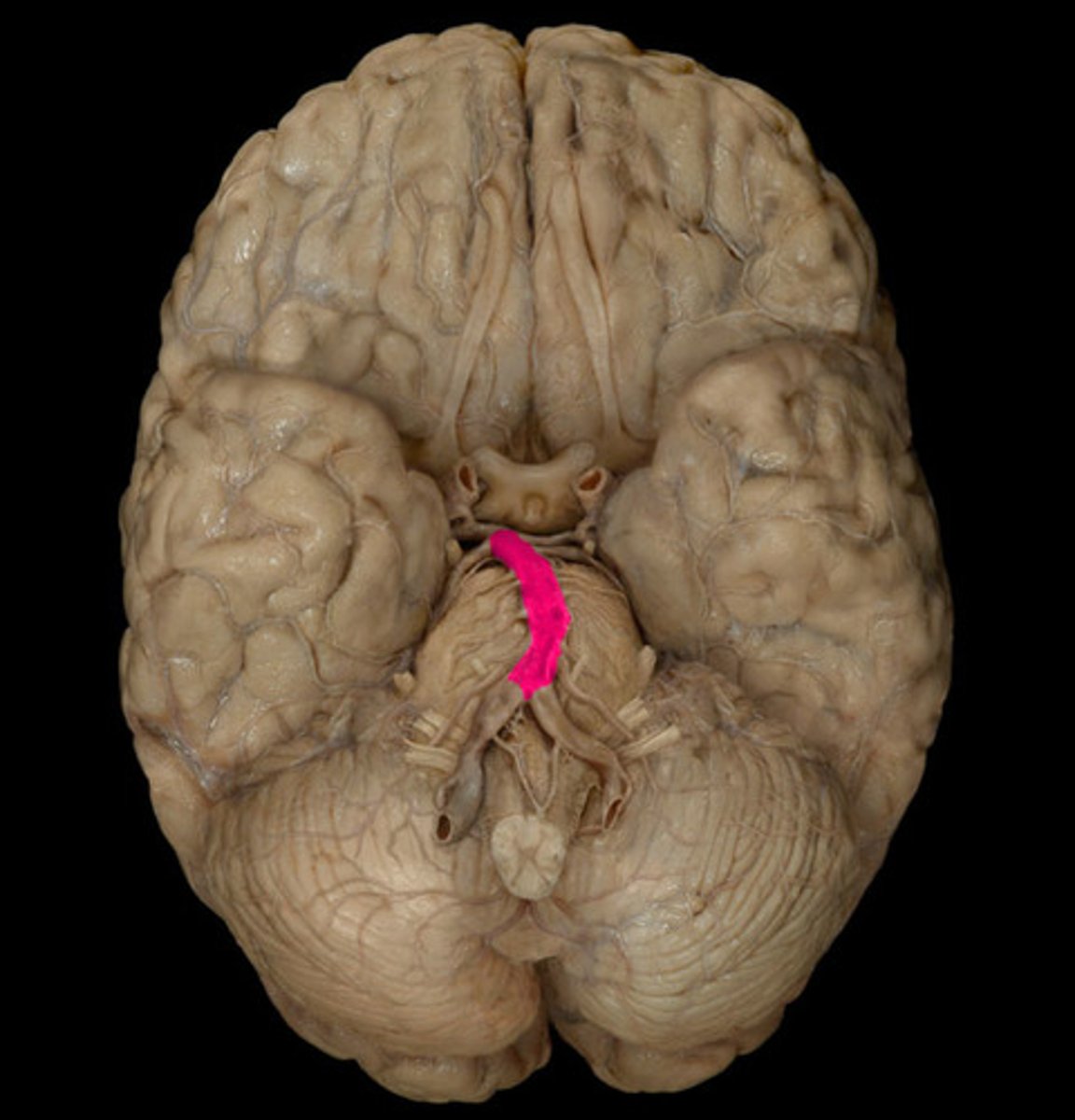
posterior communicating artery
The artery of the Circle of Willis that transports
blood from the internal carotid artery to the
posterior cerebral artery is the
posterior cerebral artery
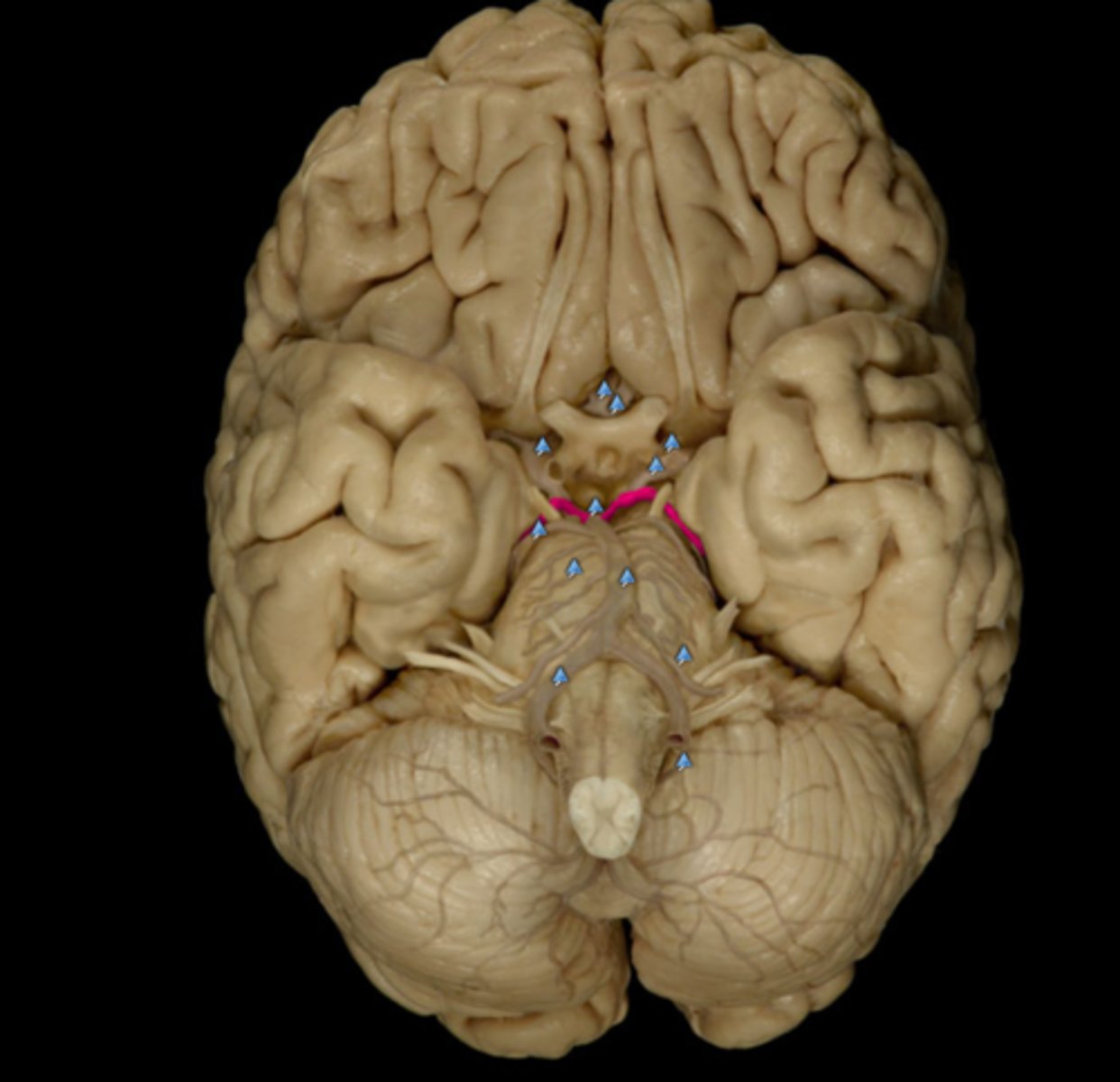
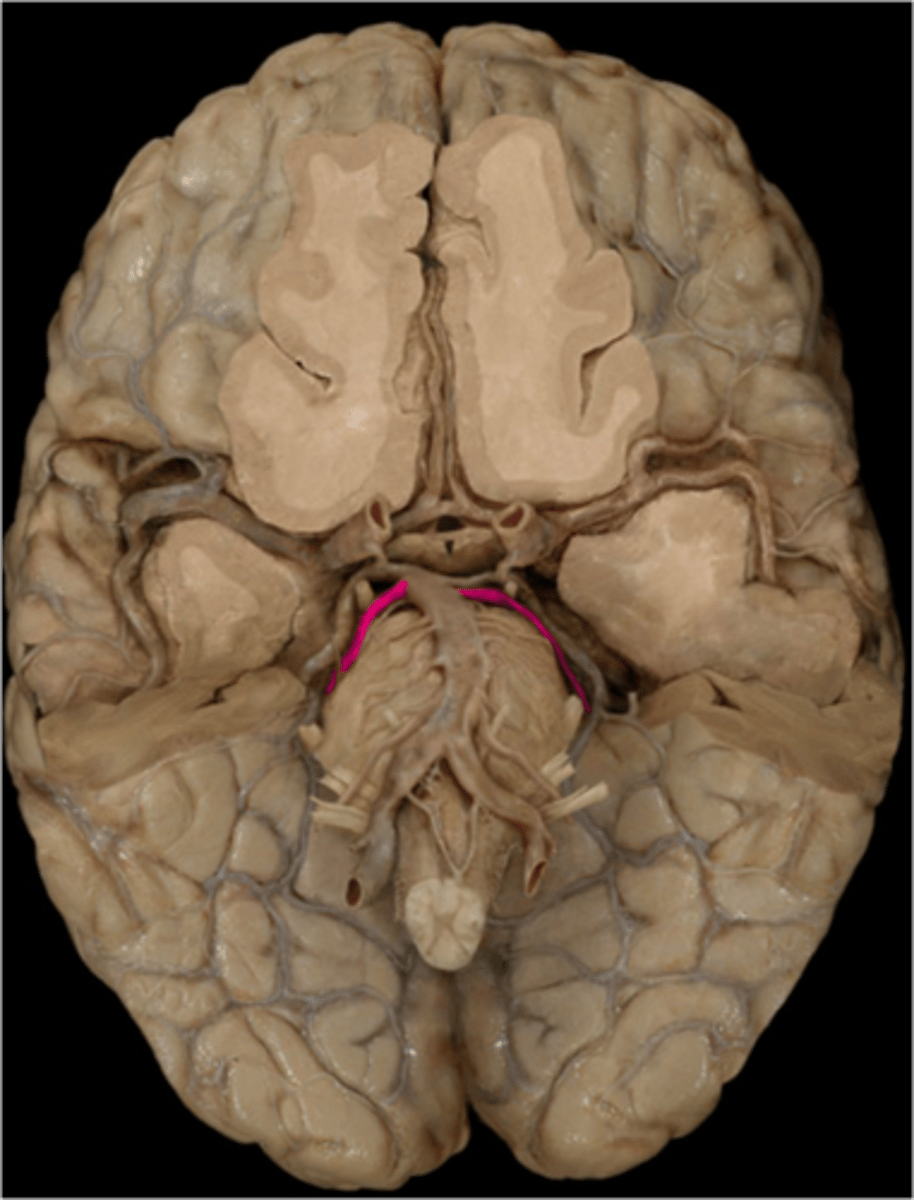
anterior communicating artery
middle cerebral artery
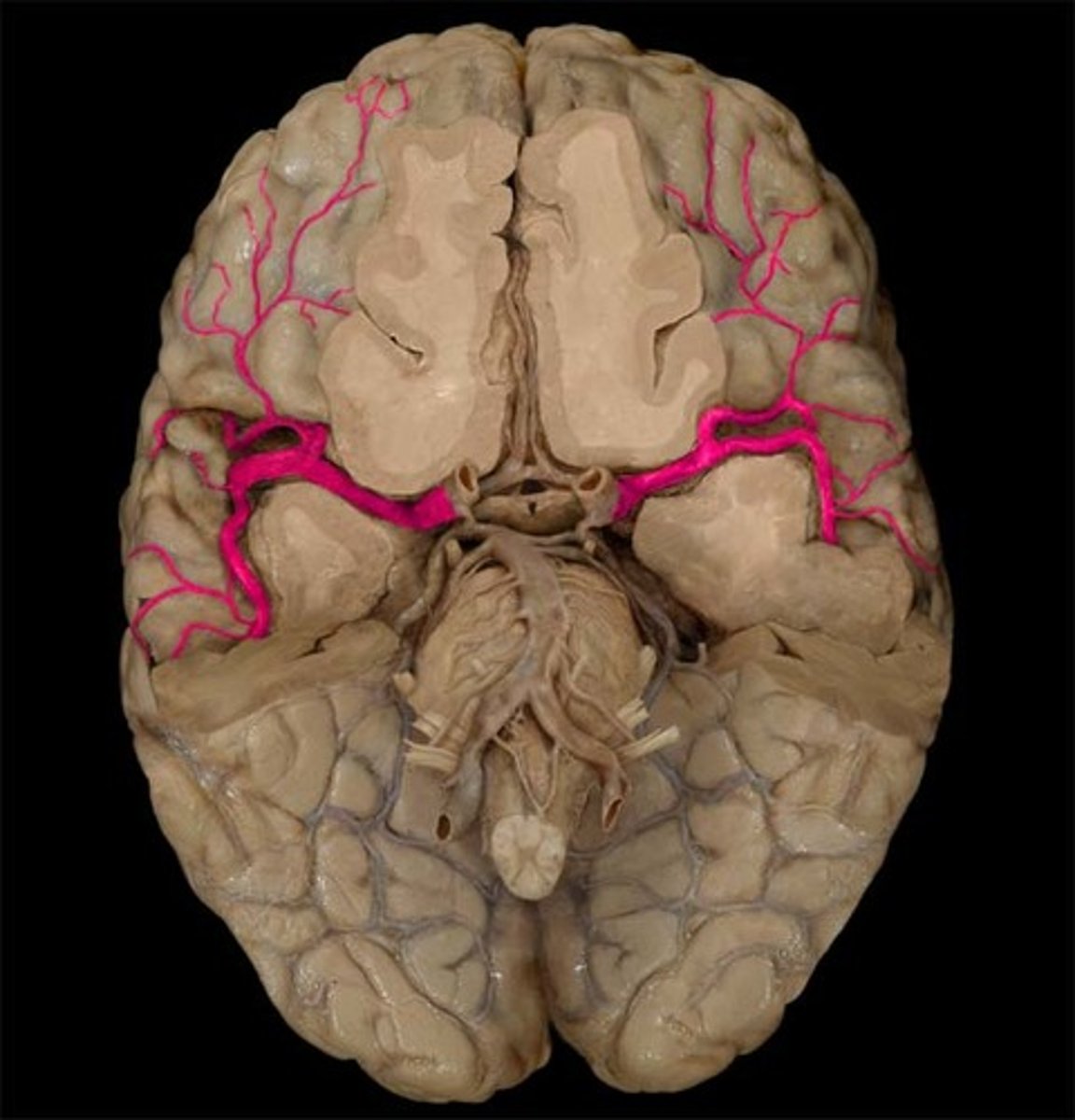
superior cerebellar artery
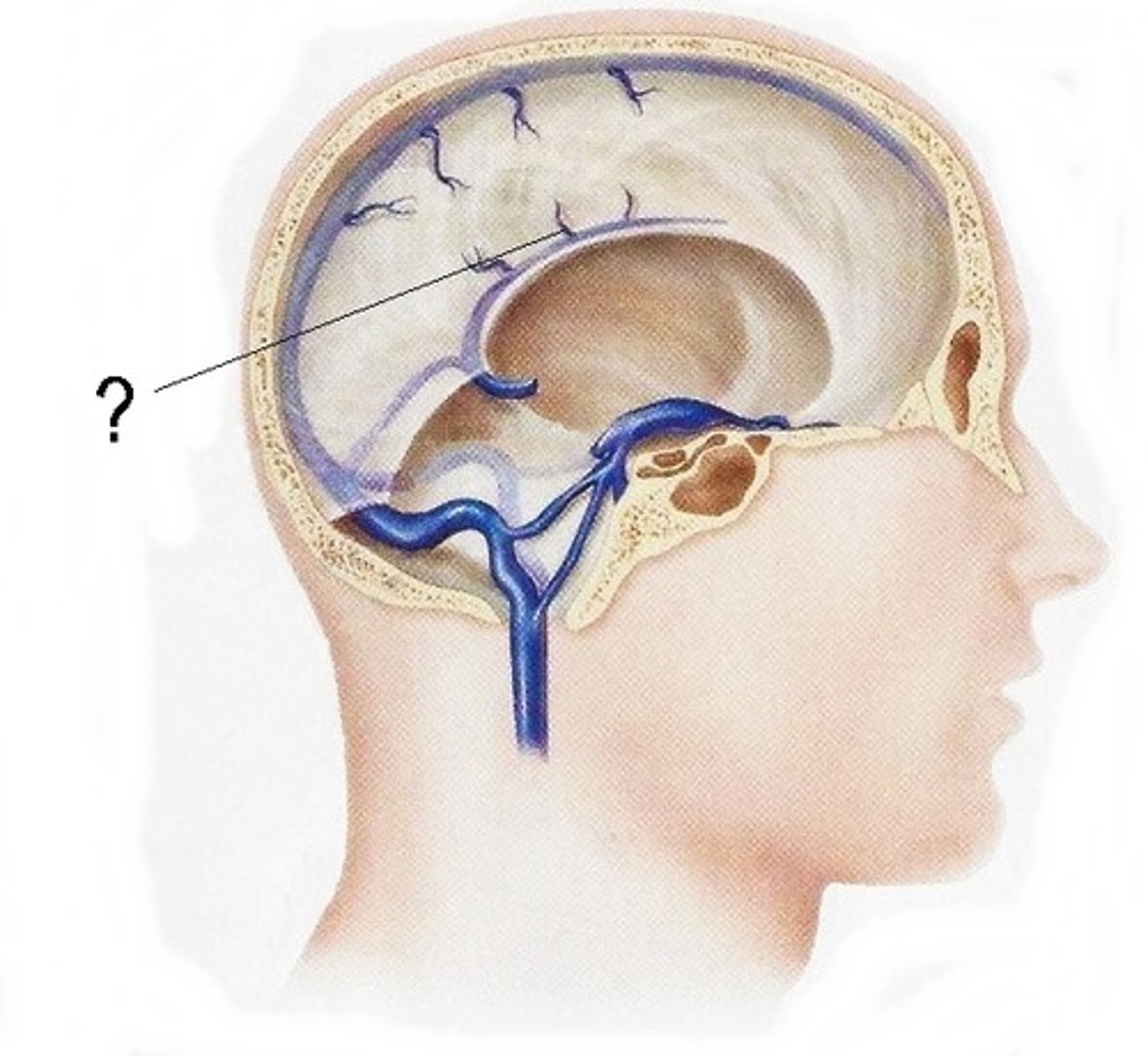
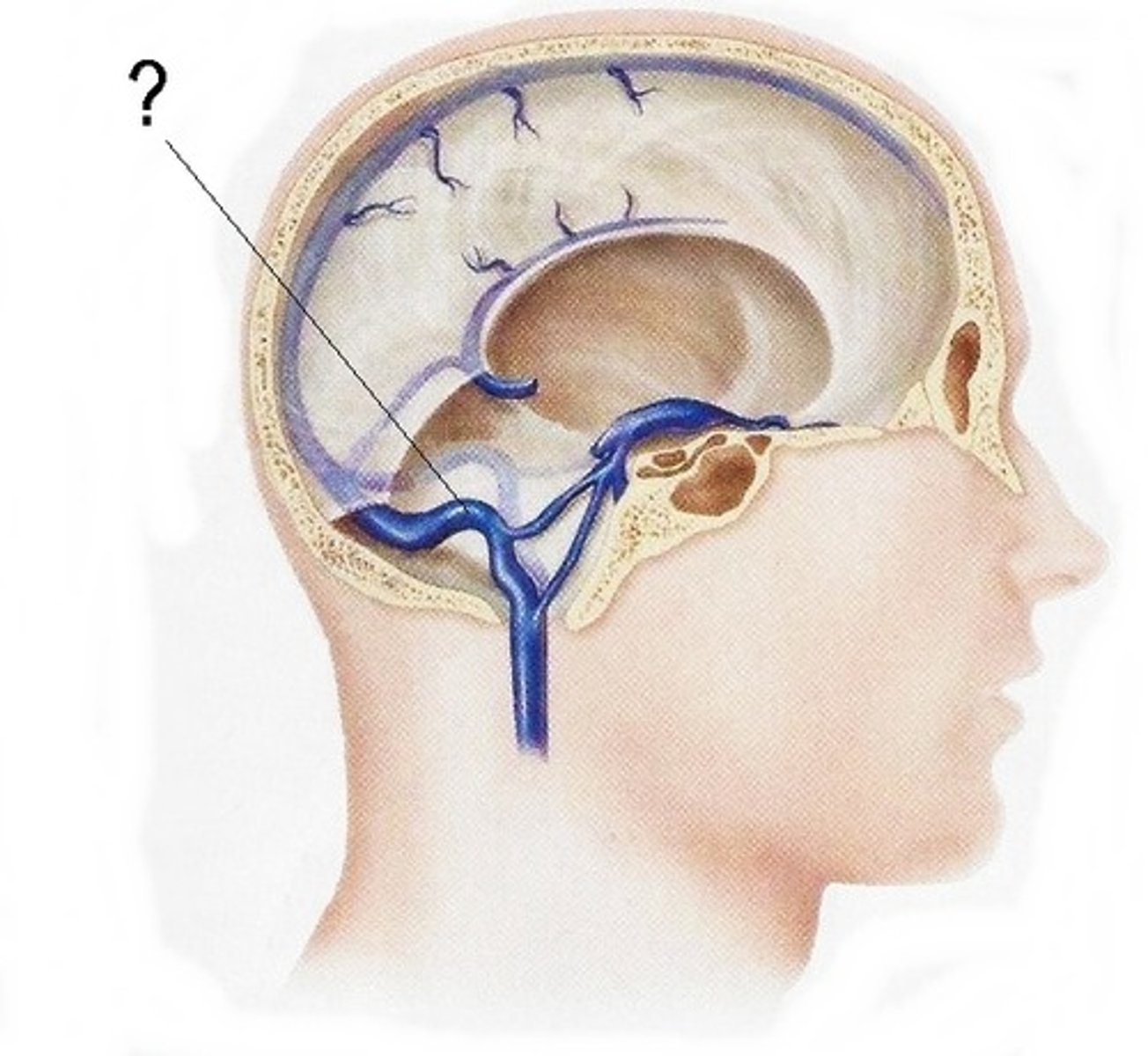
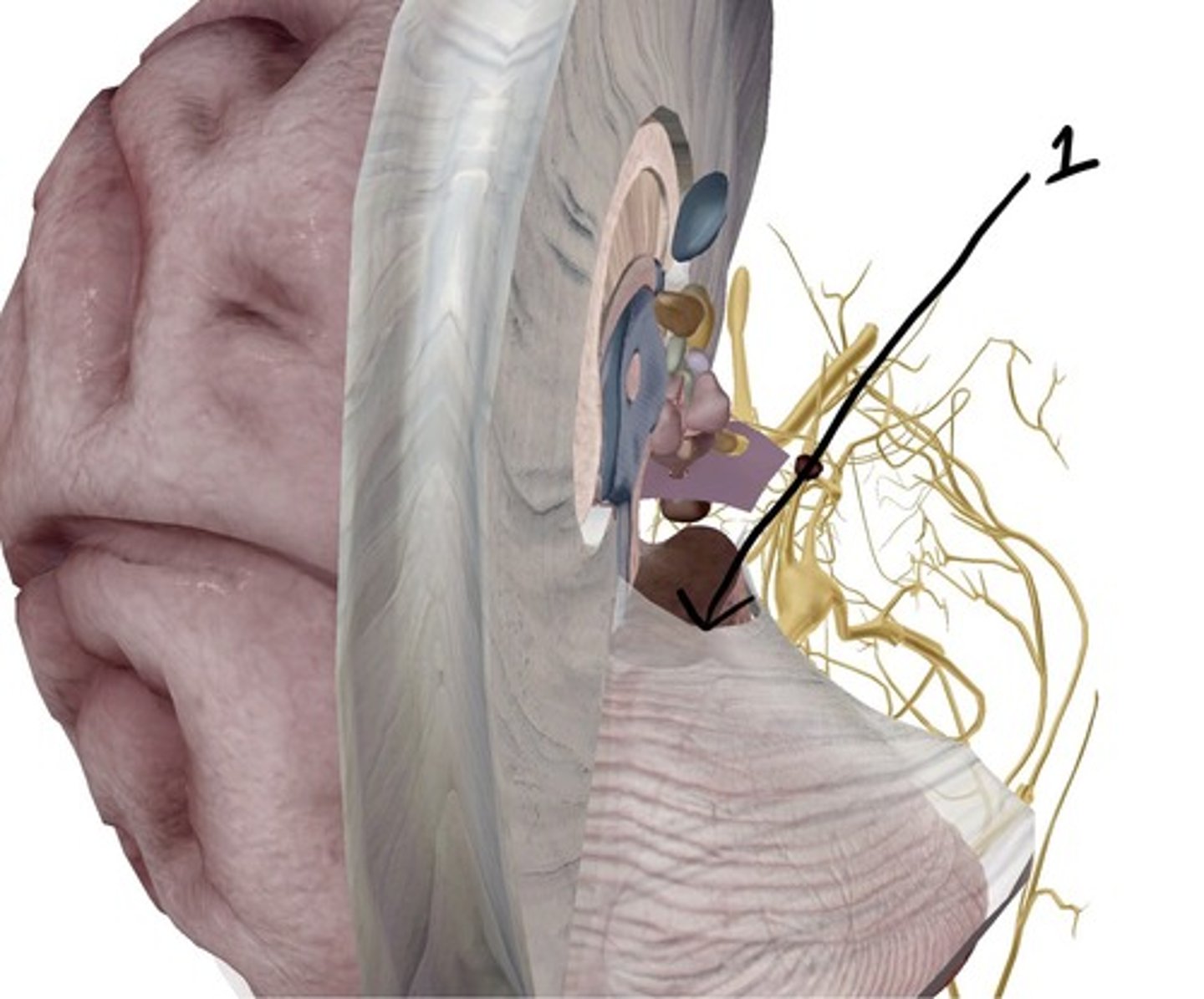
emissary veins, connect dural venous sinuses with veins outside cranium
name the structure and function
diploe
spongy bone in flat bones
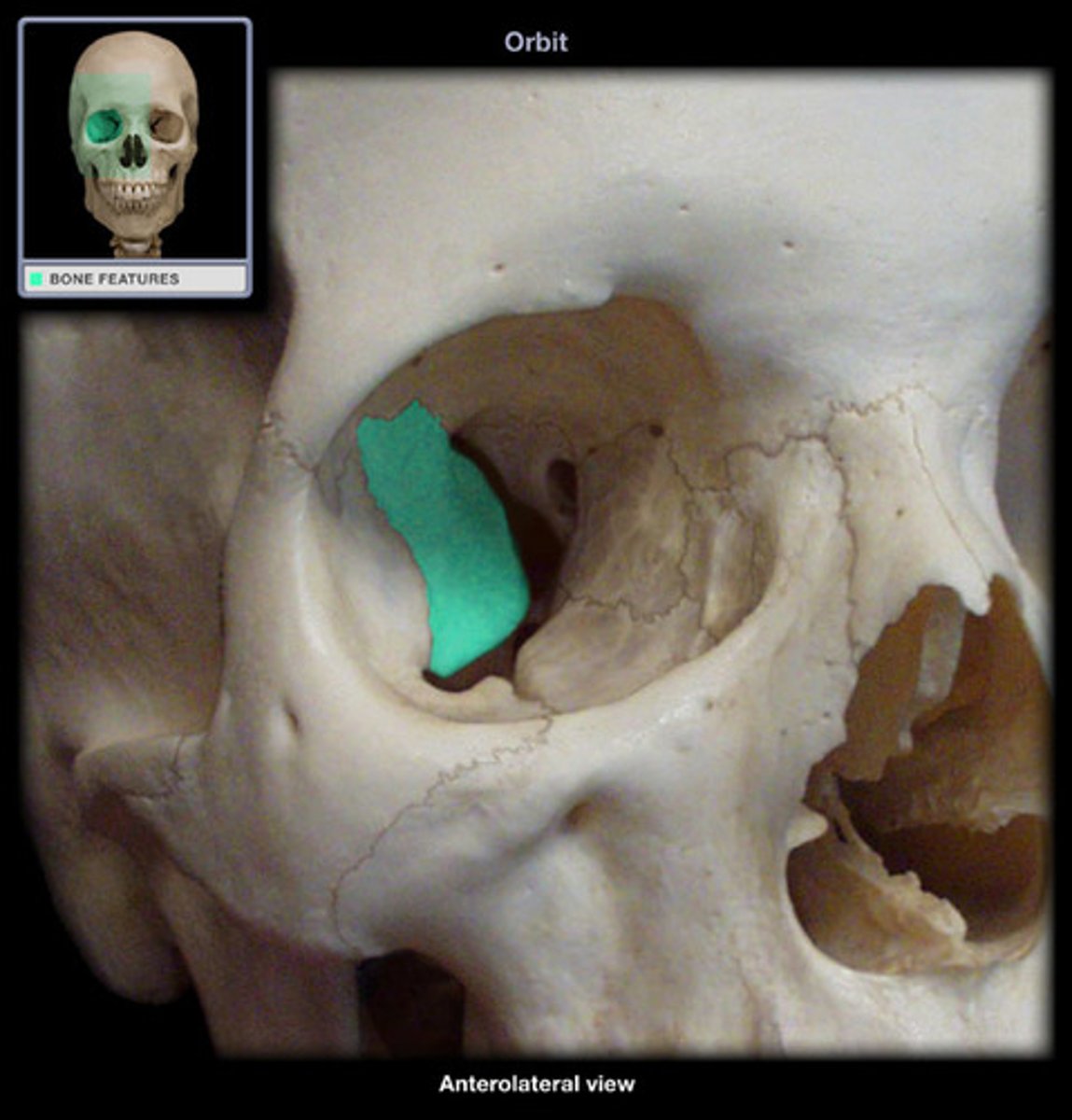
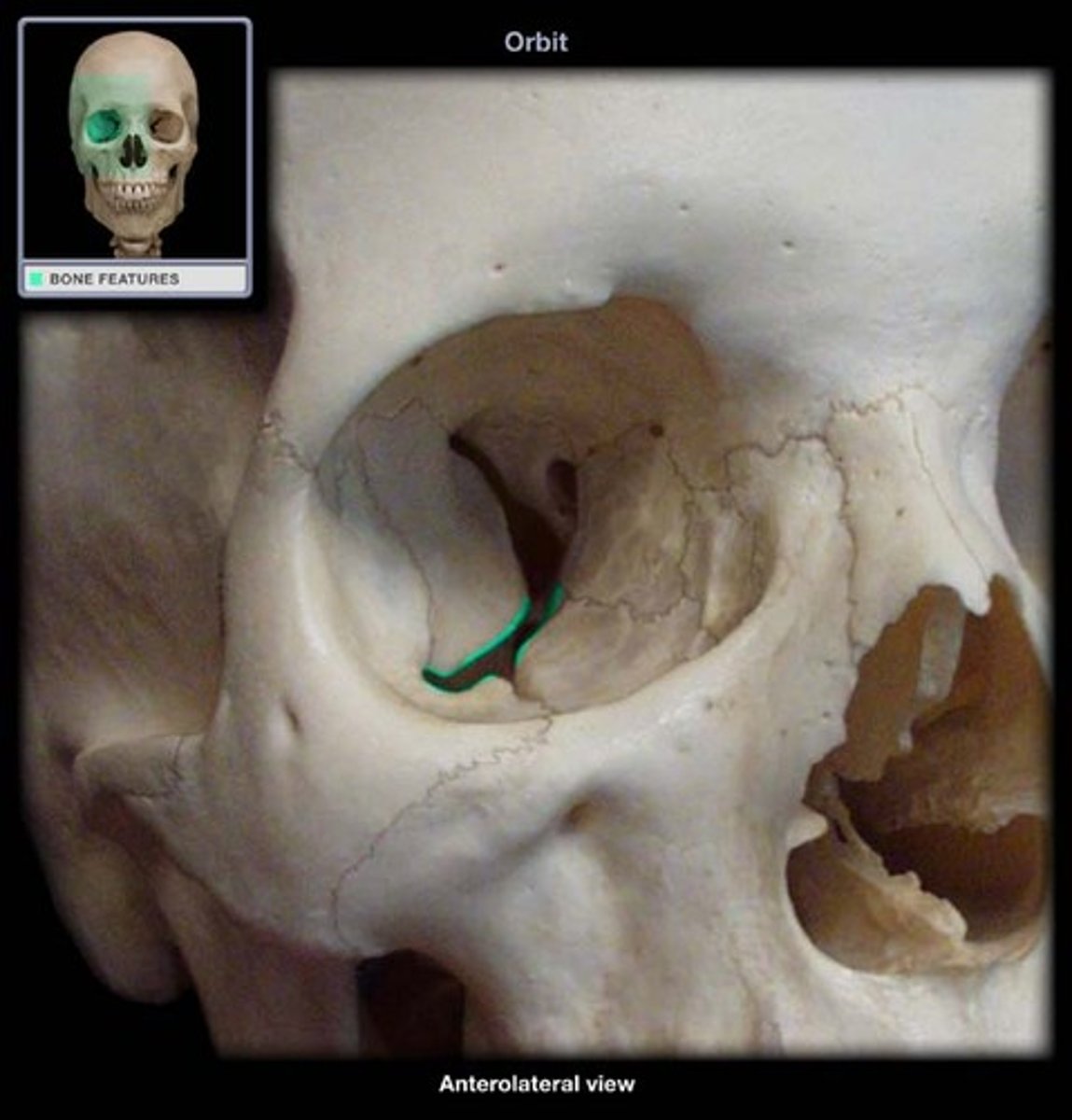
lacrimal bone
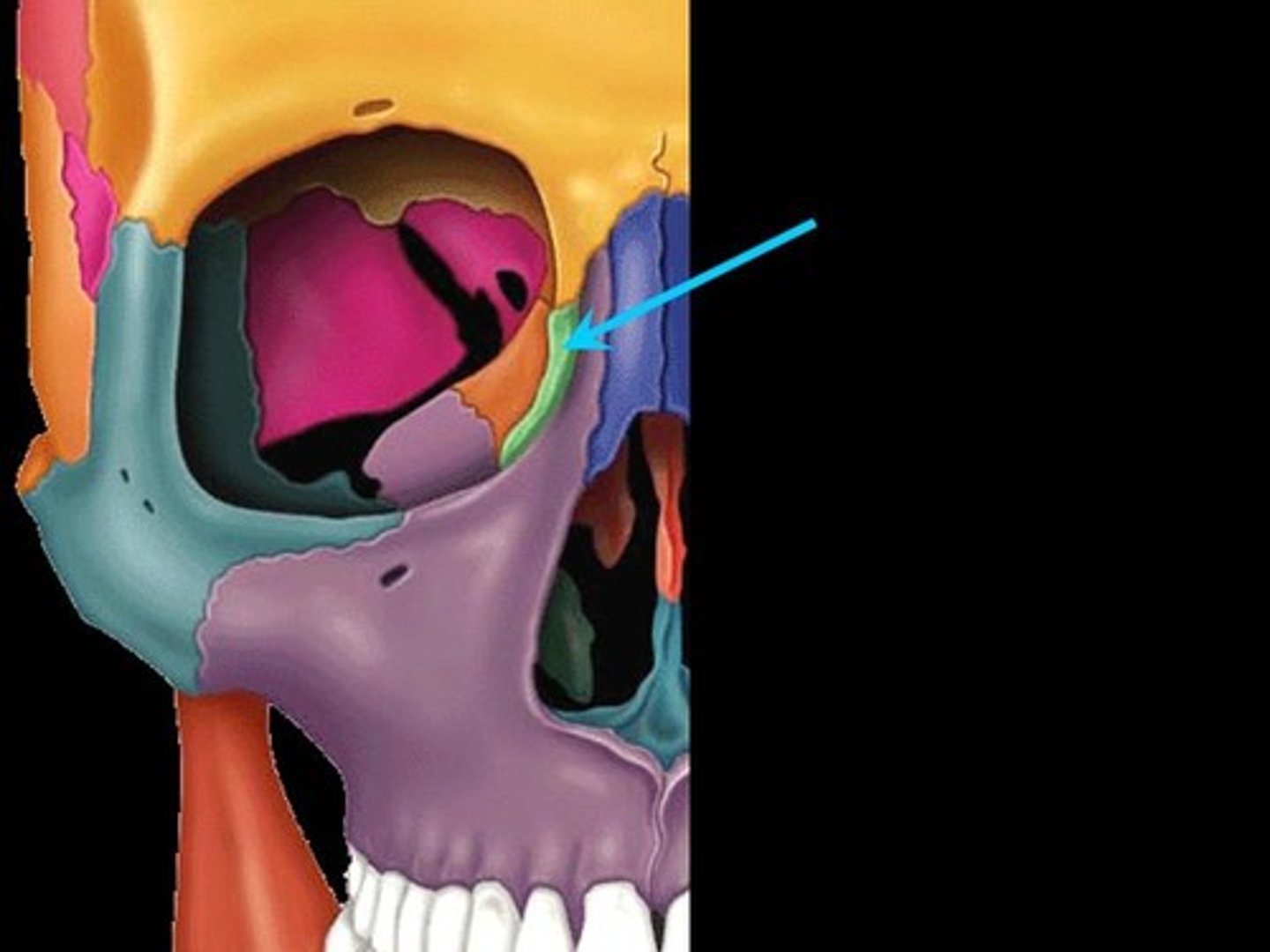
nasolacrimal canal
tear duct
ethmoid bone
Light spongy bone between the eye sockets; forms part of the nasal cavities.
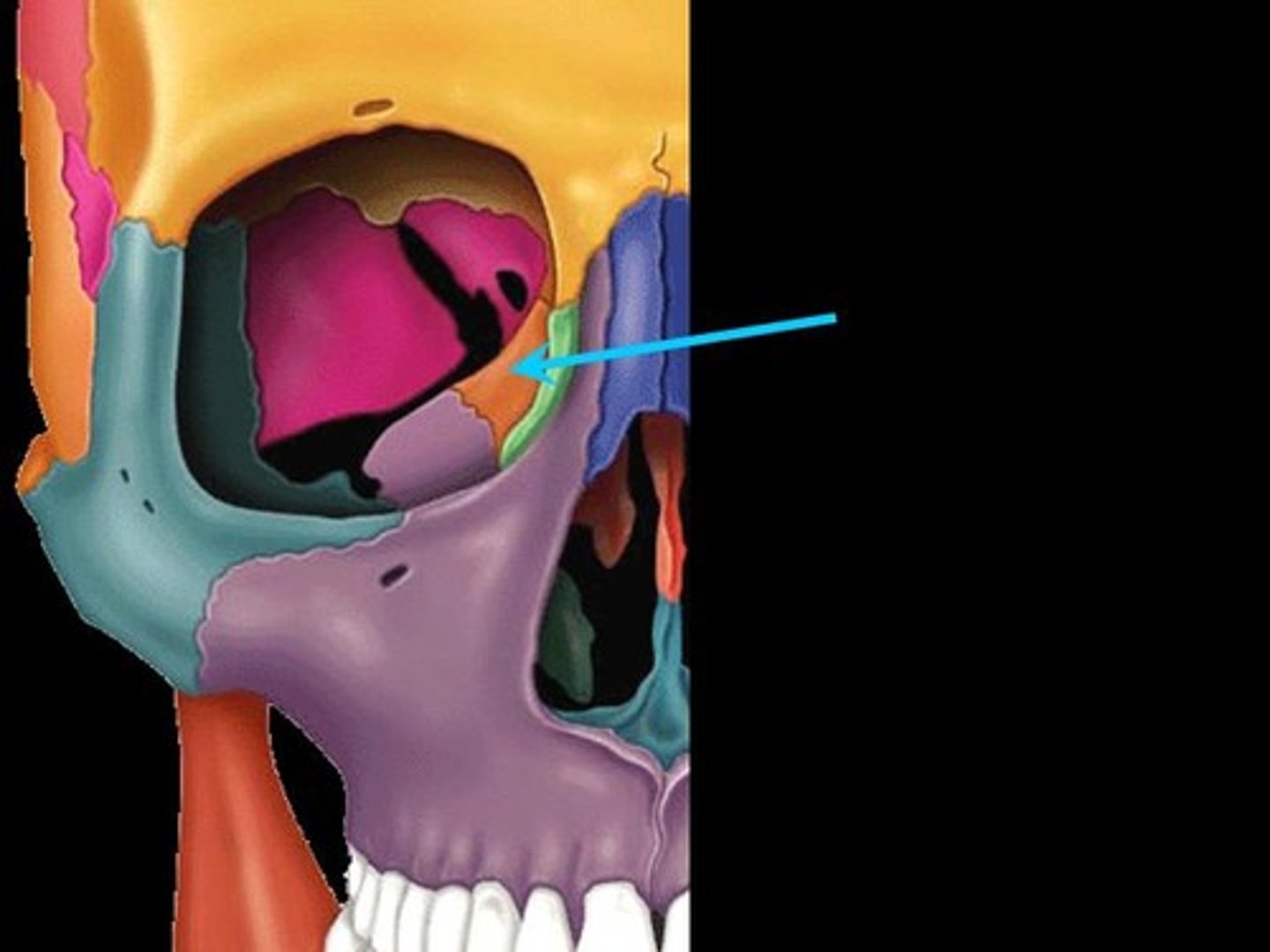
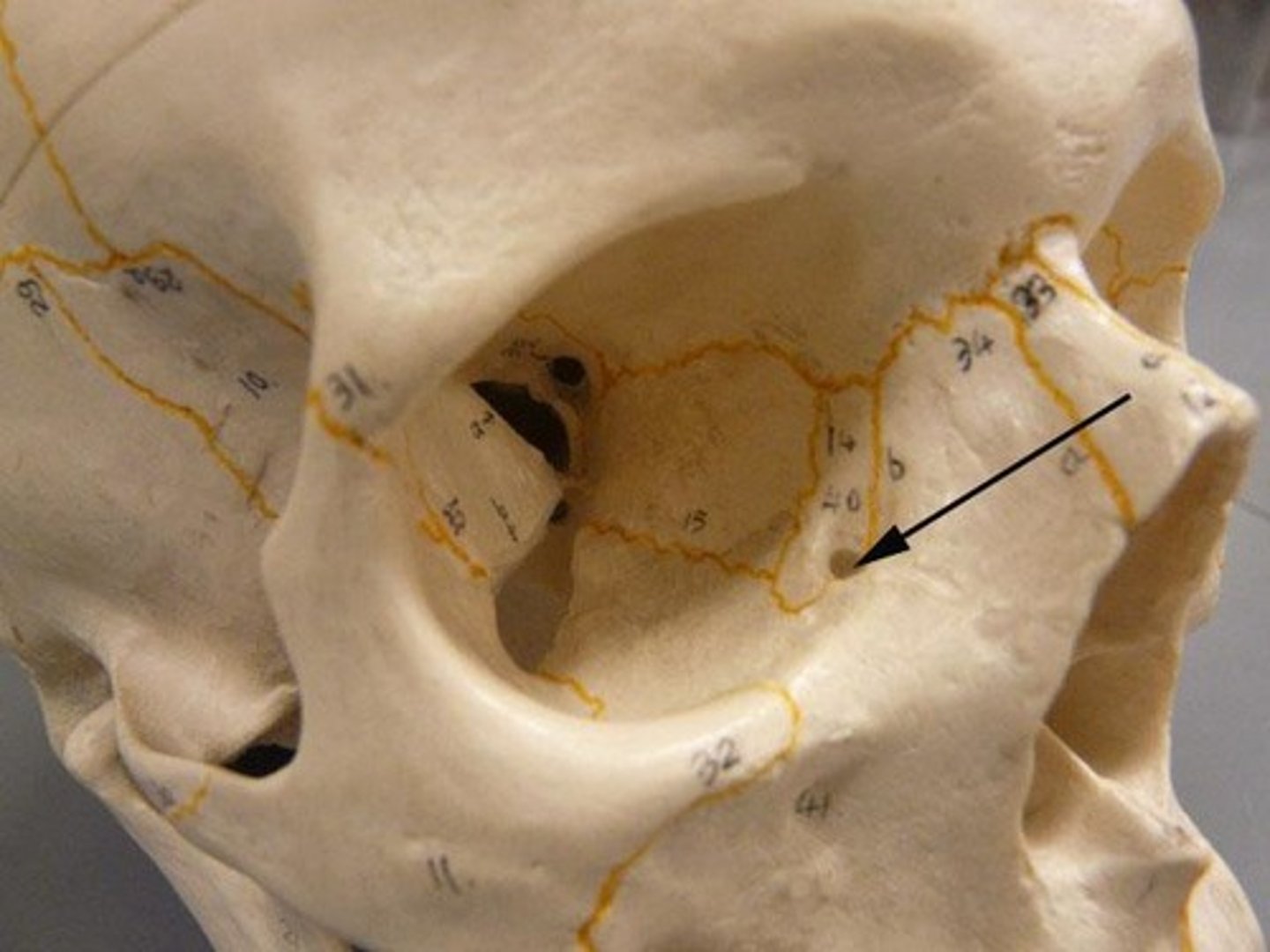
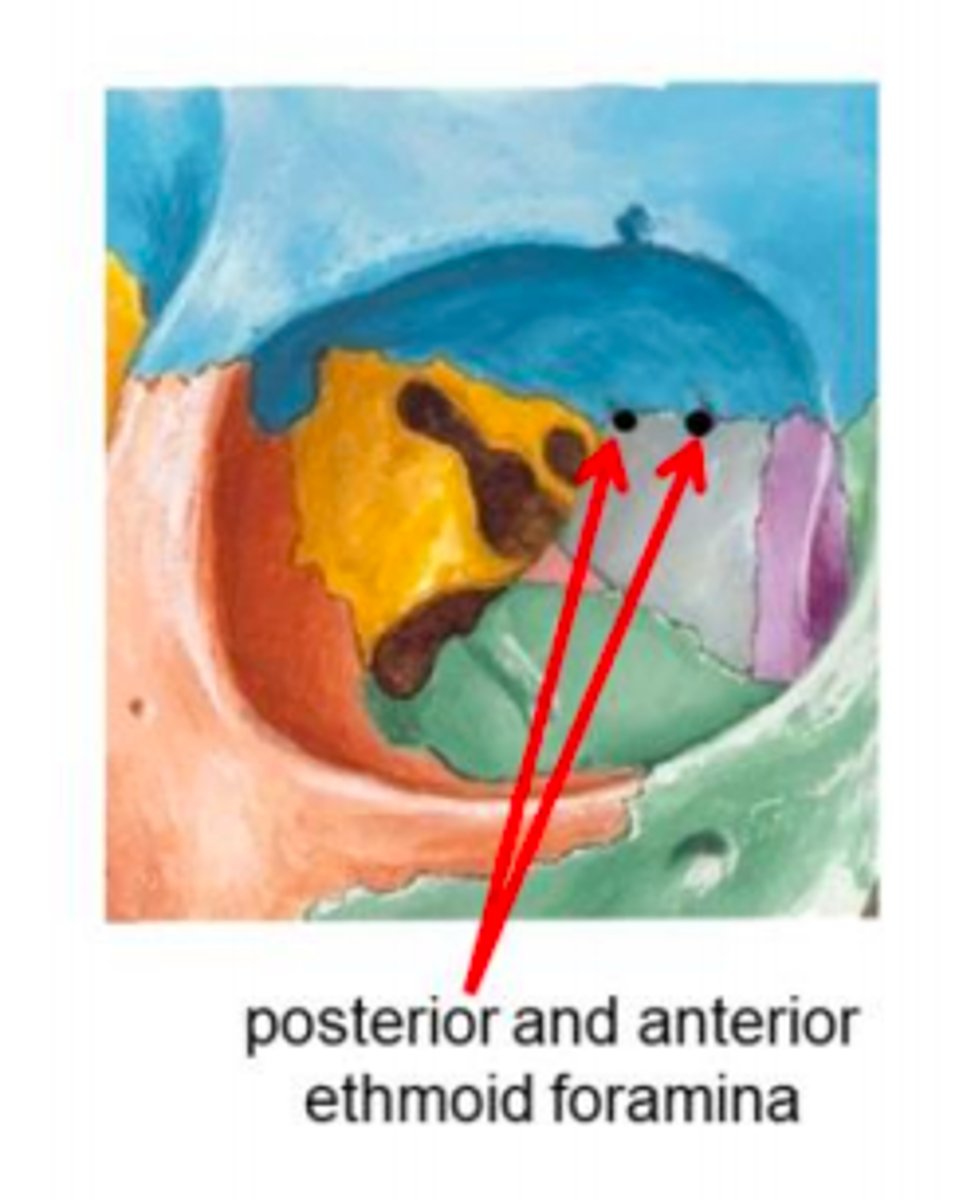
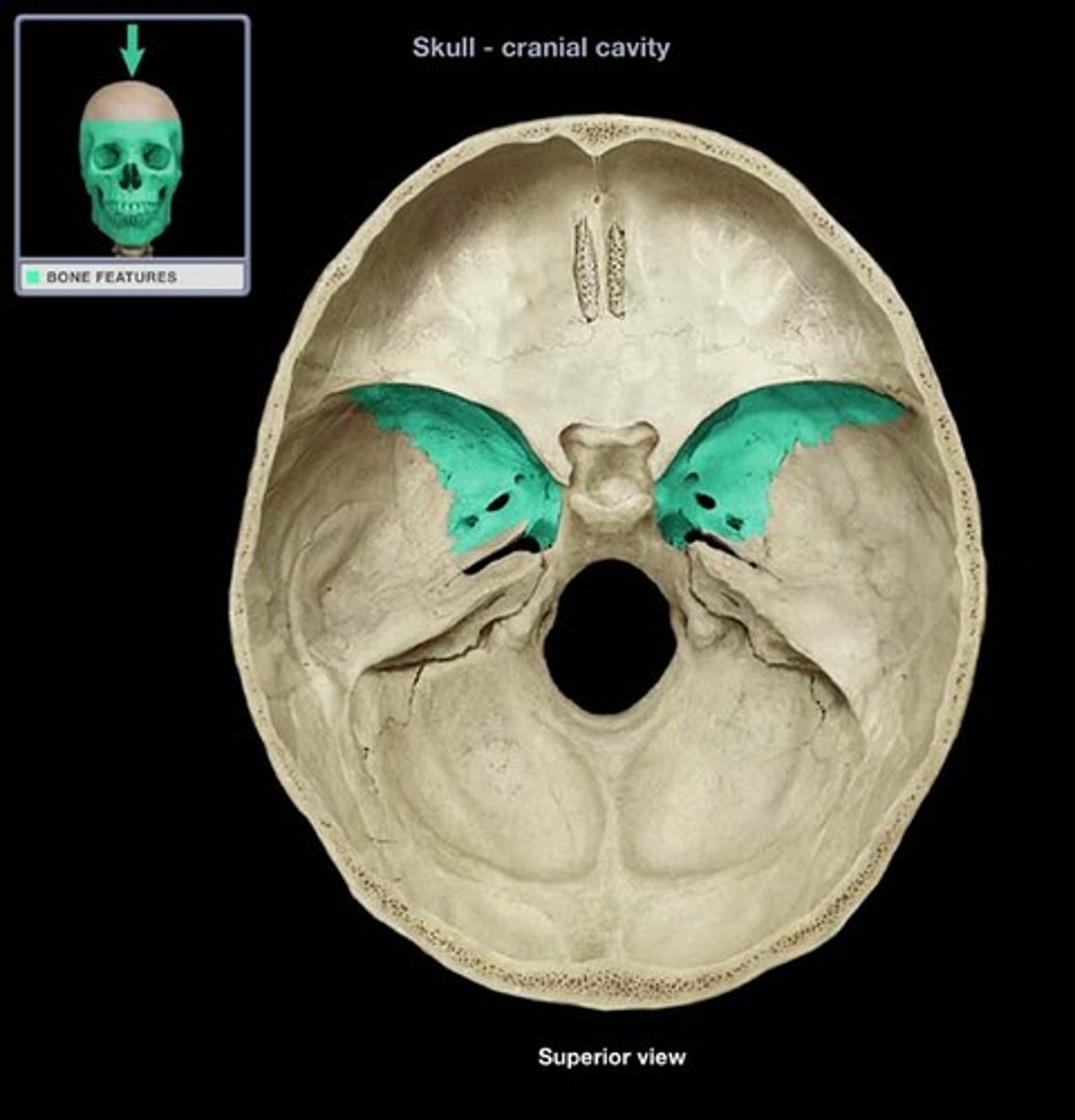
anterior/posterior ethmoid foramina
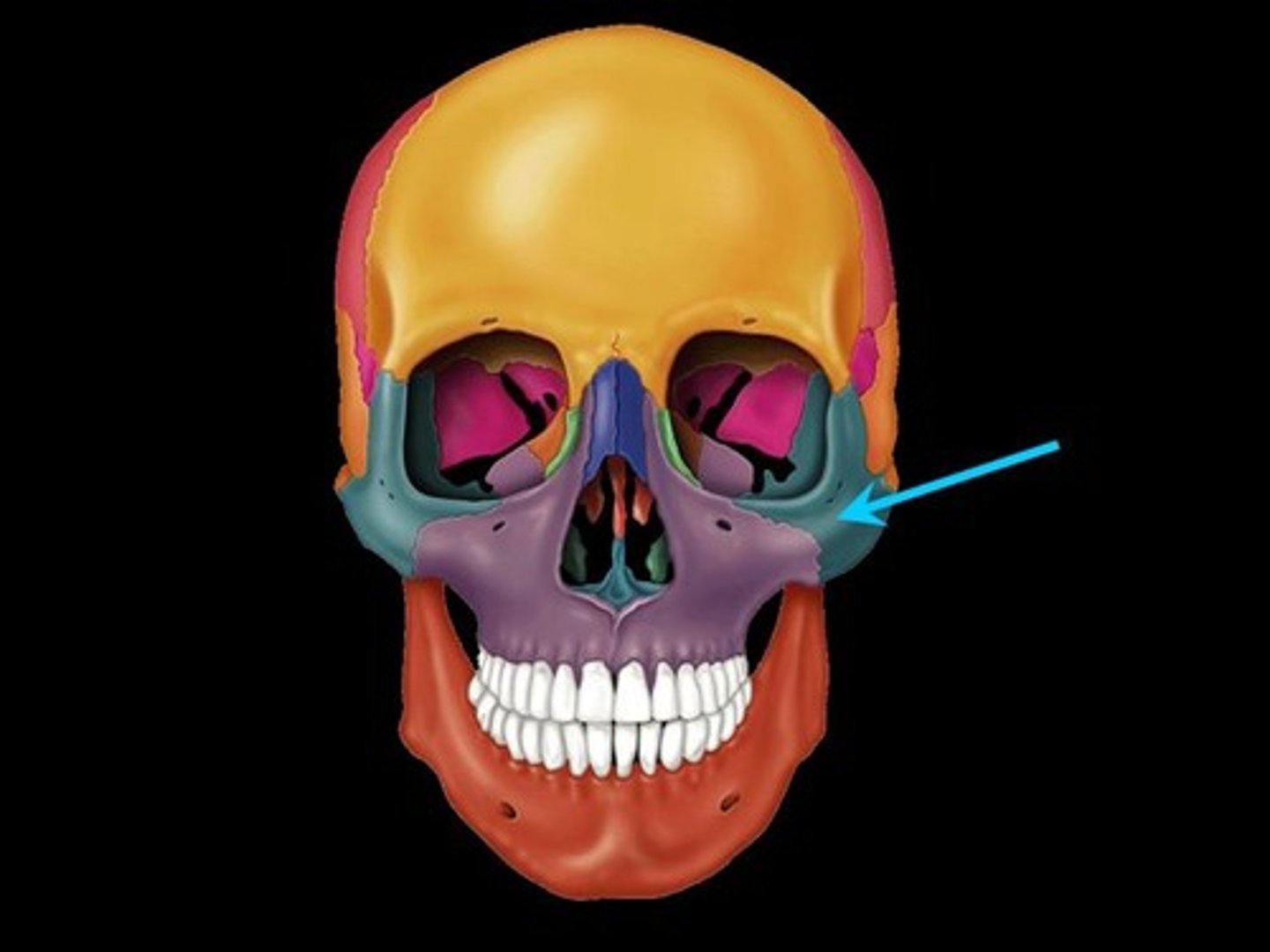
Zygomatic bone
greater wing of sphenoid bone
Frontal orbital plate
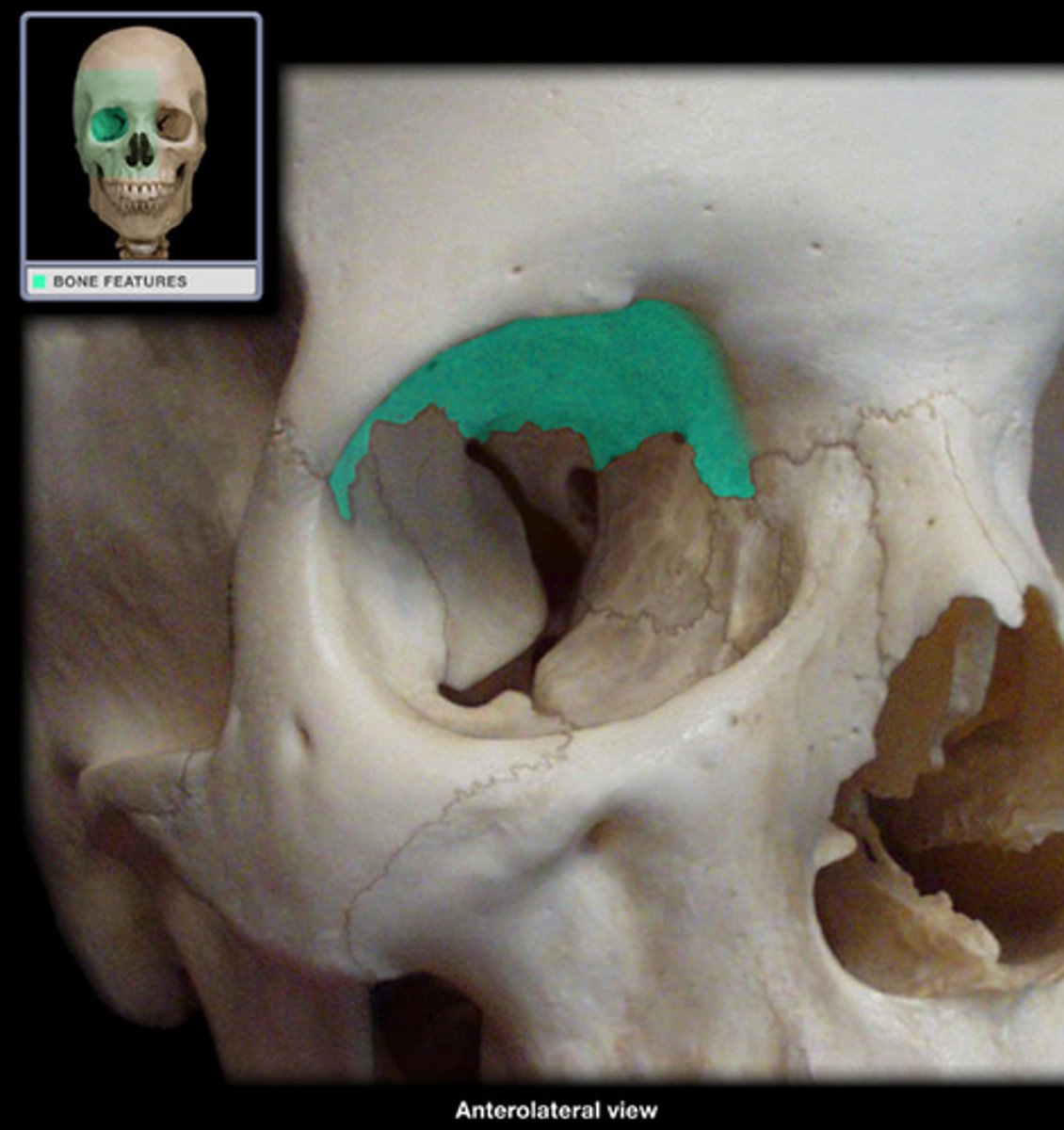
maxilla
opthalmic nerve
which nerve provides the sensory innervation for this dermatome
infraorbital canal and infraorbital nerve
what is the name of this structure and what goes through it
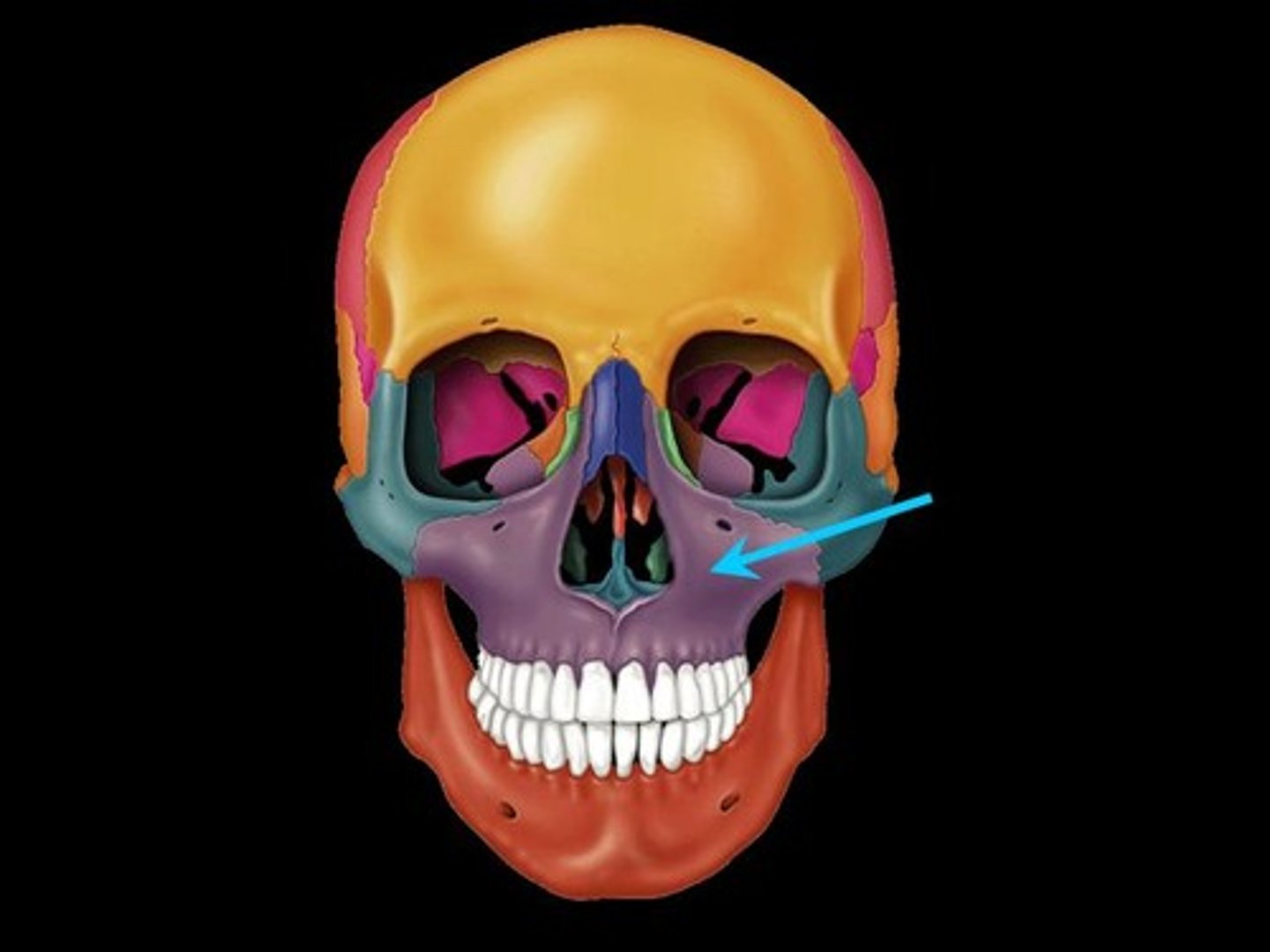
inferior orbital fissue and maxillary nerve
what is the name of this structure and what goes through it
frontal nerve
passes above the levator palpebrae muscle, and divides into supratrochlear and supraorbital nerves near the outer part of the orbit
supraorbital nerve
Affects the skin of the forehead, scalp, eyebrow, and upper eyelid.
Supratrochlear nerve
affects the skin between the eyes and upper side of the nose
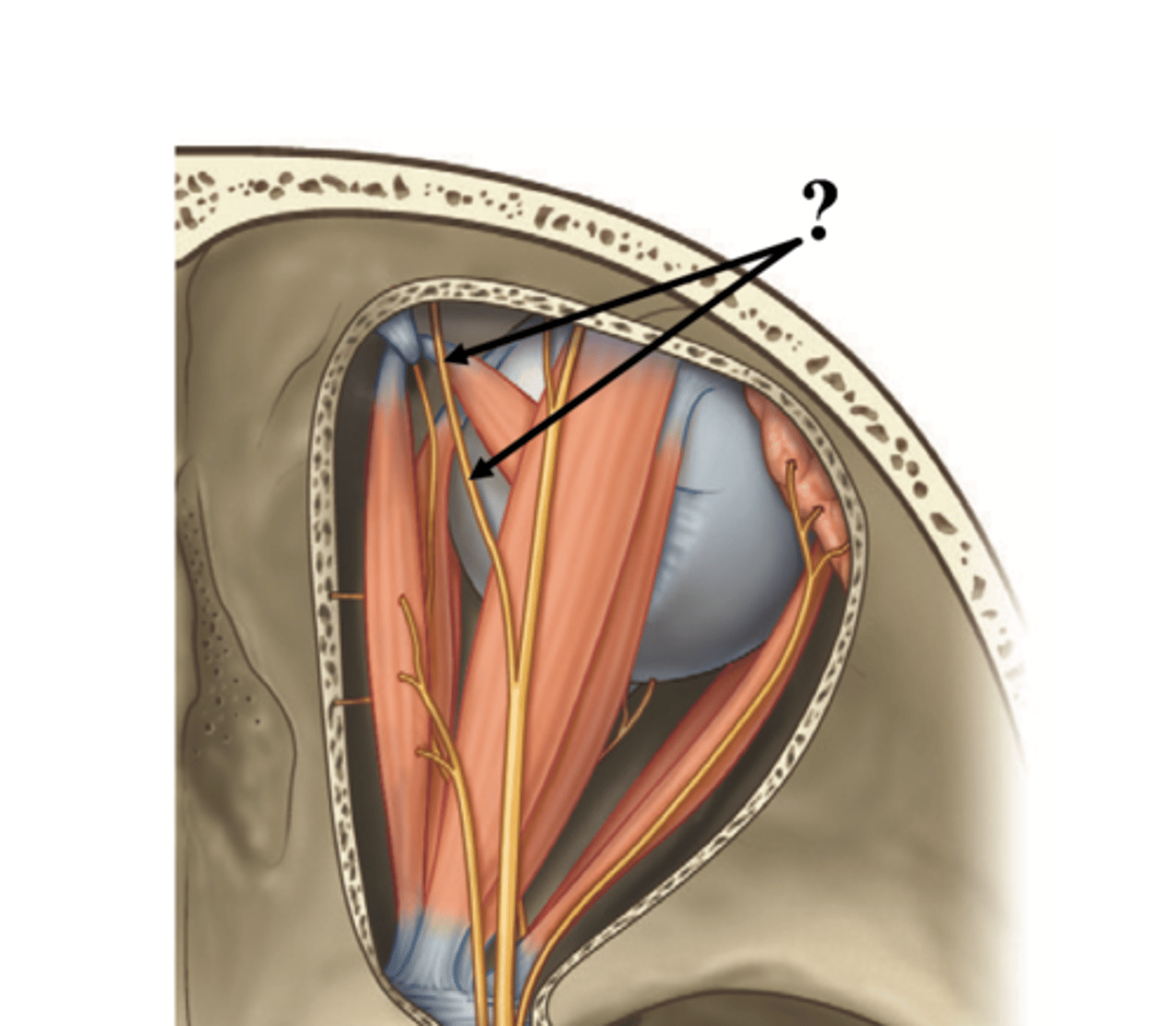
lacrimal nerve, sensory innervation to conjuctiva and carries PS fibers from VII to lacrimal gland
3) name this vessel and its function
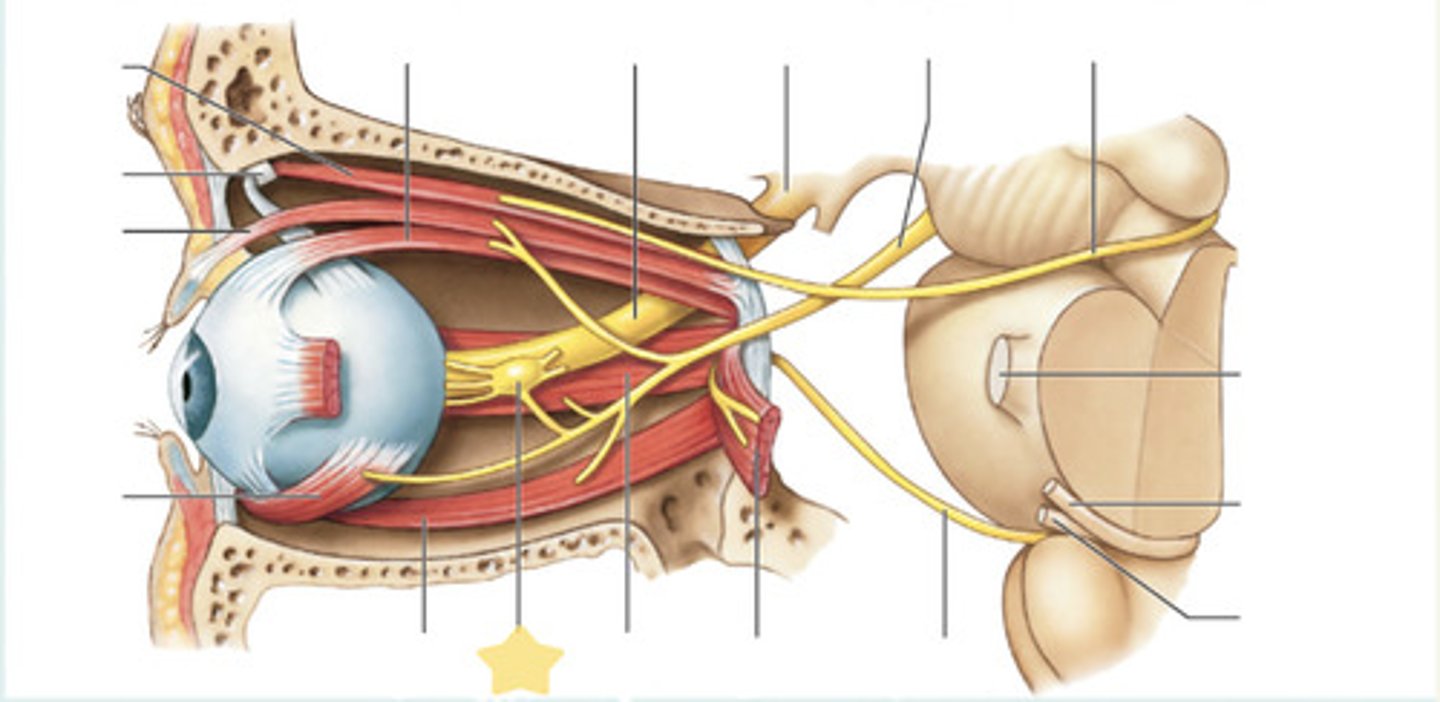
nasociliary
Opthalmic- V1 Trigeminal nerve, the branch responsible for:
Ethmoid nerves (nasal cavity)
Infratrochlear nerve (Skin at medial, inferior corner of the eye)
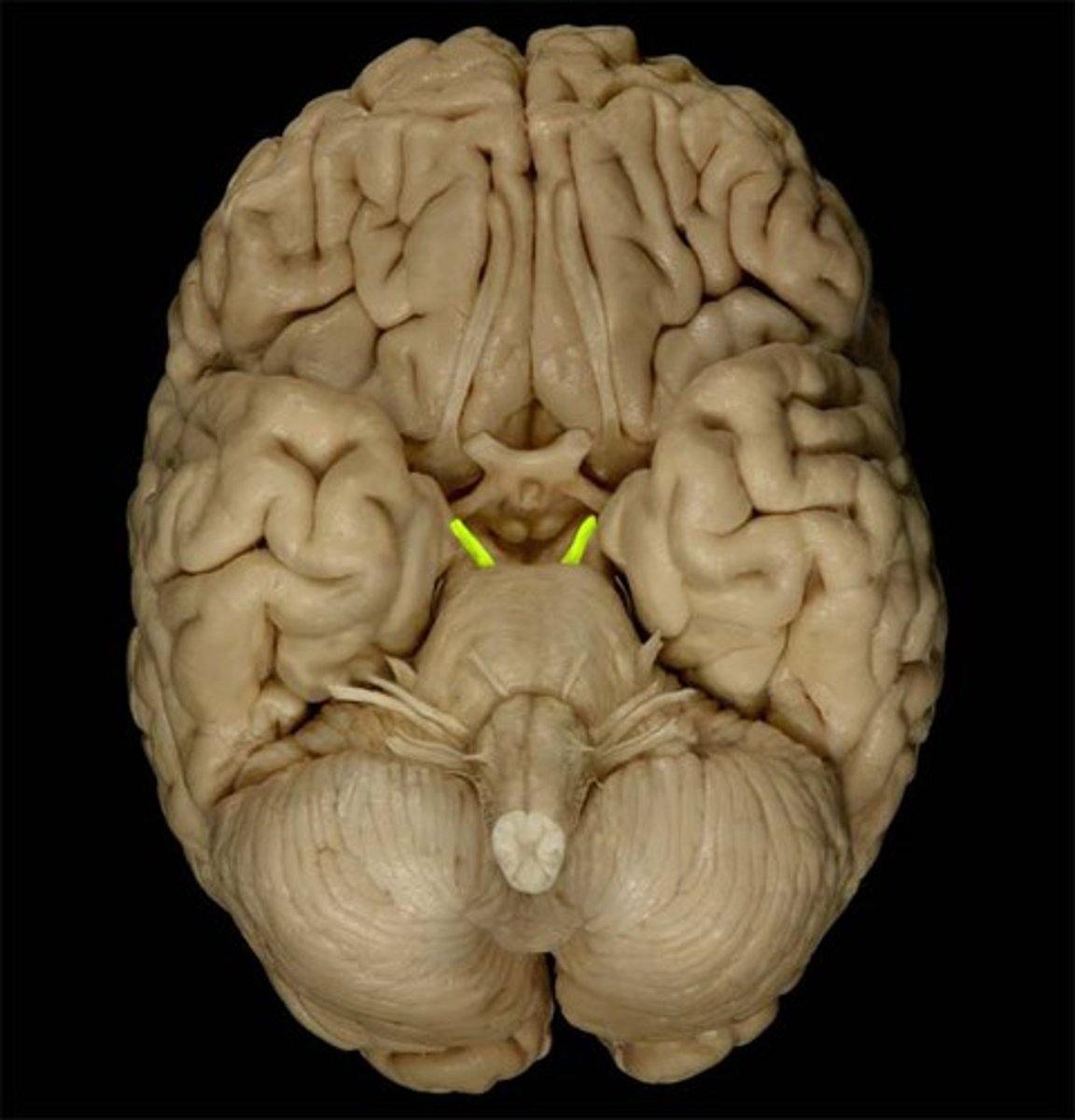
oculomotor nerve (CN III), movement of the eye
what is the name of this structure and what is the function
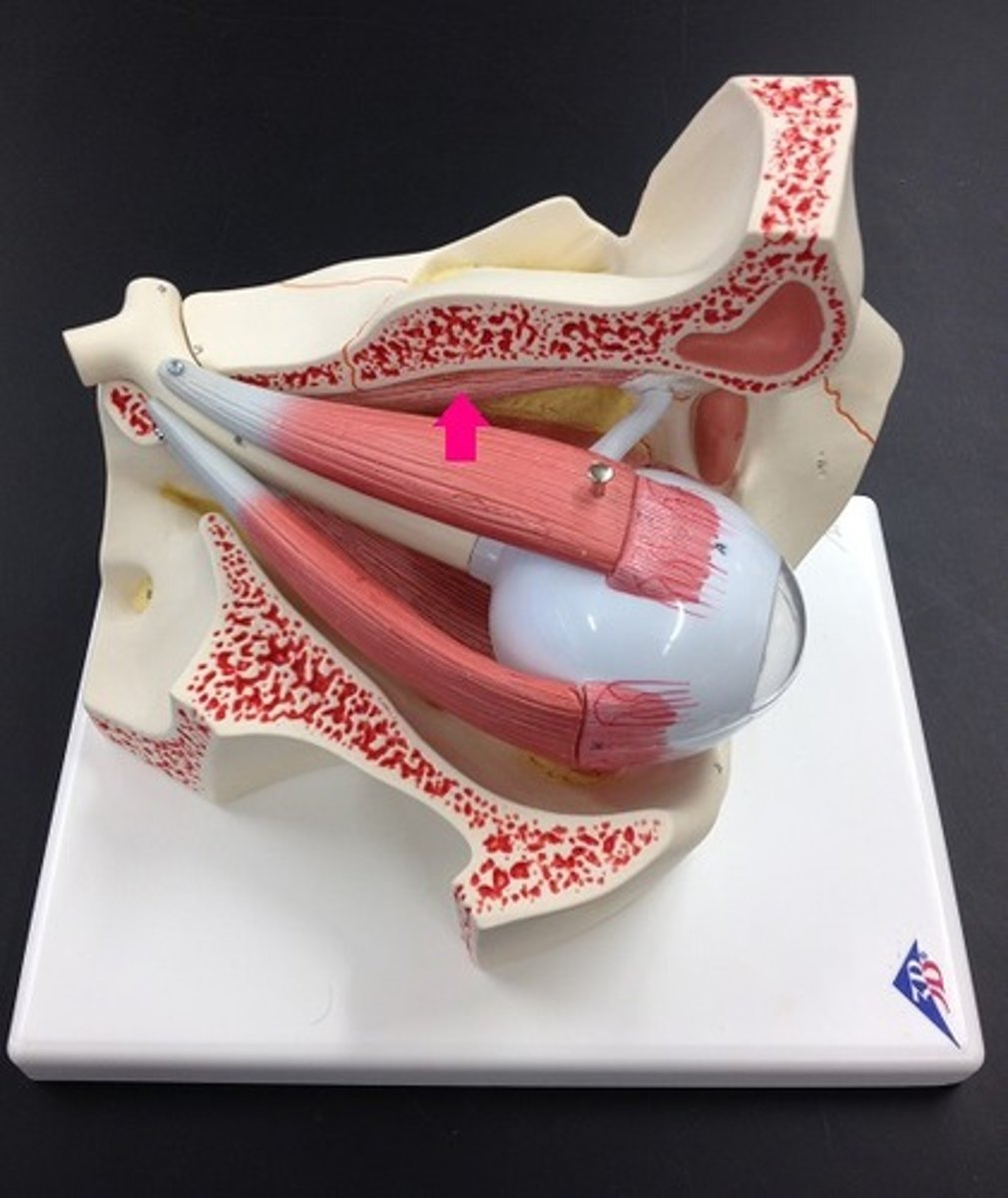
superior oblique, intortion of eye, trochlear nerve (CN IV)
what is the name of this muscle, function, and nerve that innervates it
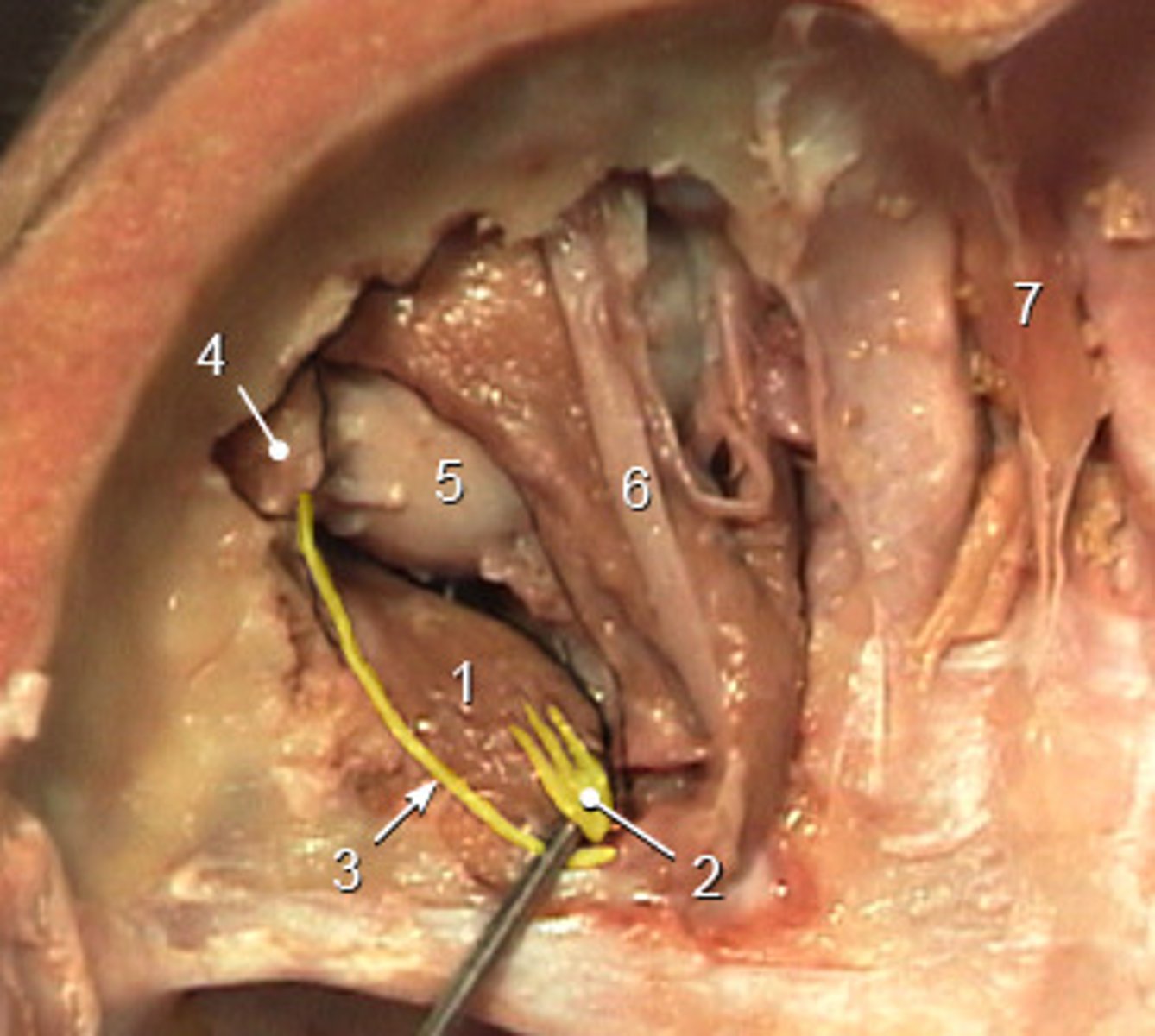
cilliary ganglion
pupil constriction (constrictor pupillae) parasympathetically
lateral rectus, abduction of eye, abducens (CN VI)
what is the name of this muscle, function, and nerve that innervates it
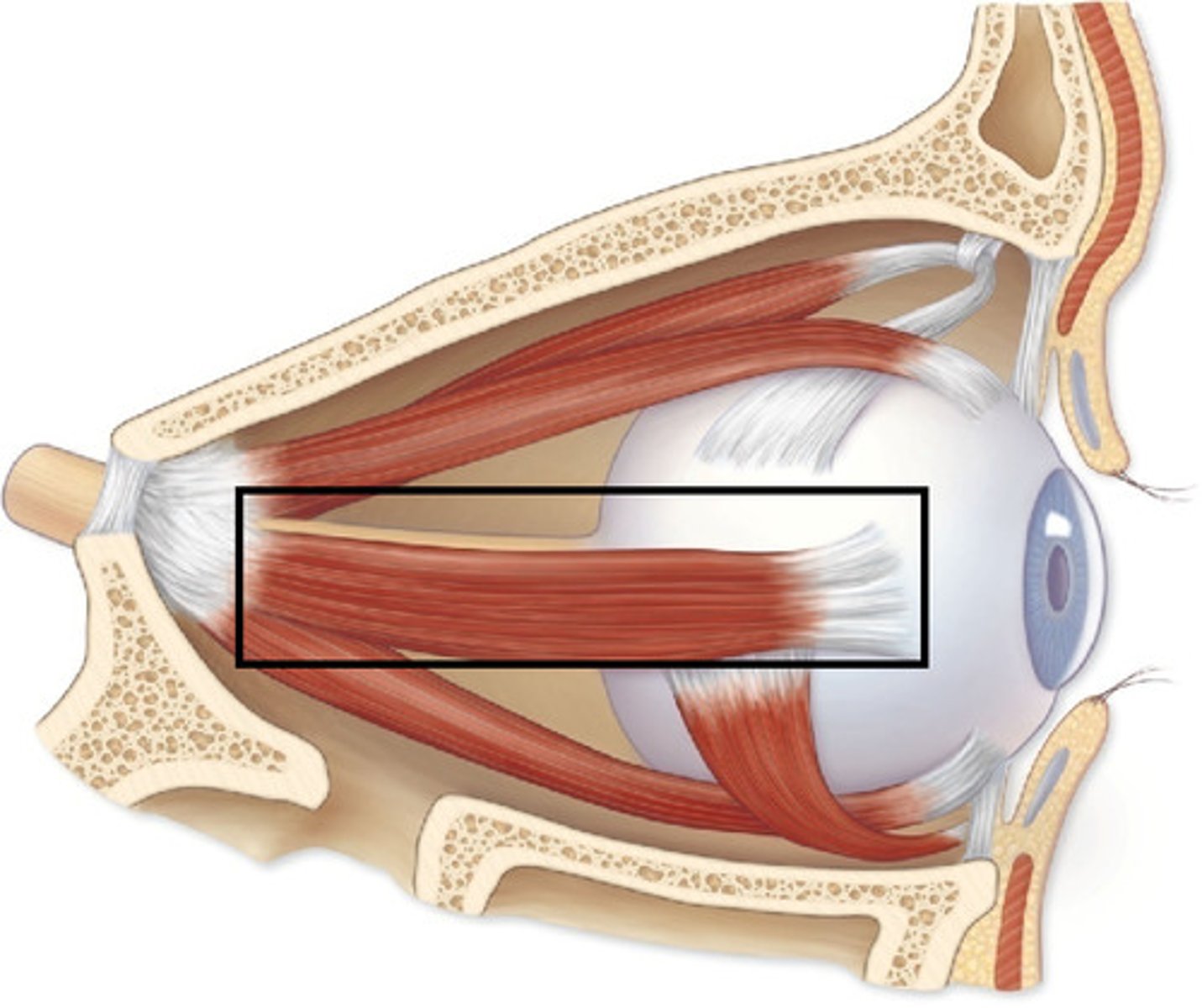
superior rectus, elevates eye
what is this structure and function
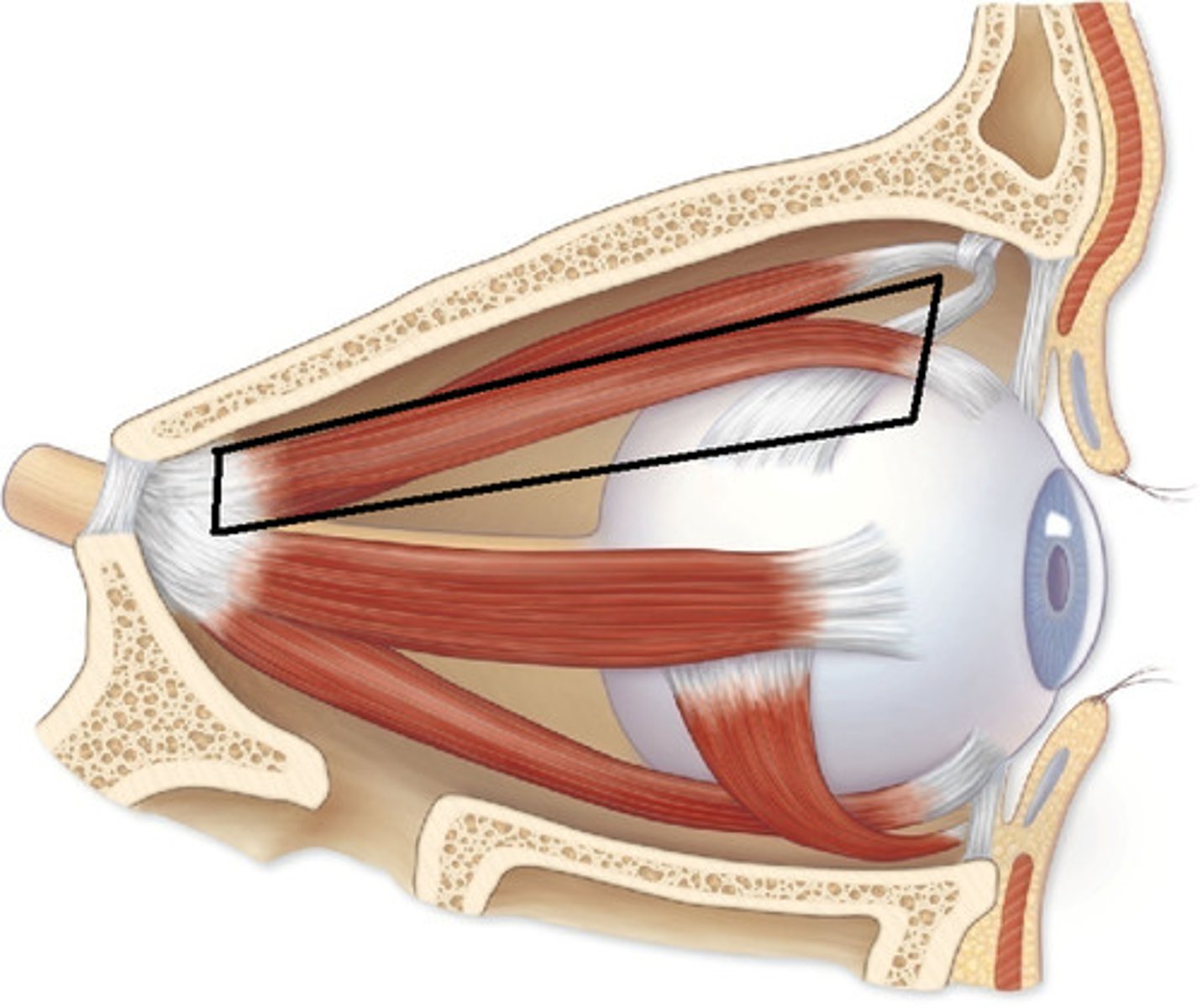
medial rectus, adduction
what is this structure and function
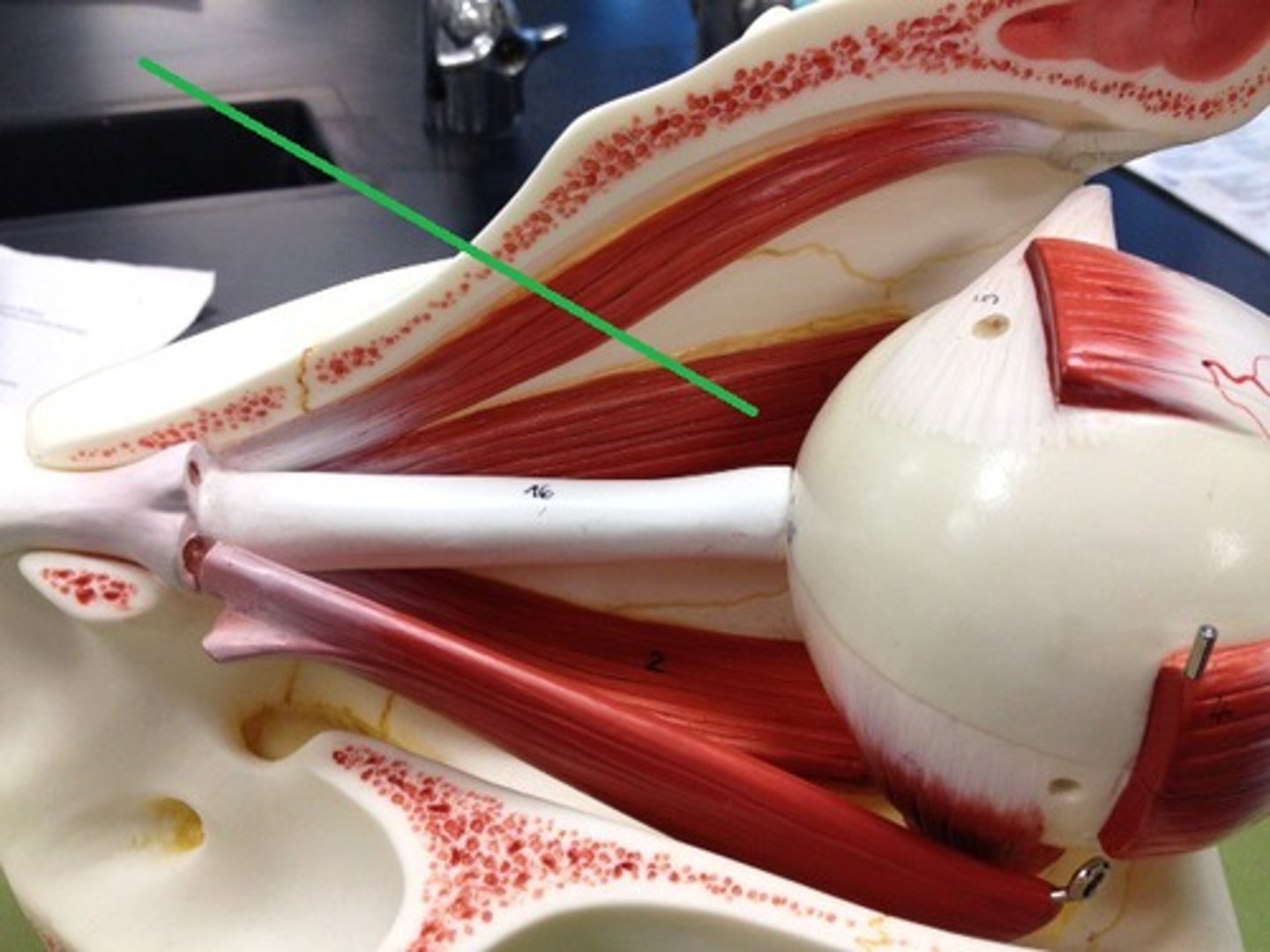
inferior rectus, lower the eye
what is this structure and function
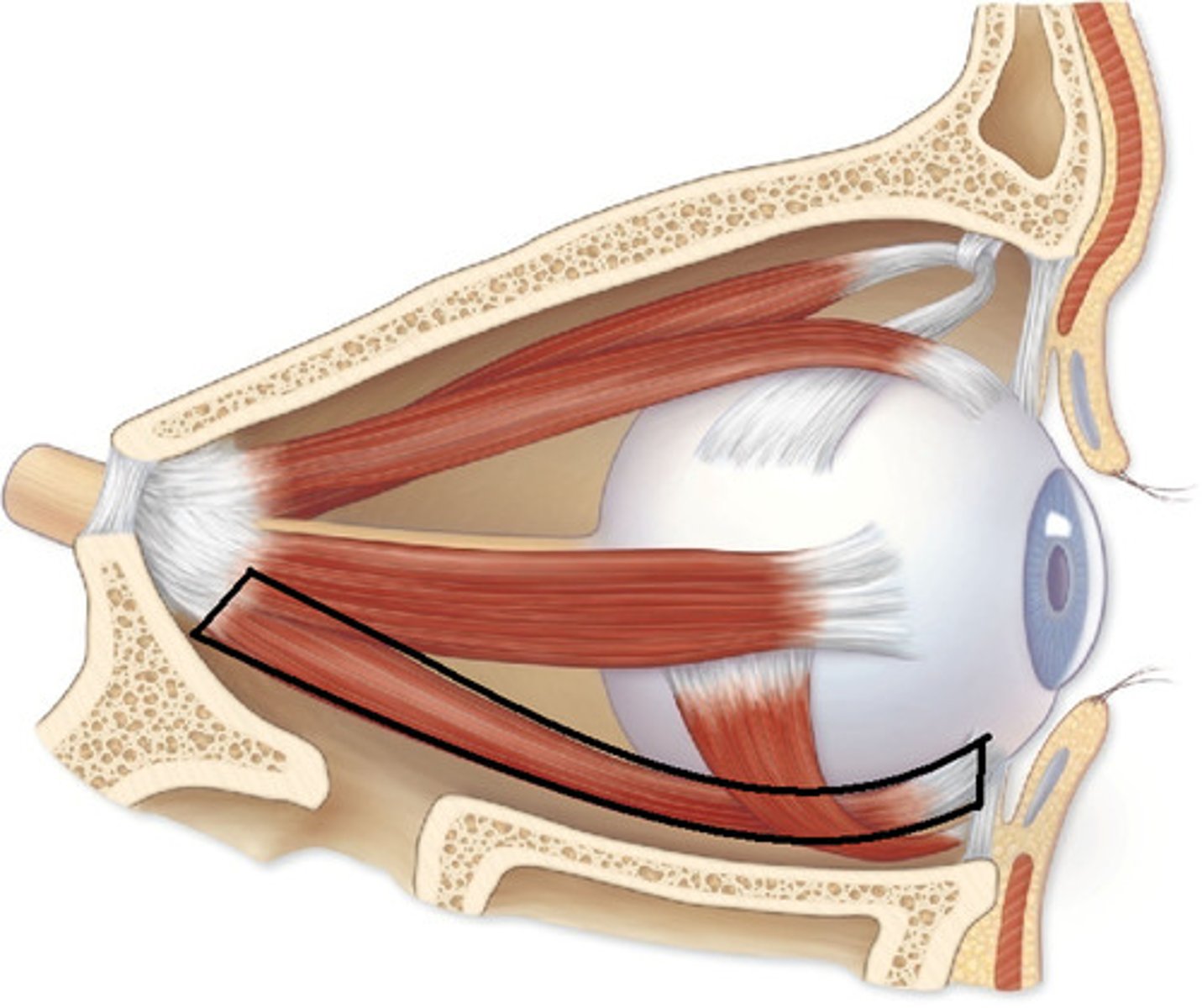
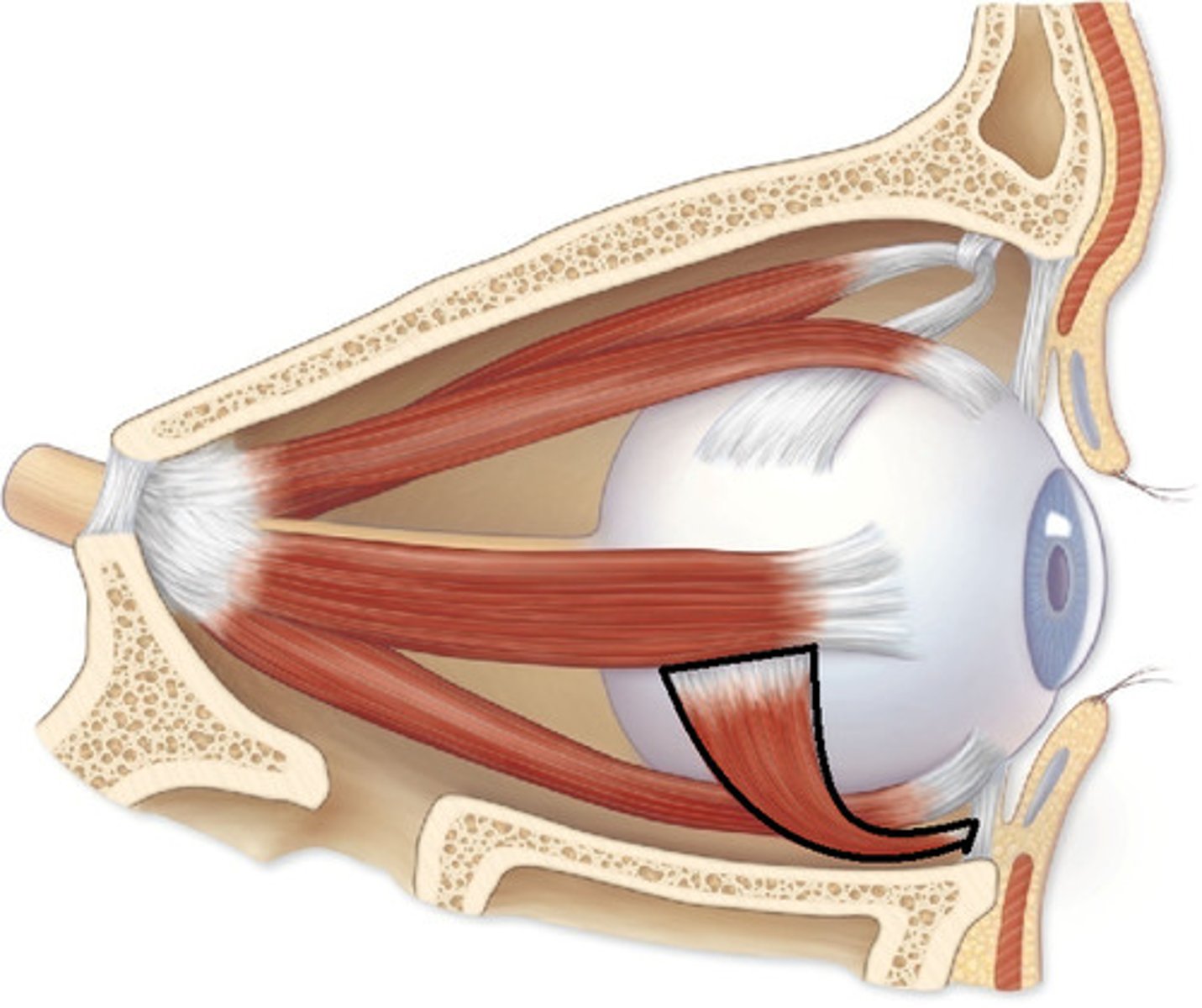
inferior oblique, extortion
what is this structure and function
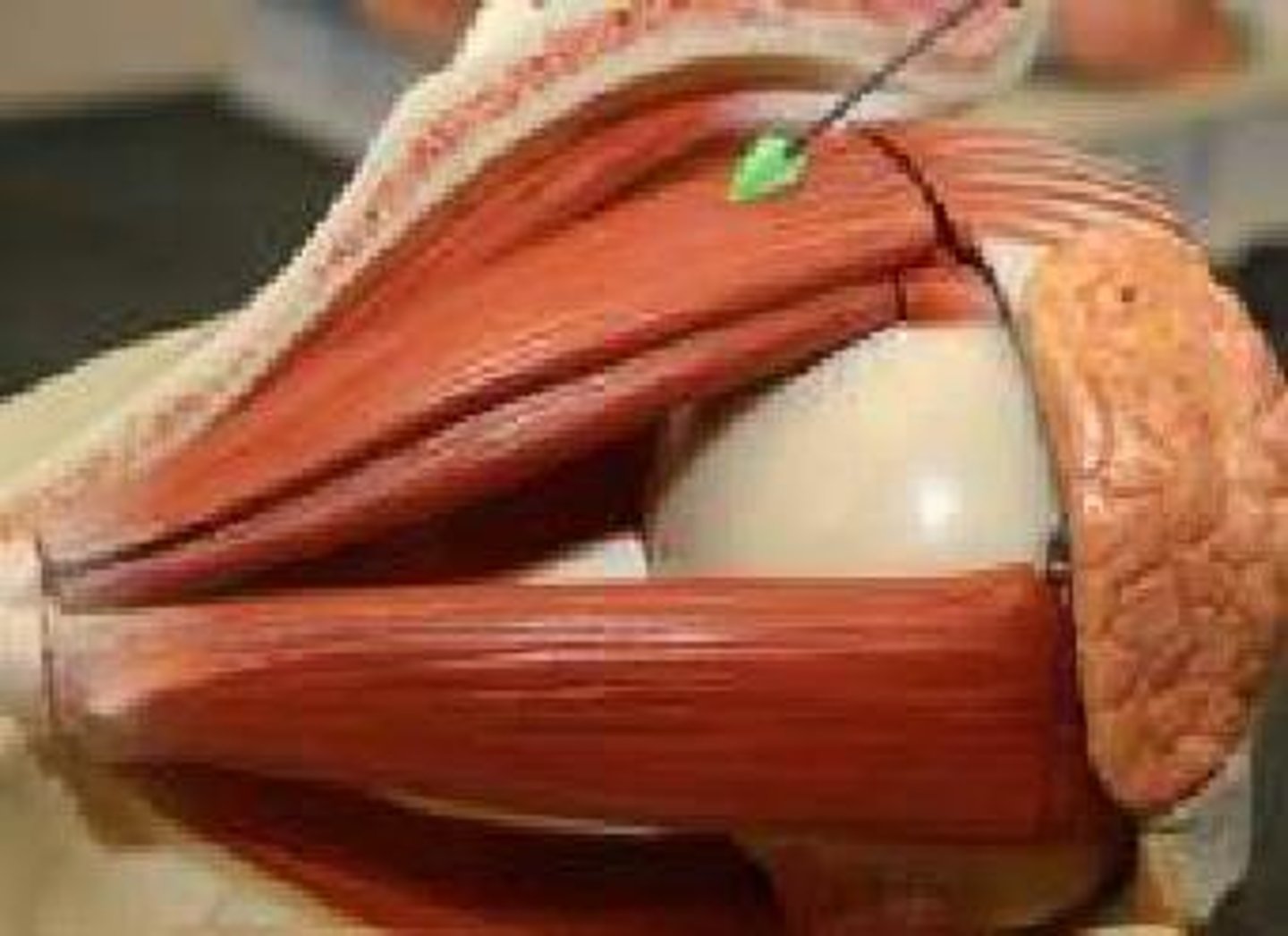
levator palpebrae superioris, elevates eyelid
what is this structure and function
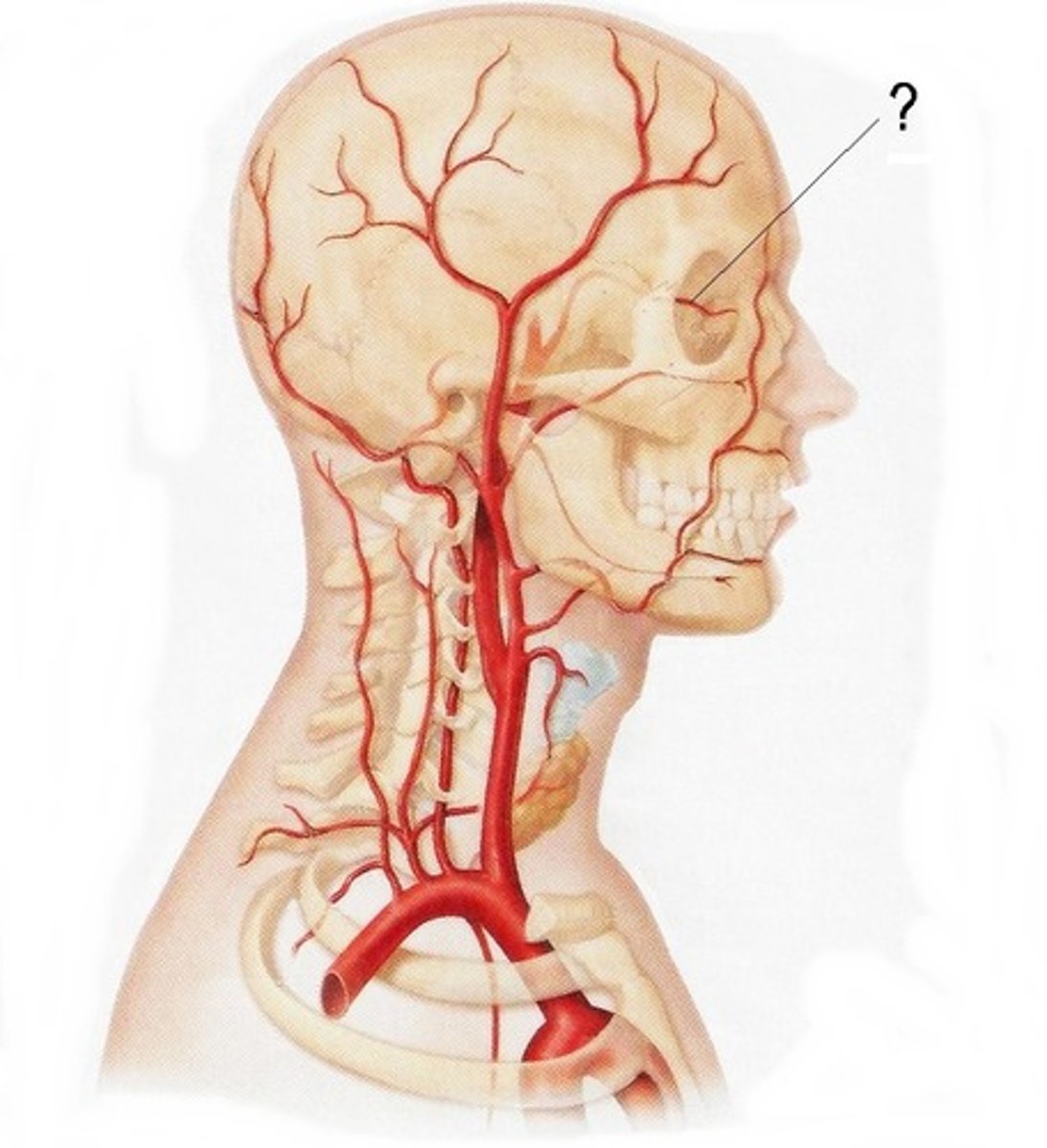
opthalmic artery
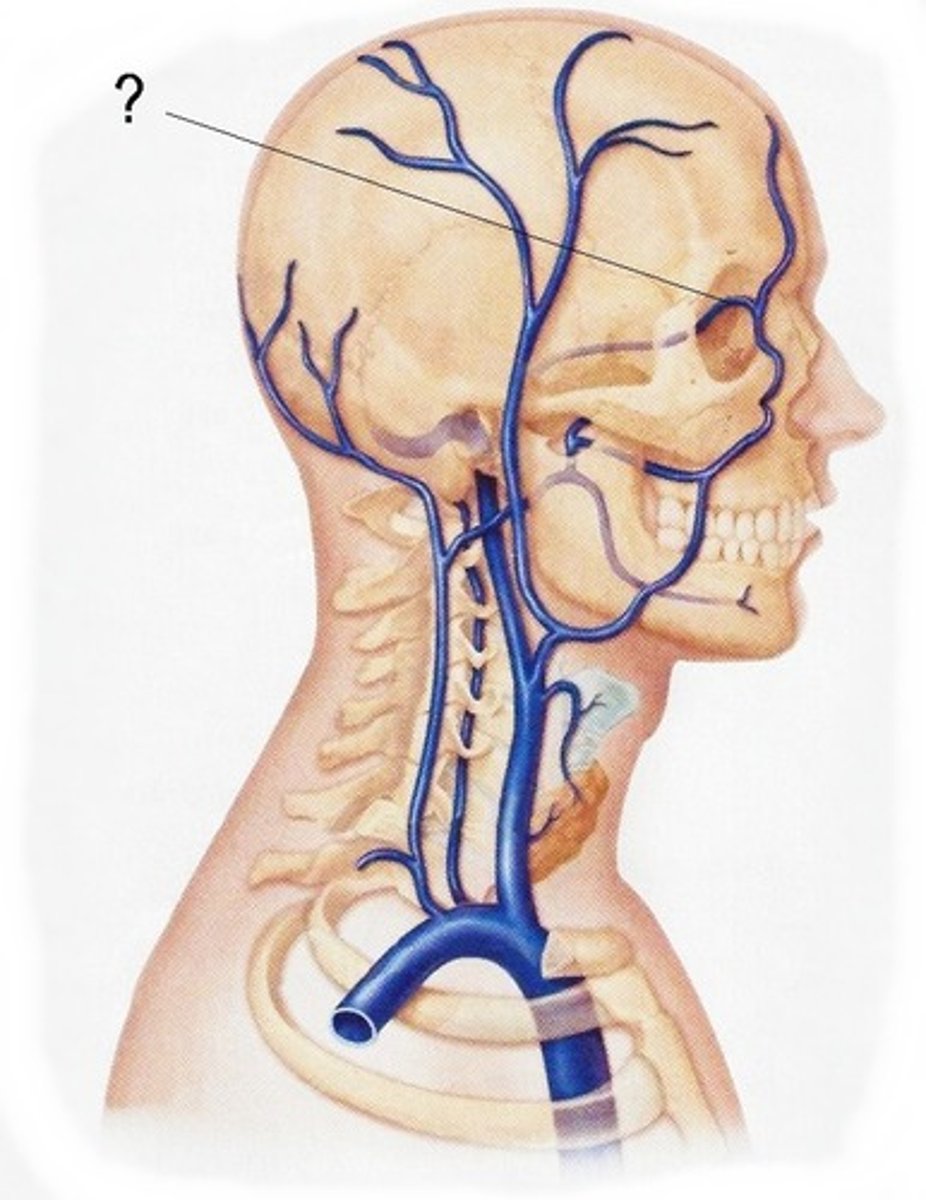
superior opthalmic vein
goes through supeerior orbital fissue, orbital vein, drains orbit nasofrontal
cornea
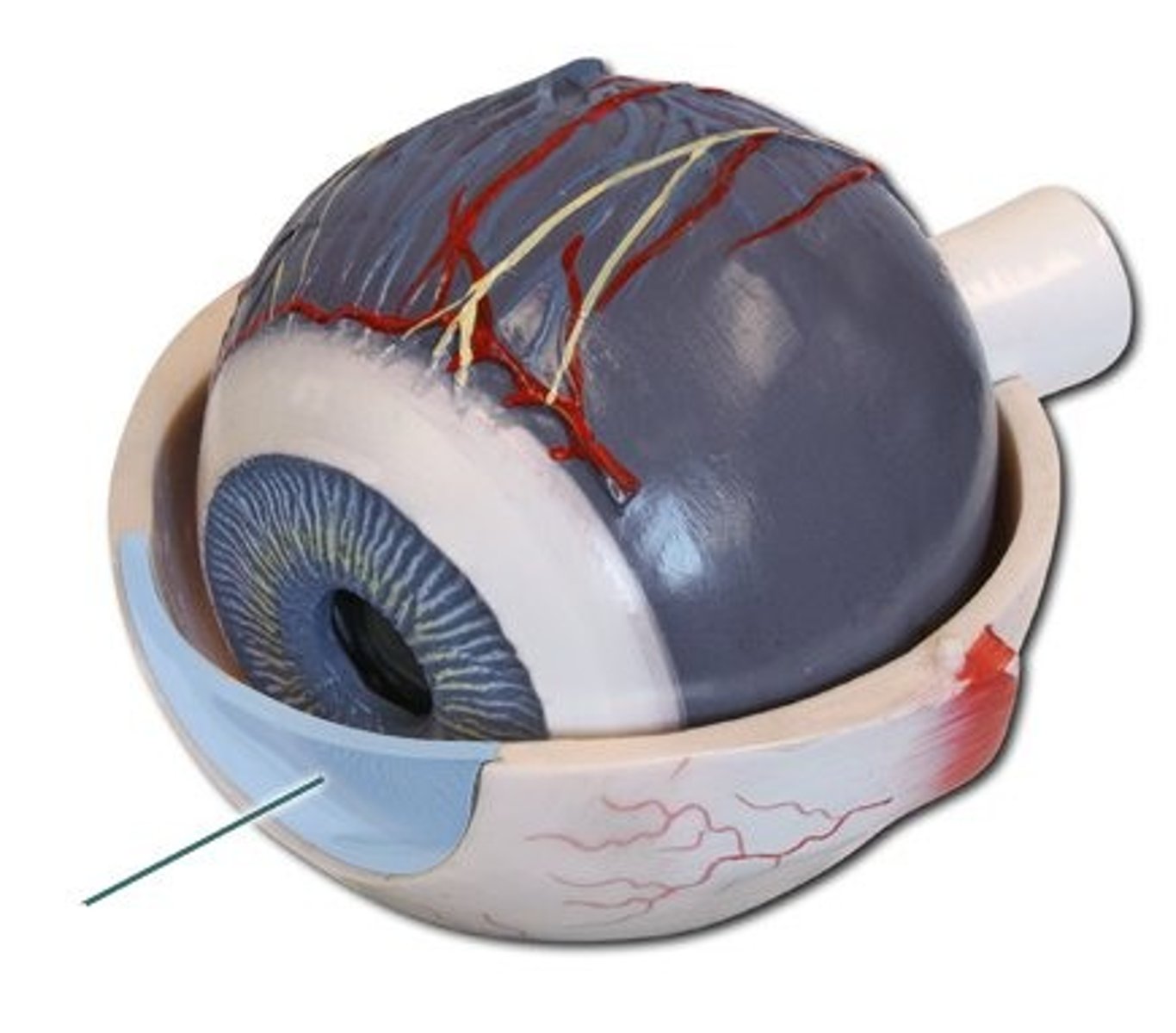
sclera
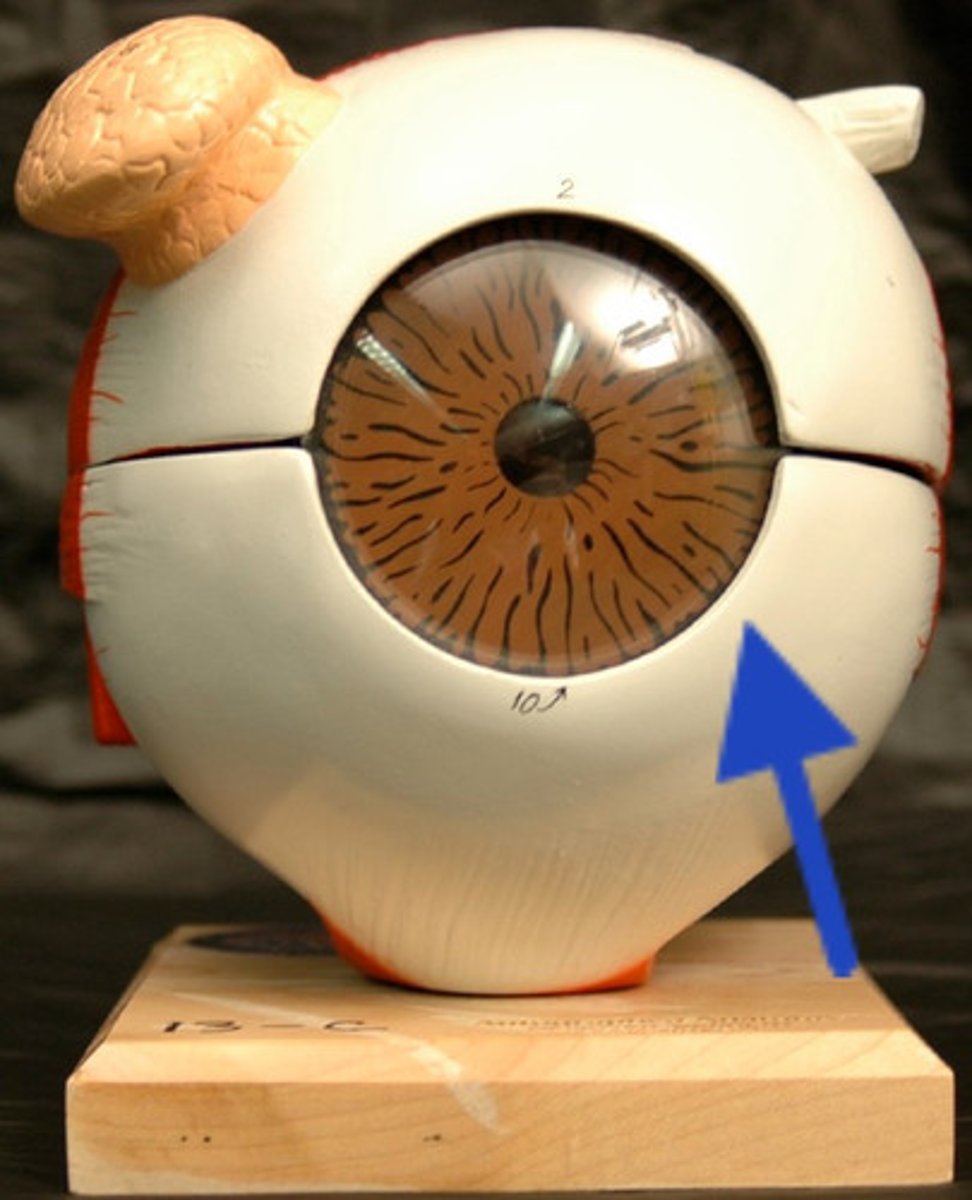
pupil
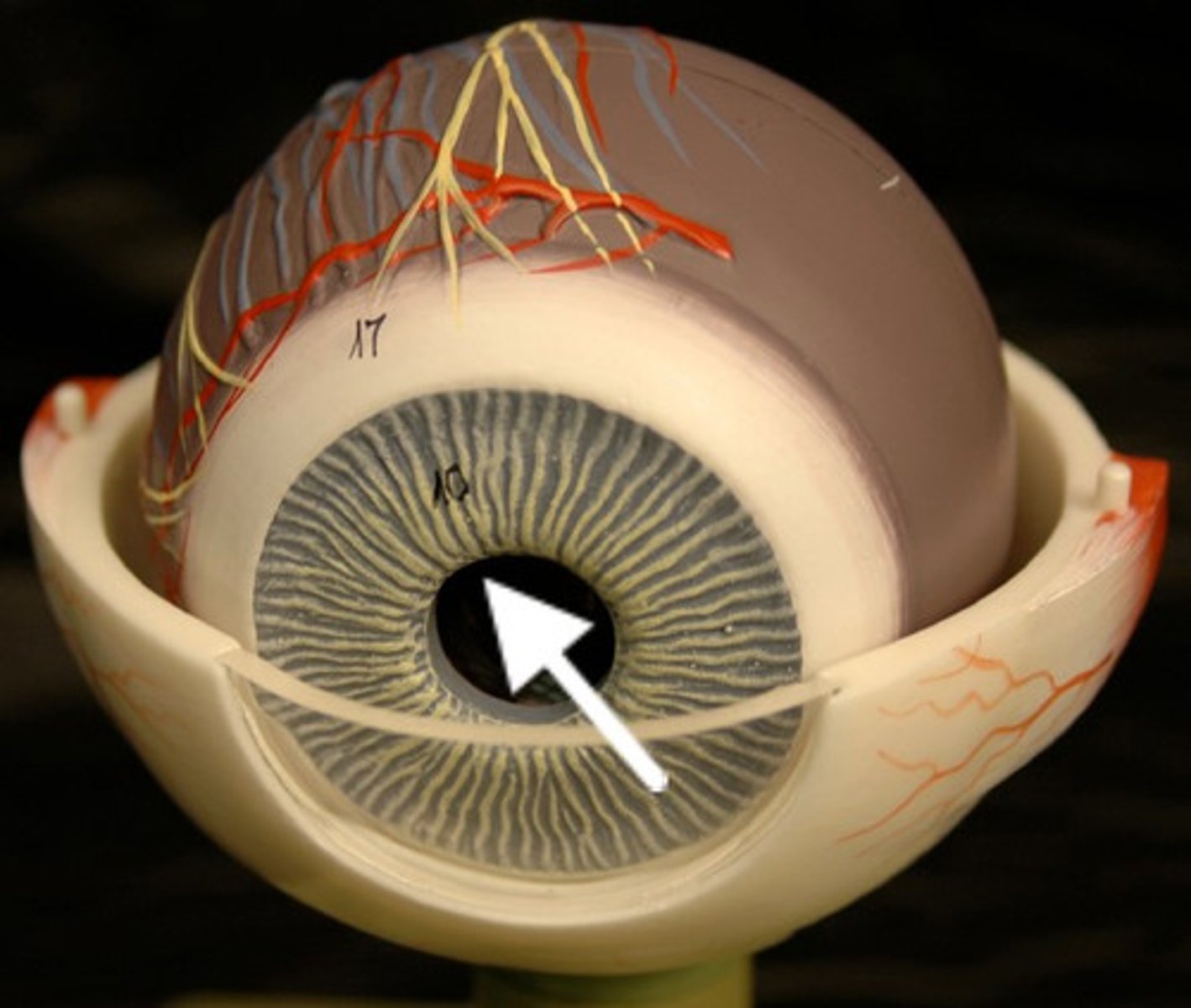
iris
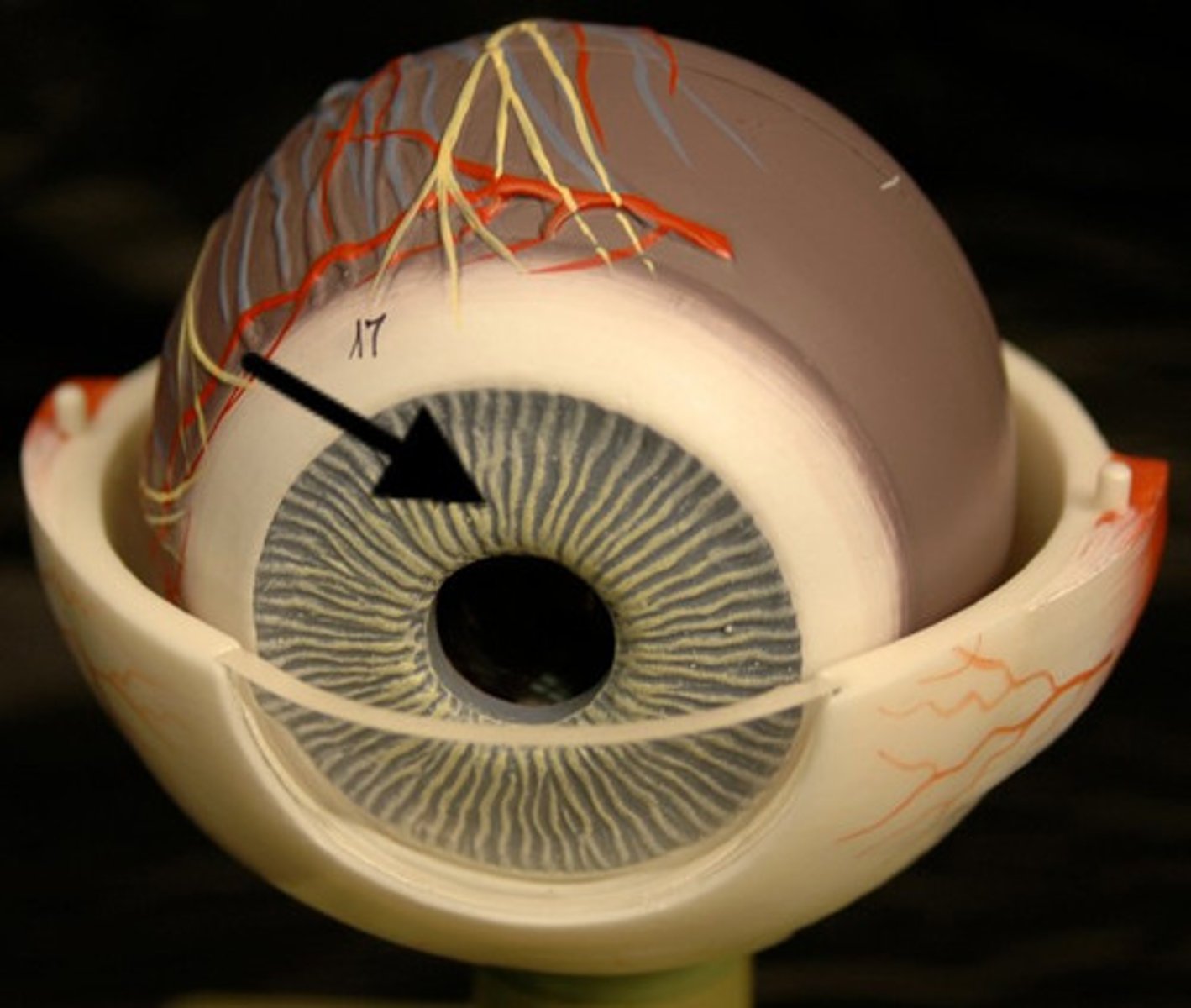
medial commissure
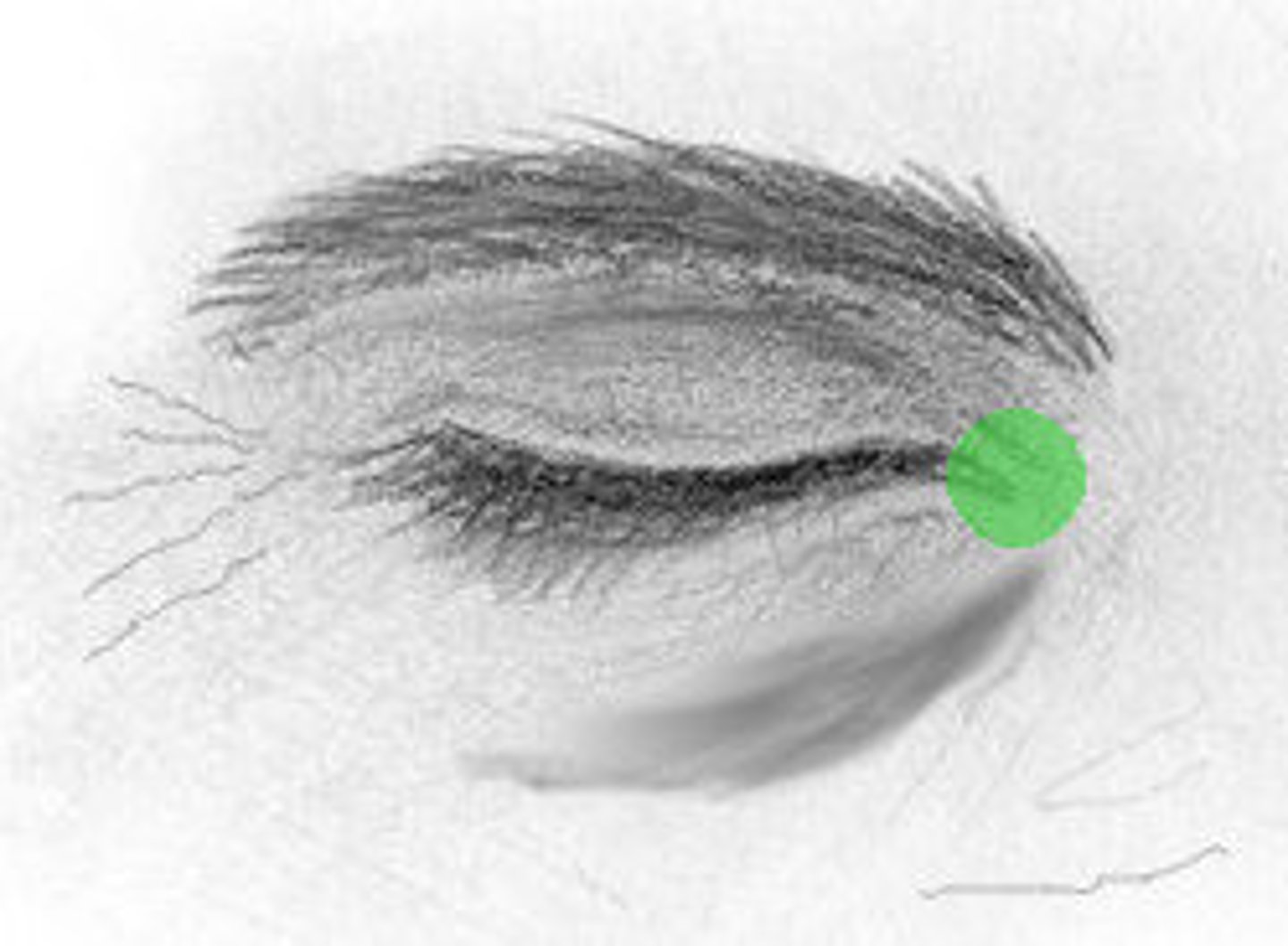

lateral commissure
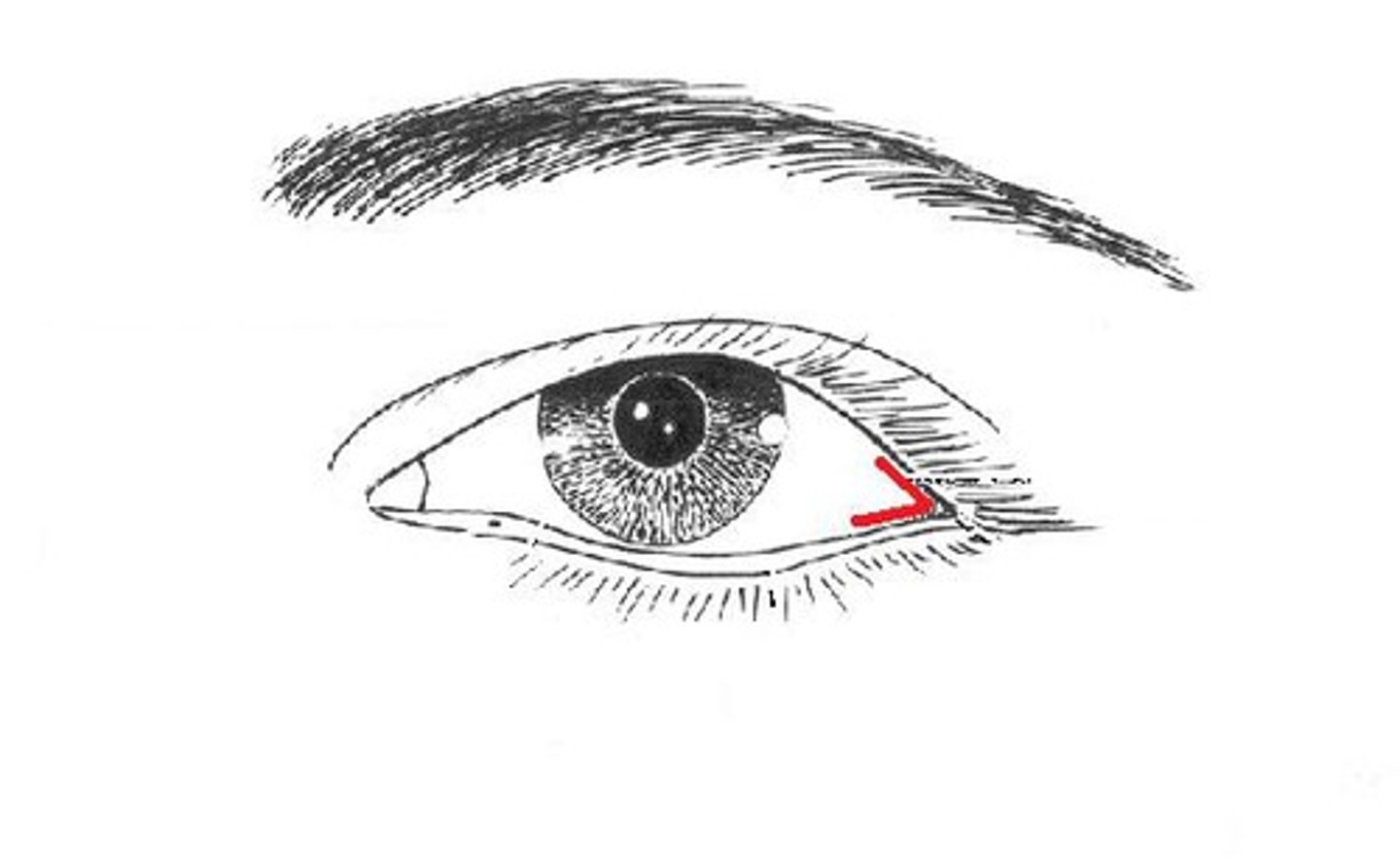
conjuctiva
mucous membrane that lines the eyelids and outer surface of the eyeball
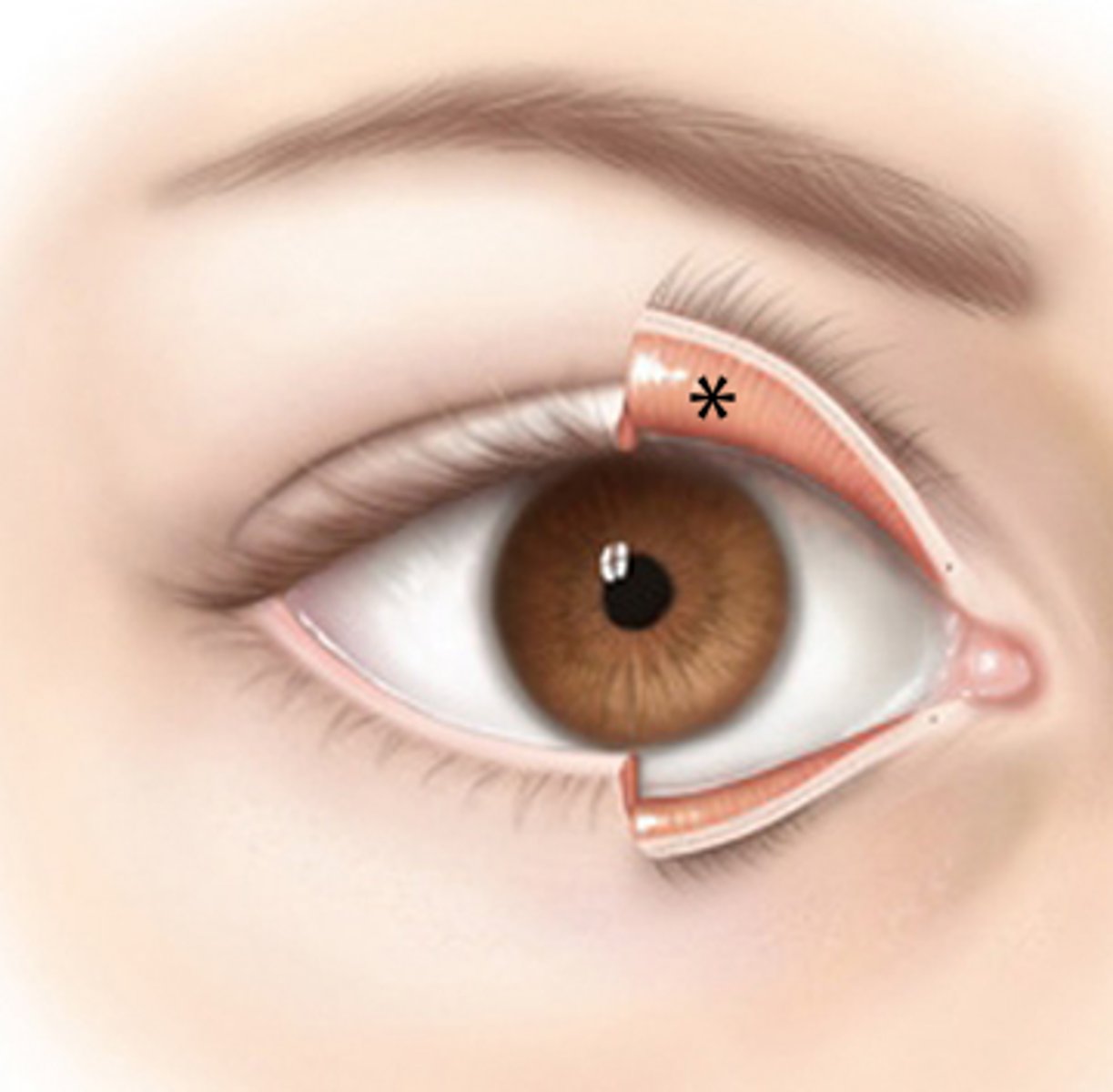
palpebral fissure
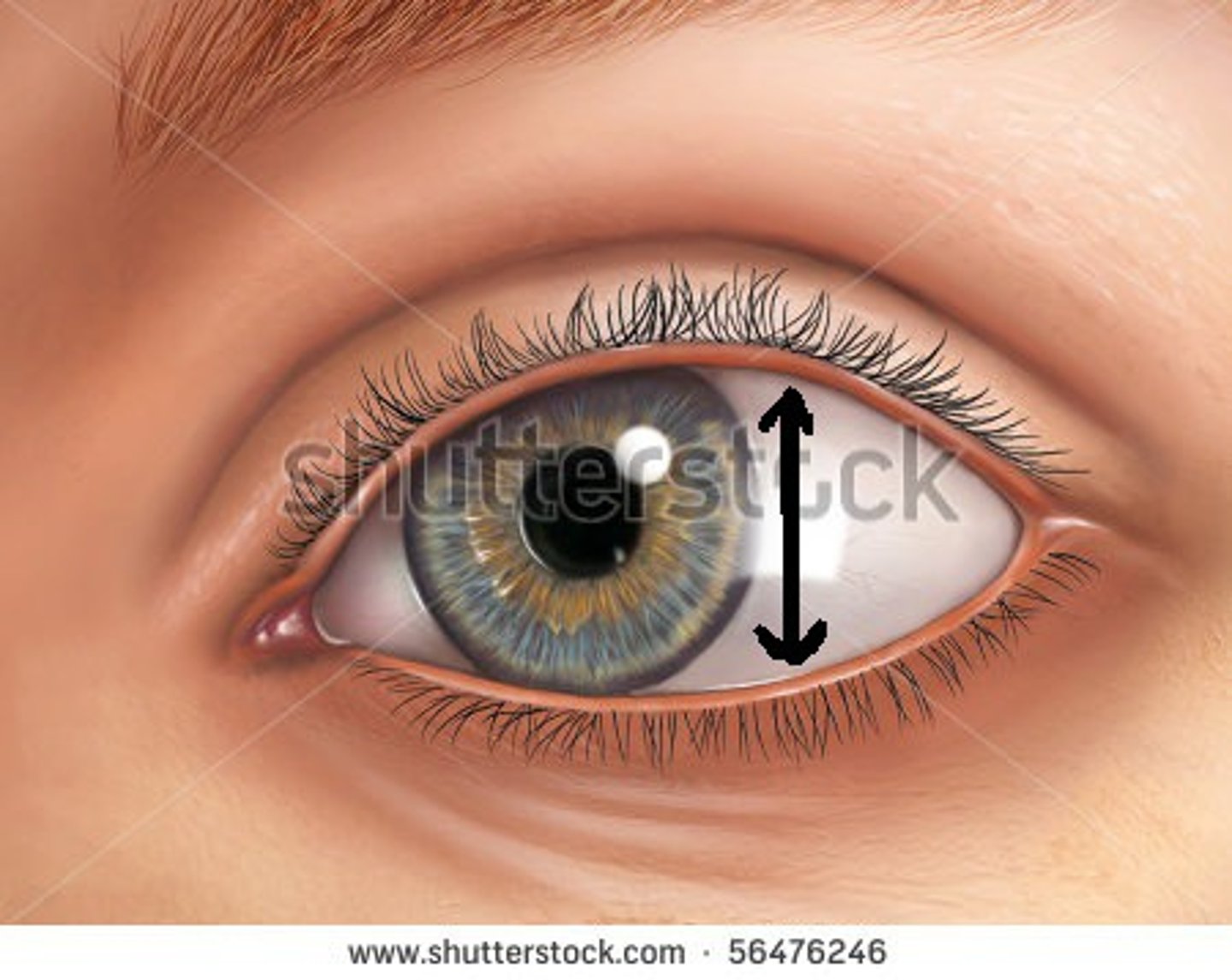
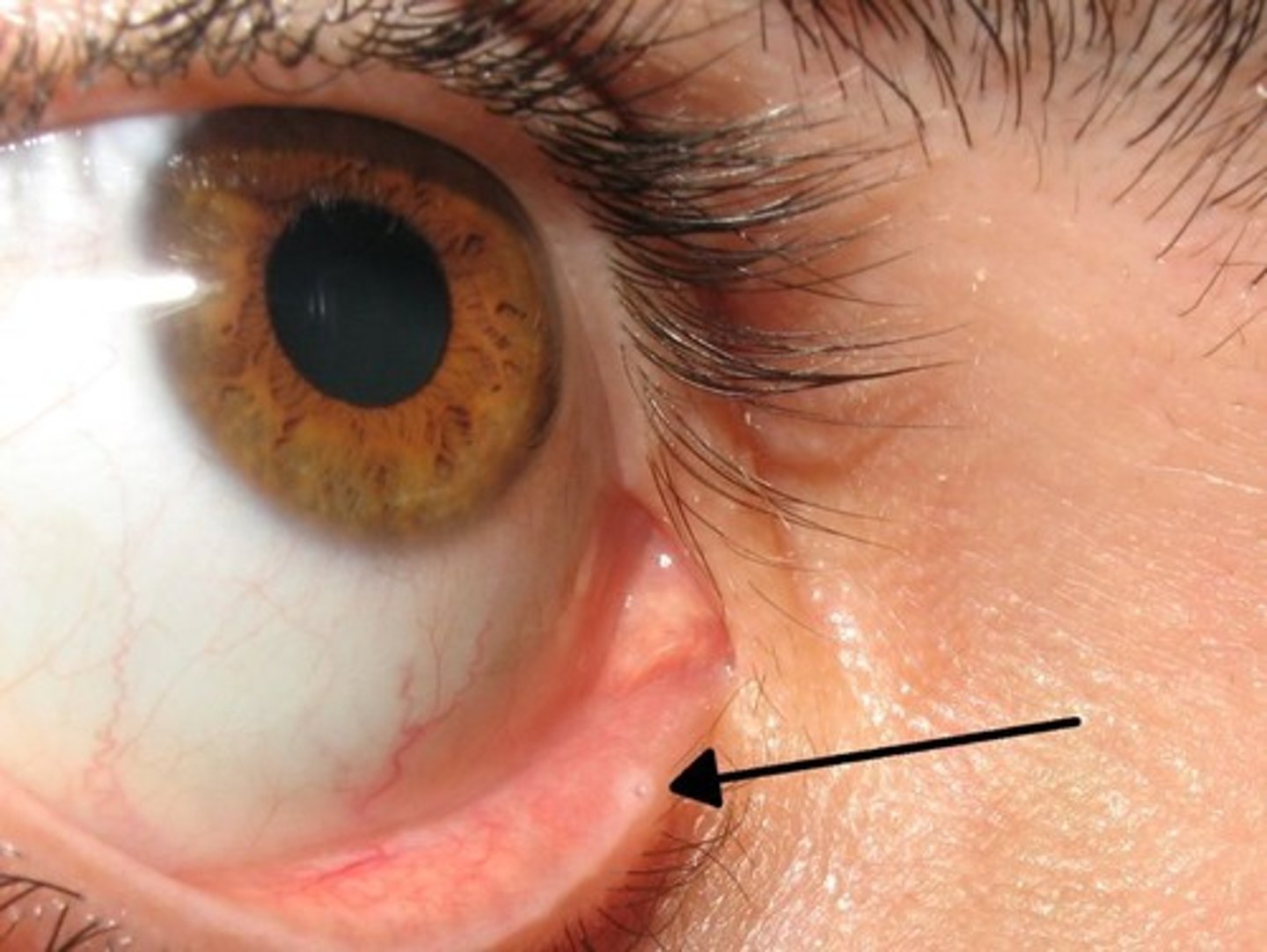
lacrimal lake, collecting area for tears
what is the structure and function
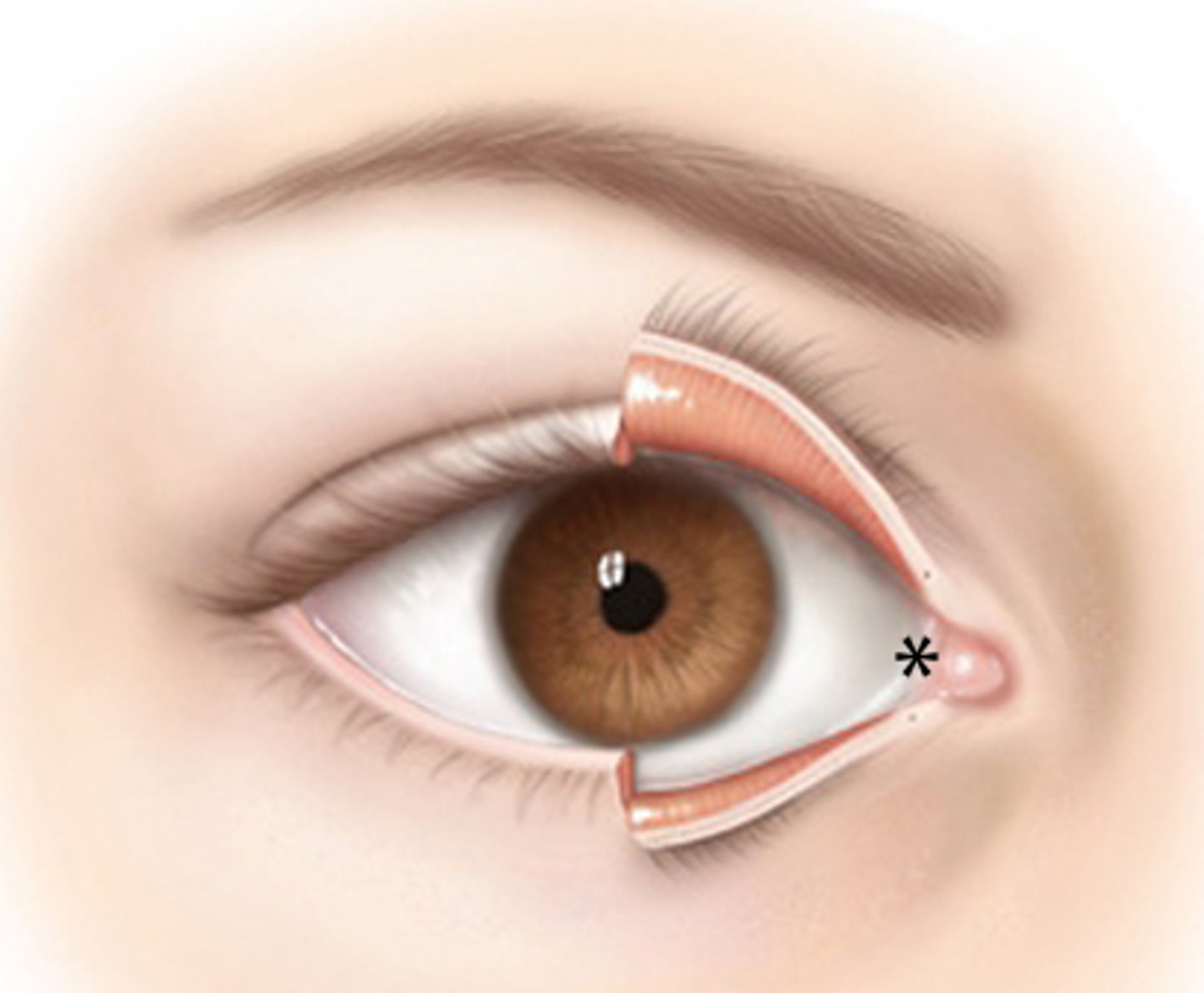
lacrimal puncta, drains the lacrimal lake
what is the structure and function
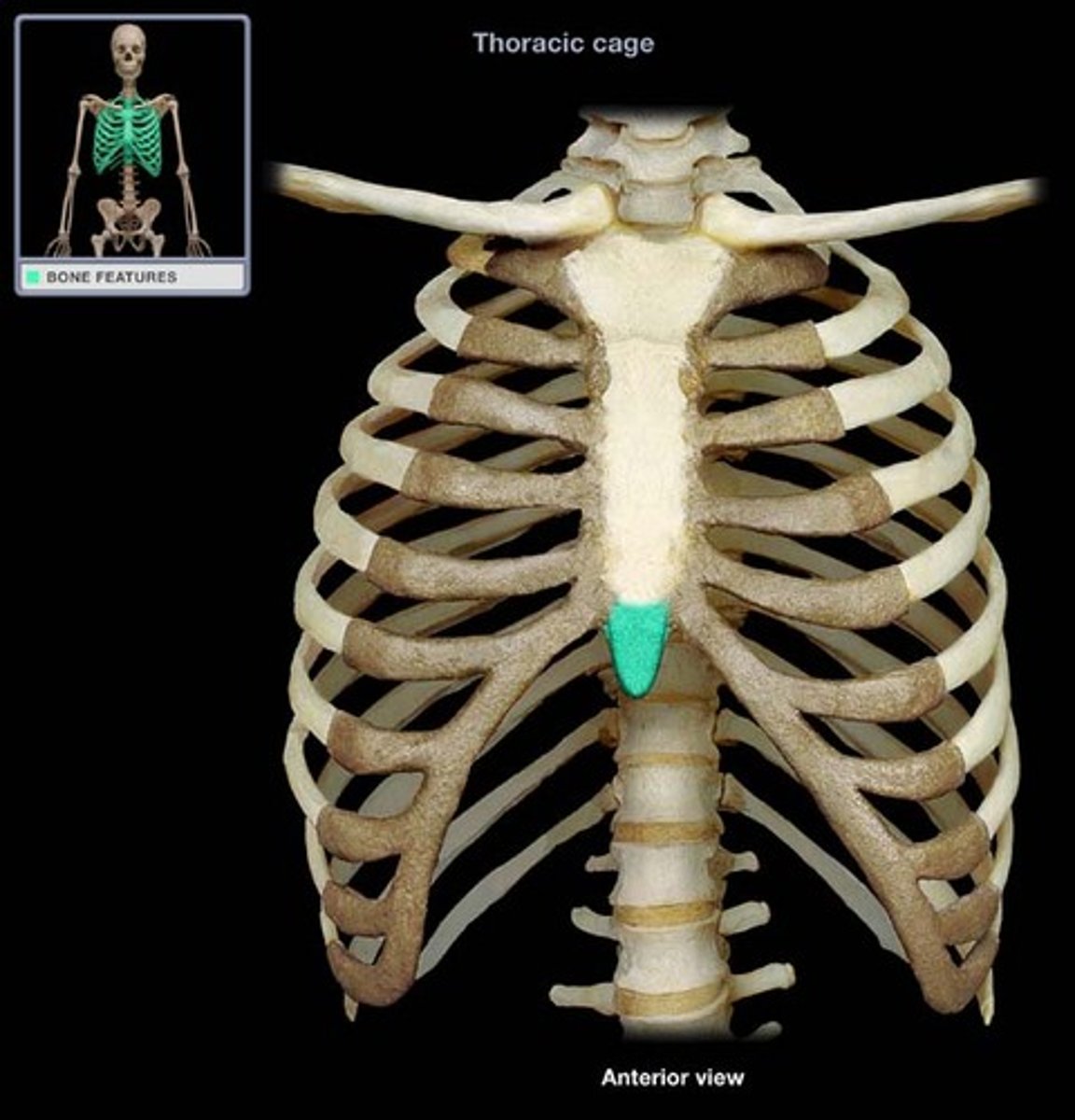
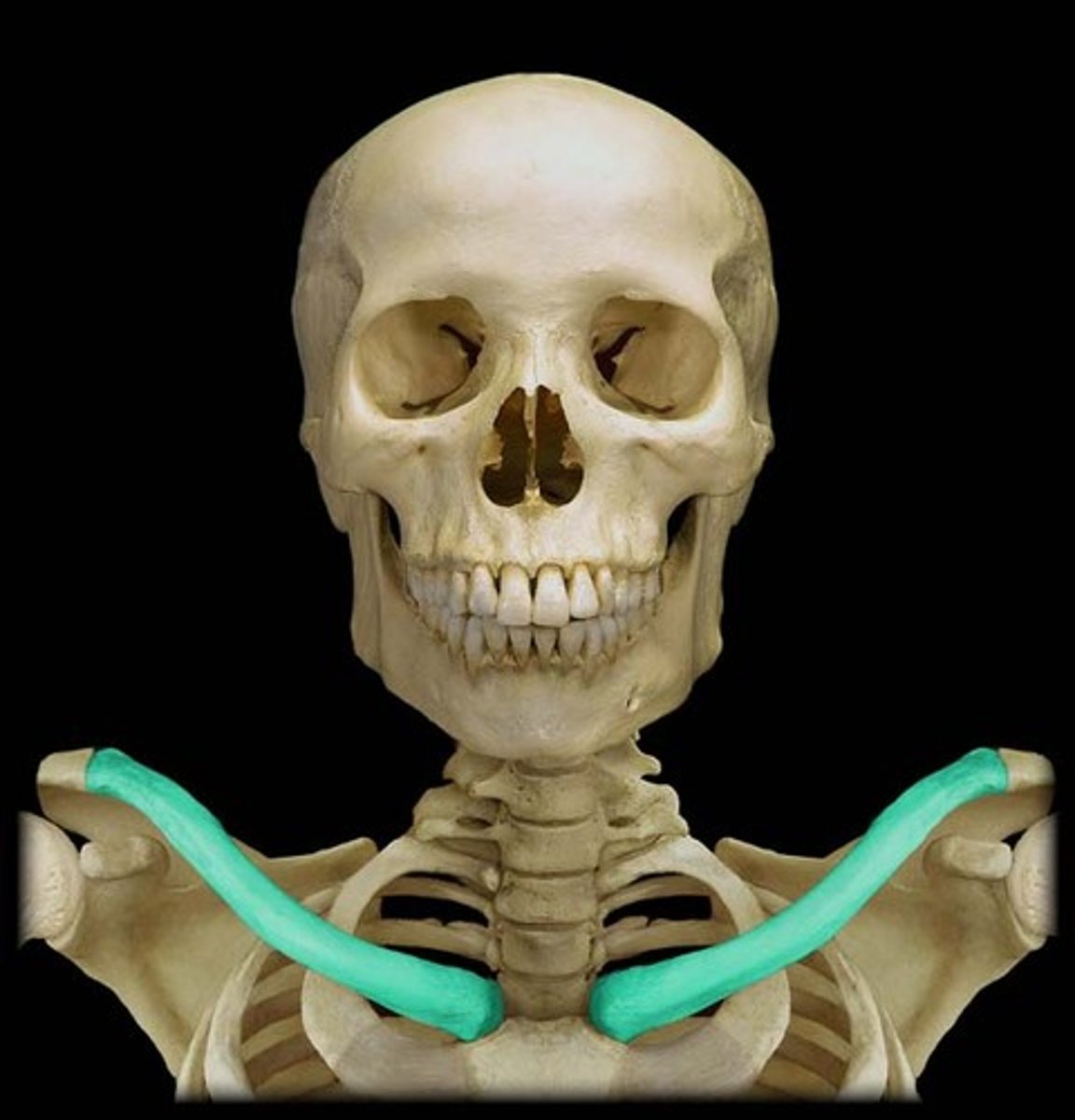
clavicle
sternum
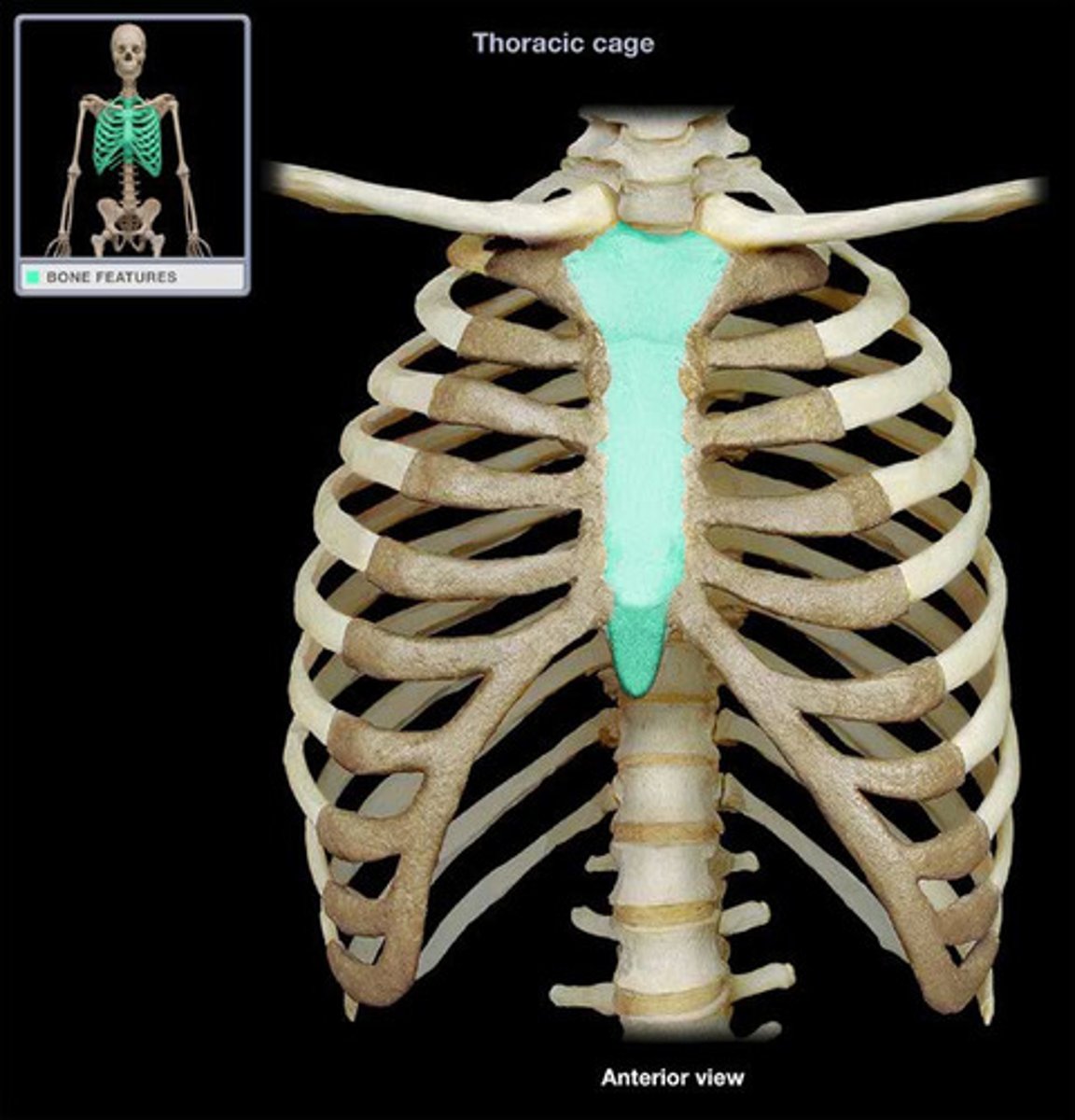
manubrium
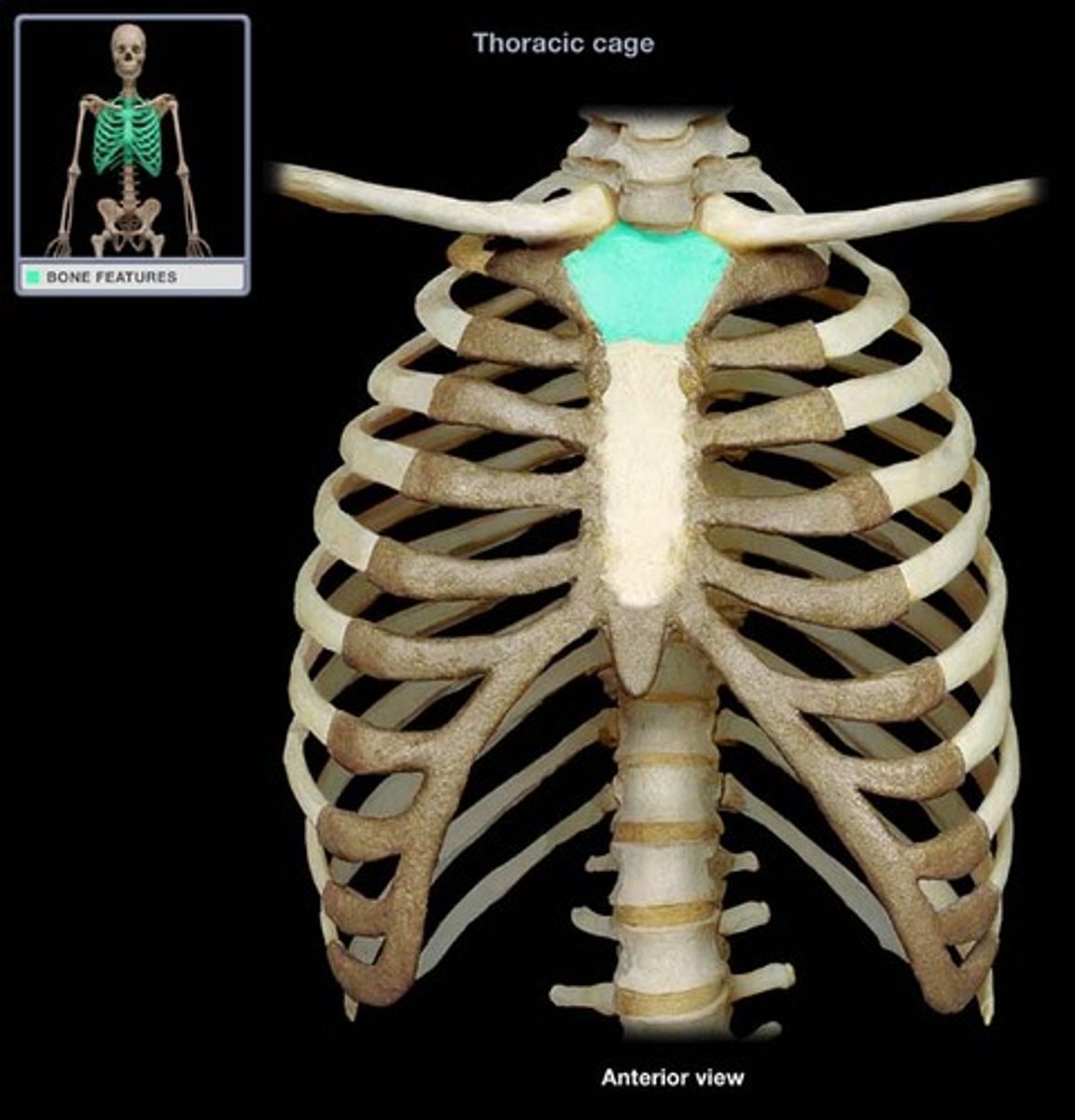
body of sternum
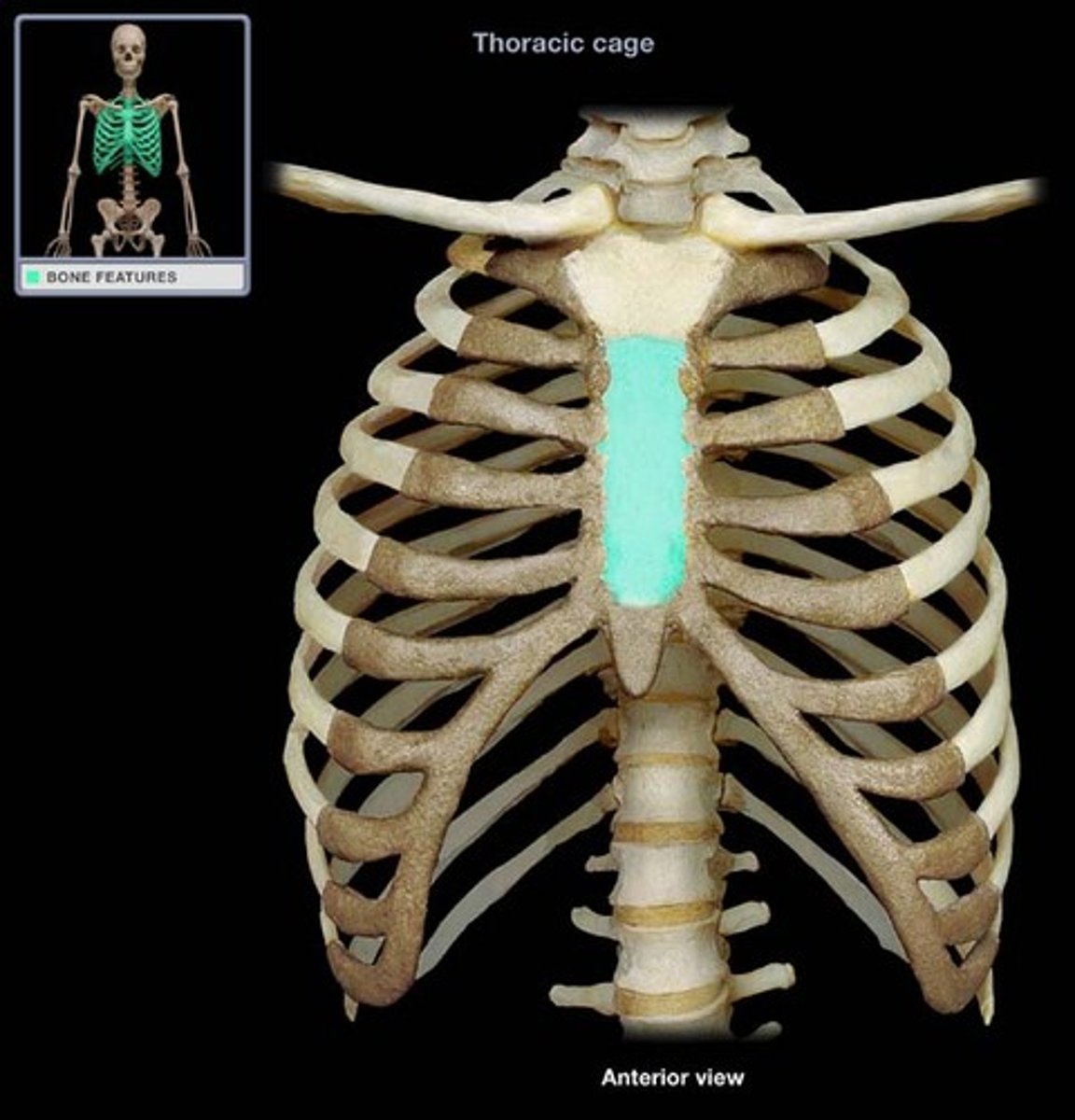
xiphoid process